Abstract
Background
Latitudinal and altitudinal patterns of plant species richness have frequently been related to different climate variables such as precipitation, temperature and evapotranspiration. However, studies assessing this relationship have mostly compared different regions and used regional scales of richness (in quadrants of several km2). It is less known the relationship between climate and geographical patterns of species richness in local scales (richness in < 1 ha plots). For central Chile some studies have described geographical patterns of plant species richness, but only using regional scales to quantify richness. It is not known how local richness of plant species varies geographically and if climate variables are related to this variation. In this paper I evaluated latitudinal and altitudinal trends of local richness of woody species within forest ecosystems of the Mediterranean-type climate region in central Chile, and explored if these patterns are related to climatic variables. We used data collected in the field as well as published data of composition of woody species in plots of 100 m2 collected in different localities within this region. Climatic variables were obtained for each locality from isoclimate curves published for the whole region.
Results
Local woody species richness was positively related to latitude and negatively related to elevation. Also, it was positively related to annual precipitation and atmospheric relative moisture, and negatively to mean minimal temperature of winter. In addition, precipitation increased with latitude, and minimal temperature of winter decreased with elevation.
Conclusion
These results suggest that climate may be an important driver of altitudinal and latitudinal patterns of local species richness of woody species in central Chile.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Spatial and geographical variation of species richness has been a widely documented pattern in ecology [1]. Factors such as abiotic constraints, biotic interactions, disturbance and historical processes have been proposed as the major drivers producing this variability [2–4]. In particular, climate has been considered as one of the most important drivers of geographical variability in woody species richness [5–8], and in recent times, studies relating climate with biodiversity have received a major attention in order to predict probable effects of climate warming (e.g. [9]).
Several significant relationships between plant species richness and latitude (e.g. [6, 7, 10, 11]) and altitude (e.g. [12–15]) have been observed, and climatic gradients associated to these geographical trends have been proposed as explanations. In general, species richness increases with precipitation and temperature, although it decreases in wetter and cold or warm and dry climates (e.g. [6, 7, 10, 11, 15, 16]). Some studies have also documented unimodal relationships between species richness and productivity as measured by evapotranspiration [17]. However, most of the studies evaluating the relationship between climate and geographical variation of species richness have included different climatic regions in the analyses, and used regional scales to quantify species richness (geographical quadrants of different latitudinal by longitudinal degrees) (e.g. [4–8, 10, 11, 16], but see [15]). Thus, geographical patterns in local species richness as well as the relationship between climate and local species richness (<1 ha plots) are less known. At local scales many other ecological processes, such as biotic interactions, disturbances, and even historical processes may also have an important influence [2, 18, 19]. Therefore, geographical or climatic patterns in regional species richness are not necessarily the same than for local species richness.
Mediterranean-type climate regions of the world have been recognised as exceptionally high-endemism zones [20, 21]. Mediterranean-type ecosystems have climate with a pronounced dry season period of nearly 4–6 months that strongly limits plant productivity, although important latitudinal and altitudinal climatic gradients also exist [22–24]. The Mediterranean climate area of Chile is distributed in the central region of the country between 31° and 37° S. Two mountain ranges are present in this area, a coastal and an Andean range, and between them a central valley approximately at 200–400 m.a.s.l. The climate in the central valley is drier than both mountain ranges [23]. Within this region, in general, precipitation increases while temperature slightly decreases with latitude [23]. In addition, temperature tipically decreases with altitude [23]. According to the theoretical and observed relationships between climate and species richness mentioned above [6, 7, 10, 11, 15, 16], within central Chile species richness should increase with latitude due to increasing moisture despite the decrease in temperature. In addition, species richness should decrease with altitude due to decreasing temperatures. Effectively, within this region, regional richness of woody species increases with latitude [25, 26], but this is not known for local species richness (plots < 1 ha, sensu [2]). On the other hand, it is very limited the knowledge about altitudinal patterns of plant species richness in Chile. In support of the climate-richness hypothesis [10, 17], within forest habitats of one coastal area in central Chile, García [27] observed a decrease in total (per habitat) woody species richness with elevation, and for the High-Andes (non-forest habitats) of central Chile, Cavieres et al. [28] described a decrease of local richness with elevation. Thus, altitudinal patterns of local species richness in forest ecosystems are still unknown in central Chile. In addition, it has also been documented greater species richness on the coastal than Andean range for different plant life forms in central Chile [22]. However, this has not been evaluated for local species richness. Finally, no study has evaluated the relationship between climate and geographical variation in plant species richness (regional or local) in central Chile.
