Abstract
Background
Digital transvaginal examination of fetal head progression is subjective evaluation with many limitations. Using ultrasound (US) in the assessment of labor progression in prolonged labor is the current trend to predict the mode of delivery. The study intends to evaluate the women’s acceptance to the transperineal ultrasound (TPUS) compared with digital transvaginal examination, and its ability to predict the mode of delivery in prolonged labor. We included 28 pregnant ladies in a prolonged active phase of first or second stages of labor and followed them till delivery. TPUS was used to measure the fetal head–perineum distance (FHPD) and the angle of fetal head descent.
Results
Of the 28 participants, 53.5% of them delivered vaginally and 46.5% by Cesarean section (CS). All pregnant ladies described the TPUS as more convenient and less painful than digital vaginal examination. Cervical dilatation was negatively correlated with FHPD, and positively correlated with angle of fetal head descent. Both FHPD and angle of fetal head descent had a strong significant negative correlation. Using a cutoff value of 115° for the angle of fetal head descent, the positive predictive value (PPV) of vaginal delivery was 87%; using a cutoff value of 4.2 cm for FHPD, the PPV for vaginal delivery was 85%.
Conclusion
TPUS is more convenient, more accepted, and less painful than digital vaginal examination. Angle of head descent and FHPD are reliable predictors of the mode of delivery in prolonged labor.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Spontaneous vaginal delivery is the optimum outcome for pregnancy; however, obstetric intervention is required in females who do not progress in the second stage of labor [1]. The period from full cervical dilatation to delivery defines the 2nd stage of labor. Duration of more than 2–3 h and 1–2 h defines prolonged second stage in nulliparous and multiparous women respectively [2, 3].
The prolonged second stage is a critical problem because the obstetrician should make one of the following decisions promptly: primary CS, instrumental delivery, or CS after failure of a trial of instrumental delivery [3, 4]. The latter decision is associated with a more prolonged second stage and a high probability of fetal and maternal trauma [5, 6]. Also, CS while the fetal head is deeply impacted is associated with maternal trauma, infection, bleeding, neonatal injury, and admission to the intensive care unit [7, 8].
The rate of CS has significantly risen, reaching 27.6% in Egypt, according to the National health survey in 2008, and failure of descent was found to be the second most common indication for CS [9, 10]. The clinical perceptions of failure of descent of the presenting part using serial digital vaginal examinations are subjective [11]. Moreover, various studies claimed that using digital pelvic examination during labor is inaccurate and misleading regarding deciding the mode of delivery. Misinterpretations are common, especially with the presence of fetal head molding and caput succedaneum [12].
Intrapartum TPUS has been successfully used for monitoring fetal head descent [4, 12]. Kalache et al. [1] published the earliest report correlating the angle of head progression with the delivery mode in the prolonged 2nd stage of labor. Therefore, combined transabdominal ultrasound (US) and TPUS were suggested to be better than vaginal examination in evaluation of fetal head position during the labor [13]. It is also hypothesized that TPUS is more accepted and less painful than digital vaginal examination, an issue which has been rarely reported in literature.
The aim of the study is to evaluate the women’s acceptance to the TPUS compared with digital transvaginal examination, and its ability to predict the mode of delivery in prolonged labor.
Methods
Pregnant women’s selection
This study was conducted at the obstetrics and gynecology emergency ward in a single tertiary center Hospital. The study was prospective, performed along a 12-month period. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board as well as the Research and Ethics Committee. A formal written consent was obtained from each participating pregnant lady after an explanation of the whole procedure.
The eligible ladies were all in prolonged labor. It is defined as prolongation or cessation of the active stage (when the cervical diameter reaches 4 cm up to 10 cm of dilatation with a slow rate of cervical change less than 1.2 cm/h for the primigravida and less than 1.5 cm/h for multiparous women). Prolonged labor also includes women with prolonged second stage more than 2 h in primigravida and 1 h in multiparous women and with failure of fetal head progression. The 2nd stage is started after full cervical dilatation.
