Abstract
Background
Surface fuel loadings are some of the most important factors contributing to fire intensity and fire spread. In old-growth forests where fire has been long excluded, surface fuel loadings can be high and can include woody debris ≥100 cm in diameter. We assessed surface fuel loadings in a long-unburned old-growth mixed-conifer forest in Yosemite National Park, California, USA, and assessed fuel consumption from a management-ignited fire set to control the progression of the 2013 Rim Fire. Specifically, we characterized the distribution and heterogeneity of pre-fire fuel loadings, both along transects and contained in duff mounds around large trees. We compared surface fuel consumption to that predicted by the standard First Order Fire Effects Model (FOFEM) based on pre-fire fuel loadings and fuel moistures. We also assessed the relationship between tree basal area—calculated for two different spatial neighborhood scales—and pre-fire fuel loadings.
Results
Pre-fire total surface fuel loading averaged 192 Mg ha−1 and was reduced by 79% by the fire to 41 Mg ha−1 immediately after fire. Most fuel components were reduced by 87% to 90% by the fire, with the exception of coarse woody debris (CWD), which was reduced by 60%. Litter depth in duff mounds were within 1 SD of plot means, but duff biomass for the largest trees (>150 cm diameter at breast height [DBH]) exceeded plot background levels. Overstory basal area generally had significant positive relationships with pre-fire fuel loadings of litter, duff, 1-hour, and 10-hour fuels, but the strength of the relationships differed between overstory components (live, dead, all [live and dead], species), and negative relationships were observed between live Pinus lambertiana Douglas basal area and CWD. FOFEM over-predicted rotten CWD consumption and under-predicted duff consumption.
Conclusions
Surface fuel loadings were characterized by heterogeneity and the presence of large pieces. This heterogeneity likely contributed to differential fire behavior at small scales and heterogeneity in the post-fire environment. The reductions in fuel loadings at our research site were in line with ecological restoration objectives; thus, ecologically restorative burning during fire suppression is possible.
Resumen
Antecedentes
La carga de combustibles de superficie es uno de los factores más importantes entre los que contribuyen a la intensidad y la velocidad de propagación del fuego. En bosques maduros, en los cuales el fuego ha sido excluido por largo tiempo, las cargas de combustibles de superficiepueden ser altas e incluir restos vegetales ≥100 cm de diámetro. Determinamos la carga de combustibles superficiales en un bosque mixto maduro ubicado en el Parque Nacional Yosemite, en California, EEUU, en el cual el fuego había sido excluido desde mucho tiempo atrás, y determinamos el consumo de combustibles mediante un fuego con objetivos de manejo iniciado para controlar la progresión del incendio Rim de 2013. Específicamente, caracterizamos la distribución y heterogeneidad de la carga de combustible previa al fuego a lo largo de transectas, y también la carga contenida en montículos alrededor de grandes árboles. Comparamos la combustión del combustible superficial con el predicho mediante el Modelo de Efectos de Fuego de Primer Orden (FOFEM) basado en cargas de combustible pre-fuego y humedad de los combustibles. También determinamos la relación entre el área basal de los árboles—calculada para dos escalas espaciales de proximidad—y las cargas de combustible pre fuego.
Resultados
La carga total de combustibles superficiales en el pre fuego promediaron 192 Mg ha−1 y fue reducida en un 79% por el fuego a 41 Mg ha−1 inmediatamente luego del fuego. La mayoría de los componentes del combustible fue reducido entre el 87% al 90% por el fuego, con la excepción del combustible grueso (CWD), que fue reducido en un 60%. La profundidad de la broza en los montículos estuvo dentro de una Desviación Standard (SD) de aquella contenida en las parcelas ubicadas en las transectas, aunque esta broza en árboles grandes (>150 cm de diámetro a la altura del pecho [DBH]) excedió a la de las parcelas de las transectas. El área basal del dosel superior tuvo, en general, una relación positiva con la carga previa al fuego en la broza (fina y gruesa), y los combustibles de 1 y 10 horas, pero la robustez de esta relación difirió entre los componentes del dosel (especies vivas, muertas [todas vivas y muertas]), y relaciones negativas fueron observadas entre el área basal de Pinus lambertiana Douglas vivos y el combustible grueso (CWD). El modelo FOFEM sobreestimó el consumo de CWD degradado y subestimó el consumo de la broza gruesa.
Conclusiones
Las cargas de combustible superficiales estuvieron caracterizadas por la heterogeneidad y la presencia de grandes trozos de material combustible. Esta heterogeneidad probablemente contribuya a un comportamiento del fuego diferencial a pequeña escala y heterogeneidad en el ambiente post fuego. Las reducciones de combustible en nuestro sitio de estudio están en línea con los objetivos de restauración ecológica; en consecuencia, las quemas restaurativas durante la supresión del fuego son factibles de ser realizadas.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
ABCO: Abies concolor
CWD: Coarse woody debris; downed wood greater than 7.62 cm (3 inches) diameter
DBH: Diameter at breast height (1.37 m)
FOFEM: First Order Fire Effects Model
PILA: Pinus lambertiana
YFDP: Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot
Background
Efforts to restore fire-dependent forest types via the reintroduction of fire, through either prescribed fire or managed wildfire, require an understanding of forest fuels (Ryan et al. 2013). Fuel properties vary with forest overstory species (van Wagtendonk et al. 1998), forest age (Agee and Huff 1987; van Wagtendonk and Moore 2010), disturbance history (Jenkins et al. 2012), and ecosystem productivity (Keane et al. 2000). Understanding the variability of pre-fire fuel loadings at spatial scales similar to that of prescribed fires (i.e., 25 ha to 250 ha) can be important both to managers seeking to reintroduce fire (Collins et al. 2010) and also for calculating the likely effects of burning on tree survival (Lutes et al. 2009; Furniss et al. 2019; Hood et al. 2018). Similarly, measurements of surface fuel combustion and residual fuel loadings immediately after fire are required to evaluate the effectiveness of fire as a fuel reduction and ecosystem restoration treatment (Knapp et al. 2005; Varner et al. 2005); to understand fire impacts to understory plant and fungal species (Moore et al. 2006; Larson et al. 2016); and to estimate fire-caused ecosystem changes, such as direct fire effects on aboveground carbon storage, pyrogenic carbon emissions (Campbell et al. 2007), soil heating (Swezy and Agee 1991), and related changes to soil chemistry and structure (Certini 2005; Hille and Den Ouden 2005).
Deposition from overstory trees is the main source of fuel in most forest ecosystems. Previous studies in relatively uniform stands have shown differences in fuel loadings between stands with different composition and structure (van Wagtendonk and Moore 2010), but other studies at fine spatial scales (0.05 ha) have shown that overstory structure has only weak relationships to fuel loading (Lydersen et al. 2015). While overstory structure determines the fluxes and distribution of fuel loadings at broad spatial scales, the tall trees and heterogeneous spatial patterns characteristic of dry, mixed-coniferous forests can obscure this relationship at sub-stand scales.
Duff and litter accumulations around the bases of large-diameter trees, particular those in genus Pinus L., are a conspicuous and important source of fuel heterogeneity in post-fire exclusion conifer forests in western North America (Ryan and Frandsen 1991; Swezy and Agee 1991). These duff mounds, created by higher inputs of exfoliated bark and leaf litter adjacent to trees, have been implicated in basal injury to tree cambial tissues when fire returns following several missed fire cycles (Ryan and Frandsen 1991; Sackett and Haas 1998; Hood 2010; Nesmith et al. 2010; Garlough and Keyes 2011). Because these accumulations are aggregated around large trees, which are rare and unevenly distributed on the landscape (e.g., at densities of 5 to 11 ha−1; Lutz et al. 2009a, 2018a), they may not be captured by traditional fuel sampling methods (e.g., “Brown’s transects;” Brown 1974) but may have a strong influence on local biomass consumption during fire and on tree mortality of those trees after fire (Swezy and Agee 1991; Hood et al. 2010). Duff mounds therefore merit consideration from restoration ecologists and managers working to restore frequent fire regimes to dry forests in western North America (Varner et al. 2005; Kolb et al. 2007) and other forest types with similar thick-barked trees that exfoliate bark, such as longleaf pine (Pinus palustris Mill., Varner et al. 2009).
Forest and fire managers use measurements of surface fuel loadings and moistures with decision support computer programs such as the First Order Fire Effects Model (FOFEM) to develop prescribed fire prescriptions and monitoring plans (Lutes et al. 2012). FOFEM and related models are essential management support tools, but have not been widely evaluated or validated across the various forest types and burning conditions in which they are used (French et al. 2011; Prichard et al. 2014). FOFEM uses a combination of empirical models (for shrub and duff consumption), rule-based predictions (100% of herbaceous and litter are consumed), and processed-based models (for woody fuels) for computing fuel consumption, which may not match the full range of burning conditions and fuel profiles present across regions and forest types (Prichard et al. 2014).
We used an intensively measured forest research site consisting of a fully stem-mapped (georeferenced tree locations) 25.6 ha study area and 2240 m of fuel transects to quantify effects of reintroduced fire after a 114-year fire-free period (Barth et al. 2015) on surface fuel loadings in an old-growth Sierra Nevada mixed-conifer forest. We quantified pre-fire and post-fire surface fuel loadings, with the expectation that there would be relatively high fuel consumption under the very dry burning conditions. Our study was guided by three research questions.
-
1.
How did fire change the pre-fire fuel loading, and how much new surface fuel was immediately deposited by the start of the next growing season after fire?
-
2.
How well did overstory structure and composition explain surface fuel variability?
-
3.
Could surface fuel consumption be well modeled by FOFEM in this fire-excluded old-growth site?
