Abstract
Background
Intimate partner violence (IPV) during pregnancy has negative physical and psychological health consequences on the pregnant women. As such, women who experience IPV during pregnancy are likely to have challenges accessing maternal healthcare services. In this study, we examined the influence of exposure to IPV on timely antenatal care (ANC) visits in sub-Saharan Africa.
Methods
Cross-sectional data from the most recent Demographic and Health Survey of twenty-two countries in sub-Saharan Africa between 2012 and 2020 were analysed. Data were obtained from 61,282 women with birth history in the five years prior to the survey. A multilevel logistic regression was used to determine the association between IPV and timely ANC visits while controlling for significant covariates. Adjusted odds ratios (aOR) with 95% Confidence Intervals (CI) were used to present results from the multilevel logistic regression analysis.
Results
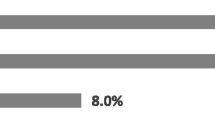
The prevalence of timely ANC visit and IPV were 38.1% and 34.9% respectively. The highest and lowest prevalence of IPV were found in Sierra Leone (52.9%) and Comoros (8.1%), respectively. Timely ANC attendance among pregnant women was more prevalent in Liberia (74.9%) and lowest in DR Congo (19.0%). Women who experienced IPV during pregnancy were less likely to utilize timely ANC (aOR = 0.89, 95% CI = 0.86–0.92) compared to those who did not experience IPV. In terms of the covariates, the odds of timely ANC were higher among women aged 40–44 compared to those aged 15–19 (aOR = 1.35, 95% CI = 1.21–1.51). Higher odds of timely ANC was found among women who were cohabiting (aOR = 1.15, 95% CI = 1.10–1.20), those from the richest wealth quintile (aOR = 1.38, 95% CI = 1.28–1.48), those exposed to watching television (aOR = 1.24, 95% CI = 1.18–1.30), and those with health insurance (aOR = 1.46, 95% CI = 1.37–1.56).
Conclusion
Findings from the study indicate the role of IPV in timely ANC visit in sub-Saharan Africa. To enhance timely ANC visits, there is the need for policy makers to strengthen and enforce the implementation of policies that alleviate IPV during pregnancy. Education and sensitization of married and cohabiting women and men on the negative effects of IPV on timely ANC should be done using media sources such as television. Inequalities in timely ANC can be eliminated through the provision and strengthening of existing maternal health policies such as health insurance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Antenatal care (ANC) is a form of preventive health care [1], and described by the World Health Organization (WHO) as care including screening for risk; prevention, diagnosis and treatment of diseases; and health education and promotion delivered by skilled healthcare personnel to pregnant women appropriate to guarantee that both mother and baby are in optimum health conditions throughout the gestation period [2]. ANC decreases maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality [2] directly by identifying complications associated with pregnancy for treatment, and indirectly by detecting women at increased risk of developing complications to ensure the appropriate needed referrals and detecting other causes of maternal death such as malaria and HIV infections [2]. Yet, pregnancy-related deaths remain unacceptably high and a public health problem worldwide [3]. It was estimated in 2017 alone that about 295,000 women lost their lives during pregnancy and after delivery worldwide [3], and about 2 million stillbirths are also reported every year [4]. These deaths are disproportionately high in low-and middle-income countries, especially in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) [3, 4].
WHO recommends a minimum of eight ANC attendance up from the previous minimum visits of four throughout pregnancy [2, 5]. It also suggests pregnant women to have timely ANC contacts/visits, with the first contact/visit taking place within the first 12 weeks of pregnancy and subsequent visits taking place at “20, 26, 30, 34, 36, 38 and 40 weeks” [5]. The timely and appropriate ANC practices are recommended during pregnancy in order to realize the optimum life-saving prospective of ANC for mothers and their babies [2]. ANC visits in a timely manner is usually indicated as a way to effectively avert adverse pregnancy related outcomes [6], as research have demonstrated that receiving the WHO recommended ANC services is associated with the timing of first ANC visit by pregnant women [7]. For instance, evidence have shown that first visit within the first trimester and/or at least four visits during pregnancy are associated with lower risk of neonatal mortality [8].
