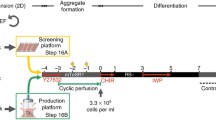
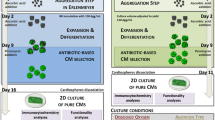
Abstract
Regenerative medicine using human-induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) is a promising approach to treat heart failure. However, a large number of cells are required to achieve the desired therapeutic effect. The stirring-type suspension culture method allows a large-scale production of hiPSC-derived cardiomyocytes (more than 1 × 108 cells/100 mL), leading to a stable cell supply. Here, we describe a method to scale-up hiPSC-derived cardiomyocyte production with a high differentiation efficiency.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sawa Y, Yoshikawa Y, Toda K et al (2015) Safety and efficacy of autologous skeletal myoblast sheets (TCD-51073) for the treatment of severe chronic heart failure due to ischemic heart disease. Circ J 79:991–999
Matsuura K, Honda A, Nagai T et al (2009) Transplantation of cardiac progenitor cells ameliorates cardiac dysfunction after myocardial infarction in mice. J Clin Invest 119:2204–2217
Masumoto H, Matsuo T, Yamamizu K et al (2012) Pluripotent stem cell-engineered cell sheets reassembled with defined cardiovascular populations ameliorate reduction in infarct heart function through cardiomyocyte-mediated neovascularization. Stem Cells 30:1196–1205
Yang L, Soonpaa MH, Adler ED et al (2008) Human cardiovascular progenitor cells develop from a KDR+ embryonic-stem-cell-derived population. Nature 453:524–528
Willems E, Spiering S, Davidovics H et al (2011) Small-molecule inhibitors of the Wnt pathway potently promote cardiomyocytes from human embryonic stem cell-derived mesoderm. Circ Res 109:360–364
Uosaki H, Fukushima H, Takeuchi A et al (2011) Efficient and scalable purification of cardiomyocytes from human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells by VCAM1 surface expression. PLoS One 6:e23657
Matsuura K, Wada M, Shimizu T et al (2012) Creation of human cardiac cell sheets using pluripotent stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 425:321–327
Acknowledgment
This was supported by Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) under Grant Number JP20bm0204003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Sougawa, N., Miyagawa, S., Sawa, Y. (2021). Large-Scale Differentiation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes by Stirring-Type Suspension Culture. In: Yoshida, Y. (eds) Pluripotent Stem-Cell Derived Cardiomyocytes. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2320. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1484-6_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1484-6_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1483-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1484-6
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols