Abstract
This paper investigates the provenance of Middle Jurassic to Early Cretaceous sediments in the Kutch Basin, western India, on the basis of mineralogical investigations of sandstones composition (Quartz–Feldspar–Lithic (QFL) fragment), Zircon–Tourmaline–Rutile (ZTR) index, and mineral chemistry of heavy detrital minerals of the framework. The study also examines the compositional variation of the sandstone in relation to the evolution of the Kutch Basin, which originated as a rift basin during the Late Triassic and evolved into a passive margin basin by the end Cretaceous. This study analyzes sandstone samples of Jhumara, Jhuran and Bhuj Formations of Middle Jurassic, Upper Jurassic and Lower Cretaceous, respectively, in the Kutch Mainland. Sandstones record a compositional evolution from arkosic to subarkosic as the feldspar content decreases from 68% in the Jhumara Formation to 27% in the Bhuj Formation with intermediate values in the Jhuran Formation. The QFL modal composition indicates basement uplifted and transitional continental settings at source. Heavy mineral content of these sandstones reveals the occurrence of zircon, tourmaline, rutile, garnet, apatite, monazite and opaque minerals. Sub-rounded to well-rounded zircon grains indicate a polycyclic origin. ZTR indices for samples in Jhumara, Jhuran and Bhuj Formations are 25%, 30% and 50% respectively. Chemistry of opaque minerals reveals the occurrence of detrital varieties such as ilmenite, rutile, hematite/magnetite and pyrite, in a decreasing order of abundances. Chemistry of ilmenites in the Jhumara Formation reveals its derivation from dual felsic igneous and metabasic source, while those in Jhuran and Bhuj Formations indicate a metabasic derivation. Chemistry of garnet reveals predominantly Fe-rich (almandine) variety of metabasic origin. X-ray microscopic study provides the percentage of heavy minerals ranging from 3% to 5.26%. QFL detrital modes reflect the evolution of the basin from an active rift to a passive margin basin during the Mesozoic. Integration of results from QFL modal composition of the sandstones, heavy mineral analysis and mineral chemistry, suggests sediment supply from both northern and eastern highlands during the Middle Jurassic. The uplift along the Kutch Mainland Fault in the Early Cretaceous results in curtailment of sediment input from north.
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
Composition of major and accessory heavy minerals in sandstones provide crucial information regarding the provenance of sedimentary basins (Armstrong-Altrin et al. 2012, 2015, 2017; Arribas et al. 2000; Caracciolo et al. 2012; Critelli and Ingersoll 1994; Critelli and Le Pera 1994; Critelli et al. 2003; Le Pera and Critelli 1997; Paikaray et al. 2008; Saha et al. 2010). Petrographic investigation of sandstone is widely used to infer tectonic setting, source rock composition, transportation and environment of deposition (Dickinson 1970, 1985; Dickinson and Suczek 1979; Dickinson et al. 1983; Ingersoll and Suczek 1979; Le Pera and Arribas 2004; Le Pera et al. 2001; Zuffa 1985, 1987). Sediments derived from cratonic sources (low-lying, granitic or gneissic with recycled platform sediments) are generally quartzose sands with high monocrystalline quartz (Qm)/polycrystalline quartz (Qp) and K-feldspar (K)/plagioclase feldspar (P) ratios, and deposited in continental interiors or passive continental margins (Dickinson 1985). Sandstones derived from fault-bounded continental basement uplifts result in lithic-poor quartzo-feldspathic sands of typically arkosic composition (Dickinson 1985; Dickinson and Suczek 1979).
Heavy mineral constituents in sandstones further refines the understanding of provenance (Andò and Garzanti 2014; Andò et al. 2012; Hounslow and Morton 2004; Hubert 1962; Mange and Maurer 1992; Mange and Morton 2007; Morton and Chenery 2009; Morton and Hallsworth 1999; Zack et al. 2004). While transmitted light optical microscopy reveals the composition of transparent heavy minerals (Mange and Maurer 1992), electron microprobe analyser (Basu and Molinaroli 1989, 1991; Dill 1998; Dill and Klosa 2011; Weibel and Friis 2004) and Raman spectroscopy (e.g., Andò and Garzanti 2014) identify the opaque constituents. Heavy minerals, like garnet, ilmenite, zircon, rutile, tourmaline, and epidote, may exhibit significant variation in chemical composition depending on conditions of formation of their parent rock (Mange and Morton 2007; Meinhold 2010; Morton and Chenery 2009; Morton et al. 2004; Preston et al. 2002). Ilmenites from mafic igneous sources exhibit higher concentrations of TiO2 (~ 50%) than those from felsic igneous sources (~ 48%) (Grigsby 1992). Ilmenites from felsic igneous rocks contain > 2% MnO (Grigsby 1992) whereas ilmenites from metamorphic source rocks contain ~ 52% TiO2 and < 0.5% MgO (Basu and Molinaroli 1989). Garnets with low Mg and variable Ca are derived from amphibolite facies metasedimentary rocks while high Mg and high Ca indicate high-grade mafic and ultramafic gneissic source rocks (Mange and Morton 2007). Although unexplored, the use of X-ray microscopic technique enables rapid visualization and quantification of dense phases (Andrews et al. 2010).
