Abstract
Background
Large-river decision-makers are charged with maintaining diverse ecosystem services through unprecedented social-ecological transformations as climate change and other global stressors intensify. The interconnected, dendritic habitats of rivers, which often demarcate jurisdictional boundaries, generate complex management challenges. Here, we explore how the Resist–Accept–Direct (RAD) framework may enhance large-river management by promoting coordinated and deliberate responses to social-ecological trajectories of change. The RAD framework identifies the full decision space of potential management approaches, wherein managers may resist change to maintain historical conditions, accept change toward different conditions, or direct change to a specified future with novel conditions. In the Upper Mississippi River System, managers are facing social-ecological transformations from more frequent and extreme high-water events. We illustrate how RAD-informed basin-, reach-, and site-scale decisions could: (1) provide cross-spatial scale framing; (2) open the entire decision space of potential management approaches; and (3) enhance coordinated inter-jurisdictional management in response to the trajectory of the Upper Mississippi River hydrograph.
Results
The RAD framework helps identify plausible long-term trajectories in different reaches (or subbasins) of the river and how the associated social-ecological transformations could be managed by altering site-scale conditions. Strategic reach-scale objectives may reprioritize how, where, and when site conditions could be altered to contribute to the basin goal, given the basin’s plausible trajectories of change (e.g., by coordinating action across sites to alter habitat connectivity, diversity, and redundancy in the river mosaic).
Conclusions
When faced with long-term systemic transformations (e.g., > 50 years), the RAD framework helps explicitly consider whether or when the basin vision or goals may no longer be achievable, and direct options may open yet unconsidered potential for the basin. Embedding the RAD framework in hierarchical decision-making clarifies that the selection of actions in space and time should be derived from basin-wide goals and reach-scale objectives to ensure that site-scale actions contribute effectively to the larger river habitat mosaic. Embedding the RAD framework in large-river decisions can provide the necessary conduit to link flexibility and innovation at the site scale with stability at larger scales for adaptive governance of changing social-ecological systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
As large rivers continue to undergo unprecedented human-induced transformations, ecosystem management can include approaches that attempt to maintain diverse ecosystem services through these transformations (Böck et al. 2018; Díaz et al. 2019). However, anticipating and managing social-ecological transformations at a large-river-system scale is challenging, given their vast spatial extent, interacting threats, dynamic nature, and multi-use management objectives (Sparks 1995; Best 2019; Arthington 2021). Additionally, the interconnected, dendritic habitats of rivers, which often demarcate jurisdictional boundaries, generate complex shared-management challenges (Moss and Newig 2010; Porreca et al. 2016; Laughlin et al 2016). Therefore, coordinated, interagency responses are essential to account for the varied and multi-scale social-ecological change occurring in large river systems (Poff 1997; Ward et al. 2002; Rahel and Olden 2008).
Effective multi-jurisdictional river management is complicated by numerous interacting threats. Damming and channelization for energy, water, and transportation (Grill et al. 2019) have altered flows, which in turn have degraded water quality, changed sediment dynamics, and fragmented floodplain and longitudinal connectivity (Brooker 1985; Dugan et al. 2010; Marschall et al. 2011; Alexander et al. 2012; Phelps et al. 2015). In some areas, non-native species have displaced native biota, altered instream nutrient processing, or shifted selective pressures on native riverine species (Chick and Pegg 2001; Sass et al. 2014; Gallardo et al. 2016; Chick et al. 2020). Accelerating climate change further introduces spatially and temporally explicit directional change and increased phenological variability, oftentimes driving social-ecological trajectories toward transformations (Thompson et al. 2021; Feiner et al. 2022).
Such complexity and variability present challenges because management decisions are traditionally conceptualized and framed at site and local scales (i.e., on-the-ground or in-the-water action). These traditional approaches lose efficacy (Milly et al. 2008) as river systems face uncertain trajectories and potential regime shifts (Bouska et al. 2022) from climate change and other anthropogenic stressors (Craig et al. 2017a; Hirsch 2020; Jackson 2021). Site- and local-scale decisions are a part of the broader governance system (e.g., entities listed in Table 1), which includes all the social, legal, and political structures that affect decision processes (Lockwood et al. 2010; Clifford et al. 2022). In changing systems, an adaptive governance structure promotes stability at large scales, balanced with flexibility for innovation at smaller scales (Craig et al. 2017b). Rapidly changing large-river systems present opportunities for developing shared goals and management approaches that cross jurisdictional boundaries and incorporate ecological scales and social-ecological realities (e.g., Wolf 2008; Pracheil et al. 2012, 2013; Bouska et al. 2019).
The Resist–Accept–Direct (RAD) framework builds on established management approaches by clearly outlining all possible approaches that managers can select when faced with social-ecological transformation due to directional forcing (Fig. 1; Box 1; Lynch et al. 2021; Thompson et al. 2021; Magness et al. 2022a; Schuurman et al. 2022). The RAD framework outlines three approaches to change, wherein managers can choose to: (1) resist change to maintain historical conditions; (2) accept change toward different system conditions; or (3) direct change to a specified future and novel system condition (Lynch et al. 2021; Thompson et al. 2021; Schuurman et al. 2022). Resist, accept, and direct change approaches are not mutually exclusive and can be applied simultaneously in a portfolio approach to achieve large-scale and long-term goals (e.g., resist in one location and accept in another; Magness and Morton 2017; Magness et al. 2022b).
Application of the RAD framework requires that decision-makers identify specific social-ecological trajectories. In systems facing likely transformations, decisions can then be framed as a deliberate choice to either: (1) intervene in a system trajectory, and thus attempt to resist or direct change along a specific path; or (2) not intervene, and thus accept the current trajectory and its eventual social-ecological transformation (Magness et al. 2022a). The goal of using the RAD framework is to brainstorm options that could be selected. Then, established decision-making processes help to identify which options should be selected in each management context. The specific options considered within each RAD category (resist, accept, or direct) are often constrained by the worldviews, culture, and understanding of decision-makers and/or their institutions (Clifford et al. 2022), necessitating deliberate approaches for open-minded and creative brainstorming. The RAD framework enhances traditional management tools (e.g., adaptive management, scenario planning; Walters 1986; Peterson et al. 2003) by explicitly outlining the full decision space of potential management approaches in the context of long-term plausible social-ecological trajectories, rather than defaulting to a limited set of status quo approaches (e.g., considering only resist options). Then, managers can select deliberate responses to social-ecological transformations and work toward identifying thresholds for changing RAD-informed decisions through time (Lynch et al. 2021, 2022b; Thompson et al 2021; Bouska et al. 2022; Magness et al. 2022b; Schuurman et al. 2022).
In large rivers, a hierarchical systems approach to the RAD framework may help link decisions across spatial scales and jurisdictions. This approach entails development of shared, basin-scale goals, formulated in response to social-ecological trajectories, that can be implemented and tailored for local conditions (e.g., Pracheil et al. 2012, 2013; Bouska et al. 2019). Successful implementation of the RAD framework requires linking ecological understanding at different spatial scales to anticipate how the river will respond differently in different areas and at different times (e.g., via spatially explicit velocities of change, directional forcing, nonstationarity, and amplified rates of change; Loarie et al. 2009; Dobrowski et al. 2013; Beever et al. 2014; Bouska et al. 2018, 2022).
Here, we describe how embedding the RAD framework into a hierarchical large-river governance system may help coordinate effective responses to unprecedented directional change from site to basin scales. Specifically, we used the Upper Mississippi River System to illustrate how including the RAD framework in hierarchical decision-making can: (1) provide framing along the river continuum and across spatial scales; and (2) open the entire decision space of potential management approaches. Together, (1) and (2) may help (3) foster coordinated inter-jurisdictional management. The Upper Mississippi River faces multiple, interacting, cross-jurisdictional threats common to other large-river systems across the world (Khoury et al. 2011; Houser et al. 2022). The U.S. Congressionally designated governance structure and well-established inter-jurisdictional partnerships of the Upper Mississippi River System (Water Resources Development Act of 1986, 33 U.S. Code, section 652) make the region ripe for coordinated, informed, and deliberate responses to climate change and may provide a template for other large-river and large-ecosystem decision-makers to navigate similar challenges.
A RAD hierarchical large river governance system
Including the RAD framework in hierarchical large-river governance systems may help coordinate effective responses to unprecedented directional change at three focal decision scales in rivers: the basin, reach, and site scale (Spitzack and Hubbell 2009; Guyon et al. 2012; Craig et al. 2017b; McCain et al. 2018):
-
Basin goals provide the backbone to a cohesive river-governance system, with the necessary stability and direction to inform decisions at smaller spatial scales. Basin goals are the desired directional outcome for fundamental social-ecological functions and services (e.g., “resist loss of ecological integrity”; Box 1).
-
Reach objectives link basin goals to site action by setting different sub-river or sub-basin priorities, as management needs vary along the river. Reach objectives are the desired directional outcomes for key ecosystem determinants that help achieve the basin goals (e.g., resist, accept, or direct habitat diversity, redundancy, or connectivity; Box 1).
-
Site actions contribute to reach objectives and basin goals and provide opportunities for experimentation and innovation that inform whether and when adjustment of priorities or goals is needed at larger scales. Site actions are management interventions, strategies, or approaches to resist, accept, or direct change at the project site scale (Box 1).
