Abstract
Definite increases in the components ratios of CO2/H2O, CO2/H2S, CO2/CH4 and He/CH4 were observed at the fumarolic gases from Owakudani geothermal area located at the center of Hakone volcanic caldera (Honshu Island, Japan), synchronized with the earthquake swarm in 2015. Such variations were due to the dominance of a magmatic component over a hydrothermal component, suggesting the earthquake swarm was produced by the injection of magmatic gases into the hydrothermal system. The CO2/H2O ratio of magmatic gas was estimated to be 0.0045 before the earthquake swarm, which increased up to 0.013 during the earthquake swarm, likely produced by the pressurization of magma as a result of magma sealing where the pressure increment in magma was estimated to be 3% to the lithostatic pressure. The H2O and CO2 concentration in magma were estimated to be 6.3 wt% and 20 wt ppm, respectively, assuming a temperature 900 °C and a rhyolitic composition. In May 2015, a few months prior to the earthquake swarm in May 2015, a sharp increase in the Ar/CO2 and N2/He ratios and a decrease in the isotopic ratio of H2O were observed at the fumarolic gas. The invasion of air into the hydrothermal system increased the Ar/CO2 and N2/He ratios. The decrease in the isotopic ratio of H2O was induced by partial condensation of H2O vapor.

Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
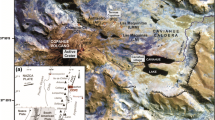
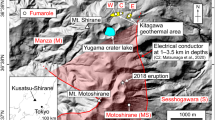
Mt. Hakone is an active volcano located on Honshu Island of Japan (Fig. 1a). The volcano has a caldera structure with several central cones (Fig. 1b). Three geothermal areas: Owakukdani (Ow in Fig. 1c), Kamiyuba (Ky) and Sounzan (So) developed as the foothill of Kamiyama (Ka) central cone. The history of caldera formation was first proposed by Kuno (1950) and modified by Mannen (2008). The geothermal area of Ow is a popular sightseeing spot visited by two million tourists every year. In order to prevent human injury by possible eruption, a monitor program was started in the 1970s at Mt. Hakone.
Location of Hakone volcano and the sampling points of fumarolic gases. a Map of the Japan and the location of Hakone volcano. b Topographic map of Hakone volcano with caldera structure. The bold dashed curve outlines the caldera rim. L, Ka and Ko represent Lake Ashinoko, Kamiyama central cone and Komagatake central cone, respectively. The ellipses marked E1, E2, E3, E4 and E5 indicate regions of hypocenters of earthquake swarms determined by Hot Springs Research Institute of Kanagawa Prefecture (HSRI). c Solid circles (N and S) indicate the fumaroles where volcanic gas was sampled in this study. Solid diamond (C) is the newly created crater at the eruption in 2015. Open circles and open square indicate location of other fumaroles (circles) and borehole, respectively. Bold lines and curves with teeth indicate the roads and cliffs, respectively
Eruptive activity at the central cones took place 50 ka ago and continued until 3 ka ago (Kobayashi et al. 1997), when a phreatic eruption occurred. With the phreatic eruption, a section of the western flank of Ka (Fig. 1c) collapsed and caused debris flow, damming a river to form Lake Ashinoko in Fig. 1b. No historical eruption has been recorded at Hakone volcano before the small phreatic eruption in 2015 at the geothermal area of Ow.
Based on the analysis of seismic wave velocities beneath Hakone caldera, Yukutake et al. (2015) recognized a region with high Vp/Vs ratio beneath Ko (Fig. 1c) likely due to a degassing magma as the depth of − 10 km. Above the degassing magma, a region with low Vp/Vs ratio was found, which was estimated to be a gas reservoir dominated by H2O and CO2. In 2001 to 2009, volcanic gases and borehole gases were analyzed by Ohba et al. (2011). The CO2/H2O and CO2/H2S ratios were high in 2001 when a seismic swarm occurred. It increased again in 2006 and 2008 when a new seismic swarm resumed. The increases in CO2/H2O and CO2/H2S ratios suggested the injection of a CO2-rich magmatic gas into the hydrothermal system, implying that a magmatic component was episodically supplied to the hydrothermal system in 2006 and 2008. The earthquake swarms resulted from the injection of the gas through the shallow crust accompanying the break of the so-called sealing zone (Fournier 1999). Daita (2013) monitored fumarole S (Fig. 1c) at Ky geothermal area in 2012 and 2013 by using a gas detector tubes system (GASTEC corp.), when a sharp increase in CO2/H2S ratio, synchronized with the start of seismic swarm, was found.
