Abstract
Background
Few data about women's sexuality practices post-acute COVID-19 syndrome are available. Many women who have had the disease experience sexual dysfunction; hence, the adverse effect of COVID-19 on sexual function has generated interest. We aimed to clarify the impact of COVID-19 on female sexual function 6 months after the illness and possible risk factors and to evaluate the relationship between psychiatric problems and female sexual dysfunction 6 months after COVID-19. Sixty-two patients were enrolled in this cross-sectional study and assigned according to female sexual function index scores to two groups: those with and without sexual dysfunction. For all participants, we documented socioeconomic status, sexual history, symptoms of COVID-19, vaccination data, and Symptom Checklist 90.
Results
Sexual dysfunction was 58% of all participants after 6 months COVID-19. Sexual frequency and sexual problems except pain were decreased in both groups with more affection in sexual dysfunction women. Sexually dysfunctional women were more likely to obtain oxygen therapy during COVID-19, received AstraZeneca, had post-vaccination myalgia and headache, and recurring COVID-19 after vaccination. No significant SCL-90 subscale differences. Sexual dysfunction was associated with renal illness, fatigue, COVID-19-related oxygen therapy, post-vaccination myalgia, and headache.
Conclusions
After 6 months COVID-19, there was a decline in the frequency of sexual intercourse and scores on all FST subscales in both groups except pain, with more affection in sexual dysfunction women. No statistical difference in psychiatric problems between both groups. Sexual dysfunction was associated with renal illness, COVID-19-related oxygen therapy and fatigue, post-COVID-19-vaccination myalgia, and headache.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The global coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has created disruptions in the health care system and in social interactions, a decline in income, and many deaths [1,2,3]. Symptoms of COVID-19 affected all ages include fever, dry cough, muscle pain, fatigue, and shortness of breath [4,5,6]. Few reports to date have focused on the effect of COVID-19 on sexual and reproductive health [7,8,9]. People who are sexually active, particularly young adults, face many health concerns worldwide [10], and COVID-19 may impair several aspects of reproductive and sexual health.
Sexuality is a vital aspect of women's lives and one of the most crucial factors influencing mental health, and it has a significant effect on interpersonal communication. Experiencing pleasure, releasing sexual tension, and expressing emotional connection are advantages of a fulfilling sexual life. Sexuality in humans is governed by numerous internal and external elements, including anatomy, hormones, and emotions [11, 12]. Sexual dysfunction is prevalent among women and negatively affects their lives. It comprises problems in female sexual arousal/interest, hypoactive sexual desire, female orgasm, and genitopelvic pain/penetration [13].
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Li and colleagues, demonstrated the direct influence of COVID-19 on sexual health, which manifested as decreases in sexual desire and in frequency of sexual activity [10]. Furthermore, previous research found that 15% of individuals have increased stress levels as a result of the pandemic [10, 14]. Numerous factors could exacerbate sexual dysfunction during the pandemic. On the one hand, for many young adults, economic and psychological stresses are caused by unemployment or dropping out of school. On the other hand, lack of access to comprehensive health care services and separation from sexual partners may increase the chance of unfavorable sexual health outcomes [4]. In addition, the pandemic has contributed to a substantial increase in anxiety, as well as a considerable drop-in sexual activity, which was driven mainly by isolation and lack of desire as a result of stress. Hall and colleagues investigated the effect of stress on the sexual health of 992 young women (aged 18 to 20) with symptoms of stress and found a correlation between depressive symptoms and the frequency of sexual activity [15]. Similarly, Liu and colleagues, who studied the reproductive health of Asian women after the 2010 Yushu earthquake, discovered that a major disaster causes widespread sexual dysfunction and decreases sexual satisfaction [16]. This finding indicates that when a problem affects many people similarly and may recur, it also negatively affects sexuality. In addition, younger age may significantly worsen the ability to cope with stress [15, 16].