At each spatial scale, the RAD framework can help contextualize decisions over long time spans (e.g., > 50 years), which inherently requires incorporating understanding of ecosystem processes and management decisions at other scales (Qiu et al. 2018). Combining the cross-scale ecosystem understanding with consideration of the full decision space of RAD (resist, accept, and direct approaches) may help decision-makers identify creative ways to develop inter-jurisdictional partnerships (e.g., by identifying new scale-specific priority funding areas). Further, the long-term view of the RAD framework may be a useful tool for non-Indigenous managers to extend the time scale of their decisions to be more comparable to the time scales commonly considered by many Indigenous peoples (e.g., the Seventh-Generation philosophy, where decisions should be made today that will sustain food and medicine for the next seven generations; Shultz et al. 2022). In this way, the RAD framework could help connect different ways of knowing (e.g., Indigenous Knowledges, scientific knowledge) to develop a shared vision for a social-ecological system (Shultz et al. 2022). This type of collective approach has been framed for Atlantic and Pacific salmon rivers (Kocik et al. 2022) and is relevant for other large river systems with Indigenous significance. Framing decisions in a long-term and cross-spatial scale may help normalize inclusive, social-ecological-system-based management where people are inextricably linked to the ecosystem, not considered separate from it.
In this section, we introduce how including the RAD framework in hierarchical large-river governance could aid in decision-making at each focal scale in large river systems in general. In subsequent sections, we use examples from the Upper Mississippi River System to illustrate how including the RAD framework in hierarchical decision-making provides cross-scale framing and consideration of the full decision space of management approaches to foster coordinated inter-jurisdictional management.
Basin goals
Key basin-scale decision points where the RAD framework can enhance efforts include (1) developing a RAD-informed shared vision and (2) identifying basin goals to achieve that vision (Box 1). Effective, inclusive, basin-scale planning is fraught with challenges; it requires significant time investment among basin partners and an openness to difficult conversations and co-produced knowledge, wherein no single party overly drives outcomes (Wolf 2017; Djenontin and Meadow 2018). A few key considerations in basin planning include identifying clear goals and objectives with inclusive and equity-based practices, coordination and cooperation, and securing and distributing adequate funding and capacity among partners (Lynch et al. 2022b). Effective approaches to basin planning and facilitation (e.g., Delphi, Structured Decision-Making, Scenario Planning, among many more) increase transparency in problem definition, compare alternative futures, and qualitatively or quantitatively clarify decision processes (Polasky et al. 2011; Gregory et al. 2012; Mukherjee et al. 2015). Successful efforts in basin planning have also applied conflict-transformation approaches rooted in Indigenous Knowledges and world faith traditions that address the emotional and spiritual aspects inherent in environmental decisions, including the shared and reciprocal nature of human–human and human–environment relationships (Wolf 2010, 2017; Reid et al. 2021). In any shared-visioning approach, the RAD framework can enhance efforts by outlining the diversity of plausible social-ecological trajectories, responses, and outcomes (Magness et al. 2022a). Establishing a RAD-informed shared vision from a shared sense of the range of potential basin futures can bring conflicting parties together to find creative and shared solutions.
RAD-informed basin goals set the desired trajectory for fundamental social-ecological outcomes (i.e., resisting, accepting, and/or directing trajectories of system functions and services) that will bring the shared vision into reality. A RAD-informed basin planning effort includes identifying the multitude of changes beyond human control (what changes must or should be accepted), with an understanding of the reciprocal relationship between the environment and society. Explicit identification of what ecosystem changes must be accepted raises questions of how humans can shift their own response and adapt to change as a part of the social-ecological river system (sensu Reid et al. 2021; Brierly and Fryirs 2022). Identifying a RAD-informed shared vision and associated goals also includes explicit conversation of how long into the future undesirable trajectories of change can be resisted. Lastly, RAD-informed shared vision and goals help identify creative direct pathways, where decision-makers may consider previously unimagined potential for the basin (e.g., new economic uses or novel ecosystems to replace or add ecosystem services).
Reach objectives
Reach-scale objectives (Box 1) specify the selected directional outcome for key determinants of ecosystem structure and function [e.g., resist, accept, or direct changes in habitat diversity, redundancy, and connectivity, following De Jager et al. (2018)] to achieve the desired basin-wide fundamental ecosystem outcomes (e.g., ecological integrity and economic use; sensu Spitzack and Hubbell 2009). At the reach scale, there is a more refined understanding of the social and ecological responses to plausible basin trajectories to support decisions on whether, when, and where to resist, accept, and/or direct social-ecological transformations. Assessing ecological responsiveness and social receptivity to change helps identify effective management interventions and clarify when any RAD strategy may be ineffective, too costly, or socially unacceptable (Lynch et al. 2022a). Achievable and effective reach objectives include understanding the extent to which managers can alter site conditions to effectively intervene in the basin trajectory of change [“ecological responsiveness” following Lynch et al. (2022a)].
The temporal and spatial distribution of many site actions to effectively achieve basin goals collectively creates a reach-scale portfolio of prioritized RAD actions (Magness and Morton 2017; Magness et al. 2022b). Because ecological responsiveness and social receptivity vary along the river continuum (Schramm 2017), a reach-scale portfolio of RAD actions will help achieve basin-scale goals. For example, a RAD-informed reach portfolio may prioritize resist actions at sites where the probability of transformation is low until resist strategies become too costly, while prioritizing accept or direct strategies in sites that are closer to a transformation or where a resist intervention is unlikely to be effective (Bouska et al. 2022; Lynch et al. 2022a). This type of prioritization of more resilient sites is counter to common restoration projects that prioritize action in more degraded and less resilient sites (Koslow et al. 2014; Lynch et al. 2021). Importantly, a RAD-informed portfolio may also resist change in one management objective (e.g., habitat diversity) while directing change in another management objective (e.g., economic uses)—even in the same site or reach (Thompson et al. 2021; Kocik et al. 2022).
Site actions
Resist, accept, or direct actions are typically implemented at the site scale (Box 1). To ensure that site actions are effective in contributing to the basin-wide vision, site-scale actions are implemented according to reach-scale prioritization. Given that basin-scale directional change is likely first observed at the site scale, assessing effectiveness of site-scale actions can aid in identifying thresholds for revisiting RAD-informed decisions over time. For example, the long-term transformations identified through the RAD framework can help site-scale managers consider how long they can or should resist, accept, or direct change before switching approaches.
Integrating the RAD framework into site-scale actions will help navigate unprecedented directional change by implementing coordinated management actions across multiple jurisdictions. Specific RAD site-scale actions could be accomplished by using different agency, partner, or community’s historical strengths or expertise. Creative direct site actions may help identify opportunities for new partnerships to support novel solutions. Further, the common language of the RAD framework can provide clearer communication for a broad circle of partners to select specific site actions that best address plausible social-ecological trajectories in the basin (Lynch et al. 2022b).
Cross-scale interactions
Heterogeneity in site-scale conditions often exists along the river continuum resulting in different ecosystem transformations in different areas of the river through time. For example, a reach characterized by well-connected, diverse, and undeveloped floodplain habitats will respond to a changing hydrograph much differently than a reach characterized by a largely disconnected agricultural floodplain with extensive levee infrastructure (De Jager et al. 2018). The understanding of whether a mosaic of site-scale changes drives reach-specific transformations is key for basin planners to assess whether the basin-scale shared vision and goals are achievable through time.
Reach-scale planning can connect basin goals to site actions and provide a conduit for the feedback necessary to support flexible change and innovation from the site to basin scales (sensu Craig et al 2017b). Since the long-term and cross-spatial-scale perspective of the RAD framework requires contextualizing site decisions within larger-scale ecosystem change, RAD-informed site actions may help ensure that reach objectives are achievable and revisited through time, as conditions change.
Overall, the RAD framework helps identify what decision-makers could do. However, it is the internal (i.e., worldviews, culture, and understanding of the system) and external factors (i.e., scientific uncertainty, institutional context, and social feasibility) that ultimately determine the final management decision (Clifford et al. 2022). Embedding the RAD framework in hierarchical governance systems will not solve all cooperation, funding, capacity, and other shared management challenges brought about by climate change and inter-jurisdictional ecosystem management. Rather, the hierarchical RAD framework for large-river governance provides a structure for considering the full decision space of resist, accept, and direct management approaches, which could help conflicting parties find common ground in effective, novel solutions.
The Upper Mississippi River: ripe for RAD management
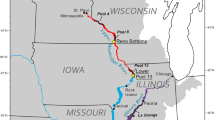
The Mississippi River is the longest river in North America, running 3770 km from its source at Lake Itasca in Minnesota to the Gulf of Mexico, and draining 41% (3,288,000 km2) of the contiguous U.S. (Rajib et al. 2021; Schramm 2017). The Mississippi River can be broadly divided into the Upper Mississippi, from Lake Itasca south to the Ohio River, and the Lower Mississippi, from the Ohio River confluence to the Gulf of Mexico near New Orleans, Louisiana. The commercially navigable portion of the Upper Mississippi River, from Minneapolis, Minnesota, to Cairo, Illinois, is U.S. Congressionally defined as a nationally significant ecosystem and navigation system (Water Resources Development Act of 1986, 33 U.S. Code, section 652). The Upper Mississippi mainstem contains three geomorphically distinct reaches: the upper impounded, lower impounded, and unimpounded reaches (Fig. 2c; Lubinski and Theiling 1999; De Jager et al. 2018). The upper impounded reach is characterized by a relatively well-connected and narrow floodplain with diverse aquatic habitat types. The lower impounded reach is characterized by a relatively wide floodplain with a mix of well-connected floodplain habitats and disconnected floodplain areas behind agricultural levees. The unimpounded reach is characterized by extensive agricultural levees that block floodplain connectivity and create low aquatic habitat diversity. Downstream of the Upper Mississippi portion, the Lower Mississippi is undammed to the Gulf of Mexico but contains extensive river engineering structures (Schramm 2017).
