Abstract
Background
Recently, we demonstrated that estrogen (E2) induces early growth response 1 (Egr1) to mediate its actions on the uterine epithelium by controlling progesterone receptor signaling for successful embryo implantation. EGR1 is a transcription factor that regulates the spectrum of target genes in many different tissues, including the uterus. E2-induced EGR1 regulates a set of genes involved in epithelial cell remodeling during embryo implantation in the uterus. However, only few target genes of EGR1 in the uterus have been identified.
Result
The expression of ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif 1 (Adamts-1) was significantly downregulated in the uteri of E2-treated ovariectomized (OVX) Egr1(−/−) mice. Immunostaining of ADAMTS-1 revealed its exclusive expression in the uterine epithelium of OVX wild-type but not Egr1(−/−) mice treated with E2. The expression profiles of Adamts-1 and Egr1 were similar in the uteri of E2-treated OVX mice at various time points tested. Pre-treatment with ICI 182, 780, a nuclear estrogen receptor (ER) antagonist, effectively inhibited the E2-dependent induction of Egr1 and Adamts-1. Pharmacologic inhibition of E2-induced ERK1/2 or p38 phosphorylation interfered with the induction of EGR1 and ADAMTS-1. Furthermore, ADAMTS-1, as well as EGR1, was induced in stroma cells surrounding the implanting blastocyst during embryo implantation. Transient transfection with EGR1 expression vectors significantly induced the expression of ADAMTS-1. Luciferase activity of the Adamts-1 promoter containing EGR1 binding sites (EBSs) was increased by EGR1 in a dose-dependent manner, suggesting functional regulation of Adamts-1 transcription by EGR1. Site-directed mutagenesis of EBS on the Adamts-1 promoter demonstrated that EGR1 directly binds to the EBS at -1151/-1134 among four putative EBSs.
Conclusions
Collectively, we have demonstrated that Adamts-1 is a novel target gene of E2-ER-MAPK-EGR1, which is critical for embryo implantation in the mouse uterus during early pregnancy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Early growth response 1 (Egr1) was initially known as an immediate-early response gene that is induced by various stress signals, including cytokines, growth factors, hormones, and DNA-damaging agents [1]. EGR1 as a transcription factor recognizes a highly conserved GC-rich promoter consensus motif on its target genes, such as Tnf-α, Pten, and Socs-1 [2, 3]. It functions either as a tumor suppressor or oncogene, depending on the cell type and environmental conditions [4]. Several growth factors, such as Igf-II, Pdgf-A, and Tgf-β1, have been identified as direct targets of EGR1 in various tissues and pathological contexts including cancers [5,6,7,8]. Under normal conditions, EGR1 participates in the transcriptional regulation of several clock genes, such as Per1, Per2, and Bmal1 [2], and is required for the transcriptional activation of MMP1 during damaged tissue remodeling [9]. Collectively, the pleiotropic actions of EGR1 are brought about through many target genes that act as key factors in various physiological and pathological conditions. However, only few target genes of EGR1 in the uterus have been identified.
The balanced function of ovarian estrogen (E2) and progesterone (P4) is critical for successful pregnancy following embryo implantation [10]. Uncontrolled estrogenic activity could be a major cause of endometrial disorders, including infertility and cancers; however, only a handful of the downstream signaling factors of E2 have been identified in the uterus [11,12,13]. E2 induces the transcription factor EGR1 to fine-tune its functions that are responsible for uterine receptivity during embryo implantation [12, 14,15,16]. In addition, E2 promotes ERK1/2-dependent activation of ELK-1 to induce EGR1 the in MCF-7 breast cancer cells [17, 18]. While Egr1(−/−) mice showed normal ovulation, fertilization, and embryo development if exogenous gonadotrophins were administered, they completely failed in embryo implantation [12, 19]. To understand the function(s) of EGR1 as a key mediator of E2 in the uterus, the identification of the genes directly targeted by EGR1 is critical. By performing multi-step in silico promoter analyses using mRNA microarray data, we identified some of the potential target genes of EGR1, such as Egr2, c-Kit, and Gadd45g, in the mouse uterus [20]. We recently demonstrated that EGR1 transcriptionally regulates c-Kit expression to maintain uterine receptivity for embryo implantation in the mouse uterus [21]. A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 1 (Adamts-1), a new member of the ADAM-related proteins family, plays an key role in normal growth, organogenesis, and fertility [22, 23]. Although Adamts-1 is a well-known target of P4-progesterone receptor (PR) signaling in the ovary during ovulation [24], the molecular mechanisms by which ovarian steroids regulate the transcription of Adamts-1 in the uterus are poorly understood. Using multiple molecular and histological approaches, we have shown that EGR1, under the control of E2, transcriptionally regulates the expression of Adamts-1 in the mouse uterus.
Results
Expression of Adamts-1 is dependent on E2-induced EGR1 in the uterine epithelium
Previously, in silico promoter analyses of the microarray data from Egr1(+/+) and Egr1(−/−) mice uteri revealed putative EGR1 binding sites (EBSs) in the Adamts-1 promoter [20]. Thus, we examined if Adamts-1 was a direct target gene of the transcription factor, EGR1, in the uterus. The results of reverse transcription (RT)-PCR and real-time RT-PCR showed that the expression of Adamts-1 was significantly reduced in the uteri of Egr1(−/−) mice treated with E2 for 3 h (Fig. 1a). Western blot analyses also showed that the expression levels of both EGR1 and ADAMTS-1 were significantly reduced in Egr1(−/−) mice (Fig. 1b). Immunofluorescence staining of ADAMTS-1 showed its localization in the uterine epithelial cells of wild-type mice, but not Egr1(−/−) mice, at 3 h post E2 treatment (Fig. 1c). To investigate the expression of Adamts-1 in uterine cell type, we isolate the epithelial and stromal cells. The results of RT-PCR and real-time RT-PCR showed that the expression of Adamts-1 was significantly increased in the epithelial cells of the uteri treated with E2 for 3 h (Fig. 1d).
