Abstract
Primary immunodeficiency disease (PIDD) with hypogammaglobulinemia is characterized by recurrent and severe bacterial infections and IgG replacement is the standard of care in many of these patients. Health-related quality of life (HRQOL) is becoming increasingly recognized as a factor that affects patient well-being and treatment preferences. In an effort to better understand what factors affect HRQOL in patients with PIDD, we reviewed the published literature that used standardized instruments for the measurement of HRQOL. We investigated HRQOL in PIDD patients compared with normal controls and patients with other chronic diseases; we also investigated the impact of treatment administration on patient satisfaction. The most commonly encountered health-related quality of life instruments were the child heath questionnaire parental form 50, short form 36, PedsQL 4.0, Lansky’s play performance scale, and Life Quality Index. Patients with PIDD scored significantly lower on many of the instruments compared with normal controls. Also, while it appears that many patients appreciate home-based and subcutaneous IgG replacement therapy, patient satisfaction ultimately involves various clinical factors and individual patient preferences. By further analyzing what factors impact HRQOL, therapy adjustments can be made to maximize patient well-being and minimize disease impact on daily functioning.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Primary immunodeficiency disease (PIDD) is a group of genetic disorders characterized by increased susceptibility to infection. The incidence of PIDD has increased markedly in the last 40 years, likely secondary to an expanded understanding of the genetic basis and defective immunological mechanisms responsible for PIDD [1–3]. The exact prevalence of PIDD is not known. Estimates state 1 in 2000 children, 1 in 1200 for all persons, and 1 in 600 households (yielding a total population estimate of between 150,000 and 360,000 persons) in the US are diagnosed with PIDD [1]. One survey estimates the most frequently occurring form of PIDD—isolated IgA deficiency—occurs in approximately 1 in 163 individuals in Spain [4]. PIDD can affect patients at any age necessitating long-term therapy with IgG replacement therapy.
Survival is often considered the most important outcome in study design; however, the impact of illness on health-related quality of life (HRQOL) is receiving increasing recognition. HRQOL measurements are becoming important when analyzing not only the effect of the disease on patient well-being, but the satisfaction of patients with specific treatment regimens. Because many patients with PIDD require therapy indefinitely, the form of administration and setting where the product is administered are important factors that can significantly affect HRQOL. Specific measures to evaluate the outcome of an illness or its treatment include quantity and quality of life, and economic cost. The following is a review of the medical literature that measured HRQOL in PIDD patients.
Health related quality of life (HRQOL) indicators
Outcomes of morbidity and mortality are considered the gold standard in most clinical studies; however, the impact of illness on HRQOL has received increasing recognition. One challenge is that HRQOL is difficult to conceptualize and even more difficult to measure. The World Health Organization defines quality of life as an individual’s perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards and concerns [5]. It is a broad ranging concept affected by the person’s physical health, psychological state, level of independence, social relationships, and their relationship to salient features of their environment. HRQOL assessments were pioneered in the field of oncology [6] and, more recently, immunologists have transitioned and employed these tools to evaluate the impact and treatment of PIDD.
HRQOL assessments range from generic health status questionnaires that are applicable to all populations to more specific questionnaires that evaluate particular aspects of disease or treatment modalities. Generic HRQOL questionnaires are usually required for studies comparing impact of a specific illness to the general population. An example of a generic questionnaire is the Short Form-36 (SF-36). This self-administered tool contains 36 items and takes approximately 5 min to complete. It measures 8 dimensions of health in the areas of functional status, well-being, and overall evaluation of health [7, 8]. At the other end of the spectrum are disease specific measurements, which are used to evaluate more specific aspects of disease or treatment modalities. An example of this instrument is the life quality index (LQI). Each of these tools has been used to compare intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) and subcutaneous immunoglobulin (SCIG) therapies in PIDD patients [9, 10]. Some studies use a combination of these tools. Table 1 lists some of the most common QOL assessment tools used to evaluate PIDD and IgG replacement therapy.
