Abstract
Cost-effective treatment strategies for liver fibrosis or cirrhosis are limited. Many clinical trials of stem cells for liver disease shown that stem cells might be a potential therapeutic approach. This review will summarize the published clinical trials of stem cells for the treatment of liver fibrosis/cirrhosis and provide the latest overview of various cell sources, cell doses, and delivery methods. We also describe the limitations and strengths of various stem cells in clinical applications. Furthermore, to clarify how stem cells play a therapeutic role in liver fibrosis, we discuss the molecular mechanisms of stem cells for treatment of liver fibrosis, including liver regeneration, immunoregulation, resistance to injury, myofibroblast repression, and extracellular matrix degradation. We provide a perspective for the prospects of future clinical implementation of stem cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Liver diseases cause about two million deaths worldwide each year, accounting for 3.5% of all annual deaths, of which one million die from complications of liver cirrhosis [1]. Liver cirrhosis is the 11th most common cause of death worldwide, and the number and proportion of global deaths with this cause will continue to increase in the future (more than 1.32 million died of cirrhosis in 2017 but less than 899,000 deaths in 1990 [2]). Chronic liver diseases are generally divided into four stages according to severity: (1) inflammation; (2) liver fibrosis; (3) cirrhosis; and (4) end-stage liver disease (ESLD) or liver cancer [3]. This is often a consecutive process in which liver function of advanced cirrhosis or ESLD is irreversibly impaired; the only curative treatment is orthotropic liver transplantation (OLT). It is high on the agenda that we should explore new therapeutic strategies because of the major limitations of OLT, such as immune rejection, adverse post-operative complications, organ shortages, etc. In 1976, the first preclinical primary human hepatocytes (PHHs) transplantation shed light on the prospect of cell therapy [4]. Since then, cell therapy for chronic liver diseases has developed rapidly. PHHs are regarded as an ideal source to treat metabolic liver disease and have been set into clinical use [5]. However, PHHs are so hard to expand in vitro and their sources are so confined, that people are forced to turn to additional cell sources. Currently, evidence that stem cells are effective for the treatment of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in phase I and II clinical trials has intensified attention, in hopes that stem cell therapy can reverse liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. Due to the ethical issues of the extraction and application of human primary stem cells, the number of clinical trials using stem cells for the treatment of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis is limited. Over the past few decades, the effectiveness, feasibility and safety of stem cell therapies in animal models have been extensively reported in the literature. Animal models bridge the translation from basic research to clinic application. Inevitably, rodent models are inconsistent with human diseases, and it is necessary to test safety and efficacy in animal models closer to humans before clinical trials [6, 7]. More importantly, due to the difficulty in obtaining clinical specimens, the current stem cell therapy for human liver diseases can only obtain the outcome of the patient. The mechanism of stem cell therapy is based on animal models. The mechanism of action for donor stem/progenitor cells has been previously summarized in two major pathways: (1) differentiation into functional cells to replace damaged cells; (2) producing bioactive factors that enhance patient’s own tissue-resident progenitor cells proliferation or maturation and immunoregulatory factors that modulate the progression of inflammation. While the first one would realistically require several weeks to be completed and insufficient to support liver function or restore the organ, the second one has been largely recognized as prominent and efficient. Moreover, in fibrotic diseases, the extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling mediators secreted by stem cells such as matrix metalloproteinase (MMP), and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP) have been reported instrumental to fibrosis reversal. Compared with conventional treatment options, stem cell-based therapies are less invasive in patients than surgical methods and carry a low risk of immune rejection. In this review, we summarize the latest clinical developments in the field of using stem cells for the management of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in the hope that they will provide insight into the subsequent clinical translation of stem cells.
Clinical progress using stem cells for liver cirrhosis/fibrosis therapy
When clinicaltrials.gov was searched for the condition “liver diseases” and other terms such as “stem cells”, a total of 160 clinical trials using stem cells for the treatment of liver diseases, including end-stage liver disease, liver cancer, liver fibrosis, and cirrhosis, were found registered, of which 75 trials (47%) focus on liver cirrhosis or fibrosis (excluding terminated and withdrawn trials). In these 75 cases, most trials concentrated on Phase I/II (36%) (Fig. 1A).
Classification of registered stem cell-related clinical trials in liver fibrosis or cirrhosis. A Clinical trials classified by clinical phase; B different stem cell applied in current clinical trials; UCMSC, umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell; BMMSC, bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell; ADMSC, adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell; LDMSC, liver-derived mesenchymal stem cell; MenSC, menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell; SHED, stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth; HSC, hematopoietic stem cell; G-CSF, granulocyte-colony stimulating factor; BMMNC, bone marrow mononuclear cell; EPC, endothelial progenitor cell; HLC, hepatocyte-like cell; C clinical trials classified by delivery route. All of data collected from www.clinicaltrials.gov
For cell therapy, the following are of particular concern: cell type, cell number, and route of administration.
The cell sources used to treat liver fibrosis or cirrhosis are diverse, with the most widely used being mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) (73%) (Fig. 1B). The MSCs currently being applied in clinical trials are obtained from different tissues such as bone marrow, umbilical cord, adipose, menstrual blood, dental pulp, and liver. Moreover, meta-analyses show that stem cells derived from bone marrow are more effective than those derived from the umbilical cord, and superior improvement in model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) score, albumin (ALB) levels, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels, and total bilirubin (TBil) occurred in the bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell (BMMSC) group than umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell (UCMSC) group [8]. This may be due to differences in the adhesive and migratory or homing properties of MSCs isolated from different tissue. The fate of cells injected into the circulation and the capacity of the cells to promote repair and immune regulation at the site of damage are affected by both properties. USMSC appears to adhere and migrate more rapidly from flow than BMMSC, but BMMSC surpasses USMSC in terms of spreading kinetics [9]. More vitally, we have no way of telling who homed better to the liver, UCMSC or BMMSC? Other possible explanations included BMMSC cleared bacteria and enhanced cell survival, and the superior regulation of the pro/anti-inflammatory response compared to UCMSC [10]. In a previous study, transplantation of MSC enhanced engraftment of hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) [11]. Ghavamzadeh et al. [12] demonstrated that co-transplantation of HSC with MSC increased the rate of replacement of recipient hepatocytes by donor-derived cells and alleviated liver fibrosis. But the most recent research showed that MSC co-transplantation with HSC or Treg is feasible, but this approach couldn’t significantly improve liver fibrosis than HSC infusion only. Robust evidence that the MSCs used to support the donor's HSCs is of recipient origin [13]. In addition, intravenous MSCs have a short lifespan and cannot migrate out of the lungs [14]. Given this, MSC infusion after HSC transplantation may be more preferred than a single dose of MSC co-transplantation with HSC.
A cell count of 1 × 106 or more is required for treatment. Cell dose depends on the patient weight, clinical situation, administration route, and cell type. In liver cirrhosis or failure, hepatocyte transplantation aims to provide functional parenchymal support to the damaged mass, bridging the recovery of the liver. Based on this concept, the cell count is roughly 10–15% of the theoretical liver mass, higher than liver metabolic disorders [15]. The maximum amount of cells injected is no more than 5% (approximately 1 × 1011 hepatocytes) of the liver parenchyma. The complications of cell infusion like portal hypertension and cell embolism limit the number of cells that can be infused [16]. Hepatocyte transplantation not only is inefficient but also needs to suppress the patient’s immune system. Local but not systemic administration of MSCs improved liver fibrosis after partial hepatectomy [17]. In the management of liver fibrosis, and cirrhosis, we found that the dose of MSCs was generally lower compared to that of hepatocytes, reflecting the fact that the dominant mechanism of action of MSC is not through replacement therapy, but rather a promotion of endogenous liver regeneration and immunomodulation mediated by secreted bioactive molecules. Within the range of safe and the lowest effective dosages for administration, there seems to be no difference in the outcome of the low, medium, and high dose groups [18]. Therapeutic effects of interval and repeated injections, such as twice per week, seem more stable and significant; however, a single and adequate injection is more effective [19].
Cell therapy routes are currently divided into two categories: infusion of suspension of stem cells or transplantation of the product of stem cells modified by bioengineering. Administration via the hepatic artery (32%) is the preferred choice for most clinical trials (Fig. 1C). This is probably because stem cells infused via the hepatic artery have a better ability to engraft than intravenous infusion [20]. Notably, of these clinical trials, only one used the bioengineered product that is an injectable collagen scaffold combined with hUCMSCs (NCT02786017).
Apart from the details in clinical trials, the safety and efficacy of cell therapy are most critical. Stem cells have made surprising progress in clinical trials for the treatment of cirrhosis or liver fibrosis. Common indicators available to evaluate the efficiency of stem cells are serum ALB level, serum bilirubin, Child–Pugh score, and MELD score. Safety is evaluated mainly in terms of postoperative adverse complications such as fever, anaphylaxis, cough, chest distress, and dyspnea, etc. Although these clinical trials seem safer, lager-scale studies are still in demand. Representative clinical trials using stem cells for the treatment of liver fibrosis or cirrhosis are shown in Table 1.
Stem cell types used for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis therapy
From the above clinical trials we learned that there is a wide selection of cell types that can be applied in the management of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, and the following is a detailed description of the cell types mentioned (Fig. 2).
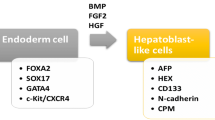
Candidate stem cell types for the treatment of liver fibrosis/cirrhosis. Different types of stem cells for the treatment of liver fibrosis/cirrhosis, especially MSCs, can originate from various tissues such as adipose, umbilical cord, teeth, bone marrow, blood, liver, etc. Differentiated hepatocyte-like cells and EPCs in vitro can also be used as alternative cell sources. MSC, mesenchymal stem cell; HSC, hematopoietic stem cell; BMMNC, bone marrow mononuclear cell; EPC, endothelial progenitor cell; FGF2, fibroblast growth factor 2; FGF4, fibroblast growth factor 4; BMP4, bone morphogenetic protein 4; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; OSM, oncostatin M; ITS, Insulin-Transferrin-Selenium; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; IGF-1, insulin-like factor-1; bFGF, basic fibroblast growth factor; EGF, epidermal growth factor
Mesenchymal stem cells
MSCs are the most widely applied type of stem cells and can be obtained from every adult or perinatal tissue including common bone marrow, umbilical cord, adipose tissue, liver, teeth, and menstrual blood. In recent years MSCs were extracted from urine [21] and different parts of the placenta [22]. MSC has the same characteristics (positive for CD73, CD90, and CD105, and negative for CD34, CD14, or CD11b, CD79 or CD19, HLA-DR) [23].
Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
UCMSCs can be obtained from Wharton’s jelly and cord blood. There are two general methods of obtaining harvesting cells: enzymatic digestion and the explants method. UCMSCs should be prepared in approved good manufacturing practice (GMP) [24].
hUCMSCs promoted liver repair and improved regenerative niche by secreting hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and increasing the expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) and Est-1 p42 protein in thioacetamide-injured mouse liver [25]. Moreover, hUCMSCs also demonstrated superior immunosuppressive capacity with high Treg promotion in a mouse model of liver disease [26]. Besides, hUCMSCs transplantation inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells by upregulating microRNA-455-3p to mediate p21-activated kinase-2 (PAK2) silence [27].
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
BMMSCs are isolated from bone marrow mononuclear cells (BMMNCs). BMMNCs are seeded in a culture flask and then the non-adherent cells are removed, resulting in colonized BMMSCs [28].
Microencapsulated BMMSCs engrafted in damaged tissue have a protective effect since anti-apoptotic interleukin (IL)-6, insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 (IGFBP-2), and anti-inflammatory IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) cytokines were released [29]. Besides, liver-specific ECM induced BMMSCs trans-differentiated to hepatic lineage and reversed liver fibrosis by replacing liver parenchymal cells to serve [30].
Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells
Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADMSCs) can be obtained from liposuction aspirates or subcutaneous fat fragments and expanded in vitro. Adipose tissues were digested with collagenase, the resultant dispersed cells were collected and cultured in the flask [31].
The number of inflammation-infiltrated CD11b+ cells, Gr-1+ cells, and the ratio of CD8+/CD4+ decreased in steatohepatitis-induced cirrhosis with ADMSCs treatment [32]. Currently, ADMSCs and BMMSCs are considered to alleviate fibrosis through similar mechanisms [33].
Liver-derived mesenchymal stem cells
In short, mononuclear cells were isolated from liver fragments and cultured in vitro to obtain liver-derived mesenchymal stem cells (LDMSCs). Laboratories have successfully isolated human liver-derived mesenchymal-like stem cells, which highly express endodermal markers such as GATA4 and FOXA1. LDMSCs are positive for CD29, CD73, CD44, CD90, CD105, and CD166 together with, albumin, α-fetoprotein, cytokeratin 8, and cytokeratin 18 these hepatic markers [34]. LDMSCs both expressed some of the surface markers of MSC and possess some of the functions of hepatocytes, therefore indicating a partial commitment toward hepatic differentiation [35].
In thioacetamide-induced immunodeficient NRG mouse models with liver injury, hLDMSCs engrafted more rapidly in the damaged liver to differentiate into mature hepatocytes compared with hUCMSCs [36]. Furthermore, LDMSCs secrete higher levels of pro-angiogenic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic cytokines compared to BMMSCs [34].
Menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells
Menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MenSCs) are isolated by density-gradient centrifugation from centrifuged human menstrual blood, they expressed MSC markers, but did not express HLA-DR, CD34, CD45, CD117. Interestingly, stage-specific embryonic antigen 4 (SSEA4) has not existed in MSCs from other sources, but SSEA4 expression in the MenSCs is controversial [37, 38].
MenSCs markedly decreased expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) in liver tissue and suppressed activated hepatic stellate cells via paracrine mediators such as monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), IL-6, HGF, etc, further degraded collagen content in carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis [39].
Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth
Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth (SHED) are isolated from remnant dental pulp tissues of healthy pediatric donors exfoliated deciduous teeth. There are differences in the properties of SHEDs obtained by different isolation methods [40]. They share MSC characteristics, including cell surface antigen expression and trilineage differentiation potential.
Transplanted SHED are capable of generating hepatocyte-like cells in vivo, under the stimulation of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), SHED-Heps showed cholangiogenic potential [41]. Moreover, SHED downregulated ECM resolution-associated mediators, such as MMP-2, MMP-9, TIMP-1, and TIMP-2 in the damaged liver [42]. In addition, SHED promoted recovery from hepatic fibrosis by preventing inflammatory infiltration [43].
Hematopoietic stem cells
HSCs are primitive cells found in the bone marrow and blood. HSCs are purified from harvested peripheral blood mononuclear cells derived from patients who received subcutaneous injections of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) or sorted from bone marrow through the flow sorting system. Besides, HSC can also be obtained from umbilical cord blood. Accordingly, HSCs are positive for CD34, CD45, and CD133 [44].
Two methods are available for the mobilization of stem cells from the bone marrow to the liver. One involves the isolation of stem cells from the marrow followed by their infusion into the body and the other is the administration of cytokines like G-CSF. Any drug with the capacity to mobilize bone marrow stem cells (BMSCs) can be used to treat liver fibrosis, but the degree of improvement may not be proportional to the efficiency of mobilization [45]. G-CSF mobilized BMSCs to reach the damaged liver for repair [46]. However, recent randomized clinical trials have shown that G-CSF cannot improve MELD scores in patients with compensated cirrhosis regardless of whether it is combined with HSCs, possibly due to adverse effects of G-CSF [44]. HSCs have negligible anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects compared to BMMSC in liver injury [47]. HSCs could home to the damaged liver but barely converge toward the hepatic line. Their contribution to liver repair is mainly through the release of paracrine factors that stimulate endogenous hepatocyte regeneration and boost intrahepatic angiogenesis [48]. HSC transplantation or HSC co-transplantation with other stem cells has been shown to be feasible in refractory ascites with liver fibrosis [49] or patients with dedicator of cytokinesis 8 protein deficiency [50].
Bone marrow mononuclear cells
BMMNCs are isolated from bone marrow which was aspirated from the posterior iliac crest of patients under local anesthesia by density-gradient centrifugation. BMMNCs are cell populations composed of multiple stem/progenitor cells. The makers of BMMNCs consist of three types: endothelial lineage markers such as CD31 and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR), BMMSC surface markers, and HSC markers [51].
Bone marrow-derived CD11b+CD14+ monocytes improved liver fibrosis by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, monocyte-treated mice had higher levels of glutathione (GSH) which represented antioxidant capacity. Moreover, the monocyte-treated group showed pro-inflammatory TNF-α and IL-6 downregulation and anti-inflammatory IL-10 upregulation [52]. Except for these, BMMNCs showed a significant decline in malondialdehyde and normalized total antioxidant capacity (TAC), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), catalase (CAT), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) [53].
Endothelial progenitor cells
Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) are obtained from various tissue, most commonly referred to in clinical practice as BMMNCs. BMMNCs were induced under an endothelial complete medium consisting of cytokine vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), insulin-like factor-1 (IGF-1), basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), and epidermal growth factor (EGF). EPCs acquired in this way are positive for VEGFR-1, von Willebrand factor (vWF), and Ulex-binding [54].
EPCs transplantation activated HGF-mediated hepatocyte proliferation and increased sinusoidal blood vessel density by secreting higher MMP-2 and VEGF in carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis [55]. Unexpectedly, the results of one study indicated that the percentage of infused EPCs and collagen proportionate area was substantially increased in the fibrotic liver, and this may be attributed to higher levers of VEGF and TGF-β caused by EPCs activated hepatic stellate cells [56].
Liver cells
The definition of liver stem cells remains controversial, as hepatocytes and bile duct epithelial cells can be regarded as their own respective specific stem cells in certain cases [57]. The liver cells currently used in clinical trials are adult or fetal hepatocytes. Hepatocytes are collected by the collagenase perfusion technique [58]. Fresh hepatocytes should be more than 60% viable and due to the specific characteristics of hepatocytes, isolated hepatocytes should be immediately transplanted or frozen for storage [16].
In liver cirrhosis or failure, hepatocyte transplantation aims to provide functional parenchymal support to the damaged mass, bridging the recovery of the liver [15]. In fact, hepatocyte transplantation not only is inefficient but also needs to suppress the patient's immune system. Transplantation of 3–5% liver mass only results in 0.5% engraftment of the host liver and grafted cell loss is due to patient’s CD8+ T-lymphocytes alloreactivity directed against a donor HLA antigen [59]. Currently, there is no standard immunosuppressive regimen for hepatocyte transplantation. Most centers adopt the same regimen as OLT, such as the combination of tacrolimus and monoclonal antibodies [16]. Strikingly, liver progenitor cells (LPCs) are a class of bipotent stem cells that can further differentiate into hepatocytes and bile duct epithelial cells; they are considered to play a crucial role in long-term liver injury [60]. LPCs are recognized as an essential chain of endogenous liver regeneration. Recent work shows that hepatocytes and bile duct epithelial cells can trans-differentiate between each other to promote liver repair without undergoing the state of hepatic progenitor cells during chronic liver injury [61, 62].
Hepatocyte-like cells
Various stem cells have shown potential for hepatic differentiation in vivo, so hepatocyte-like cells (HLCs) have also been used clinically to treat liver fibrosis or cirrhotic disease. However, MSCs, mesoderm-derived cells, have been pending for their ability to differentiate into mature hepatocytes along the endoderm.
Safe and homogenous HLCs are mainly obtained by adding cytokines, which mimics the process of embryonic development of the mammalian liver by culturing cells in a medium supplemented with growth factors necessary for liver development [63]. For MSC, hepatic specification is performed by fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2), fibroblast growth factor 4 (FGF4), bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4), and HGF. The mature stage often requires the application of oncostatin M (OSM), dexamethasone, and ITS premix [64]. Hepatic maturation can be monitored by the selective up-and down-regulation of a plethora of genes, early hepatic maturation markers such as α-fetoprotein (AFP), ALB, alpha-1-antitrypsin (A1AT), and so on, final hepatic maturation markers CytochromeP450 enzymes, hepatic transporters, and all the hepatic enzymes for urea cycle and more [65]. After hepatic differentiation, CD73 was down regulated, and MSC-derived HLCs have an upregulated ALB, A1AT, hepatocyte nuclear factor-4α (HNF4α), and a transient increase in AFP expression. In addition, it has also been reported that MSC-derived HLCs expressed CYP3A4, CYP1A2, MRP2, UTG1A6 [66], G-6-P [67], and other functional genes specific to hepatocytes. To our regret, many functions of MSC-derived HLCs are still only one percent or even one-thousandth of those of primary hepatocytes, depending on the mRNA expression level. The absence of HepPar1 and loss of hepatogenic phenotype suggested that MSCs had never differentiated into the mature hepatocytes [68].
The researchers compared the curative effect of the MSCs-treated group and the HLCs-treated group separately; liver function improved in both groups, but MSCs exhibited better results in some parameters [69, 70]. This may contribute to the fact that MSC-derived HLCs are often limited and differ functionally from primary hepatocytes [71]. In one study, differentiated induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) were suggested to engraft more efficiently than undifferentiated iPSCs. Treatment with 4.0 × 107 iPSCs-derived hepatocytes per kilogram of body weight significantly alleviated heavy liver failure in mice; yet, an equivalent dose of iPSCs had no significant therapeutic effect [72]. This suggested that embryonic stem cells (ESCs) or iPSCs need to be differentiated first to have a great therapeutic effect.