Though ANC has since seen increased attendance over the past decade [2, 5], its utilization is still suboptimal in low-and middle-income countries [2] with only 70.2% of pregnant women utilizing ANC for at least four times during the period 2015 to 2020 globally [1]. Predominately, sub-Saharan African countries report the lowest ANC utilization levels [1]. Studies have identified socio-demographic factors including maternal age, parity, education, socioeconomic status, place of residence; health facility factors such as quality of care, distance to health care facility, having insurance cover, and cost of ANC services; and psychosocial factors such as exposure to the media, partner’s support, and attitude towards ANC utilisation [6, 9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18] as predictors of the utilization of ANC and its timeliness.
Gender-based violence including intimate partner violence (IPV) during pregnancy has been shown to be a significant risk for complications during childbirth, as such pregnant women who are exposed to IPV are required to be identified during ANC [19]. IPV is a global public health problem, with an estimated 27% [Uncertain Interval (UI) 23–31%] of women aged 15–49 experiencing physical and/or sexual violence perpetrated by an intimate partner [20], and SSA is one of the regions around the world to report the highest prevalence (33%) of IPV [20]. IPV is suggested to be a sign of disempowering women in taking part in decision making in the house, controlling economic resources, and sexual consent which have been suggested to enable women to have better health outcomes [21]. Perpetrators of IPV are also found to exhibit controlling behaviors such as restriction of partner’s movement and relationships with family and friends [22, 23]. These may typically limit pregnant women exposed to IPV from accessing ANC. Studies have found IPV to be associated with reduced ANC utilization in several low-and middle-income countries [24,25,26,27,28,29]. For instance, in a meta-analysis by Musa et al. [26], experiencing IPV was found to be associated with 25% decrease in the use of adequate ANC among women.
Previous studies in SSA have examined the influence of experiencing IPV on several indicators of maternal health care service utilization such as skilled delivery attendance [21, 30] and adequate use of ANC (attendance of 4 or more) [24, 25, 31,32,33].
However, limited studies have focused on the effect of exposure to IPV on the timely use of ANC (e.g., first visit in the 12 weeks of pregnancy) among pregnant women in sub-Saharan African countries [27]. Using nationally representative surveys from several sub-Saharan African countries, we examined the association between exposure to IPV and timely utilization of ANC in SSA. Providing a comprehensive analysis across several sub-Saharan African countries could help clarify and highlight IPV as a risk factor for timely ANC visits.
Methods
Data source and study design
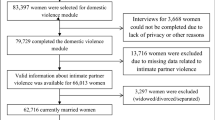
We combined data from the most recent Demographic and Health Survey (DHS) of 22 countries in SSA with a dataset between 2012 and 2020 for this study (Table 1). We included countries with observations on the domestic violence module as well as the other variables considered for this study. The data were extracted from the individual recode (IR) files in the countries' datasets. The DHS is a globally comparable nationally representative survey that was undertaken in a number of low- and middle-income countries [34]. The DHS used a structured questionnaire to collect data from respondents in a cross-sectional manner. Domestic violence, maternal health care service utilisation, mother and child health, reproductive health, and men's health are among the topics explored in the DHS [34]. The DHS used a two-stage cluster sampling method to sample the respondents. Initially, clusters were chosen, which were made up of enumeration areas (EA). A systematic sampling of households was performed in the second step. In each of the selected EAs, a household listing operation was conducted, and households to be included in the survey were chosen at random from the list. The survey methodology has been discussed in a study by Aliaga and Ruilin [35]. We included 61,282 women with children in the five years before the surveys who had complete cases on all variables of interest. We relied on the Strengthening Reporting of Observational studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) reporting guidelines in drafting this paper [36]. The dataset is freely accessible via this link: https://dhsprogram.com/data/available-datasets.cfm.
Study variables
Outcome variable
Timing of ANC was the outcome variable. It was assessed using the question “How many months pregnant were you when you first received ANC for this pregnancy?”. Women who attended their first ANC within the first 3 months of pregnancy ( ≤ 3 months) were classified as having "timely ANC visit" whilst the remaining pregnant women were grouped as having "late ANC visit". This categorisation was informed by previous studies [37,38,39,40].
