Abstract
Fungi of the complex Paracoccidioides spp. are thermodimorphic organisms that cause Paracoccidioidomycosis, one of the most prevalent mycoses in Latin America. These fungi present metabolic mechanisms that contribute to the fungal survival in host tissues. Paracoccidioides lutzii activates glycolysis and fermentation while inactivates aerobic metabolism in iron deprivation, a condition found during infection. In lungs Paracoccidioides brasiliensis face a glucose poor environment and relies on the beta-oxidation to support energy requirement. During mycelium to yeast transition P. lutzii cells up-regulate transcripts related to lipid metabolism and cell wall remodeling in order to cope with the host body temperature. Paracoccidioides spp. cells also induce transcripts/enzymes of the methylcitrate cycle (MCC), a pathway responsible for propionyl-CoA metabolism. Propionyl-CoA is a toxic compound formed during the degradation of odd-chain fatty acids, branched chain amino acids and cholesterol. Therefore, fungi require a functional MCC for full virulence and the ability to metabolize propionyl-CoA is related to the virulence traits in Paracoccidioides spp. On this way we sought to characterize the propionate metabolism in Paracoccidioides spp. The data collected showed that P. lutzii grows in propionate and activates the MCC by accumulating transcripts and proteins of methylcitrate synthase (MCS), methylcitrate dehydratase (MCD) and methylisocitrate lyase (MCL). Biochemical characterization of MCS showed that the enzyme is regulated by phosphorylation, an event not yet described. Proteomic analyses further indicate that P. lutzii yeast cells degrades lipids and amino acids to support the carbon requirement for propionate metabolism. The induction of a putative propionate kinase suggests that fungal cells use propionyl-phosphate as an intermediate in the production of toxic propionyl-CoA. Concluding, the metabolism of propionate in P. lutzii is under regulation at transcriptional and phosphorylation levels and that survival on this carbon source requires additional mechanisms other than activation of MCC.
Similar content being viewed by others
INTRODUCTION
Paracoccidioidomycosis (PCM) is a systemic and granulomatous mycosis, caused by thermodimorphic fungi of the Paracoccidioides genus, a complex of organisms geographically restricted to Latin America with high prevalence in Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela and Argentina (Brummer et al. 1993). PCM presents the highest mortality rate among the systemic mycoses in Brazil, causing 148–171 deaths per year (Prado et al. 2009) and affecting mainly farm workers who are exposed to fungal propagules during soil manipulation (Franco et al. 2000). Once in human tissues, where the temperature is above 36 °C, the hyphal fragments or conidia differentiate into the pathogenic yeast form that establishes the infection (San-Blas et al. 2002). During the infectious process Paracoccidioides spp. face a hostile environment where they are exposed to several host-imposed stresses including high temperatures, oxidative and nitrosative stresses, nutrient deprivation and low pH. Therefore, it is required that these fungi sense and adapt to those conditions to survive in host tissues (Gonzalez and Hernandez 2015; Polke et al. 2015).
Throughout the course of infection and colonization of several host sites, pathogenic fungi are confronted with one common challenge, which is nutrient acquisition and utilization. Nutrient limitation is a common strategy employed by the host to hamper fungal survival. Furthermore, each host niche encountered by a microorganism may provide a different type of carbon source (Brock 2009; Pereira et al. 2009). Therefore, the ability to acquire nutrients from the host and a metabolic flexibility are central pieces of fungal virulence arsenal. Molecular and biochemical methods have been applied to understand the metabolic status of Paracoccidioides spp. yeast cells in conditions mimicking infection. Differential gene expression studies have shown that P. lutzii yeast cells employ fermentative metabolism while mycelial cells use aerobic routes for energy production (Felipe et al. 2005), which was subsequently confirmed by proteomic studies (Rezende et al. 2011). In contrast, P. brasiliensis (PB18) utilizes a more aerobic metabolism in yeast cells compared to hyphae (Araujo et al. 2019). Further, during mycelium-to-yeast transition metabolic pathways change to support membrane and cell wall remodeling (Bastos et al. 2007). Transcriptomic analysis in a murine in vivo model revealed that during liver infection glycolysis combined with alcoholic fermentation (Bailao et al. 2006; Costa et al. 2007) are activated to counteract the low oxygen tension (Lima Pde et al. 2015) and iron starvation (Parente et al. 2011). The expression profile of yeast cells incubated with human blood or plasma revealed lipid utilization under both conditions, whereas gluconeogenesis was up-regulated only in blood (Bailao et al. 2006; Bailao et al. 2007). In a lung infection model proteomics and transcriptomics data revealed that P. brasiliensis also utilizes the beta-oxidation pathway for energy production (Lacerda Pigosso et al. 2017). Taken together, these observations strongly suggest that Paracoccidioides spp. present a niche- and species-dependent metabolic adaptation during host infection.
Investigations on other fungal pathogens revealed similar adaptation mechanisms with striking species-dependent differences on the importance of individual pathways for virulence. Exposure of Candida albicans to neutrophils or macrophages up-regulates amino acid biosynthetic genes and displays a shift from fermentative to non-fermentative metabolism (Fradin et al. 2005; Lorenz et al. 2004). Studies with GFP-fusion reporter strains confirmed that growth in tissues stimulated glycolysis, whereas the glyoxylate cycle and gluconeogenesis dominate when phagocytized by host cells (Barelle et al. 2006). This is in agreement with attenuated virulence of glyoxylate cycle mutants of C. albicans with a defect in the key enzyme isocitrate lyase (icl) and unable to utilize fatty acids as nutrient source (Lorenz and Fink 2001). However, other pathogenic fungi are not strictly dependent on ICL for successfully host infection. Aspergillus fumigatus strains deleted for ICL revealed no attenuation in virulence (Schobel et al. 2007). Furthermore, although ICL is strongly induced in Cryptococcus neoformans upon macrophage contact, the icl deleted mutant displayed virulence like wild type strain (Rude et al. 2002). On the other hand, glycolysis impairment resulted in attenuated virulence in a murine cryptococcosis inhalation model by showing decreased persistence in central nervous system, while displaying adequate persistence in lungs (Price et al. 2011). Thus, pathogenic fungi take use of different metabolic strategies to survive in host niches with specific nutrient compositions.
In general, it is likely that microbial pathogens get exposed to odd-chain or branched-chain fatty acids, branched-chain amino acids or cholesterol during the course of infection. Degradation of these compounds yields propionyl-CoA and its accumulation can be toxic for the cell. Propionyl-CoA toxicity relies mainly on its ability to competitively inhibit Coenzyme A dependent enzymatic reactions such as pyruvate dehydrogenase, ATP:citrate lyase or succinyl-CoA synthetase (Brock and Buckel 2004). To avoid this toxic propionyl-CoA accumulation, organisms developed metabolic pathways to transform propionyl-CoA into non-toxic and energy-containing metabolites. Several bacteria and higher eukaryotes use the methylmalonyl-CoA pathway to convert propionyl-CoA into succinyl-CoA. Propionyl-CoA is carboxylated to yield (S)-methylmalonyl-CoA, which is isomerized to (R)-enantiomer by methylmalonyl-CoA epimerase. This reaction is followed by a carbon chain rearrangement into succinyl-CoA catalyzed by the vitamin B12 dependent methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (Botella et al. 2009; Kaziro and Ochoa 1964; Maruyama and Kitamura 1985; Savvi et al. 2008). Fungi don’t seem to contain a functional methylmalonyl-CoA mutase and a modified version of the beta-oxidation pathway was described in C. albicans for metabolism of propionyl-CoA with 3-hydroxypropionate as key intermediate (Otzen et al. 2014). However, the main propionate metabolizing route in fungi is the methylcitrate cycle (MCC) that is also found in several bacterial species. This pathway is characterized by an α-oxidation of propionyl-CoA into pyruvate. Propionyl-CoA is condensed with oxaloacetate via the key enzyme methylcitrate synthase yielding methylcitrate. Methylcitrate is isomerized into methylisocitrate by employing a dehydration via methylcitrate dehydratase and rehydration by aconitase. Finally, a methylisocitrate lyase cleaves methylisocitrate in pyruvate and succinate. The latter is converted back into oxaloacetate by tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) enzymes, whereas pyruvate can be used either as energy source or as building block in anabolic pathways (Brock et al. 2002).
