Abstract
Background
The influence of β-glucan on the human gut microbiota is closely related to the physicochemical structure of β-glucan. We purified a homogeneous water-soluble polysaccharide from Tibetan hull-less barley 25 and studied its structure and the in vitro fermentation profile.
Results
Analysis by gas chromatography (GC), Fourier-transformed infrared (FT-IR), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and atomic force micrograph (AFM) helped determine the hull-less barley polysaccharide to be a β-glucan (molecular weight: 3.45 × 104 Da), which was further characterized as mixed-linkage (1 → 3)(1 → 4)-linked β-d-glucans. SEM images demonstrated an intricate web structure of the hull-less barley polysaccharide, while the AFM images revealed the presence of small spherical particles in its structure. In addition, the microbiota composition of the hull-less barley polysaccharide group was found to be altered, wherein the abundance of Pantoea, Megamonas, Bifidobacterium, and Prevotella-9 were increased. On the other hand, in vitro fermentation revealed that hull-less barley polysaccharide significantly decreased the pH value and increased the production of acetate, propionate, and butyrate.
Conclusions
Hull-less barley polysaccharide is a type of dietary fiber, and its analysis suggested that it may serve as a prebiotic food supplement for the regulation of the gut microbiota.

Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Hull-less barley (Hordeum vulgare L. var. nudum Hook.f.), also known as Qingke in China, is a principal food crop that is widely cultivated across the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau [1]. Hull-less barley is an excellent source of dietary fiber (both soluble and insoluble), in which the β-glucan content usually accounts for 4–8% [2]. The structure of β-glucan derived from different origins has been investigated, including β-1,3-glucan (natural yeast), β-1,6-glucan (mushrooms), and (1 → 3) (1 → 4)-β-glucan (barley, oat and rye) [3, 4]. In addition, the molecular weight (MW) of β-glucan in different crops varies; for example, it is 31–2700 × 103 Da in barley, 65–3100 × 103 Da in oat, 21–1100 × 103 Da in rye, and 209–487 × 103 Da in wheat [5]. Recently, much attention has been focused on β-glucan owing to its several beneficial properties, such as in reducing the cholesterol levels, lowering the glycemic response, enhancing immunity, and aiding in the absorption of minerals in humans [5,6,7]. β-Glucan has also been associated with a prebiotic effect owing to its resistance to digestion (it cannot be broken down by the human digestive enzymes) and absorption in the upper intestinal tract, which provides a source of carbon to the gut microbiota within the distal intestinal tract region [8, 9].
Human gut microbiota inhabit the human gut, which is composed of approximately 1000 bacterial species, comprising approximately 3 × 106 genes [10, 11]. Gut microbiota is also known to exert multiple physiological functions. For example, it plays a role in energy capturing and storage as well as in protective functions against invasion by pathogenic microorganisms [12, 13]. Several factors strongly influence the composition of the gut microbiota. Past researches on the gut microbiomes among the human populations have revealed that the age, geography, and kinship play important roles in shaping the gut microbiota, while the diet also strongly influences the composition and functional abilities of the gut microbiota [14, 15]. In the recent years, the incorporation of dietary fibers has been proposed as a dietary approach that influences the diversity of the human gut microbiota [16]. β-Glucan, which is a type of dietary fiber, can pass through the upper intestinal tract without being broken down [9]. A variety of complementary enzymes with diverse specificities are produced by the human gut microbiota, which enables depolymerization and fermentation of the dietary fibers into short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) [9, 17]. Moreover, the physicochemical properties of β-glucan are affected by their origins and they are related to the fermentation capacity of the gut microbiota [13, 18]. Cantu-Jungles et al. revealed that (1 → 3)-linked β-D-glucan has faster fermentation characteristics than those of branched (1 → 3), (1 → 6)-linked β-D-glucan, which can directly promote the butyrogenic Clostridium cluster XIVa bacteria [13]. The different MW also result in different fermentation profile. A previous study has showed that the low-MW (150 kDa) of barley β-glucan can stimulate the abundance of Bifidobacteria, while medium-weight barley (530 kDa) β-glucan can reduce the Lactobacillus population in hypercholesterolemic rats [19].
The microbial composition and activity are influenced by the type of β-glucans that escape from the upper intestinal tract digestion [19, 20]. However, only little is known about the fine chemical structure of Tibetan hull-less barley 25, and its effect on the gut microbiota is also not well-established in vitro. Thus, the purpose of the present work was to purify and characterize hull-less barley polysaccharide (HLBP) from the Tibetan hull-less barley 25. Furthermore, the effects of HLBP on the pH change, production of SCFAs, and the composition of gut microbiota were studied via in vitro feces fermentation.
Materials and methods
Materials and reagents
Tibetan hull-less barley 25 was obtained from the Tibet Autonomous Region Academy of Agriculture and Animal Husbandry. Pancreatin from porcine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Corp. (St. Louis, USA) and SCFAs (acetic, butyric and propionic acids) standards for gas chromatography (GC), D-glucose, Sepharose 6B and DEAE-Sepharose Fast Flow were obtained from Shanghai Yuanye Bio-technology Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China). All other reagents used in this experiment were of analytical grade and purchased from Shanghai Chemicals and Reagents Corp. (Shanghai, China).
Extraction and purification of barley polysaccharides
The polysaccharides obtained from the Tibetan Hull-Less Barley 25 were prepared using the method described by Maheshwari [21] with some minor modifications. Briefly, the Tibetan Hull-Less Barley 25 was ground in a grinder to pass a 0.18-mm screen. The polysaccharides (named as purified HLBP) from the ground barley powder were then extracted and purified by using the DEAE-Sepharose Fast Flow and Sepharose 6B columns, as illustrated in Fig. 1.
MW analysis
According to a previous report [22], the MW of the purified HLBP was determined on the 1260 Infinity Liquid Chromatography (Agilent Technologies Inc., Wilmington, DE, USA) equipped with the TSKgel G5000PWXL column (7.8 × 3000 mm; TOSOH CORPORATION, Japan) and the Agilent 1260 refractive index detector.
Briefly, ultrapure water was used as the flow phase (flow rate 0.5 mL/min) in which the purified HLBP was dissolved at a concentration of 1.0 mg/mL. The column temperature was kept at 30 °C and the injection volume used was 10 μL.
Fourier-transformed infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy
The purified HLBP was ground with KBr pellet and then compressed into lens. The FT-IR spectra were recorded on the Bruker Vetex70 FT-IR instrument (Bruker, Germany) within the frequency range of 4000–400 cm−1 [23].
Monosaccharide composition analysis
The monosaccharide composition analysis of purified HLBP was performed by using the method of Wang et al. [24]. This method involves the use of chromatography (Shimadzu 2014C, Japan) equipped with the DB-17 column (30 m × 0.25 mm ID, 0.25-μm film thickness; Agilent, USA). Rhamnose, fructose, arabinose, mannose, glucose, xylose, galactose, glucuronic acid, and galacturonic acid were used as the monosaccharide standards.
NMR spectroscopy
The purified HLBP (20 mg) was dissolved in 500 μL deuterium oxide (99.9%), and the solution was transferred into a nuclear tube. The NMR spectra of 1H, 13C and HSQC were acquired at 600 MHz with the Brucker AVANCE III Spectrometer [25].
Microscopic morphology analysis
Micromorphology of the purified HLBP was studied by SEM and AFM. Briefly, the freeze-dried sample was glued onto the aluminum stubs, which was then coated with gold [26]. The morphological features of purified HLBP were observed under SEM at an accelerating voltage of 10 kV (Multimode-8; Bruker, USA).
The polysaccharide solution (1 μg/mL) was prepared with distilled water. Then, 10 μL of the diluted polysaccharide solution was deposited on smooth mica for drying at the room temperature. The AFM images of polysaccharides were acquired with a scanning probe microscope (Multimode-8; Bruker, USA) in the tapping mode [27].
In vitro fecal fermentation of HLBP
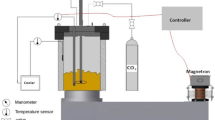
The in vitro fermentation of crude HLBP by human feces was conducted as described previously [13, 28]. Briefly, the samples were pooled from 3 healthy donors (1 male and 2 females, aged: 20–35 years) who had not received any antibiotics since the last 3 months, and immediately mixed with sterilized 0.1 M phosphate buffered saline (pH 7.2) to produce a 10% (w/v) fecal suspension. The basal nutrient growth medium was conducted as described by Xie et al. [29]. The fecal slurry (1 mL) was inoculated with the basal nutrient growth medium (9 mL) to afford the final concentration of HLBP reaching 10.0 mg/mL, while considering the basal growth medium (without HLBP) as the blank group. The samples were then incubated in an anaerobic culture (Anaero Pack System, Mitsubishi Gas Chemical Co., Inc., Japan) at 37 °C for 0, 6, 12, and 24 h (the HLBP group and the blank group share 0 h samples) [28]. Each experiment was performed in triplicate (totaling 21 fermentation samples).
Analysis of the gut microbiotas
The 16S rDNA Sequencing was conducted based on a few previous studies [30, 31]. The bacterial DNA of each sample was isolated using the NucleoSpin 96 Soil Kit (Macherey-Nagel, Duren, Germany). Then, the V3–V4 region of the primer [(forward) 5′-ACTC CTAC GGGA GGCA GCA-3′ and (reverse) 5′-GGAC TACH VGGG TWTC TAAT-3′ with dual-index barcodes] of bacterial 16S rDNA gene was amplified. Following qPCR purification and quantification, the PCR products were sequenced on the Illumina HiSeq 2500 platform and analyzed by QIIME (version 1.8.0) in accordance with the protocols of the Biomarker Technologies Company, Ltd. (Beijing, China). After splicing (FLASH v1.2.7) and filtering (Trimmomatic v0.33), a total of 1 702 069 clean tags were obtained. The chimeras were checked and removed by Uchime v4.2 to obtain effective tags. USEARCH v10.0 was performed to cluster the effective tags into operational taxonomic units (OTUs) on the basis of 97% sequence similarity threshold. Shannon index, PCA, taxonomic composition, heatmap, and LEfSe analysis were generated using Mothur, Metastats, and R package.
