Abstract
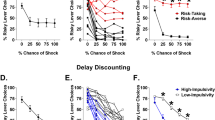
Excessive preference for risky over safe options is a hallmark of several psychiatric disorders. Here we describe a behavioral task that models such risky decision making in rats. In this task, rats are given choices between small, safe rewards and large rewards accompanied by risk of footshock punishment. The risk of punishment changes within a test session, allowing quantification of decision making at different levels of risk. Importantly, this task can yield a wide degree of reliable individual variability, allowing the characterization of rats as “risk-taking” or “risk-averse.” The task has been demonstrated to be effective for testing the effects of pharmacological agents and neurobiological manipulations, and the individual variability (which mimics the human population) allows assessment of behavioral and neurobiological distinctions among subjects based on their risk-taking profile.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bechara A, Dolan S, Denburg N, Hindes A, Anderson SW, Nathan PE (2001) Decision-making deficits, linked to dysfunctional ventromedial prefrontal cortex, revealed in alcohol and stimulant abusers. Neuropsychologia 39:376–389
Drechsler R, Rizzo P, Steinhausen HC (2008) Decision-making on an explicit risk-taking task in preadolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Neural Transm 115:201–209
Ernst M, Kimes AS, London ED, Matochik JA, Eldreth D, Tata S, Contoreggi C, Leff M, Bolla K (2003) Neural substrates of decision making in adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am J Psychiatry 160:1061–1070
Ludewig K, Paulus MP, Vollenweider FX (2003) Behavioural dysregulation of decision-making in deficit but not nondeficit schizophrenia patients. Psychiatry Res 119:293–306
Evenden JL, Ryan CN (1996) The pharmacology of impulsive behavior in rats: the effects of drugs on response choice with varying delays of reinforcement. Psychopharmacology 128:161–170
Cardinal RN, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (2000) The effects of d-amphetamine, chlordiazepoxide, α-flupenthixol and behavioural manipulations on choice of signalled and unsignalled delayed reinforcement in rats. Psychopharmacology 152:362–375
Winstanley CA, Dalley JW, Theobald DE, Robbins MJ (2003) Global 5-HT depletion attenuates the ability of amphetamine to decrease impulse choice on a delay-discounting task in rats. Psychopharmacology 170:320–331
Simon NW, Mendez IA, Setlow B (2007) Cocaine exposure causes long term increases in impulsive choice. Behav Neurosci 121:543–549
Simon NW, Gilbert RJ, Mayse JD, Bizon JL, Setlow B (2009) Balancing risk and reward: a rat model of risky decision making. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:2208–2217
Mitchell MR, Weiss VG, Beas BS, Morgan D, Bizon JL, Setlow B (2014) Adolescent risk taking, cocaine self-administration, and striatal dopamine signaling. Neuropsychopharmacology 39:955–962
Shimp KG, Mitchell MR, Beas BS, Bizon JL, Setlow B (2015) Affective and cognitive mechanisms of risky decision making. Neurobiol Learn Mem 117:60–70
Deng JV, Orsini CA, Shimp KG, Setlow B (2018) MeCP2 expression in a rat model of risky decision making. Neuroscience 369:212–221
Simon NW, Montgomery KS, Beas BS, Mitchell MR, LaSarge CL, Mendez IA, Banuelos C, Vokes CM, Taylor AB, Haberman RP, Bizon JL, Setlow B (2011) Dopaminergic modulation of risky decision making. J Neurosci 31:17460–17470
Van Den Bos R, Lasthius W, Den Heijer E, Van Der Harst J, Spruijt B (2006) Toward a rodent model of the Iowa gambling task. Behav Res Methods 38:470–478
Zeeb FD, Robbins TW, Winstanley CA (2009) Serotonergic and dopaminergic modulation of gambling behavior as assessed using a novel rat gambling task. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:2329–2343
Jentsch JD, Woods JA, Groman SM, Seu E (2010) Behavioral characteristics and neural mechanisms mediating performance in a rodent version of the Balloon Analog Risk Task. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:1797–1806
Cardinal R, Howes N (2005) Effects of lesions of the nucleus accumbens core on choice between small certain rewards and large uncertain rewards in rats. BMC Neurosci 6:37
Negus S (2005) Effects of punishment on choice between cocaine and food in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 181:244–252
Talmi D, Dayan P, Kiebel SJ, Frith CD, Dolan RJ (2009) How humans integrate the prospects of pain and reward during choice. J Neurosci 29:14617–14626
Anselme P (2015) Does reward unpredictability reflect risk? Behav Brain Res 280C:119–127
Orsini CA, Willis ML, Gilbert RJ, Bizon JL, Setlow B (2016) Sex differences in a rat model of risky decision making. Behav Neurosci 130:50–61
Gabriel, Freels, Setlow, & Simon (2019). Risky Decision-making is associated with impulsive action and sensitivity to first-time nicotine exposure. Behavioural Brain Research, 359, 579–88
Orsini CA, Hernandez CM, Singhal S, Kelly KB, Frazier CJ, Bizon JL, Setlow B (2017) Optogenetic inhibition reveals distinct roles for basolateral amygdala activity at discrete time points during risky decision making. J Neurosci 37:11537–11548
Orsini CA, Heshmati SC, Garman TS, Wall SC, Bizon JL, Setlow B (2018) Contributions of medial prefrontal cortex to decision making involving risk of punishment. Neuropharmacology 139:205–216
Zeeb FD, Winstanley CA (2011) Lesions of the basolateral amygdala and orbitofrontal cortex differentially affect acquisition and performance of a rodent gambling task. J Neurosci 31:2197–2204
Zeeb FD, Winstanley CA (2013) Functional disconnection of the orbitofrontal cortex and basolateral amygdala impairs acquisition of a rat gambling task and disrupts animals’ ability to alter decision-making behavior after reinforcer devaluation. J Neurosci 33:6434–6443
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Orsini, C.A., Blaes, S.L., Setlow, B., Simon, N.W. (2019). Recent Updates in Modeling Risky Decision Making in Rodents. In: Kobeissy, F. (eds) Psychiatric Disorders. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2011. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9554-7_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9554-7_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-9553-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-9554-7
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols