Abstract
Background
Tobacco smoking is considered as one of the lifestyles factors that influence the sperm DNA methylation and global sperm DNA methylation and that may affect the sperm phenotype. This study was performed to investigate whether tobacco cigarette heavy smoking influences sperm DNA methylation patterns and semen parameters and to determine whether there is an alteration in the transcription level of MAPK8IP3, GAA, ANXA2, PRRC2A, and PDE11A genes in heavy smokers compared to non-smokers. Thirty samples were subjected to 450K arrays as a screening study to assess the variation in sperm DNA methylation levels between heavy smokers and non-smokers. Five CpG sites have the highest difference in methylation levels (cg07869343, cg05813498, cg09785377, cg06833981, and cg02745784), which are located in the MAPK8IP3, GAA, ANXA2, PRRC2A, and PDE11A genes, respectively, and were selected for further analysis using deep bisulfite sequencing in 280 independent samples (120 proven non-smokers and 160 heavy smokers) with a mean age of 33.8 ± 8.4 years. The global sperm DNA methylation, sperm DNA fragmentation, and chromatin non-condensation were evaluated also.
Results
A significant increase was found in the methylation level at seven, three, and seventeen CpGs within the GAA, ANXA2, and MAPK8IP3 genes amplicon, respectively (P< 0.01) in heavy smokers compared to non-smokers. Additionally, a significant increase was found in the methylation levels at all CpGs within PRRC2A and PDE11A gene amplicon (P< 0.01). A significant increase was found in the level of sperm chromatin non-condensation, DNA fragmentation, and global DNA methylation (P < 0.001) in heavy smokers compared to non-smokers.
Conclusion
These results indicate that tobacco cigarette smoking can alter the DNA methylation level at several CpGs, the status of global DNA methylation, and transcription level of the following genes “MAPK8IP3, GAA, ANXA2, PRRC2A, and PDE11A” in human spermatozoa. These findings may affect negatively semen parameters and men’s fertility.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Infertility is defined as the inability of a sexually active couple to achieve a successful pregnancy after 1 year of unprotected intercourse [1]. Approximately 15% of couples worldwide suffering from infertility problems [2] and about 40% of infertility cases are identified as male factors [3, 4]. There are several factors responsible for the status of male infertility, including lifestyle (food habits, smoking, and alcohol consumption), environmental factors (exposure to relatively more temperature, pollution), and genetic factors [5].
Tobacco cigarette smoking is considered one of the lifestyle factors that contribute to the increased prevalence of male infertility and the reduction in semen parameters and sperm quality [6]. Cigarettes are made up of Nicotiana tabacum along with vaporized drugs and harmful substances, where cigarette smoke consists of carbon monoxide, tar, formaldehyde, nicotine, lead, cadmium, and many other substances [7, 8]. Previous studies reported that cigarette smoking impact negatively on spermatogenesis process and functions of spermatozoa [9, 10]. Additionally, several studies reported that the oxygen deficiency produced by cigarette smoking influences testicular function and impairs spermatogenesis, which ultimately leads to impaired sperm morphology, a decline in the progressive sperm, and increased sperm death [11,12,13]. In addition, several studies have shown that tobacco cigarette smoking-induced genetic alterations have an influence on men’s fertility through chromosomal alterations [14], mutations [15], polymorphisms [16], DNA damage [17], and epigenetic alteration [18, 19]. Furthermore, other studies reported that tobacco smoking is considered as one of the lifestyles factors that influence the sperm DNA methylation patterns and global sperm DNA methylation and that may affect the sperm phenotype and males fecundity [20,21,22].
DNA methylation is an epigenetic mechanism that occurs at the 5th carbon atom of a cytosine that is followed by guanine residues (CpG) to form 5-methylcytosine (5mC) [23], and this process occurs by DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) enzyme [24]. In humans, CpG dinucleotides can be found in clusters that have been termed CpG islands [25]; these CpG islands are found mostly in the promoter region and remain unmethylated, while the majority of all other CpG islands are methylated [26]. When CpG islands in promoter regions are methylated, the transcription of the corresponding gene is usually suppressed [27]. The methylation status of CpGs located in the promoter and intragenic regions plays a significant role in gene repression and activation, respectively [28]. Actually, DNA methylation is very necessary to facilitate the correct compaction of chromatin in the sperm head and to permanently silence the promoters of genes involved in genetic imprinting [29]. In humans, correct sperm DNA methylation is suggested to be essential for both fertilization and early fetus viability [30, 31].
Several studies have been shown a strong association between tobacco cigarette smoking and the alteration in the spermatozoa DNA methylation patterns [32,33,34]. Nevertheless, the influence of tobacco smoking on sperm DNA methylation and gene transcription level in sperm remains debatable. Therefore, this study was performed in order to (I) investigate whether tobacco cigarette heavy smoking impacts sperm DNA methylation patterns and semen parameters; (II) determine whether there is an alteration in the transcription level of MAPK8IP3, GAA, ANXA2, PRRC2A, and PDE11A genes in heavy smokers compared to non-smokers; and (III) investigate the association between the variation in the sperm DNA methylation patterns and the basic semen parameters.
Methods
Study population and participation criteria
The study population included two hundred and eighty adult males with a mean age of 33.8 ± 8.4 years old (120 non-smokers with proven fertile and 160 heavy smokers, who consume at least 25 cigarettes per day for 12 years, sub-fertile and they did not achieve pregnancy in the past 4 years). The exclusion criteria for participation in the study were as follows: consumption of alcohol, the diabetes mellitus, presence of anti-sperm antibodies, varicocele, males underwent a surgical operation in the reproductive system, Y chromosome microdeletions, abnormal hormonal parameters, abnormal body mass index, and males suffering from known infertility problems. On the other hand, the inclusion criteria were age between 20 and 48 years old, males have the same nationality, ethnicity, and food supplementation.