Key explanatory variable
The key explanatory variable was IPV. The variable was assessed using three other variables namely physical violence, emotional violence, and sexual violence. Questions from the modified version of the conflict tactics scale were used to assess these three variables [41, 42]. Details of the questions, responses to the questions, and their categorization have been used in previous studies [43, 44].
Covariates
Based on review of literature on determinants of timely ANC visits [37,38,39,40] and variables available in the DHS, we included age of the women and their partners, educational level of the women and their partners, marital status, current working status of the women, exposure to radio, exposure to television, exposure to newspapers/magazine, parity, national health insurance subscription, wealth quintile, place of residence and geographical subregions as covariates. These variables were further grouped into individual level and contextual level variables.
Individual level factors
We utilised the existing coding for maternal age, educational level of the women and their partners, current working status, and health insurance subscription in the DHS dataset. Marital status was recoded as “married” and “cohabiting”. Parity was recoded into “1”, “2”, “3”, and “4 or more”. Partner’s age was recoded as “15–24”, “25–34”, “35–44”, and “45 + ”. Exposure to listening to radio (no and yes), exposure to watching television (no and yes), and exposure to reading newspapers/magazines (no and yes) were generated from responses to questions on frequency of reading newspapers, frequency of listening to radio, and frequency of watching television.
Contextual level factors
The contextual level variables consisted of place of residence, wealth quintile, and geographical subregions. The coding for wealth quintile and place of residence as found in the DHS were maintained and used in the final analysis. With geographical sub-regions, we grouped the countries included in the study into "Eastern", "Central", "Western", and "Southern" Africa respectively based on their location in SSA.
Statistical analyses
The data analysis was carried out using Stata software version 16.0 (Stata Corporation, College Station, TX, USA). We used percentages to summarise the prevalence of timely ANC and IPV in SSA. To examine the distribution of timely ANC across IPV and the covariates, we employed cross-tabulation (Table 2). Pearson chi-square test of independence was used to determine the variables that were significantly associated with timely ANC (Table 2). In addition, we used four models in a multilevel binary logistic regression analysis to investigate the association between IPV and timely ANC while adjusting for the individual and contextual level variables (Table 3). Model 0 demonstrated how the clusters within the primary sampling units (PSUs), contributed to the variance in timely ANC. IPV and the individual level variables were incorporated into Model I. The contextual level covariates were included in Model II. Finally, IPV, individual-level, and contextual level variables were included in Model III. In order to fit the four models, we used the Stata command "melogit." We included Akaike's Information Criterion (AIC) tests for model comparison. The adjusted odds ratios (aOR) with 95 percent confidence intervals (CIs) were used to present the results of the multilevel binary logistic regression. Sample weights were applied in the analysis to deal with under-sampling and over-sampling and correction for the complex survey design was addressed.
Results
Prevalence of intimate partner violence and timely antenatal care visit in sub-Saharan Africa
Figure 1 depicts the prevalence of IPV and timely ANC attendance in SSA. In this study, the pooled prevalence of timely ANC visits and IPV was 38.1 percent and 34.9 percent, respectively. Sierra Leone had the highest prevalence of IPV (52.9%), while Comoros had the lowest (8.1%). Pregnant women's timely ANC attendance was highest in Liberia (74.9%) and lowest in DR Congo (19.0%).
Distribution of timely ANC visit across intimate partner violence and covariates
Table 2 shows the bivariate analysis of IPV and timely ANC visit in SSA. The results showed significant association between IPV and timely ANC visit. The prevalence of timely ANC visit was higher (38.6%; p < 0.001) among women aged 25–29 compared with those aged 45–49 (33.3%; p = 0.01). Cohabiting women recorded a higher proportion of timely ANC compared to married women (40.7%; < 0.001). Furthermore, there were higher proportions of timely ANC among women who were exposed to listening to radio (39.9%; < 0.001), exposed to watching television (47.2%; < 0.001), and exposed to reading newspapers (48.9%; < 0.001) compared to those who were not exposed. The results showed a higher proportion of timely ANC visits among women who were covered by national health insurance (49.7%; < 0.001), from Southern region (44.9%; < 0.001), with one child (42.4%; < 0.001), from urban centers (43.4%; < 0.001), and within richest wealth quintile (48.8%; < 0.001).