Furthermore, COVID-19 has had long-term effects on patients who recovered. A previous study of mental health symptoms 6 months after infection with COVID-19 revealed that the most common mental health problems are irregular sleep, somatization, and anxiety. Women, patients with diabetes, and patients receiving oxygen or mechanical ventilation are more prone to mental illness after COVID-19 than are men and other patients [17]. Many studies discussed possible change in metabolic pathway that might increase psychiatric symptoms for post-COVID-19 infection [18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27]. Moreover, previous research found that there was role of kynurenine pathway metabolites in depression, anxiety, and stress after 6 months of COVID-19 infection [28]. AS, SARS-CoV-2 infection affects tryptophan–kynurenine metabolism as an early inflammatory signal, increasing neurotoxic metabolites such as quinolinic acid (QA) and 3-hydroxykynurenine (3-HK) and lowering neuroprotective metabolites such as kynurenic acid (KA) [29]. Furthermore, The TKP is being studied in the pathophysiology of mental diseases [30, 31]. This system's dysregulation has been associated to major depressive disorder [31], schizophrenia [32], and anxiety disorders[33].Reduced tryptophan [34], kynurenine, and kynurenic acid in patients with MDD [35], and increased plasma kynurenine levels in patients with endogenous anxiety[36] are all associated with TKP and mental diseases.
In terms of sexual function, results of multiple studies have indicated that male patients with COVID-19 may develop sexual dysfunction such as penile and testicular atrophy, erectile dysfunction, decreased libido, and hypogonadism [37, 38]. Similarly, a prior study revealed a deterioration in female sexual function after COVID-19 [4]. However, female reproductive health and sexual function after COVID-19 have received little attention. We therefore investigated the effect of COVID-19 on female sexual function 6 months after illness and the possible risk factors. We also evaluated the relationship between psychiatric disorders and female sexual dysfunction with regard to COVID-19.
Methods
From January to August 2022, we conducted a cross-sectional observational study in which 300 COVID-19 survivors were enrolled 6 months after severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection was confirmed by real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (with the Cobas 6800 system; Roche, Basal, Switzerland) [39].
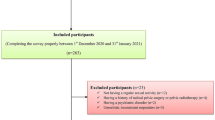
Six months after infection with COVID-19, all patients attended the post-COVID-19 outpatient [Clinic at the Assiut University Hospitals, Assiut, Egypt]. Of the 300 patients, only 62 were eligible according to the following inclusion criteria: being female, age of 18 to 50, heterosexual orientation, active sexual life, and no complaints of sexual problems, living in a stable partnership for at least 6 months, and no pregnancy or parturition in the previous 6 months. We excluded patients with a history of psychiatric disorders or sexual dysfunction before COVID-19 diagnosis, younger than 18 years or older than 50 years of age, who had no sexual activity, who used drugs that decreased libido in the 3 months before study enrollment, who had marital conflicts, and who refused to participate in the study. At the time of diagnosis, eligible participants were divided into three groups (critical, non-severe, severe) based on criteria reported by Wu and colleagues [40]. Most of participants were non-severe group members (83.8%) while only 16.1% of participants were severe group.
Sample size
According to Yuksel and colleagues [7], the minimal sample size to be recruited was calculated using Epi-Info Stat Calc, version 7 [Centre for Disease Control (CDC), WHO] using the specifications as follows: 95% confidence level, 5% margin of error, and 10% rate of non-response.
Measures
Demographic data
For each participant, we documented age, educational level, smoking history, and the presence of comorbidities such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, renal disease, and pulmonary disease.
Socioeconomic scale
The socioeconomic scale [41] elicits information about social burden and socioeconomic status. It also covers four crucial variables: the educational levels of the participant’s and her husband, their occupations, the overall family income, and the participant’s way of life.
Sexual history
For each participant, we documented age at first menstruation, age at first sexual intercourse, number of cesarean sections, partner’s age, frequency of sexual intercourse per week before and after COVID-19, problems of sexual desire before and after COVID-19 infection, problems of arousal before and after COVID-19, problems of lubrication before and after COVID-19, problems of orgasm before and after COVID-19, and degree of sexual satisfaction before and after COVID-19.
The Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI)
This index is a concise, multidimensional scale used to assess female sexual function. Answers to the first two questions are scored from 1 to 5, and answers to the remaining questions are scored from 0 to 5. All scores are summed to obtain a total; totals range from 2 to 36. The higher the total score, the healthier the participant’s sexual life. The cutoff value for determining whether sexual health is good, or poor is 26. We created a questionnaire that was based on the FSFI, and the participants provided answers in complete confidentiality. Participants were asked to respond according to their current sexual performance 6 months after their bout of COVID-19.[42]
COVID-19 symptoms and vaccination data
For each participant, we documented signs and symptoms of COVID-19 (fever, cough, throat pain, muscle pain, loss of the senses of smell and taste, diarrhea, vomiting, headache, fatigue, and need for oxygen therapy), COVID-19 vaccination and type of manufacturer, symptoms caused by the vaccine (fever, myalgia, fatigue, and headache), number of vaccine doses, length of hospitalization, need for oxygen administered or mechanical ventilation, and recurrence of COVID-19 vaccination.
Symptom Checklist 90 (SCL-90)
The SCL-90 [43] is a 90-item questionnaire designed to evaluate psychological issues. Each item is graded on a scale of 0 to 4 according to how much it bothers the individual. The SCL-90 is divided into nine subscales: somatization, obsessive–compulsive disorder, interpersonal sensitivity, depression, anxiety, anger–hostility, phobic anxiety, paranoid ideation, and psychosis.
Statistical analysis
SPSS Statistics, version 26 (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA), was used to analyze the data. For data expression, we calculated frequencies and percentages, as well as means and standard deviations. The Chi-square and Mann–Whitney U test were used to compare groups as needed. A univariate linear regression model was used to identify risk factors. We considered p values of less than 0.05 statistically significant.
Results
Demographic information
The prevalence of sexual dysfunction among all participants was 58%. Table 1 shows demographic data of the studied groups. No significant statistical difference between the studied groups regarding demographic data. However, it was noticed that women with sexual dysfunction had higher percentage in secondary and university education, chronic illness, and higher mean socioeconomic status than another group. Women with sexual dysfunction group only had ischemic heart disease, pulmonary disease, and renal disease.
Sexual history
Table 2 shows sexual history of the studied groups. There was no significant statistically significant difference between both groups. However, it was observed that women without sexual dysfunction tended to have less frequent cesarean sections, although the difference was not statistically significant. Additionally, the mean frequency of sexual intercourse per week decreased in both groups after experiencing COVID-19, compared to before the illness with more decrease in women with sexual dysfunction group but this difference also did not reach statistical significance.
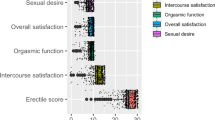
Regarding sexual problems after COVID-19, most women with and without sexual dysfunction had less sexual satisfaction and more difficulty achieving orgasm (93.5% for both groups) and more problems with desire and arousal (90.3% and 85.5%, respectively). Of all participants, 83.9% experienced problems with lubrication, and 37.1% experienced pain (Fig. 1).
We also noted a significant statistical difference between the groups regarding orgasm and pain before COVID-19. However, it was noticed that the percentage of participants with sexual problems before and after COVID-19 was higher among women with sexual dysfunction than in the other group except pain. Pain was the only sexual problem that improved after COVID-19 in both groups with more improvement in women without sexual dysfunction group.
COVID-19 symptoms and vaccination data
The two study groups differed significantly regarding oxygen therapy during COVID-19. A higher proportion of women with sexual dysfunction than of the other group experienced needed oxygen therapy (25% vs. 3.8%, respectively) (see Table 3).
Regarding vaccination history and its symptoms, there was significant statistically significant difference in received AstraZeneca, post-vaccination myalgia and headache between both groups. In comparison with women without sexual dysfunction, significantly higher percentages of women with sexual dysfunction had symptoms (myalgia and headache) caused by the vaccine. The AstraZeneca vaccine was used more commonly with sexual dysfunction group than another group.
SCL-90 subscale scores
Regarding SCL-90 subscales, there was no significant statistical difference between either groups (Table 4).
Regression studies
To identify possible risk factors for sexual dysfunction in the presence of specific parameters, we performed univariate linear regression. Participants with sexual dysfunction (decreased total FSFI scores) were more likely to have renal disease (p = 0.04), to experience fatigue (p = 0.011), and to need oxygen therapy (p = 0.028) during COVID-19 and to have myalgia (p = 0.049) and headache (p = 0.001) after vaccination. Recurrence of COVID-19 after vaccination was also significantly (p = 0.044) associated with sexual dysfunction in women (Table 5).