Samples collection and spermatozoa purification
Semen samples were collected by masturbation after 3 days of sexual abstinence. The samples were allowed to liquefy at 37 °C for 30 min, then the sperm count was assessed using the Meckler counting chamber (Sefi-Medica, Israel). The semen parameters were analyzed according to World Health Organization guidelines [35]. Before DNA extraction from human spermatozoa, somatic cells have been removed from all the semen samples through the use of somatic cell lysis buffer (SCLB) which is used widely for sperm cell purification. Briefly, the liquefied semen samples were loaded onto 45% over 90% discontinuous Puresperm gradient (Nidacon International AB, Sweden) and then centrifuged at 500g for 25 min at 25°C. After that, the pure spermatozoa were incubated with SCLB on ice for 30 min and washed three times with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and then centrifuged at 500g for 10 min [36]. Finally, the absence of somatic cell contamination was confirmed by microscopic examination.
Evaluation of sperm chromatin non-condensation
The chromomycin A3 (CMA3) staining was used to evaluate the chromatin non-condensation at human spermatozoa. Briefly, four semen smears were prepared from each sample and all smears were fixed by using a fixative solution (methanol-glacial acetic acid, 3:1 respectively) at 4°C for 20 min. The semen smears were air-dried at room temperature. After that, each smear was covered by 50 μl of staining solution (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) and then incubated in a dark place at room temperature for 20 min. The phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) was used to wash all the slides, then the slides were mounted with 1:1 (v/v) glycerol/PBS incubated overnight at 4°C. To evaluate the results of CMA3 staining, the fluorescence microscope (Zeiss Photomicroscope III, Germany) was used to analyze 300 spermatozoa on each smear. Finally, the CMA3 staining was evaluated by differentiating the spermatozoa that stained with bright yellow (positive, bad spermatozoa) from spermatozoa that stained with a dull yellow (negative, good spermatozoa) [37].
Evaluation of DNA fragmentation in human spermatozoa
The spermatozoa DNA fragmentation (apoptosis) was evaluated using the terminal deoxyribonucleotide transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) assay. The TUNEL assay was performed by using the in situ cell death detection kit following the guidelines of the manufacturer company (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Germany). Briefly, smears were prepared using 10 μl of sperm suspension on microscope slides and allowed to air-dry and then fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde phosphate-buffered saline, pH 7.4 for 2 h at room temperature, then rinsed with PBS. Smears were then permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in 0.1% sodium citrate, pH 6.0 for 15 min at room temperature; 50 μl of the TdT-labeled nucleotide mixture (50 μl of enzyme solution and 450 μl of label solution) was added to each slide and incubated in a humidified chamber at 37°C overnight in the dark. Negative controls without TdT enzyme were run in each replicate. Then, slides were rinsed two times in PBS and left to dry in the air followed by adding 25 μl of 5 μg/ml DAPI stain solution to each slide as a counterstain and then covered by coverslips. For evaluation, a total of 200 spermatozoa were analyzed on each slide, by distinguishing spermatozoa stained bright green (TUNEL positive, fragmented DNA) from those stained dull green (TUNEL negative, with intact DNA). A Zeiss Photomicroscope III was used for the fluorochrome evaluation (Zeiss Photomicroscope III, Germany) [38].
Extraction of nucleic acid from human spermatozoa
The nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) were isolated from the human spermatozoa by using Isolate II DNA/RNA/Protein Kit and all steps were performed according to the guidelines of the manufacturer company (Bioline, UK). The Nanodrop spectrophotometer-2000c (Thermo Scientific, USA) was used to evaluate the concentration and purity of extracted nucleic acids in order to ensure that the isolated nucleic acids are sufficient and suitable for global DNA methylation, deep bisulfite sequencing, and qPCR. To confirm the effectiveness of the protocol used in removing somatic cells from the semen samples that were entered in this study, the publicly available data (GEO # GSE41169) were used to define sample purity and based on a known significantly differentially methylated region (DMR) between somatic cells (White blood cell) and spermatozoa. We assessed DNA from whole blood, DNA from round cell-contaminated sperm samples, and known pure sperm DNA and compared these with sperm DNA of the study population. The data showed that the samples evaluated in this study were free from potential contamination resulting from the presence of immature sperm, white blood cells, or other somatic cells.
Evaluation of global DNA methylation in human spermatozoa
The MethylFlash™ Methylated DNA Quantification ELISA Kit was used to evaluate the level of global DNA methylation (5-methylcytosine) in the human spermatozoa; all the steps were performed according to the manufacturer’s guidelines (Epigentek Group Inc, USA). Briefly, 100 ng of extracted DNA was incubated with the DNA binding buffer solution at 37°C for 90 min (blank, a positive, and negative control have been used in triplicate during this assay). After washing the microwell three times, the methylated DNA capture solution was added to each well and incubated for 60 min at room temperature. After that, the detection antibodies were added to each well and incubated at room temperature for 30 min. After three-time washing, the developing solution was added to each well and incubated at room temperature in the dark place for 10 min, and at the end of the 10 min, the stop solution was added. The microplate ELISA reader was used to assess the absorbance at 450 nm. The global DNA methylation status (ng) was calculated using the equation: 5-mC(ng) = [(sample OD − blank OD)/100].
Sodium bisulfite treatment
Four hundred nanograms of isolated spermatozoa DNA was treated with sodium bisulfite using the Epitect bisulfite conversion kit (Qiagen, Germany) that converts unmethylated cytosines to uracil, while 5- methylcytosine (5MeC) remains unaltered, as described previously [39].