Association between IPV and timely ANC attendance among women in sub-Saharan Africa
Table 3 shows the fixed and random effects analysis of the association between IPV and timely ANC in SSA. Women who experienced IPV were less likely to utilize ANC timely (aOR = 0.89, 95% CI = 0.86–0.92) compared to those who were not exposed to IPV. In terms of the covariates, the odds of timely ANC were higher among women aged 40–44 compared to those aged 15–19 (aOR = 1.35, 95% CI = 1.21–1.51). Higher odds of timely ANC was found among women who were cohabiting (aOR = 1.15, 95% CI = 1.10–1.20), those of the richest wealth quintile (aOR = 1.38, 95% CI = 1.28–1.48), those exposed to television (aOR = 1.24, 95% CI = 1.18–1.30), and those on NHIS (aOR = 1.46, 95% CI = 1.37–1.56) compared to their counterparts.
Discussion
The influence of IPV on timely ANC attendance in SSA was investigated in this study. We found the prevalence of IPV and timely ANC to be 34.9 percent and 38.1 percent, respectively. The current prevalence of timely ANC attendance is higher than what was found in previous studies in Ethiopia (13.2%-17.4%) [45], Nigeria (15.4%) [46], Zambia (17%) [47], and Tanzania (12.4%) [48]. The possibility of high rate of timely ANC attendance could be due to the various interventions and policies such as national health insurance scheme and free maternal healthcare service implemented within the sub-region [49,50,51]. The prevalence of IPV is higher than what was found in a previous study on polygyny and IPV in 16 countries in SSA [52]. The difference in prevalence could be attributed to differences in sample sizes, geographical scope, and study periods.
Women in SSA who experienced IPV were less likely to utilize timely ANC compared to those who did not experience IPV. This finding is consistent with previous studies conducted in Benin [53], Ethiopia [54], Mozambique [55], Nigeria [33], and Pakistan [56]. The possible justification could be due to the lack of social support from their partners/husbands to inform them on their timely utilization of ANC. Therefore, women at their gestation age less than 12 weeks might not develop a positive behavioral change towards timely ANC attendance. Also, the association between IPV and timely ANC can be explained by the fact that violence can have a negative influence on a woman's mental and physical health, making it difficult for her to seek good maternal health care. The result in the present study emphasizes the need for healthcare professionals to provide counselling and trauma management services to pregnant women experiencing IPV. In view of this, the involvement and empowerment of women in decision making is crucial towards improving maternal health service utilization as found in previous studies [57, 58]. However, previous studies in Tanzania and Rwanda found no association between IPV and timely ANC visit [59, 60].
Women with a parity of four or more were less likely than those with a parity of one to begin early ANC. This finding is consistent with earlier research [61, 62], which identified high parity to be associated with later commencement of ANC attendance. The possible explanation is that women with high parity may consider themselves as experienced due to their multiple successful pregnancies and childbirth, and hence may postpone ANC commencement [63]. For women and their unborn children, starting ANC visits on time is crucial for disease prevention, health promotion, and curative therapy [12]. According to the research, decreased ANC use among high-parity women could be owing to a lack of time available for ANC attendance due to child care, unpleasant ANC experiences from previous pregnancies, and insufficient family resources [64].
Previous study has shown that being married has a protective effect on ANC use. In this study, however, cohabiting pregnant women were more likely than married pregnant women to start ANC on time. This result contradicts the findings of Okedo-Alex et al. [12]. According to Okedo-Alex et al. [12], married pregnant women receive financial and psychosocial assistance from their spouses, and societal acceptance and support for their pregnancy condition prompts them to seek ANC as soon as possible. Unmarried women were also more likely to use ANC services, according to Tarekegn, Lieberman, and Giedraistis [65].