The challenge of selecting and comparing QOL assessment tools is the variation in patient populations (children, adults, elderly, patients with comorbidities) and the applicability of individual tools to these specific patient populations. The Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory (PedsQL) and the Child Health Questionnaire (CHQ-PF50) are both widely used and valid generic measures in children, as is the SF-36 in adults [12, 13]. In a study assessing the PIDD-specific LQI in comparison to the generic CHQ-PF50 and SF-36, it was found that related scales correlated well though the LQI had internal consistency issues with measuring treatment costs [11]. There is still no universally accepted single best HRQOL measurement tool but continued efforts are being made to set quality criteria for these questionnaires [14, 15]. A strategy to combine generic and disease-specific measures in assessing PIDD HRQOL is ideal.
QOL in all PIDD patients
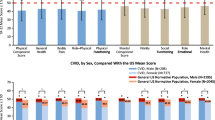
In comparison with healthy children and adults, patients with PIDD experience measurably lower general health with higher hospitalization rates and increased physical, school, and social activity limitation [11, 16–20]. Even compared to patients with other chronic diseases, patients with PIDD score lower with respect to perception of general health [19, 20]. A six-year longitudinal study of patients with common variable immunodeficiency (CVID), a common form of PIDD, found that they scored lower on the General Health scale in comparison to other patients with chronic diseases, and that they had a worse perception of their general personal health and limitations due to their physical health [19]. This same study also found that PIDD patients’ QOL changed over time; in the 6 years between the first and final assessments, a significant decline was noted in scores relating to bodily pain, general health, limitation due to emotional problems, and limitation in physical and social functioning. Notably emphasizing the importance of patient HRQOL, this study found that patients’ relative risk of death, independent of age, was affected by their perceived physical and social function; each point increase in Physical and Social functioning scores reduced the risk of death by 2 and 3 % respectively [19]. Another study comparing children with PIDD with children with other chronic diseases found that they generally experience similar HRQOL to patients with juvenile inflammatory arthritis (JIA) but that they score lower than the JIA group with respect to perception of general health and limitations on parental time and family activities [20]. Mental health impacts have also been noted; children with PIDD found that they had significantly lower emotional and social functioning compared to children with JIA, as well as significantly higher rates of parent-rated depressive and anxiety symptoms [16].
A long delay in diagnosis and a large number of infectious episodes can further negatively impact HQROL [21] as well as lead to permanent functional impairments prior to initiation of treatment [22, 23]. A recent large scale analysis of a cohort of 2212 patients with CVID found that each year of diagnostic delay and each year of increased age at diagnosis were associated with a 1.7 and 4.5 % increased risk of death, respectively [24]. The median delay in diagnosis of PIDD has decreased considerably over the past 2 decades. A United States population-based cohort study found a 17 year median delay in diagnosis for patients whose symptoms occurred before 1986; this decreased to a 6.7 year median delay from 1986 to 1996, and decreased even further to a 2.7 year delay for patients whose symptoms presented after 1996 [25]. Despite these improvements, delayed diagnosis remains a significant problem [22, 26]. In a study of 32 patients with PIDD, more than two-thirds experienced diagnostic delay, which led to serious morbidity [27]. One study revealed that these patients experienced two major infections requiring hospitalization that included pneumonia, meningitis, osteomyelitis, and septicemia during this time of diagnostic delay [22].
Other factors have also been noted to influence HRQOL in patients with PIDD; a survey of 55 patients ≥20 years of age with PIDD found that quality of life scores were lowest in patients who were unemployed, had infections in more than four organs, had more than two additional diseases, and had experienced more than two specific occurrences of stress in the last 2–3 months [28]. Additionally, female gender, older age, chronic lung disease, and chronic diarrhea have also been shown to be risk factors leading to a poor quality of life in PIDD patients [19]. Some of the pertinent studies examining HRQOL in PIDD patients are summarized in Table 2.
IVIG vs no therapy
For decades, replacement therapy with IgG has been the therapeutic cornerstone for antibody-deficient patients who have recurrent infections and are deficient in total or specific IgG. Despite the fact that IgG replacement therapy is the standard of care in many patients with PIDD, there are limited randomized controlled trials comparing IgG treatment with no treatment or placebo due to obvious ethical concerns; similarly, there is limited information on mortality [29, 30]. One study of patients with PIDD showed the proportion of persons surviving 10 years after diagnosis was 93.5 %, which is similar to the survival rate for the population at large [25]. It is known that IgG replacement therapy decreases the amount of life-threatening infections and studies have shown that there is a reduction in the rate of bacterial infections, days of antibiotic usage, days of fever, and hospital admissions following IgG therapy [31–35]. Abdou et al. found patients on IVIG therapy had a significant improvement in HRQOL and reduced number of infections after comparing a short 3-month period without treatment with 12 months of IVIG treatment [36]. In addition, it has been documented that maintaining adequate IgG levels can decrease infections and improve QOL [37–39].