The ability to promote propionyl-CoA turnover has been associated with virulence in pathogenic microbes. The disruption of the gene encoding for hydroxypropionate dehydrogenase in C. albicans strongly attenuates virulence in a murine model of systemic candidiasis (Otzen et al. 2014). In the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis, a functional methylcitrate cycle is essential for survival in macrophages (Munoz-Elias et al. 2006). Similarly, the impairment of MCC in A. fumigatus by disruption of the MCS encoding gene reduced survival of conidia in lungs and attenuated virulence in an invasive aspergillosis model (Ibrahim-Granet et al. 2008). These observations confirm that pathogenic microorganisms utilize host nutrients that lead to the production of propionyl-CoA. Therefore, specific pathways are required not only to avoid toxic effects mediated by propionyl-CoA, but also to use it as a carbon source.
Efforts have been made to characterize the metabolic mechanisms used by members of the Paracoccidioides complex and preliminary transcriptomic and proteomic studies on propionyl-CoA metabolism indicate an involvement of the MCC in virulence. Cells undergoing mycelium-to-yeast transition induce MCC genes at transcriptional and translational levels (Bastos et al. 2007; Rezende et al. 2011). The contact of yeast cells with human blood and plasma that mimics dissemination also increases transcripts encoding MCC enzymes (Bailao et al. 2006; Bailao et al. 2007). Additionally, the induction of MCC transcripts in P. lutzii cells recovered from mouse tissues suggests a role of this pathway in fungal survival in the host milieu (Bailao et al. 2006). Accordingly, the macrophage environment also requires an active propionyl-CoA turnover in fungal cells (Parente-Rocha et al. 2015). Proteomics and transcriptomic analysis showed that carbon starvation also triggers an accumulation of MCC enzymes in P. brasiliensis. (Lima et al. 2014). Altogether, these observations strongly suggest that the methylcitrate cycle composes a metabolic requirement for Paracoccidiodes spp. survival during infection and, consequently, might be a virulence determinant in this human pathogen. In this study, we characterized the molecular aspects of propionate metabolism in Paracoccidioides spp.
METHODS
Fungal maintenance and growth conditions
Paracoccidioides lutzii strain 01 (ATCC-MYA-826) and P. brasiliensis isolate 18 (ATCC 32069) were maintained on the solid culture medium Fava-Netto (Fava Netto 1955) at 36 °C for the yeast form and at 23 °C for the mycelium form during 5 and 15 days, respectively. Log phase cells were obtained by the cultivation in liquid Fava-Netto medium under agitation for 72 h at 36 °C for yeast, and 5 days at 22 °C for mycelium. Cells were then washed twice with phosphate buffered saline (PBS: 0.14 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 1.8 mM KH2HPO4, 10 mM Na2HPO4, pH 7.3) and subjected to further analyses. For assays using different carbon sources the MMcM medium was used (Restrepo and Jimenez 1980). Solid medium was prepared by the addition of 1% agarose. MMcM was supplemented with glucose and/or sodium propionate to a final concentration between 5 mM and 50 mM. The cell viability was assessed by using trypan blue in a hemocytometer chamber. For spot dilution growth analyses, Fava-Netto pre-grown yeasts were adjusted to 1 × 108 cells/mL and serially diluted (1:10 dilutions). From each dilution a total of 10 μL was spotted in MMcM medium with the specified carbon source and grown at 36 °C for 7 days. For enzymatic assays, equal wet weight of yeast and mycelium cells were inoculated in MMcM liquid medium to perform an accurate normalization of MCS activity.
Data mining and bioinformatics analysis of methylcitrate cycle enzymes
A. fumigatus and Aspergillus nidulans methylcitrate synthase, methylcitrate dehydratase and methylisocitrate lyase amino acid sequences (Maerker et al. 2005; Muller et al. 2011) were used to search for orthologous proteins encoded in Paracoccidioides spp. genomes (www.broadinstitute.org). For the propionyl-CoA syntethase we used an Aspergillus nidulans sequence (Zhang et al. 2004), and for methylmalonyl-CoA pathway the respective enzyme sequences from Caenorhabditis elegans and M. tuberculosis were used. The sequences were obtained from GenBank and the search was performed using BLASTP algorithm (Altschul et al. 1997). The subcellular localization and mitochondrial import signal sequences were obtained by using the database WoLF PSORT (http://www.genscript.com/psort/wolf_psort.html) and the online tool MitoProt (https://ihg.gsf.de/ihg/mitoprot.html), respectively. The intron/exon identification and synteny analysis was performed using the information available at Paracoccidioides spp. genome database (https://fungidb.org/fungidb/).
RNA extraction and quantitative real time PCR (qRT-PCR)
The Paracoccidioides sp. yeast and mycelium cells were grown in the presence of glucose and/or propionate at 10 mM for 24 and 48 h. RNA was extracted as described elsewhere (Tristao et al. 2014). Briefly, cells were lysed using mechanical cell rupture (Mini-Beadbeater; Biospec Products Inc., Bartlesville, OK) and total RNA was extracted using TRI Reagent (Sigma- Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions and used as template for in vitro reverse transcription using the High Capacity RNA-to-cDNA kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). The cDNAs were used for quantification of transcript levels by qRT-PCR using SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (Applied Biosystems) in a StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems). The transcript levels of the analyzed genes were normalized against the expression levels of alpha tubulin gene (accession number: XM_002796593). Data were expressed as a mean of three independent biological replicates. Relative expression levels were calculated using the standard curve method for relative quantification (Bookout et al. 2006). Standard curves were generated by pooling the cDNAs from all conditions used, which were further serially diluted. Student’s t-test was applied in the statistical analyses. Primers used in qRT-PCR are shown in Table S1.
Production and purification of recombinant MCS
The sequence of the mature PbMCS without mitochondrial import peptide was used for production of the recombinant enzyme in Escherichia coli. The coding sequence was amplified from cDNA of P. lutzii isolate Pb01 and cloned into a modified pET43 plasmid in frame with a His-Tag sequence (Hortschansky et al. 2007). The plasmid was transferred into E. coli BL21 (DE3) Rosetta 2 cells (Novagen/Merck), which were used for overproduction of the recombinant enzyme. Protein production was induced by cultivation in Overnight Express Instant TB medium at 30 °C. Cells were collected by centrifugation and resuspended in buffer A (50 mM Tris/HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, pH 8.0), and disrupted by sonication. Lysates were clarified by centrifugation and loaded onto a nickel-Sepharose 6 Fast Flow gravity-flow column (GE Healthcare). After six washes with buffer A containing 30 mM imidazole the protein was eluted in buffer A containing 200 mM imidazole. The recombinant protein purity was assessed by SDS-PAGE. Fractions with purified enzyme were combined and desalted using centrifugal filter devices (Merck). Then, glycerol was added to purified MCS and samples were stored at − 20 °C. Protein concentrations were determined by using the Bradford protein assay kit from Bio-Rad and bovine serum albumin was employed as standard.
Protein extraction and enzymatic activity
Obtention of cell extracts
Yeast and mycelium cells from cultures in glucose and/or propionate at 10 mM were subjected to protein extraction as described elsewhere (Rezende et al. 2011) with some modifications. Cells were harvested by centrifugation and subjected to disruption in a Mini-Beadbeater with glass beads and extraction buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0; 150 mM NaCl). The lysate was clarified by centrifugation and protein samples were quantified as described above. Protein extract dephosphorylation was performed as described elsewhere (Cruz et al. 2011).
MCS activity
The methylcitrate synthase activity and biochemical parameters of recombinant MCS were determined as described previously (Brock et al. 2000). Briefly, the reaction mixtures (1 ml) contained 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 1 mM DTNB, 1 mM oxaloacetate, 0.2 mM propionyl-CoA and the assays were started by adding the protein extracts (3 μg). The reaction was followed spectrophotometrically by measuring the change in A412 at 25 °C. One unit of enzyme activity was defined as the amount of enzyme producing 1 μmol min− 1 of CoASH under the assay conditions.
