Abstract
About 80% of patients resuscitated from CA are comatose at ICU admission and nearly 50% of survivors are still unawake at 72 h. Predicting neurological outcome of these patients is important to provide correct information to patient’s relatives, avoid disproportionate care in patients with irreversible hypoxic–ischemic brain injury (HIBI) and inappropriate withdrawal of care in patients with a possible favorable neurological recovery. ERC/ESICM 2021 algorithm allows a classification as “poor outcome likely” in 32%, the outcome remaining “indeterminate” in 68%. The crucial question is to know how we could improve the assessment of both unfavorable but also favorable outcome prediction. Neurophysiological tests, i.e., electroencephalography (EEG) and evoked-potentials (EPs) are a non-invasive bedside investigations. The EEG is the record of brain electrical fields, characterized by a high temporal resolution but a low spatial resolution. EEG is largely available, and represented the most widely tool use in recent survey examining current neuro-prognostication practices. The severity of HIBI is correlated with the predominant frequency and background continuity of EEG leading to “highly malignant” patterns as suppression or burst suppression in the most severe HIBI. EPs differ from EEG signals as they are stimulus induced and represent the summated activities of large populations of neurons firing in synchrony, requiring the average of numerous stimulations. Different EPs (i.e., somato sensory EPs (SSEPs), brainstem auditory EPs (BAEPs), middle latency auditory EPs (MLAEPs) and long latency event-related potentials (ERPs) with mismatch negativity (MMN) and P300 responses) can be assessed in ICU, with different brain generators and prognostic values. In the present review, we summarize EEG and EPs signal generators, recording modalities, interpretation and prognostic values of these different neurophysiological tools. Finally, we assess the perspective for futures neurophysiological investigations, aiming to reduce prognostic uncertainty in comatose and disorders of consciousness (DoC) patients after CA.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The vast majority of patients resuscitated from cardiac arrest (CA) will unfortunately not survive beyond the first days and weeks. Cerebral lesions caused by circulatory interruption and subsequent reperfusion are the main cause of these early deaths [1]. These early deaths remain mainly due to withdrawal-of-life-sustaining-treatments (WLST), presumably secondary to an irreversible hypoxic ischemic brain injury (HIBI). Most often, the severity of these lesions can only be accurately assessed after an observation phase allowing prognostic investigations to be carried out. Among the tools available to clinicians, neurophysiological investigations already occupy a major place. Neurophysiology will probably become even more important in the next future given the progress underway in different directions. In the present review, we aim to present an overview of established data and recent advances coming from neurophysiology in the particular setting of post-cardiac arrest phase.
Pathophysiology of hypoxic ischemic brain injury
Cerebral damages caused by cardiac arrest are complex and polymorphic, whose the HIBI constitutes the pathophysiological process. Experimental models as well as clinical observation show that injuries leading to HIBI are initiated by circulatory interruption (sudden anoxo-ischemia), but that these primary damages worsen during the first hours (ischemia–reperfusion), thus offering a time-window for therapeutic interventions aiming to limit these phenomena. The mechanisms that lead to the creation of the initial lesions combine to varying degrees dysfunction of the cell membranes, local and systemic inflammation, increase in local excitotoxicity, microvascular abnormalities (associating damage to the endothelium and alteration of vaso-reactivity), alteration of the blood–brain barrier and edematous reactions. The loss of cerebral homeostasis aggravates these lesions, which can be worsened due to various aggressions of systemic origin (abnormalities in blood pressure, arterial oxygen and carbon dioxide content, fever, electrolytic or glycemic disorders). Importantly, some brain regions have an increased susceptibility to these different phenomena. In the extreme, all structures can be potentially affected, explaining the very broad spectrum of clinical manifestations described in patients with HIBI, ranging from transient and totally reversible loss of consciousness to unreactive coma, and even brain death [2, 3].
Disorders of consciousness after cardiac arrest
Most patients with favorable neurological outcome after CA begin recovering consciousness a few hours after cessation of sedation, awakening being usually defined as a reproductible response to verbal command using the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) with a motor score of 6 [2, 4]. Despite this, 80% of patients resuscitated from CA are comatose at ICU admission and nearly 50% of survivors are still unawake at 72 h [2, 3]. Delayed awakening is not rare after sedation weaning and in some situations, awakening may be observed up to 12–25 days after ROSC [5]. Recognized risk factors for delayed awakening are post-resuscitation shock, renal insufficiency, older age, and use of long (i.e., midazolam) vs. short-acting (i.e., propofol) sedative agents [6,7,8]. Neurological state of consciousness and awareness after CA is highly heterogeneous and subject to time variations [9]. A complete physical examination using adapted scales and rigorous definitions is recommended (see Table 1), first to assess the neurological state as accurately as possible and second to predict consciousness recovery [9, 10]. Coma is defined as a state of unresponsiveness, in which the patient lies with eyes closed and cannot be aroused to respond appropriately to vigorous stimulation [11]. Secondarily, patients may regain arousal (eyes opened) without awareness (pragmatically defined as no reproducible response to command), defining disorders of consciousness (DoC). These DoC entities include vegetative state (VS, also called unresponsive wakefulness syndrome (UWS)) and minimally conscious state (MCS, also called cortically mediated state (CMS)). Both VS and MCS are mainly related to a preservation of brainstem arousal functions with persistent impairment of supratentorial networks implicated in consciousness [9, 10]. The distinction between these different patterns of DoC is a key point, as MCS patients are more prone to evolve toward consciousness recovery than VS patients [12,13,14]. Other DoC and behavioral impairments (as cognitive-motor dissociation (CMD) and delirium) are described in Table 1. Predicting neurological outcome of these patients is important to provide correct information to the patient’s relatives, to avoid disproportionate care in patients with irreversible HIBI, and to avoid inappropriate withdrawal of care in patients with a possible favorable neurological recovery.
The challenge of neuro-prognostication
To date, most of the studies exploring indicators of prognosis after CA have focused on unfavorable outcome (UFO) prediction. The challenge is to identify markers with the highest specificity and the lowest false positive rate (FPR), to minimize the possibility of wrong prediction [4]. However, these studies presented several risks of bias. First, the lack of blinding could induce self-fulfilling prophecy, as test results are used for decisions of WLST. To limit this risk, the current guidelines are based on the most robust indicators, which are also combined with each other (i.e., never used in isolation). Another potential bias is the use of different scales to assess neurological outcome according to studies. The most employed scale is the Cerebral Performance Categories (CPC). The CPC is directly adapted from the Glasgow Outcome Scale (GOS), although the GOS only considers disabilities related to brain injury. The CPC ranges from CPC 1 (no or minimal disability) to CPC 5 (death), CPC 1–2 being usually considered as favorable outcome [15]. Despite its widespread use, the CPC scale has a limited accuracy for discrimination of mild and moderate disabilities and does not assess psycho-cognitive functions. The CPC also does not discriminate neurological from non-neurological causes of death, although a large multicenter study suggested that in-ICU death after awakening is observed in 4.2% of CA patients who are misclassified in the CPC 5 level. The use of the «best CPC» observed during the hospital stay (and not the CPC at discharge) could further limit this bias [16]. In several recent studies, more accurate scales are used, such as the Glasgow Outcome Scale-Extended (GOS-E, ranging from 1 to 8) or the modified Rankin scale (mRS, from 0 to 6) [17, 18]. Third, the timing of neurological assessment is another major bias as it differs widely among studies, although neurological outcome may further improve over time. In a large prospective study examining ICU survivors, the CPC level at hospital discharge improved in 14.5% of subjects at 6 months, mainly due to patients who were initially CPC 3 and who then evolved to CPC 2 [19], highlighting that the neurological function should not be assessed too early [20]. Finally, an important source of bias for prognostication is the remaining effect of sedatives and analgesia drugs. Sedation is mainly used to permit post-resuscitation care (mechanical ventilation, invasive procedures, temperature management) but it may alter prognostication in different ways [21, 22]. Sedation may delay awakening [2, 6], confound clinical examination (i.e., pupillary and corneal reflexes, that are both robust markers of poor outcome) and alter some neurophysiological markers (Table 2) [23]. These different points encourage the use of light-to-moderate dose of sedation with short-acting drugs (i.e., propofol) [24]. To minimize the risk of a falsely pessimistic prediction, recent guidelines recommend a multimodal approach for prediction of UFO, using at least two markers among: loss of pupillary and corneal reflexes, clinical status myoclonus, highly malignant electroencephalogram (EEG), bilateral abolition of N20 on somato-sensory evoked potential (SSEP), high release of biomarkers (neuron-specific-enolase (NSE) > 60 µg/L at 48 or 72 h) and identification of specific damages using brain imaging [4]. However, a recent study highlighted that this algorithm allows a classification as “poor outcome likely” in 32%, the outcome remaining “indeterminate” in 68% [25].
The crucial question is now to know how we could improve the assessment of both poor but also favorable outcome prediction [26]. This review proposes an overview of neurophysiological markers potentially interesting to reduce prognostic uncertainty in comatose and DoC patients after CA.
Methods
Regarding prognostic value assessment, we considered for inclusion only clinical studies, published as full text articles between 1995 and 2022, filtered by “English language” and “humans”. We excluded case reports, commentaries, publications with less than 10 patients, abstracts, editorials, or letters. We included studies on adult patients (> 18 years old) presenting a comatose state or a DoC after CA. Search strategy included MEDLINE via Pubmed database. We assessed separately the following neurophysiological indicators: “EEG”, “SSEP”, “brainstem auditory evoked potential (BAEP)”, “middle latency auditory evoked potential (MLAEP)”, “event-related potential (ERP)” or “cognitive evoked potential”, “P300”, “P3” and “mismatch negativity (MMN)”.
Electroencephalography
EEG signal generator
The EEG is the record of brain electrical fields. It is characterized by a high temporal resolution but a low spatial resolution. EEG signals are mainly explained by the postsynaptic activities (excitatory and inhibitory) of synchronously activated neurons that generate open electrical fields within the extracellular space [27, 28]. To reach the scalp, brain electrical signals must pass several layers of tissues with different electrical properties. This implies that what is recorded using surface EEG is an attenuated and transformed image of brain sources. The spatial EEG sampling is represented by the number of surface electrodes, while the temporal sampling corresponds to the sampling rate (usually around 256 Hz). It is possible to enhance the number of surface electrodes (up to 256), the sampling rate (up to 2000–3000 Hz) to perform high resolution EEG [29, 30].