Methods
Study site
The Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot (YFDP; 37.8° N, 119.8° W; Tuolumne County, central California, USA; Fig. 1) is located in an old-growth mixed-conifer forest in northwestern Yosemite National Park. The YFDP is a 25.6 ha research site (800 m × 320 m) within which all trees ≥1 cm diameter at breast height (DBH; 1.37 m above the pre-fire soil surface) and all snags ≥10 cm DBH have been measured at DBH, mapped, and identified to species (see Lutz et al. 2012 for detailed methods). Coniferous trees dominate the plant community, with sugar pine (Pinus lambertiana Douglas), California white fir (Abies concolor [Gordon & Glend.] Hildebr.), and incense-cedar (Calocedrus decurrens [Torr.] Florin) the most abundant. Nomenclature follows Flora of North America Editorial Committee (1993); additional descriptions of the plant community can be found in (Lutz et al. 2012, 2014, 2017).
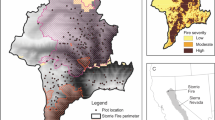
(a) The Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot (YFDP) is located in the Sierra Nevada Ecoregion of California, USA, (b) within Yosemite National Park. (c) Locations of sample points and planar transects for pre-fire and post-fire fuel measurements in the YFDP, which were run within the plot, parallel to plot boundaies. Fuel transects were measured in June 2011, before the 2013 Rim Fire, and after the fire in June 2014. Locations of P. lambertiana ≥25 cm DBH are shown in gray points, with trees where litter and duff mounds were sampled in red. Pre-fire measurements of duff mounds were taken in August 2013, and the post-fire fuel measurements were taken in June 2014. One sampled-tree duff mound was located just outside the western edge of the plot, and is not shown. Green lines represent a LiDAR-derived 5 m contour interval
Modeled mean annual precipitation at the YFDP is 1081 mm (PRISM Climate Group 2004). Mean January minimum and maximum temperatures are −1 °C and 8.9 °C, respectively, and mean July minimum and maximum temperatures are 13.0 °C and 24.5 °C (PRISM Climate Group 2004; Daly et al. 2008). There has been minimal anthropogenic disturbance in the form of tree harvesting, but fire exclusion has resulted in deviations from historical forest structure and composition. Prior to the period of fire exclusion, the fire return interval in the YFDP was estimated at 29.5 years (Barth et al. 2015), with the last widespread fire burning the plot in 1900 (Barth et al. 2015). The presence of large and old trees, especially of fire-scarred Pinus lambertiana, Abies concolor, and Calocedrus decurrens (Barth et al. 2015), throughout the plot suggests that high-severity fire had been rare and of limited spatial extent over the past 500 years.
The YFDP was burned in 2013 in a backfire set by Yosemite National Park to check the advance of the Rim Fire (Stavros et al. 2016). The backfire was ignited at the Crane Flat lookout, approximately 1 km from the plot, on 31 August 2013, when conditions were hotter and drier than for normal prescribed burn windows (see Lutz et al. 2017 for details), and was not managed subsequent to the initial ignition. After ignition, the fire backed downslope to the north during the night of 1 September 2013, burning approximately half of the YFDP, with the remainder burning during the morning of 2 September 2013. Fire behavior ranged from low-intensity backing fire to high-intensity surface fire with some torching (Lutz et al. 2017 for details of burning conditions). Within the YFDP, the overall fire severity as inferred from Landsat-derived metrics was low or moderate, with a few small patches remaining unburned or burning at high severity (Lutz et al. 2018b), which is characteristic of recent fires in Yosemite mixed-conifer forests (van Wagtendonk and Lutz 2007; Lutz et al. 2009b).
Fuel measurements
Surface fuel loadings were sampled two years before fire in June 2011, and one year after fire in June 2014, using modified Brown’s transects (Brown 1974). During pre-fire measurement, we sampled 112 20-meter transects, totaling 2240 m; during post-fire measurement, we sampled 99 of the same transects (Fig. 1). Thirteen transects were sampled along the incorrect line during post-fire measurement, so they could not be directly paired with the pre-fire sample. Fine woody material was tallied by the three diameter classes that correspond to the 1-, 10-, and 100-hour fuel classes used in the National Fire-Danger Rating System (Fosberg 1970; 0 to 0.61 cm, 0.64 to 2.51 cm, and 2.54 to 7.59 cm, respectively). At the intersection with the transect, diameter, species, and decay class (five classes, from sound to decayed) of all pieces of coarse woody debris (fuels >7.62 cm diameter, i.e., 1000-hour fuels; hereafter CWD [Maser et al. 1979, Harmon and Sexton 1996]) were recorded individually. The transect length for the 1-hour and 10-hour fuels was 2 m, for the 100-hour fuels was 4 m at pre-fire measurement and 2 m at post-fire measurement, and 20 m for CWD. Major and minor axis diameters were recorded for CWD with oval or elliptical form, and diameters were estimated for partially buried pieces. Duff and litter depths were measured at 10 locations on each 20 m transect: every 2 meters, starting at 1 m and ending at 19 m. Duff and litter were measured to the nearest 0.1 cm. The litter layer is the layer of relatively undecomposed fibric material, or the Oi organic soil horizon (Banwell et al. 2013). Duff consists of the fermentation and humus horizons (Oe and Oa, respectively), and is composed of fermenting and decomposing organic material (Brown 1974; Banwell et al. 2013). If a stump or log was over one of the sample points, we moved the point of measure 30 cm (one foot) to the right of the transect, and we recorded zero litter and duff if a rock or live tree occupied the sampling point (Brown 1974).
For the post-fire measurement, we made separate measurements of litter, woody fuels, and CWD present immediately after fire (“old”), and deposited since the fire (“new”). “Old” fuels were often charred or decomposed, while “new” fuels consisted of newly dead needles, primarily red-orange in color due to scorching, and wood that had fallen from trees or snags during fire. Uncertainty in differentiating old and new fuels was minimal for the litter, where new fuel was easily identifiable due to different color and structure. Uncertainty in this classification was greater for the CWD, since standing snags that burned then fell during the fire may have had similar characteristics (deep charring, more burning on the side closest to the ground) as woody debris that was on the ground at the time of the fire. For all fuel classes, we totaled the “old” and “new” post-fire measurements to calculate the 1-year post-fire totals.
We measured duff mounds around eight P. lambertiana in August 2013 and again in June 2014. The trees were selected to represent the diameter range found in the YFDP, with an individual sampled in every 25 cm diameter class. For each tree, four 3-meter radial transects were placed at 90-degree intervals around the base of the tree (Additional file 1). Beginning 0.2 m from the bole of the tree, we measured litter and duff every 0.2 m.
Data reduction
Woody fuel intercept counts (1-hour, 10-hour, and 100-hour fuels) or volumes (CWD), and litter and duff depths were converted to estimates of biomass and summarized at the transect scale (n = 99) for each fuel class. For 1-hour, 10-hour, and 100-hour fuels, planar intercept data were converted to weights using the equation (Brown 1974; van Wagtendonk 1996):
where LENGTH is the length of the planar intercept transect, n is the number of pieces of each fuel, CONST is a fuel constant to convert to mass (we used one from Brown 1974), QMD is the quadratic mean diameter, SG is the specific gravity, and SEC is the secant of the non-horizontal angle. For the latter three variables, we used species-specific values developed for conifer species in the Sierra Nevada derived from observations in single-species stands (van Wagtendonk 1996). Because our study site contained a mix of species, we weighted fuel loading constants by the relative basal area of the three most common species in the YFDP: A. concolor (45.24%), P. lambertiana (45.04%), and C. decurrens (7.45%). We then multiplied the calculated weights by the correction factor for Sierra Nevada conifers (0.939) provided by van Wagtendonk et al. (1998).
CWD diameter measurements were converted to volume following equation 7 in Harmon and Sexton (1996):
where V is volume, d is diameter, and L is length. For elliptical pieces, we added the square of each diameter measurement and then took the square root to calculate a mean diameter before calculating volume. Volume estimates were converted to mass using species-specific and decay-class-specific wood densities from Harmon and Sexton (1996: Table 4) and from Harmon et al. (2008: Appendix 2), for conifers and hardwoods, respectively. CWD mass was summarized at the transect scale (n = 99).
We converted depth measurements of litter and duff to mass estimates using species-specific equations for Sierra Nevada conifer species (van Wagtendonk et al. 1998). As for woody fuels, we weighted fuel-loading constants by the relative basal area of the three most common species. Litter and duff mass was summarized at the sample point scale (n = 990).
We predicted the continuous depth of litter and duff from 0 m to 2 m for each intensively sampled duff-mound tree, based on 40 depth measurements from the four transects around each tree. We did not include data from 2 m to 3 m because fuel depths became similar to background levels in the plot at 2 m from the bole. We determined the continuous depth of litter and duff from 0 m to 2 m by calculating the volume of litter and duff in concentric 0.2 m bands around each tree and then summed the section volumes from ≤1 m and ≤2 m from each tree. Duff mound volumes were converted to fuel loadings using the bulk densities for sugar pine litter and duff from van Wagtendonk et al. (1998). See Appendix: Supplemental Methods for a detailed description of the duff mound loading measurement method.
Sample size and FOFEM evaluation
We compared observed changes in fuel loadings at the transect scale to expected post-fire fuel loadings as modeled in the First Order Fire Effects Mode (FOFEM) version 6.4 (Lutes et al. 2012), a commonly used fire planning software program, which predicts fuel consumption given pre-fire fuel loadings, fuel model type, and fuel moistures. We use fuel model SAF 243 – Sierra Nevada Mixed Conifer, and subsamples of observed pre-fire fuel loadings.