Formamidase activity
Formamidase (FMD) activity was measured by ammonia generation, as described (Borges et al. 2005). Samples of 50 μL with 5 μg of protein extract were added to 200 μl of formamide substrate solution at a final concentration of 100 mM in 100 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, and 10 mM EDTA. The incubation was proceeded at 37 °C for 30 min. Subsequently, 400 μl of phenol-nitroprusside and 400 μl of alkaline hypochlorite were added to the reaction tube, and the reaction was incubated for 6 min at 50 °C. Absorbance was then read at 625 nm. The amount of ammonia released was determined from a standard curve. One unit (U) of FMD activity was defined as the amount of enzyme required to hydrolyze 1 μmol of formamide (corresponding to the formation of 1 μmol of ammonia) per minute per milligram of protein.
Production of anti-rPbMCS polyclonal antibodies and western blot assays
All animal work was conducted in agreement with the National Council of Animal Work (Conselho Nacional de Controle de Experimentação Animal-CONCEA). The recombinant PbMCS was used to generate specific polyclonal serum in mice. A total of 150 μg rPbMCS were inoculated per mice in three injections (50 μg each) with 15 days intervals. The mice were euthanized 15 days after the last injection in a CO2 chamber and the blood was collected. The serum with polyclonal antibodies was obtained by centrifugation of blood samples.
Western blot analyses were performed as described before (Parente et al. 2011). Briefly, protein extracts from propionate and glucose grown yeast cells were electrophoresed in SDS-PAGE gels or subjected to 2D gel electrophoresis (de Arruda Grossklaus et al. 2013). Then, the proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose membranes and blocked with 5% dry fat milk in PBS. The membranes were reacted with anti-rPbMCS polyclonal antibodies (1:500 dilution) and then hybridized with anti-mouse IGG coupled with alkaline phosphatase (1:2000 dilution). The reaction was developed with chromogenic substrates 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolylphosphate (BCIP) and nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT).
Label free quantitative UPLC-MSE proteomics
Proteomic analysis was performed with protein extracts from three biological replicates of cells grown in 10 mM propionate and 10 mM glucose. Protein sample aliquots (150 μg) in 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate pH 8.5 were subjected to trypsin digestion as previously described (Bailao et al. 2014). The digested samples were spiked with an internal standard (rabbit phosphorylase B, Waters Corp, Milford, MA) to reach the final concentration of 150 fmol μL− 1 of the glycogen phosphorylase. The digested peptides were analysed in triplicate by NanoUPLC-MSE (Waters Corporation, Manchester, UK) using a NanoACQUITY system coupled to a Synapt mass spectrometer. Raw data obtained were processed and searched against database using ProteinLynx Global Server (PLGS) version 2.4 (Waters Corp) with ExpressionE algorithm (Geromanos et al. 2009; Lima et al. 2014; Prado et al. 2015). PLGS was loaded with a specific Paracoccidioides sp. database (http://www.broadinstitute.org). The database was randomized to assess the false-positive rate of identification (4%). One missed cleavage site was allowed. Carbamidomethyl was specified as fixed modification and phosphorylation of STY and oxidation of methionine were set as variable modifications. Protein quantitation was based on the observed intensity measurements compared to the intensity measurements of the internal standard. A protein detected in all replicates presenting a variance coefficient less than 10% in all injections was used to normalize protein levels to accurately compare protein abundances between control and treated samples.
RESULTS
Paracoccidioides spp. utilizes propionate as a carbon source
Paracoccidioides spp. transcripts/enzymes related to propionate metabolism had been identified in infection-mimicking conditions (Bailao et al. 2006; Bailao et al. 2007; Lima et al. 2014; Parente et al. 2011; Pereira et al. 2009; Rezende et al. 2011). Therefore, fungal ability to grow and survive in the presence of propionate was analyzed. Initially, we monitored the growth in the presence of glucose, glucose/propionate and propionate in concentrations ranging from 5 mM to 50 mM (Fig. 1a). Paracoccidioides spp. growth in glucose/propionate was slightly affected at concentrations increasing to 15 mM of propionate and was strongly inhibited at 50 mM when compared to glucose. Propionate by itself supported fungal growth to a limited extent, since slow growth was observed at concentrations of 5 and 10 mM. Similar results were found using P. brasiliensis strain Pb18 (Figure S1). Additionally, since no difference in yeast cells growth were observed at 5 and 10 mM of propionate, we performed viability analysis at the concentrations 10 mM, 20 mM and 50 mM. Likewise, no difference in viability was detected among cells grown in glucose, glucose/propionate and propionate up to 24 h, although a slightly decrease occurred at 48 h in propionate (Fig. 1b). These results clearly demonstrate that glucose is the preferred carbon source when compared to propionate. Also, a high concentration of propionate is toxic for P. lutzii regardless the presence of glucose, as observed with other fungi (Brock et al. 2000; Maerker et al. 2005).
Growth and survival analysis of P. lutzii on propionate. a Serial dilutions of cell suspensions (from 106 to 103 cells) were spotted on MMcM containing propionate, glucose plus propionate and glucose as carbon sources. The plates were incubated at 36 °C for 10 days. b Viability analysis of yeast cells incubated on MMcM medium containing propionate and/or glucose from 10 to 50 mM. Cell viability was assessed by using trypan blue. Error bars represent the standard deviation from the average obtained from independent biological triplicates
Genomic characteristics of propionate metabolism in Paracoccidioides spp.
Microorganisms use variable routes or strategies to metabolize propionate in nature. The most common pathways used are the methylcitrate cycle and methylmalonyl-CoA pathway. Recently, it has been shown that C. albicans propionate degradation relies on a modified version of the beta-oxidation pathway (Otzen et al. 2014). To identify genes involved in propionyl-CoA degradation in the complex Paracoccidioides, we first screened the genomes for genes encoding enzymes of the methylcitrate cycle. For this analysis, the MCS, MCD and MCL of A. nidulans and A. fumigatus (Maerker et al. 2005; Muller et al. 2011) served as templates (Table S2). Our analysis revealed the presence of orthologs of all three- methylcitrate cycle specific enzymes in the three genomes analyzed (P. lutzii-Pb01, P. americana-Pb03 and P. brasiliensis-Pb18, Table 1). Also, the propionyl-CoA synthetase (PCS) from A. nidulans (CBF70755) (Zhang et al. 2004), an enzyme related to propionate activation by its conversion to propionyl-CoA, was used in BLASTP analysis. One homologues protein was identified in Paracoccidioides spp. genomes with identity of 74% and similarity of 84% (XP_002789592; Table 1; Table S2). The propionate degradation enzyme sequences presented high conservation among the Paracoccidioides species with identity ranging from 98 to 99%. Thus, the presence of genes coding to specific enzymes contributing to methylcitrate cycle suggest that the complex of Paracoccidioides spp. utilizes the MCC for degradation of propionate.
In order to identify genes required for a functional methylmalonyl-CoA pathway, we selected the essential enzyme methylmalonyl-CoA mutase for further genomics analysis. The analysis using the amino acid sequences of methylmalonyl-CoA mutases from C. elegans (accession number CAA84676) and M. tuberculosis (Rv1492 and Rv1493) (Savvi et al. 2008) shows no homologue in Paracoccidioides spp. Thus, it is unlikely that these fungi employ the methylmalonyl-CoA pathway in degradation of propionyl-CoA as previously shown for A. nidulans (Ledley et al. 1991).