The aim of this study is to evaluate how local richness of woody native species is related to latitude, altitude and longitude (coastal vs andean range) within forest habitats of the Mediterranean-type climate region of Chile, and to explore if these patterns are related to climate variables. Woody species are the main and more dominant component of vegetation in this region of Chile, hence I focused on these species in this study.
Methods
Study area
The study was performed in forest ecosystems of the Mediterranean-type climate region of Chile. This zone is characterised by a seasonal climate, with dry summers and cold winters during which the precipitation occurs [23].
The forest habitats of the chilean Mediterranean region present two large types of forests: Sclerophyllous forests, dominated by evergreen species such as Cryptyocarya alba, Quillaja saponaria, Lithrea caustica, Schinus latifolia and Kageneckia angustifolia, distributed in the north part of the region as well as lower elevations of the south part of this region. This region also include Mixed forests dominated by the deciduous species Nothofagus obliqua and Nothofagus glauca, and different sclerophyllous species. This forest is distributed mainly in higher areas of the south part of this region although some fragments of this forest can be found in high-elevation sites in some coastal areas of the north part of this region [29].
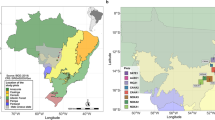
Localities used in this study were selected in such way that they cover latitudinal and altitudinal gradients in both mountain ranges and types of forest Mediterranean vegetation. The localities (Fig. 1, Table 1) covered from 32°32′ to 36°03′ S, mainly on the western versant of each mountain range. Nine sites were located on the coastal and nine on the Andean range. The latitudinal gradient was similar for both coastal and Andean ranges. However, the altitudinal range on the Andean range was smaller than on the coastal range because the coastal range starts from approximatelly the sea level, while the Andean range starts approximately from 400 m.a.s.l. at the central valley. Localities from the central valley (between the coastal and the Andean range) were not included because most of native vegetation of this area has been replaced with other land-uses within this region.
Geographic location of localities used in the study within the Mediterranean region of Chile. Names, latitude and longitude of each locality are in Table 1
Species richness, climate and analyses
Two sources of species richness data were used: from sampling in 11 localities and from published data in 7 localities (Table 1). In both sampled and published data, richness corresponded to the number of woody plant species (trees, shrubs, woody vines and woody epiphytes) in plots of 100 m2 (10 × 10 m). Only native species were included. Published data were obtained from Casassa [30], San Martin [31] and Ramírez et al. [32]. Published vegetational plots selected from each locality were sampled within an homogenous vegetation and habitat type. Original data used in this paper were sampled within each locality by 20 vegetational plots, distributed sistematically 50 m apart along two transects including ten plots on each one. Transects were also separated 50 m each other. Transects in each locality were located within a homogeneous habitat and vegetation type. Due to local species richness may vary within a locality and in order to eliminate pseudoreplication, the average of richness per locality was used to perform every analysis, either for data coming from published as well as sampled information.
Species were taxonomically identified in the field and some specimens were collected for further identification. These specimens were stored in labs of the Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad de Chile, for a subsequent storage in the Herbarium of the Natural History Museum. For this reason, no formal voucher code was assigned to these specimens. Nomenclature follows Marticorena & Quezada [33], except Raukaua laetevirens (Gay) Frodin. Sampling of plant species was authorized by Corporación Nacional Forestal (CONAF) within National Reserves and Parks, and sampling of endangered species followed CITES principles.
