Abstract
Equine influenza virus (EIV) causes a highly contagious disease in horses and other equids. Recently, we isolated an H3N8 EIV (A/equine/Kyonggi/SA1/2011) from a domestic horse in South Korea that exhibited symptoms of respiratory disease, and found that the EIV strain contained a naturally mutated NS gene segment encoding a truncated NS1 protein. In order to determine whether there was an association between the NS gene truncation and viral virulence, a reverse genetics system was applied to generate various NS gene recombinant viruses using the backbone of the H1N1 A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 (PR/8) virus. In a mouse model, the recombinant PR/8 virus containing the mutated NS gene of the Korean H3N8 EIV strain showed a dramatically reduced virulence: it induced no weight loss, no clinical signs and no histopathological lesions. However, the mice infected with the recombinant viruses with NS genes of PR/8 and H3N8 A/equine/2/Miami/1963 showed severe clinical signs including significant weight loss and 100% mortality. In addition, the levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokines; IL-6, CCL5, and IFN-γ, in the lungs of mice infected with the recombinant viruses expressing a full-length NS1 were significantly higher than those of mice infected with the virus with the NS gene from the Korean H3N8 EIV strain. In this study, our results suggest that the C-terminal moiety of NS1 contains a number of virulence determinants and might be a suitable target for the development of a vaccine candidate against equine influenza.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Equine influenza virus (EIV), which is a member of the genus Orthomyxovirus, family Orthomyxoviridae, contains a single-stranded, negative-sense RNA in the following eight gene segments: PB2, PB1, PA, HA, NP, NA, M, and NS. This virus is the causative agent of serious respiratory diseases in horses [1]. There are two distinct influenza A virus subtypes in horses; H7N7 and H3N8. Although H7N7 viruses are no longer circulating in horse populations, H3N8 EIV is continuously isolated in Europe, North America, North Africa, and Asia, including South Korea [1, 2]. It was demonstrated that H3N8 EIV was responsible for the emergence of H3N8 canine influenza A virus (CIV) in North America in 2004 [3]. Genetic analysis revealed that H3N8 CIV originated in a racing greyhound that was previously infected with an H3N8 EIV, and this emergent H3N8 CIV, the representative subtype of CIV in North America, is still circulating in pet dogs [3, 4]. Furthermore, two strains of H3N8 EIV were detected in pigs in China [5]. Thus, H3N8 EIV seems to have the potential to cross the host barrier among animal species. Recently, we isolated from a domestic horse in South Korea an H3N8 EIV strain (A/equine/Kyonggi/SA1/2011; KYG11) belonging to the Florida sublineage clade 1 [2]. Interestingly, the KYG11 strain possessed an NS gene segment that harbored a deletion of nucleotides 326 to 348 of NS1 open reading frame, resulting in a frameshift and a premature stop codon. The encoded NS1 protein was 117 amino acids long [2].
The NS gene of influenza viruses encodes two different nonstructural proteins, NS1 and nuclear export protein. The NS1 protein is known to play a role in the enhancement of influenza virus replication by antagonizing interferon (IFN) production in host cells [6, 7]. In contrast, the replication ability of influenza viruses with a truncated NS1 gene is markedly decreased by inhibited IFN-mediated anti-viral responses in host cells [6–8]. Previous studies have shown that a deletion in the NS1 gene may be associated with the virulence of several subtypes of influenza A viruses such as H3N2 and H5N1 in several animal species [9–11].
Therefore, it was hypothesized that the virulence of the Korean H3N8 EIV strain, KYG11, is influenced by the mutated NS gene. In this study, we aimed at elucidating the effect of the 23 nt deletion within the NS gene in vivo and in vitro and used a reverse genetics system to generate recombinant influenza viruses containing the truncated NS gene of KYG11 or different NS genes from other influenza viruses. The NS gene of KYG11 affected the virulence and immune-pathogenic properties of PR/8 virus in vivo and the results provide important insights into this Korean EIV strain, indicating that a specific region of the NS1 gene confers pathogenicity in mice.
Materials and methods
Cells
Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK, ATCC CRL-2936) cells, human pulmonary epithelial (A549) cells, and human embryonic kidney (293T) cells were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC). The MDCK and A549 cells were grown in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM, Gibco, Carlsbad, CA, USA) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and antibiotics. The 293T cells were cultured in Opti-MEM (Gibco) supplemented with 5% FBS and antibiotics. All cells were maintained at 37 °C in 5% CO2.
Viruses
The novel H3N8 EIV strain; A/equine/Kyonggi/SA1/2011(KYG11) and H3N8 A/equine/2/Miami/1963 (MA63) were obtained from the ATCC and propagated in the allantoic cavity of 10-day-old embryonated chicken eggs. The eight-plasmid-based reverse genetics system was kindly provided by Dr Richard J. Webby (St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, TN, USA).
Generation of recombinant viruses
Viral RNA was extracted from the allantoic fluid using a QIAamp Viral RNA Mini Kit (Qiagen Inc., Valencia, CA, USA). The RNA was reverse transcribed and NS genes were amplified by PCR using a OneStep reverse transcription PCR kit (Qiagen Inc.) with universal primers and then cloned into a pHW2000 plasmid. We used the plasmid-based reverse genetics system to generate the reverse genetics viruses [12, 13].
Briefly, eight pHW2000 plasmids, each containing an individual gene of the eight influenza A virus genes, were transfected into co-cultured MDCK and 293T cells. Recombinant PR/8 (rPR/8) and the following NS-gene reassortant viruses were rescued from the plasmids: PR/8 × NS KYG11 (rPR/8 × KYGNS) and PR/8 × NS A/equine/2/Miami/1963 (rPR/8 × MINS). The supernatant collected from transfected cells was used to inoculate 10-day-old embryonated chicken eggs for virus propagation. After the generation of the recombinant viruses, the full genome sequences of the viruses were verified with an RT-PCR and sequencing analysis. Virus stocks were stored at −80 °C until use.
Western blotting and plaque assay
For immunoblotting, MDCK cells infected with the viruses were lysed in RIPA lysis buffer (1% Triton X-100, 1% deoxycholate, and 0.1% SDS). The proteins were then separated on 10% SDS polyacrylamide gels, then transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane. The membrane was blocked in 5% skimmed milk buffer, then stained using primary monoclonal mouse antibodies against influenza A NS1 protein (1:2000; sc-130568; Santa Cruz, Dallas, TX, USA) and monoclonal mouse antibodies against influenza A virus NP protein (1:2000; sc-80481; Santa Cruz) at 4 °C overnight. For protein detection, the membrane was incubated with anti-mouse IgG HRP-conjugated secondary antibody and visualized using the ATTO Ez-Capture II system (ATTO, Japan). For the plaque assay, MDCK cells plated in 6-well tissue culture plates were inoculated with tenfold serially diluted viruses. After adsorption for 1 h, the cells were washed and overlaid with 1% low-melting agarose in DMEM containing 2% FBS. After incubation at 37 °C for 72 h, the agarose was gently removed and plaques were visualized with crystal violet staining.
Virus replication kinetics
To evaluate the kinetics of virus replication in vitro, allantoic fluid containing rPR/8, rPR/8 × KYGNS, or rPR/8 × MINS viruses was harvested, and MDCK and A549 cells were infected with the viruses at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 0.01 plaque forming unit per cell. The virus inocula were removed after 1 h. The cells were then washed and infection medium containing 1 μg/mL TPCK-treated trypsin was added. Supernatants were collected 12, 24, 36, 48, and 72 h post-inoculation and stored at −80 °C for titration by TCID50 assay. The TCID50 was calculated by the method of Reed and Muench [14]. The limit of detection was 10 TCID50/mL. In addition, the kinetics of the harvested viruses was determined by inoculating 10-day-old embryonated chicken eggs with serial dilutions of viruses. The limit of detection of the assay was 10 EID50/mL.
Mouse experiments
All animal experiments were performed in biosafety-level-2 facilities at the Korean Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (Daejeon, South Korea). We followed the General Animal Care Guideline as required by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the institute (Approval Number: # KRIBB-ACE-14096).
