Abstract
As an important player in DNA damage response, BRCA1 maintains genomic stability and suppresses tumorigenesis by promoting DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair through homologous recombination (HR). Since the cloning of BRCA1 gene, many Brca1 mutant alleles have been generated in mice. Mice carrying homozygous Brca1 mutant alleles are embryonic lethal, suggesting that BRCA1’s functions are important for embryonic development. Studies of embryonic development in Brca1 mutant mice not only reveal the physiological significance of BRCA1’s known function in HR, but also lead to the discovery of BRCA1’s new function in HR: regulation of DSB repair pathway choice.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
BRCA1 is a well-known breast and ovarian cancer susceptible gene that is frequently mutated in familial breast and ovarian cancers [1]. BRCA1 mutation carriers also have increased risk of other cancers such as pancreatic cancer and prostate cancer [2, 3]. Since the cloning of the BRCA1 gene more than two decades ago [4], the functions of BRCA1 have been extensively studied. Despite participating in multiple cellular processes, BRCA1 is most well-characterized for its functions in DNA damage response. BRCA1 translocates to DNA damage sites and coordinates both DNA damage repair and DNA damage signaling [5], which are essential for maintaining genomic stability and suppressing tumor formation [6, 7].
DNA double-strand break (DSB) is the most deleterious form of DNA damage that can be generated by exogenous DNA damaging agents or endogenous replication stress. DSBs can be repaired by homologous recombination (HR) or non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). BRCA1 functions in multiple steps to promote DSB repair by HR [8]. BRCA1-deficient cells are HR-deficient and are sensitive to DSB-inducing agents such as platinum-based drugs. Subsequent studies have found that BRCA1-deficient cells are ultra-sensitive to PARP inhibitors (PARPi) [9]. PARP inhibition blocks base excision repair and results in conversion of DNA single-strand breaks (SSBs) to DSBs. PARPi also trap PARP1 on chromatin that requires fixation by HR repair. Therefore, PARPi specifically kill HR-deficient cells, such as BRCA1-deficient cells [10]. PARPi have achieved great success in preclinical mouse models as well as in clinical trials to treat BRCA1-deficient cancers [11]. As a result, several PARPi have been approved for clinical use. However, PARPi resistance has developed over time in many cancer patients, in part by restoring HR [12]. Uncovering the mechanisms how HR is restored in these patients is essential for developing strategies to overcome PARPi resistance.
Studies from the past decade have revealed that BRCA1 promotes HR repair of DSBs at multiple stages. At DSB sites, BRCA1 regulates DSB repair pathway choice by promoting HR over NHEJ, which is achieved by countering 53BP1’s block at DSB ends and promoting DNA end resection, a pre-requisite and determinant step for HR [13,14,15]. After generation of single-strand DNA (ssDNA) by DNA end resection, BRCA1 directly interacts with PALB2 and recruits BRCA2/RAD51 to DSB sites to form RAD51-ssDNA filaments for strand invasion [16,17,18]. A recent study reveals that BRCA1, together with its dimerization partner BARD1, enhances the recombinase activity of RAD51 and promotes RAD51-mediated pairing of homologous sequences [19]. Collectively, BRCA1 functions at three key steps of HR repair of DSBs [8]. In addition, BRCA1 stabilizes stalled replication forks and prevents them from collapsing after replication stress [20]. BRCA1 also promotes the cleavage-coupled break-induced replication pathway to restart stalled replication forks [21]. These functions of BRCA1 can decrease the incidences of DSB formation after replication stress.
Overview of Brca1 mutant mice
Our current knowledge about BRCA1’s function in HR repair is obtained through numerous studies using multiple approaches, including biochemical assays, molecular and cellular studies, crystallography, human genetics, as well as mouse genetics. When BRCA1 gene was first cloned [4], techniques for generating gene knock-out and knock-in mice has become routine. Since then, many mutant alleles of Brca1 have been generated in mice [22]. Characterization of these Brca1 mutant mice has contributed tremendously to the understanding of the physiological functions of BRCA1, especially their roles in HR repair.
To date, more than 20 Brca1 mutant alleles have been generated in mice, including mutations, deletions, conditional deletions, and alleles with humanized sequence. Mice homozygous for many Brca1 mutant alleles are embryonic lethal, suggesting that BRCA1 is important for embryonic development. Conditional knockout of Brca1 in specific tissues have revealed that BRCA1 is important for the development of breast, heart, brain, hair, testis, lymphocytes, and other organs [22]. Tissue-specific Brca1 knockout or mutations, in combination with other transgene or gene knockout, have also been generated for studying BRCA1’s role in the development of breast, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers [22, 23]. Supporting the observations in human patients, most Brca1 knockout and mutations accelerate tissue-specific cancer development in mice [22, 23].
The large number of Brca1 mutant alleles generated reflects the difficulty of understanding BRCA1’s functions by interpreting mouse phenotypes of individual mutant alleles. For example, although mice homozygous for many Brca1 mutant alleles cause embryonic lethality, embryos carrying different Brca1 mutant alleles die at different stages of development, suggesting that these alleles have different impact on BRCA1’s functions. This is largely due to the size of BRCA1 proteins, and presence of distinct functional domains, different isoforms, and various post-translationally modifications. Some Brca1 mutant alleles can only disrupt the functions of certain domains but not the entire BRCA1 protein [22]. On the other hand, analyses of different phenotypes from different mutant alleles provide valuable information about the contribution of different sites, domains, or isoforms to the functions of this large protein, particular in HR repair [22]. In addition, studies of gene disruptions that rescue the embryonic lethality of Brca1 mutant mice have led to the discovery of new functions of BRCA1 in HR. In this article, we will focus on the embryonic lethality phenotypes of Brca1 mutant mice and discuss how different Brca1 mutant alleles have contributed to our understanding of BRCA1’s function in HR repair.