We sampled more transects than would typically be used for pre-fire fuel consumption modeling by managers. Therefore, we rarefied our dataset to sample sizes that would be more typical of the number of transects that managers would use in a FOFEM model run. We used two smaller sample sizes: 15 transects, and 45 transects. The former was a subjectively chosen value that a manager with limited funding or time might select, and we used it to illustrate uncertainty in fuel estimate and projects with a small sample size. The latter, 45 transects, was the minimum sample size that would allow, for our study site, estimations of loadings in each fuel class within 20% of the mean (Additional files 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8). To illustrate the range of observed and predicted means that would be obtained with 15 transects and 45 transects, we iterated this process 100 times for each of those two sample sizes. Each of those samples (200 total) was run in FOFEM using the batch-processing mode to calculate expected post-fire fuel loads.
To identify the above minimum sample size, we selected random samples of different numbers of individual transects (woody fuels; n = 1 to 99 transects) or sample point locations (litter and duff; n = 1 to 990 points) from our populations of pre-fire and post-fire samples and calculated mean and standard deviations of mass for each sample. Those summary statistics were plotted against sample size. Stabilization (stationarity) of variance was assessed graphically with the use of two envelope widths: the estimated mean within ±20% of the mean and ±10% of the mean. This procedure was repeated 10 times for each fuel class.
Additional FOFEM input parameters that were used for all transects included the percentage of CWD that was rotten (calculated per transect), and the distribution of CWD greatest mass in the >50.8 cm diameter class. The season of burning was set to summer. Fuel moistures for duff, 100-hour fuels, 1000-hour fuels, and soils were 20%, 6%, 10%, and 5%, respectively; these are the defaults for very dry conditions, which corresponded with the weather conditions before and while the plot burned (Lutz et al. 2017). Field measurements of fuel moistures were not available from the fire managers nor from the nearby weather stations, but these values are generally consistent with local studies of fuel moisture (Hille and Stephens 2005; Banwell et al. 2013).
Influence of forest structure and composition on pre-fire surface fuel loadings
We used linear regression to model total pre-fire fuel loading as a function of the overstory structure (basal area) and composition in the local tree neighborhood. Overstory variables (Table 1) were sampled in 6.91-meter-radius and 17.84-meter-radius circles (0.015 ha and 0.1 ha neighborhoods, respectively) around each sampling point (i.e., at each odd number on each transect for litter and duff; at 1 m on the transect for 1-hour and 10-hour fuels; at 2 m on the transect for 100-hour fuels; and at 15 m on the transect for CWD). We modeled the mass of litter and duff in P. lambertiana duff mounds within 1 m and 2 m of trees as a function of tree DBH using a linear model. All statistical analyses were conducted in the R, including package nlme version 3.1-131.1 (R Core Team 2017: Pinheiro et al. 2018).
Results
Pre-fire total surface fuel loadings averaged 192 Mg ha−1 (range: 67.5 to 617.07 Mg ha−1) and were reduced by an average of 79% by the fire to 41 Mg ha−1 (range: 0.65 to 336.74 Mg ha−1) immediately after the fire (Additional file 9). Most fuel components were reduced by 87% to 90% by the fire; CWD was only reduced by 60% (Additional file 9; Fig. 2). Small woody fuels contributed negligible amounts (0.3% to 1.8%) to the total surface fuel loadings, during both pre-fire and post-fire measurements. Litter and duff made up a substantial amount of the fuel (12% and 46% before fire and 14% and 19% after fire, respectively). CWD was the other substantial source of fuel (38% and 64% for pre-fire and post-fire measurements, respectively).
Surface fuel loading in the Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot, Yosemite National Park, California, USA, in 2011, before the 2013 Rim Fire, and in 2014. Gray box plots within violin plots show median (black bar), interquartile range (25% quartile and 75% quantile; gray box), 95% confidence intervals (black lines within colored areas). Width of violin plots is based on the probability density (colored shaded areas) for the range of observed observations (y-axis). Diameter classes of woody fuels are: 1-hour fuels = 0.63 cm, 10-hour fuels = 0.64 to 2.53 cm, 100-hour = 2.54 to 7.61, CWD ≥7.62 cm. Surface fuels (bottom right) are the combined total of all fuels. Post-fire old = material that persisted as ground fuels through the 2013 fire event; Post-fire new = material that became ground fuel following the fire event; Post-fire total = the sum of the pre-fire new and pre-fire old. Species-specific decay class bulk densities were used to convert estimated volumes to per-hectare biomass estimates. Woody fuel and total fuel data were summarized at the transect scale (n = 99), and litter and duff were summarized at the point sample locations (n = 990) before plotting
New inputs after fire increased the total fuel loading from 12 Mg ha−1 to 53 Mg ha−1 by the start of the first growing season after the fire, or from 21% to 28% of the pre-fire fuel loading (Additional file 9; Fig. 2). The largest new inputs were from CWD (4.9 Mg ha−1) and litter (also 4.9 Mg ha−1). One-hour fuel loadings experienced a substantial input via post-fire deposition (0.25 Mg ha−1), representing a recovery of 41% of the pre-fire fuel load.
Fire immediately reduced the total number of CWD pieces observed along the 2240 m of transects from 426 to 131 (Table 2). The biomass of C. decurrens CWD increased after fire (from 10.5 Mg ha−1 to 38.9 Mg ha−1), due to either new deposition onto transects between 2011 and the fire in 2013, or from snags felled by the fire. Large pieces (>62 cm) of P. lambertiana persisted through the fire, while large pieces of A. concolor that were present prior to the fire were largely consumed. Post-fire additions tended to be smaller in diameter (Table 2) and were dominated by P. lambertiana (55% of occurrences, 21% of mass; Table 2). P. lambertiana and C. decurrens accounted for most of the larger-diameter post-fire additions (Table 2), while A. concolor post-fire additions tended to be smaller in diameter (Table 2).
There was a positive relationship between DBH and litter and duff fuel loadings ≤1 m from each tree and ≤2 m from P. lambertiana stems (Fig. 3; Additional files 10, 11, and 12). Litter depth in duff mounds were within 1 SD of plot means (based on fuel transects), but duff depths for our two largest trees (157 cm DBH and 176 cm DBH) exceeded plot background levels (Fig. 3). The amount of litter in a 2 m radius band around the boles of P. lambertiana trees, when converted to landscape scale using the pre-fire density of similar trees in the YFDP, ranged from 4.2 Mg ha−1 (smallest diameter; 26 cm DBH) to 14.4 Mg ha−1 (157 cm DBH), and the volume of duff from 46.8 Mg ha−1 to 167.3 Mg ha−1. After fire, surface fuel consumption was not influenced by the depth or the composition of pre-fire surface fuels because the moderate-intensity surface fire that burned the YFDP consumed almost all of the litter and duff in the P. lambertiana duff mounds (Additional file 13).
Scatter plot of the fuel loading of litter and duff ≤1 m from trees (left) and ≤2 m from 830 trees (right), in the Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot, Yosemite National Park, California, USA, in 2011, before the 2013 Rim Fire. Regression lines are for linear regression (see Additional files 11 and 12 for coefficients). Solid lines show pre-fire fuel loadings, and dashed lines show post-fire total fuel loading. Gray shading shows 95% confidence intervals
Influence of overstory trees on pre-fire fuel loading
Most overstory variables had significant positive relationships with litter and duff fuel loadings at the 0.015 ha scale (Fig. 4), and there were also weak positive significant relationships between live A. concolor basal area and 1-hour and 10-hour fuel loadings at the 0.015 ha scale (Fig. 4), but these relationships explained very little of the variance. Interestingly, live P. lambertiana basal area had a significant negative relationship with CWD at the 0.015 ha scale, and a negative relationship at the 0.1 ha scale. There was also a significant positive relationships between both dead P. lambertiana basal area, and live A. concolor basal area and CWD at the 0.1 ha scale (Fig. 4). Nevertheless, even when regression model parameters were significant, the relationship only explained a small part of the overall variance (0.004 < r2 < 0.096; see scatter plots and regression in Additional files 14, 15, 16, and 17.
(a) heat map of regression coefficients (β) for when basal area (BA) at the 0.015 ha scale (a 6.91 m radius circle, center on the sample point), and (b) at the 0.1 ha scale (a 17.84 m radius circle, center on the sample point) of each overstory component predicts fuel loadings of each fuel component. Tree basal area was calculated from a complete census of all live stems ≥1 cm diameter at 1.37 m height, and all dead stems ≥10 cm and ≥2.0 m tall. Regression slopes and P-values are shown in text. In cases for which the regression was not significant, the background color is set to white. Scatter plots and significant regressions are plotted on Additional files 14, 15, 16, and 17. ABCO: Abies concolor; PILA: Pinus lambertiana. Sample sizes are n = 112 for woody fuels and total fuels, and n = 1120 for litter and duff. Regression models were for 2011 pre-fire fuel loadings at the Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot in Yosemite, California, USA
FOFEM evaluation
Pre-fire fuel loading was highly heterogeneous throughout the YFDP. Characterization of pre-fire fuel loadings to within 10% of the plot mean required 26 transects for litter, 19 for duff, and 34 for 1-hour and 10-hour fuels. Characterization of 100-hour fuels and CWD to within 20% of the plot mean required 40 and 44 Brown’s transects, respectively. Total surface fuel loadings in the YFDP could be estimated to within 10% with 23 Brown’s transects. Based on these sample size results, we subsampled our dataset with 100 samples of 45 transects in order to meet minimum sample size needs for CWD.
FOFEM predicted complete consumption of 1-hour, 10-hour, 100-hour woody fuels, and of litter, but we observed residual fuels in all of those classes (Fig. 5). FOFEM under-predicted CWD consumption, and this was driven by under-prediction in the rotten CWD class (Fig. 5). In contrast, FOFEM predicted approximately twice as much duff consumption than was observed (Fig. 5). The impacts of the high heterogeneity in fuel loadings were evident in the differences in the range of values that could be obtained when taking the mean of 15 versus 45 fuel transects: analogous high and low values (particularly high CWD values) were evident when only 15 transects were sampled (Fig. 5).