Climate data of each locality were obtained by contrasting its geographical location with isoclimate curves published by Santibáñez & Uribe [34]. These curves indicate zones of equal climate obtained from extrapolation based on information from all meteorological stations available within this region. Through this climate classification we were able to infer the climate at a scale < 1 km2. Four climatic variables were selected: mean maximal temperature of January (summer) (MTS), mean minimal temperature of July (Winter) (MTW), annual precipitation (PP), atmospheric relative moisture of summer (RMS) and atmospheric relative moisture of winter (RMW). These variables allow to represent climatic variability in each locality (e.g. annual temperature oscillation) as well as latitudinal and altitudinal variation within the region.
The relationships between climate variables and species richness were evaluated by regression analyses as local species richness showed a normal distribution of data. The correlation among climate variables was also examined. Likewise, the relationships between latitude, altitude and species richness were evaluated by regression analyses. These relationships were examined both for all the study area and separately for each mountain range. An ANOVA was used to compare species richness between the andean and coastal ranges.
Results
Geographical patterns of local species richness
A large variability in species richness between studied localities was observed (Table 1). Woody species richness varied between 4.4 and 15.8 species per 100 m2. A positive relationship between latitude and species richness either general (R2 = 0.26, F = 5.75, P = 0.029, N = 18) as well as separately for the coastal (R2 = 0.61, F = 10.85, P = 0.013, N = 9) and the Andean range (R2 = 0.49, F = 6.74, P = 0.036, N = 9) (Fig. 2) was observed. A significant negative linear relationship between altitude and species richness was observed including all localities (R2 = 0.64, F = 28.06, P < 0.001, N = 18) as well as separately for the coastal (R2 = 0.47, F = 6.24, P = 0.041, N = 9) and the Andean range (R2 = 0.71, F = 17.49, P = 0.004, N = 9) (Fig. 3). Finally, significant differences in local species richness between the Coastal and Andean ranges (ANOVA, F = 5.01, P = 0.039, N = 18) was observed, being the Coastal range richer (10.99 species/plot ± 1.27 (mean ± 1 S.D.)) than the Andean range (7.58 species/plot ± 0.84 (mean ± 1 S.D.)). Species composition observed in each locality sampled for this study is described in the Appendix 1. Species composition of other localities can be found in the bibliographic reference of the study carried out in each locality.
Climatic patterns of localities used in the study
Climate varied between localities included in the study. PP increased from 354 mm at the northern part to 1315 mm at the sourthern part of the studied region. MTW ranged from −2.4 to 7.9 °C and MTS from 18.6 to 28.2 °C. RMS varied from 46 to 80 % and RMW from 57 to 90 %. Including only localities used in the study, PP only showed a significant positive correlation with the latitude (Table 2). MTW, RMS and RMW significantly decreased with altitude and MTS was not correlated to latitude or altitude (Table 2). Among climate variables, MTW was positively correlated to RMS and RMW. Also, RMS and RMW were positively correlated (Table 2). Furthermore, MTW, RMS and RMW significantly differed between the coastal and the Andean range, being in each case higher the values on the coastal range (Table 3). The dataset used for all climatic analyses is shown in Appendix 2.
Relationships between climate variables and local species richness
From single linear regressions, local woody species richness was significantly positively related to MTW (Fig. 4b), RMW (Fig. 4d) and RMS (Fig. 4e) (Table 4). From a Forward Stepwise Regression, only precipitation and RMS were significantly related (P < 0.05) to local species richness, both of them positively (F (2,15) = 14.27, P < 0.001, R2 = 0.66, Model: Richness = −14.1 + 0.84*RMS + 0.41*PP). According to parameters of regression model, RMS (0.84) was more important at explaning variation of species richness than precipitation (0.41).