Biswas (1987) considered the Kutch Basin as a rift basin, however, other researchers contested this interpretation (Roy et al. 2007). A few studies documented major and trace element composition of clastic sediments of the Kutch Basin (Ahmad and Bhat 2006; Ahmad et al. 2014). Most of these studies lack information on petrography, and completely ignore heavy minerals. The objective of this study is to understand the source of sediments deposited in the Kutch Basin and to infer the tectonic framework of the basin during deposition of these sediments, based on conventional petrographic analysis and heavy mineral composition. We have also attempted to characterize the 3-D distribution of mineral phases of sandstone on the basis of X-ray microscopy technique.
2 Geological setting
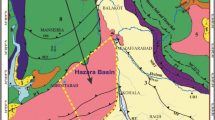
The study area, the Kutch Basin is located in the northwestern part of the western continental margin of India between latitude 22°30′ and 24°30’ N, and longitude 68° and 72°E. This basin was formed by the Late Triassic–Late Jurassic rifting during India’s northward drift post Gondwanaland breakup (Biswas 1982, 1987, 2005). Biswas (1987) considered the Kutch Basin as a pericratonic rift initiated by the reactivation of primordial faults in the Precambrian Aravalli–Delhi fold belt. The basin has accumulated ~ 3000 m of siliciclastic and carbonaceous sediments from Late Triassic to Early Cretaceous (Biswas 1987). The boundaries of the Kutch Basin are demarcated by the Nagar Parkar Fault (NPF) to the north, the North Kathiawar Fault (NKF) to the south, the Radhanpur Arch (Radhanpur–Barmer Arch) to the east and merges with the continental shelf to the west. This basin has prominent uplifted areas exposing Mesozoic rocks: the Nagar Parkar Uplift (NPU), the Island Belt Uplift (IBU) (comprising of the Patcham Uplift (PU), the Khadir Uplift (KU), the Bela Uplift (BU) and the Chorad Uplift (CU)), the Wagad Uplift (WU) and the Kutch Mainland Uplift (KMU), linked to the Nagar Parkar Fault (NPF), the Island Belt Fault (IBF), the South Wagad Fault (SWF) and the Kutch Mainland Fault (KMF), respectively (Fig. 1a).
a Tectonic elements and inferred palaeoslope of the Mesozoic in the Kutch Basin (modified after Biswas 1991). PU = Patcham Uplift; KU = Khadir Uplift; BU = Bela Uplift; CU = Chorad Uplift; WU = Wagad Uplift; KMU = Kutch Mainland Uplift; NPU = Nagar Parkar Uplift; NPF = Nagar Parkar Fault; IBF = Island Belt Fault; SWF = South Wagad Fault; KMF = Kutch Mainland Fault; KHF = Katrol Hill Fault; NKF = North Kathiawar Fault; BHG = Banni Half Graben; GoK-HG = Gulf of Kutch Half Graben. Sample locations (blue dots) are marked in the Kutch Mainland area; b Geological map of Kutch Mainland showing extents of the Mesozoic and Cenozoic outcrops (after Biswas 1981, 1977); c Composite log of the study area (after Biswas 2005; Fürsich et al. 2005; Mandal et al. 2016)
During the early syn-rift stage of Middle Jurassic, the basin had three prominent highs, the Nagar Parkar Uplift, the Island Belt Uplift and the Kathiawar Uplift. During the Kimmeridgian (Late Jurassic), the basin recorded shoreline transgression, resulting in deposition of late syn-rift sediments in most parts of the basin. During the Early Cretaceous, the basin experienced activation along Kutch Mainland Fault (KMF) resulting in the rise of Kutch Mainland Uplift (KMU), dividing the basin into the Gulf of Kutch Half Graben (GoK-HG) and the Banni Half Graben (BHG). The Kutch Mainland covers the largest part of this basin with a south-westerly dipping resultant slope (Biswas 1991, 2005). This region exposes most of the undisturbed Mesozoic rocks along the NW–SE trending chain of domal outcrops (Fig. 1b) (Alberti et al. 2013). The present study area is located within the Kutch Mainland between Zara in the west and Tapkeshwar in the east (Fig. 1a).
Biswas (2005) considered that the Mesozoic succession of the Kutch Mainland comprises poorly-exposed continental sediments of Late Triassic, marine sediments of Middle to Late Jurassic representing syn-rift stage, and fluviomarine sediments of Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous corresponding to late syn-rift to post-rift stage. The roughly 290-m-thick Bathonian–early Callovian Jhurio Formation rests unconformably over the Precambrian basement and mainly comprises of limestone-shale alternations (Fig. 1c; Table 1). This is conformably overlain by nearly 275-m-thick Callovian-Oxfordian (early syn-rift) sediments of the Jhumara Formation. It consists of argillaceous rocks at the base, which is followed upward by a predominantly carbonate succession with subordinate shale (Biswas 2005). This is overlain by ~ 750 m of Kimmeridgian to Tithonian (late syn-rift) sediments of the Jhuran Formation primarily consisting of sandstone-shale alternations, exhibiting an overall coarsening-upward trend (Arora et al. 2015). The Jhuran Formation is unconformably overlain by ~ 815 m thick Valanginian–Albian (post-rift) sediments of the Bhuj Formation comprising sandstone and shale.