Poverty is a known impediment to healthcare utilisation in SSA, and low-income women may be unable to pay the costs of using ANC [53]. Our data demonstrated that in SSA, the health insurance and wealth level were significant factors impacting timely ANC utilisation among pregnant women. Pregnant women in the greatest wealth quintile and those covered by the health insurance were more likely to start ANC on time. This result is consistent with prior studies [12, 53]. Pregnant women may begin ANC late in pregnancy because to a lack of financial resources. Previous research has shown that socioeconomic status has an impact on timely ANC usage [49, 64, 66]. Although some countries in SSA, such as Ghana, have a national policy requiring all pregnant women to enroll in the national health insurance scheme for free maternal health services, pregnant women in some countries in SSA may still pay out of pocket for some direct medical costs associated with maternal healthcare. These expenses make it difficult for pregnant women to access ANC services on time [50, 51]. As a result, maternal health services, such as ANC, should be offered free through required social health insurance to enhance utilisation and, as a result, reduce maternal death and morbidity.
Strengths and limitations
We employed nationally representative data from 22 countries in SSA, making our findings generalizable to married and cohabiting women in the countries considered. Another strength is the use of large datasets with large sample sizes and the robust statistical analysis performed. However, the study design employed by the DHS is cross-sectional and this makes it impossible to establish any causal inferences. Again, there is the likelihood of variations in relationships between IPV and timely ANC since the survey years for the surveys varied. Finally, recall and social desirability bias may affect the reporting of the prevalences of IPV and timely ANC visits.
Conclusion
Findings from the study indicate the role of IPV in timely ANC visit in SSA. To enhance timely ANC visits, there is the need for policy makers to strengthen and enforce the implementation of policies that alleviate IPV. Education and sensitization of married and cohabiting women and men on the negative effects of IPV on timely ANC should be done using media sources such as television. Inequalities in timely ANC can be eliminated through the provision of free maternal health policies such as health insurance.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ANC:
-
Antenatal care
- IPV:
-
Intimate partner violence
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
- SSA:
-
Sub-Saharan Africa
- DHS:
-
Demographic and health survey
References
UNICEF. Antenatal care. UNICEF global databases, 2021, of antenatal care, based on MICS, DHS and other nationally representative household survey data. 2021. https://data.unicef.org/topic/maternal-health/antenatal-care/ (Accessed on 24th June 2021)
World Health Organization. WHO recommendations on antenatal care for a positive pregnancy experience. Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/250796/9789241549912-eng.pdf;jsessionid=0FE0390FA18DDE09020181270DC1F689?sequence=1
World Health Organization. Maternal mortality. Key facts. 2019.https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/maternal-mortality (Accessed on 24th June, 2021).
UNICEF. A Neglected Tragedy. The global burden of stillbirths. 2020. https://data.unicef.org/resources/a-neglected-tragedy-stillbirth-estimates-report/ (Accessed on 24th June 2021)
Tuncalp Ӧ, Pena-Rosas JP, Lawrie T, Bucagu M, Oladapo OT, Portela A, Metin GA. WHO recommendations on € antenatal care for a positive pregnancy experience—going beyond survival. BJOG. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.14599.
Yaya S, Bishwajit G, Ekhouluenetale M, Shah V, Kadio B, Udenigwe O. Timing and adequate attendance of antenatal care visits among women in Ethiopia. PLOS ONE. 2017;12(9):e0184934.
Agha S, Tappis H. The timing of antenatal care initiation and the content of care in Sindh. Pakistan BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2016;16:190. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-016-0979-8.
Doku DT, Neupane S. Survival analysis of the association between antenatal care attendance and neonatal mortality in 57 low-and middle-income countries. Int J Epidemiol. 2017;46(5):1668–77. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyx125.
Gross K, Alba S, Glass TR, Schellenberg JA, Obrist B. Timing of antenatal care for adolescent and adult pregnant women in south-eastern Tanzania. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2012;12:16. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2393-12-16.
Belayneh T, Adefris M, Andargie G. Previous early antenatal service utilization improves timely booking: cross-sectional study at university of Gondar hospital, northwest Ethiopia. Journal of pregnancy, 2014 Jan 1.https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/132494
Banda I, Michelo C, Hazemba A. Factors associated with late antenatal care attendance in selected rural and urban communities of the copperbelt province of Zambia. Med J Zambia. 2012;39(3):29–36.
