Abstract
Background
Increasing hydrophilicity of poorly water-soluble drugs is a major challenge in drug discovery and development. Cocrystallization is one of the techniques to enhance the hydrophilicity of such drugs. Carvedilol (CAR), a nonselective beta/alpha1 blocker, used in the treatment of mild to moderate congestive heart failure and hypertension, is classified under BCS class II with poor aqueous solubility and high permeability. Present work is an attempt to improve the solubility of CAR by preparing cocrystals using hydrochlorothiazide (HCT), a diuretic drug, as coformer. CAR-HCT (2:0.5) cocrystals were prepared by slurry conversion method and were characterized by DSC, PXRD, FTIR, Raman, and SEM analysis. The solubility, stability, and dissolution (in vitro) studies were conducted for the cocrystals.
Results
The formation of CAR-HCT cocrystals was confirmed based on melting point, DSC thermograms, PXRD data, FTIR and Raman spectra, and finally by SEM micrographs. The solubility of the prepared cocrystals was significantly enhanced (7.3 times), and the dissolution (in vitro) was improved by 2.7 times as compared to pure drug CAR. Further, these cocrystals were also found to be stable for 3 months (90 days).
Conclusion
It may be inferred that the drug–drug (CAR-HCT) cocrystallization enhances the solubility and dissolution rate of carvedilol significantly. Further, by combining HCT as coformer could well be beneficial pharmacologically too.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Pharmaceutical formulation is a complex field by itself as it needs to adapt itself to comply with the ever-growing demands of new therapeutic requirements. Many APIs exhibit poor water solubility and dissolution rate which may correlate to their suboptimal bioavailability [1]. More particularly, it is important in case of formulating solid dosage forms of drugs by oral route as it is the most preferred and patient-friendly mode of administration. There are several ways to improve oral bioavailability, like formulations using surfactants [2], liposomes [3], nanoemulsions [4], carbon nanotube [5], polymer micelles [6], and microemulsions [7] as well as nanoparticle-based methods [8]. Many of these formulations may face problems during formulations due to tedious procedures, and some of them suffer from solubility and stability issues also. Structural modification through crystal engineering is a challenging scientific way to improve biopharmaceutical properties [9]. Crystal engineering provides several possibilities to develop single- or multi-component alterations of an API, including the synthesis of pharmaceutical cocrystals. Cocrystals are crystalline complexes of active/neutral compounds that form a unique crystalline lattice through non-covalent bonds, particularly hydrogen bonds. A distinct advantage with cocrystallization is preservation of the intrinsic pharmacological properties of APIs while altering their physicochemical profile (melting point, solubility, dissolution, etc.) [10].
Cocrystals are solid, crystalline materials that are being used increasingly for the development of APIs with improved physicochemical properties [11,12,13,14] such as solubility, stability, and bioavailability [15, 16]. Cocrystallization is a crystal engineering technique which utilizes the noncovalent interactions such as hydrogen bonding, van der Waals forces, and π–π stacking and halogen bonding [17, 18]. Among them, hydrogen bonding is the most notable because of its strength and directionality [19, 20]. Pharmaceutical cocrystals can be conventionally classified into two types based on coformer used: API-coformer cocrystals (coformer from FDA-approved GRAS list) [21] and drug–drug cocrystals (coformer is replaced by another API). The current popularity of cocrystals need not be overemphasized as some cocrystals entered the market [Suglat® (ipragliflozin l-proline) in Japan and Entresto® (sacubitril and valsartan) in USA] and several more in late stages of development [22, 23].
Drug–drug cocrystals evoked a lot of interest in crystal engineering because of tailoring the physicochemical properties of many new and existing APIs [16, 24] and protection of intellectual property in terms of their novelty, utility, and non-obviousness [25, 26]. It represents a promising area of research especially in the light of the fact that combined therapies are frequently prescribed for effective treatment options in a large number of clinical conditions. Cocrystals with multiple APIs might overcome the drawbacks of conventional combination therapy. The drug–drug cocrystals may not only lead to the modification of the fundamental properties but also provide new opportunities for the development of combined drug therapies which could offer potential advantages like synergistic and/or additive effects [27], reduction of the dose, cost-effective for treatment [28, 29] besides offering improved patient compliance [30, 31]. A good number of such attempts involving drug–drug cocrystals that are recorded in literature indicate their emerging popularity. A consolidated list of drug–drug cocrystals, their literature citation/preclinical development phase has been given chronologically in Table 1. Number of traditional techniques have been employed to address the poor solubility issues of CAR. Those include cyclodextrins [43], solid lipid nanoparticles, [44] and self-emulsifying drug delivery systems [45].