Mean post-fire surface fuel loading for each fuel class as observed in the field (dark gray) and predicted (light gray) by FOFEM for the Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot, Yosemite National Park, California, USA. Observed post-fire fuel measurements were made in June 2014. We calculated FOFEM inputs and outputs using the sampling procedures typically used by managers: multiple transects were sampled (15 in the left column, 45 in the right column), and a mean was calculated from those sampled transects. The pre-fire mean was then entered into FOFEM, which projected the post-fire fuel loadings for each fuel class. Box plots within violin plots show median (black bar), interquartile range (25% quartile and 75% quantile; small box), 95% confidence intervals (vertical lines). Width of violin plots is based on the probability density (shaded areas) for the range of observed observations (y-axis). Diameter classes of woody fuels are: 1-hour fuels = 0.63 cm, 10-hour fuels = 0.64 to 2.53 cm, 100-hour = 2.54 to 7.61 cm, CWD ≥7.62 cm. CWD consumption in FOFEM is modeled separately for the sound (CWDS) and rotten (CWDR) classes
Discussion
The pre-fire fuel loadings in our study site, which had not been burned since 1900 (Barth et al. 2015) and had not been previously logged, were similar to those of Lydersen et al. (2015), who characterized fuel loadings in a similar fire-excluded Sierra Nevada mixed-conifer forest that had been selectively logged in the 1920s (compare our Fig. 2 with their Figure 2). We observed much higher loads of CWD in our study site than Lydersen et al. (2015), likely reflecting the presence of very large trees at our unharvested site (Lutz et al. 2012), and the deposition of their branches and boles on the forest floor. Most of the observations in Lydersen et al. (2015) had higher ranges of values, likely reflecting a greater length of sample transects (5760 m of transects versus our 2240 m), but we observed higher loadings of duff, and greater variation in duff fuel loading. This difference may be due to the presence of very large trees and their associated duff mounds at our study site: large sugar pines influenced surface fuel abundance at a very local scale (<2 m) before the fire.
Overstory trees influenced the surface fuel loadings, and this relationship was dependent on spatial scale. Nevertheless, the amount of variance explained by these relationships was small. In other words, overstory structure, although associated with fuel loading of some fuel classes, could not be used to accurately predict understory fuel loadings. At both the 0.015 ha and 0.1 ha scale, overstory trees had significant positive relationships with the litter and duff classes, consistent with the results of the duff mound analyses. We and Lydersen et al. (2015) both found a relationships between Abies basal area and loading in the 1- to 100-hour woody fuel classes, which may be a result of deposition from the fine branching structure of Abies, but our observed relationship was very weak. Similarly, the negative association of CWD with live P. lambertiana and the positive association with dead P. lambertiana likely derive from its canopy architecture: standing dead P. lambertiana often shed large branches that are in the CWD, 100-hour, and 10-hour classes, but these branches are infrequently shed while the trees are still alive. At the 0.1 ha scale, both live and dead components of the overstory influenced CWD accumulation. This more pronounced relationship at the larger spatial scale may be reflective of the nature of CWD accumulation—CWD is created when a large tree falls (or the top breaks off), and this CWD typically lands farther than 6.91 m away from the rooting location.
Accurate characterization of pre-fire fuel loading is crucial to the reintroduction of fire to landscapes where it has been long excluded; reducing uncertainties in fuel loading (and therefore in burning characteristics) can give managers a higher level of confidence that a fire will have the calculated behavior. These results confirm the well-known problems of heterogeneity of surface fuels (Sikkink and Keane 2008) and the difficulty in understanding the effects of heavy fuels (Hyde et al. 2011). Pre-fire fuel loadings at the 20 m transect scale ranged over an order of magnitude (68.5 Mg ha−1 to 617.1 Mg ha−1), and immediate post-fire fuel loadings varied over two orders of magnitude (0.7 Mg ha−1 to 336.7 Mg ha−1). In the YFDP, 23 Brown’s transects were required to estimate surface fuel loadings to within 10% of the plot mean, and 44 were needed to estimate every fuel class within 20% of the plot mean. If only a very small number of transects were to be sampled (e.g., 15), mean observed fuel loads could be well outside the interquartile range of real values, and model predictions of fuel consumption and residual fuel (Fig. 5), as well as fire behavior and emissions, would be inaccurate. We recommend increasing the length of small woody fuel transects, particularly the 100-hour fuels transect, to the full 20 m transect length in future sampling efforts to capture heterogeneity in woody fuels more efficiently and decrease the number of transects with zero observations of woody fuel classes.
Fuel consumption
The Rim Fire reduced most classes of surface fuels by roughly an order of magnitude, even following three to four missed mean fire return intervals. Stephens and Moghaddas (2005b), working in a similar forest type, found that closely managed prescribed fire and thinning plus prescribed fire treatments substantially reduced surface fuels. At the YFDP, reductions in these woody fuels were achieved even though fire was ignited about 1 km away and allowed to spread naturally through the study site. Furthermore, small unburned areas persisted through the fire (Blomdahl et al. 2019), which was possibly counterbalanced by higher fuel consumption in burned areas due to very low fuel moistures. Litter was reduced from 63.9 Mg ha−1 to 3.22 Mg ha−1, similar to the 8.69 Mg ha−1 reported by Stephens (2004) for a similar frequent-fire reference ecosystem. Duff was reduced dramatically, potentially changing nutrient dynamics (Stephens and Moghaddas 2005a; Moghaddas and Stephens 2007). Reference frequent-fire ecosystems have very little duff (Stephens 2004) due to frequent consumption by fire, yet still maintain high levels of aboveground biomass. Kauffman and Martin (1989), Hille and Stephens (2005), and Knapp et al. (2005) likewise describe reductions in fuel loading of litter, duff, and woody fuels in Sierra Nevada mixed-conifer forest types, with the additional documentation of lower proportional reduction in spring burns versus fall burns. We expect that prescribed fire or wildfire that occurs earlier or later in the year would result in less complete consumption of fine fuels and forest floor layers. Our findings, therefore, indicated that lightly managed wildfire can achieve fuel reductions in support of ecosystem management and restoration objectives, even where mechanical fuel reduction activities are not possible due to access or regulatory limitations. Moreover, management-ignited backburns during a wildfire can achieve large reductions in surface fuel even while overall fire severity remains low to moderate. Thus, ecologically restorative burning during fire suppression is possible even under extremely dry fuel moistures, and could be an objective for fire managers.
Total woody debris biomass was reduced by approximately half, with some types of woody debris experiencing substantial reductions. Woody debris of A. concolor experienced a 9.2-fold reduction in biomass, greater than that experienced by the other conifers, likely due to smaller particle size (as indicated by mean intercepted diameter), thin bark, and more decayed wood, reflecting more rapid decay rates (Harmon and Sexton 1996). Woody debris unidentifiable to species, which largely consisted of material in decay classes 3 to 5 (moderately to well decayed), experienced a 3.5-fold reduction in biomass. The low bulk density of this material, its tendency to be buried to some degree in duff and litter layers, and the lower energy needed to ignite rotten logs (Albini et al. 1995; Albini and Reinhardt 1997) likely all contributed to a high rate of consumption.
While we observed large initial reductions in surface fuel loadings, our results also captured a considerable increase in surface fuels within one year of the fire. Further monitoring will be required to determine how long it will take for post-fire fuel loadings to equal or surpass pre-fire levels, but preliminary data show that this process may occur relatively quickly as fire-killed branches and trees fall (Morrison and Raphael 1993; Passovoy and Fulé 2006; Yocom-Kent et al. 2015; Grayson et al. 2019). A study of post-fire fuel dynamics in the northern Rocky Mountains, USA, only found post-fire increases in the finest fuel category (Stalling et al. 2017), whereas we found post-fire inputs of all woody fuel classes, reflecting the old-growth characteristics of our study site, specifically the large old trees and snags with large dead branches that were deposited during or after the fire. In fire-suppressed old-growth forests such as the YFDP, multiple fires may be necessary to restore and maintain characteristically low fuel loadings, as fire-related mortality of high densities of small trees can quickly replace the fuels that were consumed in a first re-entry fire. There may potentially exist a need for a “maintenance” fire shortly after the initial return of fire to the system due to initial high post-fire inputs of previously live canopy fuels (Larson et al. 2013). Another possible reason for the apparent inconsistency with the findings of Stalling et al. (2017) is that we conducted this study within a single forest type following a single fire while Stalling et al. (2017) grouped post-fire fuel measurements from four sites that spanned 500 m in elevation and overstory mortality rates from 25 to 100%. Grouping such different study sites likely contributed to the high variability that they observed in fuel loadings, and this could have obscured any underlying patterns in fuel accumulation within individual sites. By conducting our study at a single site, we were able to reduce landscape-level variability in fuel loadings and more clearly capture post-fire fuel accumulation.
FOFEM evaluation
FOFEM uses a process-based approach (the “Burnup” model; Albini and Reinhardt 1997) to model consumption of litter and woody fuels, and a separate empirical model created by Brown et al. (1985) to predict duff consumption. Burnup over-predicted consumption of litter, 1-hour, 10-hour, and 100-hour fuels, due primarily to variability in burning conditions within the YFDP that resulted in a residual amount of litter and small woody fuels. Burnup almost always predicts total consumption or 1-hour, and 10-hour fuels (D. Lutes, USDA Forest Service, Missoula, Montana, USA, personal communication), but, in practice, most fires burn with some heterogeneity. The Burnup model may be more accurate in prescribed fire applications for which fire is applied more uniformly, but our results show that heterogeneity in burning conditions is an important consideration when modeling fuel consumption post wildfire.