Embryonic development defects of Brca1 mutant mice
BRCA1 is a large protein comprising several important domains. On the N-terminus is a RING domain that interacts with the RING domain of BARD1 to form a constitutive heterodimer [24,25,26]. The RING-RING dimer also harbors E3 ubiquitin ligase activity that is important for HR repair [27, 28]. In the middle is a large region consisting around 60% of the total amino acids of BRCA1 protein, which is encoded by a single exon 11. No specific domains except two nuclear localization signals (NLS) have been identified in this region [29, 30]. This region is followed by a coiled-coiled (CC) domain that directly interacts with PALB2 and facilitates the loading of BRCA2 and RAD51 to DSB sites [16,17,18]. On the C-terminus are tandem BRCT domains that recognize phosphorylated peptides and mediate the interaction of BRCA1 with several phosphorylated proteins [31,32,33]. These domains are required for the formation of distinct BRCA1 complexes (BRCA1-A/B/C complex) with distinct functions [34]. In this section, we will categorize all Brca1 mutant alleles by the domains disrupted and discuss how they impact BRCA1’s function in embryonic development. A summary of all Brca1 mutant alleles can be found in Table 1.
Mice with complete disruption of BRCA1
Among the first batches of Brca1 mutant alleles generated, Brca1Δ5-6 allele is the only null allele [35]. In this allele, exon 5 and 6 are replaced by a neomycin cassette, disrupting sequences encoding the RING domain and generating stop codons in all reading frames. Experiments confirm that BRCA1 is indeed absent from embryos homozygous for Brca1Δ5-6 allele [35]. Mice homozygous for this allele are embryonic lethal. Homozygous embryos seem normal before implantation, but postimplantation embryos die before E7.5. Abnormal embryonic development with hindered gastrulation starts to be observed at E5.5, and there are clear defects of epiblast cell proliferation in these embryos. Consistently, inner cell mass from homozygous blastocysts do not grow in vitro and no homozygous embryonic stem cells can be obtained. Based on these observations, it is postulated that BRCA1 is required for cell proliferation. However, this hypothesis seems contradictory to the observation in BRCA1 mutant human cancers, where BRCA1 mutations do not compromise cell proliferation. It is possible that BRCA1 is only required for the proliferation of certain cell lineages. Since BRCA1 is required for HR repair, it is likely that HR deficiency contributes to the defects in homozygous Brca1Δ5-6 embryos [35]. In agreement with this possibility, loss of RAD51, the key enzyme for HR repair, leads to similar defects in mice [36, 37]. Therefore, HR repair is required for proper cell proliferation and early embryonic development in mice. Brca1flox5-6 is a Brca1 conditional null allele, which is seldomly used to study the tissue-specific function of BRCA1 [38].
Another Brca1 null allele, Brca1Δ5-13, has been generated from a Brca1 conditional null allele, Brca1flox5-13 [39]. In this allele, sequences from exon 5 to 13 are deleted, disrupting all functional domains of BRCA1. Mice homozygous for Brca1Δ5-13 allele are also early embryonic lethal, but the defects in embryonic development are not characterized. Importantly, Brca1flox5-13 allele is a Brca1 conditional null allele that is frequently used. This allele has been used to examine tissue-specific functions of BRCA1 and the phenotypes can fully reflect BRCA1’s functions in these tissues. This allele has also been used to generate tissue-specific BRCA1 null cancer models. Tumors from these mice should reflect the characteristics of human cancers with complete loss of BRCA1 expression.
Mice with Exon 11 disruptions
Exon 11 is the largest exon that spans more than half of the coding sequences of the Brca1 gene. Besides nuclear localization signals, no domains are encoded by this exon. A number of alleles disrupting exon 11 have been generated, but there are some differences in the phenotypes observed. In the first allele, Brca1Δ223-763, 330 bp of intron 10 and 1.5 kb of exon 11, including the splice acceptor for exon 11, are replaced by a neomycin cassette, deleting amino acids 223–763 of BRCA1 protein [40]. Mice homozygous for this allele are embryonic lethal. The lethality occurs between E8.5 and E13.5, which is much latter than embryos homozygous for Brca1Δ5-6 null allele. ES cells homozygous for Brca1Δ223-763 allele are viable, but HR repair efficiency is severely compromised [41]. A similar allele, Brca111−, is generated in which 330 bp of intron 10 and 407 bp of exon 11 are replaced by a neomycin cassette [42]. Although shorter sequences are deleted, embryos homozygous for this allele die earlier between E7.5 and E9.5. In the third allele, Brca1Δ300-361, an even shorter sequence within exon 11 is replaced by a neomycin cassette, deleting amino acids 300–361 of BRCA1 protein [43]. Surprisingly, although the sequence deleted in exon 11 is the shortest in Brca1Δ300-361 allele, embryos homozygous for this allele display much more severe phenotype. Homozygous embryos are abnormal starting from E4.5–5.5 and are dead by E7.5, which is similar to the phenotypes of homozygous Brca1Δ5-6 null embryos. The reasons behind these observations are not clear.
In the fourth allele, Brca1tr, a piece of 50 bp DNA is inserted in exon 11 and causes protein termination at amino acid 924 [44]. Non-sense mediated mRNA decay leads to dramatic reduction of full-length transcript, but the natural Δ11 isoform is still normally produced. Therefore, this allele is a hypomorphic allele. Mice homozygous for this allele are viable depending on genetic background. They are completely viable in 129/Sv or MF1 background, but the viability is dramatically reduced in C57BL/6J background. The viable homozygous mutant mice develop a variety of tumors including breast tumors.
An allele with precise exon 11 deletion, Brca1Δ11, is generated from a Brca1 conditional Δ11 allele, Brca1flox11 [45]. As the full-length isoform (around 220 kDa) is converted to Δ11 isoform (around 100 kDa), the expression of Δ11 isoform is higher than usual. Brca1Δ11/Δ11 mice is largely embryonic lethal, although a very small number of mice can be found in newborn mice. Brca1Δ11/Δ11 embryos die between E12.5–18.5, suggesting that the full length BRCA1 is required for embryonic development. Since Brca1Δ11/Δ11 embryos die at a later stage than Brca1 null embryos, it is likely that BRCA1Δ11 protein still retains some functions of BRCA1. This is not surprising because BRCA1Δ11 protein still contains the RING, CC, and BRCT domains. Despite partially defective in nuclear localization, this protein still dimerizes with BARD1, interacts with PALB2, and localizes to DNA damage sites [46]. Therefore, Brca1Δ11 allele is a hypomorphic allele. The conditional Δ11 allele, Brca1flox11, has been used in many studies to examine tissue-specific function of BRCA1 and to establish tissue-specific tumor models. Given that BRCA1’s function is partially retained in BRCA1Δ11 protein, caution should be taken when interpreting studies using this allele. It is also surprising that Brca1Δ11/Δ11 embryos die much later than mice homozygous for the above three alleles that disrupt exon 11, which implies that the above three alleles not only disrupt exon 11 but also affect other regions of Brca1 gene.