Relationship between climate variables and local species richness of woody plants in forest ecosystems within the mediterranean region of Chile (tendency curves are shown only for significant relationships from single or stepwise regressions) ((MTS: Maximal Temperature of January (Summer) (a), MTW: Minimal Temperature of July (Winter) (b), PP: Mean Annual Precipitation (c), RMW: Relative Moisture of July (winter) (d), RMS: Relative Moisture of January (summer) (e))
Discussion
Results observed in this study indicate that local species richness of woody plants is positively related to latitude and inversely related to altitude. Interestingly, these trends were observed along the coastal as well as the Andean range of the Mediterranean region of Chile. In addition, precipitation increased with latitude and minimal temperatures of winter and relative moisture were negatively correlated to altitude in this region, which may explain latitudinal and altitudinal patterns in local richness of woody species. In fact, these and others climate variables were also related to local species richness, which suggest that climate may be an important driver of spatial and in particular latitudinal and altitudinal variability of local richness of woody species in central Chile.
Many studies suggest that spatial and especially geographical variation of woody species richness is strongly modulated by climate (e.g. [5–8, 10, 11, 15–17, 35–37], but see [4]). However, most of studies relating climate to species richness have used regional scales to measure species richness (geographical quadrants of different latitudinal by longitudinal degrees). It is less known whether climate has also influence on geographical variation of local woody species richness (plots < 1 ha) (e.g. [15, 36, 37]), where other ecological processes, such as biotic interactions, disturbances, and even historical processes may have strong influences on local richness [2, 3, 18, 19]. In fact, important plant-plant interactions modulating species richness and abundance have been documented in central Chile [38–41]. Thus, results observed in this paper suggest that despite local biotic interactions may be playing a role in this region, climate may also be important in structuring spatial variation of local richness of woody species in central Chile.
Despite the global negative relationship between latitude and species richness [6, 42, 43], specific regions such as the Mediterranean region of Chile may have positive relationships between latitude and species richness, which probably contributes to the high variability reported for this global latitudinal pattern (e.g. [42]). In this study, the only climate variable significantly related to the latitude within central Chile was precipitation. Although the specific regression between precipitation and local species richness was not significant, the stepwise regression showed that precipitation and relative moisture of summer were more related to species richness than other climate variables. Hence, although precipitation is not the main variable explaining the geographical variation in species richness, it may contribute to produce the latitudinal pattern observed in species richness of woody species in central Chile.
On the other hand, many altitudinal patterns of woody species richness reported by different studies have shown negative trends [13–15, 18, 28, 36, 44], which is consistent with results observed in this study. These negative relationships have mainly been documented where there is no water constraints at the bottom of the altitudinal gradients, and decreasing temperature reduces growth and survival of an increasing number of species [14, 18]. Hence, although mean minimal temperature of winter was not the main variable explaining the geographical variation of species richness in this study, the negative relationship between them, along with the decrease of it with altitude, may explain the linear decrease of species richness with altitude on the coastal and Andean range of this region. However, many other studies have also reported unimodal altitudinal patterns of species richness, mainly where there are water constraints at the bottom of the elevation gradient such as in arid and semiarid regions [12, 15, 36]. This increasing water availability with altitude would enhance species richness up to constraints due to low temperatures reduce species richness again in higher altitudinal levels [15, 36]. Despite Mediterranean region of Chile may be considered as a semiarid region, no increment in precipitation with altitude, at least for localities used in the study, was found. In contrast, a reduction in relative moisture with altitude was observed. This probably occurred because no locality from the central valley between Andean and coastal ranges was included, where climate is drier than higher altitudinal levels of both mountain ranges [23, 34].
Greater local richness of woody species in the coastal than andean ranges of this region has also been observed at a regional scale of richness, and for different life forms [22]. Mean minimal temperature of winter and relative moisture of winter and summer were higher on the coastal range. In addition, local species richness was positively related to mean minimal temperature and relative moisture of summer, hence these climate variables may explain this longitudinal variation in local richness of woody species in central Chile.