Detailed investigation revealed that the Jhurio and Jhumara Formations represent shallow marine deposits in the inner to middle shelf (Fürsich et al. 1992, 2001; Krishna et al. 2000; Singh 1989), whereas the Jhuran Formation comprises storm-laid sandstones intervening with gray to black shale in outer to inner shelf environments (Arora et al. 2015, 2017). Recently Mandal et al. (2016) and Bansal et al. (2017) recorded shallow marine, estuarine and fluvial deposits within the Bhuj Formation.
3 Materials and methods
This study focuses on the entire set of the grain population, including both light and heavy minerals present in the framework sandstones of Jhumara, Jhuran and Bhuj Formations, collected from six locations viz. Zara, Nirona, Palara, Gangeshwar, Bhuj and Tapkeshwar (Fig. 1a). Framework modal analysis was carried out on 6 samples of Jhumara Formation, 19 samples of Jhuran Formation and 6 samples of Bhuj Formation (Fig. 1c). For thin section preparation, sample chips were hardened with a 3:1 mixture of Beuhler® epoxy hardener and epoxy resin inside a vacuum impregnation unit. These chips were then mounted on glass slides and polished using various grades of polishing powders (400 μm, 600 μm, 800 μm, 1200 μm, 3 μm, 1 μm, 0.3 μm and 0.05 μm). Thin sections were studied using a Leica DM 4500P polarizing microscope attached to a Leica DFC420 camera.
Fresh sandstone samples were pulverized for heavy mineral analysis. The 63–125 μm size fraction of the samples was kept in an ultrasonic bath for 10–15 min to remove clay particles and later dried in an oven at 50 °C. Sodium polytungstate liquid (density 2.9 g/ml) was used for heavy mineral separation by gravity settling (Mange and Maurer 1992). The heavy fraction was washed thoroughly using distilled water and isopropyl alcohol and allowed to dry. A small amount of the dried heavy fraction was sprinkled over a slide containing a mixture of three parts of Beuhler® epothin 2 epoxy resin with one part of Beuhler® epothin 2 epoxy hardener. Care was taken to spread the grains uniformly. The slide was kept untouched till dryness and subsequently studied using Leica DM 4500P polarizing microscope attached to a Leica DFC420 camera. Chemical analysis of heavy minerals seen in rock thin sections was carried out using a Cameca SX 5 Electron Probe Micro Analyzer at Department of Earth Sciences, IIT Bombay, India, with an accelerating voltage of 15 kV, specimen current of 20 nA and beam diameter of 1 μm.
Small chips of selected samples were used for heavy mineral investigation using X-ray microscopy. The sandstone samples were broken into fragments of nearly 1 mm × 1 mm × 1 mm. The sample was mounted on a pin-head using super-glue prior to placing the pin inside a sample holder. The analyses were carried out using XRadia Versa 520 by Carl Zeiss®. The sample holder was placed inside the instrument, and the energy of X-rays, source–detector distances, objectives and filters were adjusted using the Scout and Zoom Imaging by Carl Zeiss®. The scans were carried out with 4× and 20× objectives. For a 4× scan, the instrument was setup with 40 kV and 3 W, FOV 3208.6 μm, pixel size 3.1831 μm and exposure time 1 s. For a 20× scan, the instrument was setup with 100 kV and 9 W, FOV 507.27 μm, pixel size 0.5114 μm and exposure time 20 s.
4 Results
4.1 Sandstone framework
Sandstone framework grains are sub-angular to sub-rounded and moderately-sorted in all samples (Fig. 2). Most quartz grains are monocrystalline exhibiting undulose extinction. However, polycrystalline quartz grains with tectonic fabric (classified here as lithic fragments) also occur. K-feldspar dominates over plagioclase feldspar in most sandstones. Both types of feldspar are replaced by cement, especially in samples of the Jhumara and Jhuran Formations. However, replacement of plagioclase feldspar by cement is more extensive (Fig. 2b and c). Aphanitic lithic fragments include polycrystalline quartz with distinct metamorphic fabric (Fig. 2d). Silica overgrowth on quartz is common in many samples, particularly in samples of the Jhuran Formation. Majority of the silica overgrowths are abraded. Two types of cements have been identified using polarizing microscope, namely carbonate and zeolite.
Photomicrographs of sandstones under cross-polarized light. a General arkosic–subarkosic character of Jhuran Formation, with arrows pointing to a few feldspars showing twinning; b Carbonate cement filling pore spaces and replacing framework grains in Jhuran Formation, with arrows pointing to fully-replaced plagioclase feldspars identified by the faint remnants of twinning; c Magnified view of a plagioclase feldspar (arrow) in Jhuran Formation showing replacement by cement; d Polycrystalline quartz (arrow) with tectonic fabric in Bhuj Formation
Sandstones of Jhumara, Jhuran and Bhuj Formations are quartzofeldspathic in composition, with mean compositions of Q54F44L2, Q57F41L2 and Q59F39L2 respectively. The number of grains of quartz, feldspar and rock fragments are recalculated to 100 (Table 2) and plotted in triangular QFR plot (Fig. 3). All samples plot within the field of “arkose” except one sample of Bhuj Formation which plots in the field of “subarkose” (Folk 1974). Samples of the Jhumara Formation exhibit the largest spread of data points. Most of the data of Jhuran Formation overlaps with Bhuj Formation while a few data points of the lower part of Jhuran Formation overlap with data points of Jhumara Formation. Data points of the Bhuj Formation exhibit a shift in composition from arkosic to subarkosic.
