Abstract
Background
There are many biomarkers associated with breast cancer. Higher expression of PIK3CA (Phosphoinositide 3-kinase Cα), in its upregulated form, is associated with Hr+ and Her2− breast cancer; therefore, many drugs were synthesized against this protein to treat breast cancer patients. FDA recently approved that the drug alpelisib also inhibits PI3KCα (PDB ID-5DXT) in BC patients with Hr+ and Her2−. In present study, we have exploited fourteen coumarin-carbonodithioate derivatives and alpelisib against this protein along with eighteen others which are responsible for causing BC through computational analysis. We have used Schrödinger Maestro 11.2 version for our in silico docking study, and to calculate relative binding energies of ligands, we used prime MM-GBSA module.
Result
Docking study revealed that among all fourteen compounds, 2f, 2a, 2d, and 2e showed the highest G score than the alpelisib and coumarin against PI3KCα with − 9.3, − 9.0, − 9.0 and − 9.1 kcal/mol respectively, along with individual G score of alpelisib (− 8.9) and coumarin (− 7.9). Prime MM-GBSA analysis gave the relative binding energies of alpelisib, 2f, and 2e with − 19.94864535, − 18.63076296 and − 13.07341286 kcal/mol sequentially.
Conclusion
This study provides an insight into the coumarin-carbonodithioate derivatives that could act as inhibitors of PI3KCα like alpelisib. Further prime MM-GBSA study revealed ligand binding energies and ligands strain energies.
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Background
Breast cancer (BC) is a very common cancer worldwide in females and has overtaken cervical cancer in Indian women [17]. Many different pathways mainly mediate the BC aetiology [43]. There are many factors like lifestyle, family history, hormonal, genetic variation affecting BC, having said that, the one specific factor causing BC was out of reach [2]. The paramount challenges for researchers of BC are to understand the molecular changes in the genes associated with cell cycle progression, whose mutation or overexpression leads to BC [25]. Numerous biomarkers were presently used for the diagnosis of BC [5]. There are several known overexpressed genes associated with BC.
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase is classified under the lipid kinase family mainly involved to regulate some biologically important functions like cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, etc. [40]. There are three classes of PI3K in which class I (PI3Kα, ß, γ, and δ) express drastically the overexpression of PI3Kα which is seen in BC patients [31, 34]. In recent years, inhibitors of PI3Kα were tested clinically in patients with advanced BC malignancies which unveiled differential effectiveness [16]. Almost more than 70% of BCs are hormone receptor (HR+) and (HER2−) human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 [14, 38]. The higher mutation rate in PI3KCα is seen in most of the HR+ and HER2− and has a high survival rate among BC patients with PIK3CA-mutated patients. Lately, alpelisib had received Food and Drug Administration approval for treating postmenopausal women and men with metastatic BC whose tumours were having a mutation with the PIK3CA gene [41].
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK-5) is a Ser/Thr kinase, a regulator protein in the cell cycle that phosphorylates and activates the ATM pathway in a double standard DNA repair pathway [36]. The microarray expression study showed significant observation of the upregulation of CDK-5 in BC, colon cancer, lung, bladder, ovarian cancer, etc. In contrast, oesophageal and blood cancer exhibited downregulation of CDK5 expression [21]. The MCF7 cell lines compared to normal cell lines were correlated with the association of CDK-5 overexpression [42].
Several studies reported that compounds like purine, pyramidine [3], and coumarin derivatives exhibit anticancer activity [13]. The plant-derived natural product coumarin derivatives play a vital role in medicinal chemistry with a wide range of pharmacological activities including anticancer effects. However, the molecular mechanism of coumarin compounds exerting their anticancer effects remained unknown [44]. Alkyldithiocarbonate ligands and also with few metal complexes have also appreciable attention for their interactions and broad range of applications. Dithiocarbamate and dithiocarbonate sulphur containing ligands have been used extensively in agriculture as well as in medicinal chemistry [4].
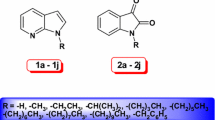
Hence, the coumarin-carbonodithioate derivative compounds (A to F) have been utilized as the secondary data from the earlier reported study [19]. Remaining (E to N) compounds identified for their antifungal and antibacterial activity in previously reported synthesis and molecular docking studies of potent coumarin–carbonodithioate hybrids [27]. Our study analysis brought about an understanding of the anticancer potential of these compounds through in silico studies and comparing both sets of ligands with standard coumarin and alpelisib. Therefore, present investigation obtained 14 different coumarin-carbonodithioate derivatives from the literature survey [16]. Docking analysis of 14 derivatives was carried out against 18 BC upregulated proteins. Furthermore, the selection of PI3KCα (PDB ID-5DXT) protein out of 18 proteins leads to a docking investigation of all 14 ligands. This protein was also docked with coumarin and with its known inhibitor to compare the dock scores with our compounds.
In silico molecular docking studies lead to innovation in synthesizing novel drugs as this study requires less time and can be performed with a large number of ligands and easy to compare between the ligand scores [7, 29]. The in silico studies also bring about the understanding of the solvation effect, molecular dynamic simulation, and molecular electrostatic potential studies with the interpretation of behaviour of the compounds in different solutions [1, 28]. In silico computational screening plays a vital role in the discovery of drugs that have success stories [33, 37].
Objectives of the work are, to study the effect of coumarin-carbonodithioate derivatives on breast cancer overexpressed proteins through the computational molecular docking method. To calculate the ligand binding energies and ligand strain energies for a given set of ligands 2a, 2f, 2c, 2d, 2 h, and 2i against a single receptor PI3KCα. And also to predict the relative binding free energies and energy properties of individual ligand, receptor, and complex structures that contribute to total binding energies using the prime MM-GBSA method.
2 Methods
2.1 Selection of proteins for docking
Literature study shows that the following proteins are in close association with BC, like FGFR2 [20], CTLA4 [10], MREII [18], BRAD1 [15], PALB2 [22], p53R2 [23], CDK 8 [6], CDK 4/6 [32], AKT1 [35], BRD4 [42], MDM2 [12], BRCA 1 and 2 [9], and RAD51 [24]. The 3D structure proteins and their respective protein data bank (PDB) Ids are given in Table 1. All the mentioned proteins were retrieved from PDB and subjected to the protein pre-process module of Schrödinger Maestro 11.2 version.
2.2 Preparation of proteins for docking
All 18 proteins used for docking were prepared using protein preparation wizard [26]. The preparation involved the assignment of the hydrogen bonds, bond orders, addition of hydrogens, optimization, minimization of the proteins, and deletion of waters beyond 5Ǻ from the het group. Determination of highly potential binding sites of ligands on proteins was carried out using SiteMap tool analysis [11]. Using Glide application protein receptor grid was generated (assignment of ligand binding site for docking). Additionally, docking of all ligands were carried out using glide’s ligand docking module. Extra-precision (XP-visualizer module) was used for the visualization of glide score (G score). Docking results of 2a to 2f with all 18 proteins are briefly given in Table 2.
2.3 Preparation of ligands
The 3D structures of all 14 ligands are prepared using Schrödinger Maestro software. Minimization of all ligands was carried out using the OPLS-2005 force field module [8]. All ligand structures and their respective chemical names are stated in Table 3. The electrostatic potential values plotted on the surface of ligands using electro-static potential fitting charge (ESP) atomic charges by OPLS2005 force field are given in Fig. 1.
2.4 Prime MM-GBSA
The prime MMGBSA method (Prime Version 4.8) exhibited the relative binding-free energy (ΔG bind) of each ligand molecule, and results are given in Table 4.
Formula expanded is given below:
ΔG(bind) = ΔG(solv) + ΔE(MM) + ΔG(SA)
where:
-
ΔGsolv is the difference in GBSA solvation energy of the PIK3CA-inhibitor complex and the sum of the solvation energies for unliganded PIK3CA and inhibitor.
-
ΔEMM is a difference in the minimized energies between PIK3CA-inhibitor complex and the sum of the energies of the unliganded PIK3CA and inhibitor.