FOFEM and the Burnup sub-model performed poorly for CWD and duff. Burnup also under-predicted consumption of CWD, particularly rotten CWD (Fig. 5), a deviation that may be due in part to the relatively high abundance of very large diameter rotten CWD woody debris within the YFDP. Burnup models consumption based on heat transfer from small fuels to larger fuels, and this relies on the assumption that there is a relatively continuous diameter distribution of fuels. The under-prediction we observed may have been due to a gap in the diameter distribution of fuels, which could have reduced heat transfer and ignition of larger fuels, or perhaps Burnup is not calibrated well for modeling consumption of fuels beyond the diameter range it was based on (up to 30 cm in diameter; Albini et al. 1995), which our CWD data far exceed (Table 2). Conversely, fuel moistures in the rotten CWD may have been lower than was entered into the model. The duff model, in contrast, greatly under-predicted consumption of duff. The extreme dry conditions of August represent a window during which duff is more combustible than the model predicts, and those conditions were likely beyond the range of duff moisture well represented by the domain of the model.
Conclusions and Management Implications
In long-unburned Sierra Nevada mixed-conifer forests, surface fuel loadings can be high, but are also heterogeneous. There was almost an order of magnitude variation in fuel loading before fire (mean = 192.6 Mg ha−1, SD = 97.5), and over two orders of magnitude in the residual fuel loading after fire (mean = 41.3 Mg ha−1, SD = 57.0). Fire dramatically reduced surface fuels, but most fuel classes—with the exception of duff—received new inputs within one year of the fire. The immediate spatial neighborhood of trees and snags in this fire-excluded, productive forest had some explanatory relationship with surface fuels but, at most, explained 10% of the variance in some fuel classes, similar to results found in nearby forests where overstory variables were sampled with a different approach (Lydersen et al. 2015). This contrasts with the results of van Wagtendonk and Moore (2010), which compared fuel loadings in stands where at least 90% of the trees at a site were of a single species and diameter class, and found significant differences in fuel loadings. In fire-excluded forests with variable tree size and species composition, local forest structure and species composition seems to be only weakly related to fuel loadings. Thus, overstory structure is not a strong enough predictor to replace measurements of surface fuels.
Our results for CWD are noteworthy throughout our analyses. CWD was a major surface fuel pool before fire, and the largest pool after fire. Of all the fuel classes, it had the lowest overall consumption—large CWD may be better able to persist in frequent fire regimes. CWD also had the strongest relationship with overstory variables, although the direction of relationships differed with overstory component: positive for total dead basal area, and negative for live P. lambertiana. Finally, FOFEM over-predicted consumption of CWD, indicating that FOFEM could potentially be improved to better model dynamics of very large woody debris. The low accuracy for rotten CWD in FOFEM is important since CWD plays an important role in many ecosystem functions, including wildlife habitat, nutrient cycling, carbon storage, and post-fire vegetation dynamics (Bull 2002; Janisch and Harmon 2002; Koenigs et al. 2002; Brown et al. 2003), in addition to functioning as a surface fuel.
Our observations suggest that beneficial structural changes, such as reduction of fine fuels without excessive losses of CWD, can result even from fire events occurring during severe fire weather. Surface fuel loadings were spatially variable within the 25.6 ha study area, reflecting variation in litter and duff near large trees, and the presence of large CWD pieces. This heterogeneity likely contributes to variation in fire severity at small scales and heterogeneity in the post-fire environment. This study makes a unique contribution by investigating variability of pre- and post-fire fuel loading within a single intensively measured site in a large-statured old-growth forest. The size of our research site is closely aligned with the size of a typical prescribed fire unit. Thus, our results have direct relevance to management and restoration of fire-excluded old-growth mixed-conifer forests.
References
Agee, J.K., and M.H. Huff. 1987. Fuel succession in a western hemlock/Douglas-fir forest. Canadian Journal of Forest Research 17: 697–704.
Albini, F.A., J.K. Brown, E.D. Reinhardt, and R.D. Ottmar. 1995. Calibration of a large fuel burnout model. International Journal of Wildland Fire 5: 173–192. https://doi.org/10.1071/WF9950173.
Albini, F.A., and E.D. Reinhardt. 1997. Improved calibration of a large fuel burnout model. International Journal of Wildland Fire 7: 21–28. https://doi.org/10.1071/WF9970021.
Banwell, E.M., J.M. Varner, E.E. Knapp, and R.W. Van Kirk. 2013. Spatial, seasonal, and diel forest floor moisture dynamics in Jeffrey pine-white fir forests of the Lake Tahoe Basin, USA. Forest Ecology and Management 305: 11–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2013.05.005.
Barth, M.A.F., A.J. Larson, and J.A. Lutz. 2015. A forest reconstruction model to assess changes to Sierra Nevada mixed-conifer forest during the fire suppression era. Forest Ecology and Management 354: 104–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2015.06.030.
Blomdahl, E.M., C.A. Kolden, A.J.H. Meddens, and J.A. Lutz. 2019. The importance of small fire refugia in the central Sierra Nevada, California, USA. Forest Ecology and Management 432: 1041–1052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2018.10.038.
Brown, J.K. 1974. Handbook for inventorying downed woody material. USDA Forest Service General Technical Report INT-16. Ogden, Utah: USDA Forest Service, Intermountain Forest and Range Experiment Station.
Brown, J.K., M.A. Marsden, K.C. Ryan, and E.D. Reinhardt. 1985. Predicting duff and woody fuel consumed by prescribed fire in the northern Rocky Mountains. USDA Forest Service Research Paper INT-337. Ogden, Utah: USDA Forest Service, Intermountain Forest and Range Experiment Station. https://doi.org/10.2737/INT-RP-337.
Brown, J.K., E.D. Reinhardt, and K.A. Kramer. 2003. Coarse woody debris: managing benefits and fire hazard in the recovering forest. USDA Forest Service General Techmical Report RMRS-GTR-105. Ogden, Utah: USDA Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station. https://doi.org/10.2737/RMRS-GTR-105.
Bull, E.L. 2002. The value of coarse woody debris to vertebrates in the Pacific Northwest. In Proceedings of the symposium on the ecology and management of dead wood in western forests. USDA Forest Service General Technical Report PSW-GTR-181, ed. W.F. Laudenslayer Jr., P.J. Shea, B.E. Valentine, C.P. Weatherspoon, and T.E. Lisle, technical coordinators. Pages 171–178. Albany, California: USDA FOrest Service, Pacific Southwest Research Station. https://doi.org/10.2737/PSW-GTR-181.
Campbell, J., D. Donato, D. Azuma, and B. Law. 2007. Pyrogenic carbon emission from a large wildfire in Oregon, United States. Journal of Geophysical Research 112: G04014. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007JG000451.
Certini, G. 2005. Effects of fire on properties of forest soils: a review. Oecologia 143: 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-004-1788-8.
Collins, B.M., S.L. Stephens, J.J. Moghaddas, and J. Battles. 2010. Challenges and approaches in planning fuel treatments across fire-excluded forested landscapes. Journal of Forestry 108: 24–31.
Daly, C., M. Halbleib, J.I. Smith, W.P. Gibson, M.K. Doggett, G.H. Taylor, J. Curtis, and P.P. Pasteris. 2008. Physiographically sensitive mapping of climatological temperature and precipitation across the conterminous United States. International Journal of Climatolology 28: 2031–2064. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1688.
Demaerschalk, J.P., and S.A.Y. Omule. 1982. Estimating breast height diameters from stump measurements in British Columbia. The Forestry Chronicle 53 (3): 143–146. https://doi.org/10.5558/tfc58143-3.
Flora of North America Editorial Committee, ed. 1993. Flora of North America north of Mexico. 20+ volumes. New York, New York: Oxford University Press.
Fosberg, M.A. 1970. Drying rates of heartwood below fiber saturation. Forest Science 16: 57–63.
French, N.H.F., W.J. de Groot, L.K. Jenkins, B.M. Rogers, E. Alvarado, B. Amiro, B. de Jong, S. Goetz, E. Hoy, E. Hyer, R. Keane, B.E. Law, D. McKenzie, S.G. McNulty, R. Ottmar, D.R. Pérez-Salicrup, J. Randerson, K.M. Robertson, and M. Turetsky. 2011. Model comparisons for estimating carbon emissions from North American wildland fire. Journal of Geophysical Research 116: G00K05. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JG001469.
Furniss, T.J., A.J. Larson, V.R. Kane, and J.A. Lutz. 2019. Multi-scale assessment of post-fire tree mortality models. International Journal of Wildland Fire 28: 46–61. https://doi.org/10.1071/WF18031.
Garlough, E.C., and C.R. Keyes. 2011. Influences of moisture content, mineral content and bulk density on smouldering combustion of ponderosa pine duff mounds. International Journal of Wildland Fire 20: 589–596. https://doi.org/10.1071/WF10048.
Grayson, L., D. Cluck, and S. Hood. 2019. Persistence of fire-killed conifer snags in California. Fire Ecology 15: 1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42408-018-0007-7.
Harmon, M.E., and J. Sexton. 1996. Guidelines for measurements of woody detritus in forest ecosystems. Long-Term Ecological Research Publication No. 20. Seattle Washington: Network Office, University of Washington.
Harmon, M.E., C.W. Woodall, B. Fasth, and J. Sexton. 2008. Woody detritus density and density reduction factors for tree species in the United States: a synthesis. USDA Forest Service General Technical Report NRS-29. Newton Square, Pennsylvania: USDA Forest Service, Northern Research Station. https://doi.org/10.2737/NRS-GTR-29.
Hille, M., and J. den Ouden. 2005. Fuel load, humus consumption and humus moisture dynamics in Central European Scots pine stands. International Journal of Wildland Fire 14: 153–159. https://doi.org/10.1071/WF04026.
Hille, M.G., and S.L. Stephens. 2005. Mixed conifer forest duff consumption during prescribed fires: tree crown impacts. Forest Science 51: 417–424.