Discussion
Female reproductive health and sexual function after infection with COVID-19 infection have received little attention. We investigated the effect of COVID-19 on female sexual function 6 months after illness and its possible risk factors; also, to evaluate the relationship between psychiatric disorders and female sexual dysfunction.
In this study, the prevalence of sexual dysfunction among all participants was 58%. No significant statistical difference between the studied groups regarding age, education, chronic illness, and socioeconomic status. Similarly, previous research reported that sexual dysfunction in women had no correlation with higher education levels [44, 45] and socioeconomic status[46]. On the other hand, previous study reported higher levels of education advancing age [47, 48], and low socioeconomic [49] were linked to more significant sexual dysfunction.
In the current study, participants with sexual dysfunction (decreased total FSFI scores) were more likely to have chronic renal disease in regression model. As a previous study demonstrated, the effects of chronic illness on sexuality are multifactorial and can affect all phases of sexual response. Sexual desire, frequency of sex, and sexual activities may be altered by illness through interference with the hormonal, vascular, and neural integrity of the genitalia, as well as the adverse effects of medications [50].
In the sexual history, there was no significant statistically significant between both groups, but it was noticed that most of women without sexual dysfunction had less frequent of cesarean sections. Numerous earlier studies had revealed long-term negative effects of cesarean procedures, including problems with the pelvic floor muscles, decreased fertility, placental anomalies, mental discomfort, and female sexual dysfunction [51,52,53]. In contrast, a systematic review revealed no such association [53].
Our results showed a reduction in the frequency of sexual intercourse per week after COVID-19 in both study groups, and the reduction was greater in women with sexual dysfunction without significant statistical. These findings were consistent with those of Schiavi and colleagues [10, 54] and Li and colleagues [10, 54], who revealed a decrease in the frequency of sexual activity during the pandemic. However, Yuksel and Ozgor reported a notable increase in the frequency of sexual activity during the pandemic [7]. Kaya and colleagues found the frequency of relationships decreased statistically among women after COVID‐19 [4].
Although women with sexual dysfunction had a higher percentage of sexual problems before and after COVID-19 infection than did the other group, except for pain—which was the only sexual problem that improved after COVID-19 in both groups—but only orgasm and pain problems were differ significantly. The results of a previous study indicated that only satisfaction decreased significantly in women after COVID-19, whereas desire, arousal, lubrication, orgasm, and pain did not differ significantly after COVID‐19 diagnosis. On the other hand, Kaya and colleagues, found a decrease, although no statistically significant, in pain scores on the 36-item short form health survey after COVID-19 diagnosis [4]. Regarding decrease pain post-COVID-19, Patients with COVID-19 frequently develop peripheral neuropathy, which is primarily brought on by immune processes or neurotoxic side effects of medications used to treat COVID-19 symptoms. Peripheral nerve compression also brought on by protracted bed rest in the intensive care unit (ICU) and pre-existing risk factors like diabetes also play a minor role [55].
In their Turkish population, Yuksel and Ozgor showed that scores for all six domains of the FSFI—aside from pain and arousal—were considerably lower during the COVID-19 pandemic [7]. According to Fuchs and colleagues, problems with orgasm, lubrication, and satisfaction increased dramatically during the pandemic [56] as it might be linked to associate symptoms of depression and anxiety [57].
In our study, a higher significant proportion of women with sexual dysfunction than of the other group experienced needed oxygen therapy. In linear regression model, Participants with sexual dysfunction (decreased total FSFI scores) were more likely to need oxygen therapy and to experience fatigue during COVID-19 pandemic.
Results of a previous study indicated that prolonged oxygenation therapy resulted in poor outcomes of post-COVID-19 symptoms [58]. Another study revealed that oxygen therapy increased the incidence of sleep disorders and phobic anxiety [17]. The use of equipment to enhance oxygen levels in patients is typically connected with unpleasant experiences such as pain, thirst [59], isolation, choking, and anxiety about running out of oxygen [60].
According to a meta-analysis, a considerable number of patients with COVID-19 experience chronic fatigue, which may have a neurological basis [61]; this affects a large number of women [62]. Some researchers hypothesized that COVID-19-related fatigue may be caused by damage to olfactory sensory neurons, which results in reduced cerebrospinal fluid outflow through the cribriform plate. This, in turn, causes congestion of the glymphatic system, which then causes a toxic build-up of cerebrospinal fluid within the central nervous system [63].