Regardless latitudinal, altitudinal and longitudinal patterns in species richness reported in this study, results observed here suggest that climate, and in particular water-related variables (precipitation and relative moisture), may be driving local richness of woody species in central Chile, although temperature patterns are also probably influencing distribution and thus richness of woody species in this region. Many other studies carried out in semiarid environments have also highlighted the role of climate and especially water-related variables on plant species distribution and richness (e.g. [15, 16, 20, 35, 45–49]). In central Chile, other vegetation processes and patterns, for example topographic variability, have also been associated to water-related variables. In particular, species composition and plant regeneration strongly differ between north-facing and south-facing slopes [38, 39, 41, 50]. Thus, climate is probably an important factor, not only driving geographical patterns in species richness, but also many other patterns and processes of plant communities in central Chile and other semiarid ecosystems. However, the relative importance of climate and other factors such as biotic interactions and disturbance, should be adressed in future research in central Chile.
The latitudinal variation of local woody plant species richness in the Mediterranean region of Chile described here is very similar to that documented for regional richness of woody species in this region [25, 26]. Similarly, coastal-andean differences in species richness observed in this study at a local scale of richness is similar to that observed at a regional scale [22]. Therefore, it is possible to speculate that local and regional richness of woody species are positively related, which has been documented in some other studies (e.g. [51–53]). This suggests that factors driving patterns of richness at one scale may be the same or similar to those driving patterns of richness at other scales. Then, it is possible that both regional and local richness of woody species are strongly influenced by climate variability within the Mediterranean region of Chile.
Finally, as response to warmer and drier conditions predicted by climate change models for semiarid regions [54], it is possible to predict that, in the future, local richness of woody species will decrease in higher latitudes due to drier conditions, and increase in higher elevations due to warmer conditions within the Mediterranean region of Chile and probably other Mediterranean climates in the world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, these results indicate that local woody species richness is related to latitudinal and altitudinal geographical gradients and that climate, in particular water-related variables (precipitation and relative moisture), may be driving these patterns, although temperature patterns are also probably influencing richness of woody species in this region. These results show that geographical patterns of species richness at a regional scale are very similar to those at a local scale within this region.
References
Rosenzweig M. Species diversity in space and time. Cambridge University Press; 1995.
Cornell H, Lawton J. Species interactions, local and regional processes, and limits to richness of ecological communities: a theoretical perspective. J Anim Ecol. 1992;61:1–12.
Huston M. Local processes and regional patterns: appropriate scales for understanding variation in the diversity of plants and animals. Oikos. 1999;86:3393–401.
Ricklefs RE, Qian H, White PS. The region effect on mesoscale plant species richness between eastern Asia and eastern North America. Ecography. 2004;27:129–36.
Allen A, Brown J, Gillooly J. Global biodiversity, biochemical kinetics, and the energetic-equivalence rule. Science. 2002;297:1545–8.
Currie DJ. Energy and large-scale patterns of animal and plant species richness. Am Nat. 1991;137:27–49.
Francis AP, Currie DJ. Global patterns of tree richness in moist forests: another look. Oikos. 1998;81:598–602.
Wright D. Species-energy theory: an extension of species-area theory. Oikos. 1983;41:496–506.
Gedan KB, Bertness MD. Experimental warming causes rapid loss of plant diversity in New England salt marshes. Ecol Lett. 2009;12:842–8.
O’ Brien E, Field R, Whittaker R. Climatic gradients in woody plant (tree and shrub) diversity: water-energy dynamics, residual variation, and topography. Oikos. 2000;89:588–600.
Whittaker RJ, Field R. Tree species richness modelling: an approach of global applicability? Oikos. 2000;89:399–402.
Arroyo MTK, Squeo F, Armesto JJ, Villagrán C. Effects of aridity on plant diversity in the northern chilean Andes: Results of a natural experiment. Ann Mo Bot Gard. 1988;75:55–78.
Grytnes JA, Vetaas OR. Species richness and altitude: a comparison between null models and interpolated plant species richness along the Himalayan altitudinal gradient, Nepal. Am Nat. 2002;159:294–304.
Grytnes JA, Beaman J. Elevational species richness patterns for vascular plants on Mount Kinabalu, Borneo. J Biogeogr. 2006;33:1838–49.