-
ΔGSA is a difference in surface area energies of the complex and the sum of the surface area energies for the unliganded PIK3CA and inhibitor.
Prime MM-GBSA calculates the energy of optimized free receptors, free ligand, and a complex of the ligand with a receptor. It also calculates the ligand strain energy by placing ligand in a solution which was autogenertated by VSGB 2.0 suit. The prime energy visualizer presented the visualization of energy.
3 Results
Various molecular changes in different types of genes cause BC. There are many identified biomarkers for BC. In our study, we used 18 upregulated proteins in BC against 14 coumarin-carbonodithioate derivatives. The accomplishment of all 18 proteins receptor grid generation using SiteMap module predicted the top three binding sites for ligands on proteins surfaces. Our present work considered the greatest G score exhibiting receptors of the respective protein. Among all proteins, 5DXT has shown the highest G score from 2a, 2b, 2d, 2e, and 2f compounds. As a screening result, we identified greater binding energy for PIK3Cα protein. Evidently, PIK3Cα gene overexpression leads to many different cancer types, mainly breast cancer in most of the cases around the globe. Hence, PIK3Cα is an attractive target for numerous therapeutic approaches. The binding of all compounds to the active site of protein is given in Fig. 2. Alpelisib is a known inhibitor of PIK3Cα which was recently approved as a drug for BC patients mainly with HR+ and HER2- by FDA. Therefore, in this study, we used 14 coumarin-carbonodithioate derivatives for docking study along with alpelisib and coumarin, and the G score values are given in Table 5.
Both the figures depicts interaction of all compounds with PIK3Cα (PDB ID-5DXT) protein active site. Electrostatic potential value plotted surface of PIK3Cα with the conformations of ligand compounds and crystal structure of proteins. The carbon atoms PIK3Cα are coloured by magenta, cyan, and green, respectively (electropositive charge, blue; electronegative charge, red; and neutral, white)
Alpelisib has a binding affinity G score of − 8.9 kcal/mol with three hydrogen bonds (Fig. 3), whereas coumarin with − 7.9 kcal/mol with one hydrogen bond against 5DXT protein given in Fig. 4. The best-docked compound is 2f with − 9.3 kcal/mol. Out of 14 compounds, A, D, H, and I had greater G score than the standard Alpelisib and coumarin. As depicted in Fig. 5, compound 2f interacts with 5DXT more tightly than other compounds with H-bond of length 2.14 Ǻ with 851st Valine residue and Pi-Pi stacking between Trp780 and Tyr 836th residue. Similarly, in Fig. 6, compounds 2d, 2e, and 2a form H-bond of length 2.18 Ǻ, 2.16 Ǻ, and 2.15 Ǻ respectively with Val 851st residue. 2e and 2d form two pi-pi stacking with Tyr836 and Trp 280th residue, whereas 2a forms only one pi-pi stacking with Trp 780th residue. Prime MM-GBSA analysis revealed the binding energy ΔG of alpelisib to 5DXT as − 19.94 kcal/mol compared with best-docked compound 2f with − 18.63 kcal/mol. Prime energy calculation analysis describes the relative binding energies of each molecule.
4 Discussion
Coumarin and their synthetic analogous contain antitumor, anti-HIV, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory properties [30]. Scopoletin is a known coumarin that acts as an antiangiogenic compound [39]. Thus, our assay comprised of coumarin derivatives to understand their ability as anticancer agents through in silico study. Some of these derivatives had a greater G score than the standard drug used against PI3KCα protein alpelisib. Among 2a to 2f, five of them have shown greater G score for 5DXT one among 18 proteins (Table 2). We have analysed, most of the derivatives showed the H-bonding interaction between compounds and valine (851) amino acid residues of the protein, although PI3KCα inhibitors were involved in treating specific hormone receptor-mediated BC and not involved in all subtypes of BC. Henceforth, the present study is applicable for HR+ and HER2- breast cancer.