Mean historical (1971–2000) annual precipitation (a) and absolute change from historical mean in predicted 2070–2099 annual mean precipitation (b) across the contiguous United States (RCP 8.5 climate forcings are the multi-model mean derived from 20 downscaled CMIP5 models, downloaded from The Climate Mapper; Taylor et al. 2012; Abatzoglou and Brown 2012). The Missouri River tributary area is outlined in pink and the remaining Upper Mississippi watershed is outlined in red. The Upper Mississippi River mainstem (c), with the Upper Impounded Reach locks and dams indicated in black and the Lower Impounded Reach locks and dams indicated in white. Ceded territory boundaries are representations and may not be the actual legally binding boundaries
The Upper Mississippi River basin crosses state and tribal jurisdictional boundaries (Fig. 2c) and, as such, is managed by different authorities operating at different spatial extents and with differing management priorities (Table 1; McCain et al. 2018). The types of management decisions being made depend on the scale of the decision, from individual project sites (e.g., habitat restoration in a side-channel through the Upper Mississippi River Restoration program) to basin-wide policy (e.g., policies advocated by the Upper Mississippi River Basin Association; Table 1). The upper impounded, lower impounded, and unimpounded reach boundaries are used in existing Upper Mississippi River governance system decisions (Spitzack and Hubbell 2009).
Though modifications for navigation are a dominant factor in the physical configuration of the river today, some multi-use management was established before construction of the current lock-and-dam infrastructure. The Upper Mississippi River National Fish and Wildlife Refuge was established in 1924 and now covers > 970 km2 of aquatic and terrestrial floodplain habitats (Sparks 2010; Schramm 2017). The Water Resources and Development Acts of 1986 and 2007 established goals to balance economic and ecological priorities. Through these Acts, federal funds support management of the: (1) lock-and-dam navigation system; and (2) diverse native flora and fauna. The Acts established interagency partnerships for multi-use management of commercial navigation, agriculture, flood control, recreation, and habitat rehabilitation (Spitzack and Hubbell 2009; DuBowy 2013; Houser et al. 2022). No analogous legislation exists to support balanced river management downstream of Cairo, IL (Schramm 2017). In recognition of the diverse benefits of the Mississippi River Basin and the detriments of singularly focused management goals, new approaches to effectively achieve multi-use goals include novel water-level management plans (Theiling et al. 2021) and more inclusive decision-making processes (Mac and Palmer 2020).
The Upper Mississippi River is a biodiversity hotspot that has high conservation value (Weitzell et al. 2003) and provides diverse ecosystem services (e.g., Thorp et al. 2010; Li et al. 2016; Schramm 2017; PIIC 2023b). The river basin is the sacred homeland of many Indigenous groups (Carlson 2020; PIIC 2023a). The construction of the lock-and-dam navigation infrastructure inundated portions of the floodplain, including numerous Indigenous sacred sites (PIIC 2023a). Climate change further threatens tribal access to spiritual, ceremonial, medicinal, subsistence, and economic needs in the Mississippi River basin ceded territories (GLIFWC 2023) and downstream areas where the U.S. Congress abrogated previously agreed-upon Dakota treaty rights (PIIC 2023a).
The Upper Mississippi River is well suited to provide an example for coordinated, informed, and deliberate responses to unprecedented directional change. The north–south orientation of the Upper Mississippi River aligns with climate gradients (e.g., cooler and wetter in the north, warmer and drier in the south), facilitating experimental and comparative research along the river continuum. The increasing frequency, duration, magnitude, and variability of climate-change-related disturbances in the Upper Mississippi River (Feiner et al. 2022; Van Appledorn 2022) highlights a need to understand shifting baselines in a system undergoing drastic changes (Pletterbauer et al. 2018) with contextualization of an already highly modified river system (Lemke et al. 2017). The long-term and cross-spatial-scale view of the RAD framework may help address the amplified rates, directional change, and increased variability affecting the system and enable decision-makers to navigate social-ecological transformations more effectively, while maintaining or enhancing critical ecosystem services and livelihoods (Thompson et al 2021; Lynch et al. 2022b).
Transformational case study: more water more of the time
To illustrate how the RAD framework may help identify effective responses to unprecedented change in a large river from site to basin scales, we focus primarily on shifts in precipitation and associated directional changes to the river hydrograph. Once the overall hierarchical RAD framework is understood, then the full suite of interacting drivers (e.g., changing air temperature, precipitation, invasive species, land use) can be included in RAD-informed large-river decision-making.
Outcomes of climate projections vary along the river continuum and are complex to predict due to multiple interacting variables. For example, though projections of mean annual precipitation show increases of 2–20% over the next 50 years in the Upper Mississippi River Basin, projections for the Lower Mississippi River Basin includes areas where precipitation is projected to increase (e.g., the Ohio River), remain the same (e.g., the Arkansas River), and decrease (e.g., Red River of the South; Fig. 2a, b). Further, the seasonal distribution of rainfall is expected to change (Additional file 1: Fig. S1) and simultaneously increasing air temperatures could result in a net loss of runoff through increased evapotranspiration, even in areas receiving increased annual precipitation (Battaglin et al. 2020; Tercek et al. 2021). Given the large range in projected changes to precipitation across global climate models (Additional file 1: Figs. S2–S5), preparing for plausible, and even divergent, climate futures will likely be necessary (Lawrence et al. 2021), including anticipating greater variability in river flow conditions.
Overall, the Upper Mississippi River Basin is experiencing precipitation events of greater intensity and longer duration more frequently than in the twentieth century (Meehl and Tebaldi 2004; Taylor et al. 2012; Pörtner et al. 2022). Precipitation changes can alter discharge, a fundamental river variable (van Vliet et al. 2013). Daily discharge throughout the year, or the annual hydrograph, is already changing in the Upper Mississippi River System. On average, over the last decade, the river system has experienced up to 42% higher annual maximum flow (Keokuk, IA), up to 177% higher mean annual flow (Valley City, IL), and high-water events that last up to 20.2 days longer (Keokuk, IA) than 30 years ago (Van Appledorn 2022). Even though observed trends and future projections indicate increases in discharge, systems approaching transformations tend to have increasing variability in ecosystem variables (Carpenter and Brock 2006; Spanbauer et al. 2014). Thus, though the focus of Upper Mississippi River futures is on greater discharge on average, decision-makers also need to prepare for more variability in flow conditions, including extreme low-water conditions (sensu Harris et al. 2018).
The system-wide hydrograph shift toward more water more of the time will likely result in varying social-ecological transformations in different reaches of the river, and some of these transformations are already being observed (Houser et al. 2022). The upper impounded reach, which has relatively well-connected and diverse floodplain habitats, is likely to see amplified rates of sedimentation in aquatic habitats and tree mortality in terrestrial habitats (De Jager et al. In Review; De Jager et al. 2019; De Jager and Rohweder 2017). Increased sedimentation may result in the transformation of open water to marsh or wet meadow habitats (Guyon et al. 2012), and a corresponding loss of the critical overwintering fish habitat that has the necessary combination of depth, temperature, and dissolved oxygen (Theiling et al. 2014). Increased inundation frequency and duration may further amplify the ongoing loss of forest habitat (e.g., a 6.4% loss of floodplain forest area from 1989 to 2010; De Jager and Rohweder 2022). Currently, the highest elevation floodplain forest stands (oak Quercus spp.) tend to remain dry during high flow, however more extreme flow conditions may threaten these higher elevation forests. Increased inundation of lower elevation swamp white oak (Quercus bicolor) and silver maple (Acer saccharinum) stands may result in the transformation to willow (Salix spp.), cottonwood (Populus spp.), herbaceous, or shrub cover, or, more likely, a transformation of forest to wet meadow or marsh (De Jager et al. In Review; Guyon et al. 2012). More frequent and extreme high-water conditions may increase longitudinal connectivity, providing benefits for native migratory aquatic species and potentially enhanced (and generally undesired) connectivity to enable upriver expansion of non-native monotypic fish communities, such as silver (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) and bighead (H. nobilis) carp (Cooper et al. 2021; Fausch et al 2009).
Ecosystem changes in the upper impounded reach ecosystem are largely intertwined with the social system, including high-value recreational uses (e.g., hunting, fishing, birdwatching) and strong personal and community connections to the river via relatively extensive conservation areas and public water access (e.g., the Upper Mississippi National Wildlife and Fish Refuge; Schramm 2017). In the most extreme high-water events, flooding threatens infrastructure (e.g., businesses, homes, roadways) and halts commercial navigation along the river, such as during the 2023 spring flood, which occurred during the final editing of this manuscript and reached the highest water levels observed in the upper impounded reach since 2001 (NWS 2023). Collectively, more frequent extreme flood conditions threaten the high habitat diversity, recreation, livelihoods, and economic uses of the upper impounded reach, and would be a major social-ecological transformation.
In contrast, in the unimpounded reach, which contains extensive agricultural levees and low aquatic habitat diversity, likely social-ecological transformations include more-frequent and -extreme levee failure and associated inundation of agricultural land during extreme floods. The disconnected floodplain sites behind levees are generally privately owned and have less established inter-jurisdictional partnerships for management actions compared with the upper impounded reach (Schramm 2017). With higher flood stages and longer duration high-water events, levee infrastructure becomes more prone to failure, with significant social-ecological implications. The 2019 flood, and associated levee failure on the Missouri River, illustrates potential social-ecological transformations that may become a more regular reality in similar landscapes, such as the unimpounded reach of the Upper Mississippi River. The levee failure in Atchison County, Missouri, inundated 227 leveed square kilometers (56,000 acres), flooding 166 homes, 14 businesses, and 1,295 agricultural buildings, causing an estimated US$25 M in lost agricultural revenue (TNC 2022). The levee failure and damages in Atchison County were among the more than 100 levee breaches throughout the Missouri River that collectively inundated 4860 square kilometers (1.2 million acres) with significant damage to farms and transportation routes (highways, railroads). When landowners and decision-makers witness large-scale loss during single extreme events, they may be more likely to come together with new partners and consider of a wider range of potential solutions, including the once-unthinkable idea of initiating levee setbacks and inundating previously productive agricultural land (TNC 2022). As levee failure occurs more frequently, or with levee setbacks, river floodplain transformations may include increased floodplain connectivity and associated increases in habitat diversity, including an expansion of backwater aquatic and floodplain forest habitat areas. The expansion of aquatic and terrestrial habitats may provide new opportunities for river recreation or novel economic uses.