Determination of SCFAs and pH
To quantify the SCFAs contents, 400 μL of the aliquots of the fermented samples were combined with 1600 μL of distilled water. H2SO4 (50%, w/w) was added to protonize the SCFAs, which were then extracted with 2 mL of diethyl ether at 4 °C for 30 min. The mixed solution was centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 5 min, and the supernatant (2 μL) was loaded on GC (Shimadzu GC-2014C; Shimadzu Corporation, Japan) equipped with the DB-FFAP Capillary column (30 m × 0.25 m × 0.25 mm; Agilent Technologies Inc., Wilmington, DE, USA). The initial temperature was held at 50 °C for 1 min, then ramped to 120 °C at the speed of 15 °C/min, to 170 °C at the speed of 5 °C/min, to 220 °C at the speed of 15 °C/min, and then maintained at 220 °C for 5 min. Nitrogen was supplied as the carrier gas at a flow rate of 2.0 mL/min. The temperatures of the injector and detector were 250 °C and 270 °C, respectively [30]. The pH values of the samples from in vitro fermentation were detected by using a pH meter (pHS-3C; Chengdu Century Fangzhou Science and Technology Co., Ltd., Chengdu, China).
Statistical analysis
The data were expressed as the mean ± SD and evaluated by single factor analysis for variance (ANOVA), followed by the Tukey’s analysis using the SPSS software. Differences were considered to be statistically significant at p < 0.05.
Results
Purification and characteristics of HLBP
Soluble HLBP from Tibetan Hull-Less Barley 25 was obtained according to method described earlier (Fig. 1). The crude HBLP was first separated by anion-exchange chromatography of the DEAE-Sepharose Fast Flow (Fig. 1a), with a yield of 3.85%. Only one fraction of polysaccharides was obtained, which was eluted with distilled water. Then, it was further purified by Sepharose 6B gel column chromatography according to their MWs. A symmetrical single peak was obtained, and the fraction was designated as purified HLBP (Fig. 1b).
The MW of the purified HLBP was determined using liquid chromatography (illustrated in Fig. 2a). The elution peak was single, symmetrical, and narrow indicating that purified HLBP is a homogeneous polysaccharide [25]. Based on the calculation curve (y = 11.772 − 0.379x, R2 = 0.996), the MW of the polysaccharide was 3.45 × 104 Da. The monosaccharide composition profile of polysaccharide is depicted in Fig. 3. The result revealed that purified HLBP was mainly composed of glucose.
FT-IR spectrum analysis
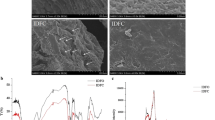
The FT-IR spectrum of purified HLBP recorded in the range of 4000–400 cm−1 is illustrated in Fig. 2b. The spectrum of the polysaccharide displayed an intense and broad band at approximately 3373 cm−1, which indicated the existence of a hydroxyl group stretching vibration. The band at around 2891 cm−1 was attributed to the C–H stretching vibration [32]. The absorption peak at approximately 1639 cm−1 could be assigned to the bound water [33]. The bands within the 1200–1000 cm−1 region were assigned to the C–O–H stretching vibrations [7, 33], whereas the presence of β-glycosidic linkage of glucosyl residue was indicated by the characteristic absorption band at 896 cm−1 [33, 34]. Thus, the FT-IR spectrum analysis revealed that the purified HLBP showed the typical absorption peaks of the polysaccharide [34].
Moreover, the peak of uronic acids was not observed at around 1730 cm−1, which further confirmed that purified HLBP was a neutral polysaccharide [33], which was conformed to the monosaccharide composition analysis provided earlier.
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analysis
The 1D/2D NMR spectra of purified HLBP are shown in Fig. 4. Two major chemical shifts of the anomeric region were noted to be 4.72 and 4.47 ppm on the 1H-NMR (Fig. 4a), which indicated that purified HLBP consists of two monosaccharide residues of the β-type glycosidic linkages [26, 35]. The anomeric signals at 102.56/4.72 ppm and 102.37/4.47 ppm belonged to (1 → 3)-β-D-Glcp and (1 → 4)-β-D-Glcp, respectively [36, 37]. The 13C-NMR spectrum (Fig. 4b) showed single resonances at 83.82 ppm for the C-3 carbon of the O-3-linked glucose, demonstrating that most of the (1 → 3) linkages occurred discontinuously [36, 37].
SEM and AFM analyses
The microscopic morphology of the purified HLBP was evaluated by SEM and AFM. The SEM imaging of polysaccharide is illustrated in Fig. 5a, b. The purified HLBP overlapped with the intricate web structure, with a smooth surface that can be attributed to the strong interaction between the molecular chains [38]. The morphological topographies of the polymers can be observed by AFM [39]. The AFM images of polysaccharide exhibited several small spherical particles (Fig. 5c, d) attributable to the intra or inter hydrogen bonds [40]. A similar aggregate of purified HLBP has been reported earlier with oat β-glucan and barley β-glucan [40, 41].
