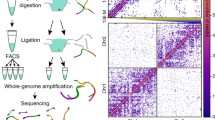
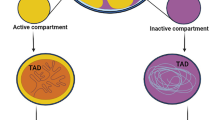
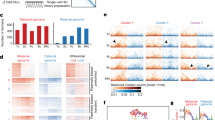
Abstract
Over the past two decades, the development of chromosome conformation capture technologies has allowed to intensively probe the properties of genome folding in various cell types. High-throughput versions of these C-based assays (named Hi-C) have released the mapping of 3D chromosome folding for the entire genomes. Applied to mammalian preimplantation embryos, it has revealed a unique chromosome organization after fertilization when a new individual is being formed. However, the questions of whether specific structures could arise depending on their parental origins or of their transcriptional status remain open. Our method chapter is dedicated to the technical description on how applying scHi-C to mouse embryos at different stages of preimplantation development. This approach capitalized with the limited amount of material available at these developmental stages. It also provides new research avenues, such as the study of mutant embryos for further functional studies.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kempfer R, Pombo A (2019) Methods for mapping 3D chromosome architecture. Nat Rev Genet. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-019-0195-2
Bickmore WA, van Steensel B (2013) Genome architecture: domain organization of interphase chromosomes. Cell 152:1270–1284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.02.001
Lieberman-Aiden E, van Berkum NL, Williams L, Imakaev M, Ragoczy T, Telling A et al (2009) Comprehensive mapping of long-range interactions reveals folding principles of the human genome. Science 326:289–293. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1181369
Dixon JR, Selvaraj S, Yue F, Kim A, Li Y, Shen Y et al (2012) Topological domains in mammalian genomes identified by analysis of chromatin interactions. Nature 485:376–380. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11082
Nora EP, Lajoie BR, Schulz EG, Giorgetti L, Okamoto I, Servant N et al (2012) Spatial partitioning of the regulatory landscape of the X-inactivation centre. Nature 485(7398):381–385. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11049
Nagano T, Lubling Y, Stevens TJ, Schoenfelder S, Yaffe E, Dean W et al (2013) Single-cell Hi-C reveals cell-to-cell variability in chromosome structure. Nature 502:59–64. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12593
Nagano T, Lubling Y, Várnai C, Dudley C, Leung W, Baran Y et al (2017) Cell-cycle dynamics of chromosomal organization at single-cell resolution. Nature 547:61–67. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23001
Eckersley-Maslin MA, Alda-Catalinas C, Reik W (2018) Dynamics of the epigenetic landscape during the maternal-to-zygotic transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 19:436–450. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-018-0008-z
Flyamer IM, Gassler J, Imakaev M, Brandão HB, Ulianov SV, Abdennur N et al (2017) Single-nucleus Hi-C reveals unique chromatin reorganization at oocyte-to-zygote transition. Nature 544:110–114. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21711
Lu F, Liu Y, Inoue A, Suzuki T, Zhao K, Zhang Y (2016) Establishing chromatin regulatory landscape during mouse preimplantation development. Cell 165:1375–1388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.050
Du Z, Zheng H, Huang B, Ma R, Wu J, Zhang X et al (2017) Allelic reprogramming of 3D chromatin architecture during early mammalian development. Nature 547:232–235. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23263
Collombet S, Ranisavljevic N, Nagano T et al (2020) Parental-to-embryo switch of chromosome organization in early embryogenesis. Nature 580:142–146. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2125-z
Nagano T, Lubling Y, Yaffe E, Wingett SW, Dean W, Tanay A et al (2015) Single-cell Hi-C for genome-wide detection of chromatin interactions that occur simultaneously in a single cell. Nat Protoc 10:1986–2003. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2015.127
Hogan B, Beddington R, Costantini F (1994) Manipulating the mouse embryo: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-019-9_13
Acknowledgments
We thank Edith Heard for her strong scientific commitment and constant support during this project. We thank Takashi Nagano and Peter Fraser for their experimental expertise and technical support during the optimization of the Hi-C procedure on single mouse blastomeres. We thank the Institut Curie Animal facility for animal welfare and husbandry. This work was supported by FRM FDM20140630223 and FDM 40917 to N.R. and by funding allocated to Pr Edith Heard (Labex DEEP, ANR-11-LBX-0044; IDEX PSL, ANR-10-IDEX-0001-02 PSL).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Ranisavljevic, N., Borensztein, M., Ancelin, K. (2021). Understanding Chromosome Structure During Early Mouse Development by a Single-Cell Hi-C Analysis. In: Ancelin, K., Borensztein, M. (eds) Epigenetic Reprogramming During Mouse Embryogenesis. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2214. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0958-3_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0958-3_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-0957-6
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-0958-3
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols