Abstract
Background
In Aristolochia (Aristolochiaceae) flowers, the congenital fusion of the anthers and the commissural, stigmatic lobes forms a gynostemium. Although the molecular bases associated to the apical–basal gynoecium patterning have been described in eudicots, comparative expression studies of the style and stigma regulatory genes have never been performed in early divergent angiosperms possessing a gynostemium.
Results
In this study, we assess the expression of five genes typically involved in gynoecium development in Aristolochia fimbriata. We found that all five genes (AfimCRC, AfimSPT, AfimNGA, AfimHEC1 and AfimHEC3) are expressed in the ovary, the placenta, the ovules and the transmitting tract. In addition, only AfimHEC3, AfimNGA and AfimSPT are temporarily expressed during the initiation of the stigma, while none of the genes studied is maintained during the elaboration of the stigmatic surfaces in the gynostemium.
Conclusions
Expression patterns suggest that CRC, HEC, NGA and SPT homologs establish ovary and style identity in Aristolochia fimbriata. Only NGA,HEC3 and SPT genes may play a role in the early differentiation of the stigmatic lobes, but none of the genes studied seems to control late stigma differentiation in the gynostemium. The data gathered so far raises the possibility that such transient expression early on provides sufficient signal for late stigma differentiation or that unidentified late identity genes are controlling stigma development in the gynostemium. Our data does not rule out the possibility that stigmas could correspond to staminal filaments with convergent pollen-receptive surfaces.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The gynoecium is one of the most complex structures in angiosperms, ensuring proper development, protection and fertilization of the ovules at anthesis and undergoing extreme transformations in the fruit to secure proper seed maturation and dispersal. It is formed by one or more carpels with highly specialized tissues, which represent the fourth and innermost whorl of the flower [1]. The gynoecium is patterned in three major axes: apical–basal, medio-lateral, and adaxial–abaxial, which are determined by specific hormonal and genetic interactions [2]. When two or more carpels are present, they may occur separately (apocarpic) or variously fused together (syncarpic) [1, 3]. Additionally, a typical gynoecium is differentiated from the base to the apex into an ovary usually located at the bottom, carrying the ovules, where fertilization takes place; a style that conducts the male gametophyte(s); and a stigma, which provides a receptive epidermis for landing and germination of the pollen grains [4, 5]. The evolutionary and developmental origins and morphoanatomical innovations shaping the gynoecium are central questions in plant evolutionary biology [6].
The gene regulatory networks involved in gynoecium patterning have been well characterized in Arabidopsis thaliana [3, 7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. These networks integrate different transcription factor families, hormones, microRNAs, peptides and chromatin-modifying proteins that ultimately define carpel identity and tissue specialization of the gynoecium from fertilization to fruit maturation [6, 14]. Carpel identity is specified by C- and E-function genes, specifically by the tetramer formed between AGAMOUS (AG) and SEPALLATA (SEP) MADS-box genes [8, 15,16,17,18]. Once carpel identity is acquired, carpel-specific tissues are successively activated (reviewed in [1, 19, 20]). Initially, the SPATULA (SPT) and CRABS CLAW (CRC) transcription factors ensure the basal–apical patterning [9]. CRC controls carpel growth, apical closure and style development, while SPT is required for proper development of the transmitting tissue in the style [9]. Together with CRC, the bHLH transcription factors, SPT and HECATE (HEC) are essential for the transmitting tract formation, suppressing the radial growth of the developing gynoecium and promoting its longitudinal growth [11]. This control also reinforces the proximal–distal patterning in syncarpic gynoecia, and the proper differentiation of the style and the stigma by regulating auxin and cytokinin responses [1, 9, 11, 21]. The differentiation of the apical tissues in the gynoecium also requires the expression of NGATHA (NGA) genes, belonging to the RAV clade of the B3-domain transcription factor family. In Arabidopsis the four NGA copies act redundantly to direct apical gynoecium development [12, 13]. Similarly to NGA, the SHORT INTERNODES/STYLISH (SHI/STY) genes, encoding zinc-finger transcription factors, contribute to style and stigma development and proper carpel fusion [10, 22,23,24]. In Arabidopsis, while single mutants in SHI/STY genes show subtle abnormal formation of the style with no evident fertility loss, the double and multiple mutants show enhanced defects in the style and stigma, similar to those of multiple NGATHA mutant combinations. This indicates that these transcription factors work together in a dosage-dependent manner, promoting style and stigma formation during Arabidopsis gynoecium development [22, 23].
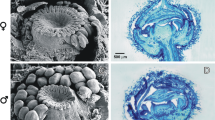
Comparative studies suggest that the above-mentioned transcriptional regulators involved in gynoecium patterning have retained similar functions across major flowering plant lineages. Most of the regulatory pathways involved in carpel identity early in the ABCE model (AG and SEP genes) and later in histogenesis during flower and fruit formation have been maintained over evolutionary time (CRC, NGA, SPT, or HEC) [6, 25,26,27,28,29,30,31]. So far the comparative studies of the genetic networks involved in the apical–basal patterning of the carpels have been largely concentrated in the syncarpic gynoecium of Arabidopsis and its relatives, but additional data have been obtained from studies in Papaveraceae and grasses, or the single-carpelled gynoecium of legumes [6, 9, 11,12,13, 29, 32,33,34,35]. Here we assess the expression patterns of these transcription factors in Aristolochia fimbriata, a species with inferior ovary and an exceptional fusion between stamens and the apices of the carpels forming a gynostemium. The gynostemium is an atypical structure that has evolved independently in a few lineages, including orchids (Orchidaceae: Asparagales), species of Pauridia (Hypoxidaceae: Asparagales), Corsia (Corsiaceae: Liliales) and in all species of Aristolochia (Aristolochiaceae: Piperales) [36, 37]. The gynostemium in Aristolochia is formed by the congenital fusion of stamens and stigmas forming a crown-like structure found inside the perianth, above the five or six carpellate, syncarpic, inferior ovary [37]. This feature contrasts with all other closely related perianth-bearing Piperales, as free stamens and stigmas are found in Asarum L., Lactoris Phil., Hydnora Thunb., and Saruma Oliver., and an incipient proximal fusion between the stamens and the stigmas is common in Thottea Rottb. (Fig. 1) [37,38,39]. Successful pollen recruitment and fertilization occurs in taxa with free stamens and stigmas, like Saruma (Fig. 1L), as well as in those with the gynostemium, like Aristolochia (Fig. 1M).
Androecium and gynoecium diversity in Aristolochiaceae. A, BSaruma henryi, top view of the flower (A) and detail of the 12 stamens in two series free from the six stigmatic lobes (B). C–EAsarum canadense;C top view of the flower with 12 stamens in two series free from the six stigmatic lobes. D Lateral view of stamens and stigmatic lobes. E Transverse section showing the twelve stamens surrounding the 6-carpellate gynoecium. F–HThottea siliquosa; F Top view of the Flower. G Detail of the 12 stamens surrounding the stigmatic lobes. H Transverse section of a preanthetic bud showing the partial fusion between the base of the stamens and stigmas. I–KAristolochia fimbriata;I young, preanthetic flower. J Detail of the gynostemium, lateral view (J). K Transverse section of the flower showing complete fusion between stamens and stigmatic lobes. L Fruit development series in Saruma henryi.M Fruit development series in Aristolochia fimbriata. dz, dehiscence zone; fw, fruit wall; o, ovule; ov, ovary; p, perianth; se, seed; st, stamens; asterisks (*) point to stigmas; black arrowheads point to anthers in transverse sections. Scale bars: 1 cm in A; 5 mm in B–D, F, G, I, J; 100 μm in E, H and K
In this work, we characterized the spatio-temporal expression patterns of the CRC, HEC, NGA, and SPT homologs in Aristolochia fimbriata to understand how these transcription factors are involved in gynostemium development, and how they contribute to the identity of the pollen-receptive gynostemium lobes. We discuss whether shifts from the canonical expression patterns of carpel patterning genes can help to explain the origin and patterning of the gynostemium in this early diverging angiosperm lineage.
