Abstract
Background
Larval source management (LSM), which requires an understanding of the ecology and composition of the local mosquito fauna, is an important parameter in successful vector control programmes. The present study was conducted to understand the distribution of larval habitats, species composition and factors associated with the seasonal abundance of mosquito larvae in Gezira irrigation Scheme in Gezira state, central Sudan.
Methods
Cross-sectional larval surveys were carried out in the communities of Barakat (urban) and El-Kareiba (semi-urban), in Wad Madani, Gezira. A standard dipper was used for sampling larvae in all possible breeding sites and enamel bowls were employed for larvae sorting. Habitats were characterised using physical features and all larvae specimens were identified morphologically.
Results
A total of 331 larval habitats were surveyed, out of which 166 were found to be positive breeding sites for Anopheles (56.78%), Culicinae (29.67%) and Aedes (13.55%) species. A total of 5 525 larvae collected were categorised as Culex (2 617, 47.37%), Anopheles (2 600, 47.06%) and Aedes (308, 5.57%). There was a high number of positive habitats during the rainy season, while the lowest proportion was reported during the hot dry season, in both study sites (Barakat [χ 2 = 10.641, P = 0.0090], El-Kareiba [χ 2 = 23.765, P = 0.0001]). The main breeding site for Anopheles larvae was leaking water pipes (51.5%), followed by irrigation channels (34.2%), hoof prints (6.4%), tyre tracks (5.5%) and water tanks (2.4%). A logistic regression analysis showed that the abundance of Anopheles larvae was reduced by the presence of predators (backswimmers, tadpoles) and grass cover. Adult productivity (number of adult females emerged/m2) was not homogeneousfor all habitats; the highest productivity was found in irrigation channels (0.78 females/m2) for Anopheles, and in septic tanks (2.86 females/m2) for Culicinae and (0.86 females/m2) for Aedes. Anopheles arabiensis was found to be the dominant Anopheles species. This study documented the presence of An. funestus in central Sudan for the first time.
Conclusions
Maintaining leaking water pipes and adopting intermittent irrigation are recommended for LSM, as these surveyed habitats represent the main source of maintaining the local mosquito population during the hot dry season.
Similar content being viewed by others
Multilingual abstracts
Please see Additional file 1 for translation of the abstract into the five official working languages of the United Nations.
Background
Mosquito-borne diseases are becoming a serious global burden. Climate changes due to global warming are leading to the spread of disease vectors and pathogens in formerly disease-free areas [1–4]. These changes affect the seasonality of vectors and, subsequently, the distribution and transmission patterns of diseases [1, 2, 5, 6].
Malaria is an important mosquito-borne disease in Sudan. Sudan is one of the countries with a high malaria burden in Sub-Saharan Africa [7]. Many recent outbreaks of mosquito-borne diseases have occurred in Gezira state, including yellow fever in 2005, and Rift Valley fever in 2007 and 2010, and malaria always occurs during and after the rainy season [3, 4, 6, 7]. In the recent, Larva; source management has gained a wide attention as it is throughout to be most useful target. It deals with a developmental stage that cannot move outside the targeted site. Hence, thought to be useful if well planed.
In Sudan, irrigated areas cover around 1.5% of the total farmland, providing suitable and stable mosquito breeding sites. Mosquito species distribution is associated with climatic zones and degrees of aridity [8, 9]. In the dry savannah areas of central and eastern Sudan, very rare larval habitats are found during the dry season [8–11]. Gezira is located in central Sudan, along the Blue Nile river, between the latitude 13–15.2 °N and longitude 32.5–34 °E. Huge ecological changes have occurred after Gezira Scheme such as increased irrigated areas, deforestation and hence became one of the largest irrigation projects in the world to became operational. It started in 1925 with 300 000 feddans, due to expansion of land size, nowadays covers an area of some 2 million feddans (one feddan = 0.42 ha) principally under gravity irrigation [12].
The current mosquito species list in Sudan is based on surveys carried out by Lewis in the mid-1950s, not taking into account the environmental and climate changes that might have influenced the re-distribution of vector species [13]. Land use patterns and climate changes are factors considered to be the drivers of species composition and dynamics [14–16]. The expansion of Gezira scheme might have influenced changes in species composition in this state [7]. Four more species of mosquitoes, Anopheles sergenti, An. domicolus, An. seydeli and An. brohieri, have been identified by studies conducted by Gillies and De Meillon [17]. In 1997, studies by Nugud et al. identified 31 Anopheles species, including two more new species [18]. These variations show that there is a change of species composition in space and time, and have raised a need for re-assessing mosquito species and composition in different areas in order to be able to better select and implement vector control and intervention tools.