Routes of administration-SCIG vs IVIG
Many patients with PIDD require life-long IgG replacement therapy, thus the route of administration has many implications on patient well-being. The first case report of a patient treated with IgG replacement therapy was in 1952 and, interestingly, this patient was treated by SC infusion with favorable results [40]. The use of IgG replacement therapy has since become the standard of care for patients with PIDD. For many years, IVIG therapy in an outpatient setting was the treatment of choice. Then in the 1980s, slow SCIG infusions using portable syringe drivers were first introduced in the United States in the 1980s [41] followed by several other reports from the United States, Europe, and New Zealand [42]. IgG replacement therapy is now commonly begun by IVIG loading for three or more doses followed by a transition to SCIG. A large European database study included 7350 patients with PIDD and found that though 42 % of patients were on IgG replacement with IVIG being the most common form (75.8 %), followed by SCIG (23.9 %), and then intramuscular immunoglobulin (IMIG) (0.3 %). IMIG is the least widely used due to the pain associated with administration [43]. A 2008 survey of patients with PIDD conducted by the Immune Deficiency Foundation had similar findings with 69 % of patients in the sample using IVIG and another 23 % using SCIG [44].
Though IVIG appears to be the most common form of IgG replacement, SCIG treatment has shown promising results. One study using SCIG loading (100 mg/kg/day for 5 consecutive days) instead of IVIG loading at treatment initiation revealed that this was well-tolerated with no serious adverse events [45]. A recent review of three clinical efficacy and two extension studies found Hizentra®, a form of SCIG, to have comparable efficacy in comparison to IVIG in the prevention of serious bacterial infections and the maintenance of IgG levels [46]. Other reviews have also found that patients on SCIG clearly achieve acceptable IgG serum levels [37, 47] with minimal risk of systemic adverse events, including anaphylaxis [47].
A recent review of 25 studies noted that 4 studies evaluating health economics in SCIG and IVIG therapy all found SCIG to be more cost effective, mainly through the reduction of lost work or school days [48]. Other studies have shown that SCIG is more cost effective due to issues with IVIG such as personnel required to administer, facility rooms, administrative overheads and productivity loss [42, 49, 50]. In comparison to patients on IVIG, patients on SCIG miss significantly fewer days of work or school [51, 52] and one study also noted they spend significantly fewer days in the hospital [51]. PIDD patients’ perceived HRQOL are also affected by their choice of treatment [41, 52–54]. A Swedish study involving 25 PIDD patients, most of whom were on IVIG therapy, reported that initiating SCIG significantly increased their health-related function and improved self-rated health [54]. Similarly, a recent study of 50 PIDD patients shifting from IVIG to SCIG found that these patients subsequently had a significant improvement in their total mean LQI at 6 months that was sustained over time [52]. However, this same study acknowledges that it is unclear whether the LQI score improvement is due to the SCIG therapy itself, the accompanying switch to home treatments, or some combination of both factors. The importance of therapy convenience is also suggested by a past randomized crossover study comparing SCIG to IVIG administration; in this study, patients on SCIG were required to visit the hospital more frequently than those on IVIG therapy (once per week in comparison to once every 3–4 weeks) and only 10 of these 26 patients chose to continue with SCIG [55]. In fact, rather than SCIG therapy itself, a 3 year study in Norway noted that parents of children with PIDD actually cited greater independence and the ability to stay at home as the most beneficial results of switching from IVIG to SCIG [53]. The review of 25 studies also noted that, though transition from hospital-based IVIG to home-based SCIG therapy improved HRQOL, this improvement seemed to be largely related to home therapy [48].