Triangular QFL plot showing compositions of sandstones in Jhumara, Jhuran and Bhuj Formations, respectively. Q = Total quartzose grains, including monocrystalline (Qm) and polycrystalline (Qp) varieties; F = Total feldspar grains; RF = Total unstable rock fragments. Field boundaries are taken from Folk’s classification of sandstones (Folk 1974)
Recalculated modal sandstone composition data in Table 2 are plotted in QFL plot with superimposed fields of Dickinson et al. (1983) (Fig. 4). Most samples of all the three formations plot in the field representing transitional continental provenance. A few samples of the Jhumara and Jhuran Formations plot in the field representing basement uplifted provenance.
Triangular QFL plot showing framework composition of sandstones from Jhumara, Jhuran Formation and Bhuj Formations, respectively. Q = Total quartzose grains, including monocrystalline (Qm) and polycrystalline (Qp) varieties; F = Total feldspar grains; L = Total unstable lithic fragments. Field boundaries are after Dickinson et al. 1983
4.2 Heavy minerals
In addition to gross composition of sandstones, a specific geochemical analysis of the heavy mineral assemblages was carried out. Heavy minerals are common in samples of all three formations. Thin section study of sandstones reveals that, the most common transparent heavy mineral species in the sandstones are zircon, rutile, tourmaline, garnet and monazite in order of decreasing abundance, and less commmon heavy minerals include epidote, apatite and chloritoid (Fig. 5). Sandstone thin sections and heavy minerals separated using heavy liquid reveal that almost all zircon grains are prismatic with sub-rounded to well-rounded terminations indicating a polycyclic origin (Figs. 5a and 6c). Tourmaline occurs as both sub-rounded (Fig. 5c) and with prismatic crystal habit (Fig. 6e). Rutile grains show angular shapes (Figs. 5b, 6c and d). Garnet shows variation from angular to rounded shapes (Figs. 5d, 6a and b). A few other grains that were identified are epidote and chloritoid (Fig. 6f). Textures of these detrital species do not show chemical etching or replacement by carbonate cementation. Separated heavy minerals were used for the calculation of Zircon–Tourmaline–Rutile (ZTR) index (e.g., Hubert 1962). The average of the calculated ZTR indices (Hubert 1962) for Jhumara, Jhuran and Bhuj Formations are 25, 30 and 50%, respectively, suggesting a low to moderate mineralogical maturity of the heavy mineral assemblage.
Chemical analysis of opaque heavy minerals reveals abundance of ilmenite in the studied samples. Less common opaque grains include pyrite, hematite and magnetite. Ilmenites in Jhumara Formation contain 57.78% TiO2, 3.56% MnO and 0.22% MgO on average (Table 3). Ilmenites in Jhuran and Bhuj Formations contain 57.72% TiO2, 1.02% MnO, 0.30% MgO, and 64.41% TiO2, 0.38% MnO, 0.28% MgO, respectively. Presence of > 50% TiO2, > 2% MnO, and < 0.5% MgO indicates a mixed felsic igneous and metabasic source for the Jhumara Formation (Basu and Molinaroli 1989; Grigsby 1992). Enriched TiO2 content (> 50%) and depleted MnO content (< 2%) in ilmenite grains of Jhuran and Bhuj Formations indicate metabasic provenance lithotype in the hinterland for these sediments.
Garnet is rarely identified in Jhumara Formation, while it is abundant in samples of Jhuran and Bhuj Formations. The compositional data of garnets in sandstones of all three formations reveal a dominance of almandine (Fe-rich) over other varietal species of the same mineral group (Tables 4, 5 and 6) indicating mafic input. The data for the elements Fe + Mn, Mg and Ca from electron probe microanalysis (EPMA) are normalized to 100 and plotted on a triangular Fe + Mn–Mg–Ca plot of Mange and Morton (2007) (Fig. 7). The analyzed garnets plot in the “Type Ci” field, indicating a source from high grade metabasic rocks (Mange and Morton 2007).
Fe + Mn–Mg–Ca triangular plot for samples of Jhumara, Jhuran and Bhuj Formations (Field boundaries for various garnet types A, Bi, Bii, Ci, Cii and D after Mange and Morton 2007)
4.3 X-ray microscopic investigations
A number of projections were produced from X-Ray microscopy scans which were then processed in Zeiss XM reconstructor and analyzed in ORS Visual software. The total sample volume was segmented into different components viz. volume of pores, volume of cement and volume of detrital grains on the basis of intensity (/density) ranges of each constituent phase. Each of these components were assigned a specific colour for distinction.
Figure 8 shows a three-dimensional view of a sample of Jhuran sandstone. Figure 8a exclusively reveals the densest mineral phases, while Fig. 8d shows each constituents. Heavy minerals appear as dark green in Fig. 8a. Petrographic and EPMA data of this sample indicate three distinguishable grain-size ranges of heavy minerals. The smallest size range of heavy minerals include zircon, tourmaline, apatite and garnet. Rutile occupies the intermediate size range, while ilmenite represents the largest grains. In Fig. 8b, the light green shade indicates carbonate cement. Density contrast is reduced to reveal the lighter framework grains of the sample. Thus quartz and feldspar (with similar density range) appear as pink shades in Fig. 8c. The density contrast is further reduced to indicate lighter phases than framework grains. Zeolite cement, the least dense phase in this sample appears as brown colour in Fig. 8d. The surface of framework grains appear pitted (with green and brown colour) as a result of replacement of grains by cements. The average volume of heavy minerals calculated using data from these scans are 3%, 5.26% and 3.44% for Jhumara, Jhuran and Bhuj Formations, respectively.