EEG is sensitive for both radial and tangential components. Neuronal assemblies that are functionally interconnected constitute a functional brain workspace. In general, the neurons that constitute those assemblies are interconnected by feedforward and feedback loops. Traditionally, EEG signals are described in terms of frequency bands: infra-slow (< 0.2 Hz), δ (0.2–3.5 Hz), θ (4–7.5 Hz), α (8–13 Hz), β (14–30 Hz), γ (30–90 Hz) and high-frequency oscillations (> 90 Hz). In normal brain are thus observed an alpha rhythm (between thalami basal ganglia and posterior cortex areas), a mu rhythm (between thalamic and central areas), and spindles during slow waves sleep (between thalami and large cortical areas). A predominant posterior alpha rhythm is usually observed in awake and resting normal condition [28, 31].
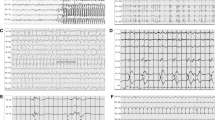
In comatose patients after CA, EEG background may display a large spectrum of abnormalities. The severity of HIBI is correlated with the predominant frequency but also with background continuity. For example, burst suppression is defined as a pattern of suppression background (during 50–99% of the record) that alternates with higher voltage activities (called “burst”, with two sub-types according to the identical or non-identical bursts characteristics) (Fig. 1) [32]. Source analysis and animal models support the theory that a deafferentation between cortical and subcortical structures exists in suppression period compared to burst phases. Indeed, brainstem “arousal system” (i.e., ascending reticular activating system) projections toward the thalamus and then cortical areas provide a key coupling for arousal, awareness and cognitive processing [33]. The central thalamus (intra laminar and para laminar nuclei) also receives upward projections from the brainstem that control the activity of many cortical and thalamic neurons. These projections are present only during the burst phases, whereas there is no coherence or interaction between cortical and subcortical structures during suppression periods [34, 35]. In DoC patients after CA, visual EEG analysis is usually not sufficient to discriminate between VS and MCS [9, 36]. Despite this, recent studies suggest that all stages of sleep (with reliable neurophysiological features, such as periods of consolidated slow wave sleep spindles and rapid eye movements) are only observed in MCS. These results suggest that sleep spindles reflect a relative preservation of thalamo-cortical connectivity, although the prognostic value of these patterns for recovery of consciousness prediction remains unknown [9, 37].
Highly malignant and benign EEG patterns (adapted from Westhall et al. [58] and ACNS terminology [32]). A, B, C Figures represented EEG longitudinal montage showing highly malignant patterns. A Suppression, defined as suppressed EEG background (amplitude < 10 µV all the time of the recording) without discharges. B Suppression with periodic discharges, defined as a suppressed EEG background with continuous periodic discharges (spikes, poly-spikes, sharp or waves). C Burst suppression, defined as suppression periods (< 10 µv) constituting > 50% of the recording with “burst”. D EEG longitudinal montage showing benign EEG, defined as the absence of a malignant or highly malignant features namely continuous or nearly continuous and reactive EEG background. Blue line indicated the nociceptive stimulus (nail pressure), inducing amplitude and frequency modifications and defining reactivity when reproductible
EEG recording modalities
Recent surveys examining current neuro-prognostication practices after CA reveal that EEG is the most widely used tool for assessing the severity of HIBI, both in Europe (63%) and United States (94.4%) [38, 39]. The timing of EEG recording remains largely heterogeneous among studies, ranging from 12 h (i.e., under sedation) to 7 days after CA [26, 40, 41]. As the EEG reflects the “real time” cortical activity, the pattern evolution over time could be an interesting prognostic information, particularly for EEG patterns predictive of UFO which may disappear over time [42,43,44,45]. Moreover, the prognostic value of EEG patterns could differ according to the timing of assessment and recent studies suggest that prognostic value of early EEG (obtained 12 to 24 h after CA) may be better than later recordings (see below). These results suggest that physicians should carry out EEG recording at 24 h and at 48–72 h after CA [31]. Importantly, neuro-prognostication issue should only be addressed in unresponsive state patients 72 h after CA and 48 h after sedation weaning. It suggests that early EEG recorded at 24 h after CA could be secondarily integrated into this neuro-prognostication process [4].
Routine discontinuous video-EEG recording is performed using 21 electrodes (minimum of 9 electrodes) including central–medial (Cz) electrode, during 20 min and coupled with a video recording [31, 46]. Recent data encourage the use of continuous EEG (cEEG) or reduced montages EEG devices [30, 47]. Whether cEEG is superior to routine intermittent EEG remains debated. In two large prospective studies, cEEG does not confer any advantage over two intermittent EEG regarding neurological outcome or time to death [48,49,50,51]. Despite this, international guidelines suggest that cEEG should be performed if available for seizure detection, treatment monitoring and prognostic assessment of HIBI [9, 30, 31]. Otherwise, the use of a limited-channel cEEG monitoring (4 or 6 frontal electrodes) could detect the most common EEG patterns associated with poor and good outcome [52, 53], although eye movement artifacts over bi-frontal electrodes could induce false positive detection of periodic discharges [52].
EEG interpretation and classification
Analysis of EEG is a complex task, requiring standardization in interpretation and classification. Concerning interpretation, EEG findings are typically categorized according to four determinants: background, sporadic epileptiform features (also called rhythmic or periodic patterns (RPPs)), electroencephalographic seizures and reactivity (Figs. 1, 2). Regarding background activity, the severity of HIBI is correlated with the predominant frequency, amplitude and continuity, ranging from slow background (delta or theta frequency), low voltage (amplitude < 20 µV), discontinuous (amplitude < 10 µV during 10–49% of the EEG recording), burst suppression (< 10 µV during > 50% and < 99%, with identical or non-identical bursts) or suppression background (< 10 µV all the time). Sporadic epileptiform discharges, electroencephalographic seizures and unreactive EEG could also reflect HIBI, with different degrees of severity.
EEG longitudinal montages showing typical malignant patterns (adapted from Westhall et al. [58] and ACNS terminology [32]). A Electroencephalographic seizure with high frequency (> 2.5 Hz) generalized spikes, more broadly defined as pattern with epileptiform discharges > 2.5 Hz for ≥ 10 s or any pattern with definite spatial and temporal evolution lasting ≥ 10 s. B Generalized periodic pattern (i.e., epileptiform features) defined as non-evolving and low frequency (<2.5 Hz) periodic discharges (spike, sharp or wave) during > 50% of the recording, without suppressed background. C Discontinuous background defined as suppression periods (< 10 µV) constituting > 10% but < 49% of the recording. D Low voltage background defined as amplitude of the background < 20 µV. Unreactive EEG is not illustrated here
Concerning classification, Young and Synek classifications were historically proposed for all critically ill patients [54, 55]. More recently, the American Clinical Neurophysiology Society (ACNS) critical care EEG terminology [32] was adapted by Hofmeijer et al. [56], Gaspard et al. [57] and Westhall et al. [58], resulting in three main categories: highly malignant, malignant and benign EEG [58], 56 (Figs. 1, 2) (Table 3). This ACNS terminology is now the most employed classification for prognostication after CA [1, 26, 45], although it does not describe pathophysiological mechanisms of EEG abnomalities [59, 60]. Nevertheless, using this classification could help to standardize interpretation, and may facilitate collaboration between intensivists and neurophysiologists.
ACNS classification definition and prognostic value
Table 3 displays the ACNS terminology adapted by Westhall et al. and the prognostic value for each pattern [32, 58]:
-
Highly malignant patterns correspond to three main patterns: suppression, suppression with periodic discharges and burst suppression. These patterns are recognized as robust markers of UFO (i.e., FPR close to 0% confidence interval CI95%(0–22.1), sensitivity 47–97%) [41, 42, 61,62,63,64,65]. Consequently, these patterns are considered as one of the six prognostic markers for poor outcome prediction in the last 2021 ERC/ESICM recommendations [4].
-
Malignant patterns include five different aspects: 1/Abundant rhythmic or periodic discharges (RPPs) (also called epileptiform features); 2/electroencephalographic seizures or status epilepticus (SE); 3/discontinuous background; 4/low voltage (< 20 µV); 5/unreactive EEG (Fig. 2). Prognostic value of malignant EEG remains very heterogeneous among the different patterns. Most studies assess the prognostic value of these different patterns all together and not their individual performance [41, 66]. Early (< 24 h after CA) non-evolving and low frequency (0.5–2.5 Hz) generalized periodic or rhythmic discharges appear to be the most robust predictors of UFO, with an FPR 0–3% despite a large CI95%(0–34.8) [62, 65, 67, 68]. Importantly, a recent multicentric randomized study highlighted that an aggressive anti-epileptic treatment of these epileptiform features does not improve neurological recovery, as compared with standard of care (CPC3–5 in 90% and 92%, respectively) [43]. To note, a minority of patients with « late» epileptiform patterns (i.e., appearing after sedation weaning ≥ 24 h after CA) may present a favorable outcome if subsequently treated [69, 70], suggesting that early epileptiform features (< 24 h) could be associated with a worse neurological outcome [63]. It is of importance to underline that these “epileptiform patterns” (i.e., periodic or rhythmic discharges) must be well-differentiated from electroencephalographic seizures, as seizures are defined as high frequency (> 2.5 Hz) epileptiform discharges for ≥ 10 s or any pattern with a temporo-spatial evolution of the discharges lasting ≥ 10 s [32]. Electroencephalographic seizures and SE are mainly associated with UFO (FPR 0–17.4%, CI95%(0–26.7)) [43, 63, 68, 71, 72]. Importantly, two studies report a favorable outcome in patients with SE, these patients presenting no other markers of unfavorable outcome [73, 74]. These results suggested that isolated SE is probably not sufficient to accurately predict a poor outcome. Others malignant features and prognostic values are described in Table 3. Ultimately, malignant patterns are associated with UFO but with high FPR and large CIs. Consequently, these markers could only be considered as « minor criteria» of severe HIBI (Fig. 2).
-
Benign patterns are defined as continuous or nearly continuous and normal voltage background without any discharges. These patterns are predictive of good outcome with a moderate to high specificity (56.5–100%) and a variable sensitivity (29.6–97.9%) among studies [44, 56, 58, 61].