Hood, S., C.A. Cansler, P. van Mantgem, and J.M. Varner. 2018. Fire and tree death: understanding and improving modeling of fire-induced tree mortality. Environmental Research Letters 13 (11): 113004. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aae934.
Hood, S.M. 2010. Mitigating old tree mortality in long-unburned, fire-dependent forests: a synthesis. USDA Forest Service General Technical Report RMRS-GTR-238. Fort Collins, Colorado: USDA Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station. https://doi.org/10.2737/RMRS-GTR-238.
Hood, S.M., S.L. Smith, and D.R. Cluck. 2010. Predicting mortality for five California conifers following wildfire. Forest Ecology and Management 260: 750–762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2010.05.033.
Hyde, J.C., A.M. Smith, R.D. Ottmar, E.C. Alvarado, and P. Morgan. 2011. The combustion of sound and rotten coarse woody debris: a review. International Journal of Wildland Fire 20: 163–174.
Janisch, J.E., and M.E. Harmon. 2002. Successional changes in live and dead wood carbon stores: implications for net ecosystem productivity. Tree Physiology 22: 77–89. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/22.2-3.77.
Jenkins, M.J., W.G. Page, E.G. Hebertson, and M.E. Alexander. 2012. Fuels and fire behavior dynamics in bark beetle-attacked forests in western North America and implications for fire management. Forest Ecology and Management 275: 23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2012.02.036.
Kauffman, J.B., and R.E. Martin. 1989. Fire behavior, fuel consumption, and forest-floor changes following prescribed understory fires in Sierra Nevada mixed conifer forests. Canadian Journal of Forest Research 53: 1689–1699. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004.
Keane, R.E., S.F. Arno, and C.A. Stewart. 2000. Ecosystem-based management in the Whitebark Pine Zone. In Bitterroot Ecosystem Management Restoration Project: what we have learned. USDA Forest Service Proceedings RMRS-P-17, ed. H. Smith. Pages 36–40. Ogden, Utah: USDA Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station.
Knapp, E.E., J.E. Keeley, E.A. Ballenger, and T.J. Brennan. 2005. Fuel reduction and coarse woody debris dynamics with early season and late season prescribed fire in a Sierra Nevada mixed conifer forest. Forest Ecology and Management 208: 383–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2005.01.016.
Koenigs, E., P.J. Shea, R. Borys, and M.L. Haverty. 2002. An investigation of the insect fauna associated with coarse woody debris of Pinus ponderosa and Abies concolor in northeastern California. In Proceedings of the symposium on the ecology and management of dead wood in Western forests. USDA Forest Service General Technical Report PSW-GTR-181, ed. W.F. Laudenslayer Jr., P.J. Shea, B.E. Valentine, C.P. Weatherspoon, and T.E. Lisle, technical coordinators. Pages 97–110. Albany, California: USDA FOrest Service, Pacific Southwest Research Station.
Kolb, T.E., J.K. Agee, P.Z. Fulé, N.G. McDowell, K. Pearson, A. Sala, and R.H. Waring. 2007. Perpetuating old ponderosa pine. Forest Ecology and Management 249: 141–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2007.06.002.
Larson, A.J., R.T. Belote, C.A. Cansler, S.A. Parks, and M.S. Dietz. 2013. Latent resilience in ponderosa pine forest: effects of resumed frequent fire. Ecological Applications 23: 1243–1249. https://doi.org/10.1890/13-0066.1.
Larson, A.J., C.A. Cansler, S.G. Cowdery, S. Hiebert, T.J. Furniss, M.E. Swanson, and J.A. Lutz. 2016. Post-fire morel (Morchella) mushroom abundance, spatial structure, and harvest sustainability. Forest Ecology and Management 377: 16–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2016.06.038.
Lutes, D., R.E. Keane, and E.D. Reinhardt. 2012. FOFEM 6.0 user guide. Fort Collins, Colorado: USDA Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station.
Lutes, D.C., R.E. Keane, and J.F. Caratti. 2009. A surface fuel classification for estimating fire effects. International Journal of Wildland Fire 18: 802–814. https://doi.org/10.1071/WF08062.
Lutz, J., A. Larson, and M. Swanson. 2018b. Advancing fire science with large forest plots and a long-term multidisciplinary approach. Fire 1(1): 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire1010005
Lutz, J.A., T.J. Furniss, S.J. Germain, K.M.L. Becker, E.M. Blomdahl, S.M.A. Jeronimo, C.A. Cansler, J.A. Freund, M.E. Swanson, and A.J. Larson. 2017. Shrub communities, spatial patterms, and shrub-mediated tree mortality following reintorduced fire in Yosemite National Park, California, USA. Fire Ecology 13: 104–126. https://doi.org/10.4996/fireecology.1301104.
Lutz, J.A., T.J. Furniss, D.J. Johnson, S.J. Davies, D. Allen, A.Alonso, K.J. Anderson-Teixeira, A. Andrade, J. Baltzer, K.M. L. Becker, E.M. Blomdahl, N.A. Bourg, S. Bunyavejchewin, D.F.R.P. Burslem, C.A. Cansler, K. Cao, M. Cao, D. Cárdenas, L.-W. Chang, K.-J. Chao, W.-C. Chao, J.-M. Chiang, C. Chu, G.B. Chuyong, K. Clay, R. Condit, S. Cordell, H.S. Dattaraja, A. Duque, C. E.N. Ewango, Gunter A. Fischer, Christine Fletcher, James A. Freund, Christian Giardina, Sara J. Germain, G.S. Gilbert, Z.Hao, T.Hart, B.C.H. Hau, F. He, A. Hector, R.W. Howe, C.-F. Hsieh, Y.-H. Hu, S.P. Hubbell, F.M. Inman-Narahari, A. Itoh, D. Janík, A.R. Kassim, D. Kenfack, L. Korte, K. Král, A.J. Larson, Y. Li, Y. Lin, S. Liu, S. Lum, K. Ma, J.-R. Makana, Y. Malhi, S.M. McMahon, W.J. McShea, H.R. Memiaghe, X. Mi, M. Morecroft, P.M. Musili, J.A. Myers, V. Novotny, A. de Oliveira, P. Ong, D.A. Orwig, R. Ostertag, G.G. Parker, R. Patankar, R.P. Phillips, G. Reynolds, L. Sack, G.-Z.M. Song, S.-H. Su, R. Sukumar, I-F. Sun, H.S. Suresh, M.E. Swanson, S.Tan, D.W. Thomas, J. Thompson, M. Uriarte, R. Valencia, A. Vicentini, T. Vrška, X. Wang, G.D. Weiblen, A.Wolf, S.-H. Wu, H. Xu, T. Yamakura, S. Yap, J.K. Zimmerman. 2018a. Global importance of large-diameter trees. Global Ecology and Biogeography 27: 849–864. https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.12747
Lutz, J.A., A.J. Larson, M.E. Swanson, and J.A. Freund. 2012. Ecological importance of large-diameter trees in a temperate mixed-conifer forest. PLoS ONE 7: e36131. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0036131.
Lutz, J.A., K.A. Schwindt, T.J. Furniss, J.A. Freund, M.E. Swanson, K.I. Hogan, G.E. Kenagy, and A.J. Larson. 2014. Community composition and allometry of Leucothoe davisiae, Cornus sericea, and Chrysolepis sempervirens. Canadian Journal of Forest Research 44: 677–683. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjfr-2013-0524.
Lutz, J.A., J.W. van Wagtendonk, and J.F. Franklin. 2009a. Twentieth-century decline of large-diameter trees in Yosemite National Park, California, USA. Forest Ecology and Management 257: 2296–2307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2009.03.009
Lutz, J.A., J.W. van Wagtendonk, A.E. Thode, J.D. Miller, and J.F. Franklin. 2009b. Climate, lightning ignitions, and fire severity in Yosemite National Park, California, USA. International Journal of Wildland Fire 18: 765-774. https://doi.org/10.1071/WF08117
Lydersen, J.M., B.M. Collins, E.E. Knapp, G.B. Roller, and S. Stephens. 2015. Relating fuel loads to overstorey structure and composition in a fire-excluded Sierra Nevada mixed conifer forest. Internatioanl Journal of Wildland Fire 24: 484–494. https://doi.org/10.1071/WF13066.
Maser, C., R.G. Anderson, K.J. Cromack, et al. 1979. Dead and down woody material. Dead and Down Woody Material. In: Thomas JW (ed) Wildlife habitats in managed forests: the Blue Mountains of Oregon and Washington, vol. 553. USDA Forest Service Agriculture Handbook. Washington, DC., US Government Printing Office
Moghaddas, E.E.Y., and S.L. Stephens. 2007. Thinning, burning, and thin-burn fuel treatment effects on soil properties in a Sierra Nevada mixed-conifer forest. Forest Ecology and Management 250: 156–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2007.05.011.
Moore, M.M., C.A. Casey, J.D. Bakker, J.D. Springer, P.Z. Fulé, W.W. Covington, and D.C. Laughlin. 2006. Herbaceous vegetation responses (1992–2004) to restoration treatments in a ponderosa pine forest. Rangeland Ecology and Management 59: 135–144. https://doi.org/10.2111/05-051R2.1.
Morrison, M.L., and M.G. Raphael. 1993. Modeling the dynamics of snags. Ecological Applications 3: 322–330. https://doi.org/10.2307/1941835.
Nesmith, J.C.B., K.L. O’Hara, P.J. van Mantgem, and P. de Valpine. 2010. The effects of raking on sugar pine mortality following prescribed fire in Sequoia and Kings Canyon national parks, California, USA. Fire Ecology 6 (3): 97–116. https://doi.org/10.4996/fireecology.0603097.
