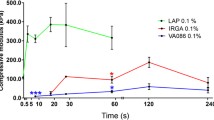
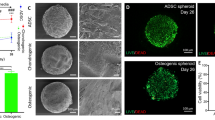
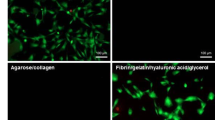
Abstract
Three-dimensional (3D) bioprinting is driving major innovations in the area of cartilage tissue engineering. As an alternative to computer-aided 3D printing, in situ additive manufacturing has the advantage of matching the geometry of the defect to be repaired without specific preliminary image analysis, shaping the bioscaffold within the defect, and achieving the best possible contact between the bioscaffold and the host tissue. Here, we describe an in situ approach that allows 3D bioprinting of human adipose-derived stem cells (hADSCs) laden in 10%GelMa/2%HAMa (GelMa/HAMa) hydrogel. We use coaxial extrusion to obtain a core/shell bioscaffold with high cell viability, as well as adequate mechanical properties for articular cartilage regeneration and repair.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daly AC, Freeman FE, Gonzalez-Fernandez T, Critchley SE, Nulty J, Kelly DJ (2017) 3D bioprinting for cartilage and osteochondral tissue engineering. Adv Healthc Mater 6:1–20
Rai V, Dilisio MF, Dietz NE, Agrawal DK (2017) Recent strategies in cartilage repair: A systemic review of the scaffold development and tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A 105:2343–2354
Mollon B, Kandel R, Chahal J, Theodoropoulos J (2013) The clinical status of cartilage tissue regeneration in humans. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 21:1824–1833
Ozbolat IT (2018) Bioprinting scale-up tissue and organ constructs for transplantation. Trends Biotechnol 33:395–400
Keriquel V, Guillemot F, Arnault I, Guillotin B, Miraux S, Amédée J et al (2010) In vivo bioprinting for computer- and robotic-assisted medical intervention: preliminary study in mice. Biofabrication 2:14101
O’Connell CD, Di Bella C, Thompson F, Augustine C, Beirne S, Cornock R et al (2016) Development of the Biopen: a handheld device for surgical printing of adipose stem cells at a chondral wound site. Biofabrication 8:15019
Duchi S, Onofrillo C, O’Connell CD, Blanchard R, Augustine C, Quigley AF et al (2017) Handheld co-axial bioprinting: application to in situ surgical cartilage repair. Sci Rep 7:1–12
Burdick JA, Chung C, Jia X, Randolph MA, Langer R (2005) Controlled degradation and mechanical behavior of photopolymerized hyaluronic acid networks. Biomacromolecules 6:386–391
Loessner D, Meinert C, Kaemmerer E, Martine LC, Yue K, Levett PA et al (2016) Functionalization, preparation and use of cell-laden gelatin methacryloyl-based hydrogels as modular tissue culture platforms. Nat Protoc 11:727–746
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to acknowledge the following funding sources: Foundation for Surgery John Loewenthal, Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, Research Endowment Funds, St Vincent’s Hospital Melbourne, Arthritis Australia, Eventide Homes Research Project Grant, and The CASS Foundation Research Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Duchi, S., Onofrillo, C., O’Connell, C., Wallace, G.G., Choong, P., Di Bella, C. (2020). Bioprinting Stem Cells in Hydrogel for In Situ Surgical Application: A Case for Articular Cartilage. In: Crook, J.M. (eds) 3D Bioprinting. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2140. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0520-2_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0520-2_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-0519-6
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-0520-2
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols