Abstract
Background
Cotton is a strategically important fibre crop for global textile industry. It profoundly impacts several countries' industrial and agricultural sectors. Sustainable cotton production is continuously threatened by the unpredictable changes in climate, specifically high temperatures. Breeding heat-tolerant, high-yielding cotton cultivars with wide adaptability to be grown in the regions with rising temperatures is one of the primary objectives of modern cotton breeding programmes. Therefore, the main objective of the current study is to figure out the effective breeding approach to imparting heat tolerance as well as the judicious utilization of commercially significant and stress-tolerant attributes in cotton breeding. Initially, the two most notable heat-susceptible (FH-115 and NIAB Kiran) and tolerant (IUB-13 and GH-Mubarak) cotton cultivars were spotted to develop filial and backcross populations to accomplish the preceding study objectives. The heat tolerant cultivars were screened on the basis of various morphological (seed cotton yield per plant, ginning turnout percentage), physiological (pollen viability, cell membrane thermostability) and biochemical (peroxidase activity, proline content, hydrogen peroxide content) parameters.
Results
The results clearly exhibited that heat stress consequently had a detrimental impact on every studied plant trait, as revealed by the ability of crossing and their backcross populations to tolerate high temperatures. However, when considering overall yield, biochemical, and physiological traits, the IUB-13 × FH-115 cross went over particularly well at both normal and high temperature conditions. Moreover, overall seed cotton yield per plant exhibited a positive correlation with both pollen viability and antioxidant levels (POD activity and proline content).
Conclusions
Selection from segregation population and criteria involving pollen viability and antioxidant levels concluded to be an effective strategy for the screening of heat-tolerant cotton germplasms. Therefore, understanding acquired from this study can assist breeders identifying traits that should be prioritized in order to develop climate resilient cotton cultivars.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Transitional environmental conditions have had an impact on the productivity and sustainability of almost every field crop by altering their growth patterns and tolerance to extreme temperatures. The extreme temperatures and other abiotic and biotic environmental factors are dynamic in the nature. These factors are strongly interlinked and the severity of each factor depends on other factors. The change in rainfall patterns, prolonged dry seasons, deforestation and introduction of new species in a new area cause changes in overall environment. Therefore, breeders are always faced with the challenge of developing novel and adaptable germplasms for crops. Cotton (especially Gossypium hirsutum L.) is a major source of oil and natural fiber. Cotton growth and productivity are severely impacted by heat stress. Cotton is primarily grown across tropical and subtropical climates where the usual temperature during the growing season is between 40 °C and 45 °C. In addition, water scarcity is closely associated with heat stress, and many cotton growing regions also face restricted or unpredictable water supplies.
It is necessary to develop appropriate selection criteria for evaluating the cotton germplasm's resilience to heat stress. During the early growth of cotton, high temperatures may adversely affect productivity and quality. Often, high temperature stress induces metabolic changes in addition to morphological and physiological changes in plants that result in elevated concentrations of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (Mittler et al., 2004). ROS include superoxide radical (·O2 −), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), hydroxyl radicals (·OH) and singlet oxygen (1O2) (Das et al., 2014). These species play an important role in the cells and regulate activities of cellular organelles, i.e., peroxisome, chloroplast, and mitochondria (Møller, 2001; Roychoudhury et al., 2012), these species are also involved in apoptosis (programmed cell death) (Gechev et al., 2006; Petrov et al., 2015). An optimal level of ROS is always maintained because these species also act as signalling molecules under several biotic and abiotic stresses (Foyer et al., 2005). High level of ROS may damage the DNA, protein and lipid components of the cells and disturb its normal functions (Apel et al., 2004; Gill et al., 2010). Plants continuously produce antioxidant molecules to maintain the optimal level of ROS because high concentrations of H2O2 and other ROS may cause irreversible damage.
When ROS level increase, concentrations of various enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants increase in response to scavenge the excess ROS (Sekmen et al., 2014). The enzymatic antioxidants include superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidases (POD), catalase (CAT) and ascorbate peroxidase (APO) (Ahmad et al., 2010; Gür et al., 2010). Non-enzymatic antioxidants include proline, carotenoids, ascorbic acid, flavonoids and phenolics. These antioxidants are actively involved in optimizing ROS level (Sakihama et al., 2002; Stahl et al., 2003; Hernández et al., 2009; Wu et al., 2015). Researchers have quantified the concentration of antioxidants and ROS in various plant species including wheat (Caverzan et al., 2016), cotton (Gossett et al., 1994; Sairam et al., 2005; Snider et al., 2010), barley (Mei et al., 2010) and rice (Vighi et al., 2017), and levels of these compounds have been used as selection criteria to identify heat stress tolerant genotypes.
Proline is an amino acid that plays a vital role in plants growing in heat and drought stress conditions. It acts as a non-enzymatic antioxidant, osmolyte and metal chelator in cotton during heat stress (Rana et al., 2017). Therefore, high concentrations of this molecule are desirable in cotton plants for induction of heat stress tolerance (De Ronde et al., 2000). Identifying accessions with genotypic variability for proline is needed to develop lines with heat stress tolerance (Sekmen et al., 2014; Ashraf et al., 1994).
One of the key factors limiting agricultural crop productivity is the rate at which global temperatures are increasing. The most effective strategy to address this challenge is to develop new genotypes that can withstand high temperatures without compromising yield (Teixeira et al., 2013). Identification of heritable variability in existing accessions is a pre-requisite to develop climate resilient germplasms. Researchers have already reported genetic variability for many desirable traits from a wide gene pool (Majeed et al., 2019; Sezener et al., 2015). Moreover, understanding the genetic basis for heat stress tolerance and its effect on yield and fibre quality related traits is essential to develop breeding programs to improve the heat tolerance of cotton (Meredith et al., 1972; Ahmad et al., 2003; Mubarik et al., 2020). Therefore, by emphasising those attributes that are strongly linked to plant's ability to adapt to a high-temperature environment, genetic gain in cotton production can be exploited.
Consequently, to develop climate resilient cotton cultivars, it is necessary to have a thorough understanding of the genetic variability for yield and related traits in the existing germplasms. The objective of this study is to investigate the potential of the notable local cotton germplasms to tolerate heat stress through the identification of key biochemical traits that influence a multitude of morphological and physiological characteristics which ultimately enhance heat stress tolerance of cotton.
Results
Generation mean analysis
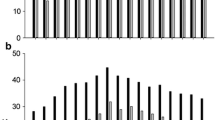
Generation means are provided in Figs. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7. Seed cotton yield per plant was maximum for P1 of cross 2 (162.23 g), while its respective BCP1 also exhibited high yield (138.53 g) under normal conditions. The lowest mean value for this trait was 37.98 g for P2 of cross 2 in heat stress. The F2 and BCP1 populations of cross 1 showed higher yield when sown in normal conditions, i.e., 108.59 g and 128.78 g, respectively. The backcross with the better parent exhibited higher yield in both crosses under high temperature stress (100.61 g and 99.66 g in cross 1 and 2, respectively. Fig. 1). Ginning turnout (GOT) under normal and heat conditions ranged from 32.25%-39.03% and 30.88%-37.22%, respectively. The F1 of both crosses under both sowing dates exhibited good GOT percentages. The BCP1 generations of cross 1 and 2 produced 36.5% GOT under heat stress and more than 37.5% GOT under optimal conditions (Fig. 2).
Overall, the viability of pollen grains was ranged from 38.43% to 80.33%. Under normal sowing conditions, F1, BCP1 and F2 populations exhibited high pollen viability in both crosses (68.5% and 65.67%, 73.93% and 69%, 65.49% and 63.59%, respectively). Under stress conditions, F2 of cross 1 exhibited the highest viability of pollen grains (53.47%) compared with BCP1 and F1 generations of this cross. Under stress conditions, the BCP1 and F2 generations of cross 2 showed 55.6% and 50.4% pollen viability, respectively (Fig. 3). The highest means for CMT were observed for P1 of both crosses under stress and normal conditions (more than 65% and 53%, respectively). Among generations, F2 exhibited higher CMT compared withF1 under heat stress, while BCP1 and BCP2 generations showed the highest and lowest mean values for this attribute under both conditions (Fig. 4).
H2O2 content ranged from 0.36 to 1.41 µmol·g−1 FW under heat stress, and 0.27 to 1.06 µmol·g−1 FW under optimal temperature. F2 and BCP1 generations exhibited lower means compared with F1 and BCP2 generations. BCP1 of cross 2 exhibited the lowest mean value of 0.52 µmol·g−1 FW for H2O2 content under heat stress compared with the other three generations derived from hybridization (Fig. 5). POD activity for parental lines under heat stress and normal temperature ranged from 12.47 to 26.23 U·mg−1 and 8.77 to 15.03 U·mg−1, respectively. F1 showed higher mean values for POD activity as compared to F2 and BCP2 generations under both normal and stress conditions. BCP1 of cross 2 had 22.93 U·mg−1 under heat stress conditions (Fig. 6). For proline content, F1 under heat stress exhibited 0.78 µmol·g−1 FW for cross 1 and 0.84 µmol·g−1 FW for cross 2. The BCP1 under the same conditions had 0.99 and 1.1 µmol·g−1 FW mean values for cross 1 and 2, respectively (Fig. 7).
Estimation of best fit model
Estimates for most suited or best fit models are provided in Table 1 where m is coefficients of the mean, (d) additive, (h) dominance, (i) additive × additive, (j) additive × dominance and (l) dominance × dominance. Seed cotton yield per plant was controlled by [mi] (additive × additive gene action) and [md] (dominance gene action) in cross 1 in normal and heat stress conditions, respectively. In cross 2, seed cotton yield per plant was predominantly influenced by [mhij] (dominance, additive × additive, and additive × dominance type gene actions) in normal sowing. In this cross, the magnitudes of dominance [h] and additive × additive [i] effects were equal to and higher than additive × dominance [j] effects. Viability of pollen was controlled by [md] effects in both crosses under normal sowing and under heat stress conditions of cross 1. In cross 2 under thermal stress, it was governed by [mdhl] (additive, dominance, and dominance × dominance gene actions). The magnitude of dominance [h] was slightly higher than dominance × dominance [l] effects. Cell membrane stability (CMT) was governed by [mi] under high temperature conditions in cross 1 while for other cross and conditions, it was controlled by [md]. The concentration of H2O2 was controlled by [mdhi] in both conditions for cross 2 and heat stress conditions of cross 1. The magnitudes of additive × additive [i] and additive [d] were higher than dominance [h] effects. POD activity and proline content were controlled by [md] in all crosses and conditions. Components of variance for generation means analysis are given in Table 2.
Heritability and heterosis estimates
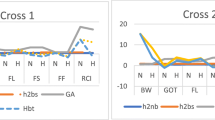
Heterosis (Ht), heterobeltiosis (Hbt), broad sense heritability (h2bs) and narrow sense heritability (h2ns) for the observed traits under both conditions are provided in Table 3. Heterosis estimates for seed cotton yield per plant in cross 1 and cross 2 under normal temperature were 21.69% and 15.64%; while under heat stress, estimates were 16.64% and 18.6%, respectively. Better parent heterosis (heterobeltiosis) was negative under all conditions. The highest narrow sense heritability (0.43) for seed cotton yield per plant was recorded in cross 2 under normal conditions. Pollen viability for both crosses exhibited negative mid parent and better parent heterosis when grown in heat stress and normal conditions. Heterobeltiosis estimates for pollen viability under heat stress for cross 1 and 2 were -20.42% and -22.7%, respectively. Under heat stress, broad sense heritability for cross 1 was 0.37 while heritability for cross 2 was 0.40. Heterosis estimates (mid parent and better parent) for CMT were negative. This trait exhibited 0.32 (or 32%) narrow sense and 0.36-0.37 broad sense heritability. Positive heterosis was observed for H2O2 in cross 1 under the normal condition while for all other conditions and crosses the estimates of heterosis for this parameter were negative. Maximum negative heterosis was -13.48% and heterobeltiosis was -44.6% when calculated under heat stress for cross 2. Broad sense and narrow sense heritability estimates ranged from 0.18 to 0.22 and 0.14 to 0.16, respectively. Negative heterosis for POD activity was recorded for normal sowing of cross 1. The heterosis for POD activity in cross 2 under heat and normal conditions were 0.19% and 0.16%, respectively. Higher heritability estimates for POD activity were observed in heat stress as compared to normal temperature conditions. Proline content exhibited positive and negative heterosis under normal sowing and heat stress, respectively. Heterosis estimates ranged from -3.44% to 3.33%. Heterobeltiosis for this trait under high temperature conditions for both crosses was around -35%. The highest broad and narrow sense heritability estimates were observed under heat stress in cross 1 (0.47 and 0.44, respectively).
Correlation studies
Seed cotton yield per plant had a positive relationship in both crosses with all traits except H2O2 content. The viability of pollen grains was negatively associated with H2O2 content, but it was positively correlated with other traits in cross 1. The physiological traits (pollen viability and CMT) had highly significant and positive associations with seed cotton yield per plant and GOT percentage. Similar relationships were observed with proline content. H2O2 content was negatively associated with seed cotton yield per plant in cross 2 under both conditions. This trait also had negative associations with biochemical attributes (POD activity and proline content) and physiological traits. Details of genotypic and phenotypic correlations for cross 1 and 2 are provided in Table 4 and 5, respectively.
Discussion
Plant breeders depend on wide genetic diversity to develop new cultivars that confer resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses. For this purpose, we assessed the response of 154 genotypes of upland cotton under heat stress and normal conditions (Majeed et al., 2019). One of the major obstacles to increasing cotton yield and fibre quality is heat stress, which has an impact on yields, biochemical composition, morpho-physiology, and other cellular processes. Cotton's morphology and physiology are altered by heat stress during the reproductive phases, significantly lowering yield. For the studied genotypes, heat stress had a significant impact on all traits. Significant differences for all traits between the two crosses and within BCP1, BCP2 and F2 generations were associated with varied allelic combinations (Ngangkham et al., 2018). Presence of variability in breeding materials indicates the potential for selection of plants having superior magnitudes for desired characteristics (Smith et al., 2015).
Based on our previous results, higher mean values for seed cotton yield per plant, GOT, boll weight, pollen viability, and other important physio-biochemical characteristics under heat stress were shown by cluster analysis of a subset of heat-tolerant parents and underperformance of subset of heat-susceptible parents for given attributes (Majeed et al., 2019). As parental material, two genotypes that are heat tolerant (IUB-13 and GH-Mubarak) and two genotypes that are heat susceptible (FH-115 and NIAB-Kiran) were selected. In order to ascertain the genetic behaviour of characteristics associated with heat stress, crosses between IUB-13 × FH-115 (Cross 1) and GH-Mubarak x NIAB-Kiran (Cross 2) were made. Six generations of each cross (P1, P2, F1, F2, BCP1, and BCP2) were then planted in the field.
The F1 of both crosses exhibited good GOT percentages. Under heat stress, the BCP1 generations of cross 1 and 2 produced 36.5% GOT, whereas under optimal conditions, they produced more than 37.5% GOT. However, genetics of seed cotton yield per plant and GOT is more complex because it is the result of multiple components. In addition, involvement of additive, dominance and epistatic effects further add to this complexity. Seed cotton yield showed moderate heritability and heterosis. The correlation of seed cotton yield per plant with other parameters also varied. Therefore, simple selection for seed cotton yield per plant without considering its components, especially physio-chemical attributes related to heat stress is not fruitful as previously reported by Singh et al. (2007), Khan et al. (2008), and Solanki et al. (2014).
Methods to determine pollen viability have been available for quite some time, but their utilization in the development of heat tolerant cultivars has been rare, particularly in literature reported from Pakistan. High means were estimated for pollen viability in the F2, BCP1 and F1 generations of these crosses. Under stress conditions, the F2 of cross 1 exhibited the highest viability of pollen grains (53.4%) compared with BCP1 and F1 generations of both crosses. Moreover, when heat stress was applied, the F2 generation showed higher CMT than the F1 generation, whereas the BCP1 and BCP2 generations displayed the highest and lowest mean values respectively for this characteristic (Figs. 1 and 2). This provides opportunities to cotton breeders and indicates the potential of selection to improve this trait within segregating generations. In cross 2 under heat stress, pollen viability was affected by both [h] and [l] genetic effects with high magnitudes and same signs that strongly suggests the involvement of complementary epistasis. Delayed selection is suggested due to low heterosis and moderate heritability estimates. Correlation of pollen viability with seed cotton yield under high temperature conditions was strongly positive. These features indicate the importance of considering this parameter in breeding programs (Song et al., 2014; 2015a, b).
In addition, CMT was positively associated with seed cotton yield, pollen viability, proline content and POD activity, and it was governed by additive genes. High proline content was observed for BCP1 of cross 1 and 2 under heat stress (0.99 and 1.1 µmol·g−1 FW, respectively). High mean values in BCP1 and F2 generations along with moderate narrow sense heritability highlights the significance for selecting genotypes based upon high CMT values (Azhar et al., 2009; Arfan et al., 2018; Salman et al., 2019).
The negative association of H2O2 content with seed cotton yield and heat tolerant traits reflects the importance for its negative selection. In the present study, in comparison to the F1 and BCP1 generations, the means of the H2O2 content were less in the F2 and BCP2 generations. Moreover, the F1 showed higher mean values for POD activity as compared to F2 and BCP2 generations under both normal and stress conditions. Heat stress leads plants to generate ROS, which causes their cellular homeostasis to be lost. To metabolise excess ROS, the plant up-regulates antioxidant defence enzymes like POD and CAT in response to ROS. H2O2 is detoxified by POD in the cytosol and chloroplasts of plant cells. Moreover, toxic H2O2 is changed into water and oxygen by CAT. H2O2 content is controlled by multiple types of gene action and heritability was low, indicating complexity in the genetic control of this trait. Previous research reported that H2O2 content is controlled by regulatory genes which are not functionally expressed all the time (Gadjev et al., 2008). This is similar to the proline content and POD activity levels in leaf tissues. In contrary to H2O2 content, these two antioxidant molecules were positively associated with pollen viability, CMT and seed cotton yield under heat stress condition.
However, gene action cannot be predicted through generation mean analysis for such complex biochemicals attributes because of their regulatory nature (Andrews et al., 2002; Roychoudhury et al., 2015). The biochemical analysis is important to consider while breeding for heat tolerant cultivars, and modern genomic tools can also be exploited to improve these traits. The correlation analysis revealed that seed cotton yield per plant was positively correlated with GOT percentage, pollen viability, CMT and POD activity under normal and heat stress conditions. Our data were consistent with the previous research (Gadjev et al., 2008; Andrews et al., 2002; Roychoudhury et al., 2015). In nutshell, cross 1 between IUB-13 and FH-115 exhibited overall high yield potential, GOT percentage, greater pollen viability, higher proline content, and other important physio-biochemical attributes. Such attributes are the result of both high heritability and genetic advance, and their combination provides clear picture of the trait in the selection process.
Conclusion
The complex genetic architecture of cotton traits requires a comprehensive understanding to improve heat stress tolerance. This study was based upon classical breeding concepts. We proposed that the use of selection criteria such as pollen viability, antioxidant content, and selecting from segregating populations provided an effective strategy for identifying heat-tolerant cotton germplasms. Furthermore, the utilization of contemporary genomics and biotechnological tools can further enhance these results by providing insights into molecular mechanisms and genes involved in tolerance to heat stress. These results and findings can be used for further cotton breeding programs.
Materials and methods
Development of experimental material
Climate change is adversely affecting the cotton productivity particularly in Pakistan where the temperature during the cotton growing season rises up to 48 ºC. One of the best ways to combat the high temperature effect on the crop plants is to improve the genetics of newly bred cultivars and to confer natural resistance. In previous work by our group (Majeed et al., 2019), 154 upland cotton accessions were screened for heat tolerance by measuring various morpho-physiological and biochemical traits. The heat stress (47-48 ºC) was applied at the first flowering stage by adjusting the sowing dates in contrast to the control. The prediction of high temperature at flowering stage was made on the basis of previous years data where June is the hottest month of the region. The same method was again applied to screen the backcross and filial generations developed after crossing to understand the genetic basis of these attributes. The method to screen the germplasm for heat tolerance by using different sowing dates was also used by some researchers (Tian et al., 2018; Abro et al., 2022). The best heat tolerant and heat susceptible genotypes were identified based on biometrical analyses, i.e., biplot and k-means cluster analysis. From the previous work, two heat tolerant genotypes (IUB-13 and GH-Mubarak) and two heat susceptible genotypes (FH-115 and NIAB-Kiran) were selected as parental materials to develop filial and backcross generations required for genetic studies. The heat tolerant genotypes were used as the female parents and designated by P1, while susceptible genotypes were used as the male parents and designated by P2. Crosses were made between IUB-13 × FH-115 (Cross 1) and GH-Mubarak × NIAB-Kiran (Cross 2) for development of F1 populations in field conditions during cotton growing season of 2018-2019 in Punjab Province (Pakistan). The BCP1, BCP2, and F2 generations were developed in glass house facility of the University of Agriculture Faisalabad. A pictorial representation of the crossing scheme is shown in Fig. 8. Crosses were made to obtain enough seeds for evaluation. Cotton seeds of parents and each generation were ginned separately using a single roller gin machine available in ginning lab of the department.