Inclusion criteria included non-high-risk singleton pregnancies ≥ 37 weeks, maternal age ranges from 18 to 35 years, and cephalic presentation. Exclusion criteria included previous CS delivery in multiparous women, any high-risk pregnancy, and the presence of any maternal or fetal indications of CS.
Pregnant women’s assessment
Clinical examination was done to detect station, position, and cervical dilatation by the digital vaginal examination performed by the obstetrician in duty (a specialist with at least four years’ experience). Those obstetricians were blinded to the US results. US examination was performed using SIEMENS ACUSON X300 US machine: transabdominal and transperineal approaches were made for all cases using 5 MHz C6-2 convex transducer. A radiologist of at least 3 years’ experience was responsible for the transabdominal US, TPUS, and data management.
Technique
The urinary bladder was emptied either by asking the ladies to void before the scan or by using a urinary catheter. They were instructed to lie in the lithotomy position. Taking US measures were avoided during uterine contractions [14].
The transabdominal US was used to assess the fetal head position with pregnant ladies supine [15]. Convex US probe was placed transversely on the suprapubic area. The direction of the orbits in relation to the US probe was used to detect the position of the fetal head.
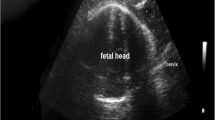
The convex US transducer was covered with a sterile surgical glove filled with antiseptic gel. After applying the antiseptic gel, the transducer was applied sagittally below the pubic bone at the midline between the labia. Small lateral transducer motions should be made to get a proper image of the symphysis pubis and fetal skull with no shadowing from the pubic rami [1].
The angle of progression was defined as an angle between an imaginary line passing to the midline of the symphysis pubis and a line inserted from the lower pole of the symphysis pubis oriented to pass tangentially to the skull of the fetus (Fig. 1) [16]. The fetal head–perineum distance (FHPD) is defined as the shortest line from the fetal skull (using its outer bony cortex) to the surface of the perineal skin using TPUS. Small angular and lateral movements should be done by the transducer to get the shortest possible distance. Firm pressure should be applied by the transducer paying attention not to induce any discomfort to the pregnant ladies (Fig. 2).
TPUS showing a FHPD of 3.1 cm. The probe was put longitudinally on the perineum; the probe was manipulated to obtain the shortest distance. The soft tissue was compressed firmly but gently without causing pain. The shortest distance from the perineal skin surface to the most distal outer bony surface of the fetal skull is measured
The decision regarding the mode of delivery was based on digital vaginal examination and not the US scan; the obstetrician was blinded to the results of the US study. The duration of the US examination was recorded. All of the examined pregnant ladies were asked verbally about the preference of US assessment in comparison with digital vaginal examination regarding the discomfort and convenience during the assessment.
Results
The study included 28 pregnant ladies with prolonged labor pain; their mean age was approximately 26 years, and the majority of them were multigravida. The mean gestational age was around 39 weeks (Table 1).
All study participants were examined by both digital vaginal examination and US to evaluate the fetal head progression. All of them reported less discomfort and more convenience during US compared with the digital vaginal examination. The mean US assessment duration was 7 ± 1.5 min.
The most common fetal head position was left occipitoposterior (64.3%), followed by right occipitoposterior and left occipitotransverse each representing 10.7%, and the least common positions were left occipitoanterior and right occipitoanterior, 7.1% for each one.
Of the 28 pregnant ladies, 15 (53.5%) of them had a vaginal delivery, and 13 (46%) had CS delivery.
The mean FHPD was 4.22 ± 1.12 and 5.2 cm ± 1.3 for those females who had vaginal delivery and CS (p = .002), respectively, while the mean angle of fetal head descent was 124° ± 15° for the former participants and 112° ± 14.8° for the latter ones (p = 0.001) (Figs. 3 and 4).
The study showed a negative strong correlation between cervical dilatation and FHPD (r = 0.70, p = 0.03) (Fig. 5), and a positive moderate correlation between cervical dilatation and angle of fetal head descent (r = 0.56, p = 0.04) (Fig. 6). Moreover, both FHPD and the angle of fetal head descent were strongly negatively correlated (r = 0.78 and p value = 0.01) (Fig. 7).