Home versus doctor’s office/hospital
Both SCIG and IVIG therapy are available for home administration, though the actual rate of use for each form of therapy differs. Of the PIDD patients surveyed in 2008 by the Immune Deficiency Foundation, 42 % of the patients on IVIG reported that they usually received their infusion at home and only 7 % were able to self-infuse; in comparison, nearly all SCIG users (93 %) received their treatment at home and were able to self-infuse [44]. Multiple studies have evaluated patient preferences regarding IgG replacement therapy at home versus in the doctor’s office or hospital. In patients treated with IVIG, Daly et al. found that home based IVIG improved independence, convenience and decreased disruption of activities [9]. Other studies have also shown that home-therapy regimens lead to greater improvement in HRQOL and treatment satisfaction [9, 11, 56, 57]. In patients treated with SCIG who had previously been treated with IVIG, Nicolay et al. investigated the impact of weekly SCIG self-infusions at home on quality of life and patient satisfaction [10, 56]. Patients who had previously been treated at the hospital/doctor’s office reported fewer limitations in their work/daily activities, significantly improved vitality, generally better health, and improved treatment satisfaction. The preference for the SC route and home therapy was 81 and 90 % respectively. In patients who were previously treated at home with IVIG, 69 % of patients preferred the SC route and 92 % preferred home therapy [56]. In an alternate study, 73 % of adult patients preferred SCIG over IVIG therapy, and correspondingly 82 % preferred home over hospital therapy; in children, 100 % preferred both SCIG and home therapy [11]. Notably, of the patients who had previously been treated with IVIG home therapy but later transitioned to SCIG home therapy, the majority preferred SCIG therapy after 1 year.
Patients’ ability to self-administer therapy at home has also been shown to impact their HRQOL. The 2008 Immune Deficiency Foundation Survey found that, while only 7 % of patients receiving home IVIG were able to self-infuse, nearly all patients receiving home SCIG were able to self-infuse [44]. Multiple studies have found that the ability to manage replacement therapy by oneself at home increases patient/family empowerment, makes it easier to work or study, improves family relations, contributes to a sense of self control among patients and families, and improves the daily living situation [53, 58–60]. Recently, a survey of 300 patients and caregivers of patients receiving IgG replacement (53 % receiving IVIG and 45 % receiving SCIG) found that patients and caregivers both preferred self-administration over administration by a health care professional [61]. This study again seems to suggest that convenience plays a large role in patient preferences, also noting that patients prefer home administration, less frequent administrations of shorter durations, and fewer needle sticks. In a German study, apprehension about self-infusion and a fear of side effects at home were cited as the main reasons that patients chose to remain on IV therapy [62]. Other factors that play into the decision of treatment location include accessibility to an infusion center, the patient’s schedule and availability during the hours that the infusion center is open, reliability of the patient as assessed by the physician, ability of the patient to learn and perform the techniques used in SCIG, safety, security, and cleanliness of the home environment, and issues related to reimbursement versus out-of-pocket costs [63]. Table 3 lists factors that positively and negatively impact HRQOL in PIDD.
Conclusion
PIDD with significant hypogammaglobulinemia is typically characterized by recurrent and severe bacterial infections of the upper and lower respiratory tracts and is associated with poorer HRQOL than patients without chronic illness. Increased knowledge of specific immunodeficiencies has led to a rise in the diagnosis and incidence of PIDD. Since patients with PIDD often require life-long treatment with IgG, choices about the route of administration have a significant impact on HRQOL. Choosing the right patient, providing proper support, and managing expectations are key to ensuring that patients with PIDD achieve the maximum benefit from therapy.
Abbreviations
- CHQ-PF50:
-
child heath questionnaire parental form 50
- HRQOL:
-
health related quality of life
- IMIG:
-
intramuscular immunoglobulin
- IVIG:
-
intravenous immunoglobulin
- JIA:
-
juvenile inflammatory arthritis
- LPPS:
-
Lansky’s play performance scale
- LQI:
-
life quality index
- PIDD:
-
primary immunodeficiency disease
- SCIG:
-
subcutaneous immunoglobulin
- SF-36:
-
short form 36
References
Boyle JM, Buckley RH. Population prevalence of diagnosed primary immunodeficiency diseases in the United States. J Clin Immunol. 2007;27:497–502.
Fischer A. Human primary immunodeficiency diseases. Immunity. 2007;27:835–45.