Screening study (infinium 450 K BeadChip array)
Thirty semen samples with a mean age of 34.0 years old (15 proven non-smokers and 15 heavy smokers) were used. After the bisulfite treatment process, the DNA was subjected to the Infinium 450K BeadChip array (Illumina, USA) following the manufacturer’s recommendations [40], and the arrays were scanned using the Illumina iScan. Beta-values were then generated by analyzing the intensity of methylation or the absence of methylation at each CpG tile on the array using the calculation: Beta-value = methylated / (methylated + unmethylated). The Beta-value ranges from 0 to 1 and indicates the methylation level for each CpG. A value of 1 represents a completely methylated CpG and a score of 0 means a completely unmethylated CpG. Raw intensity values obtained from Illumina were used to generate Beta-values; the bioinformatic processing and evaluation were performed with the RNBEADS program package [41]. The methylation level at each CpG was considered as being differentially methylated CpG (DMC) when the absolute difference in the means of the average beta values between the two groups was ≥ 20% with a Benjamini–Hochberg-corrected t-test FDR (false discovery rate) of 0.05. All CpGs that covered a common SNP site in the dbSNP137 database were excluded, and the findings were considered significant when p ≤ 0.01. In the current study, and according to the results of the Infinium 450K BeadChip array, five CpG sites have the highest difference in methylation levels (cg07869343, cg05813498, cg09785377, cg06833981, and cg02745784), which are located in the MAPK8IP3, GAA, ANXA2, PRRC2A, and PDE11A genes, respectively, were selected for further analysis using deep bisulfite sequencing according to the manufacturer’s instructions [42].
Deep bisulfite sequencing
In this part of the study, 280 independent samples (120 proven non-smokers and 160 heavy smokers) with a mean age of 33.8 ± 8.4 years were used. Briefly, 400 ng of genomic DNA was bisulfite-treated using the Epitect bisulfite conversion kit (Qiagen, Germany). PCRs encompassing the differentially methylated CpG (DMC) identified by the 450K BeadChip array were performed in a 50-μL total volume reaction using “MyTaqTM HS Red Mix” 2x concentrated (Bioline, UK) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. For the amplification, fusion primers were used that consisted of a specific 30 portion and a universal 50 portion containing the necessary nucleotide sequences for Illumina sequencing (listed in Table 1). Primers were designed using the BiSearch primer design tool (http://bisearch.enzim.hu/?m=search). In this assay, 5 μL of each PCR reaction was loaded onto a 2% agarose gel stained with ethidium bromide (New England Biolabs, USA). The PCR products were purified using Agencourt AMPure XP beads (Beckman Coulter, USA) and measured using Quant-iTTM DNA Assay Kit (Fisher Scientific, USA) according to the manufacturer’s recommendations, then diluted and pooled. Deep sequencing was performed on the Illumina MiSeq according to the manufacturer’s protocols aiming at 10,000 reads per amplicon. All data obtained from the deep sequencing step were processed, filtered, and aligned using BiQ Analyzer HT software [43], excluding all reads containing ≥ 10% of missing CpG sites (maximal fraction of unrecognized sites ≥ 0.1). The obtained alignment sequences showed an absence of alterations at CpG positions (no SNPs were detected).
Reverse transcription and qPCR
The isolated RNA from spermatozoa was converted to complementary DNA (cDNA) in a 30 μl reaction volume by using the miScript reverse transcription kit and all procured following the manufacturer’s guidelines (Qiagen, Germany). The transcription level of MAPK8IP3, GAA, ANXA2, PRRC2A, and PDE11A and the housekeeping gene as a reference gene (GAPDH) were evaluated by using the qPCR instrument (7500 Fast applied Bio-systems, USA). The cDNA was used as a template, and all the primers included in this study (QuantiTect Primer) were used according to the guidelines of the manufacturer company (Qiagen, Germany). The reverse transcriptase control (NRT) and template control (NTC) were not involved in runs. All samples were analyzed in triplicate, and all the values of Ct were normalized to GAPDH.
Data analysis
The data obtained from this study were analyzed using SPSS version 24.0 (SPSS Inc., USA). Data included in this study were non-normally distributed (nonparametric) according to the values of the skewness test, Kurtosis test, Z-value, and Shapiro test. The independent-sample U-test (Mann–Whitney test) was used to compare the quantitative variables between the study groups. Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient was applied to assess the correlation between the variation in sperm DNA methylation patterns and other investigated parameters. The comparative ΔCt method was used separately to calculate the relative RNA quantity in all samples. The ΔCt was calculated by subtracting the Ct values of GAPDH from the Ct values of the target RNA, where ΔCt = ([Ct NA of target RNA] − [Ct RNA of GAPDH]). Then, the ΔΔCt was calculated by subtracting the mean ΔCt of the non-smokers from the ΔCt of the heavy smoker (ΔΔCt = ΔCt of heavy smokers − ΔCt of non-smokers). The fold change of transcription level was calculated by using the following equation: 2−ΔΔCt equation [44]. All the results of the abovementioned tests were considered statistically significant when P < 0.05.
Results
Descriptive characteristics of heavy smokers compared to non-smokers
Table 2 illustrates the locations of the most differentially methylated CpGs (DMC), based on the DNA methylation difference of > 20% between the heavy smokers and non-smokers groups. Five CpG positions following the applied criteria (cg07869343, cg05813498, cg09785377, cg06833981, and cg02745784) were selected to validate the observed methylation difference in 280 samples. All of these CpGs located in gene bodies and CpG islands and these genes were found to be related to male fertility, sperm concentration, and sperm function.
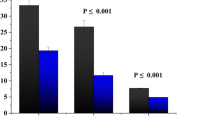
Table 3 summarizes the descriptive characteristics of the study population. The mean age of males included in this study was 33.8 ± 8.4 years old. The study population was divided into two groups: a heavy smokers group was composed of 160 males with an average age of 33.1 ± 8.4 years old, and the non-smoker’s group was composed of 120 males with an average age of 34.7 ± 8.4 years old. A significant reduction has been found in sperm concentration, percentage of total sperm motility, and sperm progressive motility in heavy smokers compared to non-smokers (P < 0.001). In contrast, a significant increase has been observed in the percentage of sperm non-progressive motility, non-motile sperm, and sperm abnormal form (P < 0.001). A significant increase has been found in the level of sperm chromatin non-condensation, sperm DNA fragmentation (Fig. 1), and sperm global DNA methylation (Fig. 2) in heavy smokers compared to non-smokers (P < 0.001).