To determine the 50% mouse lethal dose (MLD50) of each virus, 6-week-old C57BL/6 mice (Korea Animal Technology, Pyeongtaek, South Korea) were inoculated intranasally with tenfold serial dilutions containing 102 to 108 EID50 of each virus in a 30 μL volume. The MLD50 was calculated using the method of Reed and Muench. To compare the virulence of the rPR/8, rPR/8 × KYGNS, and rPR/8 × MINS viruses, ten mice were used to monitor the survival rates and body weights, and another twelve mice were used for lung titration of each recombinant virus strain. The anesthetized mice were inoculated intranasally with 300 EID50 (in a 30 μL volume) of each virus into a single nostril. For the mock control group, ten and twelve mice inoculated with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) were used for body weight measurement and lung titration, respectively.
For virus titration in the lungs, three mice in the infection group were sacrificed at 3, 5, 7, and 9 days post-infection (dpi), and lung tissues were collected and homogenized in 1 mL of PBS with antibiotics. The supernatant collected from the homogenized tissue was titrated in eggs. All mice were monitored daily for 14 days for weight changes and mortality, and mice that lost more than 25% of their body weight were euthanized.
Histopathological examination
Lung tissue samples were harvested from the mice on 7 dpi. The samples were collected in 10% buffered formalin to fix the tissues and were then embedded in paraffin wax, sectioned (4–5 μm thick sections), and placed on glass slides. For the histological examination of the tissues, they were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and examined by a pathologist.
Cytokine assay
The cytokine level in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid was determined using a Bio-Plex Pro™ cytokine assay kit (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). The pro-inflammatory cytokines: interleukin (IL)-6, interferon-gamma (IFN-γ, and CCL5 (RANTES; regulated upon activation normal T cell expressed and presumably secreted) were measured according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, 50 μL BAL fluid samples were incubated with antibody-coupled beads. These immune complexes were washed and incubated first with a biotinylated detection antibody and then with streptavidin–phycoerythrin prior to assessing the cytokine concentration. The pro-inflammatory cytokine levels were determined using a Bio-Plex 200 System multiplex array reader (Bio-Rad) using software provided by the manufacturer (Bio-Plex Manager Software 4.1.1).
Statistical analysis
The data for body weight changes, viral titers, and levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokines in the lungs of the mice were analyzed by the two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests. Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism version 5 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA). A P value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Characterization of recombinant viruses
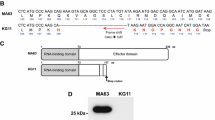
To determine the functionality of the deleted nucleotides in the truncated NS gene, we successfully generated reverse genetics viruses; rPR/8, rPR/8 × MINS; and rPR/8 × KYGNS. As a first attempt to characterize the three recombinant viruses, their sequences were checked, and we confirmed that cells infected with the recombinant virus rPR/8 × KYGNS virus expressed a ~15 kDa NS1; however full-length NS1protein of approximately 26 kDa was revealed for the rPR/8 and rPR/8 × MINS viruses by western blotting (Figure 1A).
Western blot analysis, growth kinetics, and plaque phenotyping of the recombinant viruses. Immunoblot of the NS1 protein in extracts from MDCK cells infected with PR/8, PR/8 × KYGNS, and PR/8 × MINS viruses at an MOI of 1 for 12 h (A). The protein was detected using a mouse anti-NS1 primary antibody, and the molecular weight in kDa is shown on the left of the membrane. MDCK (B) and A549 (C) cells were infected with the PR/8, PR/8 × KYGNS, or PR/8 × MINS virus at an MOI of 0.01, and the virus was titrated in the supernatant that was collected at the indicated time points. The detection limit was 1 log10 TCID50/mL (dotted line). Data are shown as the mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments. Plaque assay performed with PR/8, PR/8 × KYGNS, and PR/8 × MINS viruses (D). The tissue culture plates infected with the viruses were fixed and stained with crystal violet dye.
The growth properties of the three viruses were determined in embryonated chicken eggs. All of the reverse genetics viruses grew to high titers in eggs (Table 1), with endpoint titers after a single egg passage reaching 107.9 EID50/mL for rPR/8, 108.1 EID50/mL for rPR/8 × MINS, and 108.3 EID50/mL for rPR/8 × KYGNS.