Genes coding for enzymes related to a specific pathway or biological process are frequently clustered in the genome. Therefore, the synteny of MCC related genes was evaluated (Fig. 2). The three MCC specific genes are clustered in a region of approximately 22 kilobases. The mcl and mcs genes are located next to each other, while the MCD-encoding sequence is 16 kilobases away from MCS. Six (seven for P. brasiliensis) unrelated genes separate mcd from mcs. The catabolic repression phenomenon may play a role in the expression regulation of the MCC genes (Brock et al. 2000). CreA, a repressor acting when preferential carbon sources (such as glucose) are available, mediates this process in A. nidulans (Panozzo et al. 1998). The screening for CreA-binding sites in upstream regions of the genes revealed putative CreA binding sites (Fig. 2). Four binding sites were found in the promoter region shared by MCL and MCS in the three genomes; however, P. americana and P. brasiliensis presented two sites in each strand, while P. lutzii has three sites in positive strand and one in the negative strand. Using a 1000 bp region upstream MCD coding sequence, three CreA consensus sites were found in P. lutzii (two in positive strand and one in negative strand) and a single site was found in both P. americana and P. brasiliensis. These findings suggest that propionyl-CoA metabolism may be under control of a catabolic repressor system. Additionally, protein sequences of the MCC enzymes were analyzed for the presence of targeting signals by using the algorithm MitoProt. The results indicate a putative mitochondrial import signal for MCS, MCD and MCL whereas the putative PCS is predicted to be cytosolic; suggesting propionate metabolism likely occurs, at least in part, in mitochondrion, as reported for Toxoplasma gondii (Limenitakis et al. 2013).
Characterization of methylcitrate synthase
Although Paracoccidioides spp. present genes that likely encode methylcitrate synthase enzymes, the enzyme characteristics remained unknown for dimorphic fungi. Thus, MCS was produced as recombinant protein (rPbMCS) for further analysis. To ease purification, the recombinant enzyme was fused to an N-terminal His-tag, whereby the predicted mitochondrial import sequence was omitted from the enzyme. After expression in E. coli the protein was purified by nickel-chelate chromatography. The purified fraction yielded a protein 92% pure as judged by SDS-PAGE analysis (Fig. 3a). Investigations of substrate specificity and specific activity revealed that propionyl-CoA serves as substrate with a specific activity of 16.52 U × mg− 1. Additionally, rPbMCS showed significant activity as citrate synthase (using acetyl-CoA as substrate) with a specific activity of 37.97 U × mg− 1. In the presence of oxaloacetate the Km for propionyl-CoA was determined as 6.4 μM while 9.5 μM for acetyl-CoA (Fig. 3b). It is important to highlight that the biochemical parameters are very similar to native methylcitrate synthase from A. fumigatus (Maerker et al. 2005) and A. nidulans (Brock et al. 2000), strongly suggesting this enzyme acts as a MCS in P. lutzii.
Production, purification and biochemical parameters of recombinant MCS. a -SDS-PAGE of different purification stages of MCS; Lane M – molecular weight marker, lane 1 whole bacterial cell lysate, lane 2 – flow-through from the Ni-resin, lane 3 – wash fraction through the resin, lanes 4–7 fractions eluted with 200 mM imidazole, lane 8 – concentrated pool of the MCS elution fraction (5 μg). b – Biochemical parameters of recombinant MCS
Methylcitrate cycle enables Paracoccidioides spp. to metabolize propionate
To determine the regulation of MCC cycle in P. lutzii, MCS, MCD, MCL and PCL transcript accumulation as well as MCS activity were measured in the presence of glucose and/or propionate. The qPCR analysis was performed in mycelium and yeast phases for MCS, MCD, MCL and PCS encoding genes. In general, data showed that propionate up-regulates all the genes even in presence of glucose for both forms (Fig. 4). However, the induction is significantly higher when propionate is the sole carbon source. MCS was the most regulated gene, in both mycelium and yeast, presenting induction rates of up to 5-fold, which corroborates with the fact that this enzyme catalyzes the first irreversible step of the MCC initiating propionyl-CoA detoxification (Domin et al. 2009). Predominantly, the up-regulation of MCC related genes, upon propionate addition, in mycelium was less intense when compared to yeast cells.
Expression analysis of the genes related to propionate metabolism on different carbon sources. Expression levels of the mcs, mcd, mcl and pcl genes from mycelium (b) and yeast (a) cells of P. lutzii grown in propionate (P) and glucose plus propionate (GP). The gene expression levels of propionate and glucose plus propionate were normalized to glucose condition (control carbon source). Error bars represent the standard deviation from the average obtained from triplicates; * p < 0.05
Western blot analysis using specific rPbMCS antibodies revealed an accumulation of the respective protein in yeast cells grown in propionate (Fig. 5). In order to confirm the presence of a functional MCS in vivo, enzyme activity was measured in cells grown in propionate or glucose. In both mycelium and yeast cells, MCS activity was induced in the presence of propionate (Table 2). The induction rate in yeast cells was higher than for mycelium corroborating the transcriptional data. Also, MCS activity in mycelium grown in glucose was higher than yeast cells in propionate. Intriguingly, P. lutzii maintained an elevated methylcitrate synthase activity even when glucose is the sole carbon source. Two-dimensional western blot data revealed a different pattern in isoform distribution with low mass variation, suggesting the presence of different phosphorylation patterns in the two samples (glucose and propionate, Fig. 5). In order to evaluate whether MCS is under a phosphorylation control mechanism, enzyme activity was measured in protein extracts subjected to phosphatase treatment. The dephosphorylation event promoted a two-fold reduction in MCS activity in both glucose and propionate conditions indicating that MCS is activated upon phosphorylation (Table 2). The MCS activity of dephosphorylated extracts from propionate grown cells were lower than in the non-dephosphorylated extracts obtained from glucose-grown cells.
MCS levels and profiles in fungal cells grown in glucose or propionate. The protein extracts from yeast cells grown on propionate (Prop) and/or glucose (Glu) were subjected to 1-dimensional (a) or 2-dimensional (b) Western Blot analysis by using polyclonal antibodies raised against rPbMCS. Secondary anti-mouse antibodies coupled to alkaline phosphatase were used and the reaction was developed with BCIP and NBT
Metabolic strategies used by Paracoccidioides sp. during growth on propionate
Our results strongly suggest that P. lutzii is able to metabolize propionate and use it as carbon and energy sources. However, global analysis of the mechanisms involved in fungal adaptation to propionate remains unclear. Thus, we conducted a proteomic analysis of yeast cells grown in propionate in comparison to glucose. The quality analysis of the proteomic data showed 85 and 89% of the identified peptides were matched with 15 ppm error for glucose and propionate samples, respectively. Additionally, the peptide match distribution, which refers to the quality of the data at the peptide level, demonstrated that 11% (propionate sample) and 14% (glucose sample) of the peptides were in source and majority of the identified peptides was befitting with fragmentation in the trap CID cell. A total of 61 and 57% of the peptides was matched in the database without any modification in samples from glucose and propionate grown cells, respectively. Those numbers indicate the reliability of the proteomic data.
Comparison of the proteomic profiles obtained from propionate versus glucose utilizing yeasts identified 331 proteins with different amounts, of which 176 were induced in the presence of propionate (Tables S3 and S4). Functional categorization indicates that proteins related to general metabolism and energy production were the most influenced ones (Tables S3 and S4). The growth in propionate induced the degradation of fatty acid, with up-regulation of three β-oxidation enzymes. The accumulation of several enzymes related to amino acid degradation and protein degradation denotes that amino acids are required to support propionate metabolism. The final products of these processes might be fueling TCA and MCC to increase the propionyl-CoA turnover. The induction of enzymes aminotransferases, carbamoyl-phosphate synthase and glutamate dehydrogenase, related to nitrogen metabolism, would support adequate nitrogen metabolization. Thus, amino acid degradation would be providing TCA intermediates to support adaptation to this specific carbon source (Eoh and Rhee 2014). These observations are in agreement with previous work that observed a higher maintenance requirement necessary for growth in propionate (Brock and Buckel 2004). In propionate, the gluconeogenic enzyme FBPase-1 was up regulated while the glycolytic enzymes hexokinase and pyruvate kinase were down regulated. The induction of fatty acid oxidation, glyoxylate cycle (isocitrate lyase) and gluconeogenesis suggests fatty acids are being converted to glucose for structural purposes. Also, the joint induction of fatty acid and amino acid degradation pathways suggests the glucose-mediated catabolic repression mechanism is released since propionate is not a preferential carbon source. In a similar scenario (carbon starvation) P. lutzii induces the expression of the antigenic protein formamidase (FMD) (Borges et al. 2005; Lima et al. 2014). Growth in propionate also increases FMD levels in P. lutzii suggesting that this enzyme is required when glucose is absent. In order to confirm this theory, formamidase activity was measured. The enzyme activity in cells grown in propionate was 15 U × mg− 1, while in glucose cells the FMD activity was only 7.8 U × mg− 1. Intriguingly, riboflavin synthesis seems to be necessary for metabolic adaptation, since lumazine synthase (11.8 fold) and riboflavin synthase (1.4 fold) levels were increased. This couples with the induction of the riboflavin dependent enzymes succinate dehydrogenase and acyl-CoA dehydrogenase. An overview of the metabolic adaptation is summarized in Fig. 6.