Correlation between semen parameters and other parameters in the heavy smokers
As represented in Table 4, a significant negative association was found between the sperm concentration and the age of heavy smokers (r = −0.232, P = 0.003). Conversely, a positive correlation was found between the sperm concentration and the level of sperm chromatin non-condensation (r = 0.183, P = 0.021). However, no significant correlations were found between sperm DNA fragmentation, global DNA methylation status, and the basic semen parameters in heavy smokers have been found.
Deep bisulfite sequencing results
The results revealed that not only the target CpGs obtained from the 450K bead array experiments showed a difference in the methylation level, but also the neighboring CpGs. A significant increase in the methylation level was found in heavy smokers compared to non-smokers at seventeen of twenty-two tested CpGs tested within the MAPK8Ip3 gene-related amplicon CpG1, CpG2, CpG4, CpG5, CpG6, CpG7, CpG8, CpG10, CpG12, CpG13, CpG14, CpG15, CpG16, CpG18, CpG20, CpG21, and CpG22 (P < 0.001, P = 0.004, P = 0.001, P < 0.001, P = 0.025, P = 0.002, P < 0.001, P = 0.001, P < 0.001, P = 0.002, P = 0.001, P = 0.001, P = 0.002, P = 0.031, P < 0.001, P < 0.001, and P = 0.001, respectively) (Fig. 3A–E). Similarly, a significant increase was found at seven of ten tested CpGs within the GAA gene-related amplicon CpG1, CpG2, CpG5, CpG6, CpG7, CpG8, and CpG10 (P < 0.001, P < 0.001, P < 0.001, P = 0.002, P < 0.001, P < 0.001, and P < 0.001, respectively) in heavy smokers compared to non-smokers (Fig. 4A, B). The DNA methylation levels at three out of four CpGs related to the ANXA2 gene amplicon (CpG1, CpG2, and CpG4) showed a significant difference in the heavy smokers compared to the non-smokers (P = 0.002, P = 0.002, and P = 0.005, respectively) (Fig. 5). Additionally, the results showed that all CpGs related to the PRRC2A gene amplicon (CpG1, CpG2, and CpG3) had a significant difference in the methylation level (0.001, 0.004, and 0.001 respectively) in heavy smokers compared to non-smokers (Fig. 6). Besides that, all CpGs related to the PDE11A gene amplicon (CpG1, P = 0.002) showed a significant difference in the heavy smokers compared to non-smokers (Fig. 7).
Transcription level of studied genes
This study showed a significant reduction in the transcription levels of MAPK8IP3, GAA, ANXA2, and PRRC2A genes (P = 0.002, P < 0.001, P = 0.005, and P < 0.001, respectively) in heavy smokers compared to non-smokers (Fig. 8). Additionally, the results found upregulation in the MAPK8Ip3, ANXA2, and PRRC2A transcription levels with fold change 1.43, 4.58, and 2.52, respectively in heavy smokers compared to non-smokers. Conversely, downregulation has been found in the GAA gene transcription level with a fold change of 0.10 in heavy smokers compared to non-smokers (Table 5). No significant difference between heavy smokers and nonsmokers male in the transcription level of PDE11A (P = 0.099).
Correlation between methylation levels at different CpGs and basic semen parameters in the heavy smokers
As illustrated in Table 6, a significant negative correlation was found between the methylation levels at CpG3, CpG4, CpG5, CpG9, CpG11, CpG12, CpG13, CpG16, CpG21, and CpG22 within the MAPK8Ip3 gene-related amplicon and sperm concentration (P = 0.006, P = 0.001, P = 0.002, P = 0.012, P = 0.005, P = 0.034, P = 0.005, P = 0.005, P = 0.002, and P = 0.005, respectively). In addition, a significant negative correlation was found between percentage of total sperm motility, sperm non-progressive motility, and the methylation levels at CpG3 in the GAA gene-related amplicon (P = 0.039 and P = 0.017, respectively). Likewise, a significant negative correlation was found between the methylation in the (CpG9 within GAA gene-related amplicon, CpG3 within ANXA2 gene-related amplicon, CpG1 within PRRC2A gene-related amplicon) and percentage of sperm progressive motility (P = 0.017, P = 0.008, and P = 0.025, respectively). In contrast, a significant positive correlation was found between the methylation level at the CpG3 within ANXA2 gene-related amplicon, CpG10 within GAA gene-related amplicon and sperm concentration (r = 0.163, P = 0.040; r = 0.208, P = 0.008, respectively). Moreover, a significant positive correlation has been found between the methylation level at CpG1 (r = 0.184; P = 0.020), CpG19 (r = 0.172; P = 0.029), and CpG21 (r = 0.157, P= 0.048) within MAPK8Ip3 gene-related amplicon, and percentage of sperm abnormal form.
Discussion
Tobacco cigarette consumption is prevalent in more than a third of the world population [45]. Tobacco smoke contains around 4700 chemical compounds and several hazardous substances which are inhaled by smokers, which have harmful impacts on human germ cells [46]. Previous studies noted an association between a quality deterioration of semen including (sperm motility, sperm concentration, and sperm morphology), and smoking cigarettes [13, 47].
