Abstract
Background
Quinazoline are known to possess different biological activities which among is anti-cancer most especially NSCLC. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) belongs to the receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) family, which is known to be one of the most important therapeutic targets for the treatment of cancer most especially NSCLC.
Results
QSAR modeling was performed to develop a model with high predictive power on some non-small cell lung cancer agents (NSCLC) (EGFRWT inhibitors). The EGFRWT inhibitors were optimized using density functional theory (DFT) method utilizing B3LYP/6-31G* level of theory. Genetic function algorithm (GFA) was used to build five models. Out of these five models, the studied one was selected and reported because of its fitness statistically with the following validation parameters: R2trng = 0.9459, R2adj = 0.9311, Q2cv = 0.8947, R2test = 0.7008, and LOF = 0.1195. The selected model was further subjected to other validation test such as VIF and Y-scrambling test applicability domain and found to be statistically significant. The kind of interactions between five most active EGFRWT inhibitors and EGFRWT enzyme were explored via molecular docking. Molecule 4 was ranked top in comparison to other ligands because it has the highest docking score of − 8.3 kcal/mol. The pharmacokinetics studies indicated that these molecules have good absorption, low toxicity level, and permeability properties because none of them violate the Lipinski’s rule of five.
Conclusion
A model with a very high predictive power on some EGFRWT inhibitors was developed using QSAR model. The model was validated and found to have good internal and external assessment parameters: R2 of 0.9459, R2adj of 0.9311, Qcv2 of 0.8947, R2test of 0.7008, and LOF of 0.1195. The nature of interaction of these molecules with their target protein was explored via molecular docking and found molecule 4 to have the highest docking score of − 8.3 kcal/mol among co-ligands. Pharmacokinetics studies revealed that these molecules have good absorption, low toxicity level, and permeability properties. These findings proposed a way for designing potent EGFRWT inhibitors against their target enzyme.
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Background
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) from the receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) family, is known to be one of the most useful therapeutic targets for the mitigation of cancer most especially NSCLC. It plays a vital role in the regulation of cancer cell survival, migration, growth, proliferation, and differentiation [25, 27].
The most common and deadly type of all cancers around the globe is lung cancer which account for 25% of the cancer deaths every year ([6, 19]. Among the types of lung cancer with about 1.5 million patients and less than 20% survival rate is NSCLC [20].
In order to mitigate the problem of NSCLC, several medications were developed for up to 3 different generations. The first generation was designed for the treatment of EGFRL858R mutations, examples were gefitinib and erlotinib [16, 23]. The second generation was designed to treat EGFRT790M mutations examples are afatinib, dacomitinib and neratinib. The second generation drugs share a common structural features of quinazoline pharmacophore and acrylamide structure [18]. While in the case of the third generation, they were developed to treat EGFRT790M/L790M double mutations example AZD9291 [7].
QSAR is a computational chemistry method which correlate experimental activities (response variable) and physicochemical properties (molecular descriptors) of a compound quantitatively [11]. Furthermore, QSAR technique of computer-aided drug design plays a crucial role in physical, analytical, pharmaceutical, medicinal, organic chemistry, biochemistry, toxicology, chemical engineering, environmental sciences, and nanotechnology [2]. Another computational chemistry technique used to explore the interaction between 3D structures of a ligand and a receptor is molecular docking and contributes in virtual screening of library of compounds in computer-aided drug design. Pharmacokinetics played vital role in drug research and development by predicting ADME and drug likeness properties of drugs in hit-to-lead and lead-optimization campaigns [9].
The main aim of this work is to generate a valid QSAR model with a very high predictive power on some EGFRWT inhibitors using QSAR technique, study the nature of interactions between the EGFRWT inhibitors and EGFR enzyme via docking, and also to predict pharmacokinetics properties of these EGFRWT inhibitors.
2 Method
2.1 Dataset collection
Thirty nine (39) sets of EGFRWT inhibitors with their corresponding inhibitory activities (IC50) in nanomolar were retrieved from the work of [17] and used in this research. The inhibitory activities (IC50) of these molecules were then converted to their corresponding negative logarithms (pIC50) using Eq. 1 [3].
2.2 Structure generation and stable geometry calculations
The initial step in any QSAR modeling study after data collection is drawing of the structures of the studied molecules. For this reason, the structures of all the studied molecules were generated utilizing the ChemDraw software [10]. After structure generation of the studied molecules, constraint in the structures was reduced via energy minimizing before finding the most stable structures of the studied molecules on potential energy surface using the Spartan 14 software. DFT at B3LYP/6-311G* level of theory was used in finding the most stable structures of all the studied molecules on global minima on the potential energy surface (PES) [15].