Kluge J, Kessler M, Dunn RR. What drives elevational patterns of diversity? A test of geometric constraints, climate and species pool effects for pteridophytes on an elevational gradient in Costa Rica. Glob Ecol Biogeogr. 2006;15:358–71.
Ferrer-Castán D, Vetaas OR. Pteridophyte richness, climate and topography in the Iberian Peninsula: comparing spatial and nonspatial models of richness patterns. Glob Ecol Biogeogr. 2005;14:155–65.
Field R, O’Brien EM, Whittaker RJ. Global models for predicting woody plant richness from climate: development and evaluation. Ecology. 2005;86:2263–77.
Rahbek C. The role of spatial scale and the perception of large-scale species-richness patterns. Ecol Lett. 2005;8:224–39.
Tilman D. Resource competition and community structure. USA: Princeton University Press; 1982.
Cowling RM, Rundel PW, Lamont BB, Arroyo MTK, Arianoutsou M. Plant diversity in Mediterranean-climate regions. Trends in Ecology and Evolution. 1996;11:362–6.
Myers N, Mittermeier RA, Mittermeier CG, Da Fonseca GA, Kent J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature. 2000;403:853–8.
Arroyo MTK, Cavieres LA, Marticorena C, Muñoz M. Convergence in the Mediterranean floras in central Chile and California: insights from comparative biogeography. In: Arroyo MTK, Zedler P, Fox M, editors. Ecology and Biogeography of Mediterranean Ecosystems in Chile, California and Australia: 43–88. New York: Springer; 1995.
Di Castri F, Hajek E. Bioclimatología de Chile. Chile: Universidad Católica de Chile; 1976.
Di Castri F, Goodall D, Specht R. Mediterranean-Type Shrublands. Amsterdan: Elsevier; 1981.
Bannister JR, Vidal OJ, Teneb E, Sandoval V. Latitudinal patterns and regionalization of plant diversity along a 4270-km gradient in continental Chile. Austral Ecology. 2012;37:500–9.
Villagrán C. Quaternary History of the Mediterranean Vegetation of Chile. In: Arroyo MTK, Zedler P, Fox M, editors. Ecology and Biogeography of Mediterranean Ecosystems in Chile, California and Australia. New York: Springer; 1995. p. 3–20.
García N. Caracterización de la flora de altos de Chicauma, Chile (33° S). Gayana Botanica. 2010;67:65–112.
Cavieres LA, Peñaloza A, Arroyo MTK. Altitudinal vegetation belts in the high-Andes of central Chile (33°S). Rev Chil Hist Nat. 2000;73:331–44.
Gajardo R. La Vegetación Natural de Chile. Clasificación y Distribución geográfica. Santiago, Chile: Editorial Universitaria; 1994.
Casassa I. Estudio demográfico y florístico de los bosques de Nothofagus obliqua (Mirb.) Oerst. en Chile central. Chile: Master Thesis, University of Chile; 1986.
San Martin J. Caracterización florístico-estructural de remanentes de bosques de Nothofagus alpina, Fagaceae, del área costera de Chile central. Bosque. 2003;24:71–85.
Ramírez C, San Martin C, San Martin J, Villaseñor R. Comparación fitosociológica de los bosques de Belloto (Beilschmiedia, Lauraceae) en Chile central. Bosque. 2004;25:69–85.
Marticorena C, Quezada M. Catálogo de la flora vascular de Chile. Gayana Botanica. 1985;1–2:1–157.
Santibáñez F, Uribe J. Atlas Agroclimático de Chile. Santiago, Chile: Ministerio de Agricultura, Fondo de Investigación Agraria, CORFO; 1990.
Aronson J, Schmida A. Plant species diversity along a Mediterranean-desert gradient and its correlation with interannual rainfall fluctuations. J Arid Environ. 1992;23:235–47.
Bhattarai KR, Vetaas OR. Variation in plant species richness of different life forms along a subtropical elevation gradient in the Himalayas east Nepal. Glob Ecol Biogeogr. 2003;12:327–40.