This study evaluated the methylation levels at differentially methylated CpGs (DMC) within the MAPK8IP3, GAA, ANXA2, PRRC2A, and PDE11A, gene-related amplicon in human spermatozoa obtained from heavy smokers compared to a proven fertile nonsmoker. In spermatozoa, DNA methylation plays a necessary role in the proper spermatogenesis process [48], and several studies have observed that the decline in the reproductive potential of men and the defects in spermatogenesis could be caused by abnormal methylation in genes expressed in the testes [49, 50]. The results obtained from the validation study showed a significant increase in the methylation levels at seventeen of twenty-two tested CpGs within the MAPK8Ip3 gene-related amplicon (CpG1, CpG2, CpG4, CpG5, CpG6, CpG7, CpG8, CpG10, CpG12, CpG13, CpG14, CpG15, CpG16, CpG18, CpG20, CpG21, and CpG22) and at seven of ten tested CpGs within the GAA gene-related amplicon (CpG1, CpG2, CpG5, CpG6, CpG7, CpG8, and CpG10). Besides there is a significant increase at three out of four CpGs related to the ANXA2 gene amplicon and all CpGs related to the PRRC2A and PDE11A genes amplicon. These findings are in agreement with previous studies that showed that the methylation levels in sperm DNA tend to be altered in heavy smokers compared to non-smokers males [51, 52]. In addition, several studies have shown a significant association between tobacco cigarette smoking and the alteration in DNA methylation level at multiple CpGs in human spermatozoa [32, 53]. Another study observes a significant difference in methylation level of 11 CpGs in spermatozoa of current smokers compared to never smokers [54]. It is worth mentioning that the glucosidase alpha acid, encoded by the glucosidase alpha acid (GAA) gene, plays an essential role in the degradation of glycogen to glucose in lysosomes and that any defects in this gene lead to glycogen storage disease II “Pompe’s disease” [55], whereas the lysosomes found in the spermatozoa acrosome contain protease and hyaluronidase along with acid phosphatase, which plays a critical role in the maturation of spermatozoa and fertilization process (provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008, NCBI website). Besides, it should also be noted that members of the PDE protein superfamily, that is, phosphodiesterase 11A (PDE11A), play important roles in the control of cyclic nucleotide signaling [56]. Other studies reported that the expression of this gene was prominent in the prostate and testes [57, 58]. Another study founded that strong immune signals were obtained for PDE11A in the acrosomal cap and flagella of spermatozoa [59]. Additionally, the Annexin A2 (ANXA2) gene encodes a member of the Annexin family, a family of Ca2+-regulated phospholipid-binding and membrane-binding proteins that are found in the acrosome and flagellum of the spermatozoa and could be implicated in different events that are known to be calcium-dependent, such as flagella motility, acrosome reaction and fertilization [60]. Also, the protein encoded by the mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 interacting protein 3 (MAPK8IP3) gene is one of the MAPK family, which is found in the spermatozoa and was observed to be associated with a direct or indirect function in human sperm capacitation [61].
Several studies investigated the relationship between DNA methylation and cigarette smoking [62, 63], and these studies proposed that tobacco cigarette smoking could alter the sperm DNA methylation patterns through two mechanisms: the first mechanism is the recruitment of DNA methyltransferases after DNA damage resulting from smoking, and the second mechanism involves the alterations in the transcription and expression of genes due to the influence of nicotine and hypoxia caused by carbon monoxide, a principal component of cigarette smoke [64]. The results of this study showed a significant increase in the level of global DNA methylation, sperm chromatin non-condensation, and spermatozoa DNA fragmentation in heavy smokers compared to non-smokers males; these findings are matching with a previous study which was performed by Hamad and his colleagues who have found an increase in the level of global sperm DNA methylation and sperm chromatin decondensation in smokers compared to non-smokers [22]. Other studies have found an increase in the rate of spermatozoa DNA fragmentation in smokers than in non-smokers [65, 66]; besides other studies showed a significant increase in the abnormal level of sperm chromatin condensation (P ≤ 0.001) in smokers compared to nonsmokers [66, 67].
Regarding the semen parameters, the results found a significant reduction in sperm concentration, percentage of total sperm motility, sperm progressive motility, and sperm normal form in heavy smokers compared to non-smokers males. Conversely, a significant increase has been noted in the percentage of non-motile sperm in heavy smokers compared to non-smokers males, and these results are consistent with other studies reported the same variation in semen parameters in smoker compared to non-smokers [66, 68]. Nevertheless, these results are not consistent with previous studies that showed no significant differences between smokers and non-smokers males in the sperm count and percentage of total sperm motility [69, 70].
This study showed a significant reduction in the transcription levels of the following genes (MAPK8IP3, GAA, ANXA2, PRRC2A, and PDE11A) in heavy smokers compared to non-smokers. Furthermore, the results were found upregulation in the MAPK8Ip3, ANXA2, PRRC2A, and PDE11A transcription levels in heavy smokers compared to non-smokers. In contrast, a downregulation has been found in the GAA gene transcription level in heavy smokers compared to non-smokers. These findings are matching with a previous study that showed an alteration in the gene expression in smokers compared to non-smokers; besides another study showed a significant decline in the transcription level of PRM 1 and PRM 2 in smokers’ spermatozoa compared to non-smokers [71]. Another study reported that the smoking-related ROS might cause decreased in the transcription level of genes like IκBα and might be correlated with defective spermatogenesis [72]. All of these findings are in agreement with a hypothesis that reported that cigarette smoke may play a critical role in the alteration of the transcription level of human genes found in spermatozoa by its influence on chromatin remodeling, global DNA methylation status, and DNA methylation at different CpG sits. Further, previous studies have reported that cigarette smoking leads to increased sperm DNA damage [73].
Finally, the study investigated the correlation between the alteration in DNA methylation level at tested CpGs and semen parameters. The results showed a negative significant correlation between the methylation levels at ten out of twenty-two within the MAPK8Ip3 gene-related amplicon and sperm concentration. Moreover, a negative significant correlation was found between the percentage of total sperm motility, sperm non-progressive motility, and the methylation levels at CpG3 in the GAA gene-related amplicon. Likewise, a negative significant correlation was found between the methylation in one CpGs within the GAA, ANXA2, PRRC2A, and the percentage of sperm progressive motility. These findings are in line with other studies that observed an association between the alterations in the sperm DNA methylation patterns and semen parameters of tobacco cigarette smokers [74, 75]. Another study found a strong association between reduced sperm count, sperm motility, sperm normal form, and cigarette consumption [45, 76]. Nevertheless, the associations observed in this study contradict with other studies that showed no association between sperm global DNA methylation level and sperm parameters of smokers [77].