Brca1Δ11 transcript isoform is naturally present, but it is not clear if this isoform has specific functions. In order to address this issue, the Δ11 isoform is specifically disrupted without affecting the full-length isoform [47], creating a full-length isoform-only allele Brca1FL. Mice homozygous for this allele are fully viable. They have no obvious phenotypes except for elevated tumor formation, uterine hyperplasia, and mammary gland abnormalities. Therefore, the Δ11 isoform is dispensable for mouse development but might be required for some subtle functions of BRCA1 in older mice.
Mice with RING domain disruptions
BRCA1 is a big protein with several functional domains. Although complete gene disruption in mice reveals that BRCA1 is required for embryonic development, disruption of individual domains in mice can provide additional insights into the mechanism underlying BRCA1’s functions in this process. In addition, disruption of individual domains in mice can mimic the mutations in cancer patients so that these mice can be used for investigating the role of individual domains in tumor suppression. Currently, several alleles have been generated to disrupt the RING and the BRCT domains of BRCA1 in mice.
The RING domain of BRCA1 interacts with BARD1 to form a heterodimeric E3 ubiquitin ligase. The first allele disrupting the RING domain is Brca1ex2, in which a neomycin cassette replaces exon 2 that encodes part of the RING domain [48]. Since the translation start codon is present in exon 2, it is believed that BRCA1 translation is abolished so that Brca1ex2 allele is a null allele. Mice homozygous for Brca1ex2 allele are embryonic lethal, but lethality occurs from E6.5 to E9.5, which is later than Brca1 null mice Brca1Δ5-6/Δ5-6. Recently, it is found that disruption of exon 2 in Brca1ex2 allele generates a transcript in which exon 1 is directly spliced to exon 3. Although the original translation start codon in exon 2 is deleted, another translation start codon is activated at Met-90 or Met-99 to produce a truncated BRCA1 protein that lacks most amino acids of the RING domain but retains the amino acids for the rest of the protein. Therefore, Brca1ex2 allele is not a null allele but a mutant allele that produces a BRCA1ΔRING protein, which explains the different embryonic development defects between Brca1ex2/ex2 and Brca1Δ5-6/Δ5-6 mice. A conditional allele with precise deletion of exon 2, Brca1flex2, has also been generated [49]. Mice carrying Brca1ex2 and Brca1flex2 alleles have been used as the null and conditional null allele in several studies. Therefore, caution should be taken when interpreting the results of these studies.
A similar allele, Brca1185stop, is generated in mice to mimic the common founder mutation BRCA1185delAG in human cancer patients [50]. Similar to Brca1ex2 allele, Brca1185stop allele causes translation to start from a downstream start codon at Met-90 and produces a BRCA1ΔRING protein. Mice homozygous for Brca1185stop allele are embryonic lethal and embryos die between E9.5 to E13.5. The third allele, Brca1C61G, is generated in mice to mimic one of the most frequent missense mutations, BRCA1C61G, in human cancer patients [51]. Instead of generating stop codons and producing a BRCA1ΔRING protein, this mutation disrupts the structure of the RING domain, reduces BARD1 binding, and abolishes the E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. Similar to Brca1185stop allele, embryos homozygous for Brca1C61G allele die between E9.5 and E12.5.
Instead of disrupting the RING domain structure, a point mutation is generated in Brca1I26A allele to specifically abolish the E3 ligase activity of BRCA1 [41]. Interestingly, mice homozygous for Brca1I26A allele is viable, suggesting that the E3 ligase activity of BRCA1 is dispensable for embryonic development. In agreement with this observation, abolishing the E3 ubiquitin ligase activity of BRCA1 does not affect cell viability or HR repair either [52]. It seems that the structural role, but not the catalytic role, of the RING domain is important for BRCA1’s function in HR repair and embryonic development.
Mice with BRCT domain disruptions
The tandem BRCT domains on the C-terminus of BRCA1 interact with multiple phosphorylated proteins and are required for BRCA1’s localization at DSB sites. The first allele disrupting the tandem BRCT domains, Brca11700T, is generated by inserting a neomycin cassette into exon 20 to remove the last BRCT domain [53]. Mice homozygous for this allele are embryonic lethal and homozygous embryos die between E9.5 and E10.5, which is less severe than Brca1 null embryos. The second allele, Brca15382stop, is generated to mimic the common founder mutation BRCA15382insC in human cancer patients, which leads to deletion of the last BRCT domain as well [50]. Similarly, homozygous embryos for this allele die between E9.5 and E12.5, which is less severe than Brca1 null embryos. A conditional allele, Brca1F22-24, is also generated that deletes exons 22 to 24 and removes the last BRCT domain upon Cre-mediated incision [54]. Mice homozygous for Brca1Δ22-24 allele are not generated to analyze the embryonic development. Unlike the lethality of Brca1Δ5-6/Δ5-6 null ES cells, viable Brca1Δ22-24/Δ22-24 ES cells can be obtained by Cre-mediated incision in Brca1F22-24/Δ22-24 ES cells [55]. An allele that disrupt both CC and BRCT domains, Brca1ΔC, is recently generated [56]. Mice homozygous for this allele is also lethal, but embryonic development is not analyzed.
In Brca1Δ22-24/Δ22-24 ES cells, no truncated BRCA1ΔBRCT proteins can be detected [55]. In Brca15382stop/− mouse tumors, no truncated BRCA1ΔBRCT proteins can be detected either [50]. Similarly, no truncated BRCA1ΔC proteins can be found in Brca1ΔC/ΔC cells [56]. In agreement with these observations in mouse cells, truncated BRCA1ΔBRCT proteins cannot be detected either in several human cancer cell lines with truncating mutations at BRCA1 BRCT domains [56, 57]. It has been reported that many BRCT domain mutations cause folding defects and proteasomal degradation of these truncated proteins [58]. Based on these observations, it has been proposed that these BRCT domain mutant alleles are equivalent to Brca1 null alleles. However, the defects of Brca11700T/1700T and Brca15382stop/5382stop embryos are less severe than Brca1 null embryos, suggesting that these BRCT domain mutant alleles are unlikely true Brca1 null allele. It is possible that truncated BRCA1ΔBRCT proteins are still present at low levels in these cells [50, 53].
