Abstract
Background
Pasteurella multocida meningitis in an immunocompetent patient is rare and commonly occurs after animal bite. To our knowledge, only 48 cases have been reported in the literature since 1989. P. multocida meningitis is commonly linked to animal contagion. Here we report on a new case of P. multocida meningitis in an immunocompetent patient who is a dog owner without a dog bite. We used the matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry to investigate the clonal lineage between animal and human isolates.
Case presentation
In our case, a 25-year-old immunocompetent French Caucasian woman with nothing notable in her medical history was admitted for meningitis caused by P. multocida. Clonal lineage of P. multocida strains from cerebrospinal fluid and blood culture and her dog’s oral cavity has been recognized by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry dendrograms and clustering of the 21 P. multocida isolates in our centres. She was treated by a combination of intravenous ceftriaxone (2 g/day) and oral levofloxacin (1 g/day). She was discharged on the 6th day of admission. The antimicrobial therapy was conducted for 15 days. The dog was treated by clavulanic-acid amoxicillin for 3 weeks by the veterinarian. The evolution of the patient at the 5th month after the end of the antimicrobial therapy was normal without any neurological after-effects.
Conclusion
The meningitis caused by P. multocida could be considered a cause of human meningitis in dog lovers without an animal bite. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry should be considered as it is an accurate tool to identify clonal lineage between animal and human isolates.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Pasteurella multocida are small Gram-negative coccobacilli which appeared to be a common flora in oral cavity of dogs and cats [1]. Skin and soft tissue infection is a main human pasteurelloses; and P. multocida meningitis in an immunocompetent patient is rare and commonly occurred after animal bite [2–5].
Species identification of Pasteurella in routine clinical microbiology laboratories is mainly based on convention phenotypic identification. The variation of phenotypic characteristic between isolates from different hosts may results in imprecise species identification and needs molecular identification such as 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis in these cases [6]. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry has been recently introduced to clinical microbiology laboratories for accurate bacterial species identification [7]. Zangenah et al. have recently reported an advantage of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry in P. multocida comparing to conventional microbiological methods and VITEK® 2 microbial identification system (bioMérieux) [8].
Here we report on a rare case of P. multocida meningitis in an immunocompetent dog owner without a dog bite. We used MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry to investigate the clonal lineage between animal and human isolates.
Case presentation
In January 2015, a 25-year-old French Caucasian woman was admitted to the infectious disease department of the university hospital in Marseille for a headache, nasal congestion and vomiting. Prior to the headache, she had been fine with nothing notable in her medical history. She lives with a dog and she had not travelled to a tropical area. We did not find any recent indication of an animal bite or a skin wound in her medical history. On admission, she had a high fever (40.3 °C), her pulse was 117 beats/min, and her blood pressure was 138/41 mmHg. The clinical examination showed a subarachnoid syndrome and frontal-occipital headache. Laboratory investigations revealed an elevation of the C-reactive protein level (275 mg/L; normal < 5 mg/L), an elevation of the plasmatic fibrinogen level (6.82 g/L; normal values = 1.8–4 g/L), an elevated leukocyte count (13,000/µL), predominantly neutrophil granulocytes, a low lymphocyte level (430 µL; normal = 1500–4000 µL) involving T cells, although B and NK cells, a normal haemoglobin concentration (14.8 g/dL), and a low platelet count (148 × 103/µL; normal = 150–400 × 103/µL). Cerebrospinal fluid sample (CSF) analysis revealed an elevated protein level of 2 g/dL, a low glucose level of 74 mg/dL (plasmatic glucose level = 189 mg/dL) and a WBC count of 1200 cells/mm3 with 90 % neutrophils. CSF cultures and blood cultures revealed positive for P. multocida as identified by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Laboratory tests including complement and immunoglobulin analysis did not find immunodeficiency.
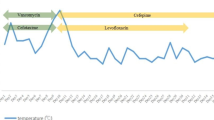
She was treated by an empirical intravenous antimicrobial therapy with a combination of cefotaxime (4 g/day), amoxicillin (12 g/day) and acyclovir (2 g/day), the antimicrobial therapy was modified for a combination of intravenous ceftriaxone (2 g/day) and oral levofloxacin (1 g/day). The patient improved rapidly with a disappearance of the subarachnoid syndrome at 2 days of treatment but the fever persisted. A cerebral magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) did not reveal any abnormality and she became afebrile only on the 4th day of antibiotic treatment. She was discharged on the 6th day of admission. The antimicrobial therapy was conducted for 15 days. The evolution at the 5th month after the end of the antimicrobial therapy was normal without any neurological after-effects.