Potential limitations and strengths of the various types of stem cells
In this section, we focused our attention and criticism on describing discrepancies and different potency in using stem cells from different sources. Table 2 describes different sources of stem cells along with their disadvantages and advantages in clinical application.
Although UCMSCs for current clinical use are allogeneic, perinatal MSCs highly expressed HLA-G, which is essential in the adaptation of the maternal immune system during pregnancy as well as a suppressive effect on all immune cells, giving UCMSCs an innate immune privilege [73]. UCMSCs displayed the strongest proliferative capacity at P3, which then slowly diminished with increased passages in vitro [74]. UCMSCs characteristically expressed transcriptomes associated with neuronal development including NPY, this implies that UCMSCs are more preferentially differentiated into neural cells and have prospective applications in neurological disorders [75]. The low cost of preparation, the ease of large-scale expansion in vitro, and the absence of ethical concerns make UCMSCs the most promising source of cells for clinical use. Compared to UCMSCs, BMMSCs have a superior capacity for differentiation along the mesoderm including osteogenesis or chondrogenesis and inferior adipogenesis. A set of genes related to antimicrobial activity was more expressed in BMMSCs, while genes related to matrix remodeling were higher expressed in UCMSCs [76]. BMMSCs possess strong differentiation potential, but human BMMSCs are obtained by invasive means and quantities are limited, both of which hinder the further development of BMMSCs in clinical applications. Because ADMSCs are more resistant to hyperoxia-induced apoptosis, and oxidative stress-induced senescence, moreover, its superior proangiogenic capacity and high activity of telomerase, ADMSCs present a unique benefit over BMMSCs in terms of regenerative capacity [77]. There are no significant differences between ADMSCs and BMMSCs in their immunophenotype. Another most obvious merit of ADMSCs is their higher isolation success and proliferation rate [78]. ADMSCs are simple to harvest, widely available, and cell viability is not constrained by the age of the donor, so they have a wide scope in regenerative medicine. LDMSCs are more closely to the environment of the liver itself, especially as they express endoderm-related markers, but the normal fetal liver is of restricted sources. LDMSCs are not currently widespread in clinical trials. Compared with BMMSCs, MenSCs without induction stimuli are able to expand at 18 passages without chromosome abnormalities [37]. MenSCs have 2–4 fold higher proliferative capacity compared to BMMSCs, with 30–47 populations doubling before senescence [79]. The concern, however, is that there are few clinical trials using MenSCs for liver disease, standard isolation protocols, and culture conditions are crucial issues. Safety and efficacy have yet to be fully verified. SHED are more potent than BMMSCs in neurogenic [80]. SHED are accessible, easy isolation, and low invasive, but the absence of rigorous clarification on these signatures and efficacy will hinder their foreground.
HSC transplantation was first applied in the field of hemopathy. Maintaining the self-renewal and the undifferentiated state of HSCs for ex vivo expansion is currently a serious challenge considering the clinical application [81]. Shortage of HSC meeting clinical management criteria and limited source of low immunogenic HLA-matched HSCs [82]. Given the complexity and high cost of preparing autologous HSCs and the restricted quantity of cells, HSCs are more appropriate for patients with regenerative disabilities accompanied by hematological disabilities.
Because of the abundance of cell types contained in BMMNCs, BMMNCs have heterogeneity. BMMNCs are increasingly being used in clinical trials with no further subdivision. BMMSCs transplantation improved limb ischemia and increased blood flow, yet BMMNCs had no significant effect [83]. Nevertheless, due to the complex composition of BMMNCs, there is still ambiguity in their clinical application.
The key limitation of EPCs in clinical treatment is the low number and one possible solution is to use BMMNCs without pre-selection [84]. EPCs need to be artificially induced to grow in vitro, the heterogeneity of EPCs and the irregularity of their manufacture have hindered their clinical development.
Liver parenchymal cells are the most ideal source of cells for the treatment of liver disease, but PHHs-derived therapy has encountered many challenges in clinical application, such as the limited ability of PHHs to proliferate under traditional culture conditions, the loss of their original phenotype and function in vitro, and difficulty in the acquisition process [71]. These forced us to hunt for a cell source comparable to hepatocyte.
The induction of HLCs in vitro requires weeks-long cytokines irrigation. Moreover, the heterogeneity of the differentiated HLCs and the hepatic function of HLCs are closely dependent on the cell source, the induction protocol, and the batch of cytokines. Currently, a standardized manufacturing process and the number of cells available for the clinic are the disturbing issues we need to address.
Mechanisms of stem cell therapy for liver fibrosis
The development of liver fibrosis is a process of wound healing, critical events such as hepatocyte death, immune cell infiltration, liver injury, myofibroblast activation, and excessive deposition of the extracellular matrix are implicated. We will provide insight into these five aspects of how stem cells modulate (Fig. 3). Of interest is the fact that more than 30 years ago, mesenchymal stem cells referred to their multipotency and highly proliferative capacity [85]. But it is currently accepted that the importance to refine such multipotent cells as stromal medicinal products [86], whose paracrine action rather than differentiation capacity is leading to regenerative potential.
Mechanisms of stem cells for liver fibrosis. Stem cells, mainly MSCs, replace the hepatocyte function through migration and transdifferentiation, secrete a variety of cytokines to promote hepatocyte proliferation, enhance anti-apoptosis and anti-oxidation capacity of hepatocytes, promote LESC proliferation, inhibit the secretion of inflammatory factors in liver macrophages, repress the activation of hepatic stellate cells and promote the apoptosis of activated cells, crucially, degrade the ECM to delay the process of liver fibrosis. MSC, mesenchymal stem cell; SDF-1, stromal cell-derived factor-1; LSEC, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells; CXCR, chemokine receptor; VACM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; MMP-2, matrix metalloproteinases-2; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; OSM, oncostatin M; bFGF, basic fibroblast growth factor; ALB, albumin; IGF-1, insulin-like factor-1; TRK, tyrosine kinase receptor; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; IL-6, interleukin-6; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; PRL-1, phosphatase of regenerating liver-1; VEGF-A, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-A; Ang-1, angiotensin-1; Flt1, Fms-like tyrosine kinase 1; Flk1, Fetal-like kinase 1; HB-EGF, heparin binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor; CTGF, connective tissue growth factor; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; IL-4, interleukin-4; iNOS, nitric oxide synthase; GPx, glutathione peroxidase; CAT, catalase; SOD, superoxide dismutase; HO-1, hemeoxygenase-1; GSH, glutathione; COX, cytochrome-c oxidase; SDH, succinate dehydrogenase; Exos, exosomes; MFGE8, milk fat globule-EGF factor 8; TGFBR1, TGF-β type I receptor; LPS, lipopolysaccharides; JAK, Janus kinase; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; α-SMA, alpha smooth muscle actin; Col1a1, Type I collage; TIMP-1, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase; MMP-1, matrix metalloproteinases-1; MMP-9, matrix metalloproteinases-9; MMP-14, matrix metalloproteinases-14; ECM, extracellular matrix
Liver regeneration
The mechanisms by which stem cells promote liver regeneration can be subdivided into three aspects: migration of stem cells into the liver and transdifferentiation into hepatocytes, secretion of angiogenesis-related cytokines to promote neovascularization synergistically enhancing liver regeneration, and activation of proliferative signaling pathways in host endogenous hepatocytes, the most vital of these.
Migration and transdifferentiation
Chemokine ligand 12 (CXCL12), also known as stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1), is present in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs), tumor cells, and hepatic stellate cells. When the liver is acutely or chronically damaged, SDF-1 is overexpressed in the liver [87]. It has been shown that CXCL12/chemokine receptor (CXCR) is a critical chemotactic signal that recruits MSC to the liver, and concentration gradients of SDF-1 significantly affect stem cell migration. SDF-1 can induce activation of α4β1 integrin in MSC, producing firm adhesion between MSC and endothelial cells [88]. SDF-1 binds to either CXCR4 or CXCR7 on the stem cells, with the CXCR7 pathway promoting liver regeneration but with the CXCR4 pathway promoting fibrosis [89]. In recent years, it has also been found that CXCR7, although expressed at low levels on the cell surface, has a ten-fold greater binding capacity to CXCL12 than CXCR4. Under hypoxic conditions and during hepatic differentiation, CXCR7 overexpression significantly increases the migratory capacity of MSC by upregulating the levels of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), CD44, and MMP-2, which promote the adhesion of MSC by their interaction with the ECM [90].
After MSC homed the damaged liver, liver-specific ECM switched hepatogenesis of MSC via integrin pathway and downstream focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and integrin-linked kinase (ILK) which upregulated the expression of MAPK but not affected the expression of AKT, resulting in a significant increase of hepatogenic molecules such as HGF, OSM and bFGF in MSC. Then, there was a significant increase in the number of ALB-positive MSC in the presence of liver-specific ECM [30].
Hepatocyte proliferation
However, there is the controversy that the therapeutic effect of MSC is due to the cytokines they secrete to activate the facultative pathway of liver cells rather than their ability to transform into hepatocytes to replace damaged liver parenchymal cells [91,92,93]. Intravenously injected MSC increased serum IGF-1 level, IGF-1 acts on insulin-like factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) and upregulates downstream PI3K/AKT pathway [94]. MSC-conditioned medium (CM) can significantly induce gene expression of IL-6, TNF-α, HGF, and TGF-β, which are closely related to hepatocyte proliferation [95]. These cytokines interact with tyrosine kinase receptors to activate the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [96]. AKT plays an important role in cell growth, proliferation, and glucose metabolism. MSC transplantation resulted in improved glucose synthesis through AKT/GSK-3β pathway. Meanwhile, MSC promotes hepatocyte proliferation mainly via the AKT/β-Catenin pathway. Cyclin D1 and Cyclin E, downstream proteins of β-Catenin, accelerated the G1/S phase in the cell cycle after MSC transplantation [97, 98].
Angiogenesis
The angiogenesis process is also involved in promoting liver regeneration. Condition medium derived from MSC treatment caused upregulation of the proangiogenic factors VEGF-A, angiotensin-1 (Ang-1), and receptors VEGF-R1 (Fms-like tyrosine kinase 1; Flt1) and VEGF-R2 (Fetal-like kinase 1; Flk1) [99]. Meanwhile, the number of regenerated microvessels was enhanced by administrating with MSC-derived exosomes [100]. Activation of VEGF-A signaling promoted liver cell proliferation through an increased blood supply and the release of paracrine factors. VEGF-A/Flt1 signaling promoted the proliferation of hepatic cells through LSEC-derived secreted factors, such as HGF, IL-6, and heparin binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor (HB-EGF), connective tissue growth factor (CTGF). MSC treatment resulted in hepatocyte proliferation and neovascularization through hepatic growth mediators WNT2 and HGF secreted by LSEC in the VEGF-A/Flk1/Id1 signaling pathway [99, 101].