Methods
Identification of the candidate genes and phylogenetic analyses
The coding sequences of the candidate genes for gynostemium and ovary development were isolated from the A. fimbriata transcriptome previously obtained by Pabón-Mora et al. [39], as well as from five newly generated transcriptomes from Aristolochia arborea, A. macrophylla, A. manshuriensis, Asarum canadense, A. europaeum and Saruma henryi (Additional file 1: Table S1). All transcriptomes were generated from mixed leaf, floral and fruit tissues, collected from living collections in the Arnold Arboretum at Harvard University (Additional file 1: Table S1). Tissues were flash frozen in liquid nitrogen. RNA extractions were performed using TRIzol (Invitrogen) following the manufacturers protocol. RNA quality was verified by spectrophotometry in a Nanodrop TM and by electrophoresis in a 1.5% agarose gel. RNA-seq experiments were done by implementing the Truseq mRNA library construction kit (Illumina) and sequenced on a HiSeq2000 instrument reading 100 bases, paired-end reads. Read cleaning was performed with PRINTSEQ-LITE with a quality threshold of Q30 and contig assembly was computed using Trinity package following default settings. The transcriptome assembly was performed for each taxa. Standard metrics for each transcriptome were calculated (Additional file 1: Table S1).
Searches for orthologous genes using the canonical Arabidopsis carpel patterning gene sequences and the Amborella trichopoda homologs as references were performed using BLASTN [40]. All the orthologous sequences for each gene lineage were compiled using BioEdit (http://www.mbio.ncsu.edu/bioedit/bioedit.html), and manually edited to keep the open reading frame (Additional file 1: Table S2). All nucleotide sequences were then aligned using the online version of MAFFT (http://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/server/), with a gap open penalty of 4.0, an offset value of 1,0, and all other default settings. The alignments were then refined manually using BioEdit considering the main domains for each gene lineage. Maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic analyses using the full nucleotide coding sequences were performed in RaxML-HPC2 BlackBox [41] on the CIPRES Science Gateway [42]. Bootstrapping was performed according to the default criteria in RAxML, and stopped after 200–600 replicates when the criteria were met. Trees were observed and edited using FigTree v1.4.0 [43]. The new sequences isolated from the transcriptomes of species of Asarum, Aristolochia and Saruma sampled here are available under Genbank numbers: MN709130-MN9154.
Plant material, RNA isolation and cDNA synthesis
Floral buds at different developmental stages of Aristolochia fimbriata were collected from plants cultivated indoors at the Universidad de Antioquia (UdeA). Floral stages 1–10 here used as reference (described in detail by Pabón-Mora et al. [39]) can be summarized as follows: S1 (perianth initiation), S2 (sepal fusion and growth led by the median sepal), S3 (anther primordia and ovary differentiation), S4 (thecae differentiation), S5 (perianth differentiation into utricle, tube and limb and emergence of the stigmatic surfaces adjacent to the anthers), S6 (closure of the limb furrow through interlocking epidermis), S7 (growth of the six stigmatic lobes above the anthers), S8 (resupination of the flower by torsion of the peduncle), S9 (differentiation of the two integuments in the ovules), and S10 (anthesis and expansion of the limb). Total RNA was extracted using TRIzol (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), and treated with DNAseI (Roche, Switzerland) to remove genomic DNA contamination. A total of 3 μg of RNA was used as template for cDNA synthesis with SuperScript III reverse transcriptase (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA).
Reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) and quantitative RT-PCR
Apices of flowering shoots and individual floral buds at stages S5, S7 and S9 were used for cDNA synthesis and PCR amplification of AfimCRC, AfimHEC1, AfimHEC3, AfimNGA, and AfimSPT. PCR assays were done using specific primers (Additional file 1: Table S3), with a thermal cycling regime consisting of one initial step at 94 °C for 10 min, 30 cycles at 94 °C for 40 s, 55 °C for 45 s and 72 °C for 1 min, and a final extension step at 72 °C for 10 min. All reactions were carried out using a MultiGeneTM OptiMax thermocycler (Labnet International, Edison, NJ, USA). The PCR products were run on a 1% agarose gel with 1X TAE, and stained with ethidium bromide, and gels were photographed using a Whatman Biometra® BioDocAnalyzer (Gottingen, Germany).
The quantitative RT-PCR assays were performed from flowers at S5, S7 and S9 using the same protocols for RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis described above. qRT-PCR was done successfully for all genes except the HEC homologs, as the similarity between their sequences complicates primer design for short amplicons. The qPCR master mix was prepared using Maxima SYBR Green/ROX qPCR Master Mix K0222 (Waltham, Massachusetts, USA). Two biological replicates and three technical replicates were performed. PCR was done using specific primers (Additional file 1: Table S3), with a thermal cycling regime consisting of one initial step at 95 °C for 3 min, then 40 cycles at 95 °C for 5 s, 54 °C for 5 s, and finally 72 °C for 20 s in a qTOWER3 G Real-Time-Thermocycler (Analytik Jena, Jena, Germany). All the target gene expression was analyzed relative to ACTIN7, ACTIN11, and UBIQUITIN using the 2−ΔΔCt method.
In situ hybridization
In situ hybridizations were performed as described by Ferrándiz et al. [44] with some modifications. CRC, HEC1, HEC3, NGA, and SPT DNA templates for RNA antisense and sense probe synthesis were obtained by PCR amplification of 200–400 bp outside of conserved domains defined for each gene lineage (Additional file 1: Table S3). Tissues for hybridization were fixed under vacuum in freshly prepared formaldehyde–acetic acid–ethanol (FAA solution 50% ethanol, 3.7% formaldehyde, and 5% glacial acetic acid) for 2 h. Then, samples were dehydrated in a standard ethanol series, embedded in paraffin and sectioned to 8 μm on a rotary microtome Leica RM2125 RTS. Hybridization was optimized with overnight incubations at 53 °C. Then, sections were washed twice at 53 °C before performing the antibody incubation and the colorimetric reaction. In situ hybridized sections were finally dehydrated and permanently mounted in Permount (Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA). Hybridizations with the sense probes were performed as negative controls. All sections were digitally photographed using the microscopes Nikon Eclipse polarizing e600 equipped with a Leica DM5000 B photographic device.
Results
Isolation and expression of carpel identity candidate genes by RT-PCR and qRT-PCR
Homologs of the CRC, SPT, NGA, and HEC genes in the studied species of Aristolochiaceae were identified from available mixed floral transcriptomes [39] or newly generated reference transcriptomes described above. Queries used for BLASTN searches included Arabidopsis and Amborella trichopoda sequences as well as putative homologs from other representative eudicot, monocot and magnoliid species. These searches were first done in the Aristolochia fimbriata transcriptome resulting in the identification of one CRC gene (named AfimCRC), one SPT gene (named AfimSPT [45]), one NGA gene (named AfimNGA), and two HEC genes (named AfimHEC1 and AfimHEC3). Similar BLAST searches were then performed in the newly generated reference transcriptomes for other species of Aristolochia, as well as in Asarum canadense, A. europaeum and Saruma henryi.
Most genes are found as single copy in all members of the Aristolochiaceae s.l. independently of whether they exhibit free stamens and stigmas or a gynostemium (Additional file 1: Figs. S1–S4). The single copy genes from Aristolochiaceae members predate the duplication events occurring in each gene lineage independently in eudicots and monocots (Additional file 1: Figs. S1–S4). The exception occurs with the HEC genes, which have duplicated prior to angiosperm diversification. The two copies found in A. fimbriata were named HEC1 and HEC3 as phylogenetic analyses assigned them to the HEC1/2 and the HEC3 clades, respectively [46]. Their homology was assessed in independent phylogenetic analyses for each gene, including sequences representative from each major angiosperm group (Additional file 1: Figs. S1–S4).