Evaluation of populations for genetic studies
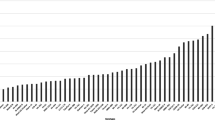
The six generations of each cross (P1, P2, F1, F2, BCP1, and BCP2) were planted in the field of the University of Agriculture Faisalabad (Pakistan) to determine genetic behaviour of traits related to heat stress during cotton growing season in 2019. The six generations of each cross were planted in the field in separate trials in a randomized complete block design (RCBD) in three replications/blocks. In each block, about 60 plants from each parental lines, F1, BCP1, and BCP2 generations and 250 plants from F2 generations were maintained. Each block covered around 88.25 m2. The plant to plant and row to row distance was maintained by 1ft and 2.5 ft, respectively. The experiment was sown on two dates, one early date providing maximum heat stress during the flowering stage, i.e., heat stress (HS), and the second date providing optimal temperatures during the flowering stage, i.e., normal sowing (NS). The early heat stress sowing happened on 29th April, while the later normal sowing occurred on 12th June under the recommended field conditions. The recommended agronomic practices were applied to the experiment. Maximum and minimum temperatures from sowing to flowering were recorded daily using a thermometer (Fig. 9). Data for various morpho-physiological and biochemical traits were recorded from 30 randomly selected plants from each of the parental, F1, BCP1, and BCP2 generations, and from 150 randomly selected plants from the F2 generation for each cross. The fresh leaf samples were collected at the time of first flowering and immediately shifted to laboratory for the determination of H2O2 content, proline content, and POD activity. CMT was also determined from freshly collected leaves from the field at the time of first flowering. The flowers were also picked at the morning time at around 10:30 AM to collect pollen grains to assess their viability in both sowing dates. Seed cotton yield per plant and GOT were collected at maturity. The details for each method are provided under. The data was collected from three replications of each of the sowing, i.e., heat stress and control.
Morpho-physiology and biochemical parameters
Pollen viability
Pollen viability was determined following the method of Nortin (1966). Pollen viability was ascertained at the time of first flowering with triphenyl-tetrazolium chloride (TTC) solution. The TTC solution was prepared by dissolving 2 g of TTC and 12 g of sucrose in 200 mL distilled water. The solution was then poured into disposable petri dishes and stored at 4 °C. Fresh pollen grains were dusted in petri dishes containing TTC solution and placed at room temperature (25 °C) for two hours. Pollen grains were then examined using a binocular light microscope (XSZ-107BN) with 100Xs objective lenses. The viability was scored according to the degree of staining, i.e., pollen grains with red color were considered as viable, while yellow stained pollen grains were counted as non-viable.
CMT
Leaves were collected from the field to measure CMT at the same time as pollen collection to determine viability. In laboratory, leaves were punched with a steel pipe (10 mm in diameter) to obtain leaf discs from either side of the midrib. The leaf discs were immediately dipped in glass vials containing deionized water and rinsed twice with deionized water to wash off any surface-adhered electrolytes. After washing, 2 mL deionized water was added to each vial, and vials were closed with cotton plugs to avoid evaporation and desiccation during the high temperature treatment. Two vials were prepared for each sample. One set was kept at room temperature (control), while the other set was heated to 48 °C (high temperature treatment) in a water bath. After one hour, both sets were well shaken to mix the contents before measuring the initial electrical conductivity (EC) using an EC meter (HI 99300 HANNA Instrument, Romania). These vials were then placed in an autoclave (Hirayama HVA-85) at 0.10 MPa pressure for 15 min to release all electrolytes from the leaf tissue. Final EC was recorded for both sets of samples when temperature dropped to 25 °C. Relative cell injury percentage (RCI%) was estimated using the following formula outlined by Sullivan (1972).
where, T and C denote EC of heat treated and controlled vials, and subscripts 1 and 2 denote initial and final EC readings, respectively. CMT was then calculated using the following formula,
H2O2 content
H2O2 content was determined according to the method described by Liu et al. (2010). Fresh leaves were collected at the time of pollen collection and stored at –80 ºC for biochemical analysis. For measuring H2O2 content, 0.1 g leaf sample was ground in liquid nitrogen. The ground tissue was homogenized with 5 mL pre-chilled acetone and centrifuged at 3 000 × g for 10 min at 4 °C in a SCILOGEX D2012 plus high-speed micro-centrifuge. From this mixture, 1 mL of supernatant was mixed with 0.2 mL ammonia, 0.1 mL of 95% (v/v) hydrochloric acid containing 20% (v/v) titanium tetrachloride and centrifuged again at 10 000 × g for 10 min at 4 °C. The sediment was repeatedly washed with cold acetone and centrifuged at 13 500 × g for 10 min and finally dissolved in 3 mL of 1 mol·L-1 H2SO4. The absorbance was measured at 410 nm using a spectrophotometer, and the concentration was calculated using a standard curve based on known concentrations of H2O2.