Okedo-Alex IN, Akamike IC, Ezeanosike OB, et al. Determinants of antenatal care utilisation in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review. BMJ Open. 2019;9: e031890. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2019-031890.
Ali SA, Dero AA, Ali SA, Ali GB. Factors affecting the utilization of antenatal care among pregnant women: a literature review. J Preg Neonatal Med. 2018;2(2):41–5.
C Pell, Men˜ aca A, Were F, Afrah NA, Chatio S, et al. Factors Affecting Antenatal Care Attendance: Results from Qualitative Studies in Ghana, Kenya and Malawi. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(1):e53747.
Kawungezi PC, AkiiBua D, Aleni C, Chitayi M, Niwaha A, Kazibwe A, Sunya E, Mumbere EW, Mutesi C, Tukei C, Kasangaki A. Attendance and utilization of antenatal care (ANC) services: multi-center study in upcountry areas of Uganda. Open J Prev Med. 2015;5(3):132–42. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojpm.2015.53016.
Kuuire VZ, Kangmennaang J, Atuoye KN, Antabe R, Boamah SA, Vercillo S, Amoyaw JA, Luginaah I. Timing and utilisation of antenatal care service in Nigeria and Malawi. Glob Public Health. 2017;12(6):711–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/17441692.2017.1316413.
Sakeah E, Okawa S, Rexford Oduro A, Shibanuma A, Ansah E, Kikuchi K, Gyapong M, Owusu-Agyei S, Williams J, Debpuur C, Yeji F. Determinants of attending antenatal care at least four times in rural Ghana: analysis of a cross-sectional survey. Glob Health Action. 2017;10(1):1291879. https://doi.org/10.1080/16549716.2017.1291879.
Manyeh AK, Amu A, Williams J, et al. Factors associated with the timing of antenatal clinic attendance among first-time mothers in rural southern Ghana. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020;20:47. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-020-2738-0.
WHO. Intimate partner violence during pregnancy: Information sheet. 2017.
WHO. Violence against women Prevalence Estimates,. Global, regional and national prevalence estimates for intimate partner violence against women and global and regional prevalence estimates for non-partner sexual violence against women. Geneva: WHO; 2018. p. 2021.
Kwagala B, Nankinga O, Wandera SO, Ndugga P, Kabagenyi A. Empowerment, intimate partner violence and skilled birth attendance among women in rural Uganda. Reprod Health. 2016;13(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-016-0167-3.
Wandera SO, Kwagala B, Ndugga P, et al. Partners’ controlling behaviors and intimate partner sexual violence among married women in Uganda. BMC Public Health. 2015;15:214. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-015-1564-1.
Kwagala B, Wandera SO, Ndugga P, et al. Empowerment, partner’s behaviours and intimate partner physical violence among married women in Uganda. BMC Public Health. 2013;13:1112. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-13-1112.
Meiksin R, Meekers D, Thompson S, et al. Domestic Violence, Marital Control, and Family Planning, Maternal, and Birth Outcomes in Timor-Leste. Matern Child Health J. 2015;19:1338–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-014-1638-1.
Leight J, Wilson N. Intimate partner violence and maternal health services utilization: evidence from 36 National Household Survey. BMC Public Health. 2021;21:405. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-10447-y.
Musa A, Chojenta C, Geleto A, et al. The associations between intimate partner violence and maternal health care service utilization: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Womens Health. 2019;19:36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-019-0735-0.
Mohammed BH, Johnston JM, Harwell JI, et al. Intimate partner violence and utilization of maternal health care services in Addis Ababa. Ethiopia BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17:178. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-017-2121-7.
Islam MJ, Broidy L, Baird K, Mazerolle P. Exploring the associations between intimate partner violence victimization during pregnancy and delayed entry into prenatal care: evidence from a population-based study in Bangladesh. Midwifery. 2017;1(47):43–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.midw.2017.02.002.
Rahman M, Nakamura K, Seino K, et al. Intimate partner violence and use of reproductive health services among married women: evidence from a national Bangladeshi sample. BMC Public Health. 2012;12:913. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-12-913.
Goo L, Harlow SD. Intimate Partner Violence Affects Skilled Attendance at Most Recent Delivery Among Women in Kenya. Matern Child Health J. 2012;16:1131–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-011-0838-1.