In order to characterize the expression patterns of the five genes putatively involved in the gynostemium and ovary development in A. fimbriata, we first used RT-PCR and qRT-PCR (Fig. 2). These results showed that all genes, except AfimHEC1, are expressed in the growing flowering shoot (apex), which contains all early flower developmental stages from S1 to S4; Fig. 2). These genes are also found throughout development in the dissected ovary and the gynostemium but only AfimNGA is found in leaves (Fig. 2; Additional file 1: Figs. S5). Expression in the dissected ovary and gynostemium across all three floral stages examined (S5, S7 and S9) showed that AfimCRC is found in the ovary and in the gynostemium at stage S5, and it is maintained in the ovary at S7, but its expression is no longer detected at stage S9 in the ovary or the gynostemium (Fig. 2; Additional file 1: Fig. S5). AfimSPT is only detected in the gynostemium at stages S5 and S7 (Fig. 2; Additional file 1: Fig. S5). AfimNGA is detected at low levels in both ovary and gynostemium at all developmental stages (Fig. 2; Additional file 1: Fig. S5). AfimHEC1 is detected only in the gynostemium at stages S5 and S7; very low to no expression was detected in the S9 gynostemium or in the ovary at these stages (Fig. 2A). Finally, AfimHEC3 has a broader expression range compared to its paralog in RT-PCR, with higher expression in both the gynostemium and the ovary at the developmental stages S5 and S7, but it is turned off in the gynostemium at S9 while it is still expressed in the ovary at the same developmental stage (Fig. 2).
Expression profiles of AfimCRC, AfimSPT, AfimNGA, AfimHEC1, and AfimHEC3 genes at different floral developmental stages, and leaves using standard RT-PCR. Actin (AfimACT) was used as a positive control in the RT-PCR. S5, stage 5 of the floral bud, when stigmatic lobes are fully developed. S7, stage 7 of the floral bud, when the stigmatic lobes grow above the anthers and the ovules initiate to develop. S9, stage 9 of the floral bud, when ovules develop the two integuments. L, leaf; A, shoot apex with early floral buds (developmental stages S1–S4); Ov, ovary; Gy, gynostemium; -C indicates the amplification reaction loaded without cDNA
Expression patterns of AfimCRC by in situ hybridization
All in situ hybridization results are described following the floral developmental stages described by Pabón-Mora et al. [39]. AfimCRC is expressed in the shoot apical meristems, the floral primordia (S1–S2), the accessory buds and the adaxial side and distal portion of the young leaves (Fig. 3A). At stages S3 and S4, during the initiation of the anther primordia and the formation of the ovary but prior to stigma initiation, AfimCRC is strongly expressed in the stamen primordia and in the ovary (Fig. 3B, C). Expression of AfimCRC in the ovary is restricted to the inner epidermis and the 3–5 sub-epidermal cell layers (Fig. 3D, E). At S5, when the stigmatic lobes begin to grow in the adaxial flank of the stamens, AfimCRC is detected in the growing stamens, until they reach their boundary with the stigmas, but no expression in the stigmatic lobes of the gynostemium was detected (Fig. 3F, G). The AfimCRC expression in the ovary at stage S5 shifts towards the periphery and the mesophyll located to the adaxial side of each vascular bundle (Fig. 3G, H); its expression in the inner epidermal and sub-epidermal layers of the ovary is no longer detected. At stage S7, AfimCRC remains expressed in the anthers and in their boundaries with the stigmas during the growth of the stigmatic lobes above the anthers and the ovule initiation (Fig. 3I–K). At this same stage, AfimCRC is specifically detected in the transmitting tract, the placenta, the ovary wall and the nucellus of the young ovules (Fig. 3I, K). During S9, AfimCRC expression drops dramatically and it is no longer detected in the gynostemium (Fig. 3L). At this stage the ovules develop the two integuments, and AfimCRC is only weakly detected in the nucellus (Fig. 3M). Between S1 and S9 AfimCRC is also expressed in the distalmost region of the growing perianth (Fig. 3A–C, F–I). Control sense probe for AfimCRC resulted in no signal (Additional file 1: Fig. S6).
In situ hybridization expression of AfimCRC. A Longitudinal section of the flowering shoot apex. B, C Flower bud at stages S3–S4 during stamen formation. D, E Detailed expression in forming stamens (D, longitudinal section) and ovary at S4 (E, transverse section). F–H Flower at S5 and details of the gynostemium in longitudinal section (G), and ovary in transverse section prior to ovule formation (H). I–K Longitudinal sections of flower at S7 and details of the gynostemium (J) and the ovary with the forming ovules in longitudinal section (K). L Longitudinal section of the gynostemium at S9. M Longitudinal section of the ovary with ovules during integument differentiation at S9. ab, accessory bud; l, leaf; mv, midvein of median carpel; o, ovule; ov, ovary; p, perianth. Arrow points to the shoot apical meristem; arrowheads point to stamens or stamen primordia; asterisks (*) point to stigmatic lobes. White arrows (I, J) show expression of AfimCRC in the putative style
Expression patterns of AfimSPT
AfimSPT has lower expression levels compared to AfimCRC. AfimSPT is not detected in the shoot apical meristem, the floral primordia at stages S1 and S2, the accessory buds or the young leaves (Fig. 4A). At stage S3 (stamen initiation and ovary differentiation), AfimSPT expression is weakly detected in the stamens and the ovary (Fig. 4B, C). During stage S4, the expression of AfimSPT can be detected in the stamens and the ovary, but it is also seen in the forming stigmatic lobes at the adaxial side of the anthers (Fig. 4D, E). Also at S4, AfimSPT is detected towards the periphery of the six septal regions of the ovary (Fig. 4F). At stage S5 (when stigmatic tips are fully developed) AfimSPT is barely detected in the anthers, and remains only weakly expressed in the ovary, but is no longer expressed in the stigmatic lobes (Fig. 4G–I). During stages S6 and S7, expression is no longer detected in the gynostemium or the ovary (Fig. 4J, K). At S9, the expression of AfimSPT is detected in the stamens, specifically in the anther wall (Fig. 4L, M). Unlike AfimCRC, AfimSPT is not expressed in the perianth during flower development (Fig. 4A–D, G). Control sense probe for AfimSPT resulted in no signal (Additional file 1: Fig. S6).
In situ hybridization expression of AfimSPT. A Flowering shoot apex in longitudinal section. B–D Successive stages S3–S4 showing initiation of the ovary and stamens. E, F Longitudinal section of the gynostemium (E) and transverse section of the ovary (F) at S4. G–I Flower at S5 with details of the gynostemium with fused stigmatic lobes and anthers (H) and ovary in transverse section prior to ovule formation (I). J, K Details of the gynostemium at S7 with the growing stigmas above the anthers (J) and ovule differentiation (K). L, M Transverse section of the gynostemium at S9 showing the detail of the fused anthers and stigmas, and the expression at the endothecium, the midvein and the stigmatic epidermis. ab, accessory bud; l, leaf; e, endothecium; ep, stigmatic epidermis; mv, midvein of median carpel; o, ovule; ov, ovary; p, perianth. Arrow points to the shoot apical meristem; arrowheads point to stamens or stamen primordia; asterisks (*) point to stigmatic lobes. Floral stages S1–S9 as in Figs. 2 and 3. Scale bars: 100 μm in A, C, F, J–M; 50 μm in B, E; 150 μm in D; 200 μm in G–I)
Expression patterns of AfimNGA
The expression of AfimNGA is localized in the shoot apical meristem, the S1 and S2 floral primordia, the accessory buds, and the young leaves (Fig. 5A). Its expression at stage S3 is detected in the stamens and the ovary (Fig. 5B), and it is maintained during stages S4 and S5 in the stamens, the developing stigmatic lobes, and the ovary (Fig. 5C–E). In the ovary, expression of AfimNGA is restricted to the inner epidermis and the sub-epidermal layers (Fig. 5E). Expression of AfimNGA during stage S6 is maintained in the stamens and the ovary while the expression in the stigmas becomes restricted to their elongating tips and the adaxial margin of the stigmatic lobes connecting to the ovary (Fig. 5F–H). At stage S7, when the stigmas grow above the fully differentiated thecae, AfimNGA is expressed in the developing ovules, the septal regions of the ovary, the adaxial margins of the stigmatic lobes, the sporogenous tissue in the anthers, and the pollen grains (Fig. 5I–K). Later, stages S8 and S9, when ovules develop the two integuments, the signal of AfimNGA is found in the nucellus, the integuments, and the epidermal cells in the transmitting tract (Fig. 5J–K). AfimNGA is also expressed in the growing perianth during flower development (Fig. 5A–C, F, I). Control sense probe for AfimNGA resulted in no signal (Additional file 1: Fig. S6).