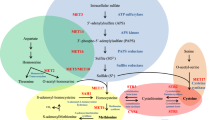
Metabolic changes of P. lutzii cells grown in propionate as deduced from proteomics. HXK hexokinase; PGI glucose-6P isomerase; ALD aldolase; TPI triose phosphate isomerase; PGAM phosphoglycerate mutase; PKM pyruvate kinase; ENO enolase; ADH alcohol dehydrogenase; PDH pyruvate dehydrogenase; HGD homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase; HDP 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase; MAIA maleyl acetoacetate isomerase; SCOT succinyl coenzyme A-acetoacetyl coenzyme A-transferase; ECH enoyl-CoA hydratase; ACAT acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase; ACO aconitase, IDH isocitrate dehydrogenase; KGD 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase; SDH succinate dehydrogenase; MDH malate dehydrogenase; FUM fumarate hydratase; ADSS adenylosuccinate synthetase; ADSL adenylosuccinate lyase; CTH cystathionine gamma lyase; MSY cobalamin independent methionine synthase; ARG arginase; CLY ATP-citrate lyase; FASa fatty acid synthase α; FASb fatty acid synthase β. The numbers indicate ratios of the induction (red) or repression (blue) of the proteins. * Enzymes detected only in glucose (blue) or propionate (red)
Our proteomic data also indicate specific mechanisms used by this fungus in propionate consumption (Fig. 7). The methylcitrate cycle specific enzymes MCS and MCD presented an increase of 1.7 and 1.5 fold in response to propionate. Although MCL was not identified as an induced protein using the 1.2 fold cutoff, this protein presented a 1.18 fold increase. The enzymes shared by TCA and MCC such as succinate dehydrogenase, fumarate hydratase and malate dehydrogenase also accumulate in response to propionate, indicating a global induction of MCC activity. Propionyl-CoA strongly inhibits the succinyl-CoA synthetase, which would lock the subsequent reactions of the citric acid cycle and hampers the utilization of pyruvate from both glucose and propionate (Brock and Buckel 2004). However, Paracoccidioides spp. yeast cells can grow in the presence of propionate as carbon source and in combination with glucose. Hence, these fungi hold an alternative reaction that converts succinyl-CoA into succinate. Corroborating with this fact the enzyme succinyl-CoA:acyl-CoA transferase, which can transfer the CoA-moiety from succinyl-CoA to a carboxylic acid (probably propionate) yielding succinate for the TCA cycle, was induced 1.7 fold (Fleck and Brock 2008).
Metabolic processes specifically related to propionyl-CoA turnover. MCS methylcitrate synthase, MCD methylcitrate dehydratase, MCL methylisocitrate lyase, PCS propionyl-CoA-synthase, FUM fumarase, MDH malate dehydrogenase, SDH succinate dehydrogenase, PDH pyruvate dehydrogenase, succinyl-CoA ligase, OXCT succinyl-CoA-3-ketoacid transferase
Intriguingly, an acetate kinase (AK) was detected only when the fungus was grown in propionate. This enzyme is described as a component of the acetate activation into acetyl-CoA in a phosphotransacetylase (PTA) dependent fashion. This route is activated in acetate growing bacteria but is not found in fungi since these organisms have no predicted PTA encoding genes (Ingram-Smith et al. 2006). Fungal AK integrates a pathway with d-xylulose 5-phosphate phosphoketolase (XFP), which produces acetate in xylose grown cells (Fig. 8a). Additionally, conversion of propionate into propionyl-CoA in Neisseria meningitides relies on enzymes such as propionate kinase (PK) and PTA in an acetate analogous route (Catenazzi et al. 2014). The AK found in our proteomic analysis is homologous to the N. meningitides PK, suggesting that the enzyme might act in propionate and propionyl-phosphate interconversion to degrade propionate. PK transcript levels were measured to investigate its putative role in propionate metabolism. The data showed that Paracoccidioides sp. presents PK encoding transcripts that accumulate in yeast cells exposed to propionate (Fig. 8b).
Roles of propionate and acetate kinases in acetate or propionate activation. a - AK acetate kinase, PK propionate kinase, PTA phosphotransacetylase, XFP d-xylulose-5-phosphate phosphoketolase, PCS propionyl-CoA syntethase. * Putative propionate kinase found only in propionate condition. b - Transcript levels of acetate kinase in yeast cells grown in glucose (G) or propionate (P)
DISCUSSION
The ability to metabolize propionate is an important characteristic of the metabolic flexibility of a microorganism, since it enables the use of propionyl-CoA generating carbon sources in both environmental and host milieus. In the saprobiotic lifestyle, the propionyl-CoA metabolizing organisms may use propionate present in the soil (the second most abundant carbon source in the soil), thus presenting a metabolic advantage over organisms that are unable to metabolize propionate. During infection, microorganisms experience a nutrient poor environment imposed by host defenses and propionyl-CoA turnover capacity enable them to use branched-chain amino acids, odd chain fatty acids and cholesterol as nutrient sources. This broadens the host tissues/niches that the pathogen may colonize and contributes to virulence. Analysis of propionate metabolism in Paracoccidioides spp. has shown that MCC enzymes are induced by propionate and, in the case of MCS, the enzyme is regulated by phosphorylation. Several MCS isoforms were detected by two-dimensional immunoblotting and dephosphorylation of protein extracts decreased the enzyme activity by half when compared to untreated controls. Proteomic data suggest that the fungus activates lipid and amino acid degradation to support propionate utilization. Additionally, the proteome approach suggests that a putative propionate kinase may participate in propionate activation and utilization.
The search for genes related to propionate metabolism revealed that Paracoccidioides spp. harbor genes coding for methylcitrate cycle enzymes. This characteristic is shared by other pathogenic fungi such as A. fumigatus (Maerker et al. 2005), Fusarium solani and Fusarium verticillioides (Domin et al. 2009) reinforcing the notion that MCC was kept as preferred pathway for use of propionyl-CoA generating sources in fungi. Carbon utilization in filamentous fungi is controlled by a catabolic repressor system. In A. nidulans, the carbon catabolite repressor CreA inhibits alternative carbon source metabolic routes when glucose is available. Acting at transcriptional level, CreA represses target genes by binding to consensus sequences (5′-(G/C)YGGRG-3′) at their promoters (Panozzo et al. 1998). A CreA homologue was found in Paracoccidioides spp. genomes and the promoter sequences of the three MCC specific genes presented the CreA binding motifs suggesting the MCC is under the carbon catabolite repression.
Although Paracoccidioides spp. carry genes putatively encoding for MCC enzymes, to date no experimental evidence has confirmed their functionality. Real time PCR data indicates that MCS, MCD and MCL genes were induced by propionate. Additionally, the MCS protein accumulates in yeast and mycelium cells incubated with propionate and this fact is accompanied by an increase in MCS enzymatic activity. The presence of glucose inhibits MCS activity by a rate of 1.6, which differs from A. fumigatus, F. solani and F. verticillioides that showed inhibition rates between 28 and 7 times (Domin et al. 2009; Ibrahim-Granet et al. 2008). This difference may be explained by the higher MCS activity in glucose grown Paracoccidioides cells (0.51 U × mg− 1 in yeast and 2.42 U × mg− 1 in mycelium) when compared to propionate. Additionally, high MCS activity detected in mycelial cells may reflect an adaptive differential metabolic characteristic of this morphology since, in nature, propionate is the second most abundant carbon source in soil (Buckel 1999). Differences in the metabolic status between Paracoccidioides yeast and mycelium phases have been described. Transcriptomic and proteomic approaches suggested that mycelium oxidizes glucose by an aerobic route while yeasts present a more fermentative glucose metabolism in P. lutzii (Bastos et al. 2007; Felipe et al. 2005; Rezende et al. 2011). However, proteomic data show the reverse for P. brasiliensis (Araujo et al. 2019). Also, enzymes of the methylcitrate and glyoxylate cycles were induced during mycelium to yeast transition (Rezende et al. 2011). Thus, Paracoccidioides genus presents a phase specific metabolic characteristic that is not restricted to propionate.