Three-dimensional images of a sample of Jhuran sandstone at 20× magnification by X-ray microscopy. The main phases present are segmented on the basis of intensity differences. The distribution of each of these phases are shown. a Heavy minerals (dark green); b Light green shades indicating carbonate cements; c Heavy minerals, carbonate cement and framework grains (pink) with prominent boundaries; d Heavy minerals (black arrow), carbonate cement (yellow arrow), framework grains (blue arrow) and zeolite cement (reddish brown shade, white arrow)
5 Discussion
The Mesozoic Kutch Basin with southwesterly palaeoslope was bounded by two prominent highs, the Nagar Parkar Uplift to the north (formed as one of the horsts of the rift basin) and the Aravalli Highlands to the east (Fig. 1a). Most of the studied siliciclastic sediments were possibly sourced from these two highs. The QFL plot reveals the basement uplifted provenance for the arenite samples of Middle Jurassic Jhumara Formation (Fig. 4). Possibly, most of the sediments are supplied from the Nagar Parkar Uplift comprising rocks of Nagar Parkar igneous complex. Samples of Upper Jurassic Jhuran Formation and Lower Cretaceous Bhuj Formation indicate transitional continental provenance signatures. This is attributed to a mixture of sediment supplies from rocks of the Nagar Parkar Uplift (basement uplifted source) and the Aravalli Highlands (cratonic source). Thus, upliftment along the Kutch Mainland Fault in the Early Cretaceous (Biswas 2005) possibly had a major impact on sediment transportation paths in the Kutch Mainland.
The Nagar Parkar igneous complex comprises the Late Proterozoic granites, rhyolites, acidic and basic dykes (Ahmad and Chaudhry 2008; Laghari et al. 2013). These rocks were uplifted and exposed by the Nagar Parker Fault in the Early Jurassic. The highlands formed by the rocks of the Proterozoic Aravalli and Delhi Supergroups in the east expose various grades of metasedimentary rocks, granite gneisses and metabasic dikes (Ramakrishnan and Vaidyanadhan 2008). In the studied samples, presence of abraded silica overgrowth and well-rounded zircons in samples of all three formations indicate a reworked polycyclic origin of detrital grains. Chemistry of ilmenites in the Middle Jurassic Jhumara Formation indicates its derivation from a mixed sediment source of felsic igneous and metabasic rocks. Ilmenites in the Upper Jurassic Jhuran Formation and Lower Cretaceous Bhuj Formation are sourced from metabasic rocks. Metabasic rocks are absent in the Nagar Parkar igneous complex. Thus, chemistry of ilmenites in the sediments of the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous suggests its derivation from the east. Elemental chemistry of garnets in all three formations further reveals a metabasic source rock provenance. This shift in sediment supply possibly relates to the upliftment along the Kutch Mainland Fault in the Early Cretaceous, blocking sediment supply from north.
High relief and rapid erosion of fault-bounded basement uplifts result in sandstones of typical arkosic composition in the nearby basins (Dickinson 1985; Dickinson and Suczek 1979). Low relief of cratons and prolonged transport of sediments through continental regions of low relief result in quartzose sands (Dickinson and Suczek 1979). QFL detrital modes indicate a shift of sandstone type from arkosic (in Middle Jurassic Jhumara Formation) to subarkosic (in Lower Cretaceous Bhuj Formation). Sandstones further exhibit a change in ZTR index from 25 to 50% through intermediate values, which records increasing tectonic stability. A climatic shift from arid to humid conditions can make a similar mineralogical change from arkosic to sub-arkosic nature of sandstones. The Kutch Basin records a transition from syn-rift to post-rift and therefore the compositional shift of sandstone may be attributed to tectonic stability of a rift basin.
6 Conclusions
The major conclusions of the study on the Mesozoic sandstones of Kutch Basin are as follows.
-
1)
The two main sediment sources of the Kutch Mainland include the predominantly felsic basement rocks of Nagar Parkar igneous complex in the north and the Proterozoic Aravalli and Delhi Supergroups in the east.
-
2)
QFL plot indicates a primarily basement-uplifted provenance for the Middle Jurassic Jhumara Formation and a mixture of basement-uplifted and cratonic-interior provenance for rocks of the Upper Jurassic Jhuran Formation and Lower Cretaceous Bhuj Formation. The change in composition of sandstones from arkose in syn-rift sediments to sub-arkose post-rift sediments supports the increasing tectonic stability of the basin.
-
3)
Ilmenites in the Middle Jurassic derived from both north and east, while those in the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous sediments relate to easterly highlands. Garnet chemistry relates to high-grade metabasic source during the deposition of sediments from Middle Jurassic to Early Cretaceous.
-
4)
The present investigation points to predominant sediment source from eastern highlands during the late syn-rift to post-rift stage. This may possibly be related to upliftment along the Kutch Mainland Fault, which prevented sediment supply from north in the Kutch Mainland.