EEG prognostic value according to sedation, hypothermia and timing of recording
About prognostic value of EEG patterns, a major and already debated point remains the potential confounding effect of sedation. Most sedative drugs have similar effects on EEG spectrum, namely, decreasing frequency and amplitude. More specifically, light-to-moderate dose of benzodiazepines as midazolam lead to diffuse fast rhythms, whereas both high dose of midazolam and propofol generates discontinuous or even burst suppression patterns, which are both an important predictor of UFO [4, 75]. It is of importance to underline that burst suppression is usually observed with higher doses than those generally used for the management of post-CA patients [42, 76, 77]. A large post hoc analysis of a prospective multicentric study highlights that light-to-moderate sedation (i.e., maximum doses of 3.0 to 3.5 mg/kg/h of propofol and 63 to 68 µg/kg/h of midazolam) does not affect the prognostic value of EEG, despite an effect on amplitude reduction, dominant frequency and background continuity. Interestingly, patients who displayed a continuous background were sedated with higher median doses (2.67 mg/kg/h) compared to patients with burst suppression or suppression patterns (2.07 mg/kg/ and 1.94 mg/kg/h, respectively) [42]. Finally, more and more studies suggest that light-to-moderate sedation (i.e., for temperature management) does probably not significantly impair the prognostic accuracy of the early EEG (i.e., 24 h after CA) compared to recordings carried out after 48–72 h [42, 75, 76, 78]. Caution is needed when patients required deep sedation or the use of two different drugs, as the association of midazolam and propofol decreased the probability to detect benign EEG patterns [42]. Regarding temperature effect on EEG, it must be recognized that its own effect remains difficult to assess independently from the effect of sedation, as sedative drugs are almost systematically used during the first 24 h of target temperature management (TTM) after CA. Indeed, EEG could be sensitive to hypothermia, inducing a decrease of the amplitude and frequency of the EEG background (around 33 °C), a burst suppression (between 33 and 31 °C) or an isoelectric pattern (at 22 °C) [79]. These different levels of hypothermia remain lower than those currently recommended for TTM management [24, 80]. Furthermore, temperature management at 36 °C does not lead to significant EEG change [31].
Prognostic value of EEG pattern could also differ according to the timing of EEG assessment [45]. About poor outcome prediction, large prospective studies suggest that a highly malignant pattern 24 h after CA is highly correlated with severe HIBI (FPR = 0%), leading to a reduced length of ICU stay and a small cost reduction [81]. Regarding prediction of good outcome, a benign EEG recorded between 12 and 24 h after CA seems to be strongly associated with favorable outcome, with a higher specificity (between 86% and 95%) [42, 56, 67] compared to a benign EEG observed at 72 h (specificity between 65% and 78%) [42, 67]. Finally, more and more studies suggest that an early EEG recording 24 h after CA might carry a higher prognostic value compared to later recordings (i.e., after 48 h), at least when a highly malignant or benign pattern is observed, even under “light-to-moderate” dose of sedation [42, 82].
EEG reactivity
EEG reactivity (EEG-r) is defined as a transient reproductible amplitude or frequency change in response to stimulation [32]. Examination of EEG-r requires integrity of peripheral (sensory receptors) to central structures (medullar, brainstem, sub cortical and cortical networks) [33]. Modalities of stimulation usually include auditory, visual and tactile stimuli, although nature and strength protocols may differ [44, 83]. Visual inspection of EEG tracing allows to classify the background as reactive or unreactive to the stimulation. Muscle activities, eye blinks and stimulus-induced rhythmic or periodic discharges (SIRPIDS) are usually not qualified as reactivity [84, 85].
Regarding its prognostic value, loss of EEG-r tends to be associated with UFO, regardless of concomitant sedation [33, 86]. However, the FPR remain heterogeneous across studies (FPR = 0–50% CI95% (0–70.9)) limiting the use of this criteria as a robust marker of UFO. Otherwise, presence of EEG-r is associated with favorable outcome, with a specificity between 57.1% and 85% and a sensitivity between 40% and 91% [42, 44, 67, 78, 86]. Two large prospective studies also suggest that timing of assessment is of importance, as an early (12 h after CA) reactive background seems to be more specific of good outcome as compared to late assessment (48–72 h after CA) (predictive positive value PPV = 88.9% vs 55.6%, respectively [78]). At that time, the use of EEG-r is limited in different ways. First, the protocol of stimulation for EEG-r recording (stimulus type, duration and number of stimulation) is not standardized [87, 88]. Second, EEG-r interpretation is subject to inter-rater variability [44]. Admiraal et al. propose a new definition of EEG-r as any of five stimuli (sternal rub, clapping, calling patient’ name, nasal tickle and eye opening) induced a change in EEG at least twice out of the three stimuli applications [44, 83]. All together, these different limitations suggest that an unreactive background is associated with UFO but should not be used alone, as it is a “minor criteria” of severe HIBI [41].
EEG quantitative analyses
Considering that visual analysis remains subjective, quantitative analyses of the EEG signals (qEEG) using machine learning have been recently developed [89]. These qEEG modalities may be broadly categorized into spectral and connectivity analyses [90].
Spectral analyses are based on the partition of the EEG signal into different frequency bands of interest using fast Fourier transformation. The power spectral density, which corresponds to the relative distribution of the different frequency bands, is used to characterize the EEG spectrum over time. This spectral analysis density allows an “automatic” detection of high frequency picks over long time periods of continuous monitoring. As these high frequency picks may reveal seizure or status epilepticus, spectral analysis could be an interesting tool to assess outcome. Regarding prognostic value, low-power spectral values in alpha band (around 10 Hz) recorded on an early EEG seems to be highly specific of UFO (sp = 100%) [91]. These low power spectral values possibly reflect impairment of cortico-thalamic connections. Recent studies also suggested that power spectral density analyses could help to assess CMD patients, during an active EEG paradigm. This “motor command protocol” compared the EEG responses during (“keep opening and closing your hand”) and after (“stop opening and closing your hand”) motor commands, EEG signal (in selected frequency ranges) being significantly different between the two commands in CMD patients [89, 92, 93].
Connectivity analyses can be divided into functional and effective connectivity. Functional connectivity refers to a statistical dependence between two signals, which can be assessed by different linear or non-linear measures (i.e., correlation, coherence, phase, power, mutual information), while effective connectivity refers to the causal influence of one neural network over another [94,95,96,97]. However, effective connectivity is much more difficult to ascertain and metrics such as Granger causality or transfer entropy can be used with many limitations [94]. EEG connectivity could also be influenced by concomitant sedation. For example, propofol induces a reorganization of neural networks with an increased connectivity in the delta band in posterior regions [99, 100] and a persistent synchronous alpha activity in anterior regions, which is a sign of changes in the dynamic of thalamo-cortical loops [101, 102].
These qEEG analyses have also been integrated into composite prognostic markers combining spectral (i.e., frequency) and connectivity (i.e., entropy) analyses, such as the revised cerebral recovery index (rCRI). Such combination extracted from resting-state EEG has been reported to predict UFO (sp = 100%, se = 66%) [103][98]. Furthermore, automated machine learning algorithms of candidate qEEG reactivity markers have recently shown a higher predictive value for poor and good outcome compared to visual analyses [104, 105]. Despite these different results, qEEG analyses are not widely employed in routine practice, notably because of a lack of availability and also because validation studies in larger cohorts are required.
Evoked potentials
EP signal description
Evoked potentials (EPs) are neural responses time-locked to some stimulus. EPs differ from EEG signals as they are stimulus induced and represent the summated activities of large populations of neurons firing in synchrony, requiring the average of numerous stimulations. EP components are named according to their polarity (“N” for negative; “P” for positive) and their latency from the stimulation (in milliseconds). Different EPs (i.e., SSEPs, BAEPs, MLAEPs and long latency event-related potentials (ERPs) with mismatch negativity (MMN) and P300 responses) can be assessed at bedside in ICU patients, with different brain generators and prognostic values (Figs. 3, 4). A multimodal approach is recommended combining different EPs modalities to reduce the FPR and the risk of self-fulfilling prophecy risk [31, 106] (Fig. 5).
Somato-sensory evoked potentials
Somato-sensory evoked potentials (SSEPs) allow evaluation of functional integrity of the somatosensory pathways [31, 107]. Median nerve SSEPs assess this functional integrity at different main levels: N9, generated by the proximal part of the median nerve; N13, generated by the posterior columns of the spinal cord; P14, generated at the cervico-medullar level; N20, generated by the primary somatosensory cortex. A five-channel device is recommended to record and analyze these distinct components (see Fig. 3 legend). A channel C’3–C’4 scalp electrodes were positioned 2 cm posterior to C3 and C4 (C3 corresponding to the left central and C4 to the right central electrodes, using the standard electrode position nomenclature [108]). This five-channel device is mandatory to differentiate the N20 cortical component from the N18 subcortical component. N20 is identified as the major negative peak (visible on the C’3–C’4 channel), while P25 is identified as the major positive peak following N20 (Fig. 3).
Somato-sensory evoked potential (SSEP) interpretation and prognostic value in comatose and DoC patients after CA. SSEPs five channels recording with N9 (proximal part of the median nerve) N13 (posterior columns of the spinal cord) P14 (cervico-medullar level), N18 (subcortical), N20 and P25 (primary somatosensory cortex). Erb-i Erb point ipsilateral, Erb-c Erb point contralatera, Fz Midline frontal electrod, CA-Cv6 cervical anterior and cervical posterior C6 electrode, Epc-Cc centro-parietal electrode contralateral to the stimulation (C’3 or C’4) and the shoulder contralateral to the stimulatio, C’3–C’4 centro-parietal electrode ipsilateral and contralateral to the stimulation. Only one side is here presented. Pre-requisite for ERP interpretation: N9 and N13 should be present. Use of neuromuscular blockage agents is recommended if artefacts limit the recording. Part A Shows that N20 and P25 are present with a high N20–P25 amplitude. Part B Shows that N20 and P25 are present with a low N20–P25 amplitude. Part C Shows an absence of N20 and P25, with preserved N9 and N13 responses
In most studies assessing neuro-prognostication value after CA, SSEPs are mostly recorded in patients still comatose 72 h after ROSC and 48 h after sedation discontinuation. Intravenous sedative drugs have little impact on SSEPs, while hypothermia (< 33 °C) and low blood pressure may have a depressant effect. Although SSEPs can be recorded 24 h after CA, expert recommendations suggest waiting 48 h after CA and discontinuing sedation for at least 6 h [31, 109] (Table 2). Concerning recording parameters, upper limbs SSEPs are elicited by electric stimulation of the right and left median nerve using a bipolar surface electrode at the wrist (stimulus duration 0.2–0.3 ms; stimulus intensity adjusted until the obtention of visible thumb twitches or reliable N9 at Erb point; stimulus frequency 3–5 Hz; usually average of three sets of > 200 responses). Subdermal needle electrodes are recommended in the ICU environment to improve the quality of the signal. Neuromuscular blockades have no deleterious impact on SSEPs and should be considered to improve the signal to noise ratio, as the noise level should not exceed 0.25 µV. Interpretation of SSEP should be performed with a sensitivity of at least 1 µV/cm. Peripheral nerve lesions can lead to the absence of N9 and spinal cord injuries to the absence of N13 [107]. Upper limbs’ SSEPs thus need a documentation of N9 and N13 to eventually document a reliable bilateral N20 abolition. Inter observer variability seems less important for SSEPs than for EEG except in case of high noise level [110, 111]. N20 amplitude may be important for prognostication (see below), and can be measured as the N20 peak versus baseline or versus P25.