Adamts-1 expression is significantly reduced in the uteri of Egr1(−/−) mice. a RT-PCR and real-time RT-PCR analyses of the relative amounts of Adamts-1 and Egr1 mRNAs in the uterus (4–5 mice in each group). b Western blot analyses of ADAMTS-1 and EGR1 expression (3–4 mice in each group). Error bars represent standard deviation. *P < 0.05. c Immunofluorescence staining of ADAMTS-1 showed that its expression was significantly reduced in the uteri of Egr1(−/−) mice. The second panels (i and ii) show the enlarged images of the boxed areas in the first panels. White arrowheads indicate ADAMTS-1 positive cells. Three independent fields were analyzed for each mouse (2–3 mice in each group). Green, blue, and red colors indicate ADAMTS-1, E-cadherin, and nucleus, respectively. GE glandular epithelial cells, LE luminal epithelial cells, S stromal cells. Scale Bar: 25 µm. d RT-PCR and real-time RT-PCR analyses of Adamts-1 mRNAs in the isolated uterine stromal cells (SC) and epithelial cells (EC). Keratin and Desmin are EC and SC marker genes, respectively (six mice in each group). *P < 0.05
Adamts-1 and Egr1 are rapidly and transiently induced by E2 in the mouse uterus
To further examine the mechanisms underlying the regulation of Adamts-1 expression by E2-induced EGR1 in the uterus, we investigated the spatiotemporal expression patterns of Adamts-1 in the uteri of ovariectomized (OVX) mice treated with E2 for 0, 3, 6, or 24 h following hormone treatment. RT-PCR and real-time RT-PCR analyses demonstrated that the expression pattern of Adamts-1 was similar to that of Egr1 in the uterus (Fig. 2a). Both Egr1 and Adamts-1 were transiently and rapidly induced by E2, with a peak at 3 h post E2 treatment. Western blot analyses revealed the unique expression pattern of ADAMTS-1 induced by E2 (Fig. 2b). Immunofluorescence staining showed that ADAMTS-1 was predominantly localized in the epithelial cells of the uterus (arrowheads in Fig. 2c).
Time-dependent expression of Adamts-1 induced by E2 in the mouse uterus. a, b Spatiotemporal expression patterns of Adamts-1 and Egr1 in the uterus at several time points after E2 treatment. RT-PCR and real-time RT-PCR a and Western blot analyses b (4–5 mice in each group). Error bars represent standard deviation. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. c Immunofluorescence staining of ADAMTS-1 showed that ADAMTS-1 is specifically localized in the uterine epithelium (white arrowheads). The second panels (i to iv) show the enlarged images of the boxed areas in the first panels. Three independent fields were analyzed for each mouse (2–3 mice in each group). Green, blue, and red colors indicate ADAMTS-1, E-cadherin, and nucleus, respectively. GE, glandular epithelial cells; LE, luminal epithelial cells; S, stromal cells. Scale Bar: 2 µm. RT-PCR and real-time RT-PCR were performed to analyze the relative levels of Adamts-1 induced in the uteri of OVX mice by P4 alone d or by a combination of E2 + P4 e at different time points post hormone treatment (4–5 mice for each time point). Hoxa10 and Cox1 represent temporal expression markers for the time-dependent hormonal response. rPL7 represents the loading control
To investigate the effects of P4 on Adamts-1 expression in the mouse uterus, P4 alone or a combination of E2 + P4 was administered to mice OVX at various time points following hormone treatment. We found that P4 alone did not induce the expression of Adamts-1 in the uteri of OVX mice (Fig. 2d). However, when a combination of E2 + P4 was used, P4 effectively inhibited the E2-induced expression of Adamts-1 in the uterus (Fig. 2e).
Activation of ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK by the E2-ER(s) pathways is required for the EGR1-dependent induction of ADAMTS-1 in the uterus
To determine whether E2 induces Egr1 and Adamts-1 expression via the activation of its nuclear estrogen receptor (ER)α and ERβ, in the mouse uterus, we examined the expression levels of Adamts-1 in OVX mice pre-treated with ICI 182,780 (an ER antagonist), 30 min before E2 injection. At 2 and 4 h post-E2 injection, the E2-dependent expression of Adamts-1 and Egr1 mRNAs was profoundly reduced in the uteri of OVX mice pre-treated with ICI 182,780 (Fig. 3a). E2 exerts its functions through both genomic and non-genomic pathways, such as MAPK pathways, which regulate EGR1 expression in various cell types [16, 25, 26]. Thus, to determine if the non-genomic function(s) of E2 is/are required for the induction of ADAMTS-1 in the uterus, we evaluated the phosphorylation patterns of the MAPK and AKT pathways in the uteri of OVX mice that were treated with E2 for various time periods. While E2 gradually increased the phosphorylation of AKT and JNK, ERK1/2 and p38 were rapidly activated, with a peak at 2 h post E2 treatment (Fig. 3b). ICI 182,780 significantly inhibited the E2-induced phosphorylation of AKT, ERK1/2, and p38. Pre-treatment with the pharmacological inhibitors of each kinase showed that the E2-ER-dependent phosphorylation of p38 and ERK1/2 was required for the induction of EGR1 and ADAMTS-1 in the uterus (Fig. 3c, d). These results suggest that the transcription of Adamts-1 could be regulated by the E2-ER-ERK/p38-EGR1 pathway in the mouse uterus.
