Abstract
Background
A Simple, sensitive, and specific stability indicating reverse phase HPLC method was developed for simultaneous estimation of Lamivudine and Dolutegravir in bulk and tablet dosage form. Effective separation was achieved by injecting10 μL of the standard solution into Xbridge Phenyl (250 × 4.6 mm, 5 μ,100 A0) column, using a mobile phase composition of methanol: buffer (0.1% v/v trifluoroacetic acid in water) (85:15 v/v) and isocratic elution programming have been done at a flow rate of 0.8 mL/min. The eluted analytes detected at 258 nm wavelength. The stress conditions such as acid, base, oxidative, thermal, and photo stability were applied as per ICH guidelines to determine the stability of the drugs in different environmental conditions.
Results
The retention times of Lamivudine and Dolutegravir were found to be 3.4 and 5.0 min respectively. The developed method was linear in the concentration range of 5–15 μg/mL and 30–90 μg/mL for Dolutegravir and Lamivudine respectively. Detection and quantification limits were observed at 3.6 and 11 μg/mL for Lamivudine and 0.50 and 1.5 μg/mL for Dolutegravir. Method validation parameters were within the acceptance criteria of ICH guidelines, and the degradation products were well resolved from Dolutegravir and Lamivudine peaks, which indicate the stability of the method.
Conclusion
The developed RP-HPLC method was highly precise, specific, sensitive, and stability indicating. Hence, the method has the ability to use in quality control department for regular analysis for the estimation of Lamivudine and Dolutegravir.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
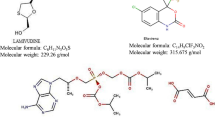
The advancement in therapy for human immune virus (HIV) led the patients to survive longer periods and offering progressively gainful lives. The use of multiple drug therapy, i.e., at least three or more drugs alone or in combination daily is in practice to treat the HIV effectively. However, extensive research on multiple drug therapy revealed that a two-drug regimen consisting of Lamivudine and Dolutegravir controls the HIV disease effectively [1, 2]. Hence, Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) recommended a fixed dose combination containing 300 mg of Lamivudine and 50 mg of Dolutegravir for the effective treatment of HIV-1 in adolescent and adult patients with no known or suspected protection from the integrase inhibitors [3]. Chemically, Dolutegravir is a (4R,12aS)-N-[(2,4-difluorophenyl)methyl]-3,4,6,8,12,12a-hexahydro-7-hydroxy-4-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2H-pyrido[1′,2′:4,5]pyrazino[2,1-b][1,3]oxazine-9-carboxamide, integrase strand transfer inhibitor (INSTI) that blocks HIV replication by preventing the integration of viral DNA into the genetic material of host (human immune cells (T cells)) [4]. Lamivudine is chemically 4-amino-1-[(2R, 5S)-2-(hydroxyl methyl)-1, 3-oxathiolan-5-yl]-1, and 2-dihydropyrimidin-2-one. Lamivudine triphosphate (3TCTP), active form of Lamivudine, acts as competitive inhibitor of reverse transcriptase enzyme and causes termination of DNA replication [5, 6]. Chemical structures of Dolutegravir and Lamivudine were shown in Fig. 1.
An effective analytical method is requisite for a drug to analyze individually or simultaneously in combination with other drugs in pharmaceutical industry. Extensive literature search revealed that few analytical methods such as UV methods and RP-HPLC methods were reported for estimation of Lamivudine and Dolutegravir individually [7,8,9,10,11]. Further, there are some RP-HPLC methods available for simultaneous estimation of Lamivudine, Dolutegravir, and tinofivir disproxil fumarate or butcaver sulfate or abacavir in triple combination [6, 12,13,14,15]. As per FDA official news, Lamivudine and Dolutegravir fixed dose film-coated tablet got an approval in April 2019 for the treatment of HIV-1. Till date, no single stability indicating RP-HPLC method has not been reported in literature for the estimation of Lamivudine and Dolutegravir in bulk and tablet dosage form simultaneously. Hence, we have undertaken current research work to develop an effective, sensitive, economical RP-HPLC method to estimate the percentage purity and to assess the stability of Dolutegravir and Lamivudine in bulk and tablet dosage form simultaneously. Validation of the developed method was performed as per Q2 specification of ICH guidelines.