The aim of the current study was to assess the factors associated with seasonal abundance of larval species and characterise larval habitats for mosquito fauna in the Gezira Scheme in central Sudan.
Methods
Study sites
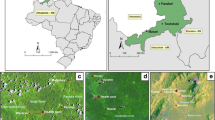
This study was carried out between February and September 2011 in the Barakat (33.32 °N; 14.18 °E) and El-Kareiba (33.27 °N; 14.24 °E) villages, located approximately 20 km from the town of Wad Madani, central Sudan (Fig. 1). The area has a dry savanna climate with an estimated annual rainfall of 140–225 mm. Relative humidity fluctuates between 37 and 86%. There are three annual seasons: a short rainy season from July to September, a dry cool season from November to March and a hot dry season from April to June. The mean temperature varies between 15 °C and 21 °C in the cool dry season and 32 °C to 42 °C in the hot dry season (Sudan Metrological Service, unpublished data).
Larval surveys
A portable geolocation system (Magellan Triton 400, PJM technology Industry Co., Ltd, Shenzhen Pengjin Technology Co., Ltd, Shenzhen China) was used to mark the breeding habitats for each survey. Surveys were conducted bi-monthly and the same habitats were visited each time.
The breeding sites were categorised as follows: (1) irrigation channels (canals used to direct water in paddy plots from the main channel); (2) broken pipes (water leakage from pipes used for drinking water); (3) animal hoof prints (which provide waterlogged sections of land resulting in small mosquito breeding sites); (4) barrels (large containers used for storing water for domestic purposes, pool storage, Jars); and (5) open basins (used for storing water for construction purposes). Hoof prints, tyre tracks and broken water pipes were considered as temporary habitats, while barrels, open basins and irrigation canals were considered as permanent productive habitats. Land use types were described as: (1) farmland (land used for the production of food crops); (2) pastures (land covered with low plants suitable and used for grazing animals); and (3) roads (land used as a passage for animals, people and vehicles).
A standard dipper (350 mls) (BioQuip Products, Inc. California, USA) was used for estimating the number of mosquito larvae, pupae and aquatic invertebrates in each habitat. A total of 20 dips were made in each habitat every visit. The immature stages, 1st and 2nd instars, were grouped together as earlier instars, while the 3rd and 4th instars were grouped together as late instars. All Anopheles larvae and pupae were collected in 25 ml vials with 75% alcohol and transported to insectaries at the Blue Nile National Institute for Communicable Diseases (BNNICD), University of Gezira, Wad Madani, Sudan. The marked coordinates were input into ArcView version 10.4 (ESRI, 380 New York Street, Redlands, CA 92373–8100 USA) for analysis and for drawing maps.
Habitat characterisation
In each survey, the habitat type, habitat size, vegetation cover (percentage/proportion of the vegetation covering the larval habitat surface), presence of predators and larval density by instars were recorded.
Data analysis
The data obtained from the entomological surveys were analysed using JMP version 5.0.1.2 (SAS Institute, Inc., NC, USA). The means of larval densities were compared between the different seasons and sites using the Tukey-Kramer test with analysis of variance (ANOVA). Associations between habitat characteristics (Grass cover, polluted habitats, turbidity, shading, Algae and predator) and larval densities were tested using logistic regression analysis. Analysis was not performed by instars because the variations between and within instars were very large and hence could distort the biological meaning of obtained results and its interpretation.
Results
Species composition and productivity
A total of 5 525 larvae were sampled from 331 breeding habitats and sent to the insectary to be identified to species level using a morphological key developed by Gillies and Coetzee [19]. Of the sampled larvae, 2 617 (47.37%) were of the Culexspecies, 2 600 (47.06%) were Anopheles and 308 (5.57%) were Aedes. Immature culicine mosquitoes were taxonomically identified as Culex antennatus (42%), Cx. Quinquefasciatus (25%), Cx. simpsoni (14%), Cx. Tritaeniorhynchus (8%), Cx. Theileri (5%), Cx. musarum (4%) and Cx. pipiens (2%). Anopheline mosquitoes were taxonomically identified as An. arabiensis (38.0%), An. funestus (27.0%), An. Rufipes (24.5%), An. Pharoensis (9.5%), An. Nili (0.5%) and An. dattali (0.5%). A total of 308 Aedes mosquitoes were identified as Aedes aegypti (n = 47, 15.3% in Barakat; n = 13, 4.2% in El-Kareiba) from positive breeding sites, which were reported during the cool dry season. In this study, adult habitat productivity (number of adult females emerged/m2) was not homogeneous. The highest productivity was observed in irrigation channels (0.78 females/m2) for Anopheles, and in septic tanks (2.86 females/m2) for Culex and (0.86 females/m2) for Aedes (Tables 1 and 2).