E2 regulates Adamts-1 expression via nuclear ER(s) in the uterus. a RT-PCR and real-time RT-PCR analyses of the expressions of Adamts-1 and Egr1 mRNAs in the uteri of adult OVX mice pre-treated with an ER antagonist, ICI 182,780 (500 µg/mouse) 30 min before E2 injection (200 ng/mouse) (4–5 mice in group). b Representative images of Western blot analyses examining the rapid changes in the phosphorylation status of AKT and MAPKs (ERK1/2 and p38) by E2 (3–4 mice in group). C Pharmacological inhibition of E2-dependent ADAMTS-1 and EGR1 induction by inhibitors of AKT (W; wortmannin, 14 μg/mouse), ERK 1/2 (U; U0126, 160 mg/kg), or p38 (SB; SB203580, 1 mg/mouse). Each inhibitor was administered to OVX mice 30 min before E2 administration (3–4 mice in each group). d Relative intensity of ADAMTS-1 protein expression *P < 0.05
ADAMTS-1 and EGR1 are induced in the stromal cells surrounding the implanting blastocyst during embryo implantation
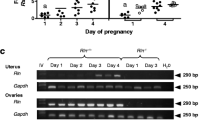
During early pregnancy, we found that the expression level of Adamts-1 mRNA increased on the day 4 of pregnancy (D4) (Fig. 4a). Previously, we had demonstrated that EGR1 was exclusively induced in the stromal cells surrounding the implanting blastocyst (Bl) during mice embryo implantation [12]. Immunostaining of EGR1 and ADAMTS-1 in the uterus containing the implantation sites on D5 showed that both EGR1 and ADAMTS-1 were induced in the decidualizing stromal cells during embryo implantation (right panels in Fig. 4b). Furthermore, ADAMTS-1 was also found in the trophoblasts of the Bl (yellow dots in BI). However, ADAMTS-1, but not EGR1, was found in a subset of decidualizing cells in the primary decidual zone (PDZ) on D6 and D8 (Fig. 4c).
The expression of Adamts-1 in the stromal cells surrounding the implanting blastocyst during embryo implantation. a RT-PCR and real-time RT-PCR of Adamts-1 expression in the uterus during pregnancy (4–6 mice for each day of pregnancy). rPL7 represents the loading control. *P < 0.05. b, c Immunostaining of ADAMTS-1 in uterine tissues. The second panels (i to iv) show the enlarged images of the boxed areas in the first panels. White arrowheads indicate ADAMTS-1 positive cells. Three independent fields were analyzed for each mouse (3–4 mice for each day). Green and red colors indicate ADAMTS-1 and nucleus, respectively. GE glandular epithelial cells, LE luminal epithelial cells, S stromal cells, Bl Blastocyst, Em embryo, PDZ primary decidual zone. Scale Bar: 2 µm
The effective EBS is present within the distal region of the Adamts-1 promoter
To further understand the molecular interaction(s) of EGR1 with the Adamts-1 promoter, we performed a series of luciferase promoter-reporter assays. First, we examined whether the forced expression of EGR1 induced ADAMTS-1 expression in 293 T cells. As shown in Fig. 5a, Western blot analyses clearly showed that transfection with an EGR1 overexpression vector significantly increased the expression of ADAMTS-1 and EGR1 in a time-dependent manner. We then performed luciferase assays on a construct with a region of the Adamts-1 promoter region (− 1705 to + 90) containing four putative EBS. We found that the luciferase activity of the Adamts-1 promoter was increased by EGR1 expression vectors in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 5b), suggesting the presence of EBS in the Adamts-1 promoter. Furthermore, we found that the distal 1 kb region of the Adamts-1 promoter (− 1705 to − 978 from the transcription start site) contained one EBS (− 1151/− 1134) that was sufficient for the EGR1-dependent activation of the Adamts-1 promoter (Fig. 5c). To further examine the function of the EBS at the distal region of the Adamts-1 promoter, luciferase assays were performed on a mutant EBS containing the Adamts-1 promoter. A mutation (mut) at the − 1151/− 1134 of the EBS completely destroyed the transcriptional activity of the plasmid construct (Fig. 5d). We also found that EGR1 did not activate the distal 1 kb region of the Adamts-1 promoter containing a − 1151/− 1134 mut, although the wild-type distal promoter region responded to EGR1 in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 5e). To elucidate the physical interaction between EGR1 and − 1151/− 1134 EBS of the Adamts-1 promoter, a FLAG-tagged EGR1 expression vector was transfected into 293 T cells and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) for FLAG was performed. ChIP-PCR and ChIP-real-time PCR for each EBS provided evidence that − 1151/− 1134 EBS was critical for EGR1-dependent Adamts-1 transcription (Fig. 5f).