Conclusion
This study clearly offers evidence that tobacco cigarette smoking can alter the DNA methylation level at several CpGs, the status of global DNA methylation, and transcription level of the following genes “MAPK8IP3, GAA, ANXA2, PRRC2A, and PDE11A” in human spermatozoa. Besides an association has been found between alterations in the methylation level at these CpGs and basic semen parameters in smokers, and these findings may affect negatively semen parameters and men’s fertility.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- DNMTs:
-
DNA methyltransferases
- 5mC:
-
5-Methylcytosine
- SCLB:
-
Somatic cell lysis buffer
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- CMA3:
-
Chromomycin A3
- TUNEL:
-
Terminal deoxyribonucleotide transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling
- qPCR:
-
Quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
- DMC:
-
Differentially methylated CpG
- cDNA:
-
Complementary DNA
References
Krausz C, Chianese C (2014) Genetic testing and counselling for male infertility. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 21(3):244–250
Poongothai JE, Gopenath TS, Manonayaki SW (2009) Genetics of human male infertility. Singapore Med J 50(4):336–347
Inhorn MC, Patrizio P (2015) Infertility around the globe: new thinking on gender, reproductive technologies and global movements in the 21st century. Hum Reprod Update 21(4):411–426
Sansone A, Di Dato C, de Angelis C, Menafra D, Pozza C, Pivonello R, Isidori A, Gianfrilli D (2018) Smoke, alcohol and drug addiction and male fertility. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 16(1):1–1
Parameswari R, Sridharan TB (2021) Cigarette smoking and its toxicological overview on human male fertility—a prospective review. Toxin Rev 40(2):145–161
Wei Y, Schatten H, Sun QY (2015) Environmental epigenetic inheritance through gametes and implications for human reproduction. Hum Reprod Update 21(2):194–208
Mostafa T (2010) Cigarette smoking and male infertility. J Adv Res 1(3):179–186
Taha EA, Ezz-Aldin AM, Sayed SK, Ghandour NM, Mostafa T (2014) Smoking influence on sperm vitality, DNA fragmentation, reactive oxygen species and zinc in oligoasthenoteratozoospermic men with varicocele. Andrologia 46(6):687–691
Jurewicz J, Hanke W, Radwan M, Bonde J (2009) Environmental factors and semen quality. Int J Occup Med Environ Health 22(4):305–329
Hansen C, Luben TJ, Sacks JD, Olshan A, Jeffay S, Strader L, Perreault SD (2010) The effect of ambient air pollution on sperm quality. Environ Health Perspect 118(2):203–209
Gaur DS, Talekar M, Pathak VP (2007) Effect of cigarette smoking on semen quality of infertile men. Singapore Med J 48(2):119
Akhter N, Jebunnaher S (2012) Evaluation of female infertility. J Med 13(2):200–209
Ranganathan P, Rao KA, Sudan JJ, Balasundaram S (2018) Cadmium effects on sperm morphology and semenogelin with relates to increased ROS in infertile smokers: an in vitro and in silico approach. Reprod Biol 18(2):189–197
Pereira CS, de Vozzi MS, Dos Santos SA, Vasconcelos MA, de Paz CC, Squire JA, Martelli L (2014) Smoking-induced chromosomal segregation anomalies identified by FISH analysis of sperm. Mol Cytogenet 7(1):1–8
Yauk CL, Berndt ML, Williams A, Rowan-Carroll A, Douglas GR, Stämpfli MR (2007) Mainstream tobacco smoke causes paternal germ-line DNA mutation. Cancer Res 67(11):5103–5106
Yu B, Chen J, Liu D, Zhou H, Xiao W, Xia X, Huang Z (2013) Cigarette smoking is associated with human semen quality in synergy with functional NRF2 polymorphisms. Biol Reprod 89(1):5–1
Viloria T, Meseguer M, Martínez-Conejero JA, O’Connor JE, Remohí J, Pellicer A, Garrido N (2010) Cigarette smoking affects specific sperm oxidative defenses but does not cause oxidative DNA damage in infertile men. Fertil Steril 94(2):631–637
Dai J, Zhan C, Xu W, Wang Z, Nie D, Zhao X, Zhang D, Gu Y, Wang L, Chen Z, Qiao Z (2015) Nicotine elevates sperm motility and induces Pfn1 promoter hypomethylation in mouse testis. Andrology 3(5):967–978
Dong H, Wang Y, Zou Z, Chen L, Shen C, Xu S, Zhang J, Zhao F, Ge S, Gao Q, Hu H (2017) Abnormal methylation of imprinted genes and cigarette smoking: assessment of their association with the risk of male infertility. Reprod Sci 24(1):114–123
Feil R, Fraga MF (2012) Epigenetics and the environment: emerging patterns and implications. Nat Rev Genet 13(2):97–109
Laqqan M, Tierling S, Alkhaled Y, Porto CL, Solomayer EF, Hammadeh ME (2017) Aberrant DNA methylation patterns of human spermatozoa in current smoker males. Reprod Toxicol 71:126–133
Hamad MF, Dayyih WA, Laqqan M, AlKhaled Y, Montenarh M, Hammadeh ME (2018) The status of global DNA methylation in the spermatozoa of smokers and non-smokers. Reprod Biomed Online 37(5):581–589
Wu X, Zhang Y (2017) TET-mediated active DNA demethylation: mechanism, function and beyond. Nat Rev Genet 18(9):517
Schübeler D (2015) Function and information content of DNA methylation. Nature 517(7534):321–326
Takai D, Jones PA (2002) Comprehensive analysis of CpG islands in human chromosomes 21 and 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99(6):3740–3745
Smith ZD, Meissner A (2013) DNA methylation: roles in mammalian development. Nat Rev Genet 14(3):204–220
Biermann K, Steger K (2007) Epigenetics in male germ cells. J Androl 28(4):466–480