Oberle B, Grace JB, Chase JM. Beneath the veil: plant growth form influences the strength of species richness-productivity relationships in forests. Glob Ecol Biogeogr. 2009;18:416–25.
Badano EI, Cavieres LA, Molina-Montenegro MA, Quiroz CL. Slope aspect influences plant association patterns in the Mediterranean matorral of central Chile. J Arid Environ. 2005;62:93–108.
Becerra PI, González-rodríguez V, Smith-ramírez C, Armesto JJ. Spatio-temporal variation in the effect of herbaceous layer on woody seedling survival in a Chilean mediterranean ecosystem. J Veg Sci. 2011;22:847–55.
Fuentes ER, Otaiza RD, Alliende MC, Hoffmann AJ, Poiani A. Shrub clumps of the Chilean matorral vegetation: structure and possible maintenance mechanisms. Oecologia. 1984;62:405–11.
Fuentes ER, Hoffmann AJ, Poiani A, Poiani MC. Vegetation change in large clearings: patterns in the Chilean matorral. Oecologia. 1986;68:358–66.
Gentry AH. Changes in plant community diversity and floristic composition on environmental and geographical gradients. Ann Mo Bot Gard. 1988;75:1–34.
Quigley MF, Platt WJ. Composition and structure of seasonally deciduous forests in the Americas. Ecological Monograph. 2003;73:87–106.
Sánchez-González A, López-Mata L. Plant species richness and diversity along an altitudinal gradient in the Sierra Nevada, México. Diversity and Distribution. 2005;11:567–75.
Bond W. On alpha diversity and the richness of the Cape flora: a study in southern Cape fynbos. The role of nutrients. In: Kruger FJ, Mitchell DT, Jarvis JU, editors. Mediterranean Type Ecosystems: 337–356. New York: Springer; 1983.
Hoffman MT, Midgley GF, Cowling RM. Plant richness is negatively related to energy availability in semi-arid southern Africa. Biodivers Lett. 1994;2:35–8.
Knight RS, Crowe TM, Siegfried WR. Distribution and species richness of trees in southern Africa. Journal of South African Botany. 1982;48:455–80.
Naveh Z, Whittaker RH. Structural and floristic diversity of shrublands and woodlands in northern Israel and other mediterranean areas. Vegetatio. 1979;41:171–90.
Richerson PJ, Lum KL. Patterns of plant species diversity in California: relation to weather and topography. Am Nat. 1980;116:504–36.
Armesto JJ, Martínez J. Relations between vegetation structure and slope aspect in the Mediterranean region of Chile. J Ecol. 1978;66:881–9.
Pärtel M, Zobel M, Van Der Maarel E. The species pool and its relation to species richness – evidence from Estonian plant communities. Oikos. 1996;75:111–7.
Pärtel M, Zobel M, Liira J, Zobel K. Species richness limitations in productive and oligotrophic plant communities. Oikos. 2000;90:191–3.
Safford H, Rejmánek M, Hadac E. Species pools and the “hump-back” model of plant species diversity and empirical analysis at a relevant spatial scale. Oikos. 2001;95:282–90.
Saxon E, Baker B, Hargrove W, Hoffman F, Zganjar C. Mapping environments at risk under different global climate change scenarios. Ecol Lett. 2005;8:53–60.
Acknowledgements
The autor thanks to Mary Kalin Arroyo for supporting this work.
Funding
This work was financed by Fondecyt N° 1980705, Institute of Ecology and Biodiversity, IEB, project P05-002 ICM and the project CONICYT FB 0002 – 2014.
Availability of data and material
The dataset supporting the conclusions of this article is included within the article.
Author’s contribution
The autor of this article carried out all sections of it.
Competing interests
The author declares that he has no competing interest.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix 1
Appendix 2
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Becerra, P.I. Relationship between climate and geographical variation of local woody species richness within the Mediterranean-type region of Chile. Rev. Chil. de Hist. Nat. 89, 12 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40693-016-0062-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40693-016-0062-x