The RAD hierarchical systems framework in the Upper Mississippi River
Applying the RAD hierarchical systems framework in the Upper Mississippi River begins with understanding key cross-scale decision interdependencies (Fig. 3). For example, the achievability of basin goals is dependent on how different reach transformations along the river continuum can be managed given the reach-specific site-scale habitat mosaic. Ensuring the example basin goal to “resist loss of ecological integrity and direct novel economic uses” is achievable in the upper impounded reach may require understanding how the mosaic of high-habitat-diversity sites can be altered to resist conversion of open water and forest habitats to wet meadow and marsh. In contrast, ensuring the basin goal is achievable in the unimpounded reach may require understanding how the mosaic of low habitat diversity and extensive levee infrastructure can be altered to direct change to floodplain connectivity (Fig. 3).
Strategic reach objectives require understanding how site conditions can be altered to resist, accept, or direct the basin trajectory of change (Fig. 3). When contrasting the upper impounded and unimpounded reaches, the upper impounded reach has comparatively high habitat diversity and overall ecosystem resilience to extreme conditions and is currently in a relatively desirable state (even though specific habitat types, such as floodplain forest, are threatened; De Jager et al. 2018; Bouska et al. 2022). Further, the upper impounded reach has strong recreational connection to floodplain habitats and extensive areas managed for conservation (e.g., the Upper Mississippi River National Wildlife and Fish Refuge) with high capacity for inter-jurisdictional management (Schramm 2017). Therefore, an ecologically effective, economically feasible, and socially favorable reach objective in the upper impounded reach may be to resist the loss of habitat diversity. By contrast, the lower habitat diversity and the risk associated with catastrophic levee failure in the unimpounded reach may make a reach objective of directing change to increase floodplain connectivity and diversify agricultural and recreational uses more effective than resisting and more desirable than accepting over the long term.
Site actions that are implemented following reach-scale prioritization through space and time could contribute to the basin vision most effectively (Fig. 3). A classic restoration mindset may prioritize resist actions within a reach in the most degraded areas. By using cross-scale understanding to identify where resistance is achievable in the long term, decision-makers may shift focus to resist in areas with existing desirable conditions. For example, site actions in the upper impounded reach to resist habitat loss by increasing bathymetric diversity and promoting forest rehabilitation in high-elevation forests will likely be most effective if they are strategically placed in sites that will remain suitable for forest during increasingly frequent and extreme high-water conditions. Along with this reprioritization comes an explicit acceptance of the site-scale loss of habitat diversity where resistance is deemed to be too costly or ecologically ineffective (e.g., expansion of marsh habitat into currently forested or open water habitats).
The hierarchical RAD framework strategically combines cross-scale information needs with explicit consideration of resist, accept, and direct approaches at the basin-, reach-, and site-scale. By ensuring that decision-makers consider all potential management approaches, the hierarchical RAD framework may help Upper Mississippi River System decision-makers identify creative ways to come together in inter-jurisdictional partnership. The reorienting of priorities at the reach scale may aid in more effective allocation of resources (e.g., funding, time, capacity) that better leverages the strengths of different partners and opens new partnership opportunities.
Basin-scale decisions
In the Upper Mississippi River, novel approaches to achieve the example basin-scale vision for “a river with sustained ecological integrity and economic uses” (Spitzack and Hubbell 2009) could include developing new types of economic uses or promoting ecological integrity through novel ecosystems. While considering resist, accept, and direct responses to plausible social-ecological futures, some questions that may arise are: Is the basin vision achievable with more-frequent and -extreme high-water conditions (e.g., will habitat homogenization in the upper impounded reach threaten the high-value recreational fishing and hunting? Will recurring levee failure threaten the viability of floodplain agriculture and communities in the unimpounded reach?) What feasible and socially acceptable management interventions to site conditions in each reach are needed to achieve the basin vision with more-extreme water conditions? Pondering these questions explicitly opens the conversation to consider if or when the vision may no longer be achievable, and ensuring that direct options are considered may foster creative solutions—including a new vision for the future (sensu Carpenter et al. 2015).
The RAD framework may be paired with the ‘safe operating space’ concept (Carpenter et al. 2017) to link the basin vision with clear and achievable basin goals. The safe operating space concept helps identify how to offset factors outside of managerial control (e.g., a shifting hydrograph) with management of factors that can be controlled locally (Carpenter et al. 2017). For example, if a shifting hydrograph is expected to result in a loss of overwintering fish habitat due to increased sedimentation, then lowering winter fishing catch limits could offset the stress from habitat limitation. Incorporation of the safe operating space concept with the RAD framework can frame discussions of climate adaptation in terms of how resist, accept, or direct can feasibly offset undesired trajectories of change to promote a desired future.
Though the level of coordination and buy-in needed to reach a truly common vision in the Upper Mississippi River may appear daunting, several large multi-agency partnerships and organizations already exist that could be leveraged. One example is the Mississippi Interstate Cooperative Resource Association (MICRA), an interagency organization of 28 state agencies, four federal agencies, and two tribal entities with shared fisheries management jurisdiction in the Mississippi River Basin. Fish monitoring data from MICRA have been used to advocate for the establishment of migratory fish “swimways” (analogous to migratory bird flyways) to support more cohesive inter-jurisdictional management (Pracheil et al. 2012). Beyond species-specific management, the existing U.S. Congressionally designated inter-jurisdictional funding to support collaborative efforts in the Upper Mississippi River System provides a foundation for a broad shared visioning process (Spitzack and Hubbell 2009). Ultimately, it is up to the basin planners, decision-makers, and partners to allocate the time and resources needed to reach a truly common vision, and to push the conversation to the depth required to truly consider all possible options with an open mind.
Reach-scale decisions
Embedding the long-term social-ecological trajectories of the RAD framework into reach-scale planning will help identify when reach objectives need to be revisited through time. If the frequency and duration of extreme flood conditions worsen through time, and/or as interactive effects between a shifting hydrograph and rising air temperatures intensify, decision-makers may adopt a reach objective to accept the loss of habitat diversity in the upper impounded reach. With an overall reach objective to accept a loss in habitat diversity (e.g., accept transformation of silver maple forest to wet meadow or marsh), individual site actions may also include direct and resist strategies. For example, managers may direct change by promoting willow and cottonwood forest communities in areas where they have previously not existed and resist change through high-elevation forest management to avoid monotypic vegetation communities such as reed canary grass. An acceptance of the loss of habitat diversity may also be paired with social direct strategies to promote novel recreational uses (e.g., nudging recreational fisheries interest to species more suited for future conditions). As the directional forcing of climate change continues to amplify through time, planners may eventually decide to shift the reach objective to direct change to a diverse and novel habitat mosaic. Direct strategies may promote a combination of open water, marsh, wet meadow, and fast-growing and flood-tolerant forests of cottonwood, river birch, and willow along with flood- and warm-temperature-tolerant species including American sycamore (Platanus occidentalis) and southern pin oak (Quercus palustris). These multitude of actions, distributed across space and time collectively create a reach-scale RAD-informed portfolio of site actions (Fig. 4).
By contrast, a reach-scale RAD-informed portfolio of site actions in the unimpounded reach, where there is low floodplain habitat diversity, low recreational connection to the river, and extensive agricultural levee infrastructure (De Jager et al. 2018; Schramm 2017) may begin with a reach-scale objective to resist levee failure and inundation of agricultural land (Fig. 4). The resist reach-scale objective may include site resist actions to reinforce currently robust levees and acceptance of levee failure in sites with lower-elevation, aging levees that would be too costly to build to new flood levels. Over time, if even the higher, robust levees see increasing catastrophic flood failure, reach planners may adopt a reach objective to accept levee failure and inundation of agricultural land. An accept objective may include diverse site actions ranging from full acceptance to direct actions with novel flood-tolerant agricultural mixes (e.g., pasture, rice or other existing flood-tolerant crops, genetically engineered flood-tolerant crops). Alternatively, reach-scale planners may eventually adopt an overall direct objective to promote a novel floodplain mosaic of agriculture and recreational uses. This could include direct actions such as levee setbacks and spillways with a landscape mosaic of backwater and floodplain habitats intermixed with novel agricultural production (Janowiak et al. 2016; Sudol et al. 2023). Critically, in heavily modified river systems with basin-wide excessive sediment and nutrient loading (e.g., in the Illinois River), reconnecting the river to its floodplain in limited spatial extents rather than systematically across the landscape may potentially create sediment-laden backwater habitats with undesirable monotypic communities (Lemke et al. 2017; Pletterbauer et al. 2018). Thus, the cross-scale and long-term perspective of the RAD framework may help ensure site-specific actions are appropriately distributed and sized to account for larger-scale drivers.
As planners evaluate plausible social-ecological trajectories, considering a multitude of potential actions can open up creative ways of prioritizing action (e.g., re-focusing on enhancing resilience in already high-quality sites; Koslow et al. 2014), communicating new conservation efforts and social accept strategies (Feola 2015), and building inter-jurisdictional partnerships. In other systems, portfolios of site actions have focused on different management objectives or entities (Magness and Morton 2017; Kocik et al 2022). In the Upper Mississippi River, it may be that certain entities (e.g., government, non-profit, tribal) are more or less inclined to implement resist vs accept vs direct strategies. Thus, different jurisdictions (Table 1) may select seemingly conflicting RAD actions but could strategically be linked in a portfolio approach to diversify efforts and enhance adaptation (Fig. 4). This could ultimately create a reach-scale mosaic that is more robust to increasingly variable extreme conditions (e.g., high- and low-water extremes). The success of multiple reach-scale climate adaptation strategies will require informed, multi-jurisdictional discussion, deliberate decisions, and incorporation of ecological, societal, and financial feasibility (Lynch et al. 2021).