Instead of disrupting the BRCT domain structure, a point mutation at BRCA1 BRCT domains is generated in Brca1S1598F allele to specifically abolish the phosphorylated protein binding pocket without affecting protein stability [41]. Surprisingly, mice homozygous for Brca1S1598F allele is viable. Interestingly, Brca1S1598F/S1598F ES cells are also viable but have deficiency in HR repair. These observations suggest that HR deficiency can be tolerated in embryonic development in certain situations. Therefore, the overall structure, but not the phosphorylated protein binding abilities, of the tandem BRCT domains is important for the function of BRCA1 in embryonic development.
Mice with disrupted phosphorylation
After DNA damage, BRCA1 is phosphorylated at serine 988 by CHK2 and is phosphorylated at serine 1189 by ATM [59, 60]. Since BRCA1 is required for certain ATM and ATR signaling, it is possible that these phosphorylation sites are important for BRCA1’s function. To address this possibility, Brca1S971A and Brca1S1152A alleles are generated in mice by mutating the amino acids corresponding to the phosphorylation sites in human BRCA1 [61, 62]. Mice homozygous for both alleles are viable and have no major developmental defects. Therefore, CHK2 and ATM-dependent phosphorylation of BRCA1 is dispensable for embryonic development.
Rescue of embryonic development defects of Brca1 mutant mice
Studies of Brca1 mutant mice have revealed that BRCA1 is essential for embryonic development, which requires most of its domains including the RING domain, the BRCT domains, and the regions encoded by exon 11. Further studies have revealed that inactivating p53 signaling or 53BP1 can rescue the lethality or prolong the survival of Brca1 mutant embryos, shedding lights on the mechanism of BRCA1’s functions in embryonic development. In this section, we will summarize our current understanding about how embryonic development of some Brca1 mutant embryos can be rescued or prolonged and discuss the underlying mechanisms. A summary of these mutant alleles can be found in Table 2.
Rescue of embryonic development defects by compromising p53 signaling
In most Brca1 mutant mice, embryonic lethality is caused by cell death in postimplantation embryos. Interestingly, the death of Brca1Δ5-6/Δ5-6 embryos before E7.5 is preceded by a dramatic increase of p21 expression in E4 Brca1Δ5-6/Δ5-6 embryos [35]. p21 is an important cell cycle regulator whose activation leads to G1/S arrest. Since p21 is downstream of p53, a master controller of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, it is likely that p53 signaling is activated in Brca1Δ5-6/Δ5-6 embryos. To test if p53 signaling activation is responsible for the lethality of Brca1Δ5-6/Δ5-6 embryos, Brca1Δ5-6/Δ5-6;p53−/− and Brca1Δ5-6/Δ5-6;p21−/− double mutant mice are generated. Although p21 KO or p53 KO fails to rescue the lethality of Brca1Δ5-6/Δ5-6 embryos, they can prolong the survival of these embryo from E7.5 to around E9.5 [63]. Similarly, p53 KO can improve the morphology of Brca1ex2/ex2 embryos at E8.5 and E9.5 [48].
Mutant mice with different Brca1 exon 11 disruptions have different phenotypes and most die at different embryonic stages. In some mutant mice, it has been examined if p53 KO can rescue the embryonic lethality. In Brca111−/− embryos, which die between E7.5 and E9.5, p53 KO can extend the survival for 2 days [42]. Brca1Δ223-763/Δ223-763 embryos die between E8.5 and E13.5, and the lethality can be significantly rescued by p53 KO so that occasional viable Brca1Δ223-763/Δ223-763;p53−/− double mutant mice can be obtained [64]. Most significantly, the embryonic lethality of Brca1Δ11/Δ11 embryos, most of which die between E12.5–18.5, can be fully rescued by p53 heterozygosity or KO [45]. These observations suggest that p53 signaling activation contributes to the death of Brca1 mutant embryos.
p53 activation is usually accompanied by its phosphorylation. After DSB formation, p53 can be phosphorylated by ATM at serine 15. ATM also phosphorylates CHK2, which can in turn phosphorylate p53 at serine 20 [65, 66]. These findings support that ATM-CHK2 signaling is important for p53 activation. Interestingly, the embryonic lethality of Brca1Δ11/Δ11 embryos can be fully rescued by Chk2 KO or Atm KO or partially rescued by Chk2 or Atm heterozygosity [67]. In line with these observations, Chk2 KO can rescue the T cell development defects of T-cell specific Brca1 knockout mice using Brca1flox5-6 mice [68]. Therefore, BRCA1 deficiency activates ATM-CHK2-p53 signaling, which plays a significant role in the death of Brca1 mutant embryos.
Rescue of embryonic lethality by 53bp1 KO
Studies have shown that Brca1Δ11/Δ11 mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) become senescent rapidly in culture, which can be suppressed by p53 KO [45]. By screening factors required for premature senescence of Brca1Δ11/Δ11 MEFs, 53BP1 is identified among proteins involved in DNA damage response and cell cycle regulation [69]. 53bp1 KO not only suppresses premature senescence of Brca1Δ11/Δ11 MEFs, but also fully rescues the embryonic lethality of Brca1Δ11/Δ11 mice [69]. Interestingly, ATM-CHK2-p53 signaling is intact in Brca1Δ11/Δ11;53bp1−/− cells, suggesting that the rescue is through a distinct mechanism. Subsequent study reveals that 53bp1 KO restores HR efficiency in Brca1Δ11/Δ11 cells [70]. Similarly, 53bp1 KO rescues the embryonic lethality of Brca1ex2/ex2 mice by restoring HR efficiency in Brca1ex2/ex2 cells [71, 72]. In line with these observations, 53BP1 loss rescues PARPi sensitivity of human BRCA1 mutant cancer cells and contributes to PARPi resistance in Brca1 null mouse breast cancer models [73]. Subsequent studies have revealed that loss of proteins associated with 53BP1, such as PTIP, RIF1, DYNLL1, and the Shielding complex, can also rescue the HR repair defect and PARPi sensitivity of human BRCA1 mutant cancer cells [74,75,76,77,78]. It will be interesting to examine if loss of these 53BP1-associated proteins can promote the embryonic development of Brca1 mutant mice.