Immunoregulation
MSC can initiate immunosuppression through both intercellular contacts and secreted signaling molecules, and the immunosuppressive microenvironment is formed mainly by MSC transforming various immune cells to maintain a tolerant state (Fig. 4).
MSC-mediated immunoregulation in liver fibrosis. MSCs secrete different cytokines that regulate the transition of immune cells in the liver from a pro-inflammatory phenotype to an anti-inflammatory phenotype. The solid line represents the promotion, and the dashed line represents the inhibition. MSC, mesenchymal stem cell; IL-6, interleukin-6, HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; IL-10, interleukin-10, IL-4, interleukin-4; PGE2, prostaglandin E2, TSG-6, TNFα simulated gene/protein 6; G-CSF, granulocyte-colony stimulating factor; IDO, indolamine 2,3-dioxygenase; DC1, type 1 dendritic cell; DC2, type 2 dendritic cell; Th1, T-helper 1; Th17, T-helper 17; Treg, regulatory T cell; Gal-9, galectin-9; HLA-G5, human leukocyte antigen-5; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β
In the presence of IL-6 and HGF secreted by UCMSC, monocytes are suppressed differentiation toward other immune cell types and it is more inclined to develop a protective IL-10-producing phenotype [102]. Macrophage is known to be an important target of MSC in the regulation of intrinsic immunity. MSC skew the polarization of macrophages M2 expressing the anti-inflammatory mediators IL-1 and IL-4 and reduces the production of pro-inflammatory macrophages M1 expressing the inflammatory signals IL-12 and TNF-α by secreting soluble molecules such as prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), TNF-α stimulated gene/protein 6 (TSG-6), IL-6, G-CSF [103], and indolamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) [104]. The increase in the ratio of M2 polarization to M1 polarization is mediated by PTEN/AKT signaling pathway activated by MSC-derived exosomes [105]. Besides, BMMSCs converted phenotypic switch from pro-fibrotic Ly6Chi subpopulation to protective Ly6Clo subset in the presence of IL-4 and IL-10 [106]. Furthermore, under the effects of IL-6 and HGF secreted from MSC, mature type 1 dendritic cells (DC1s) are prone to differentiation toward tolerogenic type 2 dendritic cells (DC2s) via the phosphorylation of AKT which increases the expression level of IL-10 and TGF-β while decrease secretion of IL-12 [107]. Interestingly, hepatic stellate cells are antigen-presenting cells, and inhibition of hepatic stellate cells activation can reduce the adaptive immune response they trigger.
In the adaptive immune response, MSC abrogates the activation and proliferation of both CD4+ T-helper (Th) and CD8+ cytotoxic T-lymphocytes [108]. Additionally, MSC downregulated T-helper 1 (Th1) through upregulation of galectin-9 (Gal-9) [109], suppressed T-helper 17 (Th17) cells in IDO-dependent manner [110], and induced regulatory T cells (Tregs) through activation of Notch1 pathway or secretion of human leukocyte antigen-5 (HLA-G5), PGE2 and TGF-β [104].
Recently, MSC secreted IL-2 receptor (IL-2R) may act as a decoy receptor to inhibit IL-2 activity, IL-2R has attracted much attention as a new immune mediator in the regulation of MSC involvement [103].
Resistance to liver injury
Hepatic fibrosis is exposed to chronic damage over a long period, a multitude of molecules such as pro-inflammatory factors, oxidative stress products, apoptotic mediators, and other cytokines can affect its progression. MSC transplantation offers anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, and anti-apoptotic benefits.
Anti-inflammatory
MSC transplantation significantly reduced the level of pro-inflammatory factors TNF-α, interferon-γ (IFN-γ), IL-6, IL-1β, TGF-β1, and IL-4 in the liver by downregulating the excessive activated IFN-γ/Stat1 and IL-6/Stat3 signaling pathways. TGF-β1, secreted by liver macrophages, is the main molecule for hepatic stellate cells activation [111]. HNF-4α overexpressing MSC exerted anti-inflammatory effects by enhancing the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in MSC via activation of the NF-κB pathway [112].
Anti-oxidant
Oxidative phosphorylation and liposome peroxidation in hepatic stellate cells and macrophages produce large amounts of NADPH oxidases (NOXs), which are one of the components mediating reactive oxygen species (ROS), reactive nitrogen species (RNS) or ROS regulate the proliferation and pro-inflammatory phenotype of hepatic stellate cells mainly through the NF-κB pathway [113]. UCMSC transplants reduce malondialdehyde (MDA), the major product of lipid peroxidation in mitochondria, by secreting antioxidant enzymes such as SOD, GPx, CAT, hemeoxygenase-1 (HO-1), and GSH [114]. It also restores normal mitochondrial function by increasing the levels of cytochrome-c oxidase (COX) and succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) in the mitochondrial ATPase and respiratory chain. UCMSC reduces the release of oxidative stress mediators by inducing antioxidant responses through upregulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Nrf2 plays an important role in maintaining the structural integrity and functional stability of mitochondria [115]. Phosphatase of regenerating liver-1 (PRL-1)-overexpressing MSC decreased endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress via PRL-1 binding to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), thereby activating PI3K expression finally regulating the release of Ca2+ in hepatic cells [116].
Anti-apoptotic
Engrafted BMMSC underwent apoptosis in fibrotic tissue. Hepatic stellate cells are prime candidates for responding to apoptotic cells in the liver, phagocytosis of apoptotic bodies leads to profibrogenic phenotype in hepatic stellate cells [117]. Interestingly, with the employment of the PtdSer/MerTK/ERK axis, Ly6Clo macrophages engulfed apoptotic bodies by secreting MMP-12 [106]. BMMSC-derived exosomes (BMMSC-Exos) can be taken up by hepatocytes and entered the cytoplasm. Treatment with BMMSC-Exos or hUCMSCs reduced hepatocyte apoptosis by producing protective autophagosomes in liver cells. Treatment with hUCMSC increased PINK1-dependent mitophagy in hepatocytes through AMPKα phosphorylation [118]. After the application of BMSC-Exos, the expression levels of autophagy marker proteins LC3II, Beclin-1, and anti-apoptotic protein BCL-2 were significantly upregulated, while the expression levels of proapoptotic protein caspase-3 and Bax were downregulated [119].
Suppression of myofibroblast activity
The appearance of myofibroblasts in the liver is closely related to fibrosis. Myofibroblasts have a pro-fibrogenic and pro-inflammatory phenotype and are highly expressed α-SMA and TIMP-1 [113]. Bone marrow, fibroblasts in circulation, hepatocytes, and bile duct cells can be transformed into myofibroblasts through epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT); however, activated hepatic stellate cells are most common [120]. Hepatic stellate cells are specific cells that are normally quiescent, and they are activated when the liver is damaged, transforming into myofibroblasts. Activation of hepatic stellate cells is initiated by various mediators such as the above pro-inflammatory factors, oxidative stress mediators, inflammatory stimuli generated by apoptosis or necrosis of liver parenchymal cells, then the activated hepatic stellate cells secrete various pro-inflammatory factors that exacerbate the inflammatory response in the liver [113, 121]. Blocking myofibroblasts is a key target for the treatment of fibrosis.
TGF-β is considered to be one of the most vital signals involved in stellate cell activation. Some studies have shown that milk fat globule-EGF factor 8 (MFGE8), one of the secretomes from MSC, is an anti-fibrotic protein that inhibited hepatic stellate cells activation by downregulating TGF-β type I receptor (TGFBR1) [122]. Caveolin-1, which is a potential target for MSC therapy, showed a significant suppression effect on hepatic stellate cells. On the one hand, the phosphorylation of SMAD2, a key link in the TGF-β/SMAD axis, was reduced by upregulated Caveolin-1. On the other hand, Caveolin-1 in activated hepatic stellate cells was restored [123, 124]. BMMSC-Exos declined the expression of Wnt pathway-associated proteins such as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ), Wnt3a, Wnt10b, β-catenin, and most critical downstream WISP1 and Cyclin D1 in hepatic stellate cells, leading to inhibit hepatic stellate cells activation [125]. Amnion-derived MSC (AMSC) was displayed to repress hepatic stellate cells activation by inhibiting earlier steps of the LPS/TLR4 pathways but not downstream NF-κB transcriptional activity [126]. MSC-originated exosomal circDIDO1 sponged miR-143-3p in hepatic stellate cells, causing cell cycle arrest, suppression, and apoptosis through promoting PTEN and repressing the ratio of p-AKT/AKT [127]. More, BMMSC transplantation significantly reduced the NOXs which are vital intermediates in the motivation of hepatic stellate cells through decreasing phosphorylation of p47phox, a ligand of NOX [128]. Besides, UCMSC-Exos increased the expression of the epithelium-associated marker E-cadherin while decreasing N-cadherin- and vimentin-positive cells, thereby inhibiting EMT [129].
Extracellular matrix degradation and remodeling
Liver fibrosis is associated with both excessive deposition of ECM and reduced activities of the ECM lysis. ECM degradation and remodeling have been considered a key step in reversing liver fibrosis and limiting the advancement of liver fibrosis to cirrhosis.
TGF-β remains a classic cytokine that participates in the regulation of ECM, BMSC transplantation significantly downregulated the mRNA expression of SMAD3 downstream of TGF-β1 and TGFBR1 in myofibroblasts and increased the mRNA levels of SMAD7. Likewise, hUCMSC treatment significantly suppressed the expression of SAMD2 protein [25]. SMAD2 and SMAD3 mediate the transcription of pro-fibrotic factor α-SMA or Col1a1, whereas SMAD7 has a negative anti-fibrotic regulatory effect [130]. BMSC overexpressing Smad7 significantly reduced plasma levels of laminin and hyaluronic acid, components of the ECM. Furthermore, Smad7-MSC mediated an increase in serum expression of MMP-1 and a decrease in TIMP-1 [131]. MMP is a class of matrix-degrading proteases that mainly degrade scarring in the subendothelial space. MMP-1 is a member of the MMP family and is responsible for the degradation of matrix type I collagen (Col1a1) and type III collagen (Col3a1). In contrast, TIMP inhibits MMP activity by forming a reversible covalent complex with the corresponding MMP. IC-2-engineered MSC sheets reverse established liver fibrosis by augmenting the secretion of activated MMP-1 and MMP-14, particularly MMP-14, although generally considered to be a membrane-bound protein but has been proven to act in a soluble form as well. MMP-14 can activate MMP-2 and MMP-13, which are mainly involved in the dissolution of Col1a1 [132]. Exogenously administered MSC protects against fibrosis by decreasing p-STAT3 levels and thereby reducing STAT3-dependent MMP-9 production [133]. It is noteworthy that MMP-9, unlike traditional MMPs, can stimulate the EMT process and thus exacerbate fibrosis. In the liver fibrosis model, the expression of MMP-9 was higher than in the normal group, probably due to the synergy between MMP-9 and MMP-2 in restoring the structural integrity of liver cells and maintaining the normal morphology of the basement membrane of the liver sinusoids. MMPs cleave matricellular proteins at specific sites in the ECM to produce new active products and regulate tissue matrix attachment is a current hot topic of interest.