Site-scale decisions
Integrating the RAD framework into site-scale decisions in the Upper Mississippi River System ensures decision-makers consider the full decision space of potential management approaches, fostering creative climate-adaptation strategies (Table 2). Site-scale decisions that used to seem non-negotiable may be up for revisioning given unprecedented directional change. For example, the flood-prone Dogtooth Bend area of the unimpounded reach was inundated in the 2016 flood, which covered agricultural land for almost nine months (Morris 2020). There, farmers are increasingly volunteering for permanent conservation easements, returning agricultural land to wetland floodplain. Similarly, the levee setback on the Missouri River after the historic 2019 flood reconnected over 4 square kilometers (1000 acres) of the river floodplain, including high-quality backwater habitat (TNC 2022). Levee setbacks and abandonment of agricultural production in the floodplain would have once been unimaginable as an economically and socially acceptable strategy. However, in the context of a rapidly changing social-ecological Upper Mississippi River, using the RAD framework to ensure all potential management approaches are considered could help proactively identify novel ways of meeting transportation, agricultural, and other economic needs, while also enhancing the overall social-ecological integrity of the river.
Another shift that may have previously been unimaginable came with the closure of the upstream-most navigation lock and dam on the Mississippi River at Upper Saint Anthony Falls in 2015. Currently, a disposition study is underway to determine the future of Upper Saint Anthony Falls Lock and Dam, and nearby Lower Saint Anthony Lock and Dam and Lock and Dam 1 (Potter et al. 2020). Community visioning to identify potential futures at the site include renderings of the lock and dam removed and restored to the type of rapids that used to be present. Given the disproportionately large contribution the Mississippi River plays in transportation of goods in the United States (Burton 2019), the current structure and context of navigation is generally accepted as non-negotiable. Though the future of the Saint Anthony Falls locks and dams remains to be determined, the existence of a conversation about potentially very different futures at the site demonstrates that considering a wide range of potential futures may become more commonplace.
Site-scale RAD strategies provide opportunities to deliberately test innovative and experimental approaches, supporting the necessary balance of flexibility at small scales with the stability at large scales for adaptive governance in changing systems (Craig et al 2017b). For example, the mechanisms driving the loss of floodplain forest throughout the Upper Mississippi River system are not well understood and are an active area of research (e.g., De Jager et al. In Review; De Jager et al. 2019). Deliberate experimentation examining plausible ecological trajectories could help tease out the relative contribution of inundation-induced tree mortality, non-native species expansion, and the necessary conditions for a well-functioning forest (e.g., the potentially underappreciated importance of bare mineral soil in natural-forest regeneration). As site actions are implemented, ecological surprises may occur (Carpenter et al. 1999), and the RAD framework allows for agility to adjust or reimagine the management course as unanticipated outcomes are encountered (Lynch et al. 2022b)—further ensuring the full decision space of potential management approaches are considered through time.
Future direction and summary
Overall, our review and perspective provides novel considerations and examples for embedding the RAD framework in large-river decision-making to better coordinate and communicate effective responses to unprecedented directional change from the site to basin scale. We build on prior research in the Upper Mississippi River System (e.g., Bouska et al. 2022; De Jager et al. In Review) to identify potential RAD basin goals, reach objectives, and site actions within existing decision-making structures (Spitzack & Hubbell 2009). The aim of our research is to set the stage for refined cross-scale and co-produced RAD-informed decisions in the Upper Mississippi River, and to provide a template for other large-river and large-ecosystem managers to navigate similar challenges.
While the directional forcing of higher and longer duration flows in the Upper Mississippi River is a relatively straightforward physical change, its social-ecological outcomes are more complex and nuanced, varying by reach and site. Decisions of how to create more flood-resilient cities and towns or modify the use of agricultural lands are outside the scope of individual natural resource management agencies. However, there is an opportunity to adopt a novel collaborative and co-produced systems approach to managing ecological outcomes along the longitudinal gradient of the river. Future directions for refining and applying the RAD framework in large rivers as well as other large ecosystems include working to decrease uncertainty in plausible trajectories and novel management interventions, linking local and regional processes, and increasing capacity for managers to make decisions with current information, even in the face of uncertainty.
Major obstacles in finding consensus around common management objectives may fundamentally lie in uncertainty around the drivers of a social-ecological trajectory. For example, despite the relatively rapid deforestation (< 2 decades) on the southern Kenai Peninsula, Alaska, ecologists lacked consensus on the drivers of change, and whether the change constituted ecological transformation or simply an extreme reset of historical succession patterns (Magness et al. 2022a; Morton et al. 2023). In the Upper Mississippi River, there is uncertainty in the drivers of floodplain forest loss. Linking simulation studies (e.g., De Jager et al. In Review; De Jager et al. 2019) with pilot studies and deliberate experimentation on site response to amplified drivers of change may be particularly powerful to anticipate plausible trajectories (Lynch et al. 2021). For example, continuing and expanding current field experimentation to determine how Upper Mississippi River tree species respond to projected frequency and duration of flooding and how flood-induced soil saturation affects seedling survival and growth may provide valuable insights to better anticipate on-the-ground outcomes (e.g., Windmuller-Campione et al. 2022). Along these lines, the Upper Mississippi River Basin Association recently recommended experimental water-level management in contrasting pools along the longitudinal gradient of the river (Heglund et al. 2022). It would be synergistic to link novel water management approaches in varying flow years with field experiments to assess a suite of ecological outcomes including the response of aquatic and terrestrial habitats.
Navigating transformations in the Upper Mississippi River System will require a more integrated basin-wide understanding of scale- and context-dependent trajectories. Ultimately, transformations in the mainstem of large rivers are linked to upstream processes, including the magnitude and timing of connectivity and disconnectivity to streams, wetlands, and terrestrial areas (Dolph et al. 2019), and the intensification in agricultural and urban land uses (Van Meter et al. 2018). Climate and land use-change interactions may limit or amplify the conservation efficacy of investments throughout large river basins (Cheng et al. 2020). Identifying plausible ecological futures in the Mississippi River Basin needs to account for scale-dependent climate-change effects, where local-scale precipitation interacts strongly with land use and land cover as well as the presence and intensity of field drainage systems (Frans et al. 2013). Populations of species in different spatial extents within the basin may respond differently to interacting drivers, depending on site or localized conditions (sensu Billman et al. 2023; Beever et al. 2010; Smith et al. 2019). Ultimately, the upstream influences and downstream consequences of precipitation and temperature changes on conservation easements, wildlife refuges, or river reaches are dependent on the relative position of a spatial domain in the watershed. Management in these complex social-ecological river basin systems requires multi-scale and well-coordinated governance with consideration of tradeoffs among multiple stakeholders and rightsholders from the mainstem river to upland basin areas (Hansen et al. 2021, 2018).
Since trajectories of change are currently underway and science alone cannot reduce all uncertainty, future work needs to increase individual and collective abilities to make decisions in uncertainty. Decision-making processes such as structured decision-making and the Delphi method work to enhance capacity by increasing transparency in problem definition, comparing alternative futures, and qualitatively or quantitatively clarifying decision processes (Polasky et al. 2011; Gregory et al. 2012; Mukherjee et al. 2015). The RAD framework can enhance these decision-making efforts by providing the diversity of possible social-ecological trajectories, responses, and outcomes (Magness et al. 2022a). Further, the RAD framework may help bring the reality of long-term directional change and social-ecological transformations, wherein entire ways of life and connections to place are threatened, to the forefront of decision conversations. Navigating these deeply human aspects of uncertainty may help decision-makers move beyond the default response to just identify additional information needs and start making novel decisions with the best available information today. Including diverse worldviews (e.g., Indigenous Knowledges) and scientific disciplines (e.g., social psychology) may enhance understanding of the emotional and spiritual aspects of social-ecological change (Wolf 2017; Reid et al. 2021; Shultz et al. 2022) and ultimately tap into a shared sense of purpose and an associated ability to move through irreducible uncertainty.