In situ hybridization expression of AfimNGA. A Flowering shoot apex in longitudinal section. B Flower bud at S3 during stamen formation. C–E Flower at S4 with details of the gynostemium (D) and ovary in transverse section (E). F–H Longitudinal sections at S5 with detailed expression in the gynostemium (G) and the ovary (H). I–K Longitudinal sections at S7 with detailed expression in the gynostemium (J) and the ovary with differentiating ovules (K); note in I and J the anthers overtopped by the stigmas. ab, accessory bud; l, leaf; mv, midvein of median carpel; o, ovule; ov, ovary; p, perianth. Arrow points to the shoot apical meristem; arrowheads point to stamens or stamen primordia; asterisks (*) point to stigmatic lobes. Floral stages S1–S9 as in Figs. 2 and 3. Scale bars: 100 μm (A–I), 200 μm (J), 250 μm (K). White arrows (G–J) show expression of AfimNGA in the putative style
Expression patterns of AfimHEC1 and AfimHEC3
AfimHEC1 is not detected at the shoot apical meristem, the floral primordia at S1 and S2, the accessory buds or the young leaves (Fig. 6A). During S3, AfimHEC1 is first detected in the ovary and the distal portions of the perianth and it is not detected in the incipient anther primordia (Fig. 6B). During S5, when stigmatic lobes are differentiated, the expression of AfimHEC1 is maintained in the ovary and in the stamens but not in the stigmatic lobes (Fig. 6C–E). During S6 and S7, AfimHEC1 expression is maintained in the stamens, the ovary, and the young ovules (Fig. 6F–H). At stages S7 and S9, the expression of AfimHEC1 is mostly restricted to the nucellus and the integuments of the developing ovules as well as in the pollen grains (Fig. 6I–K). Expression at S9 in preanthesis, can be seen only in the epidermis of the stigmatic lobes (Fig. 6L). During the ovule-to-seed transition AfimHEC1 expression is weakly detected in the nucellus remnants, but lacking in the integuments or the seed coat (Fig. 6M).
In situ hybridization expression of AfimHEC1. A Longitudinal section of the flowering shoot apex. B Longitudinal section of the floral bud at S3. C-E Longitudinal sections at S5 showing expression in stamens (C, D) and ovary (E). F–H Longitudinal section of the floral bud at S7, with expression in the gynostemium (F, G) and ovary during ovule initiation (H). I Transverse section of the gynostemium at S9. J Longitudinal section of the ovary showing the developing ovules at S9. K Detail of a tetrasporangiate anther fused to a stigmatic lobe at S9. L Expression at S9 in preanthesis of the stigmatic epidermis. M Transverse section of the ovary during ovule-to-seed transition. ab, accessory bud; l, leaf; mv, midvein of median carpel; o, ovule; ov, ovary; p, perianth. Arrow points to the shoot apical meristem; arrowheads point to stamens or stamen primordia; asterisks (*) point to stigmatic lobes. Floral stages S1–S9 as in Figs. 2 and 3. Scale bars: 100 μm in A, C–E, I; 50 μm in B, K, L; 200 μm in F–H; 150 μm in J, M. White arrowheads (C) indicate expression in the junction between stamens and stigmatic lobes
In general, the expression patterns of AfimHEC3 are stronger and broader than that of AfimHEC1 in all the stages analyzed (Figs. 6 and 7). Expression of AfimHEC3 is first detected in the shoot apical meristem, the young leaves, the young S1 and S2 flowers, and the accessory buds (Fig. 7A, B). At stage S3, AfimHEC3 is strongly expressed in the developing stamens and the ovary (Fig. 7C). At stage S4 (stigma initiation), the expression is detected in the stamens, the developing stigmas, and the ovary (Fig. 7D–F). Expression in the ovary is mostly detected in the inner epidermis (Fig. 7D, F). At stage S5, when stigmas are fully differentiated and reach the same size as the stamens, AfimHEC3 is still detected in the stamens and the ovary, but it is no longer evident in the stigmatic lobes (Fig. 7G–I). At stage S7, when the stigmatic lobes overtop the stamens, expression of AfimHEC3 is retained only at the sporogenous anther tissue, the ovules and the transmitting tract (Fig. 7J–L). Control sense probes for AfimHEC paralogs resulted in no signal (Additional file 1: Fig. S6).
In situ hybridization expression of AfimHEC3. A Longitudinal section of the flowering shoot apex. B Flower bud at S2, longitudinal section. C Floral bud at S3 during stamen initiation, longitudinal section. D–F Flower at S4 with details of the expression in stamens and stigmas (D, E) in longitudinal section, and ovary in transverse section (F). G–I Longitudinal section of a S5 floral bud with detailed gynostemium (H) and ovary (I). J–L Longitudinal sections of a S7 floral bud with detailed gynostemium (K) and ovary during ovule initiation (L). ab, accessory bud; l, leaf; mv, midvein of median carpel; o, ovule; ov, ovary; p, perianth. Arrow points to the shoot apical meristem; arrowheads point to stamens or stamen primordia; asterisks (*) point to stigmatic lobes. Floral stages S1–S9 as in Figs. 2 and 3. Scale bars: 100 μm in A, C–F, J; 50 μm in B; 250 μm in G; 150 μm in H, I; 200 μm in K, L. White arrowheads (K) indicate expression in the putative style
Discussion
The gynoecium often differentiates into the proximal ovary, and the distal style and stigma. Distal portions are highly specialized being primarily responsible for pre-zygotic selection of pollen grains [1, 47]. Aristolochia flowers provide an ideal system to study whether the genetic networks shaping the carpel patterning are retained in highly modified gynoecia, with stigmas fused to the sessile anthers forming a gynostemium. Although the gynostemium lobes are functionally stigmatic, their odd position opposite to the stamens and alternate to the carpels (as commissural structures) has led to an alternative interpretation as massive filaments rather than as true gynoecium-derived tissue, or a combination of both, with stamen identity retained externally and stigma identity retained internally (see review in [37]). Despite the occurrence of congenital fusion between stigmas and stamens [37], the flower exhibits an intricate cross-pollination system where proterogyny avoids selfing. Stigmas mature first and become wet, expanded and receptive to pollen grains, which need to germinate and pass through the stigmatic and stylar regions before the perianth and the gynostemium detaches from the inferior ovary [39, 48].
Having as a reference point previously identified key transcription factors in Arabidopsis involved in shaping and patterning of the gynoecium, we have studied here the expression patterns of CRC, SPT, NGA, and HEC homologs in Aristolochia fimbriata. We aim to understand what genes are at the core of gynoecium patterning despite such extreme modifications in a phylogenetically distant early diverging angiosperm. In addition, we also look to identify whether the expression of these genes can be linked to the identity and elaboration of the stigmatic lobes in the highly elaborated gynostemium. All the predicted roles based on expression patterns will have to be confirmed in the future with functional analyses when available for this non-model species.