Habitat characteristics
A total of 331 breeding sites were visited. The most common type of larval habitat was leaking water pipes. The presence of Anopheles larvae was significantly associated with open habitats (exposure to sunlight) (χ 2 = 5.237, P = 0.0221), turbidity (χ 2 = 2.45, P = 0.1176), presence of pollution (χ 2 = 0.35, P = 0.5522), grass cover (χ 2 = 9.12, P = 0.0025), presence of algae (χ 2 = 11.897, P = 0.0026) and abundance of predators (χ 2 = 29.92, P < 0.0001) (Table 3).
The logistic regression analysis showed that the presence of Anopheles larvae was found to decrease with the abundance of predators (backswimmers, tadpoles) and grass cover. The increase of Culicinaelarvae was associated with habitats characterised by low or absence of turbidity (χ 2 = 9.34; P = 0.0022) and absence of predators (χ 2 = 25.86; P < 0.0001). The presence of Aedes larvae was associated with open habitats (χ 2 = 934; P = 0.0129) and no grass cover (χ 2 = 9.12; P = 0.0025) (Table 3).
Determination of positive and negative mosquito breeding sites
Eight habitat types were inspected in the two study sites. Among them, 51.6% (n = 166) were found to be positive mosquito breeding sites. A significant difference was observed over the seasons between the positive and negative breeding sites in both Barakat (χ 2 = 10.641, P = 0.0050) and El-Kareiba (χ 2 = 23.754, P < 0.0001) (Fig. 2). The highest number of positive mosquito breeding sites was recorded during the rainy season in both Barakat (96.4%; 27/28) and El-Kareiba (65.6%; 21/32). A significant difference was observed in Anopheles larvae presence in the different habitats in Barakat. The most preferred habitat of Anopheles larvae was leaking water pipes (40%) (Table 2).
Mosquito larval abundance and spatial-temporal distribution among the different habitat types
Overall, 2 617 Culex larvae were collected from eight larval habitat types: leaking water pipes (54.53%), irrigation channels (19.55%), animal hoof prints (8.10%), septic tanks (10.36%), tyre tracks (4.02%), jars (0.19%) and water tanks (3.25%). Anopheles larvae were collected from six habitat types: leaking water pipes (47.61%), irrigation channels (23.48%), animal hoof prints (16.03%), tyre tracks (8.38%), Water pools (2.42%) and water tanks (1.85%) (Fig. 3 and Table 1). Ae. Aegypti are reported though in low density dominated in Jars and Septic tanks (Fig. 3 and Table 1). About 78.1% of all positive breeding sites were located on farms, followed by roads (12.3%) and houses (9.6%). Farmland type was significantly associated with positive mosquito breeding sites (χ 2 = 15.902, P = 0.0032) (Fig. 4). The density of Anopheles larvae (larvae per dip) on farmland was 4.2 compared to 2.0 on roads and 1.4 on pastures. Aedes mosquitoes preferred domestic land surroundings due to the high abundance of containers and tanks found on this area, which are all suitable breeding sites (Fig. 4).
Effectofseasonsonsites
During this study, the proportion of positive mosquito breedingsiteswassignificantly higherduringtherainyseason than in dry season for both Barakat (F =16, df = 2, P = 0.0049) and El- Kareiba (F = 16, df = 2, P < 0.0001). The proportions of positive breeding sites during the rainy season were 96.4% and 65.6% in Barakat and El-Kareiba, respectively. The proportion of positive breeding sites during the cool dry season in Barakat (4.7) was almost four or three times compared to El-Kareiba (1.7) for Culex spp.. For Anopheles spp. it was 2.69 in Barakat and 1.49 in El-Kareiba while for Aedes spp. it was 0.30 in Barakat and 0.35 in El-Kareiba for Cool dry season (Table 6).