Concerning prognostic value, bilateral absence of N20 is recognized as the most robust marker of poor outcome (FPR 0%, CI95% (0.001–0.047)) [41, 112, 113] including in a population, where WLST was not performed [65]. Bilateral N20 absence probably reflects the severity of HIBI, as all patients with a bilateral N20 absence presented cortical and thalamic injuries [114]. This tool is thus already considered as one of the six prognostic markers of ERC/ESICM algorithm [4, 115].
By contrast, sensitivity of bilaterally absent N20 remains relatively low, around 30% [41, 116]; Moreover, presence of bilateral N20 is not predictive of good neurological outcome (PPV around 50%). To improve the prognostic value of SSEP, recent studies assessed the N20 and P25 amplitudes among patients with a bilateral presence of N20. For poor outcome prediction, a low voltage amplitude (between 0.40 and 1 µV according to studies [65, 70, 86, 117,118,119,120]) improved sensitivity from 30% to 50% compared to bilateral N20 absence, with a high specificity (93–100%). Conversely, a high N20–P25 amplitude (> 2.30 to 4 µV) [26, 117,118,119,120,121] predicts a favorable outcome with a high specificity (85–96%) but a moderate sensitivity (30–61%), although one study found no association with outcome [70]. Standardization of the method (i.e., SSEP N20-baseline or N20–P25 peak-to-peak measure) is needed to consider amplitude as a prognostic marker. A recent study highlighted that N20–P25 presented a higher prognostic value (AUC = 0.85) compared to N20-baseline (AUC = 0.70) [119]. Thus, N20 amplitude could be assessed as a continuum rather than a categorical variable, the underlying concept being that the amplitude of SSEP components could be inversely related to the severity of neurological injury.
Brainstem auditory evoked potentials
Brainstem auditory evoked potentials (BAEPs) are recorded in response to the listening of monoaural clicks, in the 10 ms following stimulus onset. Five waves are observed, coming from different generators. Main generators are the distal portion of the auditory nerve (wave “I”), the bulbo-mesencephalic junction (wave “III”) ipsilateral to the stimulation side, and the inferior colliculus (wave “V”) (Fig. 4). BAEPs are poorly affected by sedative drugs, and could be recorded with moderate doses. Transient use of neuromuscular blockades may be useful to limit artefacts [31] (Table 2). BAEP abolition is highly correlated with UFO with a high specificity but a low sensitivity [41, 122,123,124,125]. Conversely, BAEPs preservation is not predictive of good outcome [126]. Importantly, BAEPs assessment is essential to confirm the integrity of peripheral and brainstem auditory pathways, to secondarily record middle and late auditory evoked potentials.
Auditory evoked potentials interpretation and prognostic value in comatose and DoC patients after CA. Pre-requisite for ERP interpretation: presence of BAEP, MLAEP and N100 (primary auditory cortices responses). Use of neuromuscular blockage agents is recommended if artefacts limit the recording. Part A Shows brainstem auditory evoked potentials (BAEP) (auditory nerves and brainstem integration of the auditory stimuli). Part B Shows middle latency auditory evoked potential (MLAEP). Part C Shows late auditory ERPs with Mismatch Negativity (MMN), P300 and “local–global” effect. MMN is elicited by an auditory passive “oddball” paradigm (series of standard frequent tones and deviant infrequent tones). MMN is obtained by subtracting the ERP of the deviant and standard tones. P300 is elicited by the same “oddball” paradigm with intermix of scarce subject’s own-name stimuli. «Local–global» effect (figure adapted from Bekinschtein et al. PNAS, 2009 [140]) is recorded during an active counting task (tones with local and global deviations), patients having to count these “global deviations” which elicit a spatially cerebral distributed response called the “global effect”
Middle latency auditory evoked potentials (MLAEPs)
Middle latency auditory evoked potentials (MLAEPs) are elicited by monoaural clicks and can be recorded simultaneously to BAEPs (Fig. 4). MLAEPs are attenuated by sedative drugs and should be performed 48 h after sedation weaning (Table 2). Responses are expected in the 100 ms following the stimulus onset and is composed of two waves: Na and Pa. Bilateral abolition of Na and Pa responses is associated with UFO with a high specificity (100%) but a low sensitivity (37%) [126]. By contrast, their preservation has no prognostic value although one study found a correlation between MLAEP and ROSC, survival and neurologic outcome [127].
N100 responses
N100 response is an auditory event-related potential (ERP), which reflects the activation of primary auditory cortices. The absence of N100 is considered to be predictive of a UFO, their recording being also an indispensable pre-requisite to record MMN [31].
Long latency event-related potentials (ERPs)
Long latency event-related potentials (ERPs), also called endogenous potentials, are supposed to reflect a cognitive attention task. Accordingly, ERPs may provide relevant markers of cognitive functions in unresponsive state patients, and thus detect patients who could be in a “recovery process”. As ERPs responses are highly sensitive to the arousal state but also to sedation, ERPs should be performed in case of persistent unresponsive state 48 h after sedation discontinuation (Table 2). Neuromuscular blockades are often useful to limit artefacts. Many auditory paradigms have been described to elicit long latency ERPs but only a few of them are used for neuro-prognostication (Fig. 4).
Mismatch negativity (MMN)
Auditory MMN is elicited by an “oddball” paradigm, in which series of standard frequent tones and deviant infrequent tones are played binaurally, without any active participation asked of the patient (i.e., passive paradigm). Standard and deviant tones differ in one of their acoustic characteristics (intensity, frequency, or duration) and their probabilities of occurrence (standard: ± 86% of time; deviant: ± 14%). MMN is obtained by subtracting the ERP of deviant tones from the ERP of standard tones on midline electrodes (Fz, Cz, Pz), between 100 and 250 ms post-stimulation (Fig. 4). According to surface and intracranial EEG, magneto-encephalography (MEG) and fMRI studies, MMN responses involve two main intracranial processes, the first one in the bilateral supratemporal cortices and the second predominantly in the frontal areas [128,129,130,131]. This response is supposed to reflect an automatic and pre-attentive detection of auditory violations [128]. Despite this, attention is a necessary prerequisite for consciousness, but possible dissociation between attention and consciousness has been demonstrated [132, 133].
About prognostic value, Fischer et al. assessed 62 DoC patients with ERPs, in a median time of 8 days after CA. In this study, the presence of MMN was a predictive marker of awakening (defined as neither dead nor permanent VS), with a PPV of 100% (CI95% (78–99)) and a negative predictive value (NPV) of 84% (CI95% (71–93)) [109]. These results were confirmed by further studies, including studies performed during therapeutic hypothermia [134,135,136,137,138]. In one study, some patients demonstrated a preserved MMN in a very acute stage (< 24 h after CA during hypothermia) and successively lost this response in a second MMN recording (performed > 24 h after CA, during normothermia) [134]. None of these patients regained consciousness. Finally, MMN predicts awakening but does not exclude mild to severe neurological disability, as this response could be observed in around 35% of MCS patients and has been sometimes described in VS patients [9]. MMN also predicts awakening with an heterogenous sensitivity (between 27% and 100% among studies [9, 139,140,141]) emphasizing the need for additional prognostic markers [9, 141]. Moreover, due to the oddball paradigm with a few number of averaged deviant stimuli, MMN responses are sometimes difficult to distinguish from background activities. Accordingly, limited inter-rater agreement has been demonstrated [142]. Some authors proposed automated procedures with statistical validations. However, these procedures displayed contradictory results and should only be used as complementary to the visual analysis [143].
P300 responses evoked by subject’s own name
P300 response is a complex positive response recorded during the oddball paradigm 300 to 350 ms after stimulus, if the patient focuses attention on deviant stimuli [144, 145] (Fig. 4). This response is amplified if the deviant stimulus is relevant for the patient. Thus, some studies demonstrated the effectiveness of the subject own-name stimuli to elicit the P300 response [146, 147]. Oddball paradigms have been developed to record simultaneously MMN and P300, also using scarce subject’s own-name for P300 recording [138, 139]. This P300 is supposed to express a brain evaluation of novelty before behavioral reaction [148]. Intracranial EEG and fMRI paradigms identified a widespread network behind the P300 response, from the prefrontal cortex to the inferior parietal areas [149,150,151].
About prognostic value, a limited cohort study suggested that P300 predicts awakening (defined as neither dead nor permanent VS or MCS) with a PPV of 100% (CI95% (61–100)), and a NPV of 93% (CI95% (66–100)) [138]. It is of importance to underline that P300 has mainly been evaluated in cohorts of sub-acute or chronic DoC patients (in 3 months after CA), the prognostic value of these responses being poorly evaluated at the acute stage of DoC after CA. Accordingly, P300 is an interesting marker for awakening prediction but does not seem to rule out mild to severe cognitive disabilities. Finally, visual interpretation of the P300 response may be sometimes challenging. Recommendations have been made for future statistical validations to be added to clinical practice [31]. These different results about prognostic value of P300 need to be confirmed in larger prospective studies.