Expression of AfimCRC is likely correlated with the receptacular inferior ovary in Aristolochia fimbriata
The CRC gene belongs to the YABBY family of transcription factors present in the last common ancestor of all angiosperms [49, 50]. Expression patterns and functional analyses in most species studied suggest conserved roles of CRC homologs in the differentiation of the stigma and the style, the fusion of the carpel margins, proper gynoecium medial–lateral patterning, and only in some cases, the development of nectaries and the termination of the floral meristem [33,34,35, 49, 51,52,53,54,55,56]. In eudicots like Arabidopsis, Petunia hybrida, Nicotiana benthamiana, and Eschscholzia californica, CRC homologs are mostly expressed in the carpel primordia, the abaxial region of the gynoecium, and the developing nectaries [9, 51, 53, 55, 56]. However, CRC homologs in grasses and in pea lack a clear abaxial expression domain and appear rather homogenously expressed in the carpels [33, 35]. The crc mutants in core eudicots show abnormally wider gynoecia with unfused carpels, and loss of nectaries [5, 9, 51, 53, 55, 56]. In species of the monocot families Asparagaceae and Poaceae, as well as in Pisum sativum (Leguminosae) and Eschscholzia californica (Papaveraceae) CRC-like genes control carpel morphology and vasculature [33,34,35, 55, 57]. CRC genes are also responsible for floral meristem termination in eudicots and monocots [33, 55, 56]. In the case of Arabidopsis, the role of CRC in meristem determinacy is masked by redundant pathways with AGAMOUS and only crc-1 ag-1/+ and crc-1 ap2-2 pi-1 ag-1 mutants show abnormal carpel proliferation in the center of the flower [5, 9, 14, 33, 55, 56].
Less is known about the role of CRC-like genes in early divergent angiosperms. However, expression studies of CRC homologs in Amborella trichopoda (Amborellaceae) and Cabomba caroliniana (Cabombaceae) show conserved expression patterns in abaxial tissues of the developing carpels [49, 52]. However, in these species, CRC homologs are also found in the floral apex, the perianth, and the stamens, indicating broader ancestral roles for CRC homologs that could have been lost before the divergence of monocots and eudicots [49]. Our results support this idea, as expression patterns of AfimCRC in Aristolochia resemble those documented in A. trichopoda and C. caroliniana, in the developing flowering shoot apex, the perianth at different developmental stages, the anthers, the ovary and its vascular tissue, the ovules, and the young leaves (Fig. 3). However, a noticeable difference when compared to the expression recorded for CRC homologs in all other angiosperms is the apparent shift of AfimCRC expression to the adaxial surfaces of the ovary in A. fimbriata. Unlike all other angiosperms with recorded CRC expression, A. fimbriata is the only one with inferior ovary, which is congenitally surrounded by the floral receptacle, resulting in a composite axial–carpellary tissue. Thus, our results point to AfimCRC expression as a marker for carpel-derived tissue on the inside of this complex structure. However, these hypotheses need to be corroborated with studies in other species with inferior ovary. Our findings in A. fimbriata, together with previous reports, suggest that the plesiomorphic role of CRC homologs include vascular differentiation in the carpels, a function maintained in other eudicots and monocots [33, 35, 55]. Also, AfimCRC expression in the inside of the ovary suggests an ancestral role in the specialization of the inner layers for placenta development and ovule initiation, shared, at least, with basal eudicots [55]. Finally, it is also possible that AfimCRC can contribute to the boundary establishment and maintenance between stamens and stigmatic lobes and the development of the transmitting tissue in A. fimbriata.
Conversely, the results presented for AfimCRC do not support its putative contribution for stigma and style development, suggesting two possible scenarios: (1) there are other transcriptional regulators controlling the identity of the apical carpel tissues, or (2) the expression detected in the ovary and the stamens could be associated with a putative non-cell-autonomous activity of AfimCRC¸ regulating in this case the activation of additional transcription factors that promote stigma identity, as it has been proposed in other eudicot species [35, 55].
Reduced levels of AfimSPT in the stigmas are only found transiently early during the gynostemium development of Aristolochia fimbriata
The SPT gene encodes a bHLH transcription factor present in both gymnosperms and angiosperms [45, 58, 59]. SPT is one of the two copies that, along with its paralog ALCATRAZ (ALC), resulted from a core eudicot duplication event. Both genes are involved in gynoecium and fruit patterning in angiosperms. In Arabidopsis thaliana, SPT promotes the development of specialized tissues of the carpel margins, and regulates the differentiation of the style, the stigma, and the transmitting tissue [5, 9, 60]. Additionally, SPT specifies the differentiation of the valve margins and the dehiscence zone during carpel development and, together with INDEHISCENT (IND), it also regulates the auxin biosynthesis and distribution in the medial tissues during development [14, 61, 62]. Expression of SPT homologs in species of Solanaceae is broad in sepals, petals, stamens and carpels [63]. Functional analyses suggest that, together with ALC, SPT genes promote cell division and organ size as well as fruit maturation and ripening, likely by repressing lignification [63]. Similar broad expression patterns in the perianth, the ovary and the lignified layer of the fruits (endocarp) has been found for SPT/ALC homologs in peach (Prunus persica, Rosaceae), and it has been suggested that they function in endocarp differentiation [64]. Expression studies of the paleo SPT/ALC in basal eudicots such as Bocconia frutescens (Papaveraceae) have shown that BofrSPT homologs have broad expression patterns in sepals, stamens, as well as in the medial fusion zone of the carpels, the growing ovules, and the dehiscence zone during fruit development [45]. Our results in A. fimbriata are different compared with those described above in eudicot species. AfimSPT expression is lacking at style and stigma initiation stages, and its expression is mostly restricted to the ovary at specific developmental stages (Fig. 4C, D, F, G). AfimSPT is only weakly detected in the stigma primordia in early developmental stages, so it cannot be disregarded as an initial signal for other regulators to control the differentiation of the apical specialized tissues (Fig. 4D–E). However, AfimSPT expression is not maintained during style and stigmatic lobe differentiation. Thus, considering that SPT homologs promote fusion between stigmatic lobes, the low levels of AfimSPT can be associated with the separation of the stigmatic tips in the gynostemium. In addition, the expression reported here in the ovary wall of Aristolochia could be associated with the longitudinal growth of the gynoecium during flower development and the formation of the dehiscence zone later on during fruit maturation (Fig. 1M), as it has been reported in other eudicot species like A. thaliana and B. frutescens [5, 9, 45]. Overall, these findings suggest that the expression patterns of AfimSPT differ from that previously reported for eudicot species, except for the expression found in the ovary walls, indicating only conserved roles for the putative dehiscence zone formation during fruit development.
The expression pattern of AfimNGA is linked to style/stigma development and differentiation in Aristolochia fimbriata
The NGA genes are members of the B3 transcription factor family in angiosperms; the four Arabidopsis paralogs result from Brassicaceae-specific duplication events [12, 13]. Functional data from Arabidopsis indicate that all four copies act redundantly to control style and stigma fusion and development [12, 13, 63, 65]. The same functions have been identified for the NGA homologs in Eschscholzia californica and Nicotiana benthamiana. Down-regulation of EcNGA and NbNGA genes results in severe defects including opened styles and reduced stigmatic tissues [6]. Based on the available data, it has been proposed that NGA genes have conserved roles in style and stigma development in eudicots [6]. NGA genes have not been evaluated in monocots, early diverging angiosperms or gymnosperms, thus our expression studies are the first to assess the putative contribution of NGA genes to gynoecium development outside eudicots. Our data show that AfimNGA is expressed in the stamen primordia, the growing stigmatic lobes at early developmental stages, the inner epidermis of the ovary, the medial zone of the short style, and the ovules at late developmental stages (Fig. 5). These patterns suggest that AfimNGA functions in the early stigma identity, similar to what has been reported in eudicot NGA homologs, but later on, it becomes restricted to the lining of the stigma and the putative style in the modified gynostemium of Aristolochia. It is possible that a limited expression of AfimNGA in concert with a low expression of AfimSPT result in the separation of the stigmatic lobes during gynostemium development. Importantly, AfimNGA is present in the short style, in the ovary, and in the ovules, suggesting that its role in the specification of the transmitting tract tissue remains intact even in the absence of a fully fused stigma, possibly allowing the growth of the pollen tubes along the style and into the ovary. Overall, these results suggest that AfimNGA is likely to be one of the essential regulators of the style and stigma development in Aristolochia, a function shared by early divergent angiosperms and eudicots studied so far. It remains to be tested whether AfimNGA is contributing in the auxin signaling in the gynostemium by the interaction with additional regulatory factors, as it occurs in Arabidopsis [10, 13, 23, 66,67,68].