Methods
API of Lamivudine and Dolutegravir was provided by Fortune Pharma, Hyderabad, as a gift sample. HPLC grade acetonitrile, methanol, Milli-Q, and remaining analytical grade chemicals were obtained from Merck India Limited, Mumbai, India.
Chromatographic conditions
RP-HPLC experiment is carried on WATERS 2695 with 2487 PDA detector with auto sampler, data-processing, and acquisition has done by using the Empower 2 software. Effective separation achieved by injecting 10 μL of the standard solution into Xbridge Phenyl (250 × 4.6 mm, 5 μ, 100 A0) column, using a mobile phase composed of methanol: buffer (0.1% v/v trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) in water) (85:15 v/v) at a flow rate of 0.8 mL/min, and the eluted analytes were detected at 258 nm wavelength. Ambient temperature was maintained in the injection port and in the analytical column. Mobile phase and standard and sample solution were filtered through a 0.45-μm nylon filter prior to injecting into the HPLC system.
Preparation of standard solution
Sixty milligrams of Lamivudine and 10 mg of Dolutegravir API powders were weighed and transferred into 100 mL volumetric flask, volume made with diluent (acetonitrile and water (50:50)) to 100 mL. One milliliter of above solution was transferred into 10 mL volumetric flask, again volume made with diluents to obtain concentration of 60 μg/mL, and 10 μg/mL for Lamivudine and Dolutegravir, respectively, said as 100% level concentrations.
Preparation of sample solution
An amount of tablet (DOVATO) powder (80 mg) equivalent to 60 mg of Lamivudine and 10 mg of Dolutegravir was weighed and transferred into 100 mL volumetric flask, volume made with diluents to 100 mL. One milliliter of above solution was transferred into 10 mL volumetric flask, volume made with diluents to obtain concentration of 60 μg/mL, and 10 μg/mL for Lamivudine and Dolutegravir respectively. Prior to injecting, sample solution was filtered through 0.4 μm Nylon filter.
Method validation
System suitability test
The system suitability test of the current method was carried out by injecting 100% level of working standard concentration in 6 replicates, and parameters like percentage relative standard deviation (% RSD), USP tailing factors (T), USP plate count (N), and resolution (R) were evaluated for the obtained chromatograms.
Linearity
The linearity of the method represents that the obtained test results are directly proportional to concentration. The linearity of the current method has performed by injecting the series of working standard concentrations ranges from 30 μg/ml to 90 μg/ml of Lamivudine and 5 μg/mL to 15 μg/mL of Dolutegravir into the HPLC system under optimized chromatographic conditions. Finally, linearity graph was plotted for concentration vs peak area and regression coefficient (r2) value determined.
Precision
The closeness relationship among observed responses of homogenous sample on multiple replications referred as precision. Usually, it can be done in the same day (intraday) and in different days (inter-day). Intraday and inter-day precision of the method were performed by injecting 100% level of working standard concentration for 6 times in a day and 3 times per day for three continuous days. Percentage RSD calculated for peak areas obtained.
Accuracy
The accuracy of the method was accomplished by recovery studies in which known amount sample solution spiked at three different standard concentration levels about 50, 100, and 150%, each level of solution injected in triplicate. The percentage mean recovery at three different levels of the drug solution was calculated.
Specificity
Specificity represents the ability of the method to determine or assess the intended drug in the presence of other substances without interferences. Ten microliter volume of prepared blank solution, 100% level pure working standard solution, and standard solution with placebo have been injected individually. The retention time (RT) of individual injection of standard sample solution alone and along with placebo was observed to assess any interference that has been happened with peaks of Dolutegravir and Lamivudine in obtained chromatograms.
Sensitivity
The LOD and LOQ were calculated by implementation of standard deviation method, in which the following formulae were used.
where σ is the standard deviation of the intercept, and S is the slope of the linear curve.