At Hakone volcano, an earthquake swarm started on April, 26, 2015. On June, 30, 2015, a small phreatic eruption occurred at the geothermal area of Ow. After the eruption, several craters formed (Mannen et al. 2018). The C crater in Fig. 1c is one of the newly born craters. In this study, we repeatedly sampled fumarolic gas at Ow and Ky geothermal areas for investigating the relationship between volcanic activity and volcanic gas chemistry.
Sampling and analysis of fumarolic gases
Fumarolic gases were sampled every month from May 2013 until February 2018, at the points N and S (Fig. 1c). In addition, fumarolic gases were sampled at point C (Fig. 1c). The outlet temperature of fumarolic gas was measured by a thermocouple with K-type sensor. Gas sampling was carried out by a titanium pipe inserted into the fumarole which was then connected to a rubber tube. The rubber tube was connected to a 120-ml pre-evacuated Pyrex glass bottle with airtight stop cock (Giggenbach 1975), where 20 ml of 5 M KOH solution was added. Steam-condensated and acidic gases (CO2, SO2, H2S, HCl etc.) were absorbed by the KOH solution, whereas the residual gases (hereafter R-gas), e.g., N2, O2, Ar, He, H2 and CH4, enriched in the headspace of glass bottle. Components in the KOH solution were analyzed according to the method by Ozawa (1968). The SO2/H2S ratio in the fumarolic gas was determined using a KI–KIO3 solution (Ozawa, 1968), the analytical accuracy of which was evaluated by Lee et al. (2016). The analysis of HCl was only carried out at the fumarole C. The total molar amount of R-gas was given by the head space volume of bottle and the inner pressure of head space as room temperature. Based on the molar amount of H2O, CO2, H2S, SO2 and R-gas, the relative concentration (µmol/mol) of those components was calculated (Tables 1, 2 and 3).
The R-gas was analyzed by using two different gas chromatographs with Ar and He as gas carriers (hereafter GC-Ar and CG-He, respectively). Concentration of He, H2, O2, N2 and CH4 was determined by GC-Ar equipped with a 6 m-long MS5A packed column and a TCD detector. The temperature of the column and detector was kept at 50 and 100 °C during analysis, respectively. The flow rate of Ar was 30 ml/min. In general, He analysis by GC is difficult due to the overlap where H2 has high concentrations. Under the above condition, the He of 64 ppm in R-gas could be separated from the H2 of 67% in R-gas without the overlap between the chromatographic peaks of He and H2. All of R-gas sample in this study had a good separation between He and H2 peaks.
The relative concentration of N2 and Ar was determined by GC-He. In the GC-He, equipped with a 6 m-long Gaskuropack-54 column (GC Sciences Inc.) and a TCD detector, the temperature of the column and detector was kept at − 70 and 50 °C, respectively. Under the above conditions, N2, O2 and Ar in R-gas were well separated on the chromatographic chart. The concentration of Ar in R-gas was calculated by,
where X and R indicate the concentration obtained by GC-Ar and GC-He, respectively.
The H2O isotopic ratio was determined by the cooling of the fumarolic gas with a double tube condenser made of Pyrex glass. The fumarolic gas flowing out of the condenser was collected in a 5-l plastic gas sampling bag. The gas collected in the bag was used for on-site determination of CO2/H2S molar ratios by gas detector tube system. We used “2HH” and “4HH” detector tubes for the measurement of CO2 and H2S, respectively. The applicable range of concentration for 2HH and 4HH was 5–40% and 0.1–2.0%, respectively.
The isotopic ratio of condensed water was determined by an IR-laser cavity ring-down analyzer (Picarro Inc., L2120-i). The analytical precision of the analyzer was ± 0.12 and ± 0.05‰ for δD and δ18O, respectively. The isotopic ratio of H2 in R-gas was determined by a continuous flow system combined with a mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific Delta V) (Tsunogai et al. 2011). The analytical precision of the analyzer was ± 0.8‰ for δD.
Results
The analytical results of fumarolic gases at N, S and C are listed in Tables 1, 2 and 3, respectively. Time variations of CO2/H2O, H2S/H2O, CO2/H2S, CO2/CH4 and He/CH4 ratios are shown in Fig. 2 with the number of earthquakes per half month at Hakone volcano observed by Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA). On April, 26, 2015, the earthquake swarm started (Mannen et al. 2018). The hypocenters of earthquakes were distributed in the regions E1 to E4 of Fig. 1b (Mannen et al. 2018). The magnitude of earthquakes during the unrest was < 2.9. The largest earthquake was observed on the July, 21, 2015 (Mannen et al. 2018). On the May, 15, 2015, the largest daily number of earthquake (955, M ≥ 0) was observed (Mannen et al. 2018). In the E5 region of Fig. 1b, a small earthquakes swarm took place in 2017 in which the largest earthquake (M = 1.5) occurred on the April 11 (https://www.onken.odawara.kanagawa.jp/earthquake/).