AfimHEC3 regulates the identity of the style and the stigma while AfimHEC1 contributes to ovary development in Aristolochia fimbriata
The bHLH HEC1-3 transcription factors control multiple developmental processes like shoot meristem activity and auxin signaling in Arabidopsis [11, 21, 69]. Also, HEC genes appear to coordinate in a partially redundant manner the transmitting tract development [11]. The hec1,2,3 triple mutants in Arabidopsis show severe defects in stigma and transmitting tissues, and milder defects in style and septum fusion resulting in complete fertility loss [11]. In other eudicots like in Solanaceae species, the expression data available suggest that only HEC3 genes are involved in gynoecium patterning, while HEC1/2 transcription factors are more likely associated with fruit maturation [59]. In our study, AfimHEC1 is detected in the ovary and in the stamens (Fig. 6) while AfimHEC3 is specifically detected in the stigmas, the stamens, the style, the mature ovules, and weakly detected in the ovary (Fig. 7). These differential expression patterns detected for the two AfimHEC genes in Aristolochia fimbriata differ from the redundant expression patterns found in the HEC homologs of Arabidopsis in the septum, the transmitting tract, and the stigma [11]. AfimHEC3 is detected in the stigmatic tips and the medial zone of the style (Fig. 7K), suggesting that together with AfimNGA, can control the differentiation of the apical specialized tissues of the carpels, and the formation of a transmitting tract for pollen tube growth to the ovules during the fertilization. Moreover, AfimHEC1 expression suggests functions associated with ovary and fruit development, more similar to what has been described for species of Solanaceae, indicating alternative roles of the AfimHEC genes during flower and fruit development.
Putative genetic mechanisms involved in the gynostemium development of Aristolochia fimbriata
Gynoecium development requires multiple biological regulators that control ovule formation and protection as well as the transformation of specialized tissues especially in response to fertilization and during fruit patterning. Multiple regulatory networks have been proposed to describe the different developmental processes that occur from floral meristem initiation until fruit maturation and seed release (reviewed in Zuñiga-Mayo et al. [14]). However, little information on the function of these genes is available in early diverging flowering plants and especially in those with unconventional stamen–stigma patterning forming a gynostemium. The gynostemium, as we previously described, is rare in flowering plants, and the fusion between the stigmas and stamens presents an excellent opportunity to study signaling pathways that control congenital organ fusion. In this work, the expression patterns of the candidate transcription factors evaluated for gynostemium development suggest a direct contribution to stamen, ovary and ovule differentiation for all AfimCRC, AfimSPT, AfimNGA and AfimHEC genes. AfimCRC also specifies carpel domains in the inferior ovary surrounded by receptacular tissue. However, only AfimSPT, AfimNGA and AfimHEC3 genes are actively participating in early stigma identity early on, although rather transiently, and in style differentiation later in development, especially in those domains where transmitting tissue will develop. In addition, and based on their overlapping expression, it is possible to speculate that these same three genes, together with AfimCRC, act maintaining the gynoecia boundaries inside the gynostemium throughout development, given that they are retained in the abaxial flanks of the stigmas even though their expression is not maintained in the stigmatic tips. Finally, the promotion of stigmatic features like the development of papillae during late stages of development and the secretion and proliferation of exudates during the female phase of the flower does not appear to depend on the canonical stigmatic genes described so far, and other genes with late activation may control such features. It is also possible that stigmatic tips in the gynostemium are in fact the result of convergent features derived from the stamens. However, the B and C class MADS-box genes that confer stamen identity have not been found to be expressed in the stigmatic tips either [39, 70], suggesting that also in this scenario, late unidentified genes may be major players in stigmatic differentiation.
Conclusion
From our study we can conclude that the gynostemium lobes in Aristolochia flowers are functionally stigmatic, however, their odd position opposite to the stamens and alternate to the carpels (as commissural structures), as well as the lack of continuous expression of canonical style–stigma genes supports two alternative scenarios: one, where the stigmatic tips are still gynoecium-derived but unidentified genes with late expression control stigma differentiation and elaboration; the other, where the gynostemium as formed by the proliferation of massive filaments externally and true gynoecium identity restricted to the transmitting tissue tract. The three genes that are most likely to turn on style–stigma identity early on, inside of the Aristolochia gynostemium are AfimSPT, AfimNGA and AfimHEC3; however, their expression is transient in early stages and may not control late identity of pollen-receptive surfaces.
Availability of supporting data
All supporting data are available in the Additional files.
Abbreviations
- AG:
-
AGAMOUS
- ALC:
-
ALCATRAZ
- bHLH:
-
Basic/helix–loop–helix
- CRC:
-
CRABS CLAW
- HEC:
-
HECATE
- IND:
-
INDEHISCENT
- ML:
-
Maximum likelihood
- NGA:
-
NGATHA
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- SEP:
-
SEPALLATA
- SPT:
-
SPATULA
- STY:
-
STYLISH
References
Ferrándiz C, Fourquin C, Nathanael Prunet N, Charlie P, Scutt CP, Eva-Sundberg E, Christophe Trehin C, Vialette-Guiraud A. Carpel development. In: Jean-Claude K, Michel D, editors. Advances in botanical research, vol. 55. Burlington: Academic Press; 2010. p. 1–73 (© Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. Academic Press). ISBN 978-0-12-380868-4.
Moubayidin L, Ostergaard L. Gynoecium formation: an intimate and complicated relationship. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2017;45:15–21.
Bowman JL, Smyth DR, Meyerowitz EM. Genes directing flower development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 1989;1:37–52.
Ferrándiz C, Pelaz S, Yanofsky MF. Control of carpel and fruit development in Arabidopsis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1999;68:321–54.
Alvarez J, Smyth DR. CRABS CLAW and SPATULA genes regulate growth and pattern formation during gynoecium development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Int J Plant Sci. 2002;163(1):17–41.
Fourquin C, Ferrándiz C. The essential role of NGATHA genes in style and stigma specification is widely conserved across eudicots. New Phyt. 2014;202:1001–13.
Yanofsky MF, Ma H, Bowman JL, Drews GN, Feldmann KA, Meyerowitz EM. The protein encoded by the Arabidopsis homeotic gene agamous resembles transcription factors. Nature. 1990;346:35–9.
Coen ES, Meyerowitz EM. The war of the whorls: genetic interactions controlling flower development. Nature. 1991;353:31–7.
Alvarez J, Smyth DR. CRABS CLAW and SPATULA, two Arabidopsis genes that control carpel development in parallel with AGAMOUS. Development. 1999;1999(126):2377–86.
Sohlberg JJ, Myren_as M, Kuusk S, Lagercrantz U, Kowalczyk M, Sandberg G, Sundberg E. STY1 regulates auxin homeostasis and affects apical-basal patterning of the Arabidopsis gynoecium. Plant J. 2006;47:112–23.
Gremski K, Ditta G, Yanofsky MF. The HECATE genes regulate female reproductive tract development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Development. 2007;134(20):3593–601.
Álvarez JP, Goldshmidt A, Efroni I, Bowman JL, Eshed Y. The NGATHA distal organ development genes are essential for style specification in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2009;21:1373–93.
Trigueros M, Navarrete-Gomez M, Sato S, Christensen SK, Pelaz S, Weigel D, Yanofsky MF, Ferrandiz C. The NGATHA genes direct style development in the Arabidopsis gynoecium. Plant Cell. 2009;21:1394–409.
Zuñiga-Mayo VM, Gómez-Felipe A, Herrera-Ubaldo H, de Folter S. Gynoecium development: networks in Arabidopsis and beyond. J Exp Bot. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erz026.
Pelaz S, Ditta GS, Baumann E, Wisman E, Yanofsky M. B and C floral organ identity functions require SEPALLATA MADS-box genes. Nature. 2000;405:200–3.
Honma T, Goto K. Complexes of MADS-box proteins are sufficient to convert leaves into floral organs. Nature. 2001;409:525–9.
Favaro R, Pinyopich A, Battaglia R, Kooiker M, Borghi L, Ditta G, Yanofski MF, Kater MM, Colombo L. MADS-box protein complexes control carpel and ovule development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2003;15:2603–11.