POD activity
The enzyme extract was prepared by homogenizing the leaf tissue using a pestle and mortar with 0.05 mol·L-1 sodium phosphate buffer. The homogenate was then centrifuged at 10 000 × g for 20 min, and supernatant was transferred to a new tube. The reaction mixture was prepared by mixing 75 mL of 100 mmol·L-1 sodium phosphate buffer, 42 µL of guaiacol, and 28.5 µL of H2O2 (30%). Finally, 1 mL of enzyme extract was added to 3 mL of reaction mixture. The absorbance was measured at 470 nm, and a unit of POD activity was defined as µmol H2O2 decomposed per minute (Liu et al., 2009).
Proline content
Proline content was measured following the protocol as described by Bates et al. (1973). Leaf extract was prepared by grinding 0.5 g frozen leaves in 5 mL of 3% sulfosalicylic acid. This extract was centrifuged at 10 000 × g for 15 min, and the supernatant was transferred to a new vial. Meanwhile, 3% ninhydrin solution was prepared using equal volumes of glacial acetic acid and 6 mol·L-1 ortho phosphoric acid. An equal volume (1 mL each) of leaf extract supernatant, glacial acetic acid and ninhydrin solution were added to cuvettes and incubated at 100 °C for 60 min. This reaction mixture was cooled on ice, and 1 mL of toluene was added before mixing the solution for 5 min. The aqueous layer was discarded, while the organic layer was retained. Finally, 150 µL of the organic layer was poured into an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) plate and absorbance was recorded at 520 nm where toluene was used as a blank for the standard curve.
Seed cotton yield per plant and GOT
Seed cotton was hand-picked from the same plants selected for biochemical and physiological analysis (tagged during leaf and pollen collection) to determine seed cotton yield per plant. Seed cotton from each plant was weighed and ginned, and GOT percentage was obtained using the following formula:
Biometrical analysis
The data from parental and crossing generations was analyzed for variability using the method described by Steel et al. (1997). Generation mean analysis was performed using the Mather et al. (1982) method implemented with R software. Broad sense heritability (H2b) was determined through the procedure described by Huhn (1975). Mid parent heterosis (Ht) and better parent heterosis (Hbt) percentages were calculated using the formulas reported by Briggle (1963) and Fonseca et al. (1968), respectively. Genotypic correlation (rg) and phenotypic correlation (rp) coefficients were estimated through the method outlined by Kwon et al. (1964).
Availability of data and materials
The plant material was collected from various research institutes to develop crosses and segregating populations, the original parental material can be available as per Institutional, National and International plant material exchange rules and policies.
Abbreviations
- [d]:
-
Coefficients of the additive
- [h] :
-
Coefficients of the dominance
- [i] :
-
Coefficients of the additive × additive
- [j] :
-
Coefficients of the additive × dominance
- [l] :
-
Coefficients of the dominance × dominance
- [m] :
-
Coefficients of the mean
- 1O2 :
-
Singlet oxygen
- APO:
-
Ascorbate peroxidase
- BCP1 :
-
Backcross with parent 1
- BCP2 :
-
Backcross with parent 2
- CMT:
-
Cell membrane thermostability
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- F1 :
-
1St filial generation
- F2 :
-
2Nd filial generation
- GOT:
-
Ginning turnout
- h 2 bs :
-
Broad sense heritability
- h 2 ns :
-
Narrow sense heritability
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- H bt :
-
Heterobeltiosis
- HS:
-
Heat stress conditions
- H t :
-
Heterosis
- NS:
-
Normal sowing conditions
- ·O2 − :
-
Superoxide radical
- ·OH :
-
Hydroxyl radicals
- P1 :
-
Parent 1
- P2 :
-
Parent 2
- POD:
-
Peroxidases
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
References
Abro S, Rizwan M, Deho ZA, et al. Identification of heat tolerant cotton lines showing genetic variation in cell membrane thermostability, stomata, and trichome size and its effect on yield and fiber quality traits. Front Plant Sci. 2022;5(12):804315. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.804315. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Ahmad S, Iqbal MZ, Hussain A, et al. Gene action and heritability studies in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L). J Biol Sci. 2003;4:443–50. https://doi.org/10.3923/jbs.2003.443.450. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Ahmad P, Jaleel CA, Salem MA, et al. Roles of enzymatic and nonenzymatic antioxidants in plants during abiotic stress. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2010;30(3):161–75. https://doi.org/10.3109/07388550903524243. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Andrews J, Adams S, Burton K, et al. Subcellular localization of peroxidase in tomato fruit skin and the possible implications for the regulation of fruit growth. J Exp Bot. 2002;53(378):2185–91. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erf070. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Apel K, Hirt H. Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2004;55:373–99. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.55.031903.141701. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Arfan M, Shakeel A, Khan TM, et al. Genetic basis of variation for high temperature tolerance in upland cotton. Int J Agric Biol. 2018;20(12):2637–46. https://doi.org/10.17957/IJAB/15.0801. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Ashraf M, Saeed M, Qureshi M. Tolerance to high temperature in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) at initial growth stages. Environ Exp Bot. 1994;34(3):275–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/0098-8472(94)90048-5. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Azhar F, Ali Z, Akhtar M, et al. Genetic variability of heat tolerance, and its effect on yield and fibre quality traits in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Plant Breed. 2009;128(4):356–62. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0523.2008.01574.x . Accessed 10 July 2023.
Bates L, Waldren R, Teare I. Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil. 1973;39(1):205–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018060. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Briggle L. Heterosis in wheat—a review. Crop Sci. 1963;3(5):407–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.16488. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Caverzan A, Casassola A, Brammer SP. Antioxidant responses of wheat plants under stress. Genet Mol Biol, 2016;39(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2015-0109. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Das K, Roychoudhury A. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and response of antioxidants as ROS-scavengers during environmental stress in plants. Front Environ Sci. 2014;2:53. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020155. Accessed 10 July 2023.