Bacterial shifts during in vitro fermentation
The sequencing analyses included 21 samples, and a total of 1,499,196 effective tags were obtained, which were then clustered into OTUs at 97% similarity, 186 ± 12 OTUs/sample were obtained. The rarefaction curves and Shannon index of all 21 samples indicated that most of the biological information was captured (Additional file 1: Fig. S1). As illustrated in Fig. 6a, the PCA revealed a significant variation between the HLBP group and blank groups, in which the PC1 and PC2 could explain 73.31% and 13.48% of the variation in the different groups, respectively.
PCA of in vitro fermentation (a). Bacterial taxonomic profiling in the phylum level of gut microbiota (b). Bacterial taxonomic profiling in the family level of gut microbiota (c). Heatmap analysis of the relative abundance at the genus level of the bacterial community. K and G represent the blank group and HLBP group, respectively, and the numbers indicate the fermentation time (h) (d)
An overview of the fecal microbiota taxonomic composition in each group at the phylum, family, and genus levels is exhibited in Fig. 6a–d. As illustrated in Fig. 6b, the predominant microbiota taxonomic composition at the phylum level included Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, and Bacteroidetes. The stacking histogram at the phylum level indicates that HLBP induced an increase in Firmicutes (42.2% in the HLBP group vs 40.4% in the blank group at 24 h) and Bacteroidetes (39.7 vs 38.2%) than in the blank group. Notably, the abundance of Actinobacteria (11.2 vs 1.7%, p < 0.05) in the HLBP group was higher than that in the blank group. At the family level, fermentation with HLBP exhibited a higher level of Prevotellaceae (36.4 vs 0.7%, p < 0.05), Veillonellaceas (36.2 vs 15.5%, p < 0.05) and Bifidobacteriaceae (10.1 vs 1.2%, p < 0.05) than in the blank group. Conversely, Enterobacteriaceae (4.6 vs 15.4%, p < 0.05), Bacteroidaceae (2.6 vs 32.9%, p < 0.05), Lachnospiraceae (1.8 vs 15.1%, p < 0.05), and Ruminococcaceae (2.2 vs 7.1%, p < 0.05) were significantly reduced in the HLBP group compared than in the blank group (Fig. 6c). Specifically, HLBP could change the composition of the gut microbiota and promote the growth of certain bacterial species. The heatmap of the in vitro fermentation microbiota is presented in Fig. 6d. The microbiota structures of the HLBP group at the genus level was significantly different from those of the blank group. The following genera were increased in the HLBP group: Megamonas (12.5 vs 3.6%, p < 0.05), Pantoea (0.4 vs 0.02%, p < 0.05), Prevotella_9 (36.3 vs 0.6%, p < 0.05), Catenibacterium (1.0 vs 0.1%, p < 0.05), Megasphaera (22.3 vs 9.2%, p < 0.05), and Bifidobacterium (10.1 vs 1.2%, p < 0.05) were observed in the HLBP group. Furthermore, LEfSe analysis identified the most differentially abundant taxons between the HLBP and blank groups (Fig. 7). After the in vitro fermentation of 24 h, the LEfSe analysis revealed 22 and 16 significantly discriminative features in the blank and HLBP groups, respectively, based on the LDA score of ≥ 4.
SCFAs production and pH change of in vitro fermentation
SCFAs are important carbon flux that connects the diet and the host through the gut microbiota [42]. SCFAs, such as acetate, butyrate, and propionate, are the principal fermentation products of indigestible carbohydrates [43].
The concentrations of SCFAs in the fermentation products between the HLBP and the blank groups are presented in Fig. 8. The concentrations of acetate, propionate, butyrate, and valerate productions were significantly (p < 0.05) increased after 24 h of fermentation of HLBP. As shown in Fig. 8, the concentrations of acetate, propionate, butyrate, and valerate in the HLBP group were significantly increased from 13.46 ± 0.13 to 37.40 ± 1.90 mM/L, from 8.77 ± 0.06 to 33.60 ± 2.57 mM/L, from 5.94 ± 0.02 to 51.36 ± 3.23, and from a negligible amount to 33.29 ± 3.36 mM/L (p < 0.05), respectively. The concentration of butyrate in the HLBP group was 2.4-fold higher than that in the blank group, while the respective concentrations for acetate and propionate were 1.2-fold and 1.5-fold greater. Meanwhile, the acetate-to-propionate ratio decreased from 1.54 (0 h) to 1.11 (24 h) (p < 0.05). The accumulation of isobutyrate and isovalerate was significantly higher in the blank group than in the HLBP group.
The SCFA produced by the gut bacteria through fermentation of polysaccharides could lower the pH value, which possibly have beneficial effects on the colon health [44]. Figure 8g illustrates the change in pH value during in vitro fermentation. The pH of HLBP fermentation culture dropped sharply during the initial 6 h, while that of the blank group decreased slightly. After fermentation for 24 h, the pH values of the HLBP and blank groups significantly declined from 7.04 to 4.51 (Δ = 2.53), and the value of the HLBP group was significantly (p < 0.05) lower than that of the blank group at each tested time point.
Discussion
The objectives of the present study were to investigate the structure of a polysaccharide extracted from Tibetan hull-less barley 25 and to evaluate the fermentation features of the HLBP. The backbone of the polysaccharide (MW: 3.45 × 104 Da) was mainly composed of (1 → 3)-linked-β-d-glucopyranosyl and (1 → 4)-linked-β-d-glucopyranosyl. High-yield SCFAs production from HLBP were recorded during the in vitro fermentation by human fecal microbiota.