Pinyopich A, Ditta GS, Savidge B, Liljegren SJ, Baumann E, Wisman E, Yanofsky MF. Assessing the redundancy of MADS-box genes during carpel and ovule development. Nature. 2003;424:85–8.
Balanza V, Navarrete M, Trigueros M, Ferrandiz C. Patterning the female side of Arabidopsis: the importance of hormones. J Exp Bot. 2006;57:3457–69.
Reyes-Olade JI, Zuniga-Mayo VM, Chavez Montes RA, Marsch-Martinez N, de Folter S. Inside the gynoecium: at the carpel margin. Trends Pl Sci. 2013;18:644–55.
Schuster C, Gaillochet C, Lohmann JU. Arabidopsis HECATE genes function in phytohormone control during gynoecium development. Development. 2015;142(19):3340–50.
Kuusk S, Sohlberg JJ, Long JA, Fridborg I, Sundberg E. STY1 and STY2 promote the formation of apical tissues during Arabidopsis gynoecium development. Development. 2002;129:4707–17.
Kuusk S, Sohlberg JJ, Magnus Eklund D, Sundberg E. Functionally redundant SHI family genes regulate Arabidopsis gynoecium development in a dose-dependent manner. Plant J. 2006;47:99–111.
Gomariz-Fernández A, Sánchez-Gerschon V, Fourquin C, Ferrándiz C. The role of SHI/STY/SRS genes in organ growth and carpel development is conserved in the distant eudicot species Arabidopsis thaliana and Nicotiana benthamiana. Front. Plant Sci. 2017;8:1–17.
Ambrose BA, Lerner DR, Ciceri P, Padilla CM, Yanofsky MF, Schmidt RJ. Molecular and genetic analyses of the Silky1 gene reveal conservation in floral organ specification between eudicots and monocots. Mol Cell. 2000;5:569–79.
Favaro R, Immink RGH, Ferioli V, Bernasconi B, Byzova M, Angenent GC, Kater MM, Colombo L. Ovule-specific MADS-box proteins have conserved protein-protein interactions in monocot and dicot plants. Mol. Gen. Genomics. 2002;268:152–9.
Kater MM, Dreni L, Colombo L. Functional conservation on MADS-box factors controlling floral organ identity in rice and Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot. 2006;57:3433–44.
Cui R, Han J, Zhao S, Su K, Wu F, Du X, Xu Q, Chong K, Theissen G, Meng Z. Functional conservation and diversification of class E floral homeotic genes in rice (Oryza sativa). Plant J. 2010;61:767–81.
Dreni L, Pilatone A, Yun D, Erreni S, Pajoro A, Caporali E, Zhang D, Kater MM. Functional analysis of all AGAMOUS subfamily members in rice reveals their roles in reproductive organ identity determination and meristem determinacy. Plant Cell. 2011;23:2850–63.
Dreni L, Kater MM. MADS reloaded: evolution of the AGAMOUS subfamily genes. New Phyt. 2014;201:717–32.
Melzer R, Härter A, Rümpler F, Kim S, Soltis PS, Soltis DE, Theißen G. DEF- and GLO-like proteins may have lost most of their interaction partners during angiosperms evolution. Ann Bot. 2014;114:1431–43.
Nagasawa N, Miyoshi M, Sano Y, Satoh H, Hirano H, Sakai H, Nagato Y. SUPERWOMAN1 and DROOPING LEAF genes control floral organ identity in rice. Development. 2003;130:705–18.
Yamaguchi T, Nagasawa N, Kawasaki S, Matsuoka M, Nagato Y, Hirano HY. The YABBY gene DROOPING LEAF regulates carpel specification and midrib development in Oryza sativa. Plant Cell. 2004;16:500–9.
Nakayama H, Yamaguchi T, Tsukaya H. Expression patterns of AaDL, a CRABS CLAW ortholog in Asparagus asparagoides (Asparagaceae), demonstrate a stepwise evolution of CRC/DL subfamily of YABBY genes. Am J Bot. 2010;97:591–600.
Fourquin C, Primo A, Martínez-Fernández I, Huet-Trujillo E, Ferrándiz C. The CRC orthologue from Pisum sativum shows conserved functions in carpel morphogenesis and vascular development. Ann Bot. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcu129.
Rudall PJ, Bateman RM. Roles of synorganisation, zygomorphy and heterotopy in floral evolution: the gynostemium and labellum of orchids and other lilioid monocots. Biol Rev. 2002;77:403–41.
González F, Stevenson DW. Gynostemium development in Aristolochia (Aristolochiaceae). Bot Jahrb Syst. 2000;122:249–91.
Wanke S, González F, Neinhuis C. Systematics of pipevines: combining morphological and fast-evolving molecular characters to investigate the relationships within subfamily Aristolochioideae (Aristolochiaceae). Int. J. Pl. Sci. 2006;167(6):1215–27. https://doi.org/10.1086/508024.
Pabón-Mora N, Suárez-Baron H, Ambrose BA, González F. Flower development and perianth identity candidate genes in the basal angiosperm Aristolochia fimbriata (Piperales: Aristolochiaceae). Front Plant Sci. 2015;1095:1–20.
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80360-2.
Stamatakis A, Hoover P, Rougemont J. A fast bootstrap- ping algorithm for the RAxML web-servers. Syst Biol. 2008;57:758–71. https://doi.org/10.1080/10635150802429642.
Miller MA, Holder HT, Vos R, Midford PE, Liebowitz T, Chan L, et al. The CIPRES Portals. 2009. http://www.phylo.org.
Rambaut A. FigTree: Tree Figure Drawing Tool, Version 1.4.2. Institute of Evolutionary Biology, University of Edinburgh. 2014. http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/. Accessed 1 Apr 2015.
Ferrándiz C, Gu Q, Martienssen R, Yanofsky MF. Redundant regulation of meristem identity and plant architecture by FRUITFULL, APETALA1 and CAULIFLOWER. Development. 2000;127:725–34.
Zumajo-Cardona C, Ambrose BA, Pabón-Mora N. Evolution of the SPATULA/ALCATRAZ gene lineage and expression analyses in the basal eudicot Bocconia frutescens L. (Papaveraceae). EvoDevo. 2017;8:5.
Pfannebecker KC, Lange M, Rupp O, Becker A. Seed plant-specific gene lineages involved in carpel development. Mol Biol Evol. 2017;34:925–42.
Endress PK, Igersheim A. Gynoecium structure and evolution in basal angiosperms. Int. J. Pl. Sci. 2000;161:S211–23.
Oelschlagel B, Gorb S, Wanke S, Neinhuis C. Structure and biomechanics of trapping flower trichomes and their role in the pollination biology of Aristolochia plants (Aristolochiaceae). New Phytol. 2009;184:988–1002.
Yamada T, Yokota S, Hirayama Y, Imaichi R, Kato M, Gasser CS. Ancestral expression patterns and evolutionary diversification of YABBY genes in angiosperms. Plant J. 2011;67:26–36.
Bartholmes C, Hidalgo O, Gleissberg S. Evolution of the YABBY gene family with emphasis on the basal eudicot Eschscholzia californica (Papaveraceae). Plant Biol. 2012;14:11–23.
Bowman JL, Smyth DR. CRABS CLAW, a gene that regulates carpel and nectary development in Arabidopsis, encodes a novel protein with zinc finger and helix-loop-helix domains. Development. 1999;126:2387–96.
Fourquin C, Vinauger-Douard M, Fogliani B, Dumas C, Scutt CP. Evidence that CRABS CLAW and TOUSLED have conserved their roles in carpel development since the ancestor of the extant angiosperms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:4649–54.
Lee J-Y, Baum SF, Oh S-H, Jiang C-Z, Chen J-C, Bowman JL. Recruitment of CRABS CLAW to promote nectary development within the eudicot clade. Development. 2005;132:5021–32.
Fourquin C, Vinauger-Douard M, Chambrier P, Berne-Dedieu A, Scutt CP. Functional conservation between CRABS CLAW orthologues from widely diverged angiosperms. Ann Bot. 2007;100:651–7.