2.3 1D, 2D, and 3D descriptors generation, data pre-treatment, and dataset splitting
For the generation of the independent variables (descriptors), the most stable structures obtained in section 2.2 above were saved in a file format (SDF) that has been recognized by the software used in generation of descriptors, PaDEL descriptor tool kit [26].
The dataset was pre-treated manually to eliminate redundant and constant descriptors. After pre-treating the data, the Data division software was further used in dividing the data into training set and test set utilizing the Kennard-Stone algorithm [14]. The model building/training set were used for the generation of the models, and the validation/test set were used for assessing the generated models [11].
2.4 Model development
The models were developed utilizing the genetic function approximation (GFA) method with the actual pIC50 as the response variable and the descriptors as independent variables. In the case of variable selection, GFA selects most highly correlated descriptors to develop so many models which is one of the distinct characteristic of GFA.
2.5 Validation of the selected model
The most widely used assessment terms for QSAR models are the following; square correlation coefficient of the training set (R2training), adjusted R2 (R2adj), cross-validation coefficient (Qcv2), and square correlation coefficient of the test set (R2test). The high value of these parameters appears to be necessary but not enough [21].
In-view of this, the inter-correlation between descriptors can be detected using their variation inflation factors (VIF), to see whether these descriptors are highly correlated with one another or not. If the computed VIF values is up to 1 it means there is no inter-correlation between the descriptors; if it falls between 1–5, the model can be accepted, and if it is higher than 10, the model cannot be accepted. It can be calculated using the equation below:
where R2 is the correlation coefficient of the selected model [5].
The evaluation of significance and contribution of each descriptor to the selected model is performed using the value of mean effect of each descriptor. The mean effect is defined by the equation below:
where MFj is the mean effect of a descriptor j in a model, βj is the coefficient of the descriptor J in that model and dij is the value of the descriptor in the data matrix for each molecule in the model building set, m is the number of descriptor that appear in the model and n is the number of molecules in the model building set [4]
To assure the robustness of a QSAR model and that the model was not obtained by chance correlation Y-Scrambling test was perform. It is done by reshuffling the actual activities and keeping the descriptors unchanged to generate new QSAR models for several trials, the new built QSAR models were anticipated to give low Q2 and R2 value. The validation parameter for this test is cRp (cR2p > 0.5) [12].
2.6 Applicability domain
A QSAR model is considered valid and void, if it is subjected to the applicability domain (AD) and found that the model can make good prediction of new activities of the training and test molecules. As such, the model is subjected to AD to find out whether there are influential or outliers molecules in the studied ones [22]. One of the methods used in assessing the AD is leverage approach and is given as hi:
where the training set matrix I is given by xi, n × k descriptor matrix of the training set is represented by X, and XT is the transpose matrix X used in generating the model. The threshold for the value of X is the warning threshold (h*) which is presented in the equation below:
where the number of chemicals of the model building set is given by q, and the number of the descriptors in the model under evaluation is represented by x.
2.7 Molecular docking
A Dell Latitude E6520 computer system, with the following specification: Intel ® Core™ i7 Dual CPU,M330 @2.75 GHz 2.75 GHz, 8 GB of RAM was utilized to explore the nature of interactions between the active site of EGFR enzyme and five most active EGFRWT inhibitors (ligands) with the help of the Pyrex virtual screening software, Chimera, PyMOL, and Discovery studio.
Before the docking analysis, ligands were prepared from the optimized structures in section 2.2 above and saved in pdb file format using Spartan’14 [1]. The 3D structure of EGFR enzyme was downloaded from the protein data bank (with pdb ID: 4zau). The enzyme was prepared with the help of Discovery Studio Visualizer for the docking analysis; in the course of the preparation, hydrogen was added. Water molecule, heteroatoms, and co-ligands were eliminated from the crystal structure saved in pdb file.
The docking of the ligands to the active site of EGFR enzyme was achieved with the help of the Pyrex software using Autodock vina [11]. After successful docking protocol, re-formation of the complexes (ligand-receptor) for further investigation was also achieved utilizing the Chimera software. Discovery studio visualizer and PyMOL were used to investigate the interactions of the complexes.
2.8 Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics studies of five (5) most active compounds among the data set was carried out using SwissADME a free web tool used in evaluating ADME and drug-likeness properties of small molecules [8]. The Lipinski’s rule of five is useful at pre-clinical stage of drug discovery which state that if any chemical violate more than 2 of these criteria (molecular weight ˂ 500, number of hydrogen bond donors ≤ 5, number of hydrogen bond acceptors ≤ 10, calculated Log p ≤ 5, and polar surface area (PSA) ˂ 140 Å2), the chemical is said to be impermeable or badly absorbed [13].