The beneficial effects of β-glucan on the human health may be attributed to its physicochemical structure. The HLBP was composed of (1 → 4)-linked β-d-Glcp and (1 → 3)-linked β-d-Glcp. Our results were consistent with those of a previous study in which β-glucans from cereals were linear homopolysaccharides of oligomeric cellulose segments separated by single (1 → 3)-linkages [5, 36]. Previous studies reported that β-glucan were composed of d-glucopyranosyl residues linked via a mixture of β-(1 → 3) and β-(1 → 6) linkages (from Glomerella cingulata) and 1,3-glucans with β-1,6 branching (from Lentinula edode and Schizophyllum commune) showed anticancer properties [45]. β-1,3-glucan (from Grifolafrondosa) demonstrated antitumor activities, while (1 → 3,1 → 4)-β-glucan (from Oats and barley) exerted a hypocholesterolemic activity [45]. On the other hand, the MW values of barley were usually in the range of 31–2700 × 103 Da, while that of HLBP was 3.45 × 104 Da, which was considered as low-MW β-glucan [5]. Moreover, the viscosity of high-MW β-glucan was also reported to be higher than that of low-MW β-glucan, while high-MW polysaccharides usually lead to poor solubility and high viscosity, which seem to have limited its application to food [19, 34, 46, 47]. The MW of β-glucan has been reported to be related to bile-acid binding and SCFAs production. For example, low-MW β-glucan (1.56 × 105 g/mol) produces more SCFAs and binds more bile acids than high-MW β-glucan (6.87 × 105 g/mol) [6]. The AFM images of purified HLBP were present in several irregular spherical lumps, consistent with the report of Zielke et al., which stated that β-glucan from barley possessed a well-defined aggregate structure [41]. The van der Waals force and hydrogen-bonding between the sequences of structural regularity (cellotriose sections) might lead to the formation of globular architectures [48, 49]. Generally speaking, β-glucan with different MW could exhibit diverse morphological structure. It was pointed out that the β-glucan with low MW has a tendency to form a more spherical architecture, compared with the extended conformation of high-MW β-glucan [40, 50]. Additionally, Wei et al. reported a lower gelation rate of high-MW wheat β-glucan than low-MW wheat β-glucan [51]. Therefore, the reasonable explanation for the microscopic morphology of the polysaccharide is that hydrogen-bonding, the van der Waals force, and the chains of the low-MW samples are more mobile and more likely to form junction zones [6, 51].
The relative abundance observed in the bacterial community after fermentation of HLBP was distinct from that of the blank group. It was obvious that Bifidobacterium and Prevotella_9 in the HLBP group were far more abundant than that in the blank group. Some relative increases in the abundances were observed in the genera, with the sharp increase noted for Prevotella_9 (60.50-folds), which has an influence on the human health in terms of regulating glucose intolerance and glycogen storage [52]. Bifidobacterium, which was significantly elevated in the HLBP group (p < 0.05, 8.42-folds), was considered to be beneficial to the human health, such as in protecting the hosts from infectious diseases. In a study performed by Cani et al., the abundance of Bifidobacterium spp. and tight-junction mRNA expression suggested a positive correlation, indicating that the Bifidobacterium spp. obviously affected the gut permeability [53]. Meanwhile, the levels of Bifidobacterium were involved in the regulation of glucose-tolerance and low-grade inflammation [54]. The utilization of (1 → 3)(1 → 4)-β-glucan needs to be supported with specific enzymes to cleave the glycoside bond of non-reducing ends (glucanases) and internal glycoside bond (glucosidase) [55]. The various metabolic enzymes are encoded by gut microbiota genes, including carbohydrate esterases, glycoside hydrolases, and polysaccharide lyases, which are involved in the depolymerization of polysaccharides [45]. Prevotella was also considered as the key gut bacteria member for the hydrolysis of dietary fibers, because it is potentially composed of some hydrolysis genes (unique enrichment of Prevotella in the rural African children with dietary fiber-rich diets) [28]. Numerous glycoside hydrolases are possessed by Bifidobacteria, and plenty of polysaccharide lyases and glycoside hydrolases are available under the Bacteroidetes genomes [55]. For example, Erica et al. reported that 88 polysaccharide utilization loci of Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron are responsible for the utilization of polysaccharides [56].