In comparison with women without sexual dysfunction, significantly higher percentages of women with sexual dysfunction had symptoms (myalgia and headache) caused by the vaccine with significant statistical. The AstraZeneca vaccine was used more significant received with sexual dysfunction group than another group. In addition, myalgia and headache after vaccination, and recurrence of COVID-19 after vaccination were associated with sexual dysfunction.
Data on the effects of anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccinations on sexual health and reproduction are contradictory because of small sample sizes and a lack of diversity in the samples. Further research is needed to investigate the long-term effects of COVID-19 and vaccinations on health in general and on sexual function.
According to our findings, there is no significant statistical difference regarding subscales of SCL-90. Previous study indicated that 91.2% of patients with COVID-19 exhibited symptoms of mental disorders 6 months after the disease [17], but no measure was done to assess sexual problems in this study. Generally, persistent psychological stress [64], and stress-related hormonal disruptions are associated with lower FSFI scores such as higher cortisol levels, which inhibit the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis, may be responsible for sexual dysfunction, decreased arousal in particular [64].
Limitations and future directions
The number of participants was relatively small because of local cultural barriers; most women in Egypt are uncomfortable discussing sexual issues, even for scientific purposes, and usually refuse to participate in such studies. The retrospective nature of responding to the assessment scales was another limitation. The last limitation was the lack of information about the COVID‐19 status and the sexual well-being of the participants’ sexual partners. Therefore, future large-scale multicenter studies including the participants’ sexual partners should be conducted. Also, long-term follow-up studies for sexual function and satisfaction after COVID-19 to confirm our findings and to estimate the changes over time. Addressing such complaints is important for ending the stigma attached to them. In general, more attention should be directed toward women's mental health in Egypt.
Conclusions
Six months after infection with coronavirus COVID-19, the prevalence of sexual dysfunction among all participants was 58%. After 6 months COVID-19, there was a decline in the frequency of sexual intercourse and scores on all FST subscales in both groups except pain, with more affection in sexual dysfunction women group. No statistical difference in psychiatric problems between both groups. Sexual dysfunction was associated with renal illness, COVID-19-related oxygen therapy and fatigue, post-COVID-19 vaccination myalgia, and headache. Furthermore, pain was the only sexual problem that improved after COVID-19 in both groups. This Indicated presence of unknown biological and neurological changes due to COVID-19 infection and its vaccination other than psychological stress and illnesses. Therefore, the results of this study recommend that women with the previous risk factors and their partners should have both sexual and psychiatric assessment 6 months post-COVID.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are available from corresponded on request.
Abbreviations
- SARS-CoV-2:
-
Coronavirus 2
- COVID-19:
-
Coronavirus disease 2019
- FSFI:
-
The Female Sexual Function Index
- The SCL-90:
-
The Symptom Checklist 90
References
World Health Organization: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19): Situation Report—72. 2020. https://www.who.int/docs/default‐source/coronaviruse/situation‐reports/20200401‐sitrep‐72‐covid‐19.pdf?sfvrsn=3dd8971b_2. Accessed 1 Apr 2020.
Ahmed GK, Ramadan HK-A, Refay SM, Khashbah MA. Comparison of knowledge, attitude, socioeconomic burden, and mental health disorders of COVID-19 pandemic between general population and health care workers in Egypt. Egypt J Neurol Psychiatry Neurosurg. 2021;57(1):25.
Osman DM, Khalaf FR, Ahmed GK, Abdelbadee AY, Abbas AM, Mohammed HM. Worry from contracting COVID-19 infection and its stigma among Egyptian health care providers. J Egypt Public Health Assoc. 2022;97(1):2.
Kaya Y, Kaya C, Tahta T, Kartal T, Tokgöz VY. Examination of the effect of COVID-19 on sexual dysfunction in women. Int J Clin Pract. 2021;75(3): e13923.
Ahmed GK, Elbeh K, Gomaa HM, Soliman S. Does COVID-19 infection have an impact on children’s psychological problems? Middle East Curr Psychiatry. 2021;28(1):77.
Ahmed GK, Mostafa S, Elbeh K, Gomaa HM, Soliman S. Effect of COVID-19 infection on psychological aspects of pre-schooler children: a cross-sectional study. Middle East Curr Psychiatry. 2022;29(1):42.