Our work may provide a starting point for investigations into how the RAD framework can facilitate effective response to change in other large river systems. For example, the Colorado River provides critical water resources to 40 million users across seven states in the western United States. Hotter and drier conditions projected for the future will further reduce water availability in this already over-allocated system, while also increasing stressors for imperiled desert fish and wildlife species dependent on this scarce water resource. Linking decisions of RAD-informed basin goals, reach objectives, and site actions may help effectively achieve desired social-ecological outcomes in the desert Colorado River, the Great Plains and temperate Upper Mississippi River, and other large river and large ecosystems facing similar challenges around the world.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
References
Abatzoglou JT, Brown TJ (2012) A comparison of statistical downscaling methods suited for wildfire applications. Int J Climatol 32(5):772–780
Alexander JS, Wilson RC, Green WR (2012) A brief history and summary of the effects of river engineering and dams on the Mississippi River System and delta. Report. U.S. Geological Survey Circular 1375:43
Arthington AH (2021) Grand challenges to support the freshwater biodiversity emergency recovery plan. Front Environ Sci 9:664313
Baker SL, Clark SJ, Fellman RC, Hendrickson J, Hauck KL, Heddlesten AD, Jordan JW, McCain K, Millhollin JL et al (2012) Upper Mississippi River Restoration Environmental Management Program. Report: US Army Corps of Engineers
Battaglin W, Hay L, Lawrence DJ, McCabe G, Norton P (2020) Baseline conditions and projected future hydro-climatic change in national parks in the conterminous united states. Water 12(6):1704
Beever EA, Ray C, Mote PW, Wilkening JL (2010) Testing alternative models of climate-mediated extirpations. Ecol Appl 20(1):164–178
Beever EA, Mattsson BJ, Germino MJ, Post van der Burg M, Bradford JB, Brunson MW (2014) Successes and challenges from formation to implementation of eleven broad-extent conservation programs. Conserv Biol 28(2):302–314
Best J (2019) Anthropogenic stresses on the world’s big rivers. Nat Geosci 12(1):7–21
Billman PD, Beever EA, Westover ML, Ryals DK (2023) Spatio-temporal variability in the strength, directionality, and relative importance of climate on occupancy and population densities in a philopatric mammal, the American pika (Ochotona princeps). Front Ecol Evol 11:1202610. https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2023.1202610
Böck K, Polt R, Schülting L (2018) Ecosystem services in river landscapes. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 413–433
Bouska KL, Houser JN, De Jager NR, Van Appledorn M, Rogala JT (2019) Applying concepts of general resilience to large river ecosystems: a case study from the Upper Mississippi and Illinois rivers. Ecol Ind 101:1094–1110
Bouska KL, Houser JN, De Jager NR, Hendrickson J (2018) Developing a shared understanding of the Upper Mississippi River: the foundation of an ecological resilience assessment. Ecol Soc 23(2):6
Bouska KL, De Jager NR, Houser JN (2022) Resisting-accepting-directing: ecosystem management guided by an ecological resilience assessment. Environ Manage 70(3):381–400
Brierley G, Fryirs K (2022) Truths of the riverscape: moving beyond command-and-control to geomorphologically informed nature-based river management. Geosci Lett 9(1):14
Brooker MP (1985) The ecological effects of channelization. Geogr J 151(1):63–69
Burton ML (2019) Agricultural freight corridors, railroad capacity, and the implication of railroad rates. Report, Knoxville: University of Tennessee
Carlson A (2020) The Mississippi Rver is the opposite of the Anthropocene. Available at: https://www.anthropocene-curriculum.org/contribution/the-mississippi-river-is-the-opposite-of-the-anthropocene. Accessed April 3 2023
Carpenter SR, Brock WA (2006) Rising variance: a leading indicator of ecological transition. Ecol Lett 9(3):311–318
Carpenter S, Brock W, Hanson P (1999) Ecological and social dynamics in simple models of ecosystem management. Conserv Ecol 3(2):4
Carpenter SR, Booth EG, Gillon S, Kucharik CJ, Loheide S, Mase AS, Motew M, Qiu J, Rissman AR et al (2015) Plausible futures of a social-ecological system: Yahara watershed, Wisconsin, USA. Ecol Soc 20(2):10
Carpenter SR, Brock WA, Hansen GJ, Hansen JF, Hennessy JM, Isermann DA, Pedersen EJ, Perales KM, Rypel AL et al (2017) Defining a safe operating space for inland recreational fisheries. Fish Fish 18(6):1150–1160
Cheng FY, Van Meter KJ, Byrnes DK, Basu NB (2020) Maximizing US nitrate removal through wetland protection and restoration. Nature 588(7839):625–630
Chick JH, Pegg MA (2001) Invasive carp in the Mississippi River Basin. Science 292(5525):2250–2251
Chick JH, Gibson-Reinemer DK, Soeken-Gittinger L, Casper AF (2020) Invasive silver carp is empirically linked to declines of native sport fish in the Upper Mississippi River System. Biol Invasions 22(2):723–734
Clifford KR, Cravens AE, Knapp CN (2022) Responding to ecological transformation: mental models, external constraints, and manager decision-making. Bioscience 72(1):57–70
Cooper AR, Infante DM, O’Hanley JR, Yu H, Neeson TM, Brumm KJ (2021) Prioritizing native migratory fish passage restoration while limiting the spread of invasive species: a case study in the Upper Mississippi River. Sci Total Environ 791:148317
Craig LS, Olden JD, Arthington AH, Entrekin S, Hawkins CP, Kelly JJ, Kennedy TA, Maitland BM, Rosi EJ et al (2017a) Meeting the challenge of interacting threats in freshwater ecosystems: a call to scientists and managers. Elementa Sci Anthrop 5:72
Craig RK, Garmestani AS, Allen CR, Arnold CAT, Birgé H, DeCaro DA, Fremier AK, Gosnell H, Schlager E (2017b) Balancing stability and flexibility in adaptive governance: an analysis of tools available in US environmental law. Ecol Soc 22(2):3
De Jager NR, Rohweder JJ (2017) Changes in aquatic vegetation and floodplain land cover in the Upper Mississippi and Illinois Rivers (1989–2000–2010). Environ Monit Assess 189:77
De Jager NR, Rogala JT, Rohweder J, Van Appledorn M, Bouska KL, Houser JN, Jankowski KJ (2018) Indicators of ecosystem structure and function for the Upper Mississippi River System. Report: U.S. Geological Survey
De Jager NR, Van Appledorn M, Fox TJ, Rohweder JJ, Guyon LJ, Meier AR, Cosgriff RJ, Vandermyde BJ (2019) Spatially explicit modelling of floodplain forest succession: interactions among flood inundation, forest successional processes, and other disturbances in the Upper Mississippi River floodplain, USA. Ecol Model 405:15–32
De Jager NR, Rohweder J (2022) Chapter D: Land cover indicators. Houser JN ed. Ecological Status and Trends of the Upper Mississippi and Illinois Rivers (ver. 1.1, July 2022): U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2022–1039, https://doi.org/10.3133/ofr20221039
Díaz S, Settele J, Brondízio ES, Ngo HT, Agard J, Arneth A, Balvanera P, Brauman KA, Butchart SHM et al (2019) Pervasive human-driven decline of life on earth points to the need for transformative change. Science 366(6471):eaax3100
Djenontin INS, Meadow AM (2018) The art of co-production of knowledge in environmental sciences and management: lessons from international practice. Environ Manage 61(6):885–903
Dobrowski SZ, Abatzoglou J, Swanson AK, Greenberg JA, Mynsberge AR, Holden ZA, Schwartz MK (2013) The climate velocity of the contiguous United States during the 20th century. Glob Change Biol 19(1):241–251
Dolph CL, Boardman E, Danesh-Yazdi M, Finlay JC, Hansen AT, Baker AC, Dalzell B (2019) Phosphorus transport in intensively managed watersheds. Water Resour Res 55(11):9148–9172
DuBowy PJ (2013) Mississippi river ecohydrology: past, present and future. Ecohydrol Hydrobiol 13(1):73–83
Dugan PJ, Barlow C, Agostinho AA, Baran E, Cada GF, Chen D, Cowx IG, Ferguson JW, Jutagate T et al (2010) Fish migration, dams, and loss of ecosystem services in the Mekong basin. Ambio 39(4):344–348
Fausch KD, Rieman BE, Dunham JB, Young MK, Peterson DP (2009) Invasion versus isolation: trade-offs in managing native salmonids with barriers to upstream movement. Conserv Biol 23(4):859–870
Feiner ZS, Dugan HA, Lottig NR, Sass GG, Gerrish GA (2022) A perspective on the ecological and evolutionary consequences of phenological variability in lake ice on north-temperate lakes. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 79(9):1590–1604
Feola G (2015) Societal transformation in response to global environmental change: a review of emerging concepts. Ambio 44(5):376–390
Frans C, Istanbulluoglu E, Mishra V, Munoz-Arriola F, Lettenmaier DP (2013) Are climatic or land cover changes the dominant cause of runoff trends in the Upper Mississippi River basin? Geophys Res Lett 40(6):1104–1110
Gallardo B, Clavero M, Sánchez MI, Vilà M (2016) Global ecological impacts of invasive species in aquatic ecosystems. Glob Change Biol 22(1):151–163
Giblin S, Strassman S, King J (2023) Mississippi river climate change: status, challenges and adaptations. Report: Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources
GLIFWC (2023) Aanji-bimaadiziimagak o’ow aki. Report, Odanah, Wisconsin: Great Lakes Indian Fish and Wildlife Commission
Gregory R, Failing L, Harstone M, Long G, McDaniels T, Ohlson D (2012) Structured decision making: a practical guide to environmental management choices. Wiley, New Jersey
Grill G, Lehner B, Thieme M, Geenen B, Tickner D, Antonelli F, Babu S, Borrelli P, Cheng L et al (2019) Mapping the world’s free-flowing rivers. Nature 569(7755):215–221
Guyon L, Deutsch C, Lundh J (2012) Upper Mississippi River systemic forest stewardship plan. US Army Corps of Engineers, St. Paul District
Hansen AT, Dolph CL, Foufoula-Georgiou E, Finlay JC (2018) Contribution of wetlands to nitrate removal at the watershed scale. Nat Geosci 11(2):127–132
Hansen AT, Campbell T, Cho SJ, Czuba JA, Dalzell BJ, Dolph CL, Hawthorne PL, Rabotyagov S, Lang Z et al (2021) Integrated assessment modeling reveals near-channel management as cost-effective to improve water quality in agricultural watersheds. Proc Natl Acad Sci 118(28):e2024912118