The densities of Culex, Anopheles and Aedes larvae during the different seasons in the two sites are shown in Tables 5 and 6. There was a significant difference in the larval densities of Anopheles mosquitoes in the different seasons and at different sites. However, no significant difference was observed in the density of both Culex and Aedes larvae over the seasons, except the density of Aedes larvae in El-Kareiba, where it was found to be restricted to the cool dry season. The highest larval density was observed during the rainy season for both Anopheles and Culex species, while the peak of Aedes larval density occurred during the cool dry season in El-Kareiba (Tables 4 and 5). The larval densities of both the Culex and Anopheles species were significantly higher in the Barakat irrigated area compared to the El-Kareiba site (Table 6).
Discussion
The findings of this study demonstrate that the main potential mosquito breeding habitats in urban areas are leaking water pipes and irrigation channels in agricultural schemes during the dry season. Of all suitable breeding sites visited, less than 52% were found to be positive mosquito breeding sites, and this percentage was found to decrease during the dry season. In Africa, the larval source management have shown to be very effective in all small scale and urban areas implemented [20] In western Kenya highlands and urban area of Dar-es-salaam, Tanzania the larval source management have shown a great impact when managed alone or in combination with IRS and LLINs implementation [19]. Decline of adult vectors and transmission of malaria parasites was found vivid [19]. Its a proof that, if LSM is implemented in large scale and integrated with LLINs and IRS, a great improvement shall be seen in malaria control efforts than we are getting for IRS and LLINs alone.
The species composition in this study was: 47.06% were Anopheles species, 47.37% were Culex species and the remaining 5.57% were Aedes species, which were identified as Ae. aegypti. These findings are similar to what was reported by previous studies on Ae. aegypti abundance, only differing in seasonality and habitat types [2, 6, 21].
The productivity of the three mosquito genera was found to be 0.78 females/m2, 2.86 females/m2 and 0.86 females/m2 for Anopheles spp., Culex spp and Aedes spp., respectively. This is the very first time that productivity of each genus has been reported in this particular location. Productivity was found to be habitat-species specific. High productivity of Anopheles spp. was found in irrigation channels, and high productivity of Culex sppand Aedes spp. was found in septic tanks. Productivity was also recorded for each genus in other habitat types, but at lower levels.
During the rainy season, the average proportion of positive mosquito breeding sites was found to be over 81% in both study areas. This results in differences in mosquito densities between dry and rainy seasons, which could be attributed to the availability of water and fluctuations in temperature and relative humidity [3, 6, 14, 15, 22, 23]. In Sudan, adult mosquito density, i.e., An. arabiensis, has been shown to either decrease or completely disappear during the hot dry season [10, 24]. An. arabiensis was is the dominant Anopheles species in Sudan [10, 12, 13] and was is considered to be the main malaria vector in the country [10, 12, 25, 26].
Importantly, this study documented for the first time the presence of An. funestus in Wad Madani. The favourable habitat for this species was found to be vegetated irrigation channels. In equatorial areas, the peak of An. funestus adult population is at the end of the rainy and beginning of the dry season [27]. Seven Culex species were recorded in this study, which was contrary to fewer species reported by previous reports [9]. All Culex species found in this study were reported by Lewis reported all Culex species found in this study in 1956 [13]. Ae. aegypti was the only species of the Aedes genus reported in the study areas during the study period. It was sampled permanently in septic tanks and jars. It is known that the local habitat profile of Ae. aegypti is associated with human dwellings and community socio-economic factors such as well-being and poverty [28, 29].
In the present study, immature mosquitoes found in turbid water were almost always of the Culex species, which is similar to the findings of Devi and Jauhari [30]. Anopheline mosquitoes preferred to breed in clear water, which was similar to the findings of Robert et al. [31]. Significant differences were observed among the three seasons for Anopheles larvae. Similar findings have shown that seasonality has an effect on An. gambiae sensu lato dynamics and abundance [15, 16], and could demonstrate that anopheline mosquitoes are more sensitive to climatic variables, mainly temperature and relative humidity [21, 27, 32]. In this study, peak vector densities were observed during the rainy season and this result agrees with other observations from the same and other dry savanna areas of eastern and central Sudan [10, 12, 33]. It is interesting to note that the most productive breeding site for anopheline mosquitoes found over the different seasons was irrigation channels, and this may explain why the density of Anopheles larvae was significantly higher in irrigation area of Barakat as compared to El-Kareiba.