Yuksel B, Ozgor F. Effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on female sexual behavior. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2020;150(1):98–102.
Jacob L, Smith L, Butler L, Barnett Y, Grabovac I, McDermott D, et al. Challenges in the practice of sexual medicine in the time of COVID-19 in the United Kingdom. J Sex Med. 2020;17(7):1229–36.
Ahmed GK, Salman SA, Elbeh K, Amer ZS, Abbas AM. Correlation between psychiatric impact of COVID-19 during pregnancy and fetal outcomes in Egyptian women. Psychiatry Res. 2022;317: 114920.
Li G, Tang D, Song B, Wang C, Qunshan S, Xu C, et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on partner relationships and sexual and reproductive health: cross-sectional, online survey study. J Med Internet Res. 2020;22(8): e20961.
Meston CM, Kilimnik CD, Freihart BK, Buss DM. Why humans have sex: development and psychometric assessment of a short-form version of the YSEX? Instrum J Sex Marital Ther. 2020;46(2):141–59.
Ventriglio A, Bhugra D. Sexuality in the 21st century: sexual fluidity. East Asian Arch Psychiatry. 2019;29(1):30–4.
Shaeer O, Skakke D, Giraldi A, Shaeer E, Shaeer K. Female orgasm and overall sexual function and habits: a descriptive study of a cohort of US women. J Sex Med. 2020;17(6):1133–43.
Pedrozo-Pupo JC, Pedrozo-Cortés MJ, Campo-Arias A. Perceived stress associated with COVID-19 epidemic in Colombia: an online survey. Cad Saude Publica. 2020;36(5): e00090520.
Hall KS, Kusunoki Y, Gatny H, Barber J. Stress symptoms and frequency of sexual intercourse among young women. J Sex Med. 2014;11(8):1982–90.
Liu S, Han J, Xiao D, Ma C, Chen B. A report on the reproductive health of women after the massive 2008 Wenchuan earthquake. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2010;108(2):161–4.
Ahmed GK, Khedr EM, Hamad DA, Meshref TS, Hashem MM, Aly MM. Long term impact of COVID-19 infection on sleep and mental health: a cross-sectional study. Psychiatry Res. 2021;305: 114243.
Veer IM, Riepenhausen A, Zerban M, Wackerhagen C, Puhlmann LMC, Engen H, et al. Psycho-social factors associated with mental resilience in the Corona lockdown. Transl Psychiatry. 2021;11(1):67.
Battaglia S, Cardellicchio P, Di Fazio C, Nazzi C, Fracasso A, Borgomaneri S. The influence of vicarious fear-learning in “infecting” reactive action inhibition. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2022.946263.
Tajti J, Szok D, Csáti A, Szabó Á, Tanaka M, Vécsei L. Exploring novel therapeutic targets in the common pathogenic factors in migraine and neuropathic pain. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24044114.
Battaglia S, Cardellicchio P, Di Fazio C, Nazzi C, Fracasso A, Borgomaneri S. Stopping in (e)motion: reactive action inhibition when facing valence-independent emotional stimuli. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2022.998714.
Tanaka M, Szabó Á, Vécsei L. Integrating armchair, bench, and bedside research for behavioral neurology and neuropsychiatry: editorial. Biomedicines. 2022;10(12):2999.
Ancora LA, Blanco-Mora DA, Alves I, Bonifácio A, Morgado P, Miranda B. Cities and neuroscience research: a systematic literature review. Front Psychiatry. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.983352.
Bizjak DA, Stangl M, Börner N, Bösch F, Durner J, Drunin G, et al. Kynurenine serves as useful biomarker in acute, long- and post-COVID-19 diagnostics. Front Immunol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.1004545.
Tanaka M, Tóth F, Polyák H, Szabó Á, Mándi Y, Vécsei L. Immune influencers in action: metabolites and enzymes of the tryptophan–kynurenine metabolic pathway. Biomedicines. 2021;9(7):734.
Tanaka M, Szabó Á, Spekker E, Polyák H, Tóth F, Vécsei L. mitochondrial impairment: a common motif in neuropsychiatric presentation? The link to the tryptophan–kynurenine metabolic system. Cells. 2022;11(16):2607.