3 Results
3.1 QSAR modeling
The results of the QSAR modeling are presented in Tables 1, 2, 3, and 4 and Figs. 1, 2, and 3.
Model 1
3.2 Molecular docking
The results of the molecular docking are presented in Table 5 and Figs. 4 and 5.
3.3 Pharmacokinetics studies
The results of the Pharmacokinetic studies are presented in Table 6 and Fig. 6.
4 Discussion
4.1 QSAR modeling
The studied model was selected and reported because it is statistically fit with the following assessment parameters as compared to other models built: R2 of 0.9459, R2adj of 0.9311, Qcv2 of 0.8947, R2test of 0.7008, and LOF of 0.1195. The selected model was found to have passed the minimum recommended values for the validation of a good QSAR models as reported by [24].
The details of the descriptors that appear in the selected model are presented in Table 1. The positive coefficient of ATSC1p, GATS1s, RDF65e, and P1e descriptors indicate the positive correlation of this descriptor to the inhibitory activities of EGFRWT inhibitors that is the more you have these types of descriptors the more the inhibitory activity of the EGFRWT inhibitors against EGFR enzyme. In-view of the other descriptors with negative coefficients (GATS8s and SpMin8_Bhm) signifies the negative correlation of the descriptors to the inhibitory activities of the EGFRWT inhibitors. The lesser the number of these descriptors in the structures of EGFRWT inhibitors the more the action of EGFRWT inhibitors against EGFR enzyme.
4.1.1 Interpretations of the descriptors in the best model
ATSC1p is a Centered Broto-Moreau autocorrelation - lag 1/weighted by polarizabilities. This is computed by changing properties of the atom (w) with it equidistant values (w’), which is gotten by subtracting the standard value w of the compound from each w’ value:
It was shown that if properties are equidistant only, then all autocorrelation descriptors are considered to be orthogonal, thus given the fitness of the succeeding statistics. The H-filled molecular graph presents the compound, which gives the properties of the compound and the sequential number of the vertices. The pairs of atoms that enter the summation were found using topological distance matrix.
GATS1s and GATS8s are Geary autocorrelation - lag 1 and 8/weighted by I-state. This descriptor measures the quality of the link between atomic charges of two atoms 8 bonds apart.
SpMin8_Bhm is the smallest absolute eigenvalue of Burden modified matrix - n 8/weighted by relative mass. SpMin is the minimum eigenvalue, called leading eigenvalue or spectral radius. This kind of function was called by Ivanciuc matrix spectrum operators (Eriksson et al., 2003). This eigenvalue has been suggested as an index of molecular branching, the smallest values corresponding to chain graphs.
RDF65e is radial distribution function - 065/weighted by relative Sanderson electronegativities, and this descriptor is based on the way atoms are arranged in the regular representation of a compound and develops a radial distribution function code (RDF code) that presents certain features in common with the 3D-MORSE code. It also explains the steric hindrance of a molecule. The RDF descriptor also provides information about ring types, atom types, the bond lengths, and planar and nonplanar systems.
P1e is the 1st component shape directional WHIM index/weighted by relative Sanderson electronegativities.
The scatter plot of predicted activities of both the test and training sets against the Actual pIC50 is shown in Fig. 1. It can be seen from the plot that the values were plotted around the straight line which shows the significance of the selected model. Also scatter plot of Actual pIC50 against the residuals of both the training and test is also shown (Fig. 2). The irregular appearance of these residuals on either side of zero on the plot shows the nonexistence of methodological error in the selected model.
The difference between the actual and the predicted activities in Table 2 is termed residual. The low residual values noted in the table verified the reliability of the selected model.
The correlation matrix of the descriptors that appear in the reported model was carried out (Table 3) and the descriptors were found to be orthogonal meaning no correlation exists between them. This indicates that the physicochemical parameters (descriptors) used in developing the reported model were of good quality. The calculated VIF values for the descriptors in the model building set of selected model were obtained to be less than 5 (Table 3) indicating the fitness of the selected model, and the descriptors were independent of one another. The MF value (Table 4) shows the contribution of a descriptor in comparison to other descriptors in the best model. The signs show the different direction of the descriptors of either improvement or reduction in the values of these descriptors will enhance the inhibitory activities.
The result of Y-scrambling test presented in Table 4 shows that ten (10) random models were generated; the R2 and Q2 values for these ten random models were found to be low. This verified the robustness of the selected model and that the model was not obtained by chance correlation.