The findings of this study show that that, targeting mosquito species of different genera can be done by LSM implementation in their specific habitats. This would make control efforts for each genus easier and more economical. Similar findings were found in previous studies conducted in western Kenyan highlands [15, 16] and Dar es Salaam, Tanzania [20] thought the coverage of programmes were limited to small scale area coverage.
Conclusions
Frequent updating of the mosquito species composition and dynamics in the Gezira Scheme are considered necessary for effect control plan. A low mosquito larval density was observed during the dry season in this study, which suggests that it would be cost-effective to conduct larval control in the dry season. Currently, vector interventions can be integrated with adult mosquito control (use of long-lasting insecticidal nets and indoor residual spraying) during the dry season. The main breeding sites were identified for each genus and earmarked for the best LSM in this area which suggested dry season better time for timed LSM.
Abbreviations
- BNNICD:
-
Blue Nile National Institute for Communicable Diseases
- Df:
-
Degree of freedom
- F:
-
F-statistics for ANOVA output
- IRS:
-
Indoor residual spray
- LLINs:
-
Long lasting Insecticidal nets
- LMS:
-
Larval source management
References
Ogden N, Milka R, Caminade C, Gachon P. Recent and projected future climatic suitability of North America for the Asian tiger mosquito Aedes albopictus. Parasit Vectors. 2014;7:532.
Medeiros-Sousa AR, Ceretti-Júnior W, de Carvalho GC, Nardi MS, Araujo AB, Vendrami DP, et al. Diversity and abundance of mosquitoes (Diptera:Culicidae) in an urban park: Larval habitats and temporal variation. Acta Trop. 2015;150:200–9.
Campbell LP, Luther C, Moo-Llanes D, Ramsey JM, Danis-Lozano R, Peterson AT. Climate change influences on global distributions of dengue and chikungunya virus vectors. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015;370:20140135.
Leaf A. Potential health effects of global climatic and environmental changes. N Engl J Med. 1989;321:1577–83.
Medlock JM, Leach SA. Effect of climate change on vector-borne disease risk in the UK. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15:721–30.
Dhimal M, Ahrens B, Kuch U. Species composition, seasonal occurrence, habitat preference and altitudinal distribution of malaria and other disease vectors in eastern Nepal. Parasit Vectors. 2014;7:540.
WHO. Progress report on Control and elimination of malaria. Geneva: World Health Organisation; 2011.
Dery DB, Brown C, Asante KP, Adams M, Dosoo D, Amenga-Etego S, et al. Patterns and seasonality of malaria transmission in the forest-savannah transitional zones of Ghana. Malar J. 2010;9:314.
Seufi AM, Galal FH. Role of Culex and Anopheles mosquito species as potential vectors of rift valley fever virus in Sudan outbreak, 2007. BMC Infect Dis. 2010;10:65.
Hamad AA, Abd El Hamid DN, Arnot DE, Giha HA, Abdel-Muhsin A-MA, Satti GM, et al. A marked seasonality of malaria transmsission in two rural sites in eastern Sudan. Acta Trop. 2002;83:71–82.
Himeidan Y, Rayah EEA. Role of some environmental factors on the breeding activity of Anopheles arabiensis in New Halfa town, eastern Sudan. East Mediterr Health J. 2008;14:252–9.
el Gaddal AA, Haridi A, Hassan F, Hussein H. Malaria control in the Gezira-Managil irrigated scheme of the Sudan. J Trop Med Hyg. 1985;88:153–9.
Lewis D. The anopheline mosquitos of the Sudan. Bull World Health Organ. 1956;47:475–94.
Munga S, Minakawa N, Zhou G, Mushinzimana E, Barrack O-OJ, Githeko AK, et al. Association between land cover and habitat productivity of malaria vectors in western kenyan highlands. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2006;74:69–75.
Kweka E, Munga S, Himeidan Y, Githeko A, Yan G. Assessment of mosquito larval productivity among different land use types for targeted malaria vector control in the western Kenya highlands. Parasit Vectors. 2015;8:356.
Kweka EJ, Zhou G, Munga S, Lee M-C, Atieli HE, Nyindo M, et al. Anopheline larval habitats seasonality and species distribution: a prerequisite for effective targeted larval habitats control programmes. PLoS One. 2012;7:e52084.
Gillies MT, De Meillon B. The Anophelinae of Africa south of the Sahara (Ethiopian zoogeographical region). In: The Anophelinae of Africa south of the Sahara (Ethiopian Zoogeographical Region). 1968.
Elkaram EHA. Epidemiology and Transmission of Lymphatic Filariasis in SouthernSudan. University of Khartoum 2015.