Mechanistic studies of the above observations have revealed a novel function of BRCA1 in HR: regulating DSB repair pathway choice [13,14,15]. BRCA1 counteracts 53BP1’s block at DSB ends, promotes CTIP and MRE11-dependent DNA end resection, and directs DSB repair pathway choice towards HR. In cells with mutant BRCA1, such as Brca1Δ11/Δ11 and Brca1ex2/ex2 cells, 53BP1 remains at DSB ends, blocks DNA end resection, directs DSB repair pathway choice towards NHEJ, and causes HR deficiency. Loss of 53BP1 in Brca1 mutant cells removes the block at DSB ends, allows DNA end resection to occur, and restores HR repair without intact BRCA1.
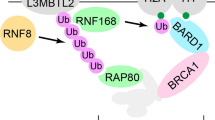
H2AX-MDC1-RNF8-RNF168 signaling pathways regulate histone ubiquitination upstream of 53BP1 in DNA damage response and are required for the recruitment of 53BP1 to DSB sites [79]. However, H2ax KO, Rnf8 KO, or Rnf168 KO fails to rescue the embryonic lethality of Brca1Δ11/Δ11 mice [69, 80]. On the contrary, Rnf168 KO can rescue the embryonic lethality of Brca1ex2/ex2 mice [80]. Subsequent analyses reveal that the ability to interact with PALB2 is compromised in BRCA1Δ11 protein (encoded by Brca1Δ11 allele) but is maintained in BRCA1ΔRING protein (encoded by Brca1Δ2 allele) [80]. In addition to promoting histone ubiquitination, RNF168 also directly interacts with PALB2 and loads PALB2 to DSB sites [81], which serves as a backup mechanism for BRCA1-dependent PALB2 loading [80]. Rnf168 KO prevents 53BP1’s block at DSB sites, restores DNA end resection, and directs DSB repair pathway choice towards HR in both Brca1Δ11/Δ11 and Brca1ex2/ex2 cells. However, due to BRCA1Δ11 protein’s defect in PALB2 interaction and loading, loss of RNF168-dependent PALB2 loading compromises overall PALB2 loading in Brca1Δ11/Δ11 cells and fails to rescue HR defects in these cells. On the contrary, since BRCA1ΔRING protein can interact and load PALB2, the loss of RNF168-dependent PALB2 loading has no impact on overall PALB2 loading in Brca1ex2/ex2 cells and HR is restored in these cells [80].
Although it is generally believed that HR deficiency is the major cause for embryonic lethality of Brca1 mutant mice and 53bp1 KO rescues embryonic lethality of these mice by restoring HR, a recent study has challenged this idea by showing that 53bp1 KO rescues the embryonic lethality of Brca1ΔC/ΔC mice without significantly restoring HR in Brca1ΔC/ΔC cells [56]. BRCA1ΔC protein lacks the CC domain to interact with PALB2 and lacks the BRCT domains to locate to DSB site. In addition, BRCA1ΔC protein is not stable enough to be detected, making Brca1ΔC/ΔC mice close to Brca1 null mice. Therefore, despite rescuing DNA end resection by 53bp1 KO, PALB2 and BRCA2/RAD51 complex fails to be efficiently recruited to DSB sites, causing HR deficiency in Brca1ΔC/ΔC;53bp1−/− cells. In agreement with this study, our recent study has also found that 53bp1 KO partially rescues the embryonic lethality of complete Brca1 null mice (Brca1Δ5-13/Δ5-13) without restoring HR in complete Brca1 null cells [82]. Similar observations have been made in a recent study that mutating 53BP1 to disrupt PTIP binding in 53bp1S25A/S25A mice can rescue the embryonic lethality of Brca1Δ11/Δ11 mice without significantly restoring HR in Brca1Δ11/Δ11 cells [83]. It is noteworthy that although largely HR deficient, minor restoration of HR is still observed in Brca1ΔC/ΔC;53bp1−/− and Brca1Δ5-13/Δ5-13;53bp1−/− cells, which is likely due to BRCA1-independent HR, such as RNF168-dependent PALB2 loading and HR. It is possible that such minor restoration of HR is sufficient for supporting embryonic development. Nevertheless, these studies suggest that HR deficiency might not be the major cause for embryonic lethality of Brca1 mutant mice.
BRCA1 is important for protecting replication fork from collapsing after replication stress [20]. However, although 53bp1 KO can rescue the lethality of Brca1Δ11/Δ11, Brca1ex2/ex2, and Brca1ΔC/ΔC embryos, it cannot rescue the replication fork protection defects in Brca1Δ11/Δ11, Brca1ex2/ex2, or Brca1ΔC/ΔC cells [20, 56, 72]. Therefore, replication fork protection defect unlikely contributes significantly to the embryonic lethality of Brca1 mutant mice. The major cause for the embryonic lethality of Brca1 mutant remains to be clarified.
Conclusions
As a key protein that promotes DSB repair by HR, BRCA1 has been extensively studied using multiple approaches. Since the first report of Brca1 mutant mice more than 20 years ago, many different Brca1 mutant mice have been generated to study the physiological functions of BRCA1 in vivo. Among various defects identified in Brca1 mutant and conditional mutant mice, embryonic lethality remains the most significant phenotypes of most Brca1 mutant mice. Analyses of embryos and cells from these mice have not only complemented the in vitro findings that BRCA1 is important for HR, but also clarified the impact of different domain deletions and mutations on HR. Importantly, studies of gene disruptions that rescue the embryonic lethality of Brca1 mutant mice have led to the discovery of a novel function of BRCA1 in DSB repair pathway choice. Collectively, studies of embryonic development of Brca1 mutant mice have significantly advanced our understanding of BRCA1’s functions in HR. Generating additional Brca1 mutant mouse models in future can facilitate addressing unsolved questions about BRCA1’s functions in HR.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
References
King MC, Marks JH, Mandell JB, New York Breast Cancer Study, G. Breast and ovarian cancer risks due to inherited mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2. Science. 2003;302:643–6.
Waddell N, Pajic M, Patch AM, Chang DK, Kassahn KS, Bailey P, Johns AL, Miller D, Nones K, Quek K, et al. Whole genomes redefine the mutational landscape of pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2015;518:495–501.
Robinson D, Van Allen EM, Wu YM, Schultz N, Lonigro RJ, Mosquera JM, Montgomery B, Taplin ME, Pritchard CC, Attard G, et al. Integrative clinical genomics of advanced prostate cancer. Cell. 2015;161:1215–28.
Miki Y, Swensen J, Shattuck-Eidens D, Futreal PA, Harshman K, Tavtigian S, Liu Q, Cochran C, Bennett LM, Ding W, et al. A strong candidate for the breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1. Science. 1994;266:66–71.