The Williams plot presented in Fig. 3 identified five (5) influential compounds from which were all in the validation set. It is essential to understand that these molecules with leverage value higher than the threshold h*(h* = 0.72) are not considered when designing new EGFRWT inhibitors. These molecules might be dissimilar/structurally different from the molecules used to generate the model and, thus may have different mechanism of action.
4.2 Molecular docking
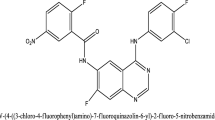
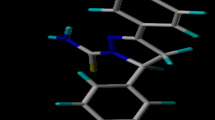
Molecular docking on the EGFR enzyme and five most active 2, 3-dihydro-[1, 4] dioxino [2, 3-f] quinazoline derivatives (ligands) (EGFRWT inhibitors) were studied (Table 5). From Table 5, we can see that molecule 4 has the highest docking score of − 8.3 kcal/mol which might be as a result of hydrophobic interactions formed with LEU718, LEU792, LYS745, LEU788, VAL726, ALA743, and LEU844 amino acid residues in the active site of EGFR enzyme. Hydrogen attach to one of the nitrogen of the quinazoline moiety (molecule 4) formed hydrogen bond in the active site of EGFR enzyme with THR790 and GLN791 amino acid residues with bond lengths of 2.9464 Å and 2.3643 Å. The most active molecule (3) has a docking score of − 8.0 kcal/mol. The hydrogen attach to one of the nitrogen of the quinazoline moiety (ligand 3) formed hydrogen bond interaction with MET793 amino acid residue of bond length of 2.4928 Å. And also, it formed hydrophobic interaction with amino acid residues LYS745, VAL726MET766, LEU718, and ALA743 of the EGFR enzyme. The 2D and 3D structures of complex 3 and 4 are shown in Figs. 4 and 5.
4.3 Pharmacokinetics studies
The results of the pharmacokinetics studies of the most active compounds are shown in Table 6. From the table it can be see that none of the molecules violate any of the criteria stated; it means there is a high tendency that all of these molecules might be pharmacologically active. In a null shell, these molecules are said to have good absorption, low toxicity level, orally bioavailable, and permeable. The bioavailability radar gives an overview of the drug-likeness of a molecule (Fig. 6). The region painted pink indicates the range for each features.
5 Conclusion
A mode with a very high predictive power on 39 non-small cell lung cancer agents (NSCLC) (EGFRWT inhibitors) was developed using QSAR. The reported model was selected because it is statistically fit with the following assessment parameters as compared to other models built: R2 of 0.9459, R2adj of 0.9311, Qcv2 of 0.8947, R2test of 0.7008, and LOF of 0.1195. The reported model was further subjected to other assessments such as applicability domain, Y-scrambling, and VIF and found to be statistically significant. Molecular docking was used to explore the kind of interactions between five most active EGFRWT inhibitors and EGFR enzyme. Molecule 4 has the highest docking score of − 8.3 kcal/mol among co-ligands. This might be a result of hydrophobic interactions formed with LEU718, LEU792, LYS745, LEU788, VAL726, ALA743, and LEU844 amino acid residues in the active site of EGFR enzyme. Hydrogen attach to one of the nitrogen of the quinazoline moiety (molecule 4) formed hydrogen bond in the active site of EGFR enzyme with THR790 and GLN791 amino acid residues with bond lengths of 2.9464 Å and 2.3643 Å. The pharmacokinetics studies indicated that these molecules have good absorption, low toxicity level, and permeability properties. The results of this study give room for designing new potent EGFRWT inhibitors against their target enzyme.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable
Abbreviations
- QSAR:
-
Quantitative structure-activity relationship
- MLR:
-
Multi-linear regression
- GFA:
-
Genetic function algorithm
- DFT:
-
Density function theory
- B3LYP:
-
Becke’s three-parameter read-Yang-Parr hybrid
- PDB:
-
Protein data bank
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer agents
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- VIF:
-
Variation inflation factor
- MF:
-
Mean effect
References
Abdulfatai U, Uba S, Umar BA, Ibrahim MT (2019) Molecular design and docking analysis of the inhibitory activities of some α_substituted acetamido-N-benzylacetamide as anticonvulsant agents SN. Applied Sci 1:499
Abdulfatai, U., Uzairu, A. & Uba, S. 2016. In silico study of some anticonvulsant compounds. Scholars’ Press Isbn: 978-3-330-65212-5.