Active counting task: the «local–global» auditory paradigm
The «local–global» effect described by Bekinschtein [140] and colleagues is an active counting task, where patients listen to an auditory paradigm including local deviations (i.e., inside a series of five brief tones: all identical or only the last one different) and global deviation (i.e., on a longer time scale, successive series constitute a global regularity, which is violated by the irruption of 20% of different series). Patients are asked to count these “global deviations” which elicit a spatially cerebral distributed response (called the “global effect”) considered as a reliable marker of consciousness. Absence of “global effect” does not exclude residual consciousness as in healthy subjects, global effect disappeared if subjects are distracted by a visual interference task [140]. The same authors confirmed the high PPV (close to 100%) of this “global effect” to probe consciousness, despite a low NPV [152]. However, Tzovara et al. identified this “global effect” in only 10/24 post-anoxic comatose patients (including 5 sedated patients) [153]. These significant discrepancies from previous studies could be explained firstly by the differences in the timing of DoC assessment (earlier than previous studies), second by the difference in acoustical characteristics of stimuli and third by the difference in EEG analysis and statistic variability [143, 154]. Further studies are mandatory to evaluate this prognostic marker.
To highlight and summarize the interest of these different tools in patients with “indeterminate neurological outcome” after CA, we propose an algorithm of neuro-prognostication involving these potentials neurophysiological prognostic markers, use as a complement of the ERC/ESICM 2021 guidelines (Fig. 5).
Algorithm of neuro-prognostication using neurophysiological markers, as a complement of the ERC/ESICM 2021 guidelines [4]. (*) We suggest to use a multimodal approach, including non-neurophysiological prognostic markers (biomarkers as NSE, brain imaging, pupillary and corneal reflexes and clinical status myoclonus). BAEP brainstem auditory evoked potential, CT computed tomography, EEG electroencephalogram, ERP event-related potential, FPR false positive rate, GCS Glasgow coma scale, MLAEP middle latency auditory evoked potential, MRI magnetic resonance imaging, NSE neuron specific enolase, SSEP somatosensory evoked potential
Conclusion
In comatose cardiac arrest patients, recent advances in clinical research now allow a better use of neurophysiological tools, including increased discernment in a multimodal approach. Importantly, their availability currently remains the main limitation to their routine use in intensive care units. Finally, if their efficacy is firmly established for the prediction of an unfavorable neurological evolution, ongoing research will probably make it possible to use them to better predict a favorable evolution in the next future.
Availability of data and materials
We confirm that the figures are original and have not been published elsewhere.
Abbreviations
- ACNS:
-
American clinical neurophysiology society
- BAEP:
-
Brainstem auditory evoked potentials
- CA:
-
Cardiac arrest
- cEEG:
-
Continuous EEG
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CMD:
-
Cognitive-motor dissociation
- CMS:
-
Cortically mediated state
- CPC:
-
Cerebral performance category
- DoC:
-
Disorders of consciousness
- EEG:
-
Electroencephalogram
- EER-r:
-
EEG reactivity
- ERP:
-
Event-related potentials
- FPR:
-
False positive rate
- GCS:
-
Glasgow coma scale
- GOS-E:
-
Glasgow outcome scale-Extended
- HIBI:
-
Hypoxic ischemic brain injury
- ICU:
-
Intensive-care-unit
- IQR:
-
Interquartile-range
- MCS:
-
Minimal consciousness state
- MEG:
-
Magneto-encephalography
- MLAEP:
-
Middle latency auditory evoked potentials
- MMN:
-
Mismatch negativity
- mRS:
-
Modified Rankin Scale
- NPV:
-
Negative Predictive Value
- NSE:
-
Neuron Specific Enolase
- PPV:
-
Positive Predictive Value
- qEEG:
-
Quantitative EEG
- RASS:
-
Richmond–Agitation–Sedation-Scale
- rCRI:
-
Revised cerebral recovery index
- ROSC:
-
Return of Spontaneous Circulation
- SD:
-
Standard Deviation
- SE:
-
Status epilepticus
- Se:
-
Sensitivity
- SIRPIDS:
-
Stimulus-induced rhythmic or periodic discharges
- Sp:
-
Specificity
- SSEP:
-
Somatosensory Evoked Potentials
- TTM:
-
Targeted Temperature Management
- UFO:
-
Unfavorable outcome
- VS:
-
Vegetative state
- WLST:
-
Withdrawal-of-Life-Sustaining-Treatments
- µV:
-
MicroVolt
References
Cronberg T, Greer DM, Lilja G, Moulaert V, Swindell P, Rossetti AO. Brain injury after cardiac arrest: from prognostication of comatose patients to rehabilitation. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19(7):611–22.
Perkins GD, Callaway CW, Haywood K, Neumar RW, Lilja G, Rowland MJ, et al. Brain injury after cardiac arrest. Lancet. 2021;398(10307):1269–78.
Sandroni C, Cronberg T, Sekhon M. Brain injury after cardiac arrest: pathophysiology, treatment, and prognosis. Intensive Care Med. 2021;47(12):1393–414.
Nolan JP, Sandroni C, Böttiger BW, Cariou A, Cronberg T, Friberg H, et al. European resuscitation council and European society of intensive care medicine guidelines 2021: post-resuscitation care. Intensive Care Med. 2021;47(4):369–421.
Lee DH, Cho YS, Lee BK, Lee HY, Jeung KW, Jung YH, et al. Late awakening is common in settings without withdrawal of life-sustaining therapy in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest survivors who undergo targeted temperature management. Crit Care Med. 2022;50(2):235–44.
Paul M, Bougouin W, Geri G, Dumas F, Champigneulle B, Legriel S, et al. Delayed awakening after cardiac arrest: prevalence and risk factors in the Parisian registry. Intensive Care Med. 2016;42(7):1128–36.
Paul M, Bougouin W, Dumas F, Geri G, Champigneulle B, Guillemet L, et al. Comparison of two sedation regimens during targeted temperature management after cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2018;128:204–10.
Rey A, Rossetti AO, Miroz JP, Eckert P, Oddo M. Late Awakening in survivors of postanoxic coma: early neurophysiologic predictors and association with ICU and long-term neurologic recovery. Crit Care Med. 2019;47(1):85–92.
Comanducci A, Boly M, Claassen J, De Lucia M, Gibson RM, Juan E, et al. Clinical and advanced neurophysiology in the prognostic and diagnostic evaluation of disorders of consciousness: review of an IFCN-endorsed expert group. Clin Neurophysiol. 2020;131(11):2736–65.
Kondziella D, Bender A, Diserens K, van Erp W, Estraneo A, Formisano R, et al. European academy of neurology guideline on the diagnosis of coma and other disorders of consciousness. Eur J Neurol mai. 2020;27(5):741–56.
Plum F, Posner JB. The diagnosis of stupor and coma. Contemp Neurol Ser. 1972;10:1–286.
Giacino JT. Disorders of consciousness: differential diagnosis and neuropathologic features. Semin Neurol. 1997;17(2):105–11.
Luauté J, Maucort-Boulch D, Tell L, Quelard F, Sarraf T, Iwaz J, et al. Long-term outcomes of chronic minimally conscious and vegetative states. Neurology. 2010;75(3):246–52.
Faugeras F, Rohaut B, Valente M, Sitt J, Demeret S, Bolgert F, et al. Survival and consciousness recovery are better in the minimally conscious state than in the vegetative state. Brain Inj. 2018;32(1):72–7.
Edgren E, Hedstrand U, Kelsey S, Sutton-Tyrrell K, Safar P. Assessment of neurological prognosis in comatose survivors of cardiac arrest BRCT I study group. Lancet. 1994;343(8905):1055–9.
Taccone FS, Horn J, Storm C, Cariou A, Sandroni C, Friberg H, et al. Death after awakening from post-anoxic coma: the “Best CPC” project. Crit Care. 2019;23(1):107.
Jennett B, Snoek J, Bond MR, Brooks N. Disability after severe head injury: observations on the use of the glasgow outcome scale. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1981;44(4):285–93.
Rankin J. Cerebral vascular accidents in patients over the age of 60. II. Prognosis. Scott Med J. 1957;2(5):200–15.
Arrich J, Zeiner A, Sterz F, Janata A, Uray T, Richling N, et al. Factors associated with a change in functional outcome between one month and six months after cardiac arrest: a retrospective cohort study. Resuscitation. 2009;80(8):876–80.
Geocadin RG, Callaway CW, Fink EL, Golan E, Greer DM, Ko NU, et al. Standards for studies of neurological prognostication in comatose survivors of cardiac arrest: a scientific statement from the American heart association. Circulation. 2019;140(9):e517–42.
Nielsen N, Wetterslev J, Cronberg T, Erlinge D, Gasche Y, Hassager C, et al. Targeted temperature management at 33°C versus 36°C after cardiac arrest. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(23):2197–206.
Dankiewicz J, Cronberg T, Lilja G, Jakobsen JC, Levin H, Ullén S, et al. Hypothermia versus normothermia after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(24):2283–94.
Rouche O, Wolak-Thierry A, Destoop Q, Milloncourt L, Floch T, Raclot P, et al. Evaluation of the depth of sedation in an intensive care unit based on the photo motor reflex variations measured by video pupillometry. Ann Intensive Care. 2013;3(1):5.
Sandroni C, Nolan JP, Andersen LW, Böttiger BW, Cariou A, Cronberg T, et al. ERC-ESICM guidelines on temperature control after cardiac arrest in adults. Intensive Care Med. 2022;48(3):261–9.
Bongiovanni F. Standardized EEG analysis to reduce the uncertainty of outcome prognostication after cardiac arrest. Intensive Care Med. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-019-05921-6.
Sandroni C, D’Arrigo S, Cacciola S, Hoedemaekers CWE, Westhall E, Kamps MJA, et al. Prediction of good neurological outcome in comatose survivors of cardiac arrest: a systematic review. Intensive Care Med. 2022;48(4):389–413.
Lopes da Silva F. EEG and MEG: relevance to neuroscience. Neuron. 2013;80(5):1112–28.
Buzsáki G, Anastassiou CA, Koch C. The origin of extracellular fields and currents–EEG, ECoG LFP and spikes. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012;13(6):407–20.
Gavaret M, Maillard L, Jung J. High-resolution EEG (HR-EEG) and magnetoencephalography (MEG). Neurophysiol Clin Clin Neurophysiol. 2015;45(1):105–11.
Claassen J, Taccone FS, Horn P, Holtkamp M, Stocchetti N, Oddo M, et al. Recommendations on the use of EEG monitoring in critically ill patients: consensus statement from the neurointensive care section of the ESICM. Intensive Care Med. 2013;39(8):1337–51.
