Abstract
In this paper, we investigate the dynamics of a nonlinear differential system, a mathematical model of the coupled hematopoiesis network. The asymptotic stability of a unique positive periodic solution of the system under certain conditions is proved theoretically. Furthermore, we propose a linear feedback control scheme to guarantee the asymptotic stability of the system when the above conditions do not hold. Finally, an example and some numerical simulations are displayed to support the obtained results.
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
Hematopoiesis (blood cell production) is an extremely complex process. As we know, all blood cells come from the hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) which can differentiate mature blood cells into the blood circulatory system so as to maintain the normal blood environment. The process of differentiation is called hematopoiesis. Over the past few decades, many researchers have studied hematopoiesis dynamics from the perspective of anatomy, physiology, and mathematics. In 1977, Mackey and Glass studied the density of mature blood cell in a hematopoietic system and proposed a nonlinear delay differential equation model (Hematopoiesis Model, HM) describing the dynamics of hematopoiesis [1, 2]. In 1991, by using a variable replacement method, Gyori and Ladas obtained sufficient conditions for the global attractivity of the unique positive equilibrium point of HM [3]. In Ref. [4], authors extended the HM to a general nonlinear delayed differential equation and proved the sufficient conditions for the existence of a periodic positive solution based on cone fixed point theorem. In Ref. [5], authors proved the existence of a unique positive almost periodic solution of a generalized model hematopoiesis with delays and impulses. In Ref. [6], Ding et al. presented several existence and uniqueness results about positive almost periodic solutions for a class of hematopoiesis model. Hereafter, some extended hematopoiesis models were also proposed, the existence and stability of a positive periodic solution of the models were discussed [7–12]. Some stability condition and control methods were put forward. In Ref. [13], authors presented a feedback control method for the global attractivity of a positive almost-periodic solution of the model of hematopoiesis. In Refs. [14–17], the authors pointed out that the hematopoiesis can be controlled by the gene regulation or drugs.
All of the above models and studies of hematopoiesis are based on a single hematopoietic organ. However, there are multiple organs or tissues with hematopoietic function, including bone marrow, lymph node, liver, spleen, etc. Moreover, bone marrow is also located in different parts of the body, and there do exist connections and effects among them. For example, the damage of a hematopoietic organ can cause other organs to increase the production of blood cells. Therefore, a normal blood circulatory system should be the synergy result of these hematopoietic organs or tissues. In this work, we consider the mathematical model of hematopoiesis with the coexistence of multiple hematopoietic organs or tissues.
The progress of complex networks theory and modeling, along with access to new data, enables humans to achieve true predictive power in areas never before imagined. In recent years, complex networks theory is widely used in biology research [18, 19]. In Ref. [20], Zemanova et al. studied relationship between the cluster structure and the function in complex brain networks based on the cluster synchronization method. In Ref. [21], Chen et al. suggested that there is an extensive network of TET2-Targeting MicroRNAs regulating malignant hematopoiesis. In Ref. [22], Swiersa et al. proposed an approach to program the HSCs and erythroid lineage specification by using genetic regulatory networks.
Motivated by the above discussions, we propose a nonlinear time-delay differential system as a model of a coupled hematopoiesis network which reflects the interactions of multiple hematopoiesis organs. The existence of a unique positive periodic solution of the model is proved rigorously, and the sufficient conditions of asymptotic stability of the periodic solution are presented and verified through theoretical analysis and numerical simulations, respectively. Furthermore, in the case of non-asymptotic stability of the periodic solution, a feedback controller is designed to ensure the stability of the system.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. In Sect. 2, the model and mathematical preliminaries are introduced. The existence and asymptotic stability of the positive periodic solutions are proved in Sect. 3. A feedback control scheme is proposed in Sect. 4. An example and some numerical simulations are provided to verify the theoretical results in Sect. 5. Finally, a brief conclusion is given in Sect. 6.
2 Model and preliminaries
The general hematopoiesis model with a single hematopoietic system is described by [1, 4]
where \(x(t)\) denotes the density of mature cells in blood circulation at time t, the delay \(\delta>0\) is the time delay between the production of immature cells in the hematopoietic organs and their maturation for release in the circulating bloodstreams, \(m>0\) is the disturbing parameter, and the disturbing functions \(a(t)\) and \(b(t)\) are continuous and ϖ-periodic.
Here, considering the synergy of the multiple hematopoietic organs or tissues, we extend the model (1) to a complex dynamical network model with multiple coupled hematopoiesis, which is described in nonlinear differential equations as follows:
where \(x_{i}(t)\in(0,\infty)\) represents the density of mature cells in the ith organ, the parameters \(b_{ij}\), \(c_{ij}\) are the connection weight and the delay connection weight between organ i and organ j, respectively. Model (2) can be rewritten in a vector form as follows:
where \(X(t)=[x_{1}(t),x_{2}(t),\ldots,x_{n}(t)]^{T} \in(R^{+})^{n}\), \(x_{i}(t)\in(0,\infty)\) is the ith state variable of equations (2) (\(i=1,2,\ldots,n\)). \(G(X(t))=[\frac{1}{1+x^{m}_{1}(t)},\frac{1}{1+x^{m}_{2}(t)},\ldots,\frac {1}{1+x^{m}_{n}(t)}]^{T} \), and \(G(\cdot)\) is a real continuous vector function in the Euclidean space. The matrices \(A(t)=\operatorname{diag}\{a_{1}(t),a_{2}(t),\ldots,a_{n}(t)\}\), \(\beta (t)=(\beta_{ij} (t))_{n\times n}\), and \(W(t)=(w_{ij}(t))_{n\times n}\) are continuous positive ϖ-periodic function matrices. The matrices \(B=(b_{ij})_{n\times n}\) and \(C=(c_{ij})_{n\times n}\) are non-negative constant matrices which represent the coupling and delay coupling strength among n organs, respectively.
The main purpose of this paper is to prove the existence and asymptotic stability of a unique periodic positive solution of system (2) under certain conditions. Then we propose a feedback control method to ensure the stability of system (2) when the above conditions do not hold.
In order to derive our results, the definition of normal cone and a lemma are given below.
Definition 1
([23])
Let κ be a real Banach space. A nonempty convex closed set \(P\subset\kappa\) is called a cone if it satisfies the following two conditions: (i) \(x \in P\), \(\lambda\geq0\) implies \(\lambda x \in P\); (ii) \(x \in P\), \(-x \in P\) implies \(x=\theta\) (where θ denotes the zero element of κ). P is said to be normal if there exists a positive constant M such that, for all \(x,y\in P\), \(\theta\preceq x \preceq y\) implies \(\| x \| \leq M \| y \|\).
Lemma 1
([24])
Let κ be a real Banach space and ℓ is a cone in κ. Suppose that
-
(i)
cone ℓ is normal, \(\wp: \ell\rightarrow\ell\) is a completely continuous operator;
-
(ii)
for \(\forall X_{0} \in\ell\), there exists \(\epsilon_{0}>0\) such that \(\| \wp(X_{0})\|>\| X_{0}\|\), \(\| \wp^{2}(X_{0})\|\ge\epsilon_{0}\| \wp(X_{0})\|\);
-
(iii)
for any \(0<\mu<1\) and \(X \in\ell\) satisfying \(\| X_{0}\|<\| X \|<\| \wp(X_{0})\|\), there exists \(\eta(X,\mu)>0\) such that \(\|\wp(\mu X)\|\leq [\mu(1+\eta)]^{-1}\| \wp(X)\|\).
Then the operator ℘ has a unique fixed point X̃. Furthermore, for any initial \(X_{0} \in\ell\) and an iterated sequence \(X_{k}=\wp(X_{k-1})\) (\(k=1,2,3,\ldots\)), we have \(\lim_{k \rightarrow\infty}\| X_{k}-\widetilde{X}\|=0\).
3 Existence and asymptotic stability of the positive periodic solution
In this section, we address the existence and asymptotic stability of the positive periodic solution of model (3).
Theorem 1
For the differential equation (3), there exists a unique positive periodic solution \(\widetilde{X}(t)\) if \(\| \Lambda(s)\|<1\) for \(s \in(0,\infty)\), where \(\Lambda(s)=\operatorname{diag}\{\frac{\mu+\mu x_{1}^{m}(s)}{1+\mu^{m} x_{1}^{m}(s)},\frac{\mu+\mu x_{2}^{m}(s)}{1+\mu^{m} x_{2}^{m}(s)}, \ldots,\frac{\mu+\mu x_{n}^{m}(s)}{1+\mu^{m} x_{n}^{m}(s)}\}\), \(0<\mu<1\).