Bacterial cultures in the oral cavity of her dog tested positive for P. multocida, which displayed the same antibiotic susceptibility pattern than isolates from the patient’s blood and CSF. In addition, main spectrum projection (MSP) enabled to group the three strains in a same cluster as defined by an arbitrary distance level <300, indicating they were closely related (Figs. 1, 2). The dog was treated by clavulanic-acid amoxicillin for 3 weeks by the veterinarian.
Discussion
We herein report a new case of meningitis caused by P. multocida in a young immunocompetent patient who was probably infected by her dog without a dog bite. In the literature, the main risk factor for P. multocida meningitis is an animal contact, which has been reported in 84 % of cases [2]. To our knowledge, only 48 adult cases of meningitis caused by P. multocida in immunocompetent and immunodeficiency patients have been reported [2–5]. Only nine cases of neurological complications have been reported including epidural empyema, cerebrals abscess, convulsion, cognitive deficit, paralysis, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis and meningoencephalitis [2–5, 9]. According to previous studies, risk factors for P. multocida meningitis include age >55 years old [2] and alcoholism [9].
In 26 % of cases a medical past-history of recent neurosurgical surgery was found [2]. In our case, the patient had no apparent immunodeficiency factors and no neurological surgery. She was discharged and cured after 15 days of antibiotic treatment with ceftriaxone 2 g/day and levofloxacin 1 g/day. In the literature, antibiotic treatment with intravenous betalactamin with median duration of 21 days (range: 10–27 days) has been usually reported [2]. Nevertheless, ten of the 48 reported cases of P. multocida meningitis died.
Human pasteurellosis is not frequent. Some cases of human pasteurellosis have occurred in animal lovers by kissing pets [10, 11] and pigs [5]. However the carriage rate of P. multocida in an animal’s oral cavity is high (12–75 %) [1]. Pulsed field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) by using 2-D gel electrophoresis and molecular analysis have long been considered as the gold standard for clonal analysis. These methods have been used in the studies of 117 porcine and human isolates of P. multocida [12], and 23 field and vaccine strains [13]. In the last decades, MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry identification become a routine method in clinical laboratories [7]. In some condition, this technique has been used to identify clonal lineage bacteria in previous studies [7, 14–16]. In our case, the P. multocida strains of the patient and her dog were revealed to be closely related as identified MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry.
Conclusion
The meningitis caused by P. multocida could be considered a rare cause of human meningitis that can be occurred in immunocompetent patient without an animal bites or scratches. In the alternative of molecular identification, MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry is a rapid and accurate identification method of P. multocida isolates. The clonal lineage characterization between animal and human isolates in our study was possible using routine MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry.
Consent
This study was approved by the institutional research ethics board (Comite de Protection des Personnes Sud Méditerranée 1), and written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. Written informed consent was obtained from the patient to take samples from her dog.
Abbreviations
- P. multocida :
-
Pasteurella multocida
- MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry:
-
the matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry
- CSF:
-
cerebrospinal fluid sample
- PFGE:
-
pulsed field gel electrophoresis
- MSP:
-
main spectrum projection
- NK cells:
-
natural killer cells
References
Griego RD, Rosen T, Orengo IF, Wolf JE. Dog, cat, and human bites: a review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;33:1019–29.
Grillon A, Guillard T, Brasme L, Limelette A, Novella J-L, de Champs C. Méningite mortelle à Pasteurella multocida. Médecine Mal Infect. 2012;42:374–5.
Foguem C. Rare case of catastrophic diffuse hemorrhage complicating sepsis and meningitis due to Pasteurella stomatis in an elderly woman mimicking hemorrhagic septicemia. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2014;15:527–8.
Nguefack S, Moifo B, Chiabi A, Mah E, Bogne J-B, Fossi M, Fru F, Mbonda E, Djientcheu V-P. Méningite à Pasteurella multocida compliquée d’abcès cérébral. Arch Pédiatrie. 2014;21:306–8.