Next, how the truncated NS gene affected the growth kinetics of the viruses was determined in vitro. We infected MDCK and A549 cells with the rPR/8, rPR/8 × KYGNS and rPR/8 × MINS viruses at an MOI of 0.01 and observed their growth kinetics for 72 h. We found that all recombinant viruses grow to a similar titer in both cell lines at each time point, indicating that the truncated NS gene did not substantially affect the replicative capacity of these viruses in cell culture (Figures 1B and C). In addition, all three viruses displayed the same plaque phenotype at 37 °C (Figure 1D).
Virulence of recombinant viruses in mice
To evaluate how the truncated NS gene affected virulence in vivo, we inoculated mice with the recombinant viruses. The rPR/8 and rPR/8 × MINS viruses showed comparable virulence, with MLD50 of 104.25 and 103.92 EID50, respectively, whereas the rPR/8 × KYGNS recombinant showed significant attenuation, with an MLD50 value of 107.75 (Table 1). To further investigate the virulence of these viruses in mice, we inoculated mice with 300 EID50 (in a 30 μL volume) of each recombinant virus and evaluated clinical signs, mortality, weight loss, and viral load in the lungs. Virus replication kinetics in the lung was determined by measuring virus titers at 3, 5, 7, and 9 dpi.
The virus titers in mice infected with rPR/8 × KYGNS were at least one hundred to one thousand fold lower than the virus loads in the lungs of mice inoculated with the two other viruses (Figure 2A). The body weights of mice inoculated with rPR/8 × KYGNS gradually increased from 1 to 14 dpi. In contrast, there was rapid and dramatic weight loss of over 25% in the mice infected with rPR/8 or rPR/8 × MINS (Figure 2B). The mice infected with rPR/8 × KYGNS exhibited no clinical signs and showed 100% survival. In contrast, all mice infected with rPR/8 or rPR/8 × MINS exhibited progressive signs such as inactivity, ruffled fur, lack of appetite, hunched backs, and labored breathing (Figure 2C).
Virulence of the recombinant viruses. The anesthetized 6-week-old C57BL/6 mice were inoculated intranasally with 300 EID50 (in a 30 μL volume) of PR/8, PR/8 × KYGNS, or PR/8 × MINS virus into a single nostril. Viral lung titers were measured at 3, 5, 7, and 9 dpi (A), and body weight changes were monitored daily for 14 days (B). Mortality was measured by defining an endpoint of 25% body weight loss (C). Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between groups (*P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001; and ****P ≤ 0.0001).
Pulmonary histopathology in mice inoculated with recombinant viruses
To examine viral pathology, we performed H&E staining on lung tissues collected on days 7 post-infection from three mice. Mice infected with PBS or rPR/8 × KYGNS showed normal lung histology characterized by well-preserved pulmonary alveoli and bronchioles, whereas those infected with rPR/8 × MINS exhibited mild interstitial and suppurative pneumonia characterized by slightly thickened alveolar septa, with moderate hyperplasia of type II pneumonocytes and infiltration of a small number of mononuclear cells in the alveoli and alveolar septa. Mice infected with rPR/8 exhibited interstitial and suppurative pneumonia characterized by disrupted lung parenchyma, notably thickened alveolar septa due to type II alveolar cell hyperplasia, and marked infiltration of lymphocytes and mononuclear cells in the alveoli and interstitium (Figure 3).
Lung histopathology of mice infected with the recombinant viruses. Histopathology of lungs from mice infected with each PR/8 virus containing a different NS gene from a different influenza virus. Mice were inoculated intranasally with each recombinant virus at a dose of 300 EID50 (in a 30 μL volume), and lung tissues were collected on day 7 following virus inoculation. Images are representative of three mice per group (A mock-infected; B PR/8 × KYGNS—infected; C PR/8 × MINS—infected; and D PR/8-infected). The bar represents 100 μm. Images were obtained at 20× magnification.