In parallel to reducing deposited ECM, MSC can also mediate the rearrangement of ECM to improve fibrosis. MSC rescue established fibrosis by reducing mRNA for integrin, which acts as a bridge between various extracellular components such as fibronectin, fibrinogen, laminin, and intracellular actin, mediating the architecture and adhesion of the ECM [134]. ILK-modified MSC conditioned medium inhibits fibrosis by reducing Col1a1 and Col3a1, TIMP, and CTGF. ILK interacts with the structural domains of intracytoplasmic integrins to regulate integrin-related functions, however, the exact mechanism by which ILK-MSC transplantation acts on integrins to cause matrix rearrangement remains unexplained [135].
MSC could improve fibrosis by downregulating or blocking the expression of secreted Frizzled-related protein 2 (sFRP2) and its downstream target Axin2, as well as increasing angiogenesis, suggesting that sFRP2 may be a potential target of action in MSC for the treatment of fibrotic disease models [136].
EVs-driven mechanisms of action
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are vesicles that form after the cell cargoes have sprouted. EVs have similar trophic and modulatory paracrine effects to stem cell-based therapy, but different mechanism of action and half-life.
The mechanism of action of EVs is currently based on two cargoes: RNA (especially miRNA) and protein. Toh et al. [137] suggested that due to the inadequate quantity of pre-miRNA in EVs, EVs are more likely to function through a protein-based network. A qualification is that the biological effect is largely based on the catalytic activity of enzymes, whereas some structural proteins in EVs are not able to induce a similar response. The uptake of EVs into recipient cells is via the binding of their lipids, carbohydrates, and some specific peptides to cell surface receptors. Uptake is only the first step; the details of how the contents of EVs are released into the cytoplasm of the recipient's cells are still unclear. Possible explanations are membrane fusion and release of cargo. Variant surface glycoprotein-G (VSG-G) present on the surface of EVs can mediate membrane fusion [138].
The fate of EVs in vivo can be divided into two phases, the first is rapid redistribution of EVs in various organs after systemic administration, with high doses of EVs first distributed in the spleen and liver, organs rich in vascularity. And the second phase is the final clearance of EVs from the body, the decay of the signal in blood followed a two-phase exponential decline, with a short half-life of 20 min and a longer half-life of more than 3 h [139]. With this in mind, locally administrated EVs could achieve higher concentrations in a target cell.
Conclusions and future prospects
We summarize the current sources of stem cells available for clinical trials in cirrhosis and liver fibrosis from the perspective of clinical progress, the clinical phases, and the administration of stem cells. As a matter of course, the limitations and prospects of the various types of stem cells for clinical application are discussed. To further elucidate how stem cells perform in vivo, we present an in-depth exploration of stem cells improve liver fibrosis from liver regeneration, immunoregulation, resistance to liver injury, inhibition of myofibroblast activity, and extracellular matrix degradation and remodeling five aspects, demonstrating the therapeutic potential of stem cells.
In the mechanism of stem cell therapy for liver fibrosis, we note that the stem cells themselves may not serve a major function, conversely, paracrine mediators are thought to be pivotal to the action of stem cells. This gave birth to the conception of cell-free therapy. Cell-free strategies have been proposed without the potential for tumorigenicity, embolism, high cost of cell preservation, or possible exogenic infections. Stem cells secrete many soluble molecules such as nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids into the CM, they are encapsulated in EVs [140]. Hirata et al. [141] injected SHEDs and CM obtained from SHEDs into mice with liver fibrosis, and the results showed that both can improve fibrosis. CM targets multiple points of fibrosis development to achieve better outcomes. ADSCs were engineered to overexpress miRNA-181-5p to selectively transfer exosomes to damaged liver fibrosis, this suggests that EVs can act as a vehicle for the transport of MSC-secreted effective molecules and that genetically engineered EVs can achieve targeted delivery and amplified performance [142]. Regrettably, however, none of the clinical trials involved the use of stem cell-derived EVs for the treatment of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. This is largely attributable to the standardized method for the extraction of large quantities of EVs or exosomes that has not been established and the dose and half-life of EVs remain unclear.
In contrast to cell-free therapies, cell-based pre-treatment is a hot topic for future research. Primary stem cells or unpretreated cells often fail to achieve the desired therapeutic effect due to poor homing ability, the very low survival rate after transplantation, and cellular senescence or decline in viability during in vitro culture. Enhancement strategies, including physiological microenvironment and pathological microenvironment to stimulate stem cell activation, have caused widespread concern [143]. A shift in the culture model is a common physiological way to enhance MSC. Compared with 2D cultured MSCs, 3D spheroids displayed a better capacity for antifibrosis both in vitro and in vivo [144]. Pathological pre-treatment includes hypoxia, inflammatory factors, bioactive compounds, and disease-associated cells or patient serum. IFN-γ pre-treatment and 3D culture of MSC showed increased production of both growth and immunoregulatory factors. Furthermore, these modified MSCs strongly reduced M1-induced inflammation [145]. Pre-activation of in vitro cultured MSCs with patient serum allows MSCs to have specific host-related functions and properties, thus allowing for individualized management strategies. The significant decrease in the infarct area, brain lesion, and apoptotic cells but the increase in neurogenesis positive cells number and trophic factors appeared in the stroke serum pretreated MSCs compared to the normal serum pretreated [146].
Integrated cell activation and cell-free therapy, Takeuchi et al. [147] found that EVs derived from IFN-γ pre-conditioned cells were more effective in relieving inflammation and fibrosis than the EVs group, signifying that IFN-γ altered the contents of EVs resulting in enhanced repair.
Availability of data and materials
All the data are included in the article.
Abbreviations
- ESLD:
-
End-stage liver disease
- OLT:
-
Orthotropic liver transplantation
- PHHs:
-
Primary human hepatocytes
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- TIMP:
-
Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase
- MSC:
-
Mesenchymal stem cell
- MELD:
-
Model for end-stage liver disease
- ALB:
-
Albumin
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- TBil:
-
Total bilirubin
- UCMSC:
-
Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell
- BMMSC:
-
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell
- HSC:
-
Hematopoietic stem cell
- GMP:
-
Good manufacturing practice
- HGF:
-
Hepatocyte growth factor
- PCNA:
-
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen
- PAK2:
-
P21-activated kinase-2
- BMMNC:
-
Bone marrow mononuclear cell
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- IGFBP-2:
-
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2
- IL-1Ra:
-
IL-1 receptor antagonist
- ADMSC:
-
Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell
- LDMSC:
-
Liver-derived mesenchymal stem cell
- MenSC:
-
Menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell
- SSEA4:
-
Stage-specific embryonic antigen 4
- α-SMA:
-
Alpha smooth muscle actin
- TGF-β1:
-
Transforming growth factor-β1
- MCP-1:
-
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
- SHED:
-
Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- G-CSF:
-
Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor
- BMSC:
-
Bone marrow stem cell
- VEGFR:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- TAC:
-
Total antioxidant capacity
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- EPC:
-
Endothelial progenitor cell
- vWF:
-
Von Willebrand factor
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- IGF-1:
-
Insulin-like factor-1
- bFGF:
-
Basic fibroblast growth factor
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- LPC:
-
Liver progenitor cell
- HLC:
-
Hepatocyte-like cell
- FGF2:
-
Fibroblast growth factor 2
- FGF4:
-
Fibroblast growth factor 4
- BMP4:
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 4
- OSM:
-
Oncostatin M
- AFP:
-
α-Fetoprotein
- A1AT:
-
Alpha-1-antitrypsin
- HNF4α:
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α
- ESC:
-
Embryonic stem cell
- iPSC:
-
Induced pluripotent stem cell
- CXCL12:
-
Chemokine ligand 12
- SDF-1:
-
Stromal cell-derived factor-1
- LSEC:
-
Liver sinusoidal endothelial cell
- CXCR:
-
Chemokine receptor
- VACM-1:
-
Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1
- FAK:
-
Focal adhesion kinase
- ILK:
-
Integrin-linked kinase
- IGF1R:
-
Insulin-like factor 1 receptor
- CM:
-
Conditioned medium
- Ang-1:
-
Angiotensin-1
- Flt1:
-
Fms-like tyrosine kinase 1
- Flk1:
-
Fetal-like kinase 1
- HB-EGF:
-
Heparin binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor
- CTGF:
-
Connective tissue growth factor
- PGE2:
-
Prostaglandin E2
- TSG-6:
-
TNFα simulated gene/protein 6
- IDO:
-
Indolamine 2,3-dioxygenase
- DC1:
-
Type 1 dendritic cell
- DC2:
-
Type 2 dendritic cell
- Th:
-
T-helper
- Th1:
-
T-helper 1
- Th17:
-
T-helper 17
- Gal-9:
-
Galectin-9
- Treg:
-
Regulatory T cell
- HLA-G5:
-
Human leukocyte antigen-5
- IL-2R:
-
IL-2 receptor
- IFN-γ:
-
Interferon-γ
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- NOXs:
-
NADPH oxidases
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- RNS:
-
Reactive nitrogen species
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- HO-1:
-
Hemeoxygenase-1
- COX:
-
Cytochrome-c oxidase
- SDH:
-
Succinate dehydrogenase
- PRL-1:
-
Phosphatase of regenerating liver-1
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- BMMSC-Exos:
-
BMMSC-derived exosomes
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- MFGE8:
-
Milk fat globule-EGF factor 8
- TGFBR1:
-
TGF-β type I receptor
- PPARγ:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ
- AMSC:
-
Amnion-derived mesenchymal stem cell
- Col1a1:
-
Type I collagen
- Col3a1:
-
Type III collagen
- sFRP2:
-
Secreted Frizzled-related protein 2
- EVs:
-
Extracellular vesicles
- VSG-G:
-
Variant surface glycoprotein-G
References
Asrani SK, Devarbhavi H, Eaton J, Kamath PS. Burden of liver diseases in the world. J Hepatol. 2019;70:151–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2018.09.014.
Sepanlou SG, Safiri S, Bisignano C, Ikuta KS, Merat S, Saberifiroozi M, et al. The global, regional, and national burden of cirrhosis by cause in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5:245–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30349-8.
Messina A, Luce E, Hussein M, Dubart-Kupperschmitt A. Pluripotent-stem-cell-derived hepatic cells: hepatocytes and organoids for liver therapy and regeneration. Cells. 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020420.
Puppi J, Strom SC, Hughes RD, Bansal S, Castell JV, Dagher I, et al. Improving the techniques for human hepatocyte transplantation: report from a consensus meeting in London. Cell Transplant. 2012;21:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3727/096368911X566208.