The functional EGR1 binding site is located in the distal region of the Adamts-1 promoter. a Western blot analyses of the expression profiles of ADAMTS-1 and EGR1 after transfection of the EGR1 expression vector. GAPDH represents the loading control. b Adamts-1 luciferase vector (− 1705/+ 90) was co-transfected with increasing concentrations of the EGR1 expression vector (pIRES dsRED2/EGR1) in 293 T cells, as indicated. At 48 h post transfection, the cells were collected, and the luciferase activity was measured. c EGR1 expression vector was transiently co-transfected with one of three different Adamts-1 promoter constructs in 293 T cells. The luciferase activity was measured at 48 h post transfection. The firefly activity was normalized to the activity of Renilla luciferase, and the luciferase activity of the untreated cells was designated as one relative value. d EGR1 expression vector was co-transfected in 293 T cells along with one of two different Adamts-1 promoter constructs containing mutations in EGR1 binding sites. The luciferase activity was measured at 48 h post transfection. e Luciferase activity of the WT and mutant (− 1151/− 1134) Adamts-1 promoters co-transfected with an increasing amount of EGR1 expression vector in 293 T cells is indicated. Luciferase activity was calculated relative to the expression of the pGL4.10 basic vector, which served as the negative control. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. f Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)-PCR and real-time ChIP-PCR for four putative EBS in the Adamts-1 promoter. The EGR1-MYC-FLAG expression vector was transfected into 293 T cells and genomic DNA was used for ChIP-PCR. A schematic cartoon (right panel in d) to show locations of four different primers on the Adamts-1 promoter to amplify genomic DNAs precipitated by FLAG antibody. Note that the genomic DNA containing − 1151/− 1134 of the Adamts-1 promoter was significantly enriched. *P < 0.05
Discussion
Previously, we had demonstrated that E2 induces the transcription factor EGR1, to fine-tune its major effects on the uterine epithelium during embryo implantation [12]. EGR1 governs the expression of an array of genes regulated by E2 in the uterus. Our in silico analyses suggested that EGR1 physically binds to the Adamts-1 promoter and induces its expression in the uterus [20]. Using multiple approaches, we have shown that EGR1 regulates the expression of Adamts-1 at the transcriptional level in the uterus. EGR1 is rapidly and transiently induced by the E2-induced phosphorylation of p38 and ERK1/2 in the uterus [21]. It is also induced in the ovary immediately after ovulation by a surge of luteinizing hormone (LH) [27]. A recent study suggested that LH-dependent ERK1/2 signaling promotes the simultaneous induction of Egr1 and Adamts-1 in bovine granulosa cells [28]. Interestingly, while the expression of Adamts-1 was significantly reduced in the uterus of Egr1(−/−) mice (Fig. 1), its expression was not altered in the ovary of Egr1(−/−) mice following the LH surge (unpublished observation). In addition, we found that the expression of Adamts-1 coincided with that of Egr1 in the uterus of mice treated with E2 (Fig. 2). However, further studies are warranted to understand the different regulatory mechanisms by which EGR1 interacts with the Adamts-1 promoter in different cellular contexts in the uterus and ovary of mice.
ADAMTS-1 is a protease that mediates follicular rupture [29]. At the time of ovulation, it cleaves the extracellular matrix of the thecal cell layer, thereby allowing the release of the cumulus oocyte complexes from the ovary [30]. In addition, it facilitates the hormonal response of granulosa cells by cleaving the proteoglycans that inhibit the binding of gonadotrophins to their receptors [23, 29]. Although Adamts-1 is a well-known target of the P4-PR signaling pathway in the ovary, during ovulation, its expression in the uterus is strictly regulated by E2, and not by P4. We found that the P4-PR signaling pathway alone did not affect the expression of Adamts-1 in the uterus (Fig. 2d). Rather, it interfered with the effects of E2 on Egr1 expression, leading to a reduction in Adamts-1 expression in the uterus (Fig. 2e). Consistent with a previous study [31], we found that the expression of Admats-1 increased during the proestrus and estrus stages when E2 is the dominant hormone (data not shown), suggesting that Adamts-1 is mainly regulated by E2 in the uterus. However, a previous report showed that the expression of Adamts-1 mRNA was not significantly altered in the bovine endometrium during the estrous cycle [32]. In addition, other studies have revealed an increase in the expression of Adamts-1 mRNA by P4 in cultured bovine and human stromal cells [32, 33]. Furthermore, E2 attenuated the positive effects of P4 on Adamts-1 in a concentration-dependent manner [33]. This discrepancy could be derived between from species differences and/or different cellular/physiological contexts.
Endometrial stromal cells undergo extensive remodeling during decidualization [34, 35]. Decidualization response is partially impaired in Egr1(−/−) mice [12], and EGR1 transcript levels are downregulated in the endometrium of patients with repeated implantation failure [36]. Furthermore, EGR1 is required to transcriptionally program pre-decidual human endometrial stromal cells for decidualization and its expression levels are required to be reduced to enable decidualization [36, 37]. This down-regulation of EGR1 in human decidualized stromal cells is consistent with our results that the expression of EGR1 is reduced in the PDZ of mice on D6 and D8 (Fig. 4c). However, ADAMTS-1 was persistently maintained in these cells on D6 and D8, suggesting the presence of other regulatory mechanisms that affect ADAMTS-1 expression during this event. ADAMTS-1, which is responsible for extracellular matrix remodeling, is known to play a crucial role in initiating and successfully maintaining decidualization [31,32,33]. However, Adamts-1(−/−) mice appear normal with respect to embryo implantation and decidualization [22, 23, 38]. This could be due to the redundant expression of other metalloproteases in the uterus during embryo implantation and decidualization [39,40,41]. In fact, not only ADAMTS-1 but also ADAMTS-5 proteins were identified in human decidualized stromal cells [40].