-
5)
X-ray microscopy reveals 3-D distribution of heavy minerals in rock samples. The high content of heavy minerals in the Jhuran Formation indicates high-degree reworking of sediments.
References
Ahmad, A.H.M., and G.M. Bhat. 2006. Petrofacies, provenance and diagenesis of the Dhosa sandstone member (Chari formation) at Ler, Kachchh sub-basin, western India. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 27 (6): 857–872.
Ahmad, A.H.M., K.N. Noufal, A.M. Masroor, and K. Tavheed. 2014. Petrography and geochemistry of Jumara dome sediments, Kachchh Basin: Implications for provenance, tectonic setting and weathering intensity. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry 33 (1): 9–23.
Ahmad, S.A., and M.N. Chaudhry. 2008. A-type granites from the Nagar Parkar complex, Pakistan: Geochemistry and origin. Geological Bulletin of Punjab University 43: 69–81.
Alberti, M., F.T. Fürsich, and D.K. Pandey. 2013. Deciphering condensed sequences: a case study from the Oxfordian (Upper Jurassic) Dhosa Oolite member of the Kachchh Basin, western India. Sedimentology 60 (2): 574–598.
Andò, S., and E. Garzanti. 2014. Raman spectroscopy in heavy-mineral studies. In Sediment provenance studies in hydrocarbon exploration and production. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, ed. R.A. Scott, H.R. Smyth, A.C. Morton, and N. Richardson, vol. 386, 395–412.
Andò, S., E. Garzanti, M. Padoan, and M. Limonta. 2012. Corrosion of heavy minerals during weathering and diagenesis: A catalog for optical analysis. Sedimentary Geology 280: 165–178.
Andrews, J.C., E. Almeida, M.C. van der Meulen, J.S. Alwood, C. Lee, Y. Liu, J. Chen, F. Meirer, M. Feser, J. Gelb, J. Rudati, A. Tkachuk, W. Yun, and P. Pianetta. 2010. Nanoscale X-ray microscopic imaging of mammalian mineralized tissue. Microscopy and Microanalysis 16 (3): 327–336.
Armstrong-Altrin, J.S., Y.I. Lee, J.J. Kasper-Zubillaga, A. Carranza-Edwards, D. Garcia, G.N. Eby, V. Balaram, and N.L. Cruz-Ortiz. 2012. Geochemistry of beach sands along the western Gulf of Mexico, Mexico: Implication for provenance. Chemie der Erde - Geochemistry 72 (4): 345–362.
Armstrong-Altrin, J.S., Y.I. Lee, J.J. Kasper-Zubillaga, and E. Trejo-Ramírez. 2017. Mineralogy and geochemistry of sands along the Manzanillo and El Carrizal beach areas, southern Mexico: Implications for palaeoweathering, provenance and tectonic setting. Geological Journal 52 (4): 559–582.
Armstrong-Altrin, J.S., R. Nagarajan, V. Balaram, and O. Natalhy-Pineda. 2015. Petrography and geochemistry of sands from the Chachalacas and Veracruz beach areas, western Gulf of Mexico, Mexico: Constraints on provenance and tectonic setting. Journal of South American Earth Sciences 64 (Part 1): 199–216.
Arora, A., S. Banerjee, and S. Dutta. 2015. Black shale in late Jurassic Jhuran formation of Kutch: Possible indicator of oceanic anoxic event? Journal of the Geological Society of India 85 (3): 265–278.
Arora, A., S. Dutta, B. Gogoi, and S. Banerjee. 2017. The effects of igneous dike intrusion on organic geochemistry of black shale and its implications: Late Jurassic Jhuran Formation, India. International Journal of Coal Geology 178 (Supplement C): 84–99.
Arribas, J., S. Critelli, E. Le Pera, and A. Tortosa. 2000. Composition of modern stream sand derived from a mixture of sedimentary and metamorphic source rocks (Henares River, central Spain). Sedimentary Geology 133 (1–2): 27–48.
Bansal, U., S. Banerjee, K. Pande, A. Arora, and S.S. Meena. 2017. The distinctive compositional evolution of glauconite in the cretaceous Ukra Hill member (Kutch Basin, India) and its implications. Marine and Petroleum Geology 82: 97–117.
Basu, A., and E. Molinaroli. 1989. Provenance characteristics of detrital opaque Fe–Ti oxide minerals. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology 59 (6): 922–934.
Basu, A., and E. Molinaroli. 1991. Reliability and application of detrital opaque Fe–Ti oxide minerals in provenance determination. In Developments in Sedimentary Provenance Studies. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, ed. A.C. Morton, S.P. Todd, and P.D.W. Haughton, vol. 57, 55–65.
Biswas, S.K. 1977. Mesozoic rock stratigraphy of Kachchh. Quarterly Journal of the Geological, Mining and Metallurgical Society of India 49: 1–52.
Biswas, S.K. 1981. Basin framework, Palaeo-environment and depositional history of the Mesozoic sediments of Kutch Basin, western India. Quarterly Journal of the Geological, Mining and Metallurgical Society of India 53: 56–85.
Biswas, S.K. 1982. Rift basins in western margin of India and their hydrocarbon prospects with special reference to Kutch Basin. AAPG Bulletin 66 (10): 1497–1513.