It has been reported that Bifidobacterium spp., Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, and Lactobacillus spp. were considered as acetate producer; Anaerotipesspp., Coprococcus spp., Roseburia spp., Ruminocococcus, Clostridium spp., Eubacterium spp., and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii (Clostridaceae), which possess the capability to produce butyrate. Meanwhile, propionate produced by Bacteroides spp., Clostridium histolyticum, Dialister spp., Roseburia spp., Ruminococcus spp., Veillonella spp., Phascolarctobacterium spp., and Prevotella spp. have been reported [29, 34]. After the in vitro fermentation, significantly increased abundances of Megamonas, Bifidobacterium (which can generate acetate), Ruminococcus (producer of butyrate and propionate), and Dialister (propionate-producing bacteria), indicated that in vitro fermentation of HLBP enhanced the SCFAs production [12, 29, 34]. The HLBP group exhibited more butyrate and propionate production, but less acetate production during the in vitro fermentation. These results were consistent with the findings of Sayar et al., who observed that the fermentation of purified oat β-glucan produced more propionate and butyrate, but less acetate [8]. However, a higher concentration of acetate and lower concentration of butyrate and propionate were produced by β-glucan from Cookeina speciosa [13]. The reason for these inconsistent results may be attributed to the gap between the sources of β-glucan and the physicochemical structure of β-glucan as well as the gut microbiota from humans. Furthermore, the acetate-to-propionate ratio decreased obviously (p < 0.05). The low acetate-to-propionate ratio was believed to be a positive indicator of the hypolipidemic effects due to the inhibition of the biosynthesis of cholesterol and fatty acids in the liver [44, 57]. SCFAs are also related to gluconeogenesis. For example, propionate and butyrate participate in the intestinal gluconeogenesis by involving free fatty acid receptor 3 and cAMP-dependent intestinal gluconeogenesis, respectively [45]. In addition, the SCFAs acetate butyrate and propionate, also participate in the glucose and hepatic lipid homeostasis through peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ [43]. These results together suggest that HLBP may be involved in the regulation of blood glucose via gut microbiota metabolites (SCFAs) [28].
Conclusions
We investigated the structure of HLBP based on its monosaccharide composition using FT-IR, NMR, SEM, and AFM. We also performed 16S compositional sequencing to explore the composition of the microbiota. Our results suggested that the polysaccharide purified from hull-less barley has a MW of 3.45 × 104 Da, and that it consists of (1 → 4)-linked β-d-Glcp and (1 → 3)-linked β-D-Glcp. Furthermore, the SEM images revealed that HLBP has an intricate web structure, while the AFM images of purified HLBP showed the presence of small spherical particles. In vitro fermentation results indicated that HLBP not only changed the structure of the microbiota, but also altered the proportion of SCFAs and the pH value of the fermentation culture. These results cumulatively indicate that HLBP may play an important role in human health by influencing the alteration of the intestinal microbiome and microbial metabolites. We believe that further studies are required to investigate the effects of the gut community structure by the fine chemical structure of dietary fibers.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- FT-IR:
-
Fourier transform infrared
- NMR:
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron micrograph
- AFM:
-
Atomic force micrograph
- SCFAs:
-
Short-chain fat acids
- GC:
-
Gas chromatography
- MW:
-
Molecular weight
- OTUs:
-
Operational taxonomic units
References
Shen Y, Hu C, Zhang H, Jiang H. Characteristics of three typical Chinese highland barley varieties: Phenolic compounds and antioxidant activities. J Food Biochem. 2018;42(2):e12488.
Izydorczyk MS, Jacobs M, Dexter JE. Distribution and structural variation of nonstarch polysaccharides in milling fractions of hull-less barley with variable amylose content. Cereal Chem. 2003;80(6):645–53.
Williams BA, Grant LJ, Gidley MJ, Mikkelsen D. Gut fermentation of dietary fibres: physico-chemistry of plant cell walls and implications for health. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(10):2203.
Kim SY, Song HJ, Lee YY, Cho KH, Roh YK. Biomedical issues of dietary fiber beta-glucan. J Korean Med Sci. 2006;21(5):781–9.
Lazaridou A, Biliaderis CG. Molecular aspects of cereal β-glucan functionality: physical properties, technological applications and physiological effects. J Cereal Sci. 2007;46(2):101–18.
Kim HJ, White PJ. In vitro bile-acid binding and fermentation of high, medium, and low molecular weight beta-glucan. J Agric Food Chem. 2010;58(1):628–34.
Shah A, Gani A, Masoodi FA, Wani SM, Ashwar BA. Structural, rheological and nutraceutical potential of β-glucan from barley and oat. Bioactive Carbohydr Dietary Fibre. 2017;10:10–6.
Sayar S, Jannink J-L, White PJ. Digestion residues of typical and high-beta-glucan oat flours provide substrates for in vitro fermentation. J Agric Food Chem. 2007;55(13):5306–11.
El Kaoutari A, Armougom F, Gordon JI, Raoult D, Henrissat B. The abundance and variety of carbohydrate-active enzymes in the human gut microbiota. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013;11(7):497–504.
Tao J, Li S, Gan RY. Targeting gut microbiota with dietary components on cancer: Effects and potential mechanisms of action. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020;60(6):1025–37.
Frame LA, Costa E, Jackson SA. Current explorations of nutrition and the gut microbiome: a comprehensive evaluation of the review literature. Nutr Rev. 2020;78(10):798–812.
Chen D, Chen G, Wan P, Hu B, Chen L, Ou S, et al. Digestion under saliva, simulated gastric and small intestinal conditions and fermentation in vitro of polysaccharides from the flowers of Camellia sinensis induced by human gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2017;8(12):4619–29.
Cantu-Jungles TM, Ruthes AC, El-Hindawy M, Moreno RB, Zhang X, Cordeiro LMC, et al. In vitro fermentation of Cookeina speciosa glucans stimulates the growth of the butyrogenic Clostridium cluster XIVa in a targeted way. Carbohydr Polym. 2018;183:219–29.