Passovoy, M.D., and P.Z. Fulé. 2006. Snag and woody debris dynamics following severe wildfires in northern Arizona ponderosa pine forests. Forest Ecology and Management 223: 237–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2005.11.016.
Pinheiro, J., D. Bates, S. DebRoy, D. Sarkar, and R. Core Team. 2018. nlme: linear and nonlinear mixed effects models. R package version 3.1-131. <https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=nlme>. Accessed 1 Mar 2018.
Prichard, S.J., E.C. Karau, R.D. Ottmar, M.C. Kennedy, J.B. Cronan, C.S. Wright, and R.E. Keane. 2014. Evaluation of the CONSUME and FOFEM fuel consumption models in pine and mixed hardwood forests of the eastern United States. Canadian Journal of Forest Research 44: 784–795. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjfr-2013-0499.
PRISM Climate Group. 2004. Northwest alliance for computational science and engineering. <http://www.prismclimate.org. Accessed 1 May 2018.
R Core Team. 2017. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Version 3.4.3. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing.
Ryan, K.C., and W.H. Frandsen. 1991. Basal injury from smoldering fires in mature Pinus ponderosa Laws. International Journal of Wildland Fire 1 (2): 107–118. https://doi.org/10.1071/WF9910107.
Ryan, K.C., E.E. Knapp, and J.M. Varner. 2013. Prescribed fire in North American forests and woodlands: history, current practice, and challenges. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 11: e15–e24. https://doi.org/10.1890/120329.
Sackett, S.S., and S.M. Haas. 1998. Two case histories for using prescribed fire to restore ponderosa pine ecosystems in northern Arizona. In Proceedings of the 20 th Tall Timbers fire ecology conference—fire in ecosystem management: shifting the paradigm from suppression to prescription, ed. T.L. Pruden and L.A. Brennan. Pages 380–389. Tallahassee, Florida: Tall Timbers Research Station.
Sikkink, P.G., and R.E. Keane. 2008. A comparison of five sampling techniques to estimate surface fuel loading in montane forests. International Journal of Wildland Fire 17: 363–379. https://doi.org/10.1071/WF07003.
Stalling, C., R.E. Keane, and M. Retzlaff. 2017. Surface fuel changes after severe disturbances in northern Rocky Mountain ecosystems. Forest Ecology and Management 400: 38–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2017.05.020.
Stavros, E.N., Z. Tane, V.R. Kane, S.R. Veraverbeke, R.J. McGaughey, J.A. Lutz, C. Ramirez, and D. Schimel. 2016. Unprecedented remote sensing data over King and Rim megafires in the Sierra Nevada mountains of California. Ecology 97: 3244–3244. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecy.1577.
Stephens, S., and J. Moghaddas. 2005a. Experimental fuel treatment impacts on forest structure, potential fire behavior, and predicted tree mortality in a California mixed conifer forest. Forest Ecology and Management 215: 21–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2005.03.070
Stephens, S.L. 2004. Fuel loads, snag abundance, and snag recruitment in an unmanaged Jeffrey pine–mixed conifer forest in northwestern Mexico. Forest Ecology and Management 199: 103–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2004.04.017.
Stephens, S.L., and J.J. Moghaddas. 2005b. Fuel treatment effects on snags and coarse woody debris in a Sierra Nevada mixed conifer forest. Forest Ecology and Management 214: 53–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2005.03.055
Swezy, D.M., and J.K. Agee. 1991. Prescribed-fire effects on fine-root and tree mortality in old-growth ponderosa pine. Canadian Journal of Forest Research 21: 626–634. https://doi.org/10.1139/x91-086.
van Wagtendonk, J.W. 1996. Physical properties of woody fuel particles Sierra Nevada conifers. International Journal of Wildland Fire 6: 117–123. https://doi.org/10.1071/WF9960117.
van Wagtendonk, J.W., J.M. Benedict, and W.M. Sydoriak. 1998. Fuel bed characteristics of Sierra Nevada conifers. Western Journal of Applied Forestry 13: 73–84.
van Wagtendonk, J.W., and J.A. Lutz. 2007. Fire regime attributes of wildland fires in Yosemite National Park, USA. Fire Ecology 3 (2): 34–52. https://doi.org/10.4996/fireecology.0302034.
van Wagtendonk, J.W., and P.E. Moore. 2010. Fuel deposition rates of montane and subalpine conifers in the central Sierra Nevada, California, USA. Forest Ecology and Management 259: 2122–2132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2010.02.024.
Varner, J.M., D.R. Gordon, F.E. Putz, and J.K. Hiers. 2005. Restoring fire to long-unburned Pinus palustris ecosystems: novel fire effects and consequences for long-unburned ecosystems. Restoration Ecology 13: 536–544. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1526-100X.2005.00067.x.
Varner, J.M., F.E. Putz, J.J. O’Brien, J.K. Hiers, R.J. Mitchell, and D.R. Gordon. 2009. Post-fire tree stress and growth following smoldering duff fires. Forest Ecology and Management 258: 2467–2474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2009.08.028.
Yocom-Kent, L.L., K.L. Shive, B.A. Strom, C.H. Sieg, M.E. Hunter, C.S. Stevens-Rumann, and P.Z. Fulé. 2015. Interactions of fuel treatments, wildfire severity, and carbon dynamics in dry conifer forests. Forest Ecology and Management 349: 66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2015.04.004.
Acknowledgements
We thank Yosemite National Park for logistical assistance and the Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot field crews, especially R. Burke, each individually acknowledged at http://yfdp.org This work was performed under National Park Service research permits YOSE-2011-SCI-0015, YOSE-2012-SCI-0059, YOSE-2013-SCI-0012, and YOSE-2014-SCI-0012 for study YOSE-0051.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Park Service (Awards P14AC00122 and P14AC00197). This work was supported by the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture (McIntire Stennis accession number 1000655), and the Utah Agricultural Experiment Station (projects 1153 and 1398).
Availability of data and materials
-
1.
The fuel datasets generated or analyzed during the current study are available through the Utah State University Digital Commons repository: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/all_datasets/51/; https://doi.org/10.15142/T3G93X
-
2.
Tree and snag data are available through the Smithsonian ForestGEO data portal: https://forestgeo.si.edu
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors designed the research, conducted field sampling, analyzed data, contributed to writing the manuscript, and approved the final manuscript. C.A. Cansler developed the final field methods and conceptual models, performed and synthesized all analyses, and wrote the manuscript. M.E. Swanson developed field methods, and developed some analyses.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Additional files
Additional file 1:
Example arrangement of litter and duff mound sampling transects in relation to a tree. Each is 3 m long. Duff mounds were measured in the Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot, Yosemite National Park, California, USA. Pre-fire measurements were taken in August 2013, prior to the Rim Fire in September 2013, and the post-fire fuel measurements were taken in June 2014. (PDF 66 kb)
Additional file 2:
Assessment of variability in estimated means as function of sample size for 1-hour fuels measured in the Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot, Yosemite National Park, California, USA. Fuel transects were measured in June 2011, before the 2013 Rim Fire, and after the fire in June 2014. To identify the minimum sample size for each fuel class, we selected random samples of different numbers of individual transects (woody fuels; n = 1 to 99 transects) from our populations of pre-fire and post-fire samples and calculated mean and standard deviations of mass for each sample. Those summary statistics were plotted against sample size. Stabilization (stationarity) of variance was assessed graphically with the use of two envelope widths: the estimated mean within ±20% of the mean and ±10% of the mean. This procedure was repeated 10 times for each fuel class. Red and blue dotted lines represent ±10% and ±20% of mean values, respectively. (PDF 522 kb)
Additional file 3:
Assessment of variability in estimated means as function of sample size for 10-hour fuels measured in the Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot, Yosemite National Park, California, USA. Fuel transects were measured in June 2011, before the 2013 Rim Fire, and after the fire in June 2014. To identify the minimum sample size for each fuel class, we selected random samples of different numbers of individual transects (woody fuels; n = 99 transects) from our populations of pre-fire and post-fire samples and calculated mean and standard deviations of mass for each sample. Those summary statistics were plotted against sample size. Stabilization (stationarity) of variance was assessed graphically with the use of two envelope widths: the estimated mean within ±20% of the mean and ±10% of the mean. This procedure was repeated 10 times for each fuel class. Red and blue dotted lines represent ±10% and ±20% of mean values, respectively. (PDF 514 kb)
Additional file 4:
Assessment of variability in estimated means as function of sample size for 100-hour fuels measured in the Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot, Yosemite National Park, California, USA. Fuel transects were measured in June 2011, before the 2013 Rim Fire, and after the fire in June 2014. To identify the minimum sample size for each fuel class, we selected random samples of different numbers of individual transects (woody fuels; n = 1 to 99 transects) from our populations of pre-fire and post-fire samples and calculated mean and standard deviations of mass for each sample. Those summary statistics were plotted against sample size. Stabilization (stationarity) of variance was assessed graphically with the use of two envelope widths: the estimated mean within ±20% of the mean and ±10% of the mean. This procedure was repeated 10 times for each fuel class. Red and blue dotted lines represent ±10% and ±20% of mean values, respectively. (PDF 512 kb)
Additional file 5:
Assessment of variability in estimated means as function of sample size for CWD fuels measured in the Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot, Yosemite National Park, California, USA. Fuel transects were measured in June 2011, before the 2013 Rim Fire, and after the fire in June 2014. To identify the minimum sample size for each fuel class, we selected random samples of different numbers of individual transects (woody fuels; n = 1 to 99 transects) from our populations of pre-fire and post-fire samples and calculated mean and standard deviations of mass for each sample. Those summary statistics were plotted against sample size. Stabilization (stationarity) of variance was assessed graphically with the use of two envelope widths: the estimated mean within ±20% of the mean and ±10% of the mean. This procedure was repeated 10 times for each fuel class. Red and blue dotted lines represent ±10% and ±20% of mean values, respectively. (PDF 516 kb)
Additional file 6:
Assessment of variability in estimated means as function of sample size for litter measured in the Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot, Yosemite National Park, California, USA. Fuel transects were measured in June 2011, before the 2013 Rim Fire, and after the fire in June 2014. To identify the minimum sample size for each fuel class, we selected random samples of different numbers of sample point locations (litter and duff; n = 1 to 990 points) from our populations of pre-fire and post-fire samples and calculated mean and standard deviations of mass for each sample. Those summary statistics were plotted against sample size. Stabilization (stationarity) of variance was assessed graphically with the use of two envelope widths: the estimated mean within ±20% of the mean and ±10% of the mean. This procedure was repeated 10 times for each fuel class. Red and blue dotted lines represent ±10% and ±20% of mean values, respectively. (PDF 469 kb)
Additional file 7:
Assessment of variability in estimated means as function of sample size for duff measured in the Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot, Yosemite National Park, California, USA. Fuel transects were measured in June 2011, before the 2013 Rim Fire, and after the fire in June 2014. To identify the minimum sample size for each fuel class, we selected random samples of different numbers of sample point locations (litter and duff; n = 1 to 990 points) from our populations of pre-fire and post-fire samples and calculated mean and standard deviations of mass for each sample. Those summary statistics were plotted against sample size. Stabilization (stationarity) of variance was assessed graphically with the use of two envelope widths: the estimated mean within ±20% of the mean and ±10% of the mean. This procedure was repeated 10 times for each fuel class. Red and blue dotted lines represent ±10% and ±20% of mean values, respectively. (PDF 461 kb)
Additional file 8:
Assessment of variability in estimated means as function of sample size for total fuels measured in the Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot, Yosemite National Park, California, USA. Fuel transects were measured in June 2011, before the 2013 Rim Fire, and after the fire in June 2014. To identify the minimum sample size for each fuel class, we selected random samples of different numbers of individual transects (total fuels; n = 1 to 99 transects) from our populations of pre-fire and post-fire samples and calculated mean and standard deviations of mass for each sample. Those summary statistics were plotted against sample size. Stabilization (stationarity) of variance was assessed graphically with the use of two envelope widths: the estimated mean within ±20% of the mean and ±10% of the mean. This procedure was repeated 10 times for each fuel class. Red and blue dotted lines represent ±10% and ±20% of mean values, respectively. (PDF 524 kb)
Additional file 9:
Mean and standard deviation (SD) in fuel mass for each fuel class in the Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot, Yosemite National Park, California, USA. Measurements were taken in June 2011 for “pre-fire” times, and in June 2014 for “post-fire” times, before and after the Rim Fire burned the research site in September 2013. “Post-fire old” refers to fuel that was present before fire and did not burn. “Post-fire new” refers to surface fuel that accumulated after fire. (PDF 23 kb)
Additional file 10:
Non-linear models of litter and duff depth for eight P. lambertiana measured in the Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot, Yosemite National Park, California, USA. Fuel transects were measured in June 2011, before the 2013 Rim Fire, and after the fire in June 2014. Error bars represent the standard error around the mean, and colors from light to dark represent small to large diameter (DBH in cm) trees. Models could not be fit for duff 1 year after fire because of the high number of zero depth measurements. Measurements were of duff mounds in the Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot, Yosemite National Park, California, USA. Pre-fire measurements were taken in August 2013, prior to the Rim Fire in September 2013, and the total post-fire fuel was measured in June 2014. (PDF 354 kb)
Additional file 11:
Ricker curve-linear model results for litter depth (cm) as a function of distance (m) from eight P. lambertiana. Measurements were of duff mounds in the Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot, Yosemite National Park, California, USA. Pre-fire measurements were taken in August 2013, prior to the Rim Fire in September 2013, and post-fire measurements were taken in June 2014. Estimates of regression coefficients (a; B) are given, as are the stand error of the estimate (SE), t-statistic, and P-values. (PDF 22 kb)
Additional file 12:
Ricker curve model results for pre-fire duff depth (cm) as a function of distance (m) from eight P. lambertiana in the Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot, Yosemite National Park, California, USA, and were taken in August 2013, prior to the Rim Fire in September 2013. Estimates of regression coefficients (a; B) are given, as are the stand error of the estimate (SE), t-statistic, and P-values. (PDF 21 kb)
Additional file 13:
Litter and duff mound regression models for the fuel loading of litter and duff normalized by surface area as a function of tree DBH for eight P. lambertiana trees. Measurements were of duff mounds in the Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot, Yosemite National Park, California, USA. Pre-fire measurements were taken in August 2013, prior to the Rim Fire in September 2013, and the post-fire fuel measurements were taken in June 2014. Models were significant for ≤1 m and ≤2 m from the trees. Intercept and slope are given, as are stand error (SE), t-statistic, and P-values. Adj. R2 = adjusted R2. (PDF 20 kb)
Additional file 14:
Scatter plots and regression between overstory basal area and fuel loadings of live basal area for all trees (left), Abies concolor (ABCO, middle), and Pinus lambertiana (PILA, right), for each fuel class. Pre-fire fuel loadings and overstory trees were measured in the Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot, Yosemite National Park, California, USA, in June 2011, before the 2013 Rim Fire. Overstory basal area was sampled at local neighborhoods around fuel sampling locations within 0.015 ha (6.91 m radius). Overstory components are labeled on the x-axis. Only significant regressions are plotted (blue lines with grey confidence intervals). The coefficient of determination is labeled on all scatter plots: note that even significant regression explained only 10% of the variance, at most. (PDF 3528 kb)
Additional file 15:
Scatter plots and regression between overstory basal area and fuel loadings of basal area for all dead trees (far left), dead Abies concolor (ABCO, middle left), and dead Pinus lambertiana (PILA, middle right), and all live and dead trees (far right) for each fuel class. Pre-fire fuel loadings and overstory trees were measured in the Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot, Yosemite National Park, California, USA, in June 2011, before the 2013 Rim Fire. Overstory basal area was sampled at local neighborhoods around fuel sampling locations within 0.015 ha (6.91 m radius). Overstory components are labeled on the x-axis. Only significant regressions are plotted (blue lines with grey confidence intervals). The coefficient of determination is labeled on all scatter plots: note that even significant regression explained only 5% of the variance, at most. (PDF 3528 kb)
Additional file 16:
Scatter plots and regression between overstory basal area and fuel loadings of live basal area for all trees (left), Abies concolor (ABCO, middle), and Pinus lambertiana (PILA, right), for each fuel class. Pre-fire fuel loadings and overstory trees were measured in the Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot, Yosemite National Park, California, USA, in June 2011, before the 2013 Rim Fire. Overstory basal area was sampled at local neighborhoods around fuel sampling locations within 0.1 ha (17.84 m radius). Overstory components are labeled on the x-axis. Only significant regressions are plotted (blue lines with grey confidence intervals). The coefficient of determination is labeled on all scatter plots: note that even significant regression explained only 7% of the variance, at most. (PDF 3528 kb)
Additional file 17:
Scatter plots and regression between overstory basal area and fuel loadings of basal area for all dead trees (far left), dead Abies concolor (ABCO, middle left), and dead Pinus lambertiana (PILA, middle right), and all live and dead trees (far right) for each fuel class. Pre-fire fuel loadings and overstory trees were measured in the Yosemite Forest Dynamics Plot, Yosemite National Park, California, USA, in June 2011, before the 2013 Rim Fire. Overstory basal area was sampled at local neighborhoods around fuel sampling locations within 0.1 ha (17.84 m radius). Overstory components are labeled on the x-axis. Only significant regressions are plotted (blue lines with grey confidence intervals). The coefficient of determination is labeled on all scatter plots: note that even significant regression explained only 5% of the variance, at most. (PDF 3528 kb)
Appendix
Appendix
Supplemental Methods
Data reduction: duff mounds
Distributions for larger pre-fire trees were humped near each tree because depth measurements were often shallower close to the tree where the trees roots were just under the litter layer. Because preliminary analysis showed that the distributions were also right-skewed, we used a Ricker curve to model the distribution (Equation 3; Additional files 10, 11 and 12.
where a and b are constants, x is distance from the tree, and y is litter or duff depth. Modeling was done using the nlme package version 3.1-131.1 (Pinheiro et al. 2018).
Because the depths of litter and duff one year after fire were often zero, we were not able to model them using a Ricker curve, or other regression. Therefore, we calculated the mean depth for each of those measurements from 0 to 1 m and 0 to 2 m, and used those means to calculate fuel loadings and bulk densities (Additional file 10).
To calculate the total volumes of litter and duff within each pre-fire duff mound, we numerically integrated the area beneath the fitted Ricker curve for each tree. We implemented this by calculating the volume of litter and duff in concentric 0.2 m bands around each tree and then summed the section volumes from ≤1 m and ≤2 m from each tree. Volumes for each band were calculated using the formula for a cylinder with a smaller cylinder missing from the center:
where V= volume, r1 = the larger radius and r2 = the smaller radius, and h = calculated mean height (depth) for each 0.2-meter section. We determined r1 and r2 by adding the basal radius of the tree to each section start and end distance. The basal radius was modeled based on the DBH of the tree, following the equation for western yellow pine in Demaerschalk and Omule (1982): Equation 4
where DS = stump diameter, and SH = stump height. Therefore, where SH = 0:
Volumes were converted to bulk densities (kg m−2) using the bulk densities for sugar pine litter and duff (40.768 kg m−3 and 160.960 kg m−3, respectively) from van Wagtendonk et al. (1998).
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Cansler, C.A., Swanson, M.E., Furniss, T.J. et al. Fuel dynamics after reintroduced fire in an old-growth Sierra Nevada mixed-conifer forest. fire ecol 15, 16 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42408-019-0035-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s42408-019-0035-y