Morra M, Geigenmuller U, Curran J, Rainville IR, Brennan T, Curtis J, Reichert V, Hovhannisyan H, Majzoub J, Miller DT. Genetic diagnosis of primary immune deficiencies. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2008;28:387–412.
Pereira LF, Sapiña AM, Arroyo J, Viñuelas J, Bardají RM, Prieto L. Prevalence of selective IgA deficiency in Spain: more than we thought. Blood. 1997;90(2):893.
World Health Organization. Study protocol for the World Health Organization project to develop a Quality of Life assessment instrument (WHOQOL). Qual Life Res. 1993;2(2):153–9.
Schag CC, Heinrich RL, Ganz PA. Karnofsky performance status revisited: reliability, validity, and guidelines. J Clin Oncol. 1984;2(3):187–93.
Brazier JE, Harper R, Jones NM, O’Cathain A, Thomas KJ, Usherwood T, Westlake L. Validating the SF-36 health survey questionnaire: new outcome measure for primary care. BMJ. 1992;305(6846):160–4.
Ware JE Jr, Sherbourne CD, The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). Conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care. 1992;30(6):473–83.
Daly PB, Evans JH, Kobayashi RH, Kobayashi AL, Ochs HD, Fischer SH, Pirofsky B, Sprouse C. Home-based immunoglobulin infusion therapy: quality of life and patient health perceptions. Ann Allergy. 1991;67(5):504–10.
Nicolay U, Haag S, Eichmann F, Herget S, Spruck D, Gardulf A. Measuring treatment satisfaction in patients with primary immunodeficiency diseases receiving lifelong immunoglobulin replacement therapy. Qual Life Res. 2005;14:1683–91.
Gardulf A, Nicolay U, Math D, Asensio O, Bernatowska E, Böck A, Costa-Carvalho BT, Granert C, Haag S, Hernández D, Kiessling P, Kus J, Matamoros N, Niehues T, Schmidt S, Schulze I, Borte M. Children and adults with primary antibody deficiencies gain quality of life by subcutaneous IgG self-infusions at home. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;114:936–42.
Raat H, Mohangoo AD, Grootenhuis MA. Pediatric health-related quality of life questionnaires in clinical trials. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;6(3):180–5.
Varni JW, Limbers CA, Burwinkle TM. How young children can reliably and validly self-report their health-related quality of life?: an analysis of 8.591 chldren across age subgroups with the PedsQL 4.0 Generic Core Scales. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2007;5:1.
Mokink LB, Terwee CB, Patrick DL, Alonso J, Stratford PW, Knol DL, Dekker J, Bouter LM, de Vet HC. The COSMIN checklist for assessing the methodological quality of studies on measurement properties of health status measurement instruments: an international Delphi study. Qual Life Res. 2010;19(4):539–49.
Terwee CB, Bot SD, de Boer MR, van der Windt DA, Knol DL, Dekker J, Bouter LM, de Vet HC. J Clin Epidemiol. 2007;60(10):24–42.
Kuburovic NB, Pasic S, Susic G, Stevanovic D, Kuburovic V, Zdravkovic S, Janicijevic Petrovic M, Pekmezovic T. Health-related quality of life, anxiety, and depressive symptoms in children with primary immunodeficiencies. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2014;8:323–30.
Mozaffari H, Pourpak Z, Pourseyed S, Moin M, Farhoodi A, Aghamohammadi A, Movahedi M, Gharagozlou M, Entezari N. Health-related quality of life in primary immune deficient patients. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006;5:23–7.
Soresina A, Nacinovich R, Bomba M, Cassani M, Molinaro A, Sciotto A, Martino S, Cardinale F, De Mattia D, Putti C, Dellepiane RM, Felici L, Parrinello G, Neri F, Plebani A. Italian network for primary immunodeficiencies: the quality of life of children and adolescents with X-linked agammaglobulinemia. J Clin Immunol. 2009;29(4):501–7.
Tabolli S, Giannantoni P, Pulvirenti F, La Marra F, Granata G, Milito C, Quinti I. Longitudinal study on health-related quality of life in a cohort of 96 patients with common variable immune deficiencies. Front Immunol. 2014;5:605.
Zebracki K, Palermo TM, Hostoffer R, Duff K, Drotar D. Health-related quality of life of children with primary immunodeficiency disease: a comparison study. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2004;93:557–61.