5 Conclusion
The molecular docking studies revealed the binding energy in kcal/mol of ligands against 18 proteins in which most of the compounds have a greater G score for PIK3Cα. Among 14 coumarin-carbonodithioate compounds, 2a, 2d, 2e, and 2f exhibited greater G score than the known inhibitor of PIK3Cα protein called alpelisib. Prime MM-GBSA analysis improves the binding energy calculations than the molecular docking energies. Thereupon, MM-GBSA analysis reveals the stronger binding of the ligands to the receptors. Our study unveiled that alpelisib and compound 2f exhibit stronger binding to PIK3Cα, compared to other ligands. Therefore, indisputably 2a, 2d, 2e, and 2f molecules could serve as a lead compounds for designing the inhibitors for PIK3Cα.
Availability of data and materials
Data will be available from the corresponding author on request.
Abbreviations
- PIK3CA:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha isoform
- Hr:
-
Hormone receptor
- Her2:
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
- FDA:
-
Food and Drug Administration
- PDB:
-
Protein data bank
- MM-GBSA:
-
Molecular Mechanics/Generalized Born Surface Area
- BC:
-
Breast cancer
- CDK 5:
-
Cyclin dependent kinase 5
- FGFR2:
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2
- CTLA4:
-
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4
- PALB2:
-
Partner and localizer of BRCA2
- p53R2:
-
p53-inducible ribonucleotide reductase
- CDK 8:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 8
- CDK 4/6:
-
Cyclin dependent kinase 4/6
- BRD4:
-
Bromodomain-containing protein 4
- MDM2:
-
Mouse double minute 2
References
Abdel-Latif MK, Abd El-Mageed HR, Mohamed HS, Mustafa FM (2019) Study the solvation effect on 6-phenyl-2-thioxo-1,2-dihydropyridine-3-carbonitrile derivatives by TD- DFT calculations and molecular dynamics simulations. J Mol Struct 1200:127056
Abdulkareem I (2013) Aetio-pathogenesis of breast cancer. Nig Med J 54(6):371
Ahmed SA, Ahmed OM, Elgendy HS (2014) Novel synthesis of puriensanalougues and thieno[2,3-b] pyridine derivatives with anticancer and antioxidant activity. J Pharm Res 8(9):1303–1313
Chauhan HP, Sapana J, Jaswant C (2016) Mixed bismuth(III) complexes with sulfur donor ligands Studies on synthetic, structural, thermal and biological properties. J Therm Anal Calorim 124:117–130
Cheang MCU, Voduc D, Bajdik C, Leung S, McKinney S, Chia SK, Perou CM, Nielsen TO (2008) Basal-like breast cancer defined by five biomarkers has superior prognostic value than triple-negative phenotype. Clin Cancer Res 14(5):1368–1376
Crown J (2017) CDK8: a new breast cancer target. Oncotarget 8(9):14269–14270
Dirar AI, Waddad AY, Mohamed MA, Mohamed MS, Osman WJ, Mohammed MS, Elbadawi MAA, Hamdoun S (2016) In silico pharmacokinetics and molecular docking of three leads isolated from Tarconanthus camphorates. Int J Pharm Sci 8(5):8
Du J, Sun H, Xi L, Li J, Yang Y, Liu H, Yao X (2011) Molecular modeling study of checkpoint kinase 1 inhibitors by multiple docking strategies and prime/MM–GBSA calculation. J Comput Chem 32(13):2800–2809
Godet I, Gilkes DM (2017) BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations and treatment strategies for breast cancer. Integ Cancer Sci Therap 4(1)
Goske M, Ramachander VRV, Komaravalli PL, Rahman PF, Rao C, Jahan P (2017) CTLA-4 Genetic Variants (rs11571317 and rs3087243): Role in susceptibility and progression of breast cancer. World J Oncol 8(5):162–170
Halgren TA (2009) Identifying and characterizing binding sites and assessing druggability. J Chem Info Mod 49(2):377–389
Haupt S, Vijayakumaran R, Miranda PJ, Burgess A, Lim E, Haupt Y (2017) The role of MDM2 and MDM4 in breast cancer development and prevention. J Mol Cell Bio 9(1):53–61