In the present study, an attempt has been made to produce drug–drug cocrystals of CAR with HCT as coformer. It is well-known that the therapeutic efficacy of CAR can be increased when used in combination with HCT as adjuvant therapy [46]. This antihypertensive drug (CAR) is free from raising metabolic concerns when combined with HCT [47]. Based on these obvious clinical advantages, and both have functional groups that are required to form hydrogen bond between CAR and HCT, this combination has been chosen for the present study. Simple combination therapy can give an additive or synergistic effect, but when we apply crystal engineering approaches as cocrystallization, it can potentially bring about certain distinct advantages like improved pharmaceutical profiles of drugs and more importantly an improved therapeutic benefit [16]. Further, CAR produces more beneficial effects than the other beta blockers like atenolol/metoprolol by improving glucose, lipid metabolism, and lipid peroxidation in hypertensive and diabetic patients [48,49,50]. But poor aqueous solubility of CAR is a major obstacle in formulation development, which leads to poor bioavailability. We aimed to prepare drug–drug cocrystals of CAR (Fig. 1) with HCT (Fig. 2) as coformer using cocrystallization technique and study the solubility and consequently bioavailability, and the results are described in this communication.
Chemically CAR is a 1-(9-carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-[[2-(2-methoxy)-ethyl]-amino]-propan-2-ol, a nonselective β-adrenergic blocker with α1 blocking activity. CAR has low water solubility (0.583 mg/L) and low bioavailability (25%) [44] which limits its absorption. In contrast to conventional beta blockers, CAR maintains cardiac output, has a less pronounced effect on heart rate, and reduces blood pressure (BP) by decreasing vascular resistance. Chemically, HCT is 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide-1,1-dioxide and belongs to the BCS class IV with low aqueous solubility (0.7 g/L) and low permeability [51], and it acts by inhibiting the ability of the kidney to retain water.
Methods
Materials
Pure APIs (I.P. grade) CAR (m.r. 114–117 °C) and HCT (m.r. 269–272 °C) were purchased from Yarrow Chem Products Mumbai, India, and were used without further purification. Ethanol (99.9%, AR grade) and hydrochloric acid (HCl) were procured from Himedia, Mumbai, India, and FINAR Chemicals, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India, respectively. All other reagents of analytical grade were purchased from commercial sources and were used directly. Melting points were measured in open capillaries on a melting point apparatus (MEL-TEMP, Barnstead, International 1001D, USA) and are uncorrected. Water filtered through a double-distilled water purification system (EROSE 1077, India) was used in all solubility experiments.
Slurry conversion method (SC) [35]
Cocrystals of CAR (MW 406.5 g/mole) and HCT (MW 297.74 g/mole) were prepared by the SC method with 2:0.5 molar ratio (i.e., 2mM of CAR and 0.5mM of HCT were taken in a flat bottom flask, and 5–8mL of ethanol was added). Magnetic stirrer (REMI 1ML, Q-19, India) was used for stirring the suspension mixture at room temperature for 24 h. The resultant slurry was dried, and the solid obtained was stored in a desiccator for their characterization.
Solvent evaporation method (SE) [51, 52]
CAR-HCT (2:0.5) cocrystals, prepared by SC method were taken in glass beaker and added 5–8 ml of ethanol to dissolve. Then, the beaker was slightly heated and stirred with glass rod until complete dissolving of the solute. To this solution, a pinch of charcoal was added and filtered. The resulted solution was kept for evaporation at room temperature until it grows a single crystal. After 5 days, colorless rectangular-shaped single crystals were formed.
Melting point determination
The m.p./m.r. is a characteristic physical property of solids (the temperature at which solid phase exists in equilibrium with the liquid phase). It was determined using melting point apparatus, in open capillaries and is uncorrected.
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC)
Thermal data were obtained by differential scanning calorimeter (Perkin Elmer 4000, USA). About 3–5mg of samples (CAR and HCT) were accurately weighed using electronic analytical balance (KERRO P7, BL-2204, India) were taken into DSC sample pans (Perkin Elmer, 20 μL) and were crimped hermetically. The samples were scanned in the temperature range of 30 to 300 °C at a heating rate of 10 °C/min under a continuously purged dry nitrogen flow rate 50 ml/min. An empty pan was used as a reference. Data analysis was performed using the Pyris software.
Powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD)
The PXRD measurements were carried out with X-ray powder diffractometer (PANalytical XPERT-PRO, PW3040/60, the Netherlands) operating at 40 kV, 40 mA, using Cu-Kα radiation (λ = 1.5418 Å) with X’ Celerator RTMS (real-time multiple strips) detectors. The powder samples (100–200 mg) were placed in a sample holder (2-mm-thick aluminum plate with 20-mm square thick center hole), and the samples were scanned from 6 to 40°, 2θ at a step size of 0.0167° and step time of 0.5 s. PXRD data and diffractograms were analyzed using the PANalytical X-pert High score plus Data viewer software version 1.4.
Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy (FTIR)
FTIR spectra were recorded individually by a FTIR spectrophotometer (Bruker, Spectrum RXI, USA). One milligram (1 mg) of sample was mixed with 60 mg of potassium bromide (KBr) and pressed to form a pellet. Scans were recorded in the range of 4000–400 cm−1 at a spectral resolution of 4 cm−1 using extended scanning mode of the instrument. The data were developed and analyzed using Omnic 6.2.
Raman spectral studies (RS)
The Raman spectra were recorded using Bruker RFS 27: Stand-alone FT-Raman spectrometer (Bruker Optics, Ettlingen, Germany) equipped with a germanium detector. Spectra were acquired using an excitation wavelength of 1064 nm of Nd:YAG laser radiation (power 250 mW). The data presented using Opus 5.5 version.
Scanning electron microscope (SEM)
The morphology of the samples was investigated by high resolution scanning electron microscope (JEOL 5400, Japan). The small amount of sample was dispersed on to a carbon tube (double adhesive carbon-coated tape) adhered to an aluminum stub. These sample stubs were coated with a thin layer of gold by employing POLARAN-E3000 sputter coater. SEM analysis was carried out using an accelerating voltage of 20 kV after gold sputtering.
Accelerated stability studies (AST)
Accelerated stability studies (AST) were performed (for 90 days) as per ICH guidelines. The samples were kept in a photostability chamber (BLS 30, 12 CFT, Samiksha Industries Co, India) at 40 ± 2 °C, 75% RH ± 5%. The samples of cocrystals (n = 3) were taken out at an interval of 0, 1, 2, and 3 months and were subjected to PXRD analysis (PANalytical X-pert High score plus Data viewer software version 1.4.) to ascertain the crystallinity of the prepared cocrystals.
Solubility studies [53]
The solubility of pure APIs and prepared cocrystals were performed in distilled water, hydrochloric acid solution (0.1 N HCl), and phosphate buffer solutions pH 6.8 and pH 7.4. Excessive amounts of pure APIs and cocrystals were added to 10 mL of the above-mentioned dissolution media separately in a vial and then agitated continuously at room temperature for 24 h using a water bath mechanical shaker (REMI RSB-12, India). After equilibrium is attained, the solutions were filtered through Whatman filter paper (pore size 0.45 μm, GE Health Care Life Sciences, USA); filtrates were suitably diluted and analyzed on UV-visible double beam spectrophotometer (ELICO SL 210, India) at wavelength (λ) 248 nm (for CAR), and no interference was observed by HCT at this wavelength. The results were analyzed (Graphpad prism, version 5 software USA) and presented as the mean of three replicates.
Phase transformation studies [13]
The prepared cocrystals were subjected to assess their stability in aqueous medium, and the study was conducted by agitating the cocrystals for 24 h using a magnetic stirrer (REMI IML, Q-19, India) at 300 rpm. The resultant slurry was filtered, dried, and was subjected to PXRD studies.
Dissolution studies (in vitro) [13]
The dissolution studies were conducted in 900 mL of dissolution medium (0.1 N HCl) at 50 rpm maintained at 37 ± 0.5 °C in a dissolution apparatus (USP-certified Electrolab TDT-08 L Mumbai, India) using the paddle apparatus (Apparatus 2, USP). The drug (CAR, 100 mg) or its equivalent cocrystals were added to the dissolution medium, and the samples were withdrawn at regular time intervals (0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 45 min) for up to 1 hour. The volume of the dissolution medium was adjusted to 900 mL by replacing it each time the sample was drawn with fresh medium in order to maintain the sink conditions. The samples were immediately filtered through a 0.45-μm membrane filter (E. Merck Pvt Ltd, India), suitably diluted, and analyzed spectrophotometrically (ELICO SL 210 Double beam UV-Visible Spectrophotometer) at 248 nm.
Results
Designing of cocrystal is the primary aspect of the cocrystallization technique. Both CAR and HCT contain hydrogen bond donor and acceptor groups. Based on hydrogen-bonding principles, we predicted that the possible intermolecular interactions between the CAR and HCT may be amino–amino interactions and same as depicted in Fig. 3 and was verified using spectral analysis.
Meting point determination
The m.p. of the CAR-HCT cocrystal was found to be 125.81 °C. The pure CAR and HCT m.p. were found to be at 116.52 °C and HCT 272.30 °C respectively.
DSC studies
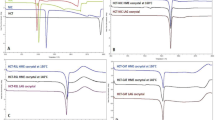
DSC thermograms of the pure CAR, HCT, and CAR-HCT cocrystals were shown single melting endothermic peaks with onset temperatures of 117.12 °C, 276.03 °C, and 126.31 °C respectively (Fig. 4).