Induction of cytokine expression
To analyze pro-inflammatory cytokine expression in mice infected with the different NS-expressing viruses, the BAL fluid from infected mice was collected at 3, 5, 7, and 9 dpi, and secreted cytokines and chemokines were measured using a Micro Bead Suspension Array. The levels of IL-6, which stimulates an immune response, and CCL5, which plays an active role in recruiting leukocytes into the site of inflammation increased by about 100-fold (IL-6) or >tenfold (CCL5) after rPR/8 and rPR/8 × MINS virus infection, whereas the rPR/8 × KYGNS infection group showed no significant increase in the levels of these two pro-inflammatory cytokines (Figures 4A and B). The results for IFN-γ were similar: the level of this cytokine in the rPR/8 and rPR/8 × MINS infection groups was significantly higher than that of the rPR/8 × KYGNS group, especially at 7 dpi (Figure 4C).
Cytokine levels in mice infected with the recombinant viruses. The concentrations of induced cytokines and chemokines were determined in the infected mice (n = 3). Levels of (A) IL-6, (B) CCL5, and (C) IFN-γ were measured in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids harvested at 3, 5, 7, and 9 dpi. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between groups (*P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001; and ****P ≤ 0.0001).
Discussion
The NS1 protein is generally regarded as the primary factor by which influenza A viruses antagonize the host INF response to enhance viral replication [15]. It has been suggested that the protein inhibits the polyadenylation of cellular mRNA and promotes the addition of poly A tails onto viral mRNA and sequesters viral dsRNA, a replicative intermediate, inactivating cellular protein kinase R (PKR) and suppressing the IFN response [15, 16].
The inhibition of PKR, which plays a critical role in host antiviral responses mediated by IFN, occurs through the direct binding of the NS1 protein of influenza A virus to PKR. It has been shown that PKR activation is blocked by direct binding to the amino acid (AA) residues 123–127 of NS1 [17]. Furthermore, p85β, a regulatory subunit protein of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3 K), which inhibits apoptosis to ensure viral replication, activates PI3K signaling [18]. For this pathway, the binding motifs located at AA 164–167 and AA 141–142 in NS1 are essential for mediating the interaction between NS1 and p85β [18]. PDZ domain-containing proteins may provide cell signaling and polarity functions in transduction pathways, and the binding motif consists of the last four C-terminal AA residues of NS1 [19]. In addition, the NS1 protein binds to the 30-kDa subunit of the cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor (CPSF30) at residues AA 144–186 of NS1 and inhibits the 3′- end processing of cellular pre-mRNA and then facilitates efficient influenza A virus replication [20]. The alignment of NS1 gene AA sequences from KYG11, MA63, and PR/8 viruses is presented in Figure 5. Consequently, for the KGY11 strain, the binding sites associated with the cell signaling pathway for the antiviral response were lacking because of the premature termination of the NS1 protein.
In particular, horses vaccinated with EIV with a C-terminally truncated NS1 gene showed protection effects and significantly reduced clinical signs in response to challenge with wild-type EIV [21]. Furthermore, influenza virus with C-terminal NS1 truncations was characterized by not only a high degree of attenuation in vitro but also a higher replication capacity and stronger IFN stimulation in vivo compared to NS1-deleted virus in vivo [22, 23]. Accordingly, it is hypothesized that EIV with the C-terminally truncated NS1 gene presents a unique advantage for the development of an EIV vaccine.
For these reasons, we hypothesized that the truncated NS gene could affect the replication of the influenza virus, and we established a reverse genetics system to characterize this effect in vitro and in vivo. Here, we report the extensive characterization of KYG11, an EIV strain isolated from a horse that possesses a unique naturally mutated NS gene segment encoding a truncated NS1 protein. The truncation did not affect the viral replication of rPR/8 in either MDCK or A549 cells; rPR/8 × KYGNS showed viral titers comparable to those of rPR/8 and rPR/8 × MINS in both cell lines. This finding was in accordance with a previously reported in vitro characterization of influenza viruses containing an NS gene segment with a long deletion [24]. Nevertheless, the finding of no difference in growth kinetics between PR8-based recombinant viruses containing NS1 from KYG11 and MA63 in vitro remains controversial because both viruses previously showed notable differences in growth kinetics in MDCK cell culture [2]. Probably, there are mechanisms other than those involving the NS1 protein used to evade the antiviral effects of interferon in cells, and several factors may contribute to the growth efficiency of influenza virus, in particular PR/8, although the NS1 protein is thought to play a significant role in virus replication [22]. Accordingly, the functional roles of viral factors that affect growth characteristics need to be further characterized.