Jones PA (2012) Functions of DNA methylation: islands, start sites, gene bodies and beyond. Nat Rev Genet 13(7):484–492
Seisenberger S, Peat JR, Hore TA, Santos F, Dean W, Reik W (2013) Reprogramming DNA methylation in the mammalian life cycle: building and breaking epigenetic barriers. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 368(1609):20110330
Jenkins TG, Carrell DT (2012) The sperm epigenome and potential implications for the developing embryo. Reproduction 143(6):727
Donkin I, Barrès R (2018) Sperm epigenetics and influence of environmental factors. Mol Metab 14:1–1
Jenkins TG, James ER, Alonso DF, Hoidal JR, Murphy PJ, Hotaling JM, Cairns BR, Carrell DT, Aston KI (2017) Cigarette smoking significantly alters sperm DNA methylation patterns. Andrology 5(6):1089–1099
Fragou D, Pakkidi E, Aschner M, Samanidou V, Kovatsi L (2019) Smoking and DNA methylation: Correlation of methylation with smoking behavior and association with diseases and fetus development following prenatal exposure. Food Chem Toxicol 129:312–327
Song B, Wang C, Chen Y, Li G, Gao Y, Zhu F, Wu H, Lv M, Zhou P, Wei Z, He X, Cao Y (2021) Sperm DNA integrity status is associated with DNA methylation signatures of imprinted genes and non-imprinted genes. J Assist Reprod Genet 38(8):2041–8
World Health Organization (2010) WHO laboratory manual for the examination and processing of human semen, 5th edn. WHO, Geneva
Sun Z, Zhang W, Xue X, Zhang Y, Niu R, Li X, Li B, Wang X, Wang J (2016) Fluoride decreased the sperm ATP of mice through inhabiting mitochondrial respiration. Chemosphere 144:1012–1017
Zeyad A, Hamad MF, Hammadeh ME (2018) The effects of bacterial infection on human sperm nuclear protamine P1/P2 ratio and DNA integrity. Andrologia 50(2):e12841
Shamsi MB, Kumar R, Dada R (2008) Evaluation of nuclear DNA damage in human spermatozoa in men opting for assisted reproduction. Indian J Med Res 127(2):115–123
Wu Y, Kang X, Zheng H, Liu H, Liu J (2015) Effect of paternal age on reproductive outcomes of in vitro fertilization. PLoS One 10(9):e0135734
Bibikova M, Barnes B, Tsan C, Ho V, Klotzle B, Le JM, Delano D, Zhang L, Schroth GP, Gunderson KL, Fan JB (2011) High density DNA methylation array with single CpG site resolution. Genomics 98(4):288–295
Assenov Y, Müller F, Lutsik P, Walter J, Lengauer T, Bock C (2014) Comprehensive analysis of DNA methylation data with RnBeads. Nat Methods 11(11):1138–1140
Gries J, Schumacher D, Arand J, Lutsik P, Markelova MR, Fichtner I, Walter J, Sers C, Tierling S (2013) Bi-PROF: bisulfite profiling of target regions using 454 GS FLX Titanium technology. Epigenetics 8(7):765–771
Lutsik P, Feuerbach L, Arand J, Lengauer T, Walter J, Bock C (2011) BiQ Analyzer HT: locus-specific analysis of DNA methylation by high-throughput bisulfite sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res 39(suppl_2):W551–W556
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Sharma R, Harlev A, Agarwal A, Esteves SC (2016) Cigarette smoking and semen quality: a new meta-analysis examining the effect of the 2010 World Health Organization laboratory methods for the examination of human semen. Eur Urol 70(4):635–645
Balawender K, Orkisz S (2020) The impact of selected modifiable lifestyle factors on male fertility in the modern world. Cent European J Urol 73(4):563–568
Tang Q, Pan F, Wu X, Nichols CE, Wang X, Xia Y, London SJ, Wu W (2019) Semen quality and cigarette smoking in a cohort of healthy fertile men. Environ Epidemiol (Philadelphia, Pa.) 3(4):e055
Bao J, Bedford MT (2016) Epigenetic regulation of the histone-to-protamine transition during spermiogenesis. Reproduction (Cambridge, England) 151(5):R55–R70
Capra E, Lazzari B, Turri F, Cremonesi P, Portela AM, Ajmone-Marsan P, Stella A, Pizzi F (2019) Epigenetic analysis of high and low motile sperm populations reveals methylation variation in satellite regions within the pericentromeric position and in genes functionally related to sperm DNA organization and maintenance in Bos taurus. BMC Genomics 20(1):1–2
Sujit KM, Singh V, Trivedi S, Singh K, Gupta G, Rajender S (2020) Increased DNA methylation in the spermatogenesis-associated (SPATA) genes correlates with infertility. Andrology 8(3):602–609
vel Szic KS, Declerck K, Vidaković M, Berghe WV (2015) From inflammaging to healthy aging by dietary lifestyle choices: is epigenetics the key to personalized nutrition? Clin Epigenet 7(1):1–8
Prince C, Hammerton G, Taylor AE, Anderson EL, Timpson NJ, Davey Smith G, Munafò MR, Relton CL, Richmond RC (2019) Investigating the impact of cigarette smoking behaviours on DNA methylation patterns in adolescence. Hum Mol Genet 28(1):155–165
Åsenius F, Danson AF, Marzi SJ (2020) DNA methylation in human sperm: a systematic review. Hum Reprod Update 26(6):841–873
Alkhaled Y, Laqqan M, Tierling S, Lo Porto C, Amor H, Hammadeh ME (2018) Impact of cigarette-smoking on sperm DNA methylation and its effect on sperm parameters. Andrologia 50(4):e12950
Raben N, Nagaraju K, Lee E, Plotz P (2000) Modulation of disease severity in mice with targeted disruption of the acid α-glucosidase gene. Neuromuscul Disord 10(4-5):283–291
Jäger R, Russwurm C, Schwede F, Genieser HG, Koesling D, Russwurm M (2012) Activation of PDE10 and PDE11 phosphodiesterases. J Biol Chem 287(2):1210–1219