André-Obadia N, Zyss J, Gavaret M, Lefaucheur JP, Azabou E, Boulogne S, et al. Recommendations for the use of electroencephalography and evoked potentials in comatose patients. Neurophysiol Clin. 2018;48(3):143–69.
Hirsch LJ, et al. American clinical neurophysiology society’s standardized critical care EEG terminology: 2021 version. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2021;38(1):1–29. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNP0000000000000806.
Benghanem S, Mazeraud A, Azabou E, Chhor V, Shinotsuka CR, Claassen J, et al. Brainstem dysfunction in critically ill patients. Crit Care Lond Engl. 2020;24(1):5.
Steriade M, Amzica F, Contreras D. Cortical and thalamic cellular correlates of electroencephalographic burst-suppression. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1994;90(1):1–16.
Japaridze N, Muthuraman M, Reinicke C, Moeller F, Anwar AR, Mideksa KG, et al. Neuronal networks during burst suppression as revealed by source analysis. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(4):e0123807.
Lehembre R, Gosseries O, Lugo Z, Jedidi Z, Chatelle C, Sadzot B, et al. Electrophysiological investigations of brain function in coma, vegetative and minimally conscious patients. Arch Ital Biol. 2012;150(2–3):122–39.
Landsness E, Bruno MA, Noirhomme Q, Riedner B, Gosseries O, Schnakers C, et al. Electrophysiological correlates of behavioural changes in vigilance in vegetative state and minimally conscious state. Brain J Neurol. 2011;134(Pt 8):2222–32.
Maciel CB, Barden MM, Youn TS, Dhakar MB, Greer DM. Neuroprognostication practices in postcardiac arrest patients: an international survey of critical care providers. Crit Care Med. 2020;48(2):e107–14.
Friberg H, Cronberg T, Dünser MW, Duranteau J, Horn J, Oddo M. Survey on current practices for neurological prognostication after cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2015;90:158–62.
Kim YJ, Kim MJ, Kim YH, Youn CS, Cho IS, Kim SJ, et al. Background frequency can enhance the prognostication power of EEG patterns categories in comatose cardiac arrest survivors: a prospective, multicenter, observational cohort study. Crit Care Lond Engl. 2021;25(1):398.
Sandroni C, D’Arrigo S, Cacciola S, Hoedemaekers CWE, Kamps MJA, Oddo M, et al. Prediction of poor neurological outcome in comatose survivors of cardiac arrest: a systematic review. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46(10):1803–51.
Ruijter BJ, van Putten MJAM, van den Bergh WM, Tromp SC, Hofmeijer J. Propofol does not affect the reliability of early EEG for outcome prediction of comatose patients after cardiac arrest. Clin Neurophysiol. 2019;130(8):1263–70.
Ruijter BJ, Keijzer HM, Tjepkema-Cloostermans MC, Blans MJ, Beishuizen A, Tromp SC, et al. Treating rhythmic and periodic EEG patterns in comatose survivors of cardiac arrest. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(8):724–34.
Admiraal MM, van Rootselaar AF, Hofmeijer J, Hoedemaekers CWE, van Kaam CR, Keijzer HM, et al. Electroencephalographic reactivity as predictor of neurological outcome in postanoxic coma: a multicenter prospective cohort study. Ann Neurol. 2019;86(1):17–27.
Beuchat I, Solari D, Novy J, Oddo M, Rossetti AO. Standardized EEG interpretation in patients after cardiac arrest: correlation with other prognostic predictors. Resuscitation. 2018;126:143–6.
André-Obadia N, Sauleau P, Cheliout-Heraut F, Convers P, Debs R, Eisermann M, et al. French guidelines on electroencephalogram. Neurophysiol Clin Clin Neurophysiol. 2014;44(6):515–612.
Battaglini D, Pelosi P, Robba C. The Importance of neuromonitoring in non brain injured patients. Crit Care Lond Engl. 2022;26(1):78.
Fatuzzo D, Beuchat I, Alvarez V, Novy J, Oddo M, Rossetti AO. Does continuous EEG influence prognosis in patients after cardiac arrest? Resuscitation. 2018;132:29–32.
Rossetti AO, Schindler K, Sutter R, Rüegg S, Zubler F, Novy J, et al. Continuous vs routine electroencephalogram in critically ill adults with altered consciousness and no recent seizure: a multicenter randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol. 2020;77(10):1225–32.
Alvarez V, Sierra-Marcos A, Oddo M, Rossetti AO. Yield of intermittent versus continuous EEG in comatose survivors of cardiac arrest treated with hypothermia. Crit Care Lond Engl. 2013;17(5):R190.
Urbano V, Novy J, Alvarez V, Schindler K, Rüegg S, Rossetti AO. EEG recording latency in critically ill patients: impact on outcome. an analysis of a randomized controlled trial (CERTA). Clin Neurophysiol. 2022;139:23–7.
Pati S, McClain L, Moura L, Fan Y, Westover MB. Accuracy of limited-montage electroencephalography in monitoring postanoxic comatose patients. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2017;48(6):422–7.
Touchard C, Cartailler J, Vellieux G, de Montmollin E, Jaquet P, Wanono R, et al. Simplified frontal EEG in adults under veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Ann Intensive Care. 2021;11(1):76.
Synek VM. Prognostically important EEG coma patterns in diffuse anoxic and traumatic encephalopathies in adults. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1988;5(2):161–74.
Young GB, McLachlan RS, Kreeft JH, Demelo JD. An electroencephalographic classification for coma. Can J Neurol Sci. 1997;24(4):320–5.
Hofmeijer J, Beernink TMJ, Bosch FH, Beishuizen A, Tjepkema-Cloostermans MC, van Putten MJAM. Early EEG contributes to multimodal outcome prediction of postanoxic coma. Neurology. 2015;85(2):137–43.
Gaspard N, Hirsch LJ, LaRoche SM, Hahn CD, Westover MB, Critical Care EEG Monitoring Research Consortium. Interrater agreement for critical care EEG terminology. Epilepsia. 2014;55(9):1366–73.
Westhall E, Rossetti AO, van Rootselaar AF, Wesenberg Kjaer T, Horn J, Ullén S, et al. Standardized EEG interpretation accurately predicts prognosis after cardiac arrest. Neurology. 2016;86(16):1482–90.
Gaspard N. ACNS critical care EEG terminology: value, limitations, and perspectives. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2015;32(6):452–5.
De Stefano P, Seeck M, Rossetti AO. Critical care EEG standardized nomenclature in clinical practice: strengths, limitations, and outlook on the example of prognostication after cardiac arrest. Clin Neurophysiol Pract. 2021;6:149–54.
Duez CHV, Johnsen B, Ebbesen MQ, Kvaløy MB, Grejs AM, Jeppesen AN, et al. Post resuscitation prognostication by EEG in 24 vs 48 h of targeted temperature management. Resuscitation. 2019;135:145–52.
Lamartine Monteiro M, Taccone FS, Depondt C, Lamanna I, Gaspard N, Ligot N, et al. The prognostic value of 48-h continuous EEG during therapeutic hypothermia after cardiac arrest. Neurocrit Care. 2016;24(2):153–62.
Backman S, Cronberg T, Friberg H, Ullén S, Horn J, Kjaergaard J, et al. Highly malignant routine EEG predicts poor prognosis after cardiac arrest in the target temperature management trial. Resuscitation. 2018;131:24–8.
Westhall E, Rosén I, Rossetti AO, van Rootselaar AF, Kjaer TW, Horn J, et al. Electroencephalography (EEG) for neurological prognostication after cardiac arrest and targeted temperature management; rationale and study design. BMC Neurol. 2014;14:159.
Scarpino M, Carrai R, Lolli F, Lanzo G, Spalletti M, Valzania F, et al. Neurophysiology for predicting good and poor neurological outcome at 12 and 72 h after cardiac arrest: the ProNeCA multicentre prospective study. Resuscitation. 2020;147:95–103.
Nadjar Y, Levy P, Nguyen-Michel VH, Luyt CE, Puybasset L, Navarro V. Prognostic value of electroencephalographic paroxysms in post-anoxic coma: a new regularity EEG-based score. Neurophysiol Clin. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucli.2022.03.007.
Rossetti AO, Rabinstein AA, Oddo M. Neurological prognostication of outcome in patients in coma after cardiac arrest. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15(6):597–609.
Sadaka F, Doerr D, Hindia J, Lee KP, Logan W. Continuous electroencephalogram in comatose postcardiac arrest syndrome patients treated with therapeutic hypothermia: outcome prediction study. J Intensive Care Med. 2015;30(5):292–6.
Rossetti AO, Oddo M, Liaudet L, Kaplan PW. Predictors of awakening from postanoxic status epilepticus after therapeutic hypothermia. Neurology. 2009;72(8):744–9.
Barbella G, Novy J, Marques-Vidal P, Oddo M, Rossetti AO. Added value of somato-sensory evoked potentials amplitude for prognostication after cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2020;149:17–23.
Amorim E, Rittenberger JC, Zheng JJ, Westover MB, Baldwin ME, Callaway CW, et al. Continuous EEG monitoring enhances multimodal outcome prediction in hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Resuscitation. 2016;109:121–6.
Youn CS, Callaway CW, Rittenberger JC, Post Cardiac Arrest Service. Combination of initial neurologic examination, quantitative brain imaging and electroencephalography to predict outcome after cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2017;110:120–5.
Legriel S, Bruneel F, Sediri H, Hilly J, Abbosh N, Lagarrigue MH, et al. Early EEG monitoring for detecting postanoxic status epilepticus during therapeutic hypothermia: a pilot study. Neurocrit Care. 2009;11(3):338–44.
Beretta S, Coppo A, Bianchi E, Zanchi C, Carone D, Stabile A, et al. Neurologic outcome of postanoxic refractory status epilepticus after aggressive treatment. Neurology. 2018;91(23):e2153–62.
Drohan CM, Cardi AI, Rittenberger JC, Popescu A, Callaway CW, Baldwin ME, et al. Effect of sedation on quantitative electroencephalography after cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2018;124:132–7.
Sivaraju A, Gilmore EJ, Wira CR, Stevens A, Rampal N, Moeller JJ, et al. Prognostication of post-cardiac arrest coma: early clinical and electroencephalographic predictors of outcome. Intensive Care Med. 2015;41(7):1264–72.