TPUS also demonstrated molding in 35.71% of cases and caput succedaneum in 28.57% of cases (Table 2). These results were clinically verified after delivery by the pediatricians.
The area under the curve for predicting the vaginal delivery was 91% (95% CI, 59–99%) regarding the angle of fetal head progression. By using a cutoff value of 115°, 91% of the women delivered vaginally (sensitivity 93%, specificity 84%, positive predictive value (PPV) 87%, negative predictive value (NPV) 91%, positive likelihood ratio (LR) 6.06, and negative LR 0.08) (Fig. 8, Table 3).
The area under the curve for predicting vaginal delivery was 84% (95% CI, 47–95%) for FHPD. By using a cutoff value of 4.2 cm, 84% of the women delivered vaginally (sensitivity 80%, specificity 84%, PPV 85%, NPV 78%, positive LR 5.2, and negative LR 0.24). (Fig. 9, Table 3).
Discussion
Digital vaginal examination is considered as the gold standard in evaluating fetal head progression, although it is subjective with many limitations [17,18,19]. TPUS is a promising tool in labor monitoring [20,21,22,23]. It gives objective data on the dynamics of labor and predicting the outcome of the operative vaginal delivery [18, 20].
In this study, TPUS was done in a short time with less discomfort to the pregnant ladies as reported by all of the participants compared with the digital vaginal examination. Only few previous studies support this finding [12, 17, 21].
Previous US studies evaluated the descent of the fetal head using the transabdominal and TPUS [18, 20, 22]. FHPD was evaluated in other studies for women with pre-labor rupture of membranes. It was found that a distance < 3 cm was associated with spontaneous vaginal delivery. This distance can also predict fetal head engagement if it was ≤ 6 cm with a sensitivity and specificity of 100% and 91% respectively [22]. They reported the inaccuracy of digital vaginal examination in monitoring progression of the fetal head during the first stage compared with the transperineal US, which is not affected by the presence of molding or caput succedaneum.
As a guide for digital vaginal exanimation, the space from the perineal surface to the ischial spine reaches 5 cm according to the guides of the WHO regarding stages of head descent. Torkildsen et al. [23] reported a cutoff value of 4.5 cm to define head engagement, which means the passage of the head of the fetus beneath the level of the ischial spine, the narrowest part of the birth canal. This agreed with the current study, whereas with a short FHPD distance of 3 cm ± 1.2 cm, the fate of labor was vaginal delivery; and with a distance of 5.4 cm ± 1.2 cm, the outcome of pregnancy was CS. The cutoff value was 4.2 cm.
However, Gilboa et al. [24] studied 65 ladies showing a prolonged second stage of labor and found no any statistically significant correlation between FHPD and the mode of labor. These previous results did not match with the current study. However, our results are concordant with Kalache et al. [1] and Barbera et al. [10, 11], who found that the less the FHPD, the more likely the labor will be spontaneous vaginal delivery.
Fetal head perineal angle by TPUS is a reflection of the dynamics of head progression [25, 26]. Kalache et al. [1] confirmed that “angle of progression” is a simple US parameter using two objective US landmarks: the symphysis pubis and the leading bony edge of the fetal skull avoiding the ischial spines which are used during digital vaginal examination. They found a high predictive value of a wide “angle of progression” and spontaneous vaginal delivery.
Amin et al. [14] stated that “angle of progression” ≥ 120° was correlated with an 85.5% probability of vaginal delivery. Malik and Singh [15] estimated an angle of progression ≥ 116° as a predictive of vaginal delivery in the late first and second stages. Barbera et al. [10, 11] and Kalache et al. [1] also noticed a continuous increase in the “angle of progression” during the second stage in all the vaginal deliveries. They claimed that all women with an angle of progression > 120° delivered spontaneously. The angle of progression ≤ 108° was used as a cutoff value for patients who are in need for CS. This agreed with the current study which shows a significant correlation between a large angle of fetal head descent and the success of vaginal delivery.
Torkildsen et al. [23] reported that the predictive value of vaginal delivery was 81% and 76% for FHPD and angle of progression, respectively. They used 110 degrees as a cutoff value for the angle of progression; 87% delivered vaginally (sensitivity 56%, specificity 75%, PPV 87%, NPV 37%, positive LR of 2.2, and negative LR of 0.6). However, in our study, using cutoff value for angle of progression of 115 degrees; 91% delivered vaginally (sensitivity 93%, specificity 84%, PPV 87%, NPV 91%, positive LR 6.06, and negative LR 0.08).
According to Torkildsen et al., [23] by using a cutoff value of 4 cm for the FHPD, 93% delivered vaginally (sensitivity 62%, specificity 85%, PPV 93%, NPV 43%, positive LR of 4.2, and negative LR of 0.4). Similar, but with a lower predictivity, to our study using 4.2 cm as a cutoff value, 84% delivered vaginally (sensitivity 80%, specificity 84%, PPV 85%, NPV 78%, positive LR 5.2, and negative LR 0.24).
Fetal complications of prolonged labor—including caput succedaneum and molding—were diagnosed easily by TPUS, which is one of the strongest points of our study. Thirty-five percent of cases developed molding, and 28% of cases developed caput succedaneum, which was confirmed clinically after delivery.
This study has several limitations as well; the small sample size and lack of control of some confounding factors like the different obstetricians managing the labor and other confounding factors regarding the general state of the pregnant ladies and fetal parameters.
Conclusion
Intrapartum TPUS is more convenient and more accepted by the pregnant ladies compared with digital vaginal examination. It is useful in predicting the mode of delivery; a cutoff value of 115° for the angle of fetal head descent and 4.2 cm of FHPD is recommended to predict vaginal delivery.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CS:
-
Cesarean section
- FHPD:
-
Fetal head–perineum distance
- LR:
-
Likelihood ratio
- TPUS:
-
Transperineal ultrasound
- PPV:
-
Positive predictive value
- NPV:
-
Negative predictive value
- SPSS:
-
Statistical package of social sciences
- US:
-
Ultrasound
References
Kalache K, Du Ckelmann A, Michaelis S (2009) Transperineal ultrasound imaging in prolonged second stage of labour with occipitoanterior presenting fetuses: how well does the ‘angle of progression’ predict the mode of delivery? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 33:326–330
Altman M, Lydon-Rochelle M (2006) Prolonged second stage of labour and risk of adverse maternal and perinatal outcomes: a systematic review. Birth 33(4):315–322
Molina F, Nicolaides K (2010) Ultrasound in labor and delivery. Fetal Diagn Ther 27:61–67
Towner D, Castro M, Eby-Wilkens E, Gilbert W (1999) Effect of mode of delivery in nulliparous women on neonatal intracranial injury. N Engl J Med 341:1709–1714
Murphy D, Liebling R, Patel R, Verity L, Swingler R (2003) Cohort study of operative delivery in the second stage of labour and standard of obstetric care. BJOG 110:610–615
Olagundoye V, MacKenzie I (2007) The impact of a trial of instrumental delivery in theatre on neonatal outcome. BJOG 114:603–608
Hale R (2nd Ed) (1988) Rosen’s management of labor. Physician’s judgement and patient care (2nd Ed.). Chapman & Hall: New York.
Murphy D, Liebling R, Verity L, Swingler R, Patel R (2001) Early maternal and neonatal morbidity associated with operative delivery in second stage of labour: a cohort study. Lancet 358:1203–1207
El-Zanaty, Fatma and Ann Way. Egypt Demographic and Health Survey 2008. Cairo, Egypt: Ministry of Health, El-Zanaty and Associates, and Macro International. Available via https://dhsprogram.com/pubs/pdf/FR220/FR220.pdf. Accessed 15 Jan 2019.