PXRD studies
The PXRD pattern of the pure CAR exhibited characteristic diffraction lines to 2θ values at 8.21°, 11.70°, 12.99°, 13.61°, 14.89°, 15.03°, 15.74°, 16.41°, 17.48°, 18.39°, 19.16°, 20.27°, 21.03°, 21.71°, 22.83°, 23.41°, 24.23°, 26.21°, 27.21°, 28.08°, 29.38°, 31.39°, 31.92°, 34.14°, and 35.34°. The PXRD pattern of HCT exhibited characteristic diffraction lines to 2θ values at 12.88°, 14.12°, 16.65°, 18.76°, 19.12°, 20.94°, 21.82°, 24.65°, 25.87°, 26.12°, 26.829°, 28.06°, 30.84°, 32.62°, 33.65°, 34.18°, 36.00°, 36.77°, 37.59°, and 39.47°. The CAR-HCT showed new characteristic interference peaks to 2θ values at 9.18°, 9.72°, and 10.49° (Fig. 5).
FTIR data
FTIR spectra of CAR contains stretching vibration of (N–H) at 3496.66 cm−1, (C–H) at 2928.39 cm−1, (C–O) at 1255.38 cm−1, (C–N) at 1339.92 cm−1, (C=C) at 1600.71 cm–1, and of HCT indicate (N–H) stretching at 3362.42 cm−1, (C–H) at 2835.36 cm−1, (C–N) at 1319.14 cm−1, (C=C) at 1604.35 cm−1, (C–Cl) at 777.48 cm–1, and (S=O) at 1151.58 cm−1. For CAR-HCT cocrystals, the bands assigned to the –NH2 group shifted to 3272.33 cm−1, CH– bands shifted to 2833.41 cm−1, (C=O) shifted to 1219.94 cm−1, and (C=C) shifted to 1591.57 cm−1 (Fig. 6) (Table 2).
RS studies
The RS analysis was carried out to investigate the intermolecular interactions between the participating APIs. The spectrum for pure CAR has a strong intensity signal at 3344.18 cm−1, 2996.23 cm−1, and 1629.55 cm−1 corresponding to NH, CH, and C=C stretching, and the spectrum of HCT shows a strong intensity signal at 3361.71 cm−1 corresponding to NH stretching, 2948.87 cm−1, 1375.89 cm−1, and 709.05 cm−1 corresponding to CH, S=O, and C–Cl stretching respectively (Fig. 7) (Table 3). The spectrum of CAR-HCT cocrystals shows NH bands shifted from 3344.18 cm−1, 3361.71 cm−1, to 3270.07 cm−1, CH signal shifted to 2941.44 cm−1, and C=C signal shifted to 1590.91.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
The SEM image of the CAR appeared to be irregular in shape and of HCT was small irregular rod-shaped, and the CAR-HCT cocrystal image appeared markedly different from parent APIs (Fig. 8).
AST studies
The AST studies (performed according to the ICH tripartite guidelines) were based on PXRD data, and it was found that CAR-HCT cocrystals were fully analogous before and after 30, 60, and 90-day period (Fig. 9).
Solubility studies
As the objective is to examine the likely enhancement in solubility of CAR using cocrystallization, saturated solubility studies of CAR alone and the prepared cocrystals were performed in an aqueous medium, 0.1 N HCl, and phosphate buffers pH = 7.4 and 6.8 by subjecting the samples to shaking in a water bath mechanical shaker for 24 h at room temperature and were analyzed using double beam UV spectrophotometer. The pure CAR showed low solubility in all the dissolution media performed (aqueous medium = 0.248 mg/mL, 0.1 N HCL = 0.675 mg/mL, phosphate buffers pH 7.4 = 0.508 mg/mL and pH 6.8 = 0.553 mg/mL), whereas the CAR-HCT showed high solubility in 0.1 N HCl with 4.94 mg/mL, in pH 6.8 phosphate buffer with 2.208 mg/mL, in pH 7.4 phosphate buffer with 1.505 mg/mL, and in aqueous medium with 0.475 mg/mL (Fig. 10).
Phase transformation studies
The phase transformation studies of CAR-HCT cocrystals were conducted in line with the solubility studies. The solids obtained after the equilibrium time were dried and subjected to PXRD analysis (Fig. 11).
In vitro dissolution studies
The in vitro dissolution studies were performed in 0.1 N HCl dissolution medium. The initial release of pure CAR was 14.41% for the first 20 min, and the same was 35.91% at 1 h. In case of CAR-HCT, cocrystal initial release was 61.66% for the first 20 min, and at 1 h, the release was 98.94% (Fig. 12).
Single crystal analysis
Our attempts to generate single crystals of the CAR-HCT cocrystals were not successful. Although the formed crystal morphologically appeared as single crystal, but it was a twin crystal (Fig. 13). Perhaps it is due to the uneven molar ratio of the two APIs involved. However, efforts are in progress to get a single crystal of the cocrystal, and the results of those studies will be part of our future communications.