Forbes SJ, Gupta S, Dhawan A. Cell therapy for liver disease: From liver transplantation to cell factory. J Hepatol. 2015;62:S157–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2015.02.040.
Epstein SE, Luger D, Lipinski MJ. Large animal model efficacy testing is needed prior to launch of a stem cell clinical trial: an evidence-lacking conclusion based on conjecture. Circ Res. 2017;121:496–8. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.311562.
Li T, Ai Z, Ji W. Primate stem cells: bridge the translation from basic research to clinic application. Sci China Life Sci. 2019;62:12–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-018-9334-2.
Zhao L, Chen S, Shi X, Cao H, Li L. A pooled analysis of mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for liver disease. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9:72. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-018-0816-2.
Alanazi A, Munir H, Alassiri M, Ward LSC, McGettrick HM, Nash GB. Comparative adhesive and migratory properties of mesenchymal stem cells from different tissues. Biorheology. 2019;56:15–30. https://doi.org/10.3233/BIR-180185.
Varkouhi AK, He X, Teixeira Monteiro AP, Amatullah H, Tsoporis JN, Gupta S, et al. Immunophenotypic characterization and therapeutics effects of human bone marrow- and umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in an experimental model of sepsis. Exp Cell Res. 2021;399:112473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112473.
Le Blanc K, Samuelsson H, Gustafsson B, Remberger M, Sundberg B, Arvidson J, et al. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells to enhance engraftment of hematopoietic stem cells. Leukemia. 2007;21:1733–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404777.
Ghavamzadeh A, Sotoudeh M, Hashemi Taheri AP, Alimoghaddam K, Pashaiefar H, Jalili M, et al. Liver fibrosis alleviation after co-transplantation of hematopoietic stem cells with mesenchymal stem cells in patients with thalassemia major. Ann Hematol. 2018;97:327–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-017-3181-9.
Rostami T, Kasaeian A, Maleki N, Nikbakht M, Kiumarsi A, Tavangar SM, et al. The effect of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell co-transplantation with hematopoietic stem cells on liver fibrosis alleviation and survival in patients with class III β-thalassemia major. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12:213. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-021-02242-8.
Eggenhofer E, Benseler V, Kroemer A, Popp FC, Geissler EK, Schlitt HJ, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells are short-lived and do not migrate beyond the lungs after intravenous infusion. Front Immunol. 2012;3:297. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2012.00297.
Nguyen MP, Jain V, Iansante V, Mitry RR, Filippi C, Dhawan A. Clinical application of hepatocyte transplantation: current status, applicability, limitations, and future outlook. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;14:185–96. https://doi.org/10.1080/17474124.2020.1733975.
Dhawan A, Puppi J, Hughes RD, Mitry RR. Human hepatocyte transplantation: current experience and future challenges. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;7:288–98. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2010.44.
van der Helm D, Barnhoorn MC, de Jonge-Muller ESM, Molendijk I, Hawinkels LJAC, Coenraad MJ, et al. Local but not systemic administration of mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorates fibrogenesis in regenerating livers. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23:6238–50. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14508.
Xu J, Liu G, Wang X, Hu Y, Luo H, Ye L, et al. hUC-MSCs: evaluation of acute and long-term routine toxicity testing in mice and rats. Cytotechnology. 2022;74:17–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-021-00502-2.
Zhou G-P, Jiang Y-Z, Sun L-Y, Zhu Z-J. Therapeutic effect and safety of stem cell therapy for chronic liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11:419. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-01935-w.
Zhang Y, Li Y, Zhang L, Li J, Zhu C. Mesenchymal stem cells: potential application for the treatment of hepatic cirrhosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9:59. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-018-0814-4.
Culenova M, Nicodemou A, Novakova ZV, Debreova M, Smolinská V, Bernatova S, et al. Isolation, culture and comprehensive characterization of biological properties of human urine-derived stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212503.
Pelekanos RA, Sardesai VS, Futrega K, Lott WB, Kuhn M, Doran MR. Isolation and expansion of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells derived from human placenta tissue. J Vis Exp JoVE. 2016. https://doi.org/10.3791/54204.
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8:315–7. https://doi.org/10.1080/14653240600855905.
Shi M, Li Y-Y, Xu R-N, Meng F-P, Yu S-J, Fu J-L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy in decompensated liver cirrhosis: a long-term follow-up analysis of the randomized controlled clinical trial. Hepatol Int. 2021;15:1431–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-021-10199-2.
Kao Y-H, Lin Y-C, Lee P-H, Lin C-W, Chen P-H, Tai T-S, et al. Infusion of human mesenchymal stem cells improves regenerative niche in thioacetamide-injured mouse liver. Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. 2020;17:671–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13770-020-00274-4.
Xie Y, Liu S, Wang L, Yang H, Tai C, Ling L, et al. Individual heterogeneity screened umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells with high Treg promotion demonstrate improved recovery of mouse liver fibrosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12:359. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-021-02430-6.
Zhou Q, Gu T, Zhang Y, Li H, Zhuansun X, Xu S, Kuang Y. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis by upregulating MicroRNA-455-3p through suppression of p21-activated kinase-2. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:6685605. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6685605.
Suk KT, Yoon J-H, Kim MY, Kim CW, Kim JK, Park H, et al. Transplantation with autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for alcoholic cirrhosis: phase 2 trial. Hepatology. 2016;64:2185–97. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.28693.
Meier RPH, Mahou R, Morel P, Meyer J, Montanari E, Muller YD, et al. Microencapsulated human mesenchymal stem cells decrease liver fibrosis in mice. J Hepatol. 2015;62:634–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2014.10.030.
Bi H, Ming L, Cheng R, Luo H, Zhang Y, Jin Y. Liver extracellular matrix promotes BM-MSCs hepatic differentiation and reversal of liver fibrosis through activation of integrin pathway. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;11:2685–98. https://doi.org/10.1002/term.2161.
Huang K-C, Chuang M-H, Lin Z-S, Lin Y-C, Chen C-H, Chang C-L, et al. Transplantation with GXHPC1 for liver cirrhosis: phase 1 trial. Cell Transplant. 2019;28:100S-111S. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963689719884885.
Seki A, Sakai Y, Komura T, Nasti A, Yoshida K, Higashimoto M, et al. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells as a regenerative therapy for a mouse steatohepatitis-induced cirrhosis model. Hepatology. 2013;58:1133–42. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.26470.
Hao T, Chen J, Zhi S, Zhang Q, Chen G, Yu F. Comparison of bone marrow-vs. adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells for attenuating liver fibrosis. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14:5956–64. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.5333.
Wang Y, Yu X, Chen E, Li L. Liver-derived human mesenchymal stem cells: a novel therapeutic source for liver diseases. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7:71. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-016-0330-3.
Bruno S, Herrera Sanchez MB, Chiabotto G, Fonsato V, Navarro-Tableros V, Pasquino C, et al. Human liver stem cells: a liver-derived mesenchymal stromal cell-like population with pro-regenerative properties. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:644088. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.644088.
Lee J, Choi J, Kang S, Kim J, Lee R, So S, et al. Hepatogenic potential and liver regeneration effect of human liver-derived mesenchymal-like stem cells. Cells. 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061521.
Wu X, Luo Y, Chen J, Pan R, Xiang B, Du X, et al. Transplantation of human menstrual blood progenitor cells improves hyperglycemia by promoting endogenous progenitor differentiation in type 1 diabetic mice. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23:1245–57. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2013.0390.
Chen L, Qu J, Xiang C. The multi-functional roles of menstrual blood-derived stem cells in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-018-1105-9.
Chen L, Zhang C, Chen L, Wang X, Xiang B, Wu X, et al. Human menstrual blood-derived stem cells ameliorate liver fibrosis in mice by targeting hepatic stellate cells via paracrine mediators. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6:272–84. https://doi.org/10.5966/sctm.2015-0265.
Lee SH, Looi CY, Chong PP, Foo JB, Looi QH, Ng CX, Ibrahim Z. Comparison of isolation, expansion and cryopreservation techniques to produce stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth (SHED) with better regenerative potential. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;16:551–62. https://doi.org/10.2174/1574888X15666200928110923.
Yuniartha R, Yamaza T, Sonoda S, Yoshimaru K, Matsuura T, Yamaza H, et al. Cholangiogenic potential of human deciduous pulp stem cell-converted hepatocyte-like cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12:57. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-02113-8.
Yamaza T, Alatas FS, Yuniartha R, Yamaza H, Fujiyoshi JK, Yanagi Y, et al. In vivo hepatogenic capacity and therapeutic potential of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth in liver fibrosis in mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:171. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-015-0154-6.
Yao J, Chen N, Wang X, Zhang L, Huo J, Chi Y, et al. Human supernumerary teeth-derived apical papillary stem cells possess preferable characteristics and efficacy on hepatic fibrosis in mice. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:6489396. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/6489396.
Newsome PN, Fox R, King AL, Barton D, Than N-N, Moore J, et al. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and autologous CD133-positive stem-cell therapy in liver cirrhosis (REALISTIC): an open-label, randomised, controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;3:25–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-1253(17)30326-6.
Tsolaki E, Athanasiou E, Gounari E, Zogas N, Siotou E, Yiangou M, et al. Hematopoietic stem cells and liver regeneration: differentially acting hematopoietic stem cell mobilization agents reverse induced chronic liver injury. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2014;53:124–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcmd.2014.05.003.
Yannaki E, Athanasiou E, Xagorari A, Constantinou V, Batsis I, Kaloyannidis P, et al. G-CSF-primed hematopoietic stem cells or G-CSF per se accelerate recovery and improve survival after liver injury, predominantly by promoting endogenous repair programs. Exp Hematol. 2005;33:108–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exphem.2004.09.005.
Pulavendran S, Vignesh J, Rose C. Differential anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic activity of transplanted mesenchymal vs. hematopoietic stem cells in carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010;10:513–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2010.01.014.
Zhou P, Wirthlin L, McGee J, Annett G, Nolta J. Contribution of human hematopoietic stem cells to liver repair. Semin Immunopathol. 2009;31:411–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-009-0166-3.
Hosoi H, Warigaya K, Murata S, Mushino T, Kuriyama K, Nishikawa A, et al. Refractory ascites with liver fibrosis developed in late phase allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: report of three patients. Hematol Rep. 2016;8:6482. https://doi.org/10.4081/hr.2016.6482.
Kuloglu Z, Balcı D, Haskoloğlu ZŞ, Kendirli T, Bingöl-Koloğlu M, Tuna-Kırsaçlıoğlu C, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell and liver transplantation in a young girl with dedicator of cytokinesis 8 protein deficiency. Pediatr Transplant. 2019;23:e13545. https://doi.org/10.1111/petr.13545.