Western blotting analysis demonstrated that mycelium and yeast cells present a different distribution of MCS isoforms. The isoforms have similar molecular masses but different isoelectric point suggesting that MCS is under a phosphorylation-based regulation. To the best of our knowledge this is first description of MCS being regulated by phosphorylation. In P. lutzii only one similar event is described for isocitrate lyase (ICL). During growth in acetate, fungal cells promote ICL activation by phosphorylation as a fast mechanism for fungal adaptation (Cruz et al. 2011). Our data suggest that phosphorylation also activates MCS since the activity decreased by at least two fold in dephosphorylated protein extracts. This fact, together with transcript and protein accumulations in propionate treated cells, indicates that MCS is regulated at transcriptional level as well as by post-translational modification. The last regulatory mechanism denotes a new strategy for the rapid adaptation to changing environmental conditions, such carbon sources.
The proteomics approach brings to light the metabolic strategies used by this pathogen to survive in propionate as carbon source. The adaptation to propionate is beyond the activation of propionyl-CoA-detoxifying pathways. Towards energy production P. lutzii activates the aerobic metabolism by the accumulation of proteins related to the respiratory chain and decreases the level of the fermentative enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase. Additionally, the fungus operates oxidation of fatty acids and amino acid degradation for ATP production and building blocks for synthesis of essential metabolites. Coping with that, the glyoxylate cycle isocitrate lyase is activated to promote the oxaloacetate anaplerosis into gluconeogenesis, since FBPase1 is also induced. Similar behavior was observed in Paracoccidioides sp. yeast cells recovered from mouse lungs, a carbon source poor environment (Lacerda Pigosso et al. 2017), indicating that this response is triggered when preferential sources are not available. This reflects that P. lutzii can rewire its metabolism in host niches where alternative carbon sources are available, as shown for other fungal pathogens. Glyoxylate cycle, glycolysis and gluconeogenesis are all required for C. albicans virulence in a disseminated mouse infection model (Barelle et al. 2006; Lorenz and Fink 2001). In a paralleled way, C. neoformans requires glycolytic (Price et al. 2011) and gluconeogenic (Panepinto et al. 2005) pathways for full virulence. The paradoxical activation of competing pathways may reflect heterogeneous nature of fungal population in complex host microenvironments with different carbon sources (Ene et al. 2014). This metabolic flexibility found in pathogenic fungi is a key aspect of fungal virulence.
Growth in propionate demands activation of specific vitamin biosynthetic routes. Lumazine synthase and riboflavin synthase induction suggests dependence of P. lutzii on riboflavin requiring processes (Guenther et al. 1999). Accordingly, fatty acid oxidation and spermidine synthesis related enzymes were also up-regulated by propionate. Fatty acid oxidation relies on FAD dependent enzymes, a derivative compound of riboflavin. Spermidine is derived from SAM (S-adenosylmethionine), a compound also synthetized by FAD-dependent enzymes. This fact is reinforced by the induction of the SAM synthesis proteins methionine synthase, adenosylhomocysteinase and S-adenosylmethionine synthase (Fontecave et al. 2004; Guenther et al. 1999). The increase in spermidine synthesis suggests that this stress related molecule (Valdes-Santiago and Ruiz-Herrera 2013) may be pertinent to survival in the carbon source propionate that produces the toxic intermediate propionyl-CoA. The ability to perform de novo synthesis of vitamins has been reported as essential in host-resembling environments. A. fumigatus iron homeostasis and virulence depends on functional riboflavin and pantothenic acid biosynthesis. Riboflavin and pantothenate de novo syntheses are also required for H. capsulatum survival in macrophage and for virulence in a murine model of respiratory histoplasmosis (Garfoot et al. 2014). The induction of riboflavin enzymes by Paracoccidioides sp. in propionate and the reported link between riboflavin and fungal virulence reinforces the idea that fungi may be exposed to propionyl-CoA generating compounds in host tissues.
Global analysis of proteins levels of yeast cells grown in propionate revealed the strategies used by P. lutzii to metabolize and counteract the toxic effects of propionate. As expected, MCS and MCD protein levels accumulated, as well as enzymes of the TCA cycle (succinate dehydrogenase, fumarate hydratase and malate dehydrogenase), which are shared with MCC. The propionyl-CoA metabolism is dependent on a functional TCA cycle; however, succinyl-CoA synthetase is inhibited by propionyl-CoA. Probably the fungus circumvents this blockage by the induction of a succinyl-CoA:acyl-CoA transferase (PAAG_05093) to fuel succinyl-CoA into the TCA cycle (Brock and Buckel 2004; Fleck and Brock 2008). Among the proteins related to propionyl-CoA detoxification, an acetate/propionate kinase was found. In Neisseria menigitidis an analogous enzyme participates in the propionyl-CoA/propionyl-phosphate interconversion (Catenazzi et al. 2014) putatively in order to keep the amount of propionyl-CoA at low levels. Thus, we hypothesized that P. lutzii may use propionate kinase activity to regulate the levels of propionyl-CoA. The induction of a lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) was surprising since glycolytic enzymes were repressed in propionate. However, lactate dehydrogenase is the final step in the conversion of propionyl-CoA into pyruvate by the acryloyl-CoA pathway. In such process, propionyl-CoA is oxidized in acrylyl-CoA, which in turn is hydrated in lactoyl-CoA. Finally, lactoyl-CoA is cleaved into lactate, which is converted into pyruvate by LDH (Fernandez-Briera and Garrido-Pertierra 1988). Putative enzymes predicted to act as acyl-CoA dehydrogenases and acyl-CoA hydratase were found as induced in our work (PAAG_06329, PAAG_06309, PAAG_04811). However, further efforts need to be done in order to confirm this hypothesis.