Sipsma H, Ofori-Atta A, Canavan M, et al. Empowerment and use of antenatal care among women in Ghana: a cross-sectional study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2014;14:364. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-014-0364-4.
Omer K, Afi NJ, Baba MC, et al. Seeking evidence to support efforts to increase use of antenatal care: a cross-sectional study in two states of Nigeria. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2014;14:380. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-014-0380-4.
Ononokpono DN, Azfredrick EC. Intimate Partner Violence and the Utilization of Maternal Health Care Services in Nigeria. Health Care Women Int. 2014;35(7–9):973–89. https://doi.org/10.1080/07399332.2014.924939.
Corsi DJ, Neuman M, Finlay JE, Subramanian SV. Demographic and health surveys: a profile. Int J Epidemiol. 2012;41(6):1602–13.
Aliaga, A., & Ruilin, R. Cluster optimal sample size for demographic and health surveys. In 7th International Conference on Teaching Statistics–ICOTS 2006,7, 2–7.
Von Elm, E., Altman, D. G., Egger, M., Pocock, S. J., Gøtzsche, P. C., Vandenbroucke, J. P., & Strobe Initiative. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. International journal of surgery, 2014,12(12), 1495–1499.
Yaya S, Bishwajit G, Ekholuenetale, M, Shah V, Kadio B, Udenigwe O. Timing and adequate attendance of antenatal care visits among women in Ethiopia. PLoS One. 2017;12(9):e0184934.
Ahinkorah BO, Ameyaw EK, Seidu AA, Odusina EK, Keetile M, Yaya S. Examining barriers to healthcare access and utilization of antenatal care services: evidence from demographic health surveys in sub-Saharan Africa. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21(1):1–16.
Ahinkorah, B. O., Seidu, A. A., Budu, E., Mohammed, A., Adu, C., Agbaglo, E., ... & Yaya, S. Factors associated with the number and timing of antenatal care visits among married women in Cameroon: evidence from the 2018 Cameroon Demographic and Health Survey. Journal of Biosocial Science, 2021b, 1–11.
Seidu AA. Factors associated with early antenatal care attendance among women in Papua New Guinea: a population-based cross-sectional study. Archives of Public Health. 2021;79(1):1–9.
Sunita Kishor. Domestic violence measurement in the demographic and health surveys: The history and the challenges. Measure DHS, ORC Macro. 2015.
Straus MA. Measuring intrafamily conflict and violence: The conflict tractics scale (CTS). J Marriage Fam. 1979;41:75–88.
Aboagye RG, Okyere J, Seidu A-A, Hagan JE Jr, Ahinkorah BO. Experience of intimate partner violence among women in sexual unions: Is supportive attitude of women towards intimate partner violence a correlate? Healthcare. 2021;9(5):563.
Seidu AA, Aboagye RG, Ahinkorah BO, Adu C, Yaya S. Intimate partner violence as a predictor of marital disruption in sub-Saharan Africa: A multilevel analysis of demographic and health surveys. SSM-Population Health. 2021 Jul 17:100877.
Damme TG, Workineh D, Gmariam A. Time of antenatal care booking and associated factors among pregnant women attending Ambo Town health facilities, Central Ethiopia. J Gynecol Obst. 2015;26(5):103.
Addah A, Omietimi J, Allagoa D. Gestational age at first antenatal booking at the federal medical centre Yenagoa, Bayelsa State, South-South. Nigeria Lancet. 2015;5(1):19–24.
Nicholas N, Kyei A, Oona M, Campbell R, Gabrysch S. The influence of distance and level of service provision on antenatal care use in rural Zambia. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):1–10.
Athanase LGDM. A G. reported knowledge, attitude and practice of antenatal care services among women in Dodoma municipal, Tanzania. Pediatr Neonatal Care. 2014;4:1–8.
Goli S, Nawal D, Rammohan A, et al. Decomposing the socioeconomic inequality in utilization of maternal health care services in selected countries of South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa. J Biosoc Sci. 2018;50:749–69.