Mohamadnejad M, Vosough M, Moossavi S, Nikfam S, Mardpour S, Akhlaghpoor S, et al. Intraportal infusion of bone marrow mononuclear or CD133+ cells in patients With decompensated cirrhosis: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5:87–94. https://doi.org/10.5966/sctm.2015-0004.
de Souza VCA, Pereira TA, Teixeira VW, Carvalho H, de Castro MCAB, D’assunção CG, et al. Bone marrow-derived monocyte infusion improves hepatic fibrosis by decreasing osteopontin, TGF-β1, IL-13 and oxidative stress. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23:5146–57. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i28.5146.
El-Yamany MF, Zaki ES, Shaltout SA, Saad MA. Bone marrow mononuclear cells boosts anti-cytogentical aberration effect of N-acetylcysteine and α-lipoic acid in rat’s liver and bone marrow: implication of oxidative and inflammatory pathways. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2021;31:437–49. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376516.2021.1906370.
D’Avola D, Fernández-Ruiz V, Carmona-Torre F, Méndez M, Pérez-Calvo J, Prósper F, et al. Phase 1–2 pilot clinical trial in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis treated with bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells. Transl Res. 2017;188:80-91.e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trsl.2016.02.009.
Abdelgwad M, Ewaiss M, Sabry D, Khalifa WA, Altaib ZM, Alhelf M. Comparative study on effect of mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells on treatment of experimental CCL4-induced liver fibrosis. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1080/13813455.2020.1752256.
Garg M, Kaur S, Banik A, Kumar V, Rastogi A, Sarin SK, et al. Bone marrow endothelial progenitor cells activate hepatic stellate cells and aggravate carbon tetrachloride induced liver fibrosis in mice via paracrine factors. Cell Prolif. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12355.
Ko S, Russell JO, Molina LM, Monga SP. Liver progenitors and adult cell plasticity in hepatic injury and repair: knowns and unknowns. Annu Rev Pathol. 2020;15:23–50. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-012419-032824.
Pietrosi G, Chinnici C. Report on liver cell transplantation using human fetal liver cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1506:283–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6506-9_20.
Fitzpatrick E, Mitry RR, Dhawan A. Human hepatocyte transplantation: state of the art. J Intern Med. 2009;266:339–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2796.2009.02152.x.
Häussinger D, Kordes C. Space of Disse: a stem cell niche in the liver. Biol Chem. 2019;401:81–95. https://doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2019-0283.
Boyd A, Newsome P, Lu W-Y. The role of stem cells in liver injury and repair. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;13:623–31. https://doi.org/10.1080/17474124.2019.1618186.
Michalopoulos GK, Bhushan B. Liver regeneration: biological and pathological mechanisms and implications. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18:40–55. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-020-0342-4.
Chistiakov DA, Chistiakov PA. Strategies to produce hepatocytes and hepatocyte-like cells from pluripotent stem cells. Hepatol Res. 2012;42:111–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1872-034X.2011.00896.x.
Snykers S, de Kock J, Tamara V, Rogiers V. Hepatic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells: in vitro strategies. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;698:305–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-999-4_23.
Ang LT, Tan AKY, Autio MI, Goh SH, Choo SH, Lee KL, et al. A roadmap for human liver differentiation from pluripotent stem cells. Cell Rep. 2018;22:2190–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.01.087.
Choi J, Kang S, Kim B, So S, Han J, Kim G-N, et al. Efficient hepatic differentiation and regeneration potential under xeno-free conditions using mass-producible amnion-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12:569. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-021-02470-y.
Wu H-H, Ho JH, Lee OK. Detection of hepatic maturation by Raman spectroscopy in mesenchymal stromal cells undergoing hepatic differentiation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-015-0259-y.
Campard D, Lysy PA, Najimi M, Sokal EM. Native umbilical cord matrix stem cells express hepatic markers and differentiate into hepatocyte-like cells. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:833–48. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2007.12.024.
Ewida SF, Abdou AG, El-Rasol Elhosary AA, El-Ghane Metawe SA. Hepatocyte-like versus mesenchymal stem cells in CCl4-induced liver fibrosis. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2017;25:736–45. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAI.0000000000000373.
Wang H, Zhao T, Xu F, Li Y, Wu M, Zhu D, et al. How important is differentiation in the therapeutic effect of mesenchymal stromal cells in liver disease? Cytotherapy. 2014;16:309–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcyt.2013.07.011.
Zhou W-L, Medine CN, Zhu L, Hay DC. Stem cell differentiation and human liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:2018–25. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i17.2018.
Chen Y-F, Tseng C-Y, Wang H-W, Kuo H-C, Yang VW, Lee OK. Rapid generation of mature hepatocyte-like cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells by an efficient three-step protocol. Hepatology. 2012;55:1193–203. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.24790.
Naji A, Rouas-Freiss N, Durrbach A, Carosella ED, Sensébé L, Deschaseaux F. Concise review: combining human leukocyte antigen G and mesenchymal stem cells for immunosuppressant biotherapy. Stem Cells (Dayton, Ohio). 2013;31:2296–303. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.1494.
Peltzer J, Montespan F, Thepenier C, Boutin L, Uzan G, Rouas-Freiss N, Lataillade J-J. Heterogeneous functions of perinatal mesenchymal stromal cells require a preselection before their banking for clinical use. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24:329–44. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2014.0327.
Kwon A, Kim Y, Kim M, Kim J, Choi H, Jekarl DW, et al. Tissue-specific differentiation potency of mesenchymal stromal cells from perinatal tissues. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23544. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep23544.
Panepucci RA, Siufi JLC, Silva WA, Proto-Siquiera R, Neder L, Orellana M, et al. Comparison of gene expression of umbilical cord vein and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells (Dayton, Ohio). 2004;22:1263–78. https://doi.org/10.1634/stemcells.2004-0024.
El-Badawy A, Amer M, Abdelbaset R, Sherif SN, Abo-Elela M, Ghallab YH, et al. Adipose stem cells display higher regenerative capacities and more adaptable electro-kinetic properties compared to bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Sci Rep. 2016;6:37801. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep37801.
Russell KA, Chow NHC, Dukoff D, Gibson TWG, LaMarre J, Betts DH, Koch TG. Characterization and immunomodulatory effects of canine adipose tissue- and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0167442. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0167442.
Bozorgmehr M, Gurung S, Darzi S, Nikoo S, Kazemnejad S, Zarnani A-H, Gargett CE. Endometrial and menstrual blood mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: biological properties and clinical application. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:497. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.00497.
Huang GT-J, Gronthos S, Shi S. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from dental tissues vs. those from other sources: their biology and role in regenerative medicine. J Dental Res. 2009;88:792–806. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034509340867.
Aggarwal R, Lu J, Pompili VJ, Das H. Hematopoietic stem cells: transcriptional regulation, ex vivo expansion and clinical application. Curr Mol Med. 2012;12:34–49. https://doi.org/10.2174/156652412798376125.
Wagner JE, Rosenthal J, Sweetman R, Shu XO, Davies SM, Ramsay NK, et al. Successful transplantation of HLA-matched and HLA-mismatched umbilical cord blood from unrelated donors: analysis of engraftment and acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 1996;88:795–802.
Lu D, Jiang Y, Deng W, Zhang Y, Liang Z, Wu Q, et al. Long-term outcomes of BMMSC compared with BMMNC for treatment of critical limb ischemia and foot ulcer in patients with diabetes. Cell Transplant. 2019;28:645–52. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963689719835177.
Hristov M, Weber C. Endothelial progenitor cells: characterization, pathophysiology, and possible clinical relevance. J Cell Mol Med. 2004;8:498–508. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2004.tb00474.x.
Caplan AI. Mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res Off Publ Orthop Res Soc. 1991;9:641–50. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.1100090504.
Caplan AI. Mesenchymal stem cells: time to change the name! Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6:1445–51. https://doi.org/10.1002/sctm.17-0051.
Miller RJ, Banisadr G, Bhattacharyya BJ. CXCR4 signaling in the regulation of stem cell migration and development. J Neuroimmunol. 2008;198:31–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2008.04.008.
Chute JP. Stem cell homing. Curr Opin Hematol. 2006;13:399–406. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.moh.0000245698.62511.3d.
Liepelt A, Tacke F. Stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) as a target in liver diseases. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016;311:G203–9. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00193.2016.
Liu L, Chen J-X, Zhang X-W, Sun Q, Yang L, Liu A, et al. Chemokine receptor 7 overexpression promotes mesenchymal stem cell migration and proliferation via secreting Chemokine ligand 12. Sci Rep. 2018;8:204. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-18509-1.
Hu C, Li L. In vitro culture of isolated primary hepatocytes and stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells for liver regeneration. Protein Cell. 2015;6:562–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-015-0180-2.
Zhou W, Nelson ED, Abu Rmilah AA, Amiot BP, Nyberg SL. Stem cell-related studies and stem cell-based therapies in liver diseases. Cell Transplant. 2019;28:1116–22. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963689719859262.
Yin F, Wang W-Y, Jiang W-H. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate liver fibrosis in vitro and in vivo: From biological characteristics to therapeutic mechanisms. World J Stem Cells. 2019;11:548–64. https://doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v11.i8.548.
Xu J, Wang X, Chen J, Chen S, Li Z, Liu H, et al. Embryonic stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote colon epithelial integrity and regeneration by elevating circulating IGF-1 in colitis mice. Theranostics. 2020;10:12204–22. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.47683.
Fouraschen SMG, Pan Q, de Ruiter PE, Farid WRR, Kazemier G, Kwekkeboom J, et al. Secreted factors of human liver-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote liver regeneration early after partial hepatectomy. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21:2410–9. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2011.0560.
Valizadeh A, Majidinia M, Samadi-Kafil H, Yousefi M, Yousefi B. The roles of signaling pathways in liver repair and regeneration. J Cell Physiol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28336.
Ding H-R, Wang J-L, Tang Z-T, Wang Y, Zhou G, Liu Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells improve glycometabolism and liver regeneration in the treatment of post-hepatectomy liver failure. Front Physiol. 2019;10:412. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.00412.
Murata S, Ohkohchi N, Matsuo R, Ikeda O, Myronovych A, Hoshi R. Platelets promote liver regeneration in early period after hepatectomy in mice. World J Surg. 2007;31:808–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-006-0772-3.
Matsumoto K, Ema M. Roles of VEGF-A signalling in development, regeneration, and tumours. J Biochem. 2014;156:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvu031.
Hu J, Chen X, Li P, Lu X, Yan J, Tan H, Zhang C. Exosomes derived from human amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells alleviate cardiac fibrosis via enhancing angiogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2021;11:348–61. https://doi.org/10.21037/cdt-20-1032.
Ding B-S, Cao Z, Lis R, Nolan DJ, Guo P, Simons M, et al. Divergent angiocrine signals from vascular niche balance liver regeneration and fibrosis. Nature. 2014;505:97–102. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12681.