Using in silico analyses, we found four putative EBS within − 2 kb of the Adamts-1 promoter (Fig. 5b). Previous studies, including ours, have shown that EBS are enriched within − 500 of the promoters of genes whose expressions are influenced by EGR1 [20, 42, 43]. For example, in many species, EBS is found within − 500 of the LH-β subunit promoter [19]. Moreover, EGR1 directly interacts with an EBS in the promoter regions of MMP9 (− 569/− 553) and MMP1 (− 137/− 119) in HeLa cells [9, 44]. Although a putative EBS at − 133/− 122 of the Adamts-1 promoter is conserved among many species, including humans, mice, and rats [20], we found that EGR1 does not interact with this EBS. Instead, we found that EGR1 binds to the EBS at the − 1151/− 1134 region of the Adamts-1 promoter, the mutation of which exclusively abrogated the transcriptional activity of EGR1 (Fig. 5). While we cannot exclude that the other EBS present within − 1 kb of the Adamts-1 promoter can play a role in the EGR1-dependent transcription of Adamts-1, our results suggest that EGR1 physically interacts with the Adamts-1 promoter at the − 1151/− 1134 region and enhances its expression.
Conclusion
We have demonstrated that the transcription of Adamts-1 is regulated exclusively by the E2-dependent EGR1 transcription factor in the uterus, whereas by the P4 signaling pathway in the ovary in mice. Collectively, Adamts-1, whose expression is localized in the uterine epithelium, is a novel target gene of E2-ER-MAPK-EGR1, critical for embryo implantation in the mouse uterus during early pregnancy.
Methods
Reagents and chemicals
E2 (17β-estradiol; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), P4 (Sigma-Aldrich), ICI 182,780 (Sigma-Aldrich), U0126 (MEK 1/2 inhibitor; Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA), wortmannin (AKT inhibitor; Cell signaling Technology), and SB203580 (p38 inhibitor; Selleck Chemicals, Houston, TX, USA) were used in this study.
Animals
All mice were housed following the institutional guidelines for laboratory animals (Animal Care Facility of CHA University). This study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC, Approval Number: 190168). Adult ICR mice (8-week-old), provided by KOATECH (Pyeontaek, Gyeonggi, Korea) were housed under temperature- and light-controlled conditions for 12 h daily and fed ad libitum. Egr1(−/−) mice were kindly provided by Dr. Jeffrey Milbrandt (Washington University, St. Louis, MO, USA). For genotyping, PCR analysis of tail genomic DNA was used, as previously described [12, 19].
Hormone treatments
To examine the effects of ovarian steroid hormones on Adamts-1 expression, adult female mice were OVX, allowed to rest for 10 days, and subsequently provided the necessary treatments for each experiment performed in the study. The mice were sacrificed, and their uterine tissues were collected for molecular and histological analyses. RNA or protein extractions were carried out following the injection of E2 and/or P4. To investigate the time-dependent action of E2 on the expression of Adamts-1 in the mouse uterus, OVX mice were subcutaneously injected with either the vehicle (sesame oil, 0.1 mL) or E2 (200 ng/mouse), and sacrificed at various time points (0.5–12 h) following the injection. To analyze whether E2 functions through the nuclear ER to induce Adamts-1 expression in the mouse uterus, adult OVX mice were pre-treated with ICI 182, 780 (500 μg/mouse), an ER antagonist, and subsequently treated with P4 (2 mg/mouse) alone or P4 + E2. To determine the signaling pathway(s) activated by the non-genomic effect(s) of E2 on Adamts-1 induction in the mouse uterus, adult OVX mice were pre-treated with the pharmacological inhibitors, U0126 (160 mg/kg), wortmannin (14 µg/mouse), and SB203580 (1 mg/mouse), in combination with E2.
RNA preparation, RT-PCR, and real-time RT-PCR
Mouse uteri (from 3 to 5 mice in experimental group) were collected and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen. Subsequently, they were individually prepared for protein and/or total RNA extraction. Total RNA was extracted individually from each uterine tissue using TRIzol Reagent (Ambion, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Two micrograms of uterine total RNA were subjected to RT using M-MLV reverse transcriptase (Promega, Madison, WI, USA), random primers, and oligo dT, to obtain cDNA. The cDNA obtained was used as the template in a PCR by using specific primers and optimized time–temperature cycles. Real-time RT-PCR was performed by using the iQ™ SYBR® Green Supermix (Bio-Rad), and by monitoring the increase in the fluorescence of the SYBR Green dye in real-time, as previously described on a real-time PCR detection system (Bio-Rad) [16, 45]. To compare transcript levels between samples, a standard curve was prepared using several serial dilutions of the cDNA sample. To calculate the relative abundance of each gene, this standard curve was used. The Ct values were normalized to the relative amounts of the ribosomal protein, L7 (rPL7) [12]. All PCR reactions were performed in duplicate.
Western blot analysis
Uterine samples were homogenized using a Polytron homogenizer (Brinkmann, Westbury, NY, USA). The protein was extracted using PRO-PREP Protein Extraction Solution (iNtRON Biotechnology, Seongnam, Gyeonggi, Korea) containing 1X phosphatase inhibitor (Roche Applied Sciences, Indianapolis, IN, USA) by lysing the cells. The protein extracts were separated by SDS-PAGE (8–10%) and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane (Bio-Rad). Subsequently, the membranes were subjected to Western blot analyses with anti-ADAMTS-1 (Abcam, Cambridge, UK, ab39194, 1:1000), anti-EGR1 (Cell Signaling, #4153, 1:1000), anti-pAKT (Cell Signaling, #9271, 1:1000), anti-AKT (Cell signaling, #9272, 1:1000), anti-pERK1/2 (Cell Signaling, #9101, 1:1000), anti-ERK1/2 (Cell Signaling, #9102, 1:1000), anti-p-p38 (Santa Cruz, sc-17852, 1:1000), anti-p38 (Ab frontier, LF-MA0126, 1:1000), anti-pJNK1/2 (Santa Cruz, 1:1000), and anti-GAPDH (Cell Signaling, #21,118, 1:2000) antibodies. The secondary antibodies were HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit or mouse (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA, 1:3000). Immunoreactive bands were detected using the Immune-Star Western™ Chemiluminescence Kit (Bio-Rad). The chemiluminescence signal was detected using the ChemiDOC™ XRS + System (Bio-Rad).