In May 2015, the CO2/H2O ratio increased up along with the frequency of earthquakes (Fig. 2a), and then, the earthquake events decreased after May 2015, as well as the CO2/H2O ratio. Similar increases and decreases were observed in the ratios CO2/H2S, CO2/CH4 and He/CH4 along the occurrence of earthquakes in 2015 (Fig. 2c, d, 2, respectively). For the indication in Fig. 2c, the CO2/H2S ratio determined by gas detector tubes system was used. The corresponding CO2/H2S curve determined by chemical analysis was not smooth compared with the curve in Fig. 2c, likely due to the contamination of native sulfur particles during the sampling. There was abundant native sulfur sublimate around the fumarole outlet, because the insertion of a titanium tube during sampling likely disturbed the fumarolic gas discharge, releasing particles of native sulfur. The native sulfur contamination increases the amount of sulfur dissolved in KOH solution.
The gradual decrease in the CO2/H2S, CO2/CH4 and He/CH4 ratios after the maximum in 2015 continued until around March 2017, followed by a gradual increase which peaked in September 2017. The increase in 2017 was not clear in CO2/H2O ratio due to the fluctuation (Fig. 2a). No increase was observed in the H2S/H2O ratio in May 2015 when the earthquake swarm observed (Fig. 2b). Beside small fluctuations, the H2S/H2O ratio was stable over the whole duration of this study.
Time variations of the SO2/H2S, H2/H2O, Ar/CO2 and N2/He ratios are shown in Fig. 3. For the calculation of Ar/CO2 and N2/He ratios, the Ar and N2 brought by the direct contamination of air during sampling were removed by the following equations,
where Ci is the concentration of i in fumarolic gas and \(C_{i}^{*}\) is the corrected concentration eliminating the effect of direct air contamination. In the equations, it was assumed that the fumarolic gas does not include O2 originally, and the O2 contaminated in fumarolic gas accompanied atmospheric N2 and Ar with the equivalent air abundance. It should be noted that the above correction does not account for O2 lost in the oxidation of reduced S in solution.
In general, the SO2/H2S ratio is a useful parameter for evaluating volcanic activity, as it tends to increase when volcanic activity was elevated (e.g., Ossaka et al. 1980). With some fluctuation, SO2/H2S ratio of N and S was < 0.06 over the whole duration of this study (Fig. 3a), being a contrast to the SO2/H2S ratio at C as high as 0.5 to 1.5 (Table 3). The H2/H2O ratio shows a weak correlation with the number of earthquakes; it started to increase slightly after May 2015; then, it maximized in the late of 2015 (Fig. 3b).
The Ar/CO2 and N2/He ratios show a sharp increase a few months prior to the earthquake swarm in May 2015. Actually, Ar/CO2 and N2/He ratios maximized on April, 24, 2015, which was 2 days before the start of earthquake swarm. On May, 8, 2015, those ratios returned to the normal levels. It should be noticed that those precursory increases only happened at fumarole N. No increase was detected at S fumarole.
The time variation in δD of H2O, δ18O of H2O, δD of H2 and the apparent equilibrium temperature (AET) are shown in Fig. 4. The AET was calculated between δD of H2O and δD of H2 based on the following equation (Richet et al. 1977),
where
The averaged H2 concentration in the gas of N, S and C is 2.6, 55 and 233 µmol/mol, respectively. The depth of the borehole, from which the gas of C is discharging, is 500 m below the surface. Therefore, the most of H2 in the gas of N and S is thought to be formed in the crust shallower than − 500 m to surface. The δD of H2 in the gas of C is much higher than the ratio of the gas N and S (see Tables 1, 2 and 3), consistent with the above estimation on H2 formation. The AET calculated between the δD of H2O and H2 means the temperature of crust shallower than − 500 m to surface. The δD and δ18O of H2O decreased significantly a few months prior to the start of earthquake swarm in May 2015 (Fig. 4a, b) at N fumarole. A similar decrease was observed in 2017 at fumarole N, whereas no decrease was observed at fumarole S.