However, the NS gene of the KYG11 strain when inserted into the PR/8 background conferred dramatically attenuated pathogenicity in mice. Higher viral loads in the lungs, significant weight loss, and 100% mortality following infection with the rPR/8 or rPR/8 × MINS virus were observed in mice, in contrast to what was seen in rPR/8 × KYGNS infections with an equivalent dose. To explain the possible association between reduced pathogenicity and the truncated NS gene, pro-inflammatory cytokines in the lungs of infected mice were measured. In assays for a panel of cytokines, infection with rPR/8 × KYGNS did not induce overexpression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, CCL5, and IFN-γ) on the contrary to what was observed with the two other viruses.
In human volunteers infected with influenza viruses, increased IL6 levels were associated with rapid activation of the innate immune response and pathological signs [25, 26]. Furthermore, IL-6 was strongly upregulated in ferrets infected with virulent strains of H1N1 and H3N2 [27]. CCL5 is a potent chemotactic cytokine that recruits Th1 and Th2 pro-inflammatory cells and contributes to immunopathology by activating cytotoxic T lymphocytes in the lungs following influenza virus infection [28, 29]. IFN-γ is a pro-inflammatory cytokine with immune regulatory activities; it also plays a role in the activation of macrophages and differentiation of Th1 cells from T cells. Increased levels of IFN-γ in response to influenza virus infection expand the virus-specific T cell population and enhance the natural killer cell response [30–32].
In this study, the elevated levels of three pro-inflammatory cytokines may have contributed to the prominent infiltration of lymphocytes and suppurative pneumonia in mice infected with rPR/8 or rPR/8 × MINS, whereas the normal lungs of the rPR/8 × KYGNS-infected mice may be associated with the virtually unchanged expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokine expression. A similar finding regarding pro-inflammatory cytokines and lung pathology associated with an H5N1 influenza virus NS gene with a deletion was previously reported [11]. This group also found that a PR/8 influenza virus engineered to incorporate the NS gene of a low pathogenic virus showed attenuated pathogenicity in mice, characterized by reduced production of pro-inflammatory cytokines [11]. Mutations or deletions within the NS1 gene have been shown to affect the ability of influenza viruses to antagonize IFN production and to alter the virulence of influenza viruses in different hosts [11, 15, 33, 34].
In this study, an attenuation of the virulence in mice of recombinant PR/8 containing the truncated NS gene segment (a nucleotide deletion from position 326 to 348) derived from H3N8 EIV was observed. Our results suggest that the C-terminal moiety of NS1 harbors virulence determinants for influenza viruses and therefore might be an appropriate target for the development of antiviral drugs and vaccine candidates against equine influenza.