CONCLUSIONS
Our study brought new insights into biochemical and molecular aspects of propionate metabolism in Paracoccidioides spp., which may be expanded to other dimorphic fungus. Biochemical data showed, for the first time, that MCS activity is under a phosphorylation regulatory mechanism. Additionally, the global view of fungal metabolism indicates that propionate metabolism requires activation of alternative carbon sources using pathways to support carbon requirement in MCC and TCA. The results also suggest that propionyl-CoA levels may be balanced by a putative propionate kinase in order to buffer the toxicity of this metabolite.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- AK:
-
Acetate kinase
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CoA:
-
Coenzyme A
- FAD:
-
Flavin adenine dinucleotide
- FMD:
-
Formamidase
- ICL:
-
Isocitrate lyase
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- MCC:
-
Methylcitrate cycle
- MCD:
-
Methylcitrate dehydratase
- MCL:
-
Methylisocitrate lyase
- MCS:
-
Methylcitrate synthase
- MMcM:
-
McVeigh and Morton medium
- PCM:
-
Paracoccidioidomycosis
- PCS:
-
Propionyl-CoA synthetase
- PK:
-
Propionate kinase
- PTA:
-
Phosphotransacetylase
- rPbMCS:
-
recombinant Paracoccidioides spp. MCS
- SAM:
-
S-adenosylmethionine
- TCA:
-
Tricarboxylic acid cycle
- XFP:
-
D-xylulose 5-phosphate phosphoketolase
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W et al (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Research 25(17):3389–3402
Araujo DS, Pereira M, Portis IG, Dos Santos Junior ACM, Fontes W, de Sousa MV et al (2019) Metabolic peculiarities of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis dimorphism as demonstrated by iTRAQ labeling proteomics. Frontiers in Microbiology 10:555
Bailao AM, Schrank A, Borges CL, Dutra V, Molinari-Madlum EEWI, Felipe MSS et al (2006) Differential gene expression by Paracoccidioides brasiliensis in host interaction conditions: representational difference analysis identifies candidate genes associated with fungal pathogenesis. Microbes and Infection 8(12–13):2686–2697
Bailao AM, Shrank A, Borges CL, Parente JA, Dutra V, Felipe MS et al (2007) The transcriptional profile of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis yeast cells is influenced by human plasma. FEMS Immunology and Medical Microbiology 51(1):43–57
Bailao EF, Parente JA, Pigosso LL, Castro KP, Fonseca FL, Silva-Bailao MG et al (2014) Hemoglobin Uptake by Paracoccidioides spp. Is Receptor-Mediated. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases 8(5):e2856
Barelle CJ, Priest CL, Maccallum DM, Gow NA, Odds FC, Brown AJ (2006) Niche-specific regulation of central metabolic pathways in a fungal pathogen. Cellular Microbiology 8(6):961–971
Bastos KP, Bailao AM, Borges CL, Faria FP, Felipe MS, Silva MG et al (2007) The transcriptome analysis of early morphogenesis in Paracoccidioides brasiliensis mycelium reveals novel and induced genes potentially associated to the dimorphic process. BMC Microbiology 7:29
Bookout AL, Cummins CL, Mangelsdorf DJ, Pesola JM, Kramer MF (2006) High-throughput real-time quantitative reverse transcription PCR. In: Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE et al (eds) Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. Wiley, Hoboken, pp 1581–1628
Borges CL, Pereira M, Felipe MS, de Faria FP, Gomez FJ, Deepe GS Jr et al (2005) The antigenic and catalytically active formamidase of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis: protein characterization, cDNA and gene cloning, heterologous expression and functional analysis of the recombinant protein. Microbes and Infection 7(1):66–77
Botella L, Lindley ND, Eggeling L (2009) Formation and metabolism of methylmalonyl coenzyme a in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Journal of Bacteriology 191(8):2899–2901
Brock M (2009) Fungal metabolism in host niches. Current Opinion in Microbiology 12(4):371–376
Brock M, Buckel W (2004) On the mechanism of action of the antifungal agent propionate. European Journal of Biochemistry 271(15):3227–3241
Brock M, Fischer R, Linder D, Buckel W (2002) Methylcitrate synthase from Aspergillus nidulans: implications for propionate as an antifungal agent. Molecular Microbiology 35(5):961–973
Brummer E, Castaneda E, Restrepo A (1993) Paracoccidioidomycosis: an update. Clinical Microbiology Reviews 6(2):89–117
Buckel W (1999) Anaerobic energy metabolism. In: Lengeler JW, Drews GD, Schelegel HG (eds) Biology of the Procaryotes. Thieme, Stuttgart, pp 278–326
Catenazzi MC, Jones H, Wallace I, Clifton J, Chong JP, Jackson MA et al (2014) A large genomic island allows Neisseria meningitidis to utilize propionic acid, with implications for colonization of the human nasopharynx. Molecular Microbiology 93(2):346–355
Costa M, Borges CL, Bailao AM, Meirelles GV, Mendonca YA, Dantas SF et al (2007) Transcriptome profiling of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis yeast-phase cells recovered from infected mice brings new insights into fungal response upon host interaction. Microbiology 153(Pt 12):4194–4207
Cruz AH, Brock M, Zambuzzi-Carvalho PF, Santos-Silva LK, Troian RF, Goes AM et al (2011) Phosphorylation is the major mechanism regulating isocitrate lyase activity in Paracoccidioides brasiliensis yeast cells. The FEBS Journal 278(13):2318–2332
de Arruda Grossklaus D, Bailao AM, Vieira Rezende TC, Borges CL, de Oliveira MA, Parente JA et al (2013) Response to oxidative stress in Paracoccidioides yeast cells as determined by proteomic analysis. Microbes and Infection 15(5):347–364
Domin N, Wilson D, Brock M (2009) Methylcitrate cycle activation during adaptation of Fusarium solani and Fusarium verticillioides to propionyl-CoA-generating carbon sources. Microbiology 155(Pt 12):3903–3912
Ene IV, Brunke S, Brown AJ, Hube B (2014) Metabolism in fungal pathogenesis. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine 4(12):a019695
Eoh H, Rhee KY (2014) Methylcitrate cycle defines the bactericidal essentiality of isocitrate lyase for survival of Mycobacterium tuberculosis on fatty acids. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 111(13):4976–4981
Fava Netto C (1955) Estudos quantitativos sobre a fixação do complemento na blastomicose sul-americana, com antígeno polissacarídico. Arquivos de Cirurgia Clinica e Experimental 18(197):242
Felipe MS, Andrade RV, Arraes FB, Nicola AM, Maranhao AQ, Torres FA et al (2005) Transcriptional profiles of the human pathogenic fungus Paracoccidioides brasiliensis in mycelium and yeast cells. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 280(26):24706–24714
Fernandez-Briera A, Garrido-Pertierra A (1988) A degradation pathway of propionate in Salmonella typhimurium LT-2. Biochimie 70(6):757–768
Fleck CB, Brock M (2008) Characterization of an acyl-CoA: carboxylate CoA-transferase from Aspergillus nidulans involved in propionyl-CoA detoxification. Molecular Microbiology 68(3):642–656
Fontecave M, Atta M, Mulliez E (2004) S-adenosylmethionine: nothing goes to waste. Trends in Biochemical Sciences 29(5):243–249
Fradin C, De Groot P, MacCallum D, Schaller M, Klis F, Odds FC et al (2005) Granulocytes govern the transcriptional response, morphology and proliferation of Candida albicans in human blood. Molecular Microbiology 56(2):397–415
Franco M, Bagagli E, Scapolio S, da Silva Lacaz C (2000) A critical analysis of isolation of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis from soil. Medical Mycology 38(3):185–191
Garfoot AL, Zemska O, Rappleye CA (2014) Histoplasma capsulatum depends on de novo vitamin biosynthesis for intraphagosomal proliferation. Infection and Immunity 82(1):393–404
Geromanos SJ, Vissers JP, Silva JC, Dorschel CA, Li GZ, Gorenstein MV et al (2009) The detection, correlation, and comparison of peptide precursor and product ions from data independent LC-MS with data dependant LC-MS/MS. Proteomics 9(6):1683–1695
Gonzalez A, Hernandez O (2015) New insights into a complex fungal pathogen: the case of Paracoccidioides spp. Yeast. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.3147
Guenther BD, Sheppard CA, Tran P, Rozen R, Matthews RG, Ludwig ML (1999) The structure and properties of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase from Escherichia coli suggest how folate ameliorates human hyperhomocysteinemia. Nature Structural Biology 6(4):359–365
Hortschansky P, Eisendle M, Al-Abdallah Q, Schmidt AD, Bergmann S, Thon M et al (2007) Interaction of HapX with the CCAAT-binding complex--a novel mechanism of gene regulation by iron. The EMBO Journal 26(13):3157–3168
Ibrahim-Granet O, Dubourdeau M, Latge JP, Ave P, Huerre M, Brakhage AA et al (2008) Methylcitrate synthase from Aspergillus fumigatus is essential for manifestation of invasive aspergillosis. Cellular Microbiology 10(1):134–148
Ingram-Smith C, Martin SR, Smith KS (2006) Acetate kinase: not just a bacterial enzyme. Trends in Microbiology 14(6):249–253
Kaziro Y, Ochoa S (1964) The metabolism of propionic acid. Advances in Enzymology and Related Areas of Molecular Biology 26:283–378