López C, Sanchez-Rubio P, Betrán A, Terré R. Pasteurella multocida bacterial meningitis caused by contact with pigs. Braz J Microbiol. 2013;44:473–4.
De Melo Oliveira MG, Abels S, Zbinden R, Bloemberg GV, Zbinden A. Accurate identification of fastidious Gram-negative rods: integration of both conventional phenotypic methods and 16S rRNA gene analysis. BMC Microbiol. 2013;13:162.
Seng P, Rolain J-M, Fournier PE, La Scola B, Drancourt M, Raoult D. MALDI-TOF-mass spectrometry applications in clinical microbiology. Future Microbiol. 2010;5:1733–54.
Zangenah S, Güleryüz G, Boräng S, Ullberg M, Bergman P, Ozenci V. Identification of clinical Pasteurella isolates by MALDI-TOF—a comparison with VITEK 2 and conventional microbiological methods. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013;77:96–8.
Kawashima S, Matsukawa N, Ueki Y, Hattori M, Ojika K. Pasteurella multocida meningitis caused by kissing animals: a case report and review of the literature. J Neurol. 2010;257:653–4.
Rhodes M. Pasturella multocida meningitis in a dog lover (or don’t kiss pets!). J R Soc Med. 1986;79:747–8.
Arashima Y, Kumasaka K, Okuyama K, Kawabata M, Tsuchiya T, Kawano K, Asano R, Hokari S. Clinicobacteriological study of Pasteurella multocida as a zoonosis (1). Condition of dog and cat carriers of Pasteurella, and the influence for human carrier rate by kiss with the pets. Kansenshōgaku Zasshi J Jpn Assoc Infect Dis. 1992;66:221–4.
Marois C, Fablet C, Gaillot O, Morvan H, Madec F, Kobisch M. Molecular diversity of porcine and human isolates of Pasteurella multocida. J Appl Microbiol. 2009;107:1830–6.
Moustafa AM, Bennett MD, Edwards J, Azim K, Mesaik MA, Choudhary MI, Pathanasophon P, Worarach A, Ali Q, Abubakar M, Anjum R. Molecular typing of haemorrhagic septicaemia-associated Pasteurella multocida isolates from Pakistan and Thailand using multilocus sequence typing and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Res Vet Sci. 2013;95:986–90.
Clark CG, Kruczkiewicz P, Guan C, McCorrister SJ, Chong P, Wylie J, van Caeseele P, Tabor HA, Snarr P, Gilmour MW, Taboada EN, Westmacott GR. Evaluation of MALDI-TOF mass spectroscopy methods for determination of Escherichia coli pathotypes. J Microbiol Methods. 2013;94:180–91.
Berrazeg M, Diene SM, Drissi M, Kempf M, Richet H, Landraud L, Rolain J-M. Biotyping of multidrug-resistant klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates from France and Algeria using MALDI-TOF MS. PLoS One. 2013;8:e61428.
Khennouchi NCEH, Loucif L, Boutefnouchet N, Allag H, Rolain J-M. MALDI-TOF MS as a tool to detect a nosocomial outbreak of extended-spectrum-β-Lactamase- and ArmA methyltransferase-producing enterobacter cloacae clinical isolates in Algeria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59:6477–83.
Authors’ contributions
MB: clinical data collection and has been involved in drafting the manuscript. EH has been involved in drafting the manuscript, clinical data verification, manuscript revising. GD: microbiological data collection, dendrograms creation, manuscript revising. CC: MALDI-TOF spectra analysis, manuscript revising. PEF: microbiological data verification, manuscript revising. PS has made substantial contributions to study conception and design, clinical data verification, discussion section, manuscript revising. AS: clinical data verification, discussion section, final approval of the version to be published. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Catherine Peruffo for her assistance in acquisition of data. The authors obtained permission from Catherine Peruffo to acknowledge.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Funding
The authors have no relevant affiliations or involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest or conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Bardou, M., Honnorat, E., Dubourg, G. et al. Meningitis caused by Pasteurella multocida in a dog owner without a dog bite: clonal lineage identification by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. BMC Res Notes 8, 626 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-015-1615-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-015-1615-9