Discussion
Cocrystallization is currently recognized as a successful method to improve the physicochemical properties of solid APIs leading to requisite therapeutic benefit; cocrystals offer an effective optimized physicochemical (i.e., solubility, stability) and mechanical properties of the active drugs but they also offer the possibility of combined therapies that come along with intellectual property opportunities [14]. In addition, multidrug cocrystals may also offer beneficial synergistic or additive pharmacological outcomes. The design of possible cocrystals involves the evaluation of potential non-covalent and non-ionic intermolecular interactions between two or more active ingredients; in general, cocrystal formers bear functional groups that can form hydrogen bonds [54].
In designing potential cocrystals, a key point is the possibility of intermolecular interactions between components, in particular, hydrogen bonding, that may trigger the molecular assembly and determine the supramolecular architecture [55]. The formation of a cocrystal depends upon the existence of a coformer that dramatically influences the cocrystal properties, mainly solubility, and dissolution [56]. To date, the selection of a suitable coformer is based on several predictive criteria [57]; however, the formation of a cocrystal can be validated only through experimental techniques. The most frequently used coformers are compounds bearing functional groups such as carboxylic, amide, hydroxylic, or amino groups [58]. Earlier, Gasper et al. reported CAR cocrystals [59] with markedly higher improvement in solubility and dissolution rate. The same group further formulated CAR cocrystals for gastroretentive drug delivery systems [60]. We assume that this new compound CAR+HCT can be linked together by amino–amino interactions through hydrogen bonds.
The m.p. of CAR-HCT cocrystal was markedly different and lower than the pure APIs. This is one of the typical characteristic features of cocrystal. In DSC analysis, the melting temperature of CAR-HCT cocrystal was distinct from pure CAR and HCT, which indicated the formation of a new crystalline phase. From the PXRD analysis, the CAR-HCT showed new characteristic interference peaks as compared to pure CAR and HCT. This resulted data suggested the formation of a new solid phase of CAR-HCT cocrystal. In the FTIR analysis of CAR-HCT, the bands assigned to the –NH2 group shifted from higher to lower as compared to pure CAR and HCT. Hence, the change in the stretching vibrations of NH indicates that the possible intermolecular interactions between CAR and HCT were amino–amino interactions. In Raman analysis results, the spectrum of CAR-HCT cocrystals NH bands were shifted from 3344.18 cm−1, 3361.71 cm−1, to 3270.07 cm−1. The signal shifted from high to low indicated the hydrogen bond formation. This shift indicates that the possible hydrogen bond formation between CAR-HCT could be the expected amino–amino interactions. The SEM images of CAR-HCT cocrystals were different from pure APIs (CAR and HCT). This morphological deviation indicated that CAR-HCT cocrystals could be different from the parent APIs. Solubility study results demonstrated that comparative high solubility of CAR-HCT cocrystals in 0.1 N HCl (7.3 times) improved as compared to pure CAR. The increase in solubility may be due to the formation of hydrogen bonding between CAR and HCT. From the phase transformation results, it was found that CAR-HCT cocrystal crystalline phase remained unchanged in aqueous medium after 24 h. In vitro dissolution studies proved that CAR-HCT release was high at 1 h as compared to pure CAR. The enhancement of dissolution of CAR (about 2.7 times) could be because of cocrystallization with HCT.
Conclusion
Cocrystallization is a simple and promising approach to improve the physicochemical and pharmacokinetic behavior of poorly water-soluble drug substances. Taking the advantages of drug–drug cocrystals in overcoming the problems associated with single drug therapy, reduction of dosage, CAR-HCT cocrystals were prepared (molar ratio 2:0.5). They were characterized by thermal (DSC), diffractometric methods (PXRD) and were further confirmed by spectral analysis (FT-IR and Raman). The SEM analysis results determined that the morphological behavior of CAR-HCT was different from individual CAR and HCT. The prepared CAR-HCT cocrystals were stable up to 3 months (90 days). Their solubility was significantly improved 7.3 times in 0.1 N HCl than the pure CAR alone. The in vitro dissolution rate of cocrystals was enhanced by 2.7 times than pure CAR which may lead to enhanced bioavailability. Enhancement in solubility and subsequent dissolution rate need to be further demonstrated in biological (in vivo) models. Formulating the cocrystals in suitable mode of clinical settings is being planned to take these encouraging observations to logical conclusion.
Availability of data and materials
Data and material are available upon request.