De Ronde J, Van Der Mescht A, Steyn H. Proline accumulation in response to drought and heat stress in cotton. Afr Crop Sci J. 2000;8:85–92. https://doi.org/10.4314/acsj.v8i1.27718. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Fonseca S, Patterson FL. Hybrid vigor in a seven-parent diallel cross in common winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Crop Sci. 1968;8(1):85–8. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1968.0011183X000800010025x. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Foyer CH, Noctor G. Redox homeostasis and antioxidant signaling: a metabolic interface between stress perception and physiological responses. Plant Cell. 2005;17(7):1866–75. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.105.033589. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Gadjev I, Stone JM, Gechev TS. Programmed cell death in plants: new insights into redox regulation and the role of hydrogen peroxide. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2008;270:87–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1937-6448(08)01403-2. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Gechev TS, Van Breusegem F, Stone JM, et al. Reactive oxygen species as signals that modulate plant stress responses and programmed cell death. BioEssays. 2006;28(11):1091–101. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.20493. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Gill SS, Tuteja N, Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2010;48(12):909–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.08.016. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Gossett DR, Millhollon EP, Lucas M. Antioxidant response to NaCl stress in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive cultivars of cotton. Crop Sci. 1994;34(3):706–14. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1994.0011183X003400030020x. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Gur A, Demirel U, Özden M, et al. Diurnal gradual heat stress affects antioxidant enzymes, proline accumulation and some physiological components in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Afr J Biotechnol. 2010;9(7):1008–15. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB09.1590. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Hernández I, Alegre L, Van Breusegem F, et al. How relevant are flavonoids as antioxidants in plants? Trends Plant Sci. 2009;14(3):125–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2008.12.003. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Huhn M. Estimation of broad sense heritability in plant populations: an improved method. Theor Appl Genet. 1975;46(2):87–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2008.12.003. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Khan AI, Sadaqat HA. Heat tolerance is variable in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) and can be exploited for breeding of better yielding cultivars under high temperature regimes. Pak J Bot. 2008;40(5):2053–8.
Kwon S, Torrie J. Heritability of and interrelationships among traits of two soybean populations. Crop Sci. 1964;4(2):196–8. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1964.0011183X000400020023x. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Liu ZJ, Guo YK, Bai JG. Exogenous hydrogen peroxide changes antioxidant enzyme activity and protects ultrastructure in leaves of two cucumber ecotypes under osmotic stress. J Plant Growth Regul. 2010;29(2):171–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-009-9121-8. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Liu D, Zou J, Meng Q, et al. Uptake and accumulation and oxidative stress in garlic (Allium sativum L.) under lead phytotoxicity. Ecotoxicology. 2009;18(1):134–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-008-0266-1. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Majeed S, Malik TA, Rana IA, et al. Antioxidant and physiological responses of upland cotton accessions grown under high-temperature regimes. Iran J Sci Technol A. 2019;43(6):2759–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-019-00781-7. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Mather K, Jinks J. Biometric genetics: the study of continuous variation. London: Chapman and Hall; 1982. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-3404-8. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Mei YQ, Song SQ. Response to temperature stress of reactive oxygen species scavenging enzymes in the cross-tolerance of barley seed germination. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2010;11(12):965–72. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1000147. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Meredith WR, Bridge R. Heterosis and gene action in cotton, Gossypium hirsutum L. Crop Sci. 1972;12(3):304–10. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1972.0011183X001200030015x. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery M, et al. Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2004;9(10):490–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2004.08.009. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Møller IM. Plant mitochondria and oxidative stress: electron transport, NADPH turnover, and metabolism of reactive oxygen species. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2001;52(1):561–91. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.52.1.561. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Mubarik MS, Ma C, Majeed S, et al. Revamping of cotton breeding programs for efficient use of genetic resources under changing climate. Agronomy. 2020;10(8):1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10081190. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Ngangkham U, Samantaray S, Yadav MK, et al. Effect of multiple allelic combinations of genes on regulating grain size in rice. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0190684. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Nortin JD. Testing of plum pollen viability with tetrazolium salts. Proc Amer Soc Hort Sci. 1966;89:132–4.
Petrov V, Hille J, Mueller-Roeber B, et al. ROS-mediated abiotic stress-induced programmed cell death in plants. Front Plant Sci. 2015;6:69. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00069. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Rana V, Ram S, Nehra K. Review-proline biosynthesis and its role in abiotic stress. Int J Agric Innov Res. 2017;23(34):234–45.