Hayakawa I, Shioya R, Agatsuma T, Furukawa H, Naruto S, Sugano Y (2004) A library synthesis of 4-hydroxy-3-methyl-6-phenylbenzofuran-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester derivatives as anti-tumor agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 14(17):4383–4387
Howlader N, Altekruse SF, Li CI, Chen VW, Clarke CA, Ries LAG, Cronin KA (2014) US incidence of breast cancer subtypes defined by joint hormone receptor and HER2 status. J Natl Cancer Inst 106(5)
Irminger-Finger I, Ratajska M, Pilyugin M (2016) New concepts on BARD1: regulator of BRCA pathways and beyond. Inter J Biochem Cell Bio 72:1–17
Juric D, Rodon J, Tabernero J, Janku F, Burris HA, Schellens JHM, Middleton MR, Berlin J, Schuler M, Gil-Martin M, Rugo HS, Seggewiss-Bernhardt R (2018) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase α–selective inhibition with alpelisib (BYL719) in PIK3CA - altered solid tumors: results from the first-in-human study. J Clin Oncol 36(13):1291–1299
Kaarthigeyan K (2012) Cervical cancer in India and HPV vaccination. Ind J Med Paedi Oncol 33(1):7
Khan RT, Siddique A, Shahid N, Khokher S, Fatima W (2018) Breast cancer risk associated with genes encoding DNA repair MRN complex: a study from Punjab, Pakistan. Breast Can 25(3):350–355
Kumbar SS, Hosamani KM, Shettar AK, Joshi D (2017) Environmentally benign synthesis, computational investigation, and mechanistic studies of novel coumarincarbonodithioate frameworks as anticancer drugs: an approach to microwave synthesis. Eur J Pharm Med Sci 4(11):389–400
Lei H, Deng C-X (2017) Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 signaling in breast cancer. Int J Biol Sci 13(9):1163–1171
Levacque Z, Rosales JL, Lee K-Y (2012) Level of cdk5 expression predicts the survival of relapsed multiple myeloma patients. Cell Cycle 11(21):4093–4095
Li J, Li M, Chen P, Ba Q (2018) High expression of PALB2 predicts poor prognosis in patients with advanced breast cancer. FEBS Open Bio 8(1):56–63
Link PA, Baer MR, James SR, Jones DA, Karpf AR (2008) p53-inducible ribonucleotide reductase (p53R2/RRM2B) is a DNA hypomethylation-independent decitabine gene target that correlates with clinical response in myelodysplastic syndrome/acute myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Res 68(22):9358–9366
Lose F, Lovelock P, Chenevix-Trench G, Mann GJ, Pupo GM, Spurdle AB (2006) Variation in the RAD51 gene and familial breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 8(3)
Ma X-J, Salunga R, Tuggle JT, Gaudet J, Enright E, McQuary P, Payette T, Pistone M, Stecker K, Zhang BM, Zhou Y-X, Varnholt H et al (2003) Gene expression profiles of human breast cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100(10):5974–5979
Madhavi Sastry G, Adzhigirey M, Day T, Annabhimoju R, Sherman W (2013) Protein and ligand preparation: parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. J Comp Aided Mol Des 27(3):221–234
Mangasuli SN, Hosamani KM, Satapute P, Joshi SD (2018) Synthesis, molecular docking studies and biological evaluation of potent coumarin–carbonodithioate hybrids via microwave irradiation. Chem Data Colle 15(16):115–125
Mohamed HSH, Ahmed SA (2019) Reviewing of synthesis and computational studies of pyrazolo pyrimidine derivatives. J Chem Rev 1(3):154–251
Moitessier N, Englebienne P, Lee D, Lawandi J, Corbeil CR (2009) Towards the development of universal, fast and highly accurate docking/scoring methods: a long way to go: Docking/scoring methods-a review. Br J Pharm 153(S1):S7–S26
Musa M, Cooperwood J, Khan MO (2008) A review of coumarin derivatives in pharmacotherapy of breast cancer. Curr Med Chem 15(26):2664–2679