Abdullahia M, Shallangwaa GA, Ibrahima MT, Bello AU, Arthura DE, Uzairua A, Mamzaa P (2018) QSAR studies on some C14-urea tetrandrine compounds as potent anti-cancer agents against leukemia cell line (K562) JKS-S
Adedirin O, Uzairu A, Shallangwa GA, Abechi SE (2018) QSAR and molecular docking based design of some N-benzylacetamide as Γ-aminobutyrate-aminotransferase inhibitors. J Eng Exact Sci 4:0065–0084
Beheshti A, Pourbasheer E, Nekoei M, Vahdani S (2016) QSAR modeling of antimalarial activity of urea derivatives using genetic algorithm–multiple linear regressions. J Saudi Chem Society 20:282–290
Chico LK, Van Eldik LJ, Watterson DM (2009) Targeting protein kinases in central nervous system disorders. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 8:892
Cross DA et al (2014) AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Discovery 4:1046–1061
Daina A, Michielin O, Zoete V (2017) SwissADME: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Scientific Reports 7:42717
Ferreira LL, Andricopulo AD (2019) ADMET modeling approaches in drug discovery Drug discovery today
Ibrahim MT, Uzairu A, Shallangwa GA, Ibrahim A (2018a) Computational studies of some biscoumarin and biscoumarin thiourea derivatives as ⍺-glucosidase inhibitors. J Eng Exact Sci 4:0276–0285
Ibrahim, M. T., Uzairu, A., Shallangwa, G. A., Ibrahim, A. (2018b) In-silico studies of some oxadiazoles derivatives as anti-diabetic compounds Journal of King Saud University-Science
Ibrahim MT, Uzairu A, Shallangwa GA, Uba S (2019) QSAR modelling and docking analysis of some thiazole analogues as ⍺-glucosidase inhibitors. J Eng Exact Sci 5:0257–0270
Ismail, S. Y., Uzairu, A., Sagagi, B., Sabiu, M. (2018) In silico molecular docking and pharmacokinetic study of selected phytochemicals with estrogen and progesterone receptors as anticancer agent for breast cancer 5:1337-1350
Kennard RW, Stone LA (1969) Computer aided design of experiments. Technometrics 11:137–148
Kohn, W., Becke, A. D., Parr, R. G. (1996) Density functional theory of electronic structure The Journal of Physical Chemistry 100:12974-12980
Maemondo M et al (2010) Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non–small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med 362:–2380, 2388
Qin X, Li Z, Yang L, Liu P, Hu L, Zeng C, Pan Z (2016) Discovery of new [1, 4] dioxino [2, 3-f] quinazoline-based inhibitors of EGFR including the T790M/L858R mutant. Bioorgan Med Chem 24:2871–2881
Solca F et al (2012) Target binding properties and cellular activity of afatinib (BIBW 2992), an irreversible ErbB family blocker. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 343:342–350
Song Z et al (2016) Challenges and perspectives on the development of small-molecule EGFR inhibitors against T790M-mediated resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer: miniperspective. J Med Chem 59:6580–6594
Tiseo, M., Bartolotti, M., Gelsomino, F., Bordi, P. (2010) Emerging role of gefitinib in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Drug Des Devel Ther 4:81
Tropsha, A., Bajorath, Jr. (2015) Computational methods for drug discovery and design. ACS Publications.
Tropsha A, Gramatica P, Gombar VK (2003) The importance of being earnest: validation is the absolute essential for successful application and interpretation of QSPR models. Mol Inform 22:69–77
Tsao M-S et al (2005) Erlotinib in lung cancer—molecular and clinical predictors of outcome. N Engl J Med 353:133–144
Veerasamy R, Rajak H, Jain A, Sivadasan S, Varghese CP, Agrawal RK (2011) Validation of QSAR models-strategies and importance. Int J Drug Design Discovery 3:511–519
Wu C-H et al (2010) Design and synthesis of tetrahydropyridothieno [2, 3-d] pyrimidine scaffold based epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) kinase inhibitors: the role of side chain chirality and Michael acceptor group for maximal potency. J Med Chem 53:7316–7326
Yap CW (2011) PaDEL-descriptor: an open source software to calculate molecular descriptors and fingerprints. J Comput Chem 32:1466–1474
Zhang L et al (2015) Structure-activity study of quinazoline derivatives leading to the discovery of potent EGFR-T790M inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 102:445–463
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the technical effort of Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria – Nigeria.
Funding
The authors declare no funding has been received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MTI contributed throughout the research work. AU gives directives and technical advices. GAS partake in technical activities. SU also partake in technical activities. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Ibrahim, M.T., Uzairu, A., Shallangwa, G.A. et al. Computer-aided molecular modeling studies of some 2, 3-dihydro-[1, 4] dioxino [2, 3-f] quinazoline derivatives as EGFRWT inhibitors. Beni-Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci 9, 20 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43088-020-00047-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43088-020-00047-x