Robustness
The robustness of the method was checked by slightly and deliberately changing the flow rate, mobile phase composition, and maximum absorption wavelength. It can be performed by evaluating the system suitability parameters after changing the HPLC flow rate (± 0.1 mL/min), wavelength maximum (± 2 nm), and mobile phase ratio (± 1 mL).
Forced degradation studies
In forced degradation studies, intentionally drug substance is exposed to conditions more intense than accelerated conditions. Chemical stability of the drug molecule can be depicted with forced degradation studies, which helps in successful development of stable formulation with appropriate storage conditions. ICH guidelines emphasized certain degradation conditions like acid hydrolysis, base hydrolysis, oxidation, thermal degradation, and photo stability in ICH Q1A, QIB, and Q2B guidelines.
Acidic degradation solution
Add 0.2 mL of 0.1 N HCl to 1 mL of the standard stock solution and reflux for 2 h at 70 °C, kept a side for 24 h at same temperature, and after that, cool the solution and neutralize with 0.1 N NaOH. Further dilution was done to get a solution having 60 μg/mL of Lamivudine and 10 μg/mL of Dolutegravir.
Alkali degradation solution
To the 1 mL of standard stock solution, add 0.2 mL of 0.1 N NaOH and reflux for 2 h at 70 °C, kept a side for 24 h at same temperature, and after that, cool the solution and neutralize with 0.1 N HCl and make up to 10 mL with diluent to obtain concentration of 60 μg/mL, and 10 μg/mL for Lamivudine and Dolutegravir respectively.
Oxidative degradation solution
To the 1 mL of standard stock solution, add 0.2 mL of 3% hydrogen peroxide and reflex for 2 h at 70 °C, kept a side for 24 h at same temperature, and after that, cool the solution and make up to10 mL with diluent to obtain concentration of 60 μg/mL and 10 μg/mL for Lamivudine and Dolutegravir respectively.
Thermal degradation solution
Place the 100 mL of standard stock solution in heating chamber at 80 °C/75% RH for 24 h. One microliter of above solution is diluted to 10 mL to obtain concentration of 60 μg/mL and 10 μg/mL for Lamivudine and Dolutegravir respectively.
To assess the percentage degradation, the prepared each solution was injected three times. In general, not more than 20% degradation of the drug is considered as effective and optimal acceptable value in analytical method with stability indicating.
Assay
Assay of the method can be done by injecting subsequent injections of standard and sample solutions, both having concentration about 60 μg/mL and 10 μg/mL of Lamivudine Dolutegravir respectively. The preparation of standard and sample solutions was mentioned prior the in methods section. Computing the percentage assay by using following formula.
where AT is the peak area of sample (tablet) solution, AS is the peak area of standard solution, WS is the weight of standard substance in mg to prepare standard solution, WT is the weight of sample (tablet) powder in mg to prepare standard solution, DS is the dilution factor of standard solution, DT is the dilution factor of sample solution, P is the percentage purity of standard substance, and AVG Wt is the average weight of the tablets in mg.
Results
Initially, solubility studies of the both drugs were done and found that Lamivudine was freely soluble in acetonitrile, water, and slightly soluble in methanol. Dolutegravir was freely soluble in water and methanol. Based on the solubility of drugs, acetonitrile and water in (50:50) ratio selected as diluent to prepare standard and sample solutions.
Method optimization
Method optimization has done by implementing trial and error method in such a way to obtain a chromatogram with good resolution (R), efficiency, accepted number of USP plates, and tailing factor. In this procedure, several trials have been done by altering mobile phase composition, columns, and flow rate. Finally, the method with Xbridge Phenyl (250 × 4.6, 5 μm) column, mobile phase composition of methanol: buffer (15:85 v/v) and a flow rate of 0.8 mL/min was selected as optimized method. The results obtained in the trial and error method were mentioned in Table 1; trial 7 selected as optimized conditions and optimized chromatogram shown in Fig. 2.