Immunofluorescence
To determine the cell-type specific localization of ADAMTS-1 following E2 treatment, the uteri were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde and embedded in paraplast (Leica Biosystems, St. Louis LLC, Diemen, Netherlands). Uterine Sects. (5 µm) were de-paraffinized and rehydrated, and the endogenous peroxidase was inactivated using 3% H2O2. The tissue sections were subjected to antigen retrieval by immersing in sodium citrate buffer (10 mM, pH 6.0) for 20 min. Serum as a protein block (Dako, Carpinteria, CA, USA) was used to block non-specific staining. The tissue sections were then incubated with primary anti-ADAMTS-1 antibody (Abcam, 1:100) at 4 °C overnight. The secondary antibodies were FITC-conjugated anti-goat (Jackson ImmunoResearch, West Grove, PA, 1:250) for 60 min at room temperature. The sections were counter-stained with TO-PRO-3-iodide (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA, 1:400). Microscopic images were obtained and analyzed using ZEN software (ZEISS, Oberkochen, Germany).
Isolation of uterine epithelial and stromal cells
Uteri were dissected from 6 female mice at 3 h after E2 treatment, minced into small pieces, and incubated in HBSS (Thermo Fisher Scientific) containing dispase (2.4 U/ml) and pancreatin (25 mg/ml) for 1 h at 4 °C and 1 h at room temperature. Tissues were incubated at 37 °C for 10 min, then the supernatant the epithelial cell-rich fraction was collected. The remaining stromal cell-rich pellet was then digested with collagenase (0.5 mg/ml) after filtration through a 70-µm nylon mesh. The epithelial and stromal cells were prepared for total RNA extraction.
In silico promoter analysis
The promoter sequence of Adamts-1, from − 2000 to + 200, was obtained from the UCSC gene sorter (http://genome.ucsc.edu), and the putative EBSs in the Adamts-1 promoter were identified using Promo (http://alggen.lsi.upc.es).
Promoter reporter assay
The Adamts-1 promoter region, ranging from − 1705 to + 90, was amplified from mouse genomic DNA by PCR with Forward (5′-ACT GTG GAT GTC AGT GAG AGC-3′) and Reverse (5′-GCT GCT TTC TAG CGA GTG CAA-3′) primers. The amplified PCR product was cloned into the pGL4.10-basic reporter, and the resulting plasmid was designated as pGL4. 10/Adamts-1 (− 1705/+ 90). Reporter vectors containing the Adamts-1 promoter region from − 1705/− 978 or − 977/+ 90 were generated using pGL4.10/Adamts-1. Mutant promoter constructs (− 1151/− 1134 mut) were produced using the EZ change™ site-directed mutagenesis kit (Enzynomics, Seoul, Korea). In 12-well plates, 293 T cells were seeded and transfected with 2 μg of the Adamts-1 promoter-reporter construct and EGR1 expression vector (pIRES dsRED2/EGR1) using Gene Porter 3000 (Genlantis, San Diego, CA, USA) transfection reagents, following the manufacturer’s instructions. A pRL-null plasmid (50 ng) encoding Renilla luciferase was incorporated in all samples to monitor the transfection efficiency. After 48 h, the firefly and Renilla luciferase activities were measured sequentially from a single sample using the Dual-Glo™ Luciferase Assay System (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) using an illuminometer.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
Human EGR1 was amplified and cloned into the pCMV6-ACIRES-GFP-Puro vector to tag EGR1 with Myc and FLAG (Origene Technologies, Rockville, MD, USA). 293 T cells were transfected with an EGR1-MYC-FLAG expression plasmid for 48 h, washed once with PBS, and added to 10 ml of PBS containing 1% formaldehyde to covalently cross-link any DNA–protein complexes at room temperature for 10 min. The beads were added to the samples, rotated for 30 min, and collected by centrifugation at 12,000×g for 1 min. The elution buffers were added to the samples and the supernatants were transferred to clean microcentrifuge tubes. The DNA samples were used for PCR reactions with the appropriate primers.
Statistics
Each experiment was performed at least three times. Data were presented as mean ± S.D. GraphPad Prism ver. 8 software (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA) was used to perform statistical analyses for the Mann–Whitney U test. Statistical significance was set at P < 0.05.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- E2 :
-
Estrogen
- P4 :
-
Progesterone
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- PR:
-
Progesterone receptor
- OVX:
-
Ovariectomized
- Egr1 :
-
Early growth response 1
- Adamts-1 :
-
ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif 1
- SC:
-
Stromal cell
- EC:
-
Epithelial cell
- EBS:
-
EGR1 binding site
- RT:
-
Reverse transcription
- LE:
-
Luminal epithelial cells
- GE:
-
Glandular epithelial cells
- S:
-
Stromal cells
- Em:
-
Embryo
- Bl:
-
Blastocyst
- PDZ:
-
Primary decidual zone
- D4:
-
Day 4 of pregnancy
- ChIP:
-
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
References
Bhattacharyya S, Fang F, Tourtellotte W, Varga J. Egr-1: new conductor for the tissue repair orchestra directs harmony (regeneration) or cacophony (fibrosis). J Pathol. 2013;229(2):286–97.