Proof
Let us set \(H(t,s)=(e^{\int^{\varpi}_{0} A(u)\,du}-I)^{-1}e^{\int^{s}_{t} A(u)\,du}\), \(s\in[t,t+\varpi]\). Let \(\ell=\{X(t): X(t+\varpi)=X(t),\| X(t)\|=\operatorname{Max}_{[1\le k\le n]}\{\operatorname{Max}_{s\in [t,t+\varpi]}\{|x_{k}(s)|\}\}\}\) denotes a continuous function set. Obviously ℓ is a cone of Banach space. For \(X(t): \| X(t)\|=\operatorname{Max}_{[1\le k\le n]}\{\operatorname{Max}_{s\in [t,t+\varpi]}\{|x_{k}(s)|\}\}\) and \(Y(t): \| Y(t)\|=\operatorname{Max}_{[1\le k\le l]}\{\operatorname{Max}_{s\in [t,t+\varpi]}\{|x_{k}(s)|\}\}\), where \(n< l\), we have \(\theta\preceq X(t) \preceq Y(t)\), which implies \(\| X(t) \| \leq\| Y(t) \|\). So ℓ is a normal cone.
Construct the following operator ℘:
Obviously, \(\wp(X(t+\varpi))=\wp(X(t))\), that is, \(\wp :\ell\rightarrow\ell\).
Then we obtain
Because \(A(t), \beta(t)\), and \(W(t)\) are ϖ-periodic function matrices, we have
Thus
Therefore, \(\| \dot{\wp}(X(t))\|\) and \(\| \wp(X(t))\|\) are bounded. Based on the Arzela–Ascoli theorem [25], the operator \(\wp: \ell\rightarrow\ell\) is a completely continuous operator. Furthermore, for \(X_{0}(t) \in\ell\), we readily obtain \(\| \wp(X_{0}(t))\| \ge\| X_{0}(t)\|\). Since matrices B and C are non-negative matrices, from (4), we have
and
Because
there exists \(\epsilon_{0}=[1+(\varpi\| H(t,s)\|(\| B\| M_{2}+\| C\| M_{3}))^{m}]^{-1}>0\) such that \(\|\wp^{2}(X_{0}(t))\| \ge \epsilon_{0} \|\wp(X_{0}(t))\|\).
If, for any \(X(t)\in\ell\), there is \(\| X_{0}(t)\|<\| X(t)\|\), then for \(0<\mu<1\), we can obtain
where
And because
Combining (5) and (6), we obtain
Then
By Lemma 1, when \(\|\Lambda(s)\|<1 \), \(s \in(0,\infty)\), the operator \(\wp:\ell\rightarrow\ell\) has a unique positive fixed point \(\widetilde{X}(t) \in\ell\). Furthermore, for the iteration \(X_{k+1}(t)=\wp(X_{k}(t))\), \(k\in N^{+}\), we have \(\lim_{k\rightarrow\infty}\| X_{k}(t)-\widetilde{X}(t)\|=0\) for any initial value \(X_{0}(t) \in\ell\). So \(\widetilde{X}(t)=\wp(\widetilde{X}(t))\), and
That is, \(\widetilde{X}(t)\) is a unique positive periodic solution of equation (3). Thus the proof is completed. □
Theorem 2
Assume that there exist positive constants \(\alpha, \beta, \gamma>0\), and a positive definite matrix P satisfying
and
where \(H(t)=A(t)+B\beta(t) J_{0}(\widetilde{X}(t))\), \(E(t-\delta)=CW(t) J_{0}(\widetilde{X}(t-\delta))\), and \(\widetilde{X}(t)\) is the periodic solution of equation (3). Then \(\widetilde{X}(t)\) is asymptotically stable.
Proof
Let \(y(t)=X(t)-\widetilde{X}(t)\), we obtain
where
Obviously, \(y(t)=0\) is the equilibrium point of (10). Linearizing \(F_{1}\) and \(F_{2}\) at the equilibrium, we have
where
The linearization of (10) is
Then we obtain
Taking the Lyapunov function
we have
According to (8) and (9), we obtain
It is obvious that \(\dot{V}(t)=0\) if and only if \(y(t)=0\). Let S be the set of all points where \(\dot{V}(t)=0\), that is, \(S=\{\dot{V}(t)=0\}=\{y(t)=0\}\). From (10), the largest invariant set of S is \(M=\{y(t)=0\}\). According to LaSalles invariance principle [26], starting with any initial values, the trajectories of system (10) will converge to M asymptotically, which implies that \(y(t)\rightarrow0\) (\(t\rightarrow\infty\)). That is, the periodic solution \(\widetilde{X}(t)\) of (3) is asymptotically stable. Now the proof is completed. □
Remark 1
It is worth noting that, conditions (8) and (9) in Theorem 2 are quite conservative and would be difficult to achieve. Fortunately, a human organ system has the ability to adjust and maintain balance. In the following section, we will discuss the feedback control law to ensure the stability of system (3).