Huotari AM, Koskinen M, Suominen K, Alahuhta S, Remes R, Hartikainen KM, et al. Evoked EEG patterns during burst suppression with propofol. Br J Anaesth. 2004;92(1):18–24.
Admiraal MM, Horn J, Hofmeijer J, Hoedemaekers CWE, van Kaam CR, Keijzer HM, et al. EEG reactivity testing for prediction of good outcome in patients after cardiac arrest. Neurology. 2020;95(6):e653–61.
Crepeau AZ, Rabinstein AA, Fugate JE, Mandrekar J, Wijdicks EF, White RD, et al. Continuous EEG in therapeutic hypothermia after cardiac arrest: prognostic and clinical value. Neurology. 2013;80(4):339–44.
Nolan JP, Soar J. Temperature control after cardiac arrest: friend or foe. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2022;28(3):244–9.
Sondag L, Ruijter BJ, Tjepkema-Cloostermans MC, Beishuizen A, Bosch FH, van Til JA, et al. Early EEG for outcome prediction of postanoxic coma: prospective cohort study with cost-minimization analysis. Crit Care Lond Engl. 2017;21(1):111.
Rossetti AO, Carrera E, Oddo M. Early EEG correlates of neuronal injury after brain anoxia. Neurology. 2012;78(11):796–802.
Admiraal MM, van Rootselaar AF, Horn J. International consensus on EEG reactivity testing after cardiac arrest: towards standardization. Resuscitation. 2018;131:36–41.
Alvarez V, Oddo M, Rossetti AO. Stimulus-induced rhythmic, periodic or ictal discharges (SIRPIDs) in comatose survivors of cardiac arrest: characteristics and prognostic value. Clin Neurophysiol. 2013;124(1):204–8.
Caporro M, Rossetti AO, Seiler A, Kustermann T, Nguepnjo Nguissi NA, Pfeiffer C, et al. Electromyographic reactivity measured with scalp-EEG contributes to prognostication after cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2019;138:146–52.
Benghanem S, Paul M, Charpentier J, Rouhani S, Ben Hadj Salem O, Guillemet L, et al. Value of EEG reactivity for prediction of neurologic outcome after cardiac arrest: insights from the Parisian registry. Resuscitation. 2019;142:168–74.
Tsetsou S, Novy J, Oddo M, Rossetti AO. EEG reactivity to pain in comatose patients: importance of the stimulus type. Resuscitation. 2015;97:34–7.
Fantaneanu TA, Tolchin B, Alvarez V, Friolet R, Avery K, Scirica BM, et al. Effect of stimulus type and temperature on EEG reactivity in cardiac arrest. Clin Neurophysiol. 2016;127(11):3412–7.
Alkhachroum A, Appavu B, Egawa S, Foreman B, Gaspard N, Gilmore EJ, et al. Electroencephalogram in the intensive care unit: a focused look at acute brain injury. Intensive Care Med. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-022-06854-3.
Asgari S, Moshirvaziri H, Scalzo F, Ramezan-Arab N. Quantitative measures of EEG for prediction of outcome in cardiac arrest subjects treated with hypothermia: a literature review. J Clin Monit Comput. 2018;32(6):977–92.
Kustermann T, Nguepnjo Nguissi NA, Pfeiffer C, Haenggi M, Kurmann R, Zubler F, et al. Electroencephalography-based power spectra allow coma outcome prediction within 24 h of cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2019;142:162–7.
Claassen J, Doyle K, Matory A, Couch C, Burger KM, Velazquez A, et al. Detection of brain activation in unresponsive patients with acute brain injury. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(26):2497–505.
Schiff ND. Cognitive motor dissociation following severe brain injuries. JAMA Neurol. 2015;72(12):1413–5.
Friston KJ. Functional and effective connectivity: a review. Brain Connect. 2011;1(1):13–36.
Sakkalis V. Review of advanced techniques for the estimation of brain connectivity measured with EEG/MEG. Comput Biol Med. 2011;41(12):1110–7.
Fingelkurts AA, Fingelkurts AA, Kähkönen S. Functional connectivity in the brain—is it an elusive concept? Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2005;28(8):827–36.
Horwitz B. The elusive concept of brain connectivity. Neuroimage. 2003;19(2 Pt 1):466–70.
Zubler F, Steimer A, Kurmann R, Bandarabadi M, Novy J, Gast H, et al. EEG synchronization measures are early outcome predictors in comatose patients after cardiac arrest. Clin Neurophysiol. 2017;128(4):635–42.
Lee M, Sanders RD, Yeom SK, Won DO, Seo KS, Kim HJ, et al. Network properties in transitions of consciousness during propofol-induced sedation. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):16791.
Numan T, Slooter AJC, van der Kooi AW, Hoekman AML, Suyker WJL, Stam CJ, et al. Functional connectivity and network analysis during hypoactive delirium and recovery from anesthesia. Clin Neurophysiol. 2017;128(6):914–24.
Ching S, Cimenser A, Purdon PL, Brown EN, Kopell NJ. Thalamocortical model for a propofol-induced alpha-rhythm associated with loss of consciousness. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(52):22665–70.
Ghassemi MM, Amorim E, Alhanai T, Lee JW, Herman ST, Sivaraju A, et al. Quantitative electroencephalogram trends predict recovery in hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Crit Care Med. 2019;47(10):1416–23.
Nagaraj SB, Tjepkema-Cloostermans MC, Ruijter BJ, Hofmeijer J, van Putten MJAM. The revised Cerebral recovery index improves predictions of neurological outcome after cardiac arrest. Clin Neurophysiol. 2018;129(12):2557–66.
Amorim E, van der Stoel M, Nagaraj SB, Ghassemi MM, Jing J, O’Reilly UM, et al. Quantitative EEG reactivity and machine learning for prognostication in hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Clin Neurophysiol. 2019;130(10):1908–16.
Admiraal MM, Ramos LA, Delgado Olabarriaga S, Marquering HA, Horn J, van Rootselaar AF. Quantitative analysis of EEG reactivity for neurological prognostication after cardiac arrest. Clin Neurophysiol. 2021;132(9):2240–7.
Pruvost-Robieux E, Marchi A, Martinelli I, Bouchereau E, Gavaret M. Evoked and event-related potentials as biomarkers of consciousness state and recovery. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2022;39(1):22–31.
Morizot-Koutlidis R, André-Obadia N, Antoine JC, Attarian S, Ayache SS, Azabou E, et al. Somatosensory evoked potentials in the assessment of peripheral neuropathies: commented results of a survey among French-speaking practitioners and recommendations for practice. Neurophysiol Clin. 2015;45(2):131–42.
Acharya JN, Hani AJ, Cheek J, Thirumala P, Tsuchida TN. American clinical neurophysiology society guideline 2: guidelines for standard electrode position nomenclature. Neurodiagnostic J. 2016;56(4):245–52.
Fischer C, Luauté J, Némoz C, Morlet D, Kirkorian G, Mauguière F. Improved prediction of awakening or nonawakening from severe anoxic coma using tree-based classification analysis. Crit Care Med. 2006;34(5):1520–4.
Pfeifer R, Weitzel S, Günther A, Berrouschot J, Fischer M, Isenmann S, et al. Investigation of the inter-observer variability effect on the prognostic value of somatosensory evoked potentials of the median nerve (SSEP) in cardiac arrest survivors using an SSEP classification. Resuscitation. 2013;84(10):1375–81.
Zandbergen EGJ, Hijdra A, de Haan RJ, van Dijk JG, Ongerboer de Visser BW, Spaans F, et al. Interobserver variation in the interpretation of SSEPs in anoxic-ischaemic coma. Clin Neurophysiol. 2006;117(7):1529–35.
Robinson LR, Micklesen PJ, Tirschwell DL, Lew HL. Predictive value of somatosensory evoked potentials for awakening from coma. Crit Care Med. 2003;31(3):960–7.
Kamps MJA, Horn J, Oddo M, Fugate JE, Storm C, Cronberg T, et al. Prognostication of neurologic outcome in cardiac arrest patients after mild therapeutic hypothermia: a meta-analysis of the current literature. Intensive Care Med. 2013;39(10):1671–82.
van Putten MJAM, Jansen C, Tjepkema-Cloostermans MC, Beernink TMJ, Koot R, Bosch F, et al. Postmortem histopathology of electroencephalography and evoked potentials in postanoxic coma. Resuscitation. 2019;134:26–32.
Wijdicks EFM, Hijdra A, Young GB, Bassetti CL, Wiebe S, Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Practice parameter: prediction of outcome in comatose survivors after cardiopulmonary resuscitation (an evidence-based review): report of the quality standards subcommittee of the american academy of neurology. Neurology. 2006;67(2):203–10.
van Putten MJAM. The N20 in post-anoxic coma: are you listening? Clin Neurophysiol. 2012;123(7):1460–4.
Endisch C, Storm C, Ploner CJ, Leithner C. Amplitudes of SSEP and outcome in cardiac arrest survivors: a prospective cohort study. Neurology. 2015;85(20):1752–60.
Glimmerveen AB, Keijzer HM, Ruijter BJ, Tjepkema-Cloostermans MC, van Putten MJAM, Hofmeijer J. Relevance of somatosensory evoked potential amplitude after cardiac arrest. Front Neurol. 2020;11:335.
Benghanem S, Nguyen LS, Gavaret M, Mira JP, Pène F, Charpentier J, et al. SSEP N20 and P25 amplitudes predict poor and good neurologic outcomes after cardiac arrest. Ann Intensive Care. 2022;12(1):25.
Scarpino M, Lolli F, Lanzo G, Carrai R, Spalletti M, Valzania F, et al. SSEP amplitude accurately predicts both good and poor neurological outcome early after cardiac arrest; a post-hoc analysis of the ProNeCA multicentre study. Resuscitation. 2021;163:162–71.
Oh SH, Park KN, Choi SP, Oh JS, Kim HJ, Youn CS, et al. Beyond dichotomy: patterns and amplitudes of SSEPs and neurological outcomes after cardiac arrest. Crit Care. 2019;23(1):224.
Huntgeburth M, Adler C, Rosenkranz S, Zobel C, Haupt WF, Dohmen C, et al. Changes in neuron-specific enolase are more suitable than its absolute serum levels for the prediction of neurologic outcome in hypothermia-treated patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Neurocrit Care. 2014;20(3):358–66.