Abbreviations
- APIs:
-
Active pharmaceutical ingredients
- BCS:
-
Biopharmaceutical Classification System
- CAR:
-
Carvedilol
- HCT:
-
Hydrochlorothiazide
- GRAS:
-
Generally regarded as safe
- m.p.:
-
Melting point
- m.r.:
-
Melting range
- DSC:
-
Differential scanning calorimetry
- PXRD:
-
Powder X-ray diffraction
- FTIR:
-
Fourier transform infrared
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- ICH:
-
International Conference on Harmonization
- HCl:
-
Hydrochloric acid
- AST:
-
Accelerated stability testing
References
Gadade DD, Pekamwar SS, Lahoti SR, Patni SD, Sarode MC (2017) Cocrystallization of etodolac: prediction of cocrystallization, synthesis, solid state characterization and in vitro drug release. Marmara Pharm J 21:78–88
Eedara BB, Veerareddy PR, Jukanti R, Bandari S (2014) Improved oral bioavailability of fexofenadine hydrochloride using lipid surfactants: ex vivo, in situ and in vivo studies. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 40:1030–1043
Mullauer FB, Van BL, Daalhuisen JB, Ten BMS, Storm G, Medema JP, Schiffelers RM, Kessler JH (2011) Betulinic acid delivered in liposomes reduces growth of human lung and colon cancers in mice without causing systemic toxicity. Anticancer Drugs 22:223–233
Dehelean CA, Feflea S, Gheorgheosu D, Ganta S, Cimpean AM, Muntean D, Amiji MM (2013) Anti-angiogenic and anti-cancer evaluation of betulin nanoemulsion in chicken chorioallantoic membrane and skin carcinoma in Balb/c mice. J Biomed Nanotechnol 9:577–589
Tan JM, Govindarajan K, Arulselvan P, Fakurazi S, Hussein MZ (2014) Sustained release and cytotoxicity evaluation of carbon nanotube-mediated drug delivery system for betulinic acid. J Nanomater https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/862148
Das J, Samadder A, Das S, Paul A, Khuda BAR (2016) Nanopharmaceutical approach for enhanced anti-cancer activity of betulinic acid in lung-cancer treatment via activation of PARP: interaction with DNA as a target: anti-cancer potential of nano-betulinic acid in lung cancer. J Pharmacopuncture 19:37–44
Hu L, Jia Y, Niu F, Zheng J, Yang X, Jiao K (2012) Preparation and enhancement of oral bioavailability of curcumin using microemulsions vehicle. J. Agric. Food Chem. 60:7137–7141
Roy A, Bulut O, Some S, Mandal AK, Yilmaz MD (2019) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: biomolecule-nanoparticle organizations targeting antimicrobial activity. RSC Adv 9:2673–2702
Yadav AV, Shete AS, Dabke AP, Kulakarni PV, Sakhare SS (2009) Co-crystals: a novel approach to modify physicochemical properties of active pharmaceutical ingredients. Indian J Pharm Sci 71:359–370
Shahram E, Mohammadreza SS, Khosro A, Mohammad BJ (2018) Recent advances in improving oral drug bioavailability by cocrystals. Bioimpacts 8:305–320
Yamashita H, Sun CC (2019) Expedited tablet formulation development of a highly soluble carbamazepine cocrystal enabled by precipitation inhibition in diffusion layer. Pharm Res 36:90
Yamashita H, Sun CC (2017) Improving dissolution rate of carbamazepine-glutaric acid cocrystal through solubilization by excess coformer. Pharm Res 35:4
Bhandaru JS, Malothu N, Akkinepally RR (2015) Characterization and solubility studies of pharmaceutical cocrystals of eprosartan mesylate cocrystals. Cryst Growth Des 15:1173–1179
Yamashita H, Sun CC (2016) Harvesting potential dissolution advantages of soluble cocrystals by depressing precipitation using the common coformer effect. Cryst Growth Des 16:6719–6721
Wang C, Tong Q, Hou X, Hu S, Fang J, Sun CC (2016) Enhancing bioavailability of dihydromyricetin through inhibiting precipitation of soluble cocrystals by a crystallization inhibitor. Cryst Growth Des 16:5030–5039
McNamara DP, Childs SL, Giordano J, Iarriccio A, Cassidy J, Shet MS, Mannion R, Ed O’D, Park A (2006) Use of glutaric acid cocrystals to improve oral bioavailability of a low solubility API. Pharm Res 23:1888–1897
Blagden N, Matas DM, Gavan PT, York P (2007) Crystal engineering of active pharmaceutical ingredients to improve solubility and dissolution rates. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59:617–630
Desiraju GR (2013) Crystal engineering: from molecule to crystal. J Am Chem Soc 135:9952–9967
Sreekanth BR, Peddy V, Vyas K (2007) Supramolecular synthon polymorphism in 2:1 cocrystal of 4-hydroxybenzoicacid and 2,3,5,6–tetramethylpyrazine. Chem Comm 9:2375–2377
Dannenberg JJ (1997) An introduction to hydrogen bonding: George AJ (University of Pittsburgh). Oxford University Press, New York
Database of select committee on GRAS substances (SCOGS) Reviews (2018) US Food and Drug Administration, http://www.acessdata.fda.gov/scripts/fcn/fcnNavigation.cfm?rpt=scogsListing.