Harris RMB, Beaumont LJ, Vance TR, Tozer CR, Remenyi TA, Perkins-Kirkpatrick SE, Mitchell PJ, Nicotra AB, McGregor S et al (2018) Biological responses to the press and pulse of climate trends and extreme events. Nat Clim Chang 8(7):579–587
Heglund P, Salvato L, Larson DM, McFarlane A (2022) Recommendations regarding water level management to achieve ecological goals in the Upper Mississippi River System. Report: UMRBA
Hein C, Turyk N, Magee MR (2023) Impacts of and adaptation strategies for climate change on Wisconsin's water resources. Report: Wisconsin Initiative on Climate Change Impacts
Hirsch SL (2020) Anticipatory practices: Shifting baselines and environmental imaginaries of ecological restoration in the Columbia River basin. Environ Plann E: Nat Space 3(1):40–57
Houser JN, Bouska KL, De Jager NR, Ickes B, Jankowski KJ, Larson DM, Van Appledorn M, Rohweder J (2022) Chapter A: Introduction. Houser JN ed. Ecological Status and Trends of the Upper Mississippi and Illinois Rivers (ver. 1.1, July 2022): U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2022–1039, https://doi.org/10.3133/ofr20221039
Jackson ST (2021) Transformational ecology and climate change. Science 373(6559):1085–1086
Janowiak MK, Dostie DN, Wilson MA, Kucera MJ, Skinner RH, Hatfield JL, Hollinger D, Swanston CW (2016) Adaptation resources for agriculture: responding to climate variability and change in the midwest and northeast. Report, Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Agriculture
Khoury M, Higgins J, Weitzell ROY (2011) A freshwater conservation assessment of the Upper Mississippi River basin using a coarse- and fine-filter approach. Freshw Biol 56(1):162–179
Kocik JF, Hayes SA, Carlson SM, Cluer B (2022) A resist-accept-direct (RAD) future for salmon in Maine and California: Salmon at the southern edge. Fish Manage Ecol 29(4):456–474
Koslow M, Glick P, Hoffman D, Inkley A, Kane M, Murray M, Reeve K (2014) Restoring the Great Lakes' coastal future: technical guidance for the design and implementation of climate-smart restoration projects. Report: National Wildlife Federation, Reston, VA and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Silver Spring, MD
Laughlin TW, Whitledge GW, Oliver DC, Rude NP (2016) Recruitment sources of channel and blue catfishes inhabiting the Middle Mississippi river. River Res Appl 32(8):1808–1818
Lawrence DJ, Runyon AN, Gross JE, Schuurman GW, Miller BW (2021) Divergent, plausible, and relevant climate futures for near- and long-term resource planning. Clim Change 167(3):38
Lemke MJ, Hagy HM, Dungey K, Casper AF, Lemke AM, VanMiddlesworth TD, Kent A (2017) Echoes of a flood pulse: short-term effects of record flooding of the Illinois River on floodplain lakes under ecological restoration. Hydrobiologia 804(1):151–175
Li P, Chaubey I, Muenich RL, Wei X (2016) Evaluation of freshwater provisioning for different ecosystem services in the Upper Mississippi River basin: current status and drivers. Water 8(7):288
Loarie SR, Duffy PB, Hamilton H, Asner GP, Field CB, Ackerly DD (2009) The velocity of climate change. Nature 462(7276):1052–1055
Lockwood M, Davidson J, Curtis A, Stratford E, Griffith R (2010) Governance principles for natural resource management. Soc Nat Resour 23(10):986–1001
Lubinski K, Theiling C (1999) Ecological status and trends of the Upper Mississippi River system 1998. A report of the long term resource monitoring program US Geological Survey, Upper Midwest Environmental Sciences Center, La Crosse, Wisconsin. 1–236
Lynch AJ, Thompson LM, Beever EA, Cole DN, Engman AC, Hawkins Hoffman C, Jackson ST, Krabbenhoft TJ, Lawrence DJ et al (2021) Managing for radical ecosystem change: applying the resist-accept-direct (RAD) framework. Front Ecol Environ 19(8):461–469
Lynch AJ, Rahel FJ, Limpinsel D, Sethi SA, Engman AC, Lawrence DJ, Mills KE, Morrison W, Peterson JO et al (2022a) Ecological and social strategies for managing fisheries using the resist-accept-direct (RAD) framework. Fish Manage Ecol 29(4):329–345
Lynch AJ, Thompson LM, Morton JM, Beever EA, Clifford M, Limpinsel D, Magill RT, Magness DR, Melvin TA et al (2022b) RAD adaptive management for transforming ecosystems. Bioscience 72(1):45–56
Mac MJ, Palmer S (2020) Stakeholder involvement in natural resource decisions: the Missouri river. Fisheries 45(2):74–83
Magness DR, Morton JM (2017) Implementing portfolios of adaptation strategies on US conservation lands in the Anthropocene. In: Reference module in earth systems and environmental sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-409548-9.10504-4
Magness DR, Hoang L, Belote RT, Brennan J, Carr W, Stuart Chapin, III F, CliffordMorrisonMorton KWJM et al (2022a) Management foundations for navigating ecological transformation by resisting, accepting, or directing social–ecological change. Bioscience 72(1):30–44
Magness DR, Wagener E, Yurcich E, Mollnow R, Granfors D, Wilkening JL (2022b) A multi-scale blueprint for building the decision context to implement climate change adaptation on national wildlife refuges in the United States. Earth 3:136–156
Marschall EA, Mather ME, Parrish DL, Allison GW, McMenemy JR (2011) Migration delays caused by anthropogenic barriers: modeling dams, temperature, and success of migrating salmon smolts. Ecol Appl 21(8):3014–3031
McCain K, Schmuecker S, De Jager NR (2018) Habitat needs assessment‐II for the Upper Mississippi River Restoration program: linking science to management perspectives. Report.
Meehl GA, Tebaldi C (2004) More intense, more frequent, and longer lasting heat waves in the 21st century. Science 305(5686):994–997
Milly PCD, Betancourt J, Falkenmark M, Hirsch RM, Kundzewicz ZW, Lettenmaier DP, Stouffer RJ (2008) Stationarity is dead: whither water management? Science 319(5863):573–574
Morris S (2020) The dogtooth bend floodplain restoration project. Mississippi River Network
Morton JM, Wolf DE, Bowser ML, Takebayashi N, Magness DR (2023) The dynamics of a changing Lutz spruce (Picea × lutzii) hybrid zone on the Kenai Peninsula, Alaska. Can J For Res. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjfr-2022-0212
Moss T, Newig J (2010) Multilevel water governance and problems of scale: setting the stage for a broader debate. Environ Manage 46(1):1–6
Mukherjee N, Hugé J, Sutherland WJ, McNeill J, Van Opstal M, Dahdouh-Guebas F, Koedam N (2015) The Delphi technique in ecology and biological conservation: applications and guidelines. Methods Ecol Evol 6(9):1097–1109
Peterson GD, Cumming GS, Carpenter SR (2003) Scenario planning: a tool for conservation in an uncertain world. Conserv Biol 17(2):358–366
Phelps QE, Tripp SJ, Herzog DP, Garvey JE (2015) Temporary connectivity: the relative benefits of large river floodplain inundation in the lower Mississippi River. Restor Ecol 23(1):53–56
PIIC (2023a) Wild rice - psiŋ. In: Charles L (ed) Prairie Island Indian Community. https://www.arcgis.com/apps/MapJournal/index.html?appid=6ef2bacce5d54431956ea76c541c4f5f: ArcGIS StoryMap
PIIC (2023b) Our history. Available at: https://prairieisland.org/who-we-are/our-history. Accessed April 3 2023
Pletterbauer F, Melcher A, Graf W (2018) Climate change impacts in riverine ecosystems. In: Schmutz S, Sendzimir J (eds) Riverine ecosystem management: science for governing towards a sustainable future. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 203–223
Poff NL (1997) Landscape filters and species traits: towards mechanistic understanding and prediction in stream ecology. J N Am Benthol Soc 16(2):391–409
Polasky S, Carpenter SR, Folke C, Keeler B (2011) Decision-making under great uncertainty: environmental management in an era of global change. Trends Ecol Evol 26(8):398–404
Porreca AP, Hintz WD, Whitledge GW, Rude NP, Heist EJ, Garvey JE (2016) Establishing ecologically relevant management boundaries: linking movement ecology with the conservation of Scaphirhynchus sturgeon. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 73(6):877–884
Pörtner HO, Roberts DC, Adams H, Adler C, Aldunce P, Ali E, Begum RA, Betts R, Kerr RB et al (2022) Climate change 2022: impacts, adaptation and vulnerability. Geneva, Switzerland: IPCC
Potter D, Bischoff N, Keenan S, Goergen L (2020) Upper St. Anthony Falls Lock and Dam section 216 Disposition Study. Report: Corps of Engineers, St. Paul District
Pracheil BM, Pegg MA, Powell LA, Mestl GE (2012) Swimways: protecting paddlefish through movement-centered management. Fisheries 37(10):449–457
Pracheil BM, McIntyre PB, Lyons JD (2013) Enhancing conservation of large-river biodiversity by accounting for tributaries. Front Ecol Environ 11(3):124–128
Qiu J, Carpenter SR, Booth EG, Motew M, Zipper SC, Kucharik CJ, Loheide SP II, Turner MG (2018) Understanding relationships among ecosystem services across spatial scales and over time. Environ Res Lett 13(5):054020
Rahel FJ, Olden JD (2008) Assessing the effects of climate change on aquatic invasive species. Conserv Biol 22(3):521–533
Rajib A, Zheng Q, Golden HE, Wu Q, Lane CR, Christensen JR, Morrison RR, Annis A, Nardi F (2021) The changing face of floodplains in the Mississippi River basin detected by a 60-year land use change dataset. Sci Data 8(1):271
Reid AJ, Eckert LE, Lane JF, Young N, Hinch SG, Darimont CT, Cooke SJ, Ban NC, Marshall A (2021) “Two-eyed seeing”: an indigenous framework to transform fisheries research and management. Fish Fish 22(2):243–261
Sass GG, Hinz C, Erickson AC, McClelland NN, McClelland MA, Epifanio JM (2014) Invasive bighead and silver carp effects on zooplankton communities in the Illinois River, Illinois, USA. J Great Lakes Res 40(4):911–921
Schramm HL (2017) The fishery resources of the Mississippi River: a model for conservation and management. Fisheries 42(11):574–585
Schuurman GW, Cole DN, Cravens AE, Covington S, Crausbay SD, Hoffman CH, Lawrence DJ, Magness DR, Morton JM et al (2022) Navigating ecological transformation: resist–accept–direct as a path to a new resource management paradigm. Bioscience 72(1):16–29