Fillinger U, Ndenga B, Githeko A, Lindsay SW. Integrated malaria vector control with microbial larvicides and insecticide-treated nets in western Kenya: a controlled trial. Bull World Health Organ. 2009;87:655–65.
Chaki P, Govella N, Shoo B, Hemed A, Tanner M, Fillinger U, et al. Achieving high coverage of larval-stage mosquito surveillance: challenges for a community-based mosquito control programme in urban Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Malar J. 2009;8:311.
Baruah S, Dutta P. Seasonal prevalence of Aedes aegypti in urban and industrial areas of Dibrugarh district, Assam. Trop Biomed. 2013;30:434–43.
Charlwood J, Vij R, Billingsley P. Dry season refugia of malaria-transmitting mosquitoes in a dry savannah zone of east Africa. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2000;62:726–32.
Ruiz D, Poveda G, Vélez ID, Quiñones ML, Rúa GL, Velásquez LE, et al. Modelling entomological-climatic interactions of Plasmodium falciparum malaria transmission in two Colombian endemic-regions: contributions to a National Malaria Early Warning System. Malar J. 2006;5:66.
Himeidan YES, Dukeen M, El Rayah EA, Adam I. Anopheles arabiensis: abundance and insecticide resistance in an irrigated area of eastern Sudan. East Mediterr Health J. 2004;10:167–74.
Dukeen MY, Omer S. Ecology of the malaria vector Anopheles arabiensis Patton (Diptera: Culicidae) by the Nile in northern Sudan. Bull Entomol Res. 1986;76:451–67.
Petrarca V, Nugud A, Ahmed M, Haridi A, Di Deco M, Coluzzi M. Cytogenetics of the Anopheles gambiae complex in Sudan, with special reference to An. arabiensis: relationships with East and West African populations. Med Vet Entomol. 2000;14:149–64.
Kelly-Hope LA, Hemingway J, McKenzie FE. Environmental factors associated with the malaria vectors Anopheles gambiae and Anopheles funestus in Kenya. Malar J. 2009;8:1–8.
Service M. Importance of ecology in Aedes aegypti control. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1992;23:681.
Troyo A, Calderón-Arguedas O, Fuller DO, Solano ME, Avendaño A, Arheart KL, et al. Seasonal profiles of Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) larval habitats in an urban area of Costa Rica with a history of mosquito control. J Vector Ecol. 2008;33:76.
Devi NP, Jauhari R. Mosquito species associated within some western Himalayas phytogeographic zones in the Garhwal region of India. J Insect Sci. 2007;7:32.
Robert V, Awono-Ambene H, Thioulouse J. Ecology of larval mosquitoes, with special reference to Anopheles arabiensis (Diptera: Culcidae) in market-garden wells in urban Dakar, Senegal. J Med Entomol. 1998;35:948–55.
Christiansen-Jucht C, Parham P, Saddler A, Koella J, Basanez M-G. Temperature during larval development and adult maintenance influences the survival of Anopheles gambiae s.s. Parasit Vectors. 2014;7:489.
Himeidan YE, Elzaki MM, Kweka EJ, Ibrahim M, Elhassan IM. Pattern of malaria transmission along the Rahad River basin, Eastern Sudan. Parasit Vectors. 2011;4:109.
Acknowledgements
The technical assistance of staff at the BNNICD, University of Gezira, Sudan is greatly acknowledged. Dr. Mo’awia M. Hassan and Mr. Tellal Ageeb from the Department of Epidemiology at the Tropical Medicine Research Institute in Khartoum, Sudan are greatly acknowledged for their guidance in geographical information system analysis and mapping.
Funding
This study obtained financial assistance from NMCP Federal Ministry of Health, Sudan.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets supporting the findings of this paper are included in this paper.
Authors’ contributions
MMM performed the data collection, interpreted the results, and drafted and wrote the paper. YEH designed the study, analysed the data, and wrote and critically revised the paper. EJK wrote and critically revised the paper. All authors approved the final paper for submission.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional file
Additional file 1:
Multilingual abstracts in the five official working languages of the United Nations. (PDF 768 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Mahgoub, M.M., Kweka, E.J. & Himeidan, Y.E. Characterisation of larval habitats, species composition and factors associated with the seasonal abundance of mosquito fauna in Gezira, Sudan. Infect Dis Poverty 6, 23 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40249-017-0242-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40249-017-0242-1