Method validation
System suitability
Up on injecting 100% level concentration, the data obtained from chromatograms illustrated that system suitability parameters include % RSD (≤ 2), USP tailing factor (≤ 2), and USP plate count (> 2000) values shown in Table 2 were satisfying the acceptance criteria as per Q2 specifications of ICH guidelines.
Linearity
The linear response of the HPLC system for Dolutegravir and Lamivudine was in the concentration range of 5 to 15 μg/mL and 30 to 90 μg/mL that was determined by constructing calibration curve between concentration and peak area (Table 3, Fig. 3). The computed regression coefficient (R2) value found to be 0.998 and 0.998 for Dolutegravir and Lamivudine, respectively, and manifests the linearity of the method within the ICH guidelines limit.
Accuracy
Percentage mean recovery of the Dolutegravir and Lamivudine at three different concentration levels that were observed as 100% ± 2 illustrates the acceptance of the method as per Q2 specifications of ICH guidelines. Results were shown in Table 4.
Precision
Percentage RSD value of peak area responses obtained by injecting 100% level working standard solution of Dolutegravir and Lamivudine were found to be 0.65 and 0.75, respectively (Table 5), and depicts the precision of the method.
Sensitivity
The LOD and LOQ determined as 3.65 μg/mL and 11 μg/mL for Lamivudine and 0.5 μg/mL and 1.52 μg/mL for Dolutegravir, respectively, which indicates that method has good sensitivity.
Robustness
Slightly deliberate changes in mobile phase ratio, flow rate, and absorption maximum of the method could not produce the system suitability parameter values beyond the acceptance limits that (Table 6) represent the method’s robustness.
Forced degradation
In general, the acceptable percentage of degradation in a stability indicating method is not more than 20%. Percentage degradation was calculated by comparing the peak areas of 100% level working standard concentration at normal and stress conditions. Results were shown in Table 7. Alkali degradation is shown in Fig. 4.
Percentage assay
Percentage assay of the Dolutegravir and Lamivudine tablets that were found as 100% ± 15 indicates that the analyzed tablets have percentage purity within the acceptance limits as per ICH guidelines. Results were shown in Table 8.
Discussion
The stability indicating RP-HPLC assay method plays a significant role in determination of intrinsic stability, both qualitative and quantitative estimation of drug product and drug substance. Till date, many analytical methods have been developed for Dolutegravir and Lamivudine individual and in combination with other anti-retroviral drugs. But, no RP-HPLC method has been existed for the simultaneous estimation of Lamivudine and Dolutegravir. Hence, attempts were made to develop an effective stability indicating RP-HPLC method. The RT in the reported method was 5.06 min for Dolutegravir and 3.34 min for Lamivudine, represents the method with good and effective retention time, and can be treated as economical as it reduces solvent consumption and analyte run time. Hence, rapid analysis of more number samples can be done. The calculated and statistical results of the validation parameters were not out of the acceptance limits stated by ICH.
Conclusion
A simple, accurate, sensitive, and specific RP HPLC with PDA detector and isocratic elution method was successfully developed for the simultaneous estimation of Dolutegravir and Lamivudine in bulk and its combined film-coated tablet formulation. Forced degradation studies were done by applying several stress conditions to assess the stability of the method. The proposed method was successfully separate both of the drugs and its degradation products with good resolution and quantifies the active contents at minute concentration levels. The developed method has specific, sensitive, and stability-indicating power. Hence, the proposed method can be adapted to regular analysis in pharmaceutical industry.
Availability of data and materials
All data and materials should be available upon request.
Abbreviations
- HIV:
-
Human immune virus
- CHMP:
-
Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use
- API:
-
Active pharmaceutical ingredient
- TFA:
-
Trifluoroacetic acid
- RT:
-
Retention time
- LOD:
-
Limit of detection
- LOQ:
-
Limit of quantification
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- RSD:
-
Relative standard deviation
- PDA:
-
Photodiode array
References
Corado KC, Caplan MR, Daar ES (2018) Two-drug regimens for treatment of naive HIV-1 infection and as maintenance therapy. Drug Des Devel Ther 12:3731–3740. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S140767
Commissioner of FDA (2019) The FDA. http://www.fda.gov. Accessed 7 Aug 2019.