Imamura M, Nakanishi K, Shiraki R, Onda K, Sasuga D, Yuda M (2012) Cocrystal of C-glycoside derivative and L-proline. US Patent 8, 097, 592 B2 (17 January 2012)
Thipparaboina R, Kumar D, Chavan RB, Shastri NR (2016) Multi drug co-crytals: towards the development of effective therapeutic hybrids. Drug Discov Today 21:481–490
Trask AV, Motherwell WDS, Jones W (2006) Physical stability enhancement of theophylline via cocrystallization. Int J Pharm 320:114–123
Singh BS (2012) Drug-drug cocrystals. Daru J Pharm Sci 20:45
Jiang L, Huang Y, Zhang Q, He H, Xu Y, Mei X (2014) Preparation and solid-state characterization of dapsone drug-drug cocrystals. Cryst Growth Des 14:4562–4573
Cosgrove SD, Jonaitis DT, Derrick SJC (2012) Novel ticagrelor co-crystal. World Intellectual Property Organization WO Patent 164, 286. 2012 A1(6 December 2012)
Sica DA (2002) Rationale for fixed-dose combinations in the treatment of hypertension: the cycle repeats. Drugs 62:443–462
Bangalore S, Kamalakkannan G, Parkar S, Messerli HF (2007) Fixed-dose combinations improve medication compliance: a meta-analysis. Am J Med 120:713–719
Cheney ML, Weyna DR, Shan N, Hanna M, Wojtas L, Zaworotko MJ (2011) Coformer selection in pharmaceutical cocrystal development: a case study of a meloxicam aspirin cocrystal that exhibits enhanced solubility and pharmacokinetics. J Pharm Sci 100:2172–2181
Nugrahani I, Asyarie S, Soewandhi SN, Ibrahim S (2007) The antibiotic potency of amoxicillin-clavulanate co–crystal. Int J Pharmacol 3:475–481
Roche FH (1937) Basel (Switzerland). Swiss Patent CH 187826:1937
Petrusevski G, Naumov P, Jovanovski G, Bogoeva GG, Ng SW (2008) Solid-state forms of sodium valproate, active component of the anticonvulsant drug epilim. Chem Med Chem 3:1377–1386
Meade EM (1991) Sodium hydrogen divalproate oligomer. US Patent 4, 988,731.A (29 January 1991)
Almansa C, Merce R, Tesson N, Farran J, Tomas J, Salaman PCR (2017) Co-crystal of tramadol hydrochloride-celecoxib (ctc): a novel API–API co-crystal for the treatment of pain. Cryst Growth Des 17:1884–1892
Buschmann HH, Tesson N, Farran J (2010) Cocrystals of tramadol and paracetamol. WO Patent 0, 69, 561 Al (24 June 2010)
Salaman PCR, Videla CS, Tesson N, Trilla CM (2011) Co-crystals of venlafaxine and celecoxib. WO Patent 0, 76, 420 A3 (30 June 2011)
Reddy JS, Dandela R, Saraswatula VG, Nagalapalli RK, Solomon AK, Iqbal J, Kruthiventi AK (2012) Novel cocrystals/molecular salts of metformin with oleoylethanolamide as an effective anti-diabetic + anti-obesity agent. WO Patent 0, 90, 225 A2 (5 July 2012)
Kruthiventi AK, Iqbal J, Reddy JS, Nagalapalli RK, Saraswatula VG, Solomon AK (2012) Pharmaceutical co-crystals of quercetin. US Patent 0, 129,923 A1 24 May 2012.
Buschmann HH, Sola CL, Benet BJ, Ceron BJC, Ramirez AJ (2013) Co-crystals of duloxetine and naproxen. EP Patent 2, 291, 345 B1 (13 March 2013)
Salaman PCR, Tesson N, Jimenez GC, Vaiana L (2013) Crystalline forms of sartans like telmisartan with beta blockers. EP Patent 2, 649, 996 A1, 16 October 2013.
Sowa C, Gold RE, Chiodo T, Vogel R (2013) Co-crystals of cyprodinil and dithianon. WO Patent 0, 30, 777 Al (7 March 2013)
Yuvaraja K, Khanam J (2014) Enhancement of carvedilol solubility by solid dispersion technique using cyclodextrins, water soluble polymers and hydroxyl acid. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 96:10–20
KM EI-S, Hosny KM (2018) Optimization of carvedilol solid lipid nanoparticles: an approach to control the release and enhance the oral bioavailability on rabbits. PLOS ONE 13(8):e0203405. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0203405
Singh B, Khurana L, Bandyopadhyay S, Kapil R, Katare OP (2011) Development of optimized self-nano-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SNEDDS) of carvedilol with enhanced bioavailability potential. Drug Deliv. 18:599–612
Carvedilol (2017) DB01136, http://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01136, Accessed 15 December 2019.
COREG (2017) www.acessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2005/020297s03lb/.pdf Accessed 15 December 2019.