4 Feedback control
According to Theorem 2, the asymptotic stability of \(\widetilde{X}(t)\) is not guaranteed when condition (8) or (9) is not met. In this section, a feedback control method is proposed to guarantee the asymptotic stability of the periodic solution \(\widetilde{X}(t)\). By employing a controller U, the controlled system (3) can be rewritten as
Theorem 3
Consider system (12) with a linear feedback controller \(U=-ky(t)\), where k is a sufficiently large positive constant. Assume that there exist constants \(\alpha, \beta, \gamma >0\), and a positive definite matrix P satisfying
and
Then system (12) can be stabilized to the periodic solution \(\widetilde{X}(t)\) of equation (3).
Proof
Let \(y(t)=X(t)-\tilde{X}(t)\).
Combining (12) and (7), we have
By linearizing the above equation, we obtain
that is,
The rest of the proof is similar to that of Theorem 2. Therefore, the equilibrium point \(y(t)=0\) of (15) is asymptotically stable, that is, \(\lim_{t\rightarrow0} y(t)=0\). Thus, an arbitrary solution \(X(t)\) of (12) is stabilized to the periodic solution \(\tilde{X}(t)\) of equation (3). The proof is thus completed. □
Remark 2
Comparing (14) with (9), one can see that the application scope of theory condition is broadened by adding a feedback controller U. It implies that a living organism is more likely to reach a steady state via appropriate feedback adjustment.
5 Example and numerical simulations
In this section, an example and some numerical simulations are provided to verify the existence and the asymptotic stability of the unique positive periodic solution of equation (3), as well as the effectiveness of the control method.
First, we provide an example of model (2) (or equation (3)) whose solution is asymptotically stable.
We take \(n=3\), \(\delta=20\), \(m=2\), and the matrices are as follows:
So the differential equation is
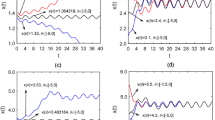
Figure 1 displays the stability of the unique positive periodic solution of equation (16). Figure 1(a) displays the evolution of each component \(x_{k}(t)\) (\(k=1,2,3\)) of solution \(X(t)\) with different initial values, and Fig. 1(b) is the phase diagram of solution \(X(t)\). It is obvious that the unique positive periodic solution \(\widetilde{X}(t)\) is asymptotically stable.
The asymptotic stability of the unique periodic positive solution of equation (16)
Next, we give an example to verify the effectiveness of the feedback control method.
Let us take \(\bar{C_{1}}=10C_{1}\) in equation (16), then we have
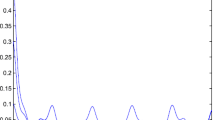
Figure 2 shows that the unique positive periodic solution \(\widetilde{X}(t)\) of equation (17) is non-asymptotically stable.
The non-asymptotic stability of the periodic solution \(\tilde{X}(t)\) of equation (17)
Then we employ a linear feedback controller U in (17), the equation is rewritten as
Here, we take the feedback gain \(k=8\), that is, \(U=-8y(t)\). As is shown in Fig. 3(a), each component \(x_{k}(t)\) (\(k=1,2,3\)) of the solution \(X(t)\) starting from different initial values tends to be the same. That is, the unique positive periodic solution \(\widetilde{X}(t)\) of the controlled system (18) is asymptotically stable. The phase diagram of solution \(X(t)\) in Fig. 3(b) displays the same result. This shows that our feedback control method is effective.
The asymptotic stability of the periodic solution \(\tilde{X}(t)\) of equation (18)
6 Conclusion
In this paper, we have studied the stability and feedback control of the hematopoiesis network model with nonlinear differential equations. On the one hand, we proved the existence and asymptotic stability of the unique positive periodic solution of the system under certain conditions. On the other hand, we designed appropriate feedback controller to stabilize an arbitrary solution of the model to the unique positive periodic solution. The result reveals that, when the hematopoietic system becomes chaotic, a living organism can return to stable states by means of appropriate physical adjustment.