Deng Y, Zhang Y, Ye L, Zhang T, Cheng J, Chen G, et al. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells instruct monocytes towards an IL10-producing phenotype by secreting IL6 and HGF. Sci Rep. 2016;6:37566. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep37566.
Cruz-Barrera M, Flórez-Zapata N, Lemus-Diaz N, Medina C, Galindo C-C, González-Acero L-X, et al. Integrated analysis of transcriptome and secretome from umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells reveal new mechanisms for the modulation of inflammation and immune activation. Front Immunol. 2020;11:575488. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.575488.
Gazdic M, Volarevic V, Arsenijevic N, Stojkovic M. Mesenchymal stem cells: a friend or foe in immune-mediated diseases. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2015;11:280–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-014-9583-3.
Liu W, Yu M, Xie D, Wang L, Ye C, Zhu Q, et al. Melatonin-stimulated MSC-derived exosomes improve diabetic wound healing through regulating macrophage M1 and M2 polarization by targeting the PTEN/AKT pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-01756-x.
Li Y-H, Shen S, Shao T, Jin M-T, Fan D-D, Lin A-F, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells attenuate liver fibrosis by targeting Ly6Chi/lo macrophages through activating the cytokine-paracrine and apoptotic pathways. Cell death discovery. 2021;7:239. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-021-00584-z.
Hu C, Wu Z, Li L. Mesenchymal stromal cells promote liver regeneration through regulation of immune cells. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16:893–903. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.39725.
Pianta S, Bonassi Signoroni P, Muradore I, Rodrigues MF, Rossi D, Silini A, Parolini O. Amniotic membrane mesenchymal cells-derived factors skew T cell polarization toward Treg and downregulate Th1 and Th17 cells subsets. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2015;11:394–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-014-9558-4.
Fan J, Tang X, Wang Q, Zhang Z, Wu S, Li W, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate experimental autoimmune cholangitis through immunosuppression and cytoprotective function mediated by galectin-9. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9:237. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-018-0979-x.
Milosavljevic N, Gazdic M, Simovic Markovic B, Arsenijevic A, Nurkovic J, Dolicanin Z, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells attenuate liver fibrosis by suppressing Th17 cells-an experimental study. Transpl Int Off J Eur Soc Organ Transplant. 2018;31:102–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/tri.13023.
He Y, Guo X, Lan T, Xia J, Wang J, Li B, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve the function of liver in rats with acute-on-chronic liver failure via downregulating Notch and Stat1/Stat3 signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12:396. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-021-02468-6.
Ye Z, Lu W, Liang L, Tang M, Wang Y, Li Z, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 alpha alleviate liver injury by modulating anti-inflammatory functions in mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10:149. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-019-1260-7.
Roehlen N, Crouchet E, Baumert TF. Liver fibrosis: mechanistic concepts and therapeutic perspectives. Cells. 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9040875.
Na J, Song J, Kim HH, Seok J, Kim JY, Jun JH, Kim GJ. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells trigger repair system in TAA-injured rat model via antioxidant effect. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;13:61–76. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.202348.
Yan W, Li D, Chen T, Tian G, Zhou P, Ju X. Umbilical cord MSCs reverse D-galactose-induced hepatic mitochondrial dysfunction via activation of Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Biol Pharm Bull. 2017;40:1174–82. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b16-00777.
Kim SH, Kim JY, Park SY, Jeong WT, Kim JM, Bae SH, Kim GJ. Activation of the EGFR-PI3K-CaM pathway by PRL-1-overexpressing placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates liver cirrhosis via ER stress-dependent calcium. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12:551. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-021-02616-y.
Mehal W, Imaeda A. Cell death and fibrogenesis. Semin Liver Dis. 2010;30:226–31. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1255352.
Zheng J, Chen L, Lu T, Zhang Y, Sui X, Li Y, et al. MSCs ameliorate hepatocellular apoptosis mediated by PINK1-dependent mitophagy in liver ischemia/reperfusion injury through AMPKα activation. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:256. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2424-1.
Zhao S, Liu Y, Pu Z. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes attenuate D-GaIN/LPS-induced hepatocyte apoptosis by activating autophagy in vitro. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13:2887–97. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S220190.
Wynn TA. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of fibrosis. J Pathol. 2008;214:199–210. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.2277.
Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:1655–69. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.003.
An SY, Jang YJ, Lim H-J, Han J, Lee J, Lee G, et al. Milk fat globule-EGF factor 8, secreted by mesenchymal stem cells, protects against liver fibrosis in mice. Gastroenterology. 2017;152:1174–86. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2016.12.003.
Yao Y, Xia Z, Cheng F, Jang Q, He J, Pan C, et al. Human placental mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate liver fibrosis in mice by upregulation of Caveolin1 in hepatic stellate cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12:294. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-021-02358-x.
Tourkina E, Richard M, Oates J, Hofbauer A, Bonner M, Gööz P, et al. Caveolin-1 regulates leucocyte behaviour in fibrotic lung disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:1220–6. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.117580.
Rong X, Liu J, Yao X, Jiang T, Wang Y, Xie F. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviate liver fibrosis through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10:98. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-019-1204-2.
Ohara M, Ohnishi S, Hosono H, Yamamoto K, Yuyama K, Nakamura H, et al. Extracellular vesicles from amnion-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate hepatic inflammation and fibrosis in rats. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:3212643. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3212643.
Ma L, Wei J, Zeng Y, Liu J, Xiao E, Kang Y, Kang Y. Mesenchymal stem cell-originated exosomal circDIDO1 suppresses hepatic stellate cell activation by miR-141-3p/PTEN/AKT pathway in human liver fibrosis. Drug Delivery. 2022;29:440–53. https://doi.org/10.1080/10717544.2022.2030428.
Qiao H, Zhou Y, Qin X, Cheng J, He Y, Jiang Y. NADPH oxidase signaling pathway mediates mesenchymal stem cell-induced inhibition of hepatic stellate cell activation. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:1239143. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1239143.
Li T, Yan Y, Wang B, Qian H, Zhang X, Shen L, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate liver fibrosis. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22:845–54. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2012.0395.
Hernandez-Gea V, Friedman SL. Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2011;6:425–56. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-011110-130246.
Su D-N, Wu S-P, Xu S-Z. Mesenchymal stem cell-based Smad7 gene therapy for experimental liver cirrhosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11:395. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-01911-4.
Itaba N, Kono Y, Watanabe K, Yokobata T, Oka H, Osaki M, et al. Reversal of established liver fibrosis by IC-2-engineered mesenchymal stem cell sheets. Sci Rep. 2019;9:6841. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-43298-0.
Matsui F, Babitz SK, Rhee A, Hile KL, Zhang H, Meldrum KK. Mesenchymal stem cells protect against obstruction-induced renal fibrosis by decreasing STAT3 activation and STAT3-dependent MMP-9 production. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017;312:F25–32. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00311.2016.
Periera-Simon S, Xia X, Catanuto P, Coronado R, Kurtzberg J, Bellio M, et al. Anti-fibrotic effects of different sources of MSC in bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in C57BL6 male mice. Respirology. 2021;26:161–70. https://doi.org/10.1111/resp.13928.
Mao Q, Lin C-X, Liang X-L, Gao J-S, Xu B. Mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing integrin-linked kinase attenuate cardiac fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis through paracrine actions. Mol Med Rep. 2013;7:1617–23. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2013.1348.
Mastri M, Shah Z, Hsieh K, Wang X, Wooldridge B, Martin S, et al. Secreted Frizzled-related protein 2 as a target in antifibrotic therapeutic intervention. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014;306:C531–9. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00238.2013.
Toh WS, Lai RC, Zhang B, Lim SK. MSC exosome works through a protein-based mechanism of action. Biochem Soc Trans. 2018;46:843–53. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20180079.
György B, Hung ME, Breakefield XO, Leonard JN. Therapeutic applications of extracellular vesicles: clinical promise and open questions. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2015;55:439–64. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010814-124630.
Lai CP, Mardini O, Ericsson M, Prabhakar S, Maguire C, Chen JW, et al. Dynamic biodistribution of extracellular vesicles in vivo using a multimodal imaging reporter. ACS Nano. 2014;8:483–94. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn404945r.
Hu C, Zhao L, Zhang L, Bao Q, Li L. Mesenchymal stem cell-based cell-free strategies: safe and effective treatments for liver injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11:377. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-01895-1.
Hirata M, Ishigami M, Matsushita Y, Ito T, Hattori H, Hibi H, et al. Multifaceted therapeutic benefits of factors derived from dental pulp stem cells for mouse liver fibrosis. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5:1416–24. https://doi.org/10.5966/sctm.2015-0353.
Qu Y, Zhang Q, Cai X, Li F, Ma Z, Xu M, Lu L. Exosomes derived from miR-181-5p-modified adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent liver fibrosis via autophagy activation. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21:2491–502. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13170.
Li M, Jiang Y, Hou Q, Zhao Y, Zhong L, Fu X. Potential pre-activation strategies for improving therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells: current status and future prospects. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13:146. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-022-02822-2.
Zhang X, Hu M-G, Pan K, Li C-H, Liu R. 3D spheroid culture enhances the expression of antifibrotic factors in human adipose-derived MSCs and improves their therapeutic effects on hepatic fibrosis. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:4626073. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4626073.
Zito G, Miceli V, Carcione C, Busà R, Bulati M, Gallo A, et al. Human amnion-derived mesenchymal stromal/stem cells pre-conditioning inhibits inflammation and apoptosis of immune and parenchymal cells in an in vitro model of liver ischemia/reperfusion. Cells. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11040709.
Tang W, Lv X, Huang J, Wang B, Lin L, Shen Y, Yao Y. Neuroprotective effect of stroke pretreated MSCs against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. World Neurosurg. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2021.04.114.
Takeuchi S, Tsuchiya A, Iwasawa T, Nojiri S, Watanabe T, Ogawa M, et al. Small extracellular vesicles derived from interferon-γ pre-conditioned mesenchymal stromal cells effectively treat liver fibrosis. NPJ Regen Med. 2021;6:19. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41536-021-00132-4.
Acknowledgements
We sincerely appreciate all the participants in our work.
Funding
This work was supported by Grant(s) from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32160230), the Key Research Development Programs of the Provincial Science and Technology Research Projects of Gansu Province (18YF1FA109), and 1st Hospital of Lanzhou University Scientific Research Foundation (ldyyyn2019-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PL contributed to this paper with literature review and drafting the manuscript. YM contributed to this paper with literature review and editing. YX contributed to this paper with literature review and editing. JW contributed to this paper with literature review and editing. JY contributed to this paper with conception, suggestion, drafting and editing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, P., Mao, Y., Xie, Y. et al. Stem cells for treatment of liver fibrosis/cirrhosis: clinical progress and therapeutic potential. Stem Cell Res Ther 13, 356 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-022-03041-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-022-03041-5