The δD of H2 and AET were stable over the whole duration of this study with the exception of two periods. In September to December 2014, those values significantly decreased relative to normal level (Fig. 4c, d). A slight decrease was also observed in March and April in 2017. It should be noticed that the both decreases happened almost simultaneously at N and S fumaroles.
Discussion
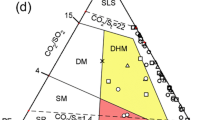
We try to group the components in fumarolic gas by use of triangular diagrams (Fig. 5). The He–N2–Ar ternary diagram shows a linear distribution of data points, suggesting two common-end members in fumarolic gases N, S and C. The end member with high He/Ar and N2/Ar ratios is estimated to be the magmatic component which is ubiquitous at the volcanoes on subduction zone (Kita et al. 1993; Giggenbach 1997). Another end member with low He/Ar and N2/Ar ratios could be air or ASW. The ASW is the atmospheric components saturated in water at 15 °C. A similar feature also found in the diagram for He–CO2–Ar system (Fig. 5), suggesting the fumarolic gases N, S and C, contains a common magmatic component.
In Fig. 6a–c, respectively, for He–H2S–Ar, He–H2–Ar and He–CH4–Ar, the distributions of data points are different from the distribution in Fig. 5. No definite value can be found in H2S/He, H2/He and CH4/He ratios for non-atmospheric end member, suggesting H2S, H2 and CH4 belongs to a group different from the magmatic component. As explained by Giggenbach (1987), the reduced molecules group, H2S, H2 and CH4, are originating in hydrothermal system. Those molecules are generated by the reaction between magmatic gas and Fe2+ contained in crustal rock. For example, the following reaction can be written for the formation of CH4.
The behavior of magmatic gas and hydrothermal fluid is illustrated in Fig. 7. The magmatic gases such as CO2 and SO2 are converted to CH4 and H2S in hydrothermal system due to the reduction by Fe2+ in crustal rock. The reduced components are stored in hydrothermal system and entrained by the flow of magmatic gas. The fumarolic gas discharged at the surface contains both components. When the flux of magmatic gas increases, if the flux of hydrothermal entrainment is constant, the magmatic/hydrothermal component ratios such as CO2/CH4 and CO2/H2S are expected to be elevated. This situation is consistent with the observed changes of CO2/H2O, CO2/H2S, CO2/CH4 and He/CH4 ratios in May 2015 (Fig. 2a, c–e). Actually, the flux of hydrothermal component entrained in the flow of magmatic component would not be constant. However, the variation of the flux by entrainment may be much smaller than the variation in the magmatic component flow.
Substituting He by CH4, the triangular diagrams of Fig. 6 can be converted to Fig. 8, where definite non-atmospheric end members can be found for H2S/CH4 ratio (Fig. 8a). It should be noticed that the H2S/CH4 ratio is similar for N and C. The H2S/CH4 ratio for S is much lower than the ratio for N and C. The geothermal area Ky, where fumarole S is located, was developed newly after the earthquake swarm in 2001. Before 2001, the place of Ky was densely forested. After 2001, the trees in Ky area were completely devastated due to geotherm. The averaged H2S concentration in the gas of N, S and C is 2800, 660 and 1900 µmol/mol, respectively. The H2S concentration of the gas S is much lower than that of N and C. The reason for the low H2S/CH4 ratio of S may be the removal of H2S along the reaction with Fe in crustal rock or soil as,
Since Ky area has been developed recently, the crustal rock or soil contacting volcanic gas flow may contain plenty of Fe. The reaction (7) at Ky area may be effective relative to Ow area. The averaged CH4 concentration in the gas of N, S and C is 0.49, 1.6 and 0.15 µmol/mol, respectively. The concentration in the gas S is higher than that of N and C. Because the Ky area is the newly developed geothermal area, the shallow crust is expected to contain much organic matter. A part of CH4 in the gas of S originates in the thermogenic component (Taran and Giggenbach, 2003). The high CH4/H2S ratio of the gas S relative to N and C seems to be brought by the two effects, the removal of H2S and the addition of thermogenic CH4.
Figure 8b shows the existence of non-atmospheric end member for H2/CH4 ratio although the range of ratio is much wider than H2S/CH4 ratio in Fig. 8a. It should be noticed that the H2/CH4 ratio for fumarole C is significantly lower than that for fumarole N and S. Methane is a component generated in the deep part of hydrothermal system (Giggenbach 1987). The fumarole C is the newly created crater in 2015. The fumarolic gas of C represents the fluid which is transported to surface bypassing the shallow part of hydrothermal system. Therefore, the abundant H2 contained in N and S fumarolic gases would be generated in shallow part of hydrothermal system.