Barbera A, Pombar X, Perugino G (2009) A new method to assess fetal head descent in labor with transperineal ultrasound. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 33:313–319
Barbera A, Imani F, Becker T, Lezotte DC, Hobbins JC (2009) Anatomic relationship between the pubic symphysis and ischial spines and its clinical significance in the assessment of fetal head engagement and station during labour. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 33(3):320–325
Wiafe YA, Whitehead B, Venables H, Dassah ET (2020) Acceptability of intrapartum ultrasound by mothers in an African population. J Ultrasound 23(1):55–59
Kreiser D, Schiff E, Lipitz S, Kayam Z, Avraham A, Achiron R (2001) Determination of fetal occiput position by ultrasound during the second stage of labor. J Matern Fetal Med 10:283–286
Amin M, Eltomey M, El-Dorf A (2014) Role of transperineal ultrasound measurements in women with prolonged second stage of labour as predictors of the mode of delivery. EJRNM 45:1295–1299
Malik R, Singh S (2020) Measurement of angle of descent (AOD) by transperineal ultrasound in labour to predict successful vaginal delivery. J Obstet Gynaecol India 70:126–132
Minajagi P, Srinivas S, Hebbar S (2020) Predicting the mode of delivery by angle of progression (AOP) before the onset of labor by transperineal ultrasound in nulliparous women. Current Women's Health Reviews 16(1):39–45
Duckelmann A, Michaelis S (2010) Measurement of fetal head descent using the ‘angle of progression’ on transperineal ultrasound imaging is reliable regardless of fetal head station or ultrasound expertise. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 35:216–222
Buchmann E, Libhaber E (2008) Interobserver agreement in intrapartum estimation of fetal head station. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 101:285–289
Dupuis O, Silveira R, Zentner A, Dittmar A, Gaucherand P, Cucherate M, Redarce T, Rudigoz RC (2005) Birth simulator: reliability of transvaginal assessment of fetal head station as defined by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists classification. Am J Obstet Gynecol 192(3):868–874
Henrich W, Dudenhausen J, Fuchs I, Kamena A, Tutschek B (2006) Intrapartum translabial ultrasound (ITU): sonographic landmarks and correlation with successful vacuum extraction. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 28(6):753–760
Usman S, Barton H, Wilhelm-Benartzi C, Lees CC (2019) Ultrasound is better tolerated than vaginal examination in and before labour. AustN Z J Obstet Gynaecol 59(3):362–366
Ibrahim Z, Ahmed W, Elmorsy M, Albiely M, Taha O (2020) The accuracy of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of fetal head engagement. Bioned J Sci & Tech Res 24(5):18641–18644
Torkildsen E, Salvesen K, Eggebo T (2011) Prediction of delivery mode with transperineal ultrasound in women with prolonged first stage of labour. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 37(6):702–708
Gilboa Y, Kivilevitch Z, Spira M, Kedem A, Katorza E, Moran O, Achiron R (2013) Head progression distance in prolonged second stage of labour: relationship with mode of delivery and fetal head station. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 41(4):436–441
Cunningham FG, Leveno KJ, Bloom SL, Hauth JC, Gilstrap LC III, Wenstrom KD (2005) Normal labor and delivery. In Williams Obstetrics (22nd ed), McGraw-Hill, pp 409–441.
Ali J, Hibbar S (2019) Ultrasound assessment of foetal head-perineum distance prior to induction of labour as a predictor of successful vaginal delivery. J Obstet Gynaecol India 69(2):129–135
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
The study was self-funded by the authors. No external funds were obtained for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SS collected the data, performed the analysis, and wrote the manuscript. KA, AG, and MA conceived and designed the study. KA followed up the clinical aspects of the study. MA edited the manuscript for publication and he is the corresponding author. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the local ethical research committee of the Suez Canal University and Faculty of medicine. The reference numbers are unfortunately unavailable, because at the time the research protocol was passed through the ethical approval process, there was no reference numbers assigned to the research protocol at our faculty. All patients included in this study gave written informed consent to participate in this research by the patients themselves or by primary degree relatives.
Consent for publication
Patients included in this research gave written informed consent to publish the data contained within this study.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Solaiman, S.A., Atwa, K.A., Gad, A.A. et al. Transperineal ultrasound of fetal head progression in prolonged labor: women’s acceptance and ability to predict the mode of delivery. Egypt J Radiol Nucl Med 51, 94 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43055-020-00215-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43055-020-00215-0