Service NW (2023) Mississippi River spring flood—2023. Available at: https://www.weather.gov/arx/MississippiRiver_SpringFlood_2023. Accessed April 28 2023
Shultz A, Luehring M, Ray A, Rose JD, Croll R, Gilbert J, Price M, Graveen J, Chapman L (2022) Case study: applying the resist–accept–direct framework to an Ojibwe Tribe’s relationship with the natural world. Fish Manage Ecol 29(4):392–408
Smith AB, Beever EA, Kessler AE, Johnston AN, Ray C, Epps CW, Lanier HC, Klinger RC, Rodhouse TJ et al (2019) Alternatives to genetic affinity as a context for within-species response to climate. Nat Clim Chang 9(10):787–794
Spanbauer TL, Allen CR, Angeler DG, Eason T, Fritz SC, Garmestani AS, Nash KL, Stone JR (2014) Prolonged instability prior to a regime shift. PLoS ONE 9(10):e108936
Sparks RE (1995) Need for ecosystem management of large rivers and their floodplains: these phenomenally productive ecosystems produce fish and wildlife and preserve species. Bioscience 45(3):168–182
Sparks RE (2010) Forty years of science and management on the Upper Mississippi River: an analysis of the past and a view of the future. Hydrobiologia 640:3–15
Spitzack CP, Hubbell ME (2009) Upper Mississippi River ecosystem restoration objectives. Report, USACE. https://www.mvr.usace.army.mil/Portals/48/docs/Environmental/UMRR/UMRR_Ecosystem_Restoration_Objectives_2009.pdf
Sudol TA, Miller Hesed CD, Clark JM, Moser FC (2023) Resisting-accepting-directing sea level rise on the Chesapeake Bay: agricultural producers’ motivations and actions. J Environ Manage 332:117355
Taylor KE, Stouffer RJ, Meehl GA (2012) An overview of CMIP5 and the experiment design. Bull Am Meteor Soc 93(4):485–498
Tercek MT, Thoma D, Gross JE, Sherrill K, Kagone S, Senay G (2021) Historical changes in plant water use and need in the continental united states. PLoS ONE 16(9):e0256586
Theiling CH, Janvrin JA, Hendrickson J (2014) Upper Mississippi River Restoration: implementation, monitoring, and learning since 1986. Restor Ecol 23(2):157–166. https://doi.org/10.1111/rec.12170.1-10
Theiling CH, McGuire B, Benjamin G, Busse D, Hendrickson JS, Kenow K, Landwehr KJ, Schlagenhaft T, Stefanski M (2021) Water level management for enhanced fish and wildlife habitat production in Upper Mississippi River navigation pools: an engineering with nature® review of practice
Thompson LM, Lynch AJ, Beever EA, Engman AC, Falke JA, Jackson ST, Krabbenhoft TJ, Lawrence DJ, Limpinsel D et al (2021) Responding to ecosystem transformation: resist, accept, or direct? Fisheries 46(1):8–21
Thorp JH, Flotemersch JE, Delong MD, Casper AF, Thoms MC, Ballantyne F, Williams BS, O’Neill BJ, Haase CS (2010) Linking ecosystem services, rehabilitation, and river hydrogeomorphology. Bioscience 60(1):67–74
TNC (2022) Reconnecting the Missouri River floodplain. Large-Scale Levee Setback Playbook
Van Appledorn M (2022) Chapter B: Hydrologic indicators. Houser JN ed. Ecological Status and Trends of the Upper Mississippi and Illinois Rivers (ver. 1.1, July 2022): U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2022–1039, https://doi.org/10.3133/ofr20221039
Van Meter KJ, Van Cappellen P, Basu NB (2018) Legacy nitrogen may prevent achievement of water quality goals in the Gulf of Mexico. Science 360(6387):427–430
van Vliet M, Franssen W, Yearsley J, Ludwig F, Haddeland I, Lettenmaier D, Kabat P (2013) Global river discharge and water temperature under climate change. Glob Environ Change Hum Policy Dimens 23(2):450–464
Walters CJ (1986) Adaptive management of renewable resources. Macmillan Publishers Ltd, New York
Ward JV, Tockner K, Arscott DB, Claret C (2002) Riverine landscape diversity. Freshw Biol 47(4):517–539
Weitzell R, Khoury M, Gagnon P, Schreurs B, Grossman D, Higgins J (2003) Conservation priorities for freshwater biodiversity in the Upper Mississippi River basin. Nature Serve and The Nature Conservancy
Windmuller-Campione M, Van Appledorn M, Meier A, Reuling L (2022) Survival and growth of four floodplain forest species in an Upper Mississippi River underplanting. Tree Planters' Notes
Wolf AT (2008) Healing the enlightenment rift: rationality, spirituality and shared waters. J Int Aff 61(2):51–73
Wolf AT (2010) Sharing water, sharing benefits: working towards effective transboundary water resources management. UNESCO
Wolf AT (2017) The spirit of dialogue: lessons from faith traditions in transforming conflict. Island Press, Washington DC
Acknowledgements
We thank Kate Malpeli (U.S. Geological Survey [USGS]) for assistance with figures and Lucie Sawyer (US Army Corps of Engineers), Daniel Gibson-Reinemer (USGS), Jon Hansen (MN Dept of Natural Resources), Brian Nerbonne (MN Dept of Natural Resources), Dean Paron (MN Dept of Natural Resources), and Trevor Krabbenhoft (University at Buffalo) for insightful contributions to this manuscript and early brainstorming conversations. We thank Scott Covington for conducting an internal review of this manuscript for USGS. Any use of trade, firm, or product names is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Government. The findings and conclusions in this article are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily represent the views of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
Funding
NKW and KLB were funded as part of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers’ Upper Mississippi River Restoration Program, Long Term Resource Monitoring (LTRM) element. LTRM is a cooperative effort between the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, U.S. Geological Survey, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, and the states of Illinois, Iowa, Minnesota, Missouri, and Wisconsin. GGS was funded by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service Federal Aid in Sportfish Restoration program and the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources. BMM was funded under Assistance Agreement No 839401101 awarded by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to the University of Wisconsin Aquatic Sciences Center. This document has not been formally reviewed by EPA. The views expressed in this document are those of the listed authors and do not necessarily reflect those of EPA. EPA does not endorse any products or commercial services mentioned in this publication. Any use of trade, firm, or product names is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Government. The findings and conclusions in this article are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily represent the views of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NKW and AJL initiated the study and led development of the manuscript. DCO developed Fig. 2 with iterative feedback from all coauthors. NKW developed Fig. 1 and Fig. 3 with iterative feedback from all coauthors. LMT developed Fig. 4 with feedback from all coauthors. BMM, GGS, KLB, HMR, and JDM led the development of draft manuscript sections. All authors made substantial contributions to the conception of the work, writing, and editing of the manuscript, approved the final manuscript, and agree to be accountable for their own contributions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Figure S1.
Absolute change in total precipitation from ensemble historical (1971–2000) and future (2070–2099) model predictions in A) Summer (June, July, August), B) Winter (December, January, February), C) Fall (September, October, November), and D) Spring (March, April, May). RCP 8.5 Climate forcings using from Taylor et al. 2010; Abatzoglou and Brown 2012. The Missouri River tributary area is outlined in pink and the remaining Upper Mississippi watershed is outlined in red. Figure S2. Annual Mean Temperature Anomaly from the 1950–2005 average (grey-demarcated period) of 20 CMIP5 climate models and 2 emissions scenarios (RCP 4.5 and 8.5), downscaled to a ~4-km resolution and selected to a rough rectangular area of the Upper Mississippi River mainstem 38.0179°N to 45.9814°N, 96.2695°W to 89.4355°W. Figure generated using Hegewisch, K.C., Abatzoglou, J.T., 'Future Time Series' web tool. Climate Toolbox (https://climatetoolbox.org/), accessed on 23 January 2023. Figure S3. The Annual Total Precipitation as a percent difference from the 1950–2005 average (grey-demarcated period) of 20 CMIP5 climate models and 2 scenarios (RCP 4.5 and 8.5), downscaled to a ~4-km resolution and selected to a rough rectangular area of the Upper Mississippi River mainstem 38.02°N to 45.98°N, 96.27°W to 89.44°W. Figure generated using Hegewisch, K.C., Abatzoglou, J.T., 'Future Time Series' web tool. Climate Toolbox (https://climatetoolbox.org/), accessed on 23 January 2023. Figure S4. Spring (Mar, Apr, May) Total Precipitation as a percent difference from 1950–2005 average (grey-demarcated period) of projections from 20 CMIP5 climate models and 2 emission scenarios (RCP 4.5 and 8.5), downscaled to a ~4-km resolution and selected to a rough rectangular area of the Upper Mississippi River mainstem 38.0179°N to 45.9814°N, 96.2695°W to 89.4355°W. Figure generating using Hegewisch, K.C., Abatzoglou, J.T., 'Future Time Series' web tool. Climate Toolbox (https://climatetoolbox.org/), accessed on 23 January 2023. Figure S5. Summer (Jun, Jul, Aug) Total Precipitation as a percent difference from 1950–2005 average (grey-demarcated period) of projections from 20 CMIP5 climate models and 2 scenarios (RCP 4.5 and 8.5), downscaled to a ~4-km resolution and selected to a rough estimate rectangular area of the Upper Mississippi River mainstem 38.0179°N to 45.9814°N, 96.2695°W to 89.4355°W. Figure generated using Hegewisch, K.C., Abatzoglou, J.T., 'Future Time Series' web tool. Climate Toolbox (https://climatetoolbox.org/), accessed on 23 January 2023.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Ward, N.K., Lynch, A.J., Beever, E.A. et al. Reimagining large river management using the Resist–Accept–Direct (RAD) framework in the Upper Mississippi River. Ecol Process 12, 48 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13717-023-00460-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13717-023-00460-x