The stable isotopic ratio of H2O in fumarolic gas enables us to estimate the fluid evolution. As shown in Fig. 9, the data points are distributed linearly on δD versus δ18O plane. In order to explain the distribution, a model calculation was carried out. The method of calculation has been demonstrated by Ohba et al. (2011). The parameters used in the calculation are summarized in Table 4. For the isotopic ratio of H2O of magmatic gas, the typical values for andesitic volcano on subduction zone (Giggenbach 1992) are assigned. In the model calculation, a high enthalpy magmatic gas (M in Fig. 9) mixed with a low enthalpy meteoric water (L in Fig. 9). As the result of mixing, a vapor phase (V in Fig. 9) and thermal water phase were generated. Their temperature was set to be 265 °C, which is the average apparent equilibrium temperature assuming the equilibrium of,
for the chemical composition of gas from borehole of Ow geothermal area (Ohba et al. 2011). During the mixing of M and L, the conservation of enthalpy, isotopic ratio and CO2/H2O ratio were assumed. After the mixing, vapor–liquid separation occurs. The conservation of enthalpy, isotopic ratio and CO2/H2O ratio was assumed also during the separation step, where the isotopic fractionation and CO2/H2O distribution took place between vapor phase (V) and liquid phase. The vapor phase (V) could suffer a cooling and a removal of condensed water. During the condensation, the isotopic composition of vapor moves along the line A. The temperature was set to be 100 °C during the condensation. The observed decrease in the isotopic ratio of H2O can be attributed to a condensation of H2O vapor. The correctness of the above model is supported by the data points for fumarole C, which were plotted near the cross-point between the line V and the line M–L. In the model calculation, at the cross-point, the amount of thermal water is zero. The fumarolic gas of C contains HCl (Table 3), suggesting the amount of liquid phase coexisting with fumarolic gas C was limited. The fumarolic gas C is interpreted to be the gas phase of direct mixing between magmatic gas (M) and meteoric water (L).
In the model calculation, CO2/H2O ratio of fumarolic gas can be correlated with isotopic ratio of H2O. In Fig. 10a, b, the result of model calculation is compared with observed fumarolic gas composition. In the diagrams, CO2/H2O ratio is converted to the scaled CO2 fraction (ScF) as
where CCO2 and CH2O are the concentration of CO2 and H2O in gases, respectively. The difference between Fig. 10a and b is the CO2/H2O ratio of magmatic gas (M) and the period of fumarolic gas. In Fig. 10a, CO2/H2O ratio of M is 0.0045 and the data of fumarolic gases in March and April 2015 are plotted when the CO2/H2O ratio was low (Fig. 2a). In Fig. 10b, CO2/H2O ratio of M is 0.013. The fumarolic gas N in June and July 2015 and S in May and June 2015 are plotted. In the above period, the CO2/H2O ratios of N and S were maximized (Fig. 2a). The ScF(CO2) of fumarole N in Fig. 10a, b is separated from the line A. The separation could be explained by the addition of vapor phase originating in local meteoric water (L). The composition of the vapor phase is indicated on the bold line on the y-axis. Figure 10a, b suggests that the CO2/H2O ratio of magmatic gas was high as 0.013 when the number of earthquake increased in May 2015, and low as 0.0045 before the start of earthquake swam (Fig. 2a).