Aghamohammadi A, Montazer A. Health-related quality of life in primary antibody deficiency. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2011;10(1):47–51.
Seymour B, Miles J, Haeney M. Primary antibody deficiency and diagnostic delay. J Clin Pathol. 2005;58:546–7.
Eades-Perner AM, Gathmann B, Knerr V, Guzman D, Veit D, Kindle G, Grimbacher B. ESID Registry Working Party: the European internet-based patient and research database for primary immunodeficiencies: results 2004–06. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007;147:306–12.
Gathmann B, Mahlaoui N; CEREDIH et al. (2014) European Society for Immunodeficiencies Registry Working Party. Clinical picture and treatment of 2212 patients with common variable immunodeficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol 134(1):116–26.
Joshi AY, Iyer VN, Hagan JB, St Sauver JL, Boyce TG. Incidence and temporal trends of primary immunodeficiency: a population-based cohort study. Mayo Clin Proc. 2009;84:16–22.
Spickett GP, Misbah SA, Chapel HM. Primary antibody deficiency in adults. Lancet. 1991;337:281–4.
Blore J, Haeney MR. Primary antibody deficiency and diagnostic delay. BMJ. 1989;298:516–7.
Sigstad HM, Stray-Pedersen A, Froland SS. Coping, quality of life, and hope in adults with primary antibody deficiencies. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2005;3:31.
Cunningham-Rundles C, Bodian C. Common variable immunodeficiency: clinical and immunological features of 248 patients. Clin Immunol. 1999;92:34–48.
Antoine C, Müller S, Cant A, et al. European group for blood and marrow transplantation; European Society for immunodeficiency: long-term survival and transplantation of haemapoietic stem cells for immunodeficiencies: report of the European experience 1968–99. Lancet. 2003;361:553–60.
Busse PJ, Razvi S, Cunningham-Rundles C. Efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin in the prevention of pneumonia in patients with common variable immunodeficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;109:1001–4.
Cunningham-Rundles C, Siegal FP, Smithwick EM, Lion-Boulé A, Cunningham-Rundles S, O’Malley J, Barandun S, Good RA. Efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin in primary humoral immunodeficiency disease. Ann Intern Med. 1984;101:435–9.
Skull S, Kemp A. Treatment of hypogammaglobulinaemia with intravenous immunoglobulin, 1973–93. Arch Dis Child. 1996;74:527–30.
Quartier P, Debré M, De Blic J, de Sauverzac R, Sayegh N, Jabado N, Haddad E, Blanche S, Casanova JL, Smith CI, Le Deist F, de Saint Basile G, Fischer A. Early and prolonged intravenous immunoglobulin replacement therapy in childhood agammaglobulinemia: a retrospective survey of 31 patients. J Pediatr. 1999;134:589–96.
Roifman CM, Rao CP, Lederman HM, Lavi S, Quinn P, Gelfand E. Increased susceptibility to Mycoplasma infection in patients with hypogammaglobulinemia. Am J Med. 1986;80:590–4.
Abdou NI, Greenwell CA, Mehta R, Narra M, Hester JD, Halsey JF. Efficacy of intravenous gammaglobulin for immunoglobulin G subclass and/or antibody deficiency in adults. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2009;149(3):267–74.
Abolhassani H, Sadaghiani MS, Aghamohammadi A, Ochs HD, Rezaei N. Home-based subcutaneous Immunoglobulin versus hospital-based intravenous immunoglobulin in treatment of primary antibody deficiencies: systematic review and meta analysis. J Clin Immunol. 2012;32(6):1180–92.
Eijkhout HW, van Der Meer JW, Kallenberg CG, Weening RS, van Dissel JT, Sanders LA, Strengers PF, Nienhuis H, Schellekens PT. The effect of two different dosages of intravenous immunoglobulin on the incidence of recurrent infections in patients with primary hypogammaglobulinemia. A randomized, double-blind, multicenter crossover trial. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135(3):165–74.
Hoffmann F, Grimbacher B, Thiel J, Peter HH, Belohradsky BH, Vivaglobin Study Group. Home-based subcutaneous immunoglobulin G replacement therapy under real-life conditions in children and adults with antibody deficiency. Eur J Med Res. 2010;15(6):238–45.