References
Cullinane A, Newton JR (2013) Equine influenza—a global perspective. Vet Microbiol 167:205–214
Na W, Kang B, Kim HI, Hong M, Park SJ, Jeoung HY, An DJ, Moon H, Kim JK, Song D (2014) Isolation and genetic characterization of naturally NS-truncated H3N8 equine influenza virus in South Korea. Epidemiol Infect 142:759–766
Crawford PC, Dubovi EJ, Castleman WL, Stephenson I, Gibbs EP, Chen L, Smith C, Hill RC, Ferro P, Pompey J, Bright RA, Medina MJ, Johnson CM, Olsen CW, Cox NJ, Klimov AI, Katz JM, Donis RO (2005) Transmission of equine influenza virus to dogs. Science 310:482–485
Payungporn S, Crawford PC, Kouo TS, Chen LM, Pompey J, Castleman WL, Dubovi EJ, Katz JM, Donis RO (2008) Influenza A virus (H3N8) in dogs with respiratory disease, Florida. Emerg Infect Dis 14:902–908
Tu J, Zhou H, Jiang T, Li C, Zhang A, Guo X, Zou W, Chen H, Jin M (2009) Isolation and molecular characterization of equine H3N8 influenza viruses from pigs in China. Arch Virol 154:887–890
Wang X, Li M, Zheng H, Muster T, Palese P, Beg AA, Garcia-Sastre A (2000) Influenza A virus NS1 protein prevents activation of NF-kappaB and induction of alpha/beta interferon. J Virol 74:11566–11573
Garcia-Sastre A, Egorov A, Matassov D, Brandt S, Levy DE, Durbin JE, Palese P, Muster T (1998) Influenza A virus lacking the NS1 gene replicates in interferon-deficient systems. Virology 252:324–330
Talon J, Horvath CM, Polley R, Basler CF, Muster T, Palese P, Garcia-Sastre A (2000) Activation of interferon regulatory factor 3 is inhibited by the influenza A virus NS1 protein. J Virol 74:7989–7996
Solorzano A, Webby RJ, Lager KM, Janke BH, Garcia-Sastre A, Richt JA (2005) Mutations in the NS1 protein of swine influenza virus impair anti-interferon activity and confer attenuation in pigs. J Virol 79:7535–7543
Li Y, Chen S, Zhang X, Fu Q, Zhang Z, Shi S, Zhu Y, Gu M, Peng D, Liu X (2014) A 20-amino-acid deletion in the neuraminidase stalk and a five-amino-acid deletion in the NS1 protein both contribute to the pathogenicity of H5N1 avian influenza viruses in mallard ducks. PLoS One 9:e95539
Lipatov AS, Andreansky S, Webby RJ, Hulse DJ, Rehg JE, Krauss S, Perez DR, Doherty PC, Webster RG, Sangster MY (2005) Pathogenesis of Hong Kong H5N1 influenza virus NS gene reassortants in mice: the role of cytokines and B- and T-cell responses. J Gen Virol 86:1121–1130
Hoffmann E, Neumann G, Kawaoka Y, Hobom G, Webster RG (2000) A DNA transfection system for generation of influenza A virus from eight plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:6108–6113
Hoffmann E, Stech J, Guan Y, Webster RG, Perez DR (2001) Universal primer set for the full-length amplification of all influenza A viruses. Arch Virol 146:2275–2289
Biacchesi S, Skiadopoulos MH, Yang L, Murphy BR, Collins PL, Buchholz UJ (2005) Rapid human metapneumovirus microneutralization assay based on green fluorescent protein expression. J Virol Methods 128:192–197
Killip MJ, Fodor E, Randall RE (2015) Influenza virus activation of the interferon system. Virus Res 209:11–22
Hale BG, Randall RE, Ortin J, Jackson D (2008) The multifunctional NS1 protein of influenza A viruses. J Gen Virol 89:2359–2376
Cheng A, Wong SM, Yuan YA (2009) Structural basis for dsRNA recognition by NS1 protein of influenza A virus. Cell Res 19:187–195
Li Y, Anderson DH, Liu Q, Zhou Y (2008) Mechanism of influenza A virus NS1 protein interaction with the p85beta, but not the p85alpha, subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and up-regulation of PI3K activity. J Biol Chem 283:23397–23409
Kochs G, Garcia-Sastre A, Martinez-Sobrido L (2007) Multiple anti-interferon actions of the influenza A virus NS1 protein. J Virol 81:7011–7021
Twu KY, Noah DL, Rao P, Kuo RL, Krug RM (2006) The CPSF30 binding site on the NS1A protein of influenza A virus is a potential antiviral target. J Virol 80:3957–3965
Chambers TM, Quinlivan M, Sturgill T, Cullinane A, Horohov DW, Zamarin D, Arkins S, Garcia-Sastre A, Palese P (2009) Influenza A viruses with truncated NS1 as modified live virus vaccines: pilot studies of safety and efficacy in horses. Equine Vet J 41:87–92