Correlation between δ18O of H2O and CO2/H2O ratio. The bold line on y-axis indicates the vapor phase generated from local meteoric water (L) at 100 °C. M: magmatic H2O with CO2 (900 °C), L: local meteoric water (15 °C), V: H2O vapor with CO2 (265 °C), A: condensation of H2O vapor with CO2 at 100 °C. In the figures (a) and (b), the CO2/H2O ratio of M was set to be 0.0045 and 0.013, respectively
The above variation in CO2/H2O ratio is consistent with the magma sealing model (Fournier 1999). Accepting the estimation by Yukutake et al. (2015), the depth of degassing magma and the pressure were assumed to be − 10 km and 2256 bar, respectively. A degassing magma should be saturated in term of H2O and CO2. Therefore, the H2O and CO2 concentration in magma is located on the isobaric line G0 of Fig. 11. The isobaric line was drawn by use of the PC software VolatileCalc (Newman and Lowenstern 2002). For the calculation of isobaric line, the temperature and composition of magma were assumed to be 900 °C and rhyolitic (Tsujihara et al. 2017), respectively. On the line G0, the CO2/H2O ratio of gas phase can be calculated by VolatileCalc at any point, assuming equilibrium distribution of H2O and CO2 between magma and gas phase. VolatileCalc gave 0.0045 for the CO2/H2O ratio of gas phase at the point C0. The value 0.0045 is the CO2/H2O ratio of magmatic gas (M) when the number of earthquake was low. The H2O and CO2 concentration at the point C0 was 6.235 wt% (a0) and 6.75 wt ppm (b0), respectively. The above concentration represents the portion of magma equilibrated with gas phase, namely the inner surface of bubbles generated in degassing magma. We assign a1 and b1, respectively, to the bulk concentration of H2O and CO2 in magma. The point C1 defined by a1 and b1 should be located on the line with 0.0045 of slope starting from the point C0 (Fig. 11). Fournier (1999) proposed the magma sealing model explaining the episodic volcanic activity without magma intrusion. If the sealing zone restricts the emission of degassed gas, magma is compressed by the gas itself. When the sealing zone is broken, the gas stored within the sealing zone is supplied to hydrothermal system producing earthquakes and activation of fumarolic activity or phreatic eruption. Therefore, the CO2/H2O ratio of magmatic gas, 0.013, during the earthquake swarm can be attributed to the gas phase when magma was compressed by gas itself. Assuming that CO2/H2O ratio is 0.013 in the gas equilibrium, the magma at the point C1, a1 and b1 was calculated to be 6.33 wt% and 20.04 wt ppm, respectively. The isobaric line for 2325 bar is drawn on the point C1.
The sequence of events over the earthquake swarm in May 2015 is summarized schematically in Fig. 12. In 2014, a steady degassing of magma and the transport of magmatic gas to hydrothermal system were kept (Fig. 12a). In this period, the magmatic gas pressure PF equals to the lithostatic pressure PL. The PF equals to PC0 which is the gas pressure equilibrated with the inner surface of bubbles in magma. In February 2015 until April 2015, the magma sealing took place (Fig. 12b), restricting the emission of magmatic gas resulting in the pressurization of magma by gas itself. At the end of the period, PF was elevated up to PC1. During the magma sealing, the supply of magmatic gas to hydrothermal system was restricted. The fluid pressure in hydrothermal system may be decreased, and enthalpy of hydrothermal system may be also decreased. The pressure decrease could cause an invasion of air, which elevated Ar/CO2 and N2/He ratios prior to the earthquake swarm (Figs. 3c, d, 12b). The enthalpy decrease could prompt the condensation of H2O vapor, which reduced the isotopic ratio of H2O (Fig. 4a, b). In May 2015, the sealing zone was broken (Fig. 12c). The magmatic gas with high CO2/H2O ratio was supplied to hydrothermal system as a surge. The supply of magmatic gas lifted the fluid pressure and produced large number of earthquake and a small phreatic eruption in June 2015.
Sequence at Hakone volcano before and after the earthquake swarm in May 2015. a Normal situation represented by the period in 2014. M: degassing magma, R: magmatic gas reservoir, S: sealing zone, B: hydrothermal system made of brittle crust, G: fumarolic gas, PL: lithostatic pressure, PF: magmatic gas pressure, PC0 and PC1: gas pressure equilibrated with magma the composition of which is CO and C1 in Fig. 11. b Sealing zone is restricting the magmatic gas transport to hydrothermal system, corresponding to the period in few months prior to May 2015. Air invasion was allowed into hydrothermal system. c Break of sealing zone in May 2015. A large number of earthquakes (cross-marks) happened in hydrothermal system
Based on the structure estimated by Yukutake et al. (2015) and the discussions in this study, the magmatic hydrothermal system of Hakone volcano is illustrated in Fig. 13a. The magmatic gas is supplied by the degassing magma (M). The gas contains H2O, CO2, SO2, HCl, N2, H2 and He. A magmatic gas reservoir (R) is developed above the degassing magma (Yukutake et al. 2015), and it was surrounded by a sealing zone (S). According to Itadera et al. (2016), a pressure source (star mark in Fig. 13a) is located at − 8.4 km below the sea level and beneath Ka, which produced the inflation of volcanic body in May 2015. The pressure source is located within the magmatic gas reservoir (R). Through the sealing zone, magmatic gas is transported to the hydrothermal system made of brittle crust (B). Most of SO2 and a part of CO2 in the magmatic gas are converted to H2S and CH4 in the hydrothermal system with the reaction of Fe2+ contained in crustal rock within the crust shallower than − 500 m (Fig. 13b). The magmatic gas was discharged as fumarolic gas N and S with the entrainment of hydrothermal components such as H2S and CH4.