Jiang Q, Greenberg RA. Deciphering the BRCA1 tumor suppressor network. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:17724–32.
Li ML, Greenberg RA. Links between genome integrity and BRCA1 tumor suppression. Trends Biochem Sci. 2012;37:418–24.
Kass EM, Moynahan ME, Jasin M. When genome maintenance goes badly Awry. Mol Cell. 2016;62:777–87.
Zhao W, Wiese C, Kwon Y, Hromas R, Sung P. The BRCA tumor suppressor network in chromosome damage repair by homologous recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 2019;88:221–45.
Farmer H, McCabe N, Lord CJ, Tutt AN, Johnson DA, Richardson TB, Santarosa M, Dillon KJ, Hickson I, Knights C, et al. Targeting the DNA repair defect in BRCA mutant cells as a therapeutic strategy. Nature. 2005;434:917–21.
D'Andrea AD. Mechanisms of PARP inhibitor sensitivity and resistance. DNA Repair. 2018;71:172–6.
Lord CJ, Ashworth A. PARP inhibitors: synthetic lethality in the clinic. Science. 2017;355:1152–8.
Mateo J, Lord CJ, Serra V, Tutt A, Balmana J, Castroviejo-Bermejo M, Cruz C, Oaknin A, Kaye SB, de Bono JS. A decade of clinical development of PARP inhibitors in perspective. Ann Oncol. 2019;30:1437–47.
Daley JM, Sung P. 53BP1, BRCA1, and the choice between recombination and end joining at DNA double-strand breaks. Mol Cell Biol. 2014;34:1380–8.
Ceccaldi R, Rondinelli B, D'Andrea AD. Repair pathway choices and consequences at the double-strand break. Trends Cell Biol. 2016;26:52–64.
Scully R, Panday A, Elango R, Willis NA. DNA double-strand break repair-pathway choice in somatic mammalian cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20:698–714.
Zhang F, Ma J, Wu J, Ye L, Cai H, Xia B, Yu X. PALB2 links BRCA1 and BRCA2 in the DNA-damage response. Curr Biol. 2009;19:524–9.
Sy SM, Huen MS, Chen J. PALB2 is an integral component of the BRCA complex required for homologous recombination repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:7155–60.
Zhang F, Fan Q, Ren K, Andreassen PR. PALB2 functionally connects the breast cancer susceptibility proteins BRCA1 and BRCA2. Mol Cancer Res. 2009;7:1110–8.
Zhao W, Steinfeld JB, Liang F, Chen X, Maranon DG, Jian Ma C, Kwon Y, Rao T, Wang W, Sheng C, et al. BRCA1-BARD1 promotes RAD51-mediated homologous DNA pairing. Nature. 2017;550:360–5.
Ray Chaudhuri A, Callen E, Ding X, Gogola E, Duarte AA, Lee JE, Wong N, Lafarga V, Calvo JA, Panzarino NJ, et al. Replication fork stability confers chemoresistance in BRCA-deficient cells. Nature. 2016;535:382–7.
Xu Y, Ning S, Wei Z, Xu R, Xu X, Xing M, Guo R, Xu D. 53BP1 and BRCA1 control pathway choice for stalled replication restart. Elife. 2017;6:e30523.
Dine J, Deng CX. Mouse models of BRCA1 and their application to breast cancer research. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2013;32:25–37.
Barcellos-Hoff MH, Kleinberg DL. Breast cancer risk in BRCA1 mutation carriers: insight from mouse models. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(Suppl 8):viii8–viii12.
Wu LC, Wang ZW, Tsan JT, Spillman MA, Phung A, Xu XL, Yang MC, Hwang LY, Bowcock AM, Baer R. Identification of a RING protein that can interact in vivo with the BRCA1 gene product. Nat Genet. 1996;14:430–40.
Joukov V, Chen J, Fox EA, Green JB, Livingston DM. Functional communication between endogenous BRCA1 and its partner, BARD1, during Xenopus laevis development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:12078–83.
Brzovic PS, Rajagopal P, Hoyt DW, King MC, Klevit RE. Structure of a BRCA1-BARD1 heterodimeric RING-RING complex. Nat Struct Biol. 2001;8:833–7.
Brzovic PS, Keeffe JR, Nishikawa H, Miyamoto K, Fox D 3rd, Fukuda M, Ohta T, Klevit R. Binding and recognition in the assembly of an active BRCA1/BARD1 ubiquitin-ligase complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:5646–51.
Densham RM, Garvin AJ, Stone HR, Strachan J, Baldock RA, Daza-Martin M, Fletcher A, Blair-Reid S, Beesley J, Johal B, et al. Human BRCA1-BARD1 ubiquitin ligase activity counteracts chromatin barriers to DNA resection. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2016;23:647–55.
Chen CF, Li S, Chen Y, Chen PL, Sharp ZD, Lee WH. The nuclear localization sequences of the BRCA1 protein interact with the importin-alpha subunit of the nuclear transport signal receptor. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:32863–8.
Thakur S, Zhang HB, Peng Y, Le H, Carroll B, Ward T, Yao J, Farid LM, Couch FJ, Wilson RB, et al. Localization of BRCA1 and a splice variant identifies the nuclear localization signal. Mol Cell Biol. 1997;17:444–52.
Manke IA, Lowery DM, Nguyen A, Yaffe MB. BRCT repeats as phosphopeptide-binding modules involved in protein targeting. Science. 2003;302:636–9.
Yu X, Chini CC, He M, Mer G, Chen J. The BRCT domain is a phospho-protein binding domain. Science. 2003;302:639–42.
Wang B. BRCA1 tumor suppressor network: focusing on its tail. Cell Biosci. 2012;2:6.
Huen MS, Sy SM, Chen J. BRCA1 and its toolbox for the maintenance of genome integrity. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:138–48.
Hakem R, de la Pompa JL, Sirard C, Mo R, Woo M, Hakem A, Wakeham A, Potter J, Reitmair A, Billia F, et al. The tumor suppressor gene Brca1 is required for embryonic cellular proliferation in the mouse. Cell. 1996;85:1009–233.
Tsuzuki T, Fujii Y, Sakumi K, Tominaga Y, Nakao K, Sekiguchi M, Matsushiro A, Yoshimura Y, Morita T. Targeted disruption of the Rad51 gene leads to lethality in embryonic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:6236–40.