Kochs G, Koerner I, Thiel L, Kothlow S, Kaspers B, Ruggli N, Summerfield A, Pavlovic J, Stech J, Staeheli P (2007) Properties of H7N7 influenza A virus strain SC35M lacking interferon antagonist NS1 in mice and chickens. J Gen Virol 88:1403–1409
Kochs G, Martinez-Sobrido L, Lienenklaus S, Weiss S, Garcia-Sastre A, Staeheli P (2009) Strong interferon-inducing capacity of a highly virulent variant of influenza A virus strain PR8 with deletions in the NS1 gene. J Gen Virol 90:2990–2994
Egorov A, Brandt S, Sereinig S, Romanova J, Ferko B, Katinger D, Grassauer A, Alexandrova G, Katinger H, Muster T (1998) Transfectant influenza A viruses with long deletions in the NS1 protein grow efficiently in Vero cells. J Virol 72:6437–6441
Hayden FG, Fritz R, Lobo MC, Alvord W, Strober W, Straus SE (1998) Local and systemic cytokine responses during experimental human influenza A virus infection. Relation to symptom formation and host defense. J Clin Invest 101:643–649
Gentile D, Doyle W, Whiteside T, Fireman P, Hayden FG, Skoner D (1998) Increased interleukin-6 levels in nasal lavage samples following experimental influenza A virus infection. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 5:604–608
Svitek N, Rudd PA, Obojes K, Pillet S, von Messling V (2008) Severe seasonal influenza in ferrets correlates with reduced interferon and increased IL-6 induction. Virology 376:53–59
Culley FJ, Pennycook AM, Tregoning JS, Dodd JS, Walzl G, Wells TN, Hussell T, Openshaw PJ (2006) Role of CCL5 (RANTES) in viral lung disease. J Virol 80:8151–8157
Zhou J, Law HK, Cheung CY, Ng IH, Peiris JS, Lau YL (2006) Differential expression of chemokines and their receptors in adult and neonatal macrophages infected with human or avian influenza viruses. J Infect Dis 194:61–70
He XS, Draghi M, Mahmood K, Holmes TH, Kemble GW, Dekker CL, Arvin AM, Parham P, Greenberg HB (2004) T cell-dependent production of IFN-gamma by NK cells in response to influenza A virus. J Clin Invest 114:1812–1819
Hagau N, Slavcovici A, Gonganau DN, Oltean S, Dirzu DS, Brezoszki ES, Maxim M, Ciuce C, Mlesnite M, Gavrus RL, Laslo C, Hagau R, Petrescu M, Studnicska DM (2010) Clinical aspects and cytokine response in severe H1N1 influenza A virus infection. Crit Care 14:R203
McGill J, Heusel JW, Legge KL (2009) Innate immune control and regulation of influenza virus infections. J Leukoc Biol 86:803–812
Li Z, Jiang Y, Jiao P, Wang A, Zhao F, Tian G, Wang X, Yu K, Bu Z, Chen H (2006) The NS1 gene contributes to the virulence of H5N1 avian influenza viruses. J Virol 80:11115–11123
Zhu Q, Yang H, Chen W, Cao W, Zhong G, Jiao P, Deng G, Yu K, Yang C, Bu Z, Kawaoka Y, Chen H (2008) A naturally occurring deletion in its NS gene contributes to the attenuation of an H5N1 swine influenza virus in chickens. J Virol 82:220–228
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
DS, KSL, and JKK conceived and designed this study. WN and SWY contributed to the majority of laboratory experiments and animal experiments. MY, BK, HM, and HKK helped with the laboratory experiments and interpreted the data. KSL prepared the manuscript. DS, JKK, and DGJ reviewed and critically revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a Korea University Grant, and Global Frontier Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea(NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (Grant Number: 2015M3A6B2063544) and the International Research & Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (Grant Number: 2013K1A3A1A20046998). We thank Dr Richard J. Webby (St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, TN, USA) for the plasmid used for the reverse genetics performed in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Woonsung Na, Kwang-Soo Lyoo and Sun-Woo Yoon contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Na, W., Lyoo, KS., Yoon, SW. et al. Attenuation of the virulence of a recombinant influenza virus expressing the naturally truncated NS gene from an H3N8 equine influenza virus in mice. Vet Res 47, 115 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13567-016-0400-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13567-016-0400-7