South to North cross section of Hokone volano. a Star mark: pressure source appeared in 2015 (Itadera et al. 2016). M: degassing magma, R: magmatic gas reservoir, S: sealing zone, B: hydrothermal system made of brittle crust, L: local meteoric water, G: fumarolic gas, Ko: Komagatake central cone, Ka: Kamiyama central cone, Ki: Mt. Kintoki, Cross-marks: occurrence of earthquakes. The rectangle of broken line indicates the region drawn in b. b Hydrothermal system beneath the fumarole of N, S, C and borehole (Bh). The shallow part of the hydrothermal system is reduced (Red), whereas the relatively deep part is oxidized (Oxi). The boundary between the region of Red and Oxi has not been certainly determined
Conclusions
Sharp increases in the components ratios such as CO2/H2O, CO2/H2S, CO2/CH4 and He/CH4 were observed at the fumarolic gas on Hakone volcano synchronized with the earthquake swarm in 2015. The increases could be explained by the dominance of magmatic component relative to hydrothermal component. The CO2/H2O ratio of magmatic gas was 0.0045 before the earthquake swarm. It increased to 0.013 during the earthquake swarm. The increase in CO2/H2O ratio can be explained by the pressurization of magma caused by magma sealing. The magma pressure increased from 2256 to 2325 bar, consistent with the increase in the CO2/H2O ratio. The bulk H2O and CO2 concentration in magma were estimated to be 6.33 wt% and 20.0 wt ppm, respectively assuming the temperature of magma is 900 °C and the composition of magma is rhyolitic. Prior to the earthquake swarm in May 2015, sharp increase in Ar/CO2 and N2/He ratios was observed at the fumarolic gas in Ow geothermal area. The increase could be explained by the invasion of air in hydrothermal system. A definite decrease in the isotopic ratio of H2O in the fumarolic gas in Ow geothermal area was observed prior to the earthquake swarm in May 2015. The decrease could be explained by the partial condensation of H2O vapor probably due to the enthalpy loss in hydrothermal system beneath Ow geothermal area. It should be noticed that the above changes prior to the earthquake swarm were not observed in the fumarolic gas S in Ky geothermal area.
Abbreviations
- AET:
-
apparent equilibrium temperature
- ASW:
-
atmospheric components saturated in water
- GC:
-
gas chromatograph
- HSRI:
-
Hot Springs Research Institute of Kanagawa Prefecture
- JMA:
-
Japan Meteorological Agency
- Ka:
-
Kamiyama
- Ko:
-
Komagatake
- Ky:
-
Kamiyuba
- Ow:
-
Owakudani
- R-gas:
-
residual gas
- SMOW:
-
Standard Mean Ocean Water
- So:
-
Sounzan
- wt:
-
weight
References
Daita Y (2013) Temporal variation of the fumarolic gas composition during the swarm earthquake activity in Hakone volcano in 2013. Bull Hot Spring Res Inst Kanagawa Prefect 45:29–34 (in Japanese)
Fournier RO (1999) Hydrothermal processes related to movement of fluid from plastic into brittle rock in the magmatic-epithermal environment. Econ Geol 94:1193–1212
Giggenbach WF (1975) A simple method for the collection and analysis of volcanic gas samples. Bull Volcanol 39:132–145
Giggenbach WF (1987) Redox processes governing the chemistry of fumarolic gas discharges from White Island, New Zealand. Appl Geochem 2:143–161
Giggenbach WF (1992) Isotopic shifts in waters from geothermal and volcanic systems along convergent plate boundaries and their origin. Earth Planet Sci Lett 113:495–510
Giggenbach WF (1997) The origin and evolution of fluids in magmatic-hydrothermal systems. In: Barnes HL (ed) Geochemistry of hydrothermal ore deposits, 3rd edn. Wiley, Hoboken
Itadera K, Harada M, Yoshida A (2016) Relationship between ground tilts and earthquake swarms during the 2015 Hakone volcanic activity. Bull Hot Spring Res Inst Kanagawa Prefect 48:1–10 (in Japanese)
Kita I, Nitta K, Nagao K, Taguchi S, Koga A (1993) Difference in N/Ar ratio of magmatic gases from northeast and southwest Japan: new evidence for different states of plate subduction. Geology 21:391–394
Kobayashi M, Okuno M, Nakamura T (1997) 14C ages of pyroclastic-flow deposits from central cones on the western slope of old Somma of Hakone volcano, central Japan. Bull Volcanol Soc Japan 42:355–358 (in Japanese)
Kuno H (1950) Geology of Hakone volcano and adjacent areas. Part-I. J Fac Sci Univ Tokyo Sect II 7:257–279
Lee S, Ohba T, Yun SH, Yang K, Jeong HY (2016) Evaluation of sampling methods for sulfur speciation in volcanic gases. Chem Geol 438:123–133
Mannen K (2008) Hakone Caldera: mode of formation, and role in present-day volcanism. Res Rep Kanagawa Prefect Mus Nat Hist 13:61–76 (in Japanese with English abstract)