Tao W, Wu J, Zhang Q, Lai SS, Jiang S, Jiang C, Xu Y, Xue B, Du J, Li CJ. EGR1 regulates hepatic clock gene amplitude by activating Per1 transcription. Sci Rep. 2015;5:15212.
Mostecki J, Showalter BM, Rothman PB. Early growth response-1 regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 transcription. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(4):2596–605.
Pagel JI, Deindl E. Disease progression mediated by egr-1 associated signaling in response to oxidative stress. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(10):13104–17.
Svaren J, Ehrig T, Abdulkadir SA, Ehrengruber MU, Watson MA, Milbrandt J. EGR1 target genes in prostate carcinoma cells identified by microarray analysis. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(49):38524–31.
Virolle T, Krones-Herzig A, Baron V, De Gregorio G, Adamson ED, Mercola D. Egr1 promotes growth and survival of prostate cancer cells. Identification of novel Egr1 target genes. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(14):11802–10.
Havis E, Duprez D. EGR1 transcription factor is a multifaceted regulator of matrix production in tendons and other connective tissues. Int J Mole Sci. 2020;21(5):1664.
Magee N, Zhang Y. Role of early growth response 1 in liver metabolism and liver cancer. Hepatoma Res. 2017;3:268–77.
Yeo H, Lee JY, Kim J, Ahn SS, Jeong JY, Choi JH, Lee YH, Shin SY. Transcription factor EGR-1 transactivates the MMP1 gene promoter in response to TNFalpha in HaCaT keratinocytes. BMB Rep. 2020;53(6):323–8.
Fukui Y, Hirota Y, Matsuo M, Gebril M, Akaeda S, Hiraoka T, Osuga Y. Uterine receptivity, embryo attachment, and embryo invasion: multistep processes in embryo implantation. Reprod Med Biol. 2019;18(3):234–40.
Ramathal C, Bagchi IC, Bagchi MK. Lack of CCAAT enhancer binding protein beta (C/EBPbeta) in uterine epithelial cells impairs estrogen-induced DNA replication, induces DNA damage response pathways, and promotes apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30(7):1607–19.
Kim HR, Kim YS, Yoon JA, Yang SC, Park M, Seol DW, Lyu SW, Jun JH, Lim HJ, Lee DR, et al. Estrogen induces EGR1 to fine-tune its actions on uterine epithelium by controlling PR signaling for successful embryo implantation. FASEB J. 2018;32(3):1184–95.
Sun X, Bartos A, Whitsett JA, Dey SK. Uterine deletion of Gp130 or Stat3 shows implantation failure with increased estrogenic responses. Mol Endocrinol. 2013;27(9):1492–501.
Guo B, Tian XC, Li DD, Yang ZQ, Cao H, Zhang QL, Liu JX, Yue ZP. Expression, regulation and function of Egr1 during implantation and decidualization in mice. Cell Cycle. 2014;13(16):2626–40.
Liang XH, Deng WB, Li M, Zhao ZA, Wang TS, Feng XH, Cao YJ, Duan EK, Yang ZM. Egr1 protein acts downstream of estrogen-leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF)-STAT3 pathway and plays a role during implantation through targeting Wnt4. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(34):23534–45.
Kim HR, Kim YS, Yoon JA, Lyu SW, Shin H, Lim HJ, Hong SH, Lee DR, Song H. Egr1 is rapidly and transiently induced by estrogen and bisphenol A via activation of nuclear estrogen receptor-dependent ERK1/2 pathway in the uterus. Reprod Toxicol. 2014;50:60–7.
Chen F, Wang Q, Wang X, Studzinski GP. Up-regulation of Egr1 by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 contributes to increased expression of p35 activator of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 and consequent onset of the terminal phase of HL60 cell differentiation. Can Res. 2004;64(15):5425–33.
Min DY, Jung E, Ahn SS, Lee YH, Lim Y, Shin SY. Chrysoeriol prevents TNFalpha-induced CYP19 gene expression via EGR-1 downregulation in MCF7 breast cancer cells. Int J Mole Sci. 2020;21(20):7523.
Lee SL, Sadovsky Y, Swirnoff AH, Polish JA, Goda P, Gavrilina G, Milbrandt J. Luteinizing hormone deficiency and female infertility in mice lacking the transcription factor NGFI-A (Egr-1). Science. 1996;273(5279):1219–21.
Seo BJ, Son JW, Kim HR, Hong SH, Song H. Identification of egr1 direct target genes in the uterus by in silico analyses with expression profiles from mRNA microarray data. Dev Reprod. 2014;18(1):1–11.
Park M, Kim HR, Kim YS, Yang SC, Yoon JA, Lyu SW, Lim HJ, Hong SH, Song H. Estrogen-induced transcription factor EGR1 regulates c-Kit transcription in the mouse uterus to maintain uterine receptivity for embryo implantation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2018;470:75–83.
Shindo T, Kurihara H, Kuno K, Yokoyama H, Wada T, Kurihara Y, Imai T, Wang Y, Ogata M, Nishimatsu H, et al. ADAMTS-1: a metalloproteinase-disintegrin essential for normal growth, fertility, and organ morphology and function. J Clin Investig. 2000;105(10):1345–52.
Mittaz L, Russell DL, Wilson T, Brasted M, Tkalcevic J, Salamonsen LA, Hertzog PJ, Pritchard MA. Adamts-1 is essential for the development and function of the urogenital system. Biol Reprod. 2004;70(4):1096–105.
Robker RL, Akison LK, Russell DL. Control of oocyte release by progesterone receptor-regulated gene expression. Nucl Recep Signal. 2009;7: e012.