Biswas, S.K. 1987. Regional tectonic framework, structure and evolution of the western marginal basins of India. Tectonophysics 135 (4): 307–327.
Biswas, S.K. 1991. Stratigraphy and sedimentary evolution of the Mesozoic basin of Kutch, western India. In Stratigraphy and Sedimentary Evolution of Western India, ed. S.K. Tandon, C.C. Pant, and S.M. Casshyap, 74–103. Nainital: Gyanodaya Prakashan.
Biswas, S.K. 2005. A review of structure and tectonics of Kutch Basin, western India, with special reference to earthquakes. Current Science 88 (10): 1592–1600.
Caracciolo, L., R. Tolosana-Delgado, E. Le Pera, H. von Eynatten, J. Arribas, and S. Tarquini. 2012. Influence of granitoid textural parameters on sediment composition: implications for sediment generation. Sedimentary Geology 280: 93–107.
Critelli, S., J. Arribas, E. Le Pera, A. Tortosa, K.M. Marsaglia, and K.K. Latter. 2003. The recycled orogenic sand provenance from an uplifted thrust belt, Betic Cordillera, southern Spain. Journal of Sedimentary Research 73 (1): 72–81.
Critelli, S., and R.V. Ingersoll. 1994. Sandstone petrology and provenance of the Siwalik group (northwestern Pakistan and western–southeastern Nepal). Journal of Sedimentary Research 64 (4a): 815–823.
Critelli, S., and E. Le Pera. 1994. Detrital modes and provenance of Miocene sandstones and modern sands of the southern Apennines thrust-top basins (Italy). Journal of Sedimentary Research 64 (4a): 824–835.
Dickinson, W.R. 1970. Interpreting detrital modes of graywacke and arkose. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology 40 (2): 695–707.
Dickinson, W.R. 1985. Interpreting provenance relations from detrital modes of sandstones. In Provenance of arenites, 333–361. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands.
Dickinson, W.R., L.S. Beard, G.R. Brakenridge, J.L. Erjavec, R.C. Ferguson, K.F. Inman, R.A. Knepp, F.A. Lindberg, and P.T. Ryberg. 1983. Provenance of North American Phanerozoic sandstones in relation to tectonic setting. GSA Bulletin 94 (2): 222–235.
Dickinson, W.R., and C.A. Suczek. 1979. Plate tectonics and sandstone compositions. AAPG Bulletin 63 (12): 2164–2182.
Dill, H.G. 1998. A review of heavy minerals in clastic sediments with case studies from the alluvial-fan through the nearshore-marine environments. Earth-Science Reviews 45 (1–2): 103–132.
Dill, H.G., and D. Klosa. 2011. Heavy mineral-based provenance analysis of Mesozoic continental–marine sediments at the western edge of the Bohemian Massif, SE Germany: with special reference to Fe–Ti minerals and the crystal morphology of heavy minerals. International Journal of Earth Sciences 100 (7): 1497–1513.
Folk, R.L. 1974. Petrology of sedimentary rocks. Austin: Hemphill.
Fürsich, F.T., W. Oschmann, I.B. Singh, and A.K. Jaitly. 1992. Hardgrounds, reworked concretion levels and condensed horizons in the Jurassic of western India: Their significance for basin analysis. Journal of the Geological Society 149 (3): 313–331.
Fürsich, F.T., D.K. Pandey, J.H. Callomon, A.K. Jaitly, and I.B. Singh. 2001. Marker beds in the Jurassic of the Kachchh Basin, western India: Their depositional environment and sequence-stratigraphic significance. Journal of the Palaeontological Society of India 46: 173–198.
Fürsich, F.T., I.B. Singh, M. Joachimski, S. Krumm, M. Schlirf, and S. Schlirf. 2005. Palaeoclimate reconstructions of the middle Jurassic of Kachchh (western India): an integrated approach based on palaeoecological, oxygen isotopic, and clay mineralogical data. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 217 (3–4): 289–309.
Grigsby, J.D. 1992. Chemical fingerprinting in detrital ilmenite: a viable alternative in provenance research? Journal of Sedimentary Petrology 62 (2): 331–337.
Hounslow, M.W., and A.C. Morton. 2004. Evaluation of sediment provenance using magnetic mineral inclusions in clastic silicates: comparison with heavy mineral analysis. Sedimentary Geology 171: 13–36.
Hubert, J.F. 1962. A zircon–tourmaline–rutile maturity index and the interdependence of the composition of heavy mineral assemblages with the gross composition and texture of sandstones. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology 32 (3): 440–450.
Ingersoll, R.V., and C.A. Suczek. 1979. Petrology and provenance of Neogene sand from Nicobar and Bengal fans, DSDP sites 211 and 218. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology 49 (4): 1217–1228.
Krishna, J., D.B. Pathak, B. Pandey, and J.R. Ojha. 2000. Transgressive sediment intervals in the Late Jurassic of Kachchh, India. GeoResearch Forum 6: 321–332.
Laghari, A., M.Q. Jan, M.A. Khan, M.H. Agheem, A.G. Sahito, and S. Anjum. 2013. Petrography and major element chemistry of mafic dykes in the Nagar Parkar igneous complex, Tharparkar, Sindh. Journal of Himalayan Earth Science 46: 1–11.