Roychoudhury A, Basu S, Sengupta DN. Antioxidants and stress-related metabolites in the seedlings of two indica rice varieties exposed to cadmium chloride toxicity. Acta Physiol Plant. 2012;34(3):835–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-011-0881-y. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Roychoudhury A, Banerjee A, Lahiri V. Metabolic and molecular-genetic regulation of proline signaling and itscross-talk with major effectors mediates abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Turk J Bot. 2015;39(6):887–910. https://doi.org/10.3906/bot-1503-27. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Sairam R, Srivastava G, Agarwal S, et al. Differences in antioxidant activity in response to salinity stress in tolerant and susceptible wheat genotypes. Biol Plant. 2005;49(1):85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-005-5091-2. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Sakihama Y, Cohen MF, Grace SC, et al. Plant phenolic antioxidant and prooxidant activities: phenolics-induced oxidative damage mediated by metals in plants. Toxicology. 2002;177(1):67–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0300-483x(02)00196-8. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Salman M, Majeed S, Rana IA, et al. Novel breeding and biotechnological approaches to mitigate the effects of heat stress on cotton. In: Wani S, editor. Recent approaches in omics for plant resilience to climate change. Cham: Springer; 2019. p. 251–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-21687-0_11. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Sekmen AH, Ozgur R, Uzilday B, et al. Reactive oxygen species scavenging capacities of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) cultivars under combined drought and heat induced oxidative stress. Environ Exp Bot. 2014;99:141–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2013.11.010. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Sezener V, Basal H, Peynircioglu C, et al. Screening of cotton cultivars for drought tolerance under field condition. Turk J Field Crops. 2015;20(2):223–32. https://doi.org/10.17557/tjfc.57032. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Singh RP, Prasad PV, Sunita K, et al. Influence of high temperature and breeding for heat tolerance in cotton: a review. Adv Agron. 2007;93:313–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2113(06)93006-5. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Smith S, Bubeck D, Nelson B, et al. Genetic diversity and modern plant breeding. In: Ahuja M, Jain S, editors. Genetic diversity and erosion in plants. Cham: Springer; 2015. p. 55–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-25954-3. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Snider JL, Oosterhuis DM, Kawakami EM. Genotypic differences in thermotolerance are dependent upon prestress capacity for antioxidant protection of the photosynthetic apparatus in Gossypium hirsutum. Physiol Plant. 2010;138(3):268–77. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2009.01325.x. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Solanki H, Mehta D, Rathod V, et al. Heterosis for seed cotton yield and its contributing characters in cotton. Electron J Plant Breed. 2014;5(1):124–30.
Song G, Chen Q, Tang C. The effects of high-temperature stress on the germination of pollen grains of upland cotton during square development. Euphytica. 2014;200(2):175–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-014-1141-1. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Song GC, Jiang CL, Ge XY, et al. Pollen thermotolerance of upland cotton related to anther structure and HSP expression. Agron J. 2015a;107(4):1269–79. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj14.0458. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Song GC, Wang MM, Zeng B, et al. Anther response to high-temperature stress during development and pollen thermotolerance heterosis as revealed by pollen tube growth and in vitro pollen vigor analysis in upland cotton. Planta. 2015b;241(5):1271–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-015-2259-7. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Stahl W, Sies H. Antioxidant activity of carotenoids. Mol Aspects Med. 2003;24(6):345–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0098-2997(03)00030-x. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Steel RG, Torrie JH, Dickey DA. Principles and procedures of statistics, a biometrical approach. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1997.
Sullivan CY. Mechanisms of heat and drought resistance in grain sorghum and methods of measurement. In: Rao NGP, House LR, editors. Sorghum in seventies. New Delhi: Oxford & IBH Pub Co.; 1972.
Teixeira EI, Fischer G, van Velthuizen H, et al. Global hot-spots of heat stress on agricultural crops due to climate change. Agric for Meteorol. 2013;170:206–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2011.09.002. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Tian BJ, Zhu JC, Nie YS, et al. Mitigating heat and chilling stress by adjusting the sowing date of maize in the North China Plain. J Agron Crop Sci. 2018;205(1):77–87. https://doi.org/10.1111/jac.12299. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Vighi I, Benitez L, Amaral M, et al. Functional characterization of the antioxidant enzymes in rice plants exposed to salinity stress. Biol Plant. 2017;61(3):540–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-017-0727-6. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Wu SW, Hu CX, Tan QL, et al. Drought stress tolerance mediated by zinc-induced antioxidative defense and osmotic adjustment in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). Acta Physiol Plant. 2015;37(8):167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-015-1919-3. Accessed 10 July 2023.
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge the support of Dr. Kemp AH, USDA-ARS, for supervising the first author (Majeed S) for carrying out research activities and providing learning opportunities with USDA in North Carolina State University, USA.
Disclaimer
USDA is an equal opportunity provider and employer.
Funding
Authors are thankful to Centre for Advance Studies in Agricultural Food Security and Punjab Agricultural Research Board for providing funds under CAS-PARB project (No. 964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Majeed S performed the experiments, analysed the data, prepared figures and tables, authored and reviewed drafts of the article. Chaudhary MT and Shaban M assisted in performing the experiments and review the manuscript. Mubarik MS, Hinze L, Du XM, Tan DKY, and Jia YH reviewed the manuscript. Azhar MT and Rana IA conceived and designed the experiments and approved the final draft along with Majeed S.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for publication
All authors have agreed to submit the review article in Journal of Cotton Research.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1:
Figure S-1. Genotype GH-Mubarak grown under heat stress conditions. Figure S-2. Genotypes FH-142 grown under heat stress conditions. Figure S-3. Genotype NIAB-Kiran grown under heat stress conditions. Figure S-4. Populations sown under normal temperature (Control) conditions. Figure S-5. Microscopic image of cotton pollen grains tested for viability a) Yellow colored non-viable pollen b) red colored viable pollen.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Majeed, S., Chaudhary, M.T., Mubarik, M.S. et al. Genetics of biochemical attributes regulating morpho-physiology of upland cotton under high temperature conditions. J Cotton Res 7, 3 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42397-023-00164-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s42397-023-00164-9