Yatsunenko T, Rey FE, Manary MJ, Trehan I, Dominguez-Bello MG, Contreras M, et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature. 2012;486(7402):222–7.
Alou MT, Lagier J-C, Raoult D. Diet influence on the gut microbiota and dysbiosis related to nutritional disorders. Hum Microbiome J. 2016;1:3–11.
Maccaferri S, Klinder A, Cacciatore S, Chitarrari R, Honda H, Luchinat C, et al. In vitro fermentation of potential prebiotic flours from natural sources: impact on the human colonic microbiota and metabolome. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2012;56(8):1342–52.
Desai MS, Seekatz AM, Koropatkin NM, Kamada N, Hickey CA, Wolter M, et al. A dietary fiber-deprived gut microbiota degrades the colonic mucus barrier and enhances pathogen susceptibility. Cell. 2016;167(5):1339-1353.e21.
Yu L, Dong L, Liu TJ, Kong LS, Feng T. Difference in Physicochemical Property of β-Glucan from Barley Flour and Bran. Adv Mater Res. 2014;1033–1034:209–15.
Mikkelsen MS, Jensen MG, Nielsen TS. Barley beta-glucans varying in molecular mass and oligomer structure affect cecal fermentation and microbial composition but not blood lipid profiles in hypercholesterolemic rats. Food Funct. 2017;8(12):4723–32.
Paturi G, Butts CA, Stoklosinski HM, Herath TD, Monro JA. Short-term feeding of fermentable dietary fibres influences the gut microbiota composition and metabolic activity in rats. Int J Food Sci Technol. 2017;52(12):2572–81.
Maheshwari G, Sowrirajan S, Joseph B. Extraction and isolation of β-glucan from grain sources-a review. J Food Sci. 2017;82(7):1535–45.
Liu Z, Zhang Z, Qiu L, Zhang F, Xu X, Wei H, et al. Characterization and bioactivities of the exopolysaccharide from a probiotic strain of Lactobacillus plantarum WLPL04. J Dairy Sci. 2017;100(9):6895–905.
Ji X, Yan Y, Hou C, Shi M, Liu Y. Structural characterization of a galacturonic acid-rich polysaccharide from Ziziphus Jujuba cv. Muzao Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;147:844–52.
Wang X, Zhang L, Wu J, Xu W, Wang X, Lü X. Improvement of simultaneous determination of neutral monosaccharides and uronic acids by gas chromatography. Food Chem. 2017;220:198–207.
Shi Y, Xiong Q, Wang X, Li X, Yu C, Wu J, et al. Characterization of a novel purified polysaccharide from the flesh of Cipangopaludina chinensis. Carbohydr Polym. 2016;136:875–83.
Wang J, Zhao X, Tian Z, Yang Y, Yang Z. Characterization of an exopolysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus plantarum YW11 isolated from Tibet Kefir. Carbohydr Polym. 2015;125:16–25.
Lin X, Ji X, Wang M, Yin S, Peng Q. An alkali-extracted polysaccharide from Zizyphus jujuba cv Muzao: Structural characterizations and antioxidant activities. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;136:607–15.
Zhou W, Yan Y, Mi J, Zhang H, Lu L, Luo Q, et al. Simulated Digestion and Fermentation in Vitro by Human Gut Microbiota of Polysaccharides from Bee Collected Pollen of Chinese Wolfberry. J Agric Food Chem. 2018;66(4):898–907.
Xie M, Chen G, Wan P, Dai Z, Hu B, Chen L, et al. Modulating effects of dicaffeoylquinic acids from ilex kudingcha on intestinal microecology in vitro. J Agric Food Chem. 2017;65(47):10185–96.
Qu W, Nie C, Zhao J, Ou X, Zhang Y, Yang S, et al. Microbiome-metabolomics analysis of the impacts of long-term dietary advanced-glycation-end-product consumption on C57BL/6 mouse fecal microbiota and metabolites. J Agric Food Chem. 2018;66(33):8864–75.
Ji X, Hou C, Gao Y, Xue Y, Yan Y, Guo X. Metagenomic analysis of gut microbiota modulatory effects of jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill) polysaccharides in a colorectal cancer mouse model. Food Funct. 2020;11(1):163–73.
Gnanasambandam R, Proctor A. Determination of pectin degree of esterification by diffuse reflectance Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2000;68(3):327–32.
Yan J-K, Wang Y-Y, Wang Z-B, Ma H-L, Pei J-J, Wu J-Y. Structure and antioxidative property of a polysaccharide from an ammonium oxalate extract of Phellinus linteus. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;91:92–9.
Fu X, Cao C, Ren B, Zhang B, Huang Q, Li C. Structural characterization and in vitro fermentation of a novel polysaccharide from Sargassum thunbergii and its impact on gut microbiota. Carbohydr Polym. 2018;183:230–9.
Shi X-D, Li O-Y, Yin J-Y, Nie S-P. Structure identification of α-glucans from Dictyophora echinovolvata by methylation and 1D/2D NMR spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2019;271:338–44.
Lazaridou A, Biliaderis CG, Izydorczyk MS. Molecular size effects on rheological properties of oat β-glucans in solution and gels. Food Hydrocolloids. 2003;17(5):693–712.