Stafylas PC, Sarafidis PA (2008) Carvedilol in hypertension treatment. Vasc Health Risk Manag 4:23–30
Giugliano D, Acampora R, Marfella R, Rosa DN, Ziccardi P, Ragone R, Angelis DL, Donofrio F (1997) Metabolic and cardiovascular effects of carvedilol and atenolol in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and hypertension. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 126:955–959
Uzunlulu M, Oguz A, Yorulmaz E (2006) The effect of carvedilol on metabolic parameters in patients with metabolic syndrome. Int Heart J 47:421–430
Palash S, Kusuma VD, Clara D, Malviya N, Ganguly S, Gautam DR (2015) Cocrystals of hydrochlorothiazide: solubility and diffusion/permeability enhancements through drug–coformer interactions. Mol Pharm 12:1615–1622
Syarifah AR, Nurul AR, Siti SMK (2015) Screening of carbamazepine-ibuprofen co-crystal formation using non-stoichiometric and stoichiometric methods. Adv Mate Res 1113:417–421
Glomme A, Marz J, Dressman JB (2005) Comparison of a miniaturized shake-flask solubility method with automated potentiometric acid/base titrations and calculated solubilities. J Pharm Sci 94:1–16
Du Y, Cai Q, Xue J, Zhang Q (2016) Raman and terahertz spectroscopic investigation of cocrystal formation involving antibiotic nitrofurantoin drug and coformer 4-aminobenzoic acid. Crystals 6:164
Venugopalaiah P, Sravanthi D, Gobinath M, Kumar B, Dinesh R (2016) Pharmaceutical co-crystals - an approach to increase solubility and bioavailability. IJPIB 1:63–70
Tomaszewska I, Karki S, Shur J, Price R, Fotaki N (2013) Pharmaceutical characterisation and evaluation of cocrystals: importance of in vitro dissolution conditions and type of conformer. Int J Pharm 453:380–388
Schultheiss N, Newman A (2009) Pharmaceutical cocrystals and their physicochemical properties. Cryst Growth Des 9:2950–2967
Jain S, Patel N, Lin S (2015) Solubility and dissolution enhancement strategies: current understanding and recent trends. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 41:875–887
Gasper JF, Rathnanand M, Kulkarni V (2018) Mechanochemical synthesis of carvedilol cocrystals utilizing hot melt extrusion technology. J Pharm Innov. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12247-018-9360-y
Gasper JF, Rathnanand M (2019) Formulation optimization for gastroretentive drug delivery system of carvedilol cocrystals using design of experiment. J Pharm Innov. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12247-019-09393-5
Buschmann HH, Sola CL, Benet BJ, Ceron BJC (2010) Cocrystals of tramadol and NSAIDs. EP Patent 2, 177, 215 A1 (21 April 210)
Brittain HG, Felice PV (2015) Intravenous formulation with water-soluble cocrystals of acetyl salicylic acid and theanine. EP Patent 2, 427, 196 B1 (4 November 2015).
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to NIT Warangal, India, for recording DSC and PXRD samples; IIT Madras, India, for recording the Raman spectra; and IICT Hyderabad, India, for SEM analysis. One of the authors, SE, thanks University Grant Commission (UGC), New Delhi, India, for granting a fellowship under RGNFHEST Scheme [F1-17.1/2015-16/NFST-2015-17-ST-TEL-1365/SAIII/Website]. We thankfully acknowledge support of Prof. Arvind K Bansal (Professor and Head, Department of Pharmaceutics, NIPER, SAS Nagar), Prof. KV Ramana Murthy (Principal, University College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam), and Prof. P. Venugopalan (Department of Chemistry, Panjab University, Chandigarh) for their kind suggestions and help, and the Principal, University College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Kakatiya University, Warangal, India, for providing necessary facilities. The authors dedicate this work to Professor V. Malla Reddy, a great teacher and researcher on his 75th birthday.
Funding
The authors acknowledge the financial support by University Grant Commission (UGC), New Delhi, India, for granting a fellowship to SE under RGNFHEST Scheme [F1-17.1/2015-16/NFST-2015-17-ST-TEL-1365/ SA-III/Website]. The funding agency, UGC, granted a fellowship and contingency to SE for the purpose of conducting research study. The funds were utilized for purchasing chemicals, data collection, instrumentational analysis charges, and all other related expenses. We declare that the funding agency had no role in the data interpretation and writing the manuscript.
*UGC in India is the premier funding agency which provides funds for research projects (fellowships, contingencies, and infrastructural support) to students to conduct research activities in university departments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SE designed and conducted all the experimental activities. JSB helped in designing the study and drafting the manuscript. CN and RK helped in sequence alignment; RRA conceived the study, participated in designing, coordination, drafting the manuscript, and supervised. Further “All authors have read and approved the manuscript”.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Eesam, S., Bhandaru, J.S., Naliganti, C. et al. Solubility enhancement of carvedilol using drug–drug cocrystallization with hydrochlorothiazide. Futur J Pharm Sci 6, 77 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43094-020-00083-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43094-020-00083-5