Kim J, Jung E, Choi J, Min DY, Lee YH, Shin SY. Leptin is a direct transcriptional target of EGR1 in human breast cancer cells. Mol Biol Rep. 2019;46(1):317–24.
Mishra JP, Mishra S, Gee K, Kumar A. Differential involvement of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-activated AP-1 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase-activated EGR-1 signaling pathways in tumor necrosis factor-alpha and lipopolysaccharide-induced CD44 expression in human monocytic cells. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(29):26825–37.
Russell DL, Doyle KM, Gonzales-Robayna I, Pipaon C, Richards JS. Egr-1 induction in rat granulosa cells by follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone: combinatorial regulation by transcription factors cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate regulatory element binding protein, serum response factor, sp1, and early growth response factor-1. Mol Endocrinol. 2003;17(4):520–33.
Schuermann Y, Rovani MT, Gasperin B, Ferreira R, Ferst J, Madogwe E, Goncalves PB, Bordignon V, Duggavathi R. ERK1/2-dependent gene expression in the bovine ovulating follicle. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):16170.
Robker RL, Russell DL, Espey LL, Lydon JP, O’Malley BW, Richards JS. Progesterone-regulated genes in the ovulation process: ADAMTS-1 and cathepsin L proteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97(9):4689–94.
Russell DL, Doyle KM, Ochsner SA, Sandy JD, Richards JS. Processing and localization of ADAMTS-1 and proteolytic cleavage of versican during cumulus matrix expansion and ovulation. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(43):42330–9.
Kim J, Kim H, Lee SJ, Choi YM, Lee SJ, Lee JY. Abundance of ADAM-8, -9, -10, -12, -15 and -17 and ADAMTS-1 in mouse uterus during the oestrous cycle. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2005;17(5):543–55.
Mishra B, Koshi K, Kizaki K, Ushizawa K, Takahashi T, Hosoe M, Sato T, Ito A, Hashizume K. Expression of ADAMTS1 mRNA in bovine endometrium and placenta during gestation. Domest Anim Endocrinol. 2013;45(1):43–8.
Wen J, Zhu H, Murakami S, Leung PC, MacCalman CD. Regulation of a disintegrin And Metalloproteinase with ThromboSpondin repeats-1 expression in human endometrial stromal cells by gonadal steroids involves progestins, androgens, and estrogens. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91(12):4825–35.
Cha J, Sun X, Dey SK. Mechanisms of implantation: strategies for successful pregnancy. Nat Med. 2012;18(12):1754–67.
Ng SW, Norwitz GA, Pavlicev M, Tilburgs T, Simon C, Norwitz ER. Endometrial decidualization: the primary driver of pregnancy health. Int J Mole Sci. 2020;21(11):4092.
Szwarc MM, Hai L, Gibbons WE, Mo Q, Lanz RB, DeMayo FJ, Lydon JP. Early growth response 1 transcriptionally primes the human endometrial stromal cell for decidualization. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019;189:283–90.
Kommagani R, Szwarc MM, Vasquez YM, Peavey MC, Mazur EC, Gibbons WE, Lanz RB, DeMayo FJ, Lydon JP. The promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger transcription factor is critical for human endometrial stromal cell decidualization. PLoS Genet. 2016;12(4): e1005937.
Russell DL, Brown HM, Dunning KR. ADAMTS proteases in fertility. Matrix Biol. 2015;44–46:54–63.
Das SK, Yano S, Wang J, Edwards DR, Nagase H, Dey SK. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in the mouse uterus during the peri-implantation period. Dev Genet. 1997;21(1):44–54.
Ng YH, Zhu H, Pallen CJ, Leung PC, MacCalman CD. Differential effects of interleukin-1beta and transforming growth factor-beta1 on the expression of the inflammation-associated protein, ADAMTS-1, in human decidual stromal cells in vitro. Hum Reprod. 2006;21(8):1990–9.
Ren Q, Guan S, Fu J, Wang A. Expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 messenger RNA and protein in porcine endometrium during implantation. Mol Biol Rep. 2011;38(6):3829–37.
Arora S, Wang Y, Jia Z, Vardar-Sengul S, Munawar A, Doctor KS, Birrer M, McClelland M, Adamson E, Mercola D. Egr1 regulates the coordinated expression of numerous EGF receptor target genes as identified by ChIP-on-chip. Genome Biol. 2008;9(11):R166.
Shin HJ, Lee JB, Park SH, Chang J, Lee CW. T-bet expression is regulated by EGR1-mediated signaling in activated T cells. Clin Immunol. 2009;131(3):385–94.
Shin SY, Kim JH, Baker A, Lim Y, Lee YH. Transcription factor Egr-1 is essential for maximal matrix metalloproteinase-9 transcription by tumor necrosis factor alpha. Mole Cancer Res. 2010;8(4):507–19.
Rutledge RG, Cote C. Mathematics of quantitative kinetic PCR and the application of standard curves. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31(16): e93.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported in part by a Grant of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Korean Government (NRF-2019R1A6A1A03032888, 2020R1A2C1004122, and 2020R1A2C2005012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HJL and HS conceived and designed the experiments in the manuscript. MP and SHP performed the formal analysis. MP and SHP performed the experiments and analyzed data. MP, SHP, HP, and HRK performed the data visualization. HRK, HJL, and HS supervised this study. MP and HS wrote the original draft. MP, HJL, and HS reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
The content of the manuscript has been approved by all the authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Park, M., Park, S.H., Park, H. et al. ADAMTS-1: a novel target gene of an estrogen-induced transcription factor, EGR1, critical for embryo implantation in the mouse uterus. Cell Biosci 11, 155 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-021-00672-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-021-00672-8