Mannen K, Yukutake Y, Kikugawa G, Harada M, Itadera K, Takenaka J (2018) Chronology of the 2015 eruption of Hakone volcano, Japan: geological background, mechanism of volcanic unrest and disaster mitigation measures during the crisis. Earth Planets Space 70:68. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40623-018-0844-2
Newman S, Lowenstern JB (2002) VolatileCalc: a silicate melt–H2O–CO2 solution model written in Visual Basic for excel. Comput Geosci 28:597–604
Ohba T, Daita Y, Sawa T, Taira N, Kakuage Y (2011) Coseismic changes in the chemical composition of volcanic gases from the Owakudani geothermal area on Hakone volcano, Japan. Bull Volcanol 73:457–469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-010-0445-9
Ossaka J, Ozawa T, Nomura T, Ossaka T, Hirabayashi J, Takaesu A, Hayashi T (1980) Variation of chemical compositions in volcanic gases and waters at Kusatsu-Shirane volcano and its activity in 1976. Bull Volcanol 43:207–216
Ozawa T (1968) Chemical analysis of volcanic gases: I. Chemical analysis of volcanic gases containing water vapor, hydrogen chloride, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, carbon dioxide, etc. Geochem Int 5:939–947
Richet P, Bottinga Y, Javoy M (1977) A review of hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, sulphur, and chlorine stable isotope fractionation among gaseous molecules. Ann Rev Earth Planet Sci 5:65–110
Taran YA, Giggenbach WF (2003) Geochemistry of light hydrocarbons in subduction-related volcanic and hydrothermal fluids. Soc Econ Geol Special Publ 10(2003):61–74
Tsujihara R, Ishibashi H, Hokanishi N, Yasuda A (2017) Pre-eruptive process of the 60Ka caldera-forming eruption at Hakone volcano. In: Program and abstracts the volcanological Society of Japan, P005. https://doi.org/10.18940/vsj.2017.0_125 (in Japanese)
Tsunogai U, Kamimura K, Anzai S, Nakagawa F, Komatsu D (2011) Hydrogen isotopes in volcanic plumes: tracers for remote temperature sensing of fumaroles. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 75:4531–4546
Yukutake Y, Honda R, Harada M, Arai R, Matsubara M (2015) A magma-hydrothermal system beneath Hakone volcano, central Japan, revealed by highly resolved velocity structures. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 120:3293–3308. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JB011856
Authors’ contributions
TO drafted the manuscript. MY, KN, NN and YD sampled fumarolic gases and analyzed them. CS, MI and UT analyzed fumarolic gas samples. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sorts, Science and Technology, under grant of the Integrated Program for Next Generation Volcano Research and Human Resource Development in 2016 to 2017, also under its Earthquake and Volcano Hazards Observation and Research Program in 2015 to 2017. This work was supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant Numbers 15K12485 in 2015 to 2017. This work was supported by the Earthquake Research Institute, The University of Tokyo Joint Usage/Research Program in 2015 to 2017. This work was supported by General Research Institute of Tokai University in 2016 to 2017. We sincerely thank the above fund providers for the support in this work. We also thank Nagoya group: Kosuke Ikeya and Fumiko Nakagawa for δD(H2) measurement.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Availability of data and materials
The csv files for Tables 1, 2 and 3 will be stored in repositories.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Endnotes
None.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sorts, Science and Technology under grant of the Integrated Program for Next Generation Volcano Research and Human Resource Development in 2016 to 2017. This work was supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant Numbers 15K12485 in 2015 to 2017. This study was supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) of Japan, under its Earthquake and Volcano Hazards Observation and Research Program in 2015 to 2017. This study was supported by the Earthquake Research Institute, The University of Tokyo Joint Usage/Research Program in 2015 to 2017. This work was supported by General Research Institute of Tokai University in 2016 to 2017.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Ohba, T., Yaguchi, M., Nishino, K. et al. Time variations in the chemical and isotopic composition of fumarolic gases at Hakone volcano, Honshu Island, Japan, over the earthquake swarm and eruption in 2015, interpreted by magma sealing model. Earth Planets Space 71, 48 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40623-019-1027-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40623-019-1027-5