Lim DS, Hasty P. A mutation in mouse rad51 results in an early embryonic lethal that is suppressed by a mutation in p53. Mol Cell Biol. 1996;16:7133–43.
Mak TW, Hakem A, McPherson JP, Shehabeldin A, Zablocki E, Migon E, Duncan GS, Bouchard D, Wakeham A, Cheung A, et al. Brca1 required for T cell lineage development but not TCR loci rearrangement. Nat Immunol. 2000;1:77–82.
Liu X, Holstege H, van der Gulden H, Treur-Mulder M, Zevenhoven J, Velds A, Kerkhoven RM, van Vliet MH, Wessels LF, Peterse JL, et al. Somatic loss of BRCA1 and p53 in mice induces mammary tumors with features of human BRCA1-mutated basal-like breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:12111–6.
Gowen LC, Johnson BL, Latour AM, Sulik KK, Koller BH. Brca1 deficiency results in early embryonic lethality characterized by neuroepithelial abnormalities. Nat Genet. 1996;12:191–4.
Shakya R, Reid LJ, Reczek CR, Cole F, Egli D, Lin CS, deRooij DG, Hirsch S, Ravi K, Hicks JB, et al. BRCA1 tumor suppression depends on BRCT phosphoprotein binding, but not its E3 ligase activity. Science. 2011;334:525–8.
Shen SX, Weaver Z, Xu X, Li C, Weinstein M, Chen L, Guan XY, Ried T, Deng CX. A targeted disruption of the murine Brca1 gene causes gamma-irradiation hypersensitivity and genetic instability. Oncogene. 1998;17:3115–244.
Liu CY, Flesken-Nikitin A, Li S, Zeng Y, Lee WH. Inactivation of the mouse Brca1 gene leads to failure in the morphogenesis of the egg cylinder in early postimplantation development. Genes Dev. 1996;10:1835–43.
Ludwig T, Fisher P, Ganesan S, Efstratiadis A. Tumorigenesis in mice carrying a truncating Brca1 mutation. Genes Dev. 2001;15:1188–93.
Xu X, Wagner KU, Larson D, Weaver Z, Li C, Ried T, Hennighausen L, Wynshaw-Boris A, Deng CX. Conditional mutation of Brca1 in mammary epithelial cells results in blunted ductal morphogenesis and tumour formation. Nat Genet. 1999;22:37–433.
Huber LJ, Yang TW, Sarkisian CJ, Master SR, Deng CX, Chodosh LA. Impaired DNA damage response in cells expressing an exon 11-deleted murine Brca1 variant that localizes to nuclear foci. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21:4005–15.
Kim SS, Cao L, Lim SC, Li C, Wang RH, Xu X, Bachelier R, Deng CX. Hyperplasia and spontaneous tumor development in the gynecologic system in mice lacking the BRCA1-Delta11 isoform. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26:6983–92.
Ludwig T, Chapman DL, Papaioannou VE, Efstratiadis A. Targeted mutations of breast cancer susceptibility gene homologs in mice: lethal phenotypes of Brca1, Brca2, Brca1/Brca2, Brca1/p53, and Brca2/p53 nullizygous embryos. Genes Dev. 1997;11:1226–411.
Shakya R, Szabolcs M, McCarthy E, Ospina E, Basso K, Nandula S, Murty V, Baer R, Ludwig T. The basal-like mammary carcinomas induced by Brca1 or Bard1 inactivation implicate the BRCA1/BARD1 heterodimer in tumor suppression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:7040–5.
Drost R, Dhillon KK, van der Gulden H, van der Heijden I, Brandsma I, Cruz C, Chondronasiou D, Castroviejo-Bermejo M, Boon U, Schut E, et al. BRCA1185delAG tumors may acquire therapy resistance through expression of RING-less BRCA1. J Clin Investig. 2016;126:2903–18.
Drost R, Bouwman P, Rottenberg S, Boon U, Schut E, Klarenbeek S, Klijn C, van der Heijden I, van der Gulden H, Wientjens E, et al. BRCA1 RING function is essential for tumor suppression but dispensable for therapy resistance. Cancer Cell. 2011;20:797–809.
Reid LJ, Shakya R, Modi AP, Lokshin M, Cheng JT, Jasin M, Baer R, Ludwig T. E3 ligase activity of BRCA1 is not essential for mammalian cell viability or homology-directed repair of double-strand DNA breaks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:20876–81.
Hohenstein P, Kielman MF, Breukel C, Bennett LM, Wiseman R, Krimpenfort P, Cornelisse C, van Ommen GJ, Devilee P, Fodde R. A targeted mouse Brca1 mutation removing the last BRCT repeat results in apoptosis and embryonic lethality at the headfold stage. Oncogene. 2001;20:2544–50.
McCarthy A, Savage K, Gabriel A, Naceur C, Reis-Filho JS, Ashworth A. A mouse model of basal-like breast carcinoma with metaplastic elements. J Pathol. 2007;211:389–98.
Foray N, Marot D, Gabriel A, Randrianarison V, Carr AM, Perricaudet M, Ashworth A, Jeggo P. A subset of ATM- and ATR-dependent phosphorylation events requires the BRCA1 protein. EMBO J. 2003;22:2860–71.
Nacson J, Krais JJ, Bernhardy AJ, Clausen E, Feng W, Wang Y, Nicolas E, Cai KQ, Tricarico R, Hua X, et al. BRCA1 mutation-specific responses to 53BP1 loss-induced homologous recombination and PARP Inhibitor resistance. Cell Rep. 2018;24(3513–3527):e3517.
Johnson N, Johnson SF, Yao W, Li YC, Choi YE, Bernhardy AJ, Wang Y, Capelletti M, Sarosiek KA, Moreau LA, et al. Stabilization of mutant BRCA1 protein confers PARP inhibitor and platinum resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:17041–6.
Williams RS, Chasman DI, Hau DD, Hui B, Lau AY, Glover JN. Detection of protein folding defects caused by BRCA1-BRCT truncation and missense mutations. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:53007–16.
Lee JS, Collins KM, Brown AL, Lee CH, Chung JH. hCds1-mediated phosphorylation of BRCA1 regulates the DNA damage response. Nature. 2000;404:201–4.
Cortez D, Wang Y, Qin J, Elledge SJ. Requirement of ATM-dependent phosphorylation of brca1 in the DNA damage response to double-strand breaks. Science. 1999;286:1162–6.