Bruton OC. Agammaglobulinemia. Pediatrics. 1952;9:722–8.
Berger M, Cupps TR, Fauci AS. Immunoglobulin replacement therapy by slow subcutaneous infusion. Ann Intern Med. 1980;93:55–6.
Gardulf A, Andersen V, Björkander J, Ericson D, Frøland SS, Gustafson R, Hammarström L, Jacobsen MB, Jonsson E, Möller G. Subcutaneous immunoglobulin replacement in patients with primary antibody deficiencies: safety and costs. Lancet. 1995;345:365–9.
Knerr V, Gathmann B, Grimbacher B, Beauté J, Dudoit Y, Mahlaoui N, Fischer A, Knerr V, Kindle G. ESID Registry Working Party: The European internet-based patient and research database for primary immunodeficiencies: results 2006–2008. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009;157(Suppl 1):3–11.
Treatment experiences and preferences of patients with primary immune deficiency diseases: 2008 national survey of patients, 2009. http://www.primaryimmune.org/survey_research/surveys.htm.
Borte M, Quinti I, Soresina A, Fernández-Cruz E, Ritchie B, Schmidt DS, McCusker C. Efficacy and safety of subcutaneous Vivaglobin® replacement therapy in previously untreated patients with primary immunodeficiency: a prospective, multicenter study. J Clin Immunol. 2011;31(6):952–61.
Wasserman RL. Hizentra for the treatment of primary immunodeficiency. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2014;10(10):1293–307.
Gardulf A. Immunoglobulin treatment for primary antibody deficiencies: advantages of the subcutaneous route. BioDrugs. 2007;21:105–16.
Lingman-Framme J, Fasth A. Subcutaneous immunoglobulin for primary and secondary immunodeficiencies: an evidence-based review. Drugs. 2013;73(12):1307–19.
Igarashi A, Kanegane H, Kobayashi M, Miyawaki T, Tsutani K. Cost-minimization analysis of IgPro20, a subcutaneous immunoglobulin, in Japanese patients with primary immunodeficiency. Clin Ther. 2014;36(11):1616–24.
Högy B, Keinecke HO, Borte M. Pharmacoeconomic evaluation of immunoglobulin treatment in patients with antibody deficiencies from the perspective of the German statutory health insurance. Eur J Health Econ. 2005;6(1):24–9.
Knerr V, Gathmann B, Eades-Perner AM, Kindle G, Grimbacher B. The ESID Online Database for primary immunodeficiencies. First analyses with regard to Germany and Europe. Med Klin (Munich). 2008;103:620–7.
Vultaggio A, Azzari C, Milito C, Finocchi A, Toppino C, Spadaro G, Trizzino A, Baldassarre M, Paganelli R, Moschese V, Soresina A, Matucci A. Subcutaneous immunoglobulin replacement therapy in patients with primary immunodeficiency in routine clinical practice: The VISPO Prospective Multicenter Study. Clin Drug Investig. 2015;35(3):179–85.
Abrahamsen TG, Sandersen H, Bustnes A. Home therapy with subcutaneous immunoglobulin infusions in children with congenital immunodeficiencies. Pediatrics. 1996;98:1127–31.
Gardulf A, Bjorvell H, Gustafson R, Hammarstrom L, Smith CI. The life situations of patients with primary antibody deficiency untreated or treated with subcutaneous gammaglobulin infusions. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993;92:200–4.
Chapel HM, Spickett GP, Ericson D, Engl W, Eibl MM, Bjorkander J. The comparison of the efficacy and safety of intravenous versus subcutaneous immunoglobulin replacement therapy. J Clin Immunol. 2000;20:94–100.
Nicolay U, Kiessling P, Berger M, Gupta S, Yel L, Roifman CM, Gardulf A, Eichmann F, Haag S, Massion C, Ochs HD. Health-related quality of life and treatment satisfaction in North American patients with primary immunodeficiency diseases receiving subcutaneous IgG self-infusions at home. J Clin Immunol. 2006;26(1):65–72.
Gaspar J, Gerritsen B, Jones A. Immunoglobulin replacement treatment by rapid subcutaneous infusion. Arch Dis Child. 1998;79:48–51.