Le Pera, E., and J. Arribas. 2004. Sand composition in an Iberian passive-margin fluvial course: the Tajo River. Sedimentary Geology 171: 261–281.
Le Pera, E., J. Arribas, S. Critelli, and A. Tortosa. 2001. The effects of source rocks and chemical weathering on the petrogenesis of siliciclastic sand from the Neto River (Calabria, Italy): implications for provenance studies. Sedimentology 48 (2): 357–378.
Le Pera, E., and S. Critelli. 1997. Sourceland controls on the composition of beach and fluvial sand of the northern Tyrrhenian coast of Calabria, Italy: implications for actualistic petrofacies. Sedimentary Geology 110 (1–2): 81–97.
Mandal, A., A. Koner, S. Sarkar, H.A. Tawfik, N. Chakraborty, S. Bhakta, and P.K. Bose. 2016. Physico-chemical tuning of palaeogeographic shifts: Bhuj Formation, Kutch, India. Marine and Petroleum Geology 78: 474–492.
Mange, M.A., and H.F.W. Maurer. 1992. Heavy minerals in colour. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands.
Mange, M.A., and A.C. Morton. 2007. Chapter 13 geochemistry of heavy minerals. In Heavy minerals in use. Developments in sedimentology, ed. M.A. Mange and D.T. Wright, vol. 58, 345–391. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Meinhold, G. 2010. Rutile and its applications in earth sciences. Earth-Science Reviews 102 (1–2): 1–28.
Morton, A., and S. Chenery. 2009. Detrital rutile geochemistry and thermometry as guides to provenance of Jurassic–Paleocene sandstones of the Norwegian Sea. Journal of Sedimentary Research 79 (7): 540–553.
Morton, A., C. Hallsworth, and B. Chalton. 2004. Garnet compositions in Scottish and Norwegian basement terrains: A framework for interpretation of North Sea sandstone provenance. Marine and Petroleum Geology 21 (3): 393–410.
Morton, A.C., and C.R. Hallsworth. 1999. Processes controlling the composition of heavy mineral assemblages in sandstones. Sedimentary Geology 124: 3–29.
Paikaray, S., S. Banerjee, and S. Mukherji. 2008. Geochemistry of shales from the Paleoproterozoic to Neoproterozoic Vindhyan Supergroup: implications on provenance, tectonics and paleoweathering. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 32 (1): 34–48.
Preston, J., A. Hartley, M. Mange-Rajetzky, M. Hole, G. May, S. Buck, and L. Vaughan. 2002. The provenance of Triassic continental sandstones from the Beryl Field, northern North Sea: Mineralogical, geochemical, and sedimentological constraints. Journal of Sedimentary Research 72 (1): 18–29.
Ramakrishnan, M., and R. Vaidyanadhan. 2008. Geology of India. Vol. 1, 261–333. Bangalore: Geological Society of India.
Roy, P., S. Bardhan, A. Mitra, and S.K. Jana. 2007. New Bathonian (Middle Jurassic) ammonite assemblages from Kutch, India. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 30 (5–6): 629–651.
Saha, S., S. Banerjee, S.D. Burley, A. Ghosh, and P.K. Saraswati. 2010. The influence of flood basaltic source terrains on the efficiency of tectonic setting discrimination diagrams: an example from the Gulf of Khambhat, western India. Sedimentary Geology 228 (1–2): 1–13.
Singh, I.B. 1989. Dhosa Oolite — A transgressive condensation horizon of Oxfordian age in Kachchh, western India. Journal of the Geological Society of India 34 (2): 152–160.
Weibel, R., and H. Friis. 2004. Opaque minerals as keys for distinguishing oxidising and reducing diagenetic conditions in the Lower Triassic Bunter Sandstone, North German Basin. Sedimentary Geology 169 (3–4): 129–149.
Zack, T., H. von Eynatten, and A. Kronz. 2004. Rutile geochemistry and its potential use in quantitative provenance studies. Sedimentary Geology 171: 37–58.
Zuffa, G.G. 1985. Optical analyses of arenites: Influence of methodology on compositional results. In Provenance of arenites. NATO ASI series (Series C: mathematical and physical sciences), ed. G.G. Zuffa, vol. 148, 165–189. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands.
Zuffa, G.G. 1987. Unravelling hinterland and offshore palaeogeography from deep-water arenites. In Marine clastic sedimentology, ed. J.K. Leggett and G.G. Zuffa, 39–61. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands.
Acknowledgements
Authors are indebted to Indian Institute of Technology Bombay for infrastructure facilities. Santanu Banerjee is thankful to Department of Science and Technology, Government of India for financial support through grant SR/S4/ES-709/2014. Authors are thankful to S.C. Patel and Javed M. Shaikh for providing analytical support at the DST-IITB National facility for EPMA, Department of Earth Sciences, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay. Authors are also grateful to George Mathew for facilitating heavy mineral study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AC and SB carried out fieldwork, elemental chemistry of heavy minerals and X-ray microscopy. ELP carried out petrographic investigation of heavy minerals and supervised petrographic work. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhuri, A., Banerjee, S. & Le Pera, E. Petrography of Middle Jurassic to Early Cretaceous sandstones in the Kutch Basin, western India: Implications on provenance and basin evolution. J. Palaeogeogr. 7, 2 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42501-018-0002-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s42501-018-0002-6