Orashakova S, Lange M, Lange S, Wege S, Becker A. The CRABS CLAW ortholog from California poppy (Eschscholzia californica, Papaveraceae), EcCRC, is involved in floral meristem termination, gynoecium differentiation and ovule initiation. Plant J. 2009;58:682–93.
Morel P, Heijmans K, Ament K, Chopy M, Trehin C, Chambrier P, Rodrigues Bento S, Bimbo A, Vandenbussche M. The floral C-lineage genes trigger nectary development in Petunia and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2018;30:2020–37.
Ishikawa M, Ohmori Y, Tanaka W, Hirabayashi C, Murai K, Ogihara Y, Yamaguchi T, Hirano HY. The spatial expression patterns of DROOPING LEAF orthologs suggest a conserved function in grasses. Genes Genet Sys. 2009;84:137–46.
Pabón-Mora N, Wong KG, Ambrose BA. Evolution of fruit development genes in flowering plants. Front Pl Sci. 2014;5:300.
Ortíz-Ramírez CI, Plata-Arboleda S, Pabón-Mora N. Evolution of genes associated with gynoecium patterning and fruit development in Solanaceae. Ann Bot. 2018;121:1211–30.
Heisler MG, Atkinson A, Bylstra YH, Walsh R, Smyth DR. SPATULA, a gene that controls development of carpel margin tissues in Arabidopsis, encodes a bHLH protein. Development. 2001;128:1089–98.
Girin T, Paicu T, Stephenson P, Fuentes S, Korner E, O’Brien M, Sorefan K, Wood TA, Balanza V, Ferrandiz C, Smyth DR, Ostergaard L. INDEHISCENT and SPATULA interact to specify carpel and valve margin tissue and thus promote seed dispersal in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2011;23:3641–53.
Reyes-Olalde JI, Zúñiga-Mayo VM, Serwatowska J, Chavez Montes RA, Lozano-Sotomayor P, Herrera-Ubaldo H, Gonzalez-Aguilera KL, Ballester P, Ripoll JJ, Ezquer I, Paolo D, Heyl A, Colombo L, Yanofsky MF, Ferrandiz C, Marsch-Martinez N, de Folter S. The bHLH transcription factor SPATULA enables cytokinin signaling, and both activate auxin biosynthesis and transport genes at the medial domain of the gynoecium. PLoS Genet. 2017;13:e1006726.
Ortiz-Ramírez CI, Giraldo MA, Ferrandiz C, Pabón-Mora N. Expression and function of the bHLH genes ALCATRAZ and SPATULA in selected Solanaceae species. Plant J. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14352.
Tani E, Tsaballa A, Stedel C, Kalloniati C, Papaefthimiou D, Polidoros A, Darzentas N, Ganopoulos I, Flemetakis E, Katinakis P, Tsaftaris A. The study of a SPATULA-like bHLH transcription factor expressed during peach (Prunus persica) fruit development. Plant Phys Biochem. 2011;49:654–63.
Lee BH, Kwon SH, Lee SJ, Park SK, Song JT, Lee S, Lee MM, Hwang YS, Kim JH. The Arabidopsis thaliana NGATHA transcription factors negatively regulate cell proliferation of lateral organs. Plant Mol Biol. 2015;89:529–38.
Eklund DM, Staldal V, Valsecchi I, Cierlik I, Eriksson C, Hiratsu K, Ohme-Takagi M, Sundstrom JF, Thelander M, Ezcurra I, Sundberg E. The Arabidopsis thaliana STYLISH1 protein acts as a transcriptional activator regulating auxin biosynthesis. Plant Cell. 2010;22:349–63.
Martínez-Fernández I, Sanchis S, Marini N, Balanza V, Ballester P, Navarrete-Gómez M, Oliveira AC, Colombo L, Ferrándiz C. The effect of NGATHA altered activity on auxin signaling pathways within the Arabidopsis gynoecium. Front Plant Sci. 2014;5:210.
Ståldal V, Sohlberg J, Eklund D, Ljung K, Sundberg E. Auxin can act independently of CRC, LUG, SEU, SPT and STY1 in style development but not apical-basal patterning of the Arabidopsis gynoecium. New Phytol. 2008;180:798–808. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02625.x.
Gaillochet C, Jamge S, van der Wal F, Angenent G, Immink R, Lohmann JU. A molecular network for functional versatility of HECATE transcription factors. Plant J. 2018;95:57–70.
Suárez-Baron H, Pérez-Mesa P, Ambrose BA, González F, Pabón-Mora N. Deep into the Aristolochia flower: expression of C, D and E-class genes in Aristolochia fimbriata (Aristolochiaceae). J Exp Zool. 2016;328:55–71.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Aura Urrea Trujillo for allowing the use of equipment and reagents at the University of Antioquia, Juan Fernando Alzate (Centro Nacional de Secuenciación Genómica, SIU, Universidad de Antioquia) for the assembly and storage of the perianth-bearing reference transcriptomes, and Marisol Gascón (IBMCP) for technical advice in microscopy. NPM thanks the Arnold Arboretum at Harvard University for the 2018 Jewett Price which facilitated access to the living collections and funds for sequencing.
Funding
This work was funded by Estrategia de Sostenibilidad 2018–2019 and Convocatoria Programáticas 2017-16302 given to the grupo Evo Devo en Plantas at the Universidad de Antioquia, Medellín, Colombia; the iCOOP + 2016 grant COOPB20250 from Centro Superior de Investigación Científica, CSIC and the 2018–2019 Fondo de Internacionalización (code 2019-26230) from the Universidad de Antioquia linked to the international ExpoSEED (H2020.MSCA-RISE-2015-691109) EU Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PPM, NPM and FG planned and designed the research. All authors performed experiments, analyzed the data and wrote the final version of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
The work was done with plants so animal ethical approval and consent to participate are not applicable. As the plants are cultivated, they are exempt of legal access to genetic resources as stated by the Andean and Colombian law.
Consent for publication
All authors have provided consent for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Table
1. Plant collections, locations, and statistics from the TRINITY assembly of mixed transcriptomes obtained for each of the members of the perianth-bearing Piperales. Table S2. Accession numbers of CRABS CLAW, SPATULA, NGATHA, and HECATE homolog sequences used in this study. Table S3. Primers used in this study. Gene specific primers used in this study to amplify AfimCRC, AfimSPT, AfimNGA, and AfimHEC1, and AfimHEC3 orthologs in Aristolochia fimbriata, using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), quantitative reverse transcription (qRT-PCR), and in situ hybridization (ISH) experiments. Figure S1. Maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic analysis of the CRC gene lineage in flowering plants. The outgroup used was the Amborella trichopoda AmtrCRC. Bootstrap (BS) supports shown above the nodes. Colors follow conventions on the figure. Figure S2. Maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic analysis of the SPT gene lineage in flowering plants. Outgroup used was Cycas micholitzii SPT. Star points to a duplication event. BS supports shown in the nodes. Colors follow conventions on the figure. Figure S3. Maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic analysis of the NGA gene lineage in flowering plants. The outgroup used was Arabidopsis thaliana RAV. Star points to a duplication event. BS supports shown in the nodes. Colors follow conventions on the figure. Figure S4. Maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic analysis of the HEC gene lineage in flowering plants. Outgroup used was Arabidopsis thaliana bHLH87. Star points to a duplication event. BS supports shown in the nodes. Colors follow conventions on the figure. Figure S5. Relative expression profiles of AfimCRC, AfimSPT and AfimNGA at different floral developmental stages, and leaves using standard qRT-PCR. Ubiquitin (AfimUBC) was used as a positive control. Figure S6. In situ hybridization with sense probes for all tested genes in Aristolochia fimbriata.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Peréz-Mesa, P., Ortíz-Ramírez, C.I., González, F. et al. Expression of gynoecium patterning transcription factors in Aristolochia fimbriata (Aristolochiaceae) and their contribution to gynostemium development. EvoDevo 11, 4 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13227-020-00149-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13227-020-00149-8