References
Mackey, M.C., Glass, L.: Oscillations and chaos in physiological control systems. Science 197, 287–289 (1977)
Mackey, M.C.: Unified hypothesis of the origin of aplastic anaemia and periodic hematopoiesis. Blood 51, 941–956 (1978)
Gyoyi, I., Ladas, G.: Oscillation Theory of Delay Differential Equations with Applications. Clarendon, Oxford (1991)
Mallet-Paret, J., Nussbaum, R.: Global continuation and asymptotic behavior for periodic solutions of a differential-delay equation. Ann. Mat. Pura Appl. 145, 33–128 (1986)
Anh, T.T., Nhung, T.V., Hien, L.V.: On the existence and exponential attractivity of a unique positive almost periodic solution to an impulsive hematopoiesis model with delays. Acta Math. Vietnam. 41, 337–354 (2016)
Ding, H.S., Liu, Q.L., Nieto, J.J.: Existence of positive almost periodic solutions to a class of hematopoiesis model. Appl. Math. Model. 40, 3289–3297 (2016)
Ding, H.S., N’Guérékata, G.M., Nieto, J.J.: Weighted pseudo almost periodic solutions for a class of discrete hematopoiesis model. Rev. Mat. Complut. 26, 427–443 (2013)
Braverman, E., Saker, S.H.: Oscillation and attractivity of the discrete hematopoiesis model with variable coefficients. Nonlinear Anal. 67, 2955–2965 (2007)
Liu, G., Yan, J., Zhang, F.: Existence and global attractivity of unique positive periodic solution for a model of hematopoiesis. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 334, 157–171 (2007)
Peixoto, D., Dingli, D., Pacheco, J.M.: Modelling hematopoiesis in health and disease. Math. Comput. Model. 53, 1546–1557 (2011)
Wan, A., Jiang, D., Xu, X.: A new existence theory for positive periodic solutions to functional differential equations. Comput. Math. Appl. 47, 1257–1262 (2004)
Peixoto, D., Dingli, D., Pacheco, J.M.: Modelling hematopoiesis in health and disease. Math. Comput. Model. 53, 1546–1557 (2011)
Hong, P., Weng, P.: Global attractivity of almost-periodic solution in a model of hematopoiesis with feedback control. Nonlinear Anal. 12, 2267–2285 (2011)
Jing, L., Zon, L.: Zebrafish as a model for normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Dis. Models Mech. 4(4), 433–438 (2011)
Kannan, R., Vincent, S.G.P.: Screening of herbal extracts influencing hematopoiesis and their chemical genetic effects in embryonic zebrafish. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2, S1002–S1009 (2012)
Novershtern, N., Subramanian, A., et al.: Densely interconnected transcriptional circuits control cell states in human hematopoiesis. Cell 144(2), 296–309 (2011)
Zhao, J.Y., Ding, H.S., N’Guérékata, G.M.: S-Asymptotically periodic solutions for an epidemic model with superlinear perturbation. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2016, 221 (2016)
Newman, M.E.J.: The structure and function of complex networks. SIAM Rev. 45, 167–256 (2003)
Boccaletti, S., Latora, V., Moreno, Y., Chavez, M., Hwamg, D.: Complex network: structure and dynamics. Phys. Rep. 424, 175–308 (2006)
Zemanova, L., Zhou, C., Kurths, J.: Structural and functional cluster of complex brain networks. Physica D 224, 202–212 (2006)
Chen, J., Guo, S., et al.: An extensive network of TET2-targeting MicroRNAs regulates malignant hematopoiesis. Cell Rep. 5, 1–11 (2013)
Swiersa, G., Patientb, R., Loosea, M.: Genetic regulatory networks programming hematopoietic stem cells and erythroid lineage specification. Dev. Biol. 294(2), 525–540 (2006)
Liu, H., Xu, S.: Cone metric spaces with Banach algebras and fixed point theorems of generalized Lipschitz mappings. Fixed Point Theory Appl. 2013(1), 320 (2013)
Guo, D., Lakshmikantham, V.: Nonlinear Problems in Abstract Cones, pp. 47–48. Academic Press, Boston (1988)
Li, R.L., Zhong, S.H., Swartz, C.: An improvement of the Arzela–Ascoli theorem. Topol. Appl. 159(8), 2058–2061 (2012)
Khalil, H.K.: Nonlinear Systems, 3rd edn. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River (2002)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the editors and the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions that have helped to improve the present paper.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61563013, 61663006, 61505037, 61473338) and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi (Nos. 2018GXNSFAA138095, 2015GXNSFBA139259).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally and significantly in this manuscript, and they read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Z., Chen, H., Tu, L. et al. Stability and feedback control for a coupled hematopoiesis nonlinear system. Adv Differ Equ 2018, 401 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13662-018-1838-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13662-018-1838-x