ViiV Healthcare (2019) D-ovato (dolutegravir and lamivudine). https://www.centerwatch.com . Accessed 7 Aug 2019.
Kandel CE, Walmsley SL (2015) Dolutegravir - a review of the pharmacology, efficacy, and safety in the treatment of HIV. Drug Des Devel Ther 9:3547–3555
Maggiolo F, Gulminetti R, Pagnucco L, Digaetano M, Benatti S, Valenti D, Callegaro A, Ripamonti D, Mussini C (2017) Lamivudine/dolutegravir dual therapy in HIV-infected, virologically suppressed patients. BMC Infect Dis 17:215
Mallikarjuna Rao N, Gowri Sankar D (2015) Development and validation of stability-indicating HPLC method for simeltaneous determination of Lamivudine, tenofovir, and Dolutegravir in bulk and their tablet dosage form. Future J Pharm Sci 1:73–77
Balasaheb BG, Balasaheb AK, Subhash TR, Jijabapu K, Sudhakar PS (2015) Development and validation of UV spectrophotometric method for estimation of Dolutegravir sodium in tablet dosage form. Malaysian J Anal Chem 19:1156–1163
Madu KC, Ukoha PO, Attama AA (2011) Spectrophotometric determination of Lamivudine using chloranilic acid and 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone (DDQ). Am J Anal Chem 2:849–856
Deepali G, Elvis M (2010) UV Spectrophotometric method for assay of the anti-retroviral agent Lamivudine in active pharmaceutical ingredient and in its tablet formulation. J Young Pharm JYP 2:417–419
Bhavar GB, Pekamwar SS, Aher KB, Thorat RS, Chaudhari SR (2016) High-performance liquid chromatographic and high-performance thin-layer chromatographic method for the quantitative estimation of Dolutegravir Sodium in bulk drug and pharmaceutical dosage form. Sci Pharm 84:305–320
Vikram Singh A, Nath LK, Pani NR (2011) Development and validation of analytical method for the estimation of Lamivudine in rabbit plasma. J Pharm Anal 1:251–257
Mastanamma S, Jyothi JA, Saidulu P, Varalakshmi M (2018) Development and validation of RP-HPLC method for the simultaneous estimation of Lamivudine, Tenofovir Alafenamide and Dolutegravir bulk and their combined dosage form. Pharm Methods 9:49–55
Kalpana T, Rajeswari DTR, Ganji RR (2017) Development and validation of analytical method for determination of Dolutegravir sodium, Lamivudine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate using reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography. Pharma Chem 9:117–127
Ashok G, Mondal DS (2018) Development and validation of stability indicating method for the simultaneous estimation of batcaver sulfate, Lamivudine and Dolutegravir sodium in pharmaceutical dosage forms by RP-HPLC. Saudi J Med Pharm Sci 4:289–296. https://doi.org/10.21276/sjmps.2018.4.2.18
Pal N, Avanapu SR, Ravikumar P (2016) Simultaneous HPLC method development and validation for estimation of Lamivudine, abacavir and Dolutegravir in combined dosage form with their stability studies. Asian J Chem 28:273–276
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Fortune Pharma, Hyderabad, for providing drug substances and lab facilities. The authors are also thankful to the Department of pharmaceutical Analysis, GITAM University, Vishakhapatnam, India, for encouragement.
Funding
It is self-financed, and no funding was sponsored from any organization, funding agency, and non-profit research bodies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RG and GS contributed equally in design of the work, acquisition and interpretation of data, and manuscript preparation. Both authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
No animals and human subjected used in this study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Godela, R., G, S. An effective stability indicating RP-HPLC method for simultaneous estimation of Dolutegravir and Lamivudine in bulk and their tablet dosage form. Futur J Pharm Sci 6, 9 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43094-020-00026-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43094-020-00026-0