Dalinjong PA, Wang AY, Homer CSE. Has the free maternal health policy eliminated out of pocket payments for maternal health services? views of women, health providers and insurance managers in northern Ghana. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0184830.
Kalu-Umeh NN, Sambo MN, Idris SH, et al. Costs and patterns of financing maternal health care services in rural communities in northern Nigeria: evidence for designing national fee exemption policy. Int J MCH AIDS. 2013;2:163–72.
Ahinkorah BO. Polygyny and intimate partner violence in sub-Saharan Africa: Evidence from 16 cross-sectional demographic and health surveys. SSM-Population Health. 2021;1(13):100729.
Dina Idriss-Wheeler and Sanni Yaya Exploring antenatal care utilization and intimate partner violence in Benin – are lives at stake? BMC Public Health,2021,21:830. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-10884-9
Azene ZN, Yeshita YH, Mekonnen FA. Intimate partner violence and associated factors among pregnant women attending antenatal care services in Debro Markos town health facilities, Northwest Ethiopia. PLOS ONE. 2019;14(7):e0218722.
Tura H, Licoze A. Women’s experience of intimate partner violence and uptake of antenatal Care in Sofala, Mozambique. PLoS One. 2017;14(5):e0217407.
Ferdous N, Kabir R, Khan H, Khan Chowdhury MR. Exploring the relationship of domestic violence on health seeking behavior and empowerment of women in Pakistan. Epidemiol Biostat Public Health. 2017;14. https://doi.org/10.2427/12231.
Tekelab T, Chojenta C, Smith R, et al. Factors affecting utilization of antenatal care in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0214848.
Tesfaye G, Loxton D, Chojenta C, et al. Delayed initiation of antenatal care and associated factors in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Reprod Health. 2017;14:150.
Kabir R. Impact of intimate partner violence on ever-married women and utilization of antenatal care services in Tanzania. Rev Epidemiol Sante Publique. 2018;66:S376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respe.2018.05.377.
Rurangirwa AA, Mogren I, Ntaganira J, Krantz G. Intimate partner violence among pregnant women in Rwanda, its associated risk factors and relationship to ANC services attendance: a population-based study. BMJ Open. 2017;7(2): e013155. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-013155.
Agus Y, Horiuchi S. Factors influencing the use of antenatal care in rural West Sumatra, Indonesia. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2012;12(1):9.
Gitonga E. Determinants of focused antenatal care uptake among women in tharaka nithi county. Kenya Adv Public Health. 2017;2017:1–4.
Pell C, Meñaca A, Were F, Afrah NA, Chatio S, Manda-Taylor L, Hamel MJ, Hodgson A, Tagbor H, Kalilani L, Ouma P. Factors affecting antenatal care attendance: results from qualitative studies in Ghana. Kenya and Malawi PloS one. 2013;8(1):1–11.
Simkhada B, Teijlingen ER, Porter M, Simkhada P. Factors affecting the utilization of antenatal care in developing countries: systematic review of the literature. J Adv Nurs. 2008;61(3):244–60.
Tarekegn SM, Lieberman LS, Giedraitis V. Determinants of maternal health service utilization in Ethiopia: analysis of the 2011 Ethiopian demographic and health survey. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2014;14:161.
Carvajal-Aguirre L, Amouzou A, Mehra V, et al. Gap between contact and content in maternal and newborn care : An analysis of data from 20 countries in sub–Saharan Africa. J Glob Health. 2017;7:1–8.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
Funding
The study did not receive any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RGA, AS and BOA conceived the study. RGA and BOA carried out the data analysis. RGA, AS, BYAA, CA and BOA designed first draft of the manuscript. RGA, AS, BYAA, CA and BOA revised the manuscript to enhance its intellectual content. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
In this study, ethical clearance was not sought since the data is freely available in the public domain. Before the commencement of the survey, ethical clearance was sought and all ethical guidelines governing the use of human subjects in research were strictly adhered to. The detailed ethical guidelines are available at http://goo.gl/ny8T6X.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Aboagye, R.G., Seidu, AA., Asare, B.YA. et al. Intimate partner violence and timely antenatal care visits in sub-Saharan Africa. Arch Public Health 80, 124 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13690-022-00853-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13690-022-00853-y