Ghotra BS, Vasanthan T, Temelli F. Structural characterization of barley β-glucan extracted using a novel fractionation technique. Food Res Int. 2008;41:957–63.
Xiao X, Tan C, Sun X, Zhao Y, Zhang J, Zhu Y, et al. Effects of fermentation on structural characteristics and in vitro physiological activities of barley β-glucan. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;231:115685.
Shang N, Xu R, Li P. Structure characterization of an exopolysaccharide produced by Bifidobacterium animalis RH. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;91:128–34.
Wu J, Zhang Y, Wang L, Xie B, Wang H, Deng S. Visualization of single and aggregated hulless oat (Avena nuda L) (1–>3), (1–>4)-beta-D-glucan molecules by atomic force microscopy and confocal scanning laser microscopy. J Agric Food Chem. 2006;54(3):925–34.
Zielke C, Stradner A, Nilsson L. Characterization of cereal β-glucan extracts: Conformation and structural aspects. Food Hydrocolloids. 2018;79:218–27.
Szychlinska MA, Di Rosa M, Castorina A, Mobasheri A, Musumeci G. A correlation between intestinal microbiota dysbiosis and osteoarthritis. Heliyon. 2019;5(1):e01134.
Morrison DJ, Preston T. Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut Microbes. 2016;7(3):189–200.
Chen C, Huang Q, Fu X, Liu RH. In vitro fermentation of mulberry fruit polysaccharides by human fecal inocula and impact on microbiota. Food Funct. 2016;7(11):4637–43.
Jayachandran M, Chen J, Chung SSM, Xu B. A critical review on the impacts of β-glucans on gut microbiota and human health. J Nutr Biochem. 2018;61:101–10.
Mikkelsen MS, Jespersen BM, Larsen FH, Blennow A, Engelsen SB. Molecular structure of large-scale extracted β-glucan from barley and oat: Identification of a significantly changed block structure in a high β-glucan barley mutant. Food Chem. 2013;136(1):130–8.
Hou C, Chen L, Yang L, Ji X. An insight into anti-inflammatory effects of natural polysaccharides. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;153:248–55.
Huo J, Wu J, Sun B, Zhao M, Sun W, Sun J, et al. Isolation, purification, structure characterization of a novel glucan from Huangshui, a byproduct of Chinese Baijiu, and its immunomodulatory activity in LPS-stimulated THP-1 cells. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;161:406–16.
Bhm N, Kulicke WM. Rheological studies of barley (1→3)(1→4)-β-glucan in concentrated solution: mechanistic and kinetic investigation of the gel formation. Carbohydr Res. 1999;315:302–11.
Morgan KR, Roberts CJ, Tendler SJB, Davies MC, Williams PM. A13C CP/MAS NMR spectroscopy and AFM study of the structure of Glucagel, a gelling β-glucan from barley. Carbohydr Res. 1999;315:169–79.
Wei L, Cui SW, Kakuda Y. Extraction, fractionation, structural and physical characterization of wheat β-D-glucans. Carbohydr Polym. 2006;63(2):408–16.
Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Nilsson A, Akrami R, Lee YS, De Vadder F, Arora T, et al. Dietary fiber-induced improvement in glucose metabolism is associated with increased abundance of prevotella. Cell Metab. 2015;22(6):971–82.
Cani PD, Possemiers S, Van de Wiele T, Guiot Y, Everard A, Rottier O, et al. Changes in gut microbiota control inflammation in obese mice through a mechanism involving GLP-2-driven improvement of gut permeability. Gut. 2009;58(8):1091–103.
Gowd V, Xie L, Zheng X, Chen W. Dietary fibers as emerging nutritional factors against diabetes: focus on the involvement of gut microbiota. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2019;39(4):524–40.
Singh RP, Rajarammohan S. Linear and branched β-Glucans degrading enzymes from versatile Bacteroides uniformis JCM 13288(T) and their roles in cooperation with gut bacteria. Gut Microbes. 2020;12(1):1–18.
Sonnenburg ED, Zheng H, Joglekar P, Higginbottom SK, Firbank SJ, Bolam DN, et al. Specificity of polysaccharide use in intestinal bacteroides species determines diet-induced microbiota alterations. Cell. 2010;141(7):1241–52.
Jones RM. The influence of the gut microbiota on host physiology: pursuit of mechanisms. Yale J Biol Med. 2016;89(3):285–97.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to instrument shared platform of college of food science & engineering of NWAFU.
Funding
The study was supported by the Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (Grant No. 2018JM3008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CN designed and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. XY analyzed the data. XX, ZZ, JZ, YW, XW, NX, YL, ZS and XL participated in sample and data collections. HL, QM, BT and MZ assisted in interpretation and revising the article. JL and ZC revised the research article, provided expert advice and support during the development and implementation of the research article, and share co-corresponding authorship. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Fig. S1.
Rarefaction curves and Shannon index.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Nie, C., Yan, X., Xie, X. et al. Structure of β-glucan from Tibetan hull-less barley and its in vitro fermentation by human gut microbiota. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 8, 12 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40538-021-00212-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40538-021-00212-z