Lacerda Pigosso L, Baeza LC, Vieira Tomazett M, Batista Rodrigues Faleiro M, Brianezi Dignani de Moura VM, Melo Bailao A et al (2017) Paracoccidioides brasiliensis presents metabolic reprogramming and secretes a serine proteinase during murine infection. Virulence:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/21505594.2017.1355660
Ledley FD, Crane AM, Klish KT, May GS (1991) Is there methylmalonyl CoA mutase in Aspergillus nidulans? Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 177(3):1076–1081
Lima PS, Casaletti L, Bailao AM, de Vasconcelos AT, Fernandes Gda R, Soares CM (2014) Transcriptional and proteomic responses to carbon starvation in Paracoccidioides. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases 8(5):e2855
Lima Pde S, Chung D, Bailao AM, Cramer RA, Soares CM (2015) Characterization of the Paracoccidioides hypoxia response reveals new insights into pathogenesis mechanisms of this important human pathogenic fungus. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases 9(12):e0004282
Limenitakis J, Oppenheim RD, Creek DJ, Foth BJ, Barrett MP, Soldati-Favre D (2013) The 2-methylcitrate cycle is implicated in the detoxification of propionate in Toxoplasma gondii. Molecular Microbiology 87(4):894–908
Lorenz MC, Bender JA, Fink GR (2004) Transcriptional response of Candida albicans upon internalization by macrophages. Eukaryotic Cell 3(5):1076–1087
Lorenz MC, Fink GR (2001) The glyoxylate cycle is required for fungal virulence. Nature 412(6842):83–86
Maerker C, Rohde M, Brakhage AA, Brock M (2005) Methylcitrate synthase from Aspergillus fumigatus. Propionyl-CoA affects polyketide synthesis, growth and morphology of conidia. The FEBS Journal 272(14):3615–3630
Maruyama K, Kitamura H (1985) Mechanisms of growth inhibition by propionate and restoration of the growth by sodium bicarbonate or acetate in Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides S. Journal of Biochemistry 98(3):819–824
Muller S, Fleck CB, Wilson D, Hummert C, Hube B, Brock M (2011) Gene acquisition, duplication and metabolic specification: the evolution of fungal methylisocitrate lyases. Environmental Microbiology 13(6):1534–1548
Munoz-Elias EJ, Upton AM, Cherian J, McKinney JD (2006) Role of the methylcitrate cycle in Mycobacterium tuberculosis metabolism, intracellular growth, and virulence. Molecular Microbiology 60(5):1109–1122
Otzen C, Bardl B, Jacobsen ID, Nett M, Brock M (2014) Candida albicans utilizes a modified beta-oxidation pathway for the degradation of toxic propionyl-CoA. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 289(12):8151–8169
Panepinto J, Liu L, Ramos J, Zhu X, Valyi-Nagy T, Eksi S et al (2005) The DEAD-box RNA helicase Vad1 regulates multiple virulence-associated genes in Cryptococcus neoformans. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 115(3):632–641
Panozzo C, Cornillot E, Felenbok B (1998) The CreA repressor is the sole DNA-binding protein responsible for carbon catabolite repression of the alcA gene in Aspergillus nidulans via its binding to a couple of specific sites. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 273(11):6367–6372
Parente AF, Bailao AM, Borges CL, Parente JA, Magalhaes AD, Ricart CA et al (2011) Proteomic analysis reveals that iron availability alters the metabolic status of the pathogenic fungus Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. PLoS One 6(7):e22810
Parente-Rocha JA, Parente AF, Baeza LC, Bonfim SM, Hernandez O, McEwen JG et al (2015) Macrophage interaction with Paracoccidioides brasiliensis yeast cells modulates fungal metabolism and generates a response to oxidative stress. PLoS One 10(9):e0137619
Pereira M, Bailao AM, Parente JA, Borges CL, Salem-Izacc SM, Soares CMA (2009) Preferential transcription of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis genes: host niche and time-dependent expression. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz 104(3):486–491
Polke M, Hube B, Jacobsen ID (2015) Candida survival strategies. Advances in Applied Microbiology 91:139–235
Prado M, da Silva MB, Laurenti R, Travassos LR, Taborda CP (2009) Mortality due to systemic mycoses as a primary cause of death or in association with AIDS in Brazil: a review from 1996 to 2006. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz 104(3):513–521
Prado RS, Bailao AM, Silva LC, de Oliveira CM, Marques MF, Silva LP et al (2015) Proteomic profile response of Paracoccidioides lutzii to the antifungal argentilactone. Frontiers in Microbiology 6:616
Price MS, Betancourt-Quiroz M, Price JL, Toffaletti DL, Vora H, Hu G et al (2011) Cryptococcus neoformans requires a functional glycolytic pathway for disease but not persistence in the host. MBio 2(3):e00103–e00111
Restrepo A, Jimenez BE (1980) Growth of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis yeast phase in a chemically defined culture medium. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 12(2):279–281
Rezende TC, Borges CL, Magalhaes AD, de Sousa MV, Ricart CA, Bailao AM et al (2011) A quantitative view of the morphological phases of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis using proteomics. Journal of Proteomics 75(2):572–587
Rude TH, Toffaletti DL, Cox GM, Perfect JR (2002) Relationship of the glyoxylate pathway to the pathogenesis of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infection and Immunity 70(10):5684–5694
San-Blas G, Nino-Vega G, Iturriaga T (2002) Paracoccidioides brasiliensis and paracoccidioidomycosis: molecular approaches to morphogenesis, diagnosis, epidemiology, taxonomy and genetics. Medical Mycology 40(3):225–242
Savvi S, Warner DF, Kana BD, McKinney JD, Mizrahi V, Dawes SS (2008) Functional characterization of a vitamin B12-dependent methylmalonyl pathway in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: implications for propionate metabolism during growth on fatty acids. Journal of Bacteriology 190(11):3886–3895
Schobel F, Ibrahim-Granet O, Ave P, Latge JP, Brakhage AA, Brock M (2007) Aspergillus fumigatus does not require fatty acid metabolism via isocitrate lyase for development of invasive aspergillosis. Infection and Immunity 75(3):1237–1244
Tristao GB, Assuncao Ldo P, Dos Santos LP, Borges CL, Silva-Bailao MG, Soares CM et al (2014) Predicting copper-, iron-, and zinc-binding proteins in pathogenic species of the Paracoccidioides genus. Frontiers in Microbiology 5:761
Valdes-Santiago L, Ruiz-Herrera J (2013) Stress and polyamine metabolism in fungi. Frontiers in Chemistry 1:42
Zhang YQ, Brock M, Keller NP (2004) Connection of propionyl-CoA metabolism to polyketide biosynthesis in Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics 168(2):785–794
Acknowledgements
We thank the CAPES and CNPq for providing fellowships to LPAS, LPA, GBT and PSL. We are grateful to Juliano Domiraci Paccez for valuable suggestions during manuscript writing.
Adherence to national and international regulations
Not applicable
Funding
This study was supported in part by funds from grants CNPQ 422016/2016–0, FAPEG INCT-IPH 201410267001777, FAPEG NEWTON FUND 201510267000251, FAPEG PRONEX, and by CNPq/CAPES predoctoral fellowships to LPAS, LPA and GBT, as well as, pos-doctoral fellowship to PSL. Part of the work was also funded with personal resources of the research coordinators AMB and MGSB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LPAS, LPA, MB, GBT and PSL performed the experiments. MGSB, CLB performed data analysis. AMB and MGSB designed the research. AMB, CMAS and CLB contributed with reagents and/or funds for research. AMB, MB, CLB and MGSB contributed to data interpretation and manuscript writing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All the animal work was performed in accordance to the Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals as indicated by AAALAC. The protocol for animal use was approved by the National Council of Animal Work (Conselho Nacional de Controle de Experimentação Animal-CONCEA).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Primers used in qRT-PCR experiments.
Additional file 2: Table S2.
Genbank accession numbers of the sequences used in this study.
Additional file 3: Table S3.
Up-regulated proteins in propionate grown yeast cells.
Additional file 4: Table S4.
Dow-regulated proteins in propionate grown yeast cells.
Additional file 5: Figure S1.
Growth analysis of P. brasiliensis on propionate. Serial dilutions of cell suspensions (from 106 to 103 cells) were spotted on MMcM containing propionate (Prop), glucose plus propionate (Gluc/Prop) or glucose (Gluc) as carbon sources. The plates were incubated at 36°C for 10 days.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Santos, L.P.A., Assunção, L.d., Lima, P.d. et al. Propionate metabolism in a human pathogenic fungus: proteomic and biochemical analyses. IMA Fungus 11, 9 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43008-020-00029-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43008-020-00029-9