Kim SS, Cao L, Li C, Xu X, Huber LJ, Chodosh LA, Deng CX. Uterus hyperplasia and increased carcinogen-induced tumorigenesis in mice carrying a targeted mutation of the Chk2 phosphorylation site in Brca1. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:9498–507.
Kim SS, Cao L, Baek HJ, Lim SC, Li C, Wang RH, Xu X, Cho KH, Deng CX. Impaired skin and mammary gland development and increased gamma-irradiation-induced tumorigenesis in mice carrying a mutation of S1152-ATM phosphorylation site in Brca1. Cancer Res. 2009;69:9291–300.
Hakem R, de la Pompa JL, Elia A, Potter J, Mak TW. Partial rescue of Brca1 (5–6) early embryonic lethality by p53 or p21 null mutation. Nat Genet. 1997;16:298–302.
Cressman VL, Backlund DC, Avrutskaya AV, Leadon SA, Godfrey V, Koller BH. Growth retardation, DNA repair defects, and lack of spermatogenesis in BRCA1-deficient mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:7061–75.
Matsuoka S, Huang M, Elledge SJ. Linkage of ATM to cell cycle regulation by the Chk2 protein kinase. Science. 1998;282:1893–7.
Hirao A, Kong YY, Matsuoka S, Wakeham A, Ruland J, Yoshida H, Liu D, Elledge SJ, Mak TW. DNA damage-induced activation of p53 by the checkpoint kinase Chk2. Science. 2000;287:1824–7.
Cao L, Kim S, Xiao C, Wang RH, Coumoul X, Wang X, Li WM, Xu XL, De Soto JA, Takai H, et al. ATM-Chk2-p53 activation prevents tumorigenesis at an expense of organ homeostasis upon Brca1 deficiency. EMBO J. 2006;25:2167–77.
McPherson JP, Lemmers B, Hirao A, Hakem A, Abraham J, Migon E, Matysiak-Zablocki E, Tamblyn L, Sanchez-Sweatman O, Khokha R, et al. Collaboration of Brca1 and Chk2 in tumorigenesis. Genes Dev. 2004;18:1144–53.
Cao L, Xu X, Bunting SF, Liu J, Wang RH, Cao LL, Wu JJ, Peng TN, Chen J, Nussenzweig A, et al. A selective requirement for 53BP1 in the biological response to genomic instability induced by Brca1 deficiency. Mol Cell. 2009;35:534–41.
Bunting SF, Callen E, Wong N, Chen HT, Polato F, Gunn A, Bothmer A, Feldhahn N, Fernandez-Capetillo O, Cao L, et al. 53BP1 inhibits homologous recombination in Brca1-deficient cells by blocking resection of DNA breaks. Cell. 2010;141:243–54.
Bunting SF, Callen E, Kozak ML, Kim JM, Wong N, Lopez-Contreras AJ, Ludwig T, Baer R, Faryabi RB, Malhowski A, et al. BRCA1 functions independently of homologous recombination in DNA interstrand crosslink repair. Mol Cell. 2012;46:125–35.
Li M, Cole F, Patel DS, Misenko SM, Her J, Malhowski A, Alhamza A, Zheng H, Baer R, Ludwig T, et al. 53BP1 ablation rescues genomic instability in mice expressing 'RING-less' BRCA1. EMBO Rep. 2016;17:1532–41.
Jaspers JE, Kersbergen A, Boon U, Sol W, van Deemter L, Zander SA, Drost R, Wientjens E, Ji J, Aly A, et al. Loss of 53BP1 causes PARP inhibitor resistance in Brca1-mutated mouse mammary tumors. Cancer Discov. 2013;3:68–81.
Setiaputra D, Durocher D. Shieldin—the protector of DNA ends. EMBO Rep. 2019;20:pii:e47560.
Zimmermann M, de Lange T. 53BP1: pro choice in DNA repair. Trends Cell Biol. 2014;24:108–17.
He YJ, Meghani K, Caron MC, Yang C, Ronato DA, Bian J, Sharma A, Moore J, Niraj J, Detappe A, et al. DYNLL1 binds to MRE11 to limit DNA end resection in BRCA1-deficient cells. Nature. 2018;563:522–6.
Becker JR, Cuella-Martin R, Barazas M, Liu R, Oliveira C, Oliver AW, Bilham K, Holt AB, Blackford AN, Heierhorst J, et al. The ASCIZ-DYNLL1 axis promotes 53BP1-dependent non-homologous end joining and PARP inhibitor sensitivity. Nat Commun. 2018;9:5406.
West KL, Kelliher JL, Xu Z, An L, Reed MR, Eoff RL, Wang J, Huen MSY, Leung JWC. LC8/DYNLL1 is a 53BP1 effector and regulates checkpoint activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:6236–49.
Uckelmann M, Sixma TK. Histone ubiquitination in the DNA damage response. DNA Repair. 2017;56:92–101.
Zong D, Adam S, Wang Y, Sasanuma H, Callen E, Murga M, Day A, Kruhlak MJ, Wong N, Munro M, et al. BRCA1 haploinsufficiency is masked by RNF168-mediated chromatin ubiquitylation. Mol Cell. 2019;73(1267–1281):e1267.
Luijsterburg MS, Typas D, Caron MC, Wiegant WW, van den Heuvel D, Boonen RA, Couturier AM, Mullenders LH, Masson JY, van Attikum H. A PALB2-interacting domain in RNF168 couples homologous recombination to DNA break-induced chromatin ubiquitylation. Elife. 2017;6:e20922.
Chen J, Li P, Song L, Bai L, Huen MS, Liu Y, Lu L. 53BP1 loss rescues embryonic lethality but not genomic instability of BRCA1 total knockout mice. Cell Death Differ. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-020-0521-4.
Callen E, Zong D, Wu W, Wong N, Stanlie A, Ishikawa M, Pavani R, Dumitrache LC, Byrum AK, Mendez-Dorantes C, et al. 53BP1 enforces distinct pre- and post-resection blocks on homologous recombination. Mol Cell. 2020;77:26–38.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work is funded by National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC1004900 and 2016YFC1000600), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LY19C050002), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (81602263 and 81471494).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL and LL prepared the tables and wrote the manuscript. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Consent for publication have been obtained from all authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Lu, LY. BRCA1 and homologous recombination: implications from mouse embryonic development. Cell Biosci 10, 49 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-020-00412-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-020-00412-4