Brasso C, Bellino S, Blua C, Bozzatello P, Rocca P. The impact of SARS-CoV-2 infection on youth mental health: a narrative review. Biomedicines. 2022;10(4):772.
Kucukkarapinar M, Yay-Pence A, Yildiz Y, Buyukkoruk M, Yaz-Aydin G, Deveci-Bulut TS, et al. Psychological outcomes of COVID-19 survivors at sixth months after diagnose: the role of kynurenine pathway metabolites in depression, anxiety, and stress. J Neural Transm. 2022;129(8):1077–89.
Lawler NG, Gray N, Kimhofer T, Boughton B, Gay M, Yang R, et al. Systemic perturbations in amine and kynurenine metabolism associated with acute SARS-CoV-2 infection and inflammatory cytokine responses. J Proteome Res. 2021;20(5):2796–811.
Myint AM. Kynurenines: from the perspective of major psychiatric disorders. Febs j. 2012;279(8):1375–85.
Pu J, Liu Y, Zhang H, Tian L, Gui S, Yu Y, et al. An integrated meta-analysis of peripheral blood metabolites and biological functions in major depressive disorder. Mol Psychiatry. 2021;26(8):4265–76.
Noyan H, Erdağ E, Tüzün E, Yaylım İ, Küçükhüseyin Ö, Hakan MT, et al. Association of the kynurenine pathway metabolites with clinical, cognitive features and IL-1β levels in patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorder and their siblings. Schizophr Res. 2021;229:27–37.
Butler MI, Long-Smith C, Moloney GM, Morkl S, O’Mahony SM, Cryan JF, et al. The immune-kynurenine pathway in social anxiety disorder. Brain Behav Immun. 2022;99:317–26.
Ogawa S, Fujii T, Koga N, Hori H, Teraishi T, Hattori K, et al. Plasma L-tryptophan concentration in major depressive disorder: new data and meta-analysis. J Clin Psychiatry. 2014;75(9):e906–15.
Ogyu K, Kubo K, Noda Y, Iwata Y, Tsugawa S, Omura Y, et al. Kynurenine pathway in depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018;90:16–25.
Orlikov A, Ryzov I. Caffeine-induced anxiety and increase of kynurenine concentration in plasma of healthy subjects: a pilot study. Biol Psychiatry. 1991;29(4):391–6.
Nassau DE, Best JC, Kresch E, Gonzalez DC, Khodamoradi K, Ramasamy R. Impact of the SARS-CoV-2 virus on male reproductive health. BJU Int. 2022;129(2):143–50.
Sengupta P, Dutta S. COVID-19 and hypogonadism: secondary immune responses rule-over endocrine mechanisms. Hum Fertil (Camb). 2021. https://doi.org/10.1080/14647273.2020.1867902.
World Health O. Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection (SARI) when COVID-19 disease is suspected: interim guidance, 13 March 2020. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2020.
Wu C, Chen X, Cai Y, Zhou X, Xu S, Huang H, et al. Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Internal Med. 2020;180(7):934–43.
Abdel-Tawab MA. Socioeconomic scale for family, revised edition. M.D. thesis in educational basics, Faculty of Education, Assiut University, 3: 32–55. 2010.
Rosen R, Brown C, Heiman J, Leiblum S, Meston C, Shabsigh R, et al. The Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI): a multidimensional self-report instrument for the assessment of female sexual function. J Sex Marital Ther. 2000;26(2):191–208.
Derogatis LR. SCL-90-R: Administration, scoring and procedures. Manual II for the revised version and other instruments of the psychopathology rating scale series. 1983.
Abdo CH, Oliveira WM Jr, Moreira ED Jr, Fittipaldi JA. Prevalence of sexual dysfunctions and correlated conditions in a sample of Brazilian women–results of the Brazilian study on sexual behavior (BSSB). Int J Impot Res. 2004;16(2):160–6.
Blümel JE, Chedraui P, Baron G, Belzares E, Bencosme A, Calle A, et al. Sexual dysfunction in middle-aged women: a multicenter Latin American study using the Female Sexual Function Index. Menopause. 2009;16(6):1139–48.
Moreno-Lozano M, Durán-Ortíz S, Pérez-Zavala R, Quinzaños-Fresnedo J. Sociodemographic factors associated with sexual dysfunction in Mexican women with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2016;54(9):746–9.