Gardulf A, Nicolay U, Asensio O, Bernatowska E, Böck A, Carvalho BC, Granert C, Haag S, Hernández D, Kiessling P, Kus J, Pons J, Niehues T, Schmidt S, Schulze I, Borte M. Rapid subcutaneous IgG replacement therapy is effective and safe in children and adults with primary immunodeficiencies—a prospective, multi-national study. J Clin Immunol. 2006;26(2):177–85.
Hansen S, Gustafson R, Smith CI, Gardulf A. Express subcutaneous IgG infusions: decreased time of delivery with maintained safety. Clin Immunol. 2002;104:237–41.
Shapiro RS. Why I use subcutaneous immunoglobulin (SCIG). J Clin Immunol. 2013;33(Suppl 2):S95–8.
Espanol T, Prevot J, Drabwell J, Sondhi S, Olding L. Improving current immunoglobulin therapy for patients with primary immunodeficiency: quality of life and views on treatment. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2014;8:621–9.
Waniewski J, Gardulf A, Hammarstrom L. Bioavailability of gamma-globulin after subcutaneous infusions in patients with common variable immunodeficiency. J Clin Immunol. 1994;14:90–7.
Berger M. Principles of and advances in immunoglobulin replacement therapy for primary immunodeficiency. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2008;28:413–37.
Raat H, Bonsel GJ, Essink-Bot ML, Landgraf JM, Gemke RJ. Reliability and validity of comprehensive health status measures in children: The Child Health Questionnaire in relation to the Health Utilities Index. J Clin Epidemiol. 2002;55(1):67–76.
Landgraf JM, Maunsell E, Speechley KN, Bullinger M, Campbell S, Abetz L, Ware JE. Canadian-French, German and UK versions of the Child Health Questionnaire: methodology and preliminary item scaling results. Qual Life Res. 1998;7(5):433–45.
Klaassen RJ, Krahn M, Gaboury I, Hughes J, Anderson R, Grundy P, Ali SK, Jardine L, Abla O, Silva M, Barnard D, Cappelli M. Evaluating the ability to detect change of health-related quality of life in children with Hodgkin disease. Cancer. 2010;116(6):1608–14.
Varni JW, Burwinkle TM, Seid M. The PedsQL 4.0 as a school population health measure: feasibility, reliability, and validity. Qual Life Res. 2006;15(2):203.
Lansky LL, List MA, Lansky SB, Cohen ME, Sinks LF. Toward the development of a play performance scale for children (PPSC). Cancer. 1985;56(7 Suppl):1837–40.
Al-Herz W, Zainal ME, Alenezi HM, Husain K, Alshemmari SH. Performance status and deaths among children registered in Kuwait National Primary ImmunoDeficiency Disorders Registry. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2010;28(2–3):141–6.
Tcheurekdjian H, Palermo T, Hostoffer R. Quality of life in common variable immunodeficiency requiring intravenous immunoglobulin therapy. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2004;93(2):160–5.
Berger M, Murphy E, Riley P, Bergman GE. VIRTUE Trial Investigators: improved quality of life, immunoglobulin G levels, and infection rates in patients with primary immunodeficiency diseases during self-treatment with subcutaneous immunoglobulin G. South Med J. 2010;103(9):856–63.
Fasth A, Nyström J. Safety and efficacy of subcutaneous human immunoglobulin in children with primary immunodeficiency. Acta Paediatr. 2007;96(10):1474–8.
Fasth A, Nyström J. Quality of life and health-care resource utilization among children with primary immunodeficiency receiving home treatment with subcutaneous human immunoglobulin. J Clin Immunol. 2008;28(4):370–7.
Authors’ contributions
AA and TT conceived the study and conducted the initial literature review and original manuscript. FJ provided updates with new relevant literature from 2012 to present and edited the manuscript to the final draft. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Baxter pharmaceuticals for coming to us with the idea for this review. No financial compensation was received from Baxter for this review. The authors are fully responsible for all content and editorial decisions, and meet criteria for authorship as recommended by the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors.
Compliance with ethical guidelines
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, F., Torgerson, T.R. & Ayars, A.G. Health-related quality of life in patients with primary immunodeficiency disease. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol 11, 27 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13223-015-0092-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13223-015-0092-y