De Santis P, Lamanna I, Mavroudakis N, Legros B, Vincent JL, Creteur J, et al. The potential role of auditory evoked potentials to assess prognosis in comatose survivors from cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2017;120:119–24.
Elmer J, Steinberg A. Auditory evoked responses have limited utility after cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2020;154:115–6.
Tiainen M, Kovala TT, Takkunen OS, Roine RO. Somatosensory and brainstem auditory evoked potentials in cardiac arrest patients treated with hypothermia. Crit Care Med. 2005;33(8):1736–40.
Logi F, Fischer C, Murri L, Mauguière F. The prognostic value of evoked responses from primary somatosensory and auditory cortex in comatose patients. Clin Neurophysiol. 2003;114(9):1615–27.
Tsurukiri J, Mishima S, Ohta S. Initial middle latency auditory evoked potentials index helps to predict resuscitated outcomes in patients with cardiac arrest. Am J Emerg Med. 2013;31(6):895–9.
Näätänen R, Sussman ES, Salisbury D, Shafer VL. Mismatch negativity (MMN) as an index of cognitive dysfunction. Brain Topogr. 2014;27(4):451–66.
Alho K. Cerebral generators of mismatch negativity (MMN) and its magnetic counterpart (MMNm) elicited by sound changes. Ear Hear. 1995;16(1):38–51.
Halgren E, Baudena P, Clarke JM, Heit G, Liégeois C, Chauvel P, et al. Intracerebral potentials to rare target and distractor auditory and visual stimuli. I. superior temporal plane and parietal lobe. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1995;94(3):191–220.
Rinne T, Degerman A, Alho K. Superior temporal and inferior frontal cortices are activated by infrequent sound duration decrements: an fMRI study. Neuroimage. 2005;26(1):66–72.
Mashour GA, Roelfsema P, Changeux JP, Dehaene S. Conscious processing and the global neuronal workspace hypothesis. Neuron. 2020;105(5):776–98.
Madl T, Baars BJ, Franklin S. The timing of the cognitive cycle. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(4):e14803.
Tzovara A, Rossetti AO, Spierer L, Grivel J, Murray MM, Oddo M, et al. Progression of auditory discrimination based on neural decoding predicts awakening from coma. Brain J Neurol. 2013;136(Pt 1):81–9.
Rossetti AO, Tzovara A, Murray MM, De Lucia M, Oddo M. Automated auditory mismatch negativity paradigm improves coma prognostic accuracy after cardiac arrest and therapeutic hypothermia. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2014;31(4):356–61.
Rodriguez RA, Bussière M, Froeschl M, Nathan HJ. Auditory-evoked potentials during coma: do they improve our prediction of awakening in comatose patients? J Crit Care. 2014;29(1):93–100.
Pfeiffer C, Nguissi NAN, Chytiris M, Bidlingmeyer P, Haenggi M, Kurmann R, et al. Auditory discrimination improvement predicts awakening of postanoxic comatose patients treated with targeted temperature management at 36°C. Resuscitation. 2017;118:89–95.
Fischer C, Dailler F, Morlet D. Novelty P3 elicited by the subject’s own name in comatose patients. Clin Neurophysiol. 2008;119(10):2224–30.
Fischer C, Luaute J, Morlet D. Event-related potentials (MMN and novelty P3) in permanent vegetative or minimally conscious states. Clin Neurophysiol. 2010;121(7):1032–42.
Bekinschtein TA, Dehaene S, Rohaut B, Tadel F, Cohen L, Naccache L. Neural signature of the conscious processing of auditory regularities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(5):1672–7.
Liu Y, Huang H, Su Y, Wang M, Zhang Y, Chen W, et al. The combination of N60 with mismatch negativity improves the prediction of awakening from coma. Neurocrit Care. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-021-01308-y.
Azabou E, Rohaut B, Porcher R, Heming N, Kandelman S, Allary J, et al. Mismatch negativity to predict subsequent awakening in deeply sedated critically ill patients. Br J Anaesth. 2018;121(6):1290–7.
Gabriel D, Muzard E, Henriques J, Mignot C, Pazart L, André-Obadia N, et al. Replicability and impact of statistics in the detection of neural responses of consciousness. Brain J Neurol. 2016;139(Pt 6):e30.
Sutton S, Braren M, Zubin J, John ER. Evoked-potential correlates of stimulus uncertainty. Science. 1965;150(3700):1187–8.
Squires KC, Wickens C, Squires NK, Donchin E. The effect of stimulus sequence on the waveform of the cortical event-related potential. Science. 1976;193(4258):1142–6.
Berlad I, Pratt H. P300 in response to the subject’s own name. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1995;96(5):472–4.
Li R, Song W, Du J, Huo S, Shan G. Electrophysiological correlates of processing subject’s own name. NeuroReport. 2015;26(16):937–44.
Friedman D, Cycowicz YM, Gaeta H. The novelty P3: an event-related brain potential (ERP) sign of the brain’s evaluation of novelty. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2001;25(4):355–73.
Mulert C, Pogarell O, Juckel G, Rujescu D, Giegling I, Rupp D, et al. The neural basis of the P300 potential. Focus on the time-course of the underlying cortical generators. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2004;254(3):190–8.
Horn H, Syed N, Lanfermann H, Maurer K, Dierks T. Cerebral networks linked to the event-related potential P300. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2003;253(3):154–9.
Linden DEJ. The p300: where in the brain is it produced and what does it tell us? Neuroscientist. 2005;11(6):563–76.
Faugeras F, Rohaut B, Weiss N, Bekinschtein T, Galanaud D, Puybasset L, et al. Event related potentials elicited by violations of auditory regularities in patients with impaired consciousness. Neuropsychologia. 2012;50(3):403–18.
Tzovara A, Simonin A, Oddo M, Rossetti AO, De Lucia M. Neural detection of complex sound sequences in the absence of consciousness. Brain J Neurol. 2015;138(Pt 5):1160–6.
Naccache L, Sitt J, King JR, Rohaut B, Faugeras F, Chennu S, et al. Reply: replicability and impact of statistics in the detection of neural responses of consciousness. Brain J Neurol. 2016;139(Pt 6):e31.
Wijdicks EFM, Bamlet WR, Maramattom BV, Manno EM, McClelland RL. Validation of a new coma scale: The FOUR score. Ann Neurol. 2005;58(4):585–93.
Sessler CN, Gosnell MS, Grap MJ, Brophy GM, O’Neal PV, Keane KA, et al. The richmond agitation-sedation scale: validity and reliability in adult intensive care unit patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166(10):1338–44.
Rohaut B, Eliseyev A, Claassen J. Uncovering consciousness in unresponsive ICU patients: technical, medical and ethical considerations. Crit Care Lond Engl. 2019;23(1):78.
Giacino JT, Kalmar K, Whyte J. The JFK coma recovery scale-revised: measurement characteristics and diagnostic utility. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;85(12):2020–9.
Naccache L. Minimally conscious state or cortically mediated state? Brain J Neurol. 2018;141(4):949–60.
Edlow BL, Claassen J, Schiff ND, Greer DM. Recovery from disorders of consciousness: mechanisms, prognosis and emerging therapies. Nat Rev Neurol. 2021;17(3):135–56.
Ely EW, Inouye SK, Bernard GR, Gordon S, Francis J, May L, et al. Delirium in mechanically ventilated patients: validity and reliability of the confusion assessment method for the intensive care unit (CAM-ICU). JAMA. 2001;286(21):2703–10.
Girard TD, Jackson JC, Pandharipande PP, Pun BT, Thompson JL, Shintani AK, et al. Delirium as a predictor of long-term cognitive impairment in survivors of critical illness. Crit Care Med. 2010;38(7):1513–20.
Slooter AJC, Otte WM, Devlin JW, Arora RC, Bleck TP, Claassen J, et al. Updated nomenclature of delirium and acute encephalopathy: statement of ten societies. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46(5):1020–2.
Westhall E, Rosén I, Rundgren M, Bro-Jeppesen J, Kjaergaard J, Hassager C, et al. Time to epileptiform activity and EEG background recovery are independent predictors after cardiac arrest. Clin Neurophysiol. 2018;129(8):1660–8.
Barbella G, Lee JW, Alvarez V, Novy J, Oddo M, Beers L, et al. Prediction of regaining consciousness despite an early epileptiform EEG after cardiac arrest. Neurology. 2020;94(16):e1675–83.
Benarous L, Gavaret M, SodaDiop M, Tobarias J, de BourmontdeGhaisne S, Allez C, et al. Sources of interrater variability and prognostic value of standardized EEG features in post-anoxic coma after resuscitated cardiac arrest. Clin Neurophysiol Pract. 2019;4:20–6.
Rundgren M, Westhall E, Cronberg T, Rosén I, Friberg H. Continuous amplitude-integrated electroencephalogram predicts outcome in hypothermia-treated cardiac arrest patients. Crit Care Med. 2010;38(9):1838–44.
Dragancea I, Backman S, Westhall E, Rundgren M, Friberg H, Cronberg T. Outcome following postanoxic status epilepticus in patients with targeted temperature management after cardiac arrest. Epilepsy Behav. 2015;49:173–7.
Legriel S. Electroencephalographic monitoring in comatose survivors of cardiac arrest. Crit Care Lond Engl. 2013;17(6):1010.
Cloostermans MC, van Meulen FB, Eertman CJ, Hom HW, van Putten MJAM. Continuous electroencephalography monitoring for early prediction of neurological outcome in postanoxic patients after cardiac arrest: a prospective cohort study. Crit Care Med. 2012;40(10):2867–75.
Liu G, Su Y, Jiang M, Chen W, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, et al. Electroencephalography reactivity for prognostication of post-anoxic coma after cardiopulmonary resuscitation: a comparison of quantitative analysis and visual analysis. Neurosci Lett. 2016;626:74–8.
Acknowledgements
We are obliged to the EEG-technicians for their assistance in the EEG and evoked potentials recording. We thank Nancy Kentish Barnes for her help in preparing the manuscript. We thank the reviewers for their relevant comments and propositions.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Concept and design: SB, AC. Drafting of the manuscript: SB, EPR, EB, MG, AC; Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: all authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Benghanem, S., Pruvost-Robieux, E., Bouchereau, E. et al. Prognostication after cardiac arrest: how EEG and evoked potentials may improve the challenge. Ann. Intensive Care 12, 111 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13613-022-01083-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13613-022-01083-9