Paplomata E, O’Regan R (2014) The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in breast cancer: targets, trials and biomarkers. Ther Adv Med Onco 6(4):154–166
Pernas S, Tolaney SM, Winer EP, Goel S (2018) CDK4/6 inhibition in breast cancer: current practice and future directions. Ther Adv Med Oncol 10:1–15
Pierce AC, Jacobs M, Stuver-Moody C (2008) Docking study yields four novel inhibitors of the protooncogene Pim-1 kinase. J Med Chem 51(6):1972–1975
Qin H, Liu L, Sun S, Zhang D, Sheng J, Li B, Yang W (2018) The impact of PI3K inhibitors on breast cancer cell and its tumour microenvironment. Peer J 6:5092
Riggio M, Perrone MC, Polo ML, Rodriguez MJ, May M, Abba M, Lanari C, Novaro V (2017) AKT1 and AKT2 isoforms play distinct roles during breast cancer progression through the regulation of specific downstream proteins. Sci Rep 7:44244
Rosales JL, Lee K-Y (2006) Extraneuronal roles of cyclin-dependent kinase 5. BioEssay 28(10):1023–1034
Salam NK, Huang TH-W, Kota BP, Kim MS, Li Y, Hibbs DE (2007) Novel PPARgamma agonists identified from a natural product library: a virtual screening, induced-fit docking and biological assay study: novel PPAR-γ agonists from natural products. Chem Bio Drug Des 71(1):57–70
Setiawan VW, Monroe KR, Wilkens LR, Kolonel LN, Pike MC, Henderson BE (2009) Breast cancer risk factors defined by estrogen and progesterone receptor status: the multiethnic cohort study. Ame J Epide 169(10):1251–1259
Tabana YM, Hassan LEA, Ahamed MBK, Dahham SS, Iqbal MA, Saeed MAA, Khan MSS, Sandai D, Majid ASA, Oon CE, Majid AMSA (2016) Scopoletin, an active principle of tree tobacco (Nicotiana glauca) inhibits human tumor vascularization in xenograft models and modulates ERK1, VEGF-A, and FGF-2 in computer model. Microvasc Res 107:17–33
Thorpe LM, Yuzugullu H, Zhao JJ (2015) PI3K in cancer: divergent roles of isoforms, modes of activation and therapeutic targeting. Nat Rev Cancer 15(1):7–24
US Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-informationapproveddrugs/fda-approves-alpelisib-metastatic-breast-cancer. Accessed 28 May 2019
Wang R, Cao X-J, Kulej K, Liu W, Ma T, MacDonald M, Chiang C-M, Garcia BA, You J (2017) Uncovering BRD4 hyperphosphorylation associated with cellular transformation in NUT midline carcinoma. Proc Nat Acad Sci 114(27):5352–E5361
Yamane K, Tateishi K, Klose RJ, Fang J, Fabrizio LA, Erdjument-Bromage H, Taylor-Papadimitriou J, Tempst P, Zhang Y (2007) PLU-1 is an H3K4 demethylase involved in transcriptional repression and breast cancer cell proliferation. Mol Cell 25(6):801–812
Zhou Y, Zhao W, Xie G, Huang M, Hu M, Jiang X, Zeng D, Liu J, Zhou H, Chen H (2014) Carcinogenesis 35(12):2660–2669
Acknowledgements
Research team greatly acknowledges Department of Science and Technology, India.
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledges DST PURSE PHASE-II programme for financial support through the Grant No. SR/PURSE PHASE-2/13(G).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SVP and CMK designed the research work; SAA and SSK conducted the review and editing part. SVP conducted the research work and prepared the manuscript. Finally, all authors have read and approved the final research manuscript for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1.
Prime MM-GBSA results.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Pattar, S.V., Adhoni, S.A., Kamanavalli, C.M. et al. In silico molecular docking studies and MM/GBSA analysis of coumarin-carbonodithioate hybrid derivatives divulge the anticancer potential against breast cancer. Beni-Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci 9, 36 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43088-020-00059-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43088-020-00059-7