Oindi FM, Murage A, Lema VM, Mukaindo AM. Association of female sexual dysfunction and fertility: a cross sectional study. Fertil Res Pract. 2019;5(1):12.
Dr E, Dr N, Msc I, Dr A, Msc B, Aslan E, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for low sexual function in women: a study of 1009 women in an outpatient clinic of a university hospital in Istanbul. J Sex Med. 2008;5:2044–52.
McCool-Myers M, Theurich M, Zuelke A, Knuettel H, Apfelbacher C. Predictors of female sexual dysfunction: a systematic review and qualitative analysis through gender inequality paradigms. BMC Womens Health. 2018;18(1):108.
McInnes RA. Chronic illness and sexuality. Med J Aust. 2003;179(5):263–6.
Zelop C, Heffner LJ. The downside of cesarean delivery: short- and long-term complications. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2004;47(2):386–93.
Fan D, Wu S, Wang W, Xin L, Tian G, Liu L, et al. Prevalence of placenta previa among deliveries in Mainland China: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(40): e5107.
National Institutes of Health state-of-the-science conference statement. Cesarean delivery on maternal request March 27–29, 2006. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;107(6):1386–97.
Schiavi MC, Spina V, Zullo MA, Colagiovanni V, Luffarelli P, Rago R, et al. Love in the time of COVID-19: sexual function and quality of life analysis during the social distancing measures in a group of Italian reproductive-age women. J Sex Med. 2020;17(8):1407–13.
Finsterer J, Scorza FA, Scorza CA, Fiorini AC. Peripheral neuropathy in COVID-19 is due to immune-mechanisms, pre-existing risk factors, anti-viral drugs, or bedding in the intensive care unit. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2021;79(10):924–8.
Fuchs A, Matonóg A, Pilarska J, Sieradzka P, Szul M, Czuba B, et al. The impact of COVID-19 on female sexual health. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17197152.
Bhambhvani HP, Chen T, Kasman AM, Wilson-King G, Enemchukwu E, Eisenberg ML. Female sexual function during the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States. Sex Med. 2021;9(4): 100355.
Ray A, Chaudhry R, Rai S, Mitra S, Pradhan S, Sunder A, et al. Prolonged oxygen therapy post COVID-19 infection: factors leading to the risk of poor outcome. Cureus. 2021;13(2): e13357.
Puntillo KA, Arai S, Cohen NH, Gropper MA, Neuhaus J, Paul SM, et al. Symptoms experienced by intensive care unit patients at high risk of dying. Crit Care Med. 2010;38(11):2155–60.
de Haro C, Ochagavia A, López-Aguilar J, Fernandez-Gonzalo S, Navarra-Ventura G, Magrans R, et al. Patient-ventilator asynchronies during mechanical ventilation: current knowledge and research priorities. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2019;7(1):43.
Ceban F, Ling S, Lui LMW, Lee Y, Gill H, Teopiz KM, et al. Fatigue and cognitive impairment in post-COVID-19 syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Behav Immun. 2022;101:93–135.
Sykes DL, Holdsworth L, Jawad N, Gunasekera P, Morice AH, Crooks MG. Post-COVID-19 symptom burden: what is long-COVID and how should we manage it? Lung. 2021;199(2):113–9.
Wostyn P. COVID-19 and chronic fatigue syndrome: is the worst yet to come? Med Hypotheses. 2021;146: 110469.
Hamilton LD, Meston CM. Chronic stress and sexual function in women. J Sex Med. 2013;10(10):2443–54.
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RRS, GA, AMH and MAM recruited participants, analysis, and interpreted data, and were the contributors in writing the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The institutional review board of the Faculty of Medicine at Assiut University gave ethical permission for the study (17300748), and the study was registered as a clinical trial with NCT04344834 with link https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/nct04344834. All participants were assured of data security and that their data would be anonymized. This study was conducted in accordance with the most recent version of the Helsinki Declaration.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Shehata, R.R., Ahmed, G.K., Hussien, A.A.R.M. et al. Does post-acute COVID-19 syndrome women's sex problems link to psychiatry after 6 months?. Egypt J Neurol Psychiatry Neurosurg 59, 119 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41983-023-00722-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s41983-023-00722-7