Loughney K, Taylor J, Florio VA (2005) 3′, 5′-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 11A: localization in human tissues. Int J Impot Res 17(4):320–325
Makhlouf A, Kshirsagar A, Niederberger C (2006) Phosphodiesterase 11: a brief review of structure, expression and function. Int J Impot Res 18(6):501–509
Baxendale RW, Fraser LR (2005) Mammalian sperm phosphodiesterases and their involvement in receptor-mediated cell signaling important for capacitation. Mol Reprod Dev 71(4):495–508
Skrahina T, Piljić A, Schultz C (2008) Heterogeneity and timing of translocation and membrane-mediated assembly of different annexins. Exp Cell Res 314(5):1039–1047
De Lamirande E, Gagnon C (2002) The extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway is involved in human sperm function and modulated by the superoxide anion. Mol Hum Reprod 8(2):124–135
Ambatipudi S, Cuenin C, Hernandez-Vargas H, Ghantous A, Le Calvez-Kelm F, Kaaks R, Barrdahl M, Boeing H, Aleksandrova K, Trichopoulou A, Lagiou P (2016) Tobacco smoking-associated genome-wide DNA methylation changes in the EPIC study. Epigenomics 8(5):599–618
Kobayashi N, Miyauchi N, Tatsuta N, Kitamura A, Okae H, Hiura H, Sato A, Utsunomiya T, Yaegashi N, Nakai K, Arima T (2017) Factors associated with aberrant imprint methylation and oligozoospermia. Sci Rep 7(1):1–9
Lee KW, Pausova Z (2013) Cigarette smoking and DNA methylation. Front Genet 4:132
Cui X, Jing X, Wu X, Wang Z, Li Q (2016) Potential effect of smoking on semen quality through DNA damage and the downregulation of Chk1 in sperm. Mol Med Rep 14(1):753–761
Amor H, Zeyad A, Hammadeh ME (2021) Tobacco smoking and its impact on the expression level of sperm nuclear protein genes: H2BFWT, TNP1, TNP2, PRM1 and PRM2. Andrologia 53(3):e13964
Mostafa RM, Nasrallah YS, Hassan MM, Farrag AF, Majzoub A, Agarwal A (2018) The effect of cigarette smoking on human seminal parameters, sperm chromatin structure and condensation. Andrologia 50(3):e12910
Oyeyipo IP, Maartens PJ, Du Plessis SS (2014) In vitro effects of nicotine on human spermatozoa. Andrologia 46(8):887–892
Aghamohammadi A, Zafari M (2011) The impact of cigarette smoking on sperm parameters: a cross-sectional study. Age 36(7.76):35–23
Cinar O, Dilbaz S, Terzioglu F, Karahalil B, Yücel C, Turk R, Taskin L, Kose SK (2014) Does cigarette smoking really have detrimental effects on outcomes of IVF? Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 174:106–110
Hamad M, Shelko N, Montenarh M, Hammadeh ME (2019) The impact of cigarette smoking on protamines 1 and 2 transcripts in human spermatozoa. Hum Fertil 22(2):104–110
Yu B, Ding Q, Zheng T, Jiang L, Li Q, Sun X, Bai C, Huang Z (2015) Smoking attenuated the association between IκBα rs696 polymorphism and defective spermatogenesis in humans. Andrologia 47(9):987–994
Dai JB, Wang ZX, Qiao ZD (2015a) The hazardous effects of tobacco smoking on male fertility. Asian J Androl 17(6):954–960
Montjean D, Ravel C, Benkhalifa M, Cohen-Bacrie P, Berthaut I, Bashamboo A, McElreavey K (2013) Methylation changes in mature sperm deoxyribonucleic acid from oligozoospermic men: assessment of genetic variants and assisted reproductive technology outcome. Fertil Steril 100(5):1241–1247
Barcelona V, Huang Y, Brown K, Liu J, Zhao W, Yu M, Kardia SL, Smith JA, Taylor JY, Sun YV (2019) Novel DNA methylation sites associated with cigarette smoking among African Americans. Epigenetics 14(4):383–391
Kiziler AR, Aydemir B, Onaran I, Alici B, Ozkara H, Gulyasar T, Akyolcu MC (2007) High levels of cadmium and lead in seminal fluid and blood of smoking men are associated with high oxidative stress and damage in infertile subjects. Biol Trace Elem Res 120(1):82–91
Benchaib M, Braun V, Ressnikof D, Lornage J, Durand P, Niveleau A, Guerin JF (2005) Influence of global sperm DNA methylation on IVF results. Hum Reprod 20(3):768–773
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to all the doctors and clinical staff in the Al Bassma Fertility Center in the Palestinian Territories.
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M. M. L collected and processed the samples. Additionally, sample analysis including DNA/RNA extraction, bisulfite treatment, PCR, PCR purification, and qPCR and data analysis were done by M. M. L, and he was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. M. M. Y performed a review for data analysis, discussion preparation, and the writing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Health Research Council, Palestinian Territories (Reference No. PHRC/HC/13/14), and consent was provided according to the Declaration of Helsinki Committee. Besides, all participants signed an informed approval form to participate in this study. The samples were analyzed according to the guidelines and standard procedures of the Al Basma Fertility Center.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
There is no potential conflict of interest relevant to this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Laqqan, M.M., Yassin, M.M. Influence of tobacco cigarette heavy smoking on DNA methylation patterns and transcription levels of MAPK8IP3, GAA, ANXA2, PRRC2A, and PDE11A genes in human spermatozoa. Middle East Fertil Soc J 26, 41 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43043-021-00084-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43043-021-00084-1