Abstract
Organophosphate and carbamate insecticides have largely been used worldwide to control mosquito populations. As a response, the same amino acid substitution in the ace-1 gene (G119S), conferring resistance to both insecticides, has been selected independently in many mosquito species. In Anopheles gambiae, it has recently been shown that the G119S mutation is actually part of homogeneous duplications that associate multiple resistance copies of the ace-1 gene. In this study, we showed that duplications of resistance copies of the ace-1 gene also exist in the Culex pipiens species complex. The number of copies is variable, and different numbers of copies are associated with different phenotypic trade-offs: we used a combination of bioassays and competition in population cages to show that having more resistance copies conferred higher resistance levels, but was also associated with higher selective disadvantage (or cost) in the absence of insecticide. These results further show the versatility of the genetic architecture of resistance to organophosphate and carbamate insecticides around the ace-1 locus and its role in fine-tuned adaptation to insecticide treatment variations.
Graphical Abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Whether for sanitary or economic (agriculture, tourism) reasons, pest and vector species have been the target of intense xenobiotic exposure to control their populations. As a response, resistances have been selected for and have spread worldwide in many diverse organisms [1,2,3]. Resistance has been the focus of many studies with a management perspective, in particular in vector species where long-term monitoring and resistance evolution surveys took place, for instance in mosquitoes ([3] and references therein). However, resistance to insecticides also provides a wealth of information for evolutionary biologists as it is an iconic example of rapid adaptation to a new environment.
Mutations conferring resistance to insecticides are adaptive in the sense that they provide greater fitness in presence of insecticide. However, in mosquitoes, most of the mutations conferring resistance described so far are also disadvantageous in the insecticide-free environment [4,5,6,7,8,9]. For instance, the mutated allele could encode for a protein that is less efficient than the susceptible one, or metabolic equilibria could be dysregulated. Both can result in strong deleterious effects [3], affecting many different life history traits (hereafter termed ‘selective disadvantage;’ see useful criticism of use of the term ‘cost’ for these selective disadvantages by Lenormand et al. [10]). Because both advantages and disadvantages can vary between resistance mutations, they convey different evolutionary trade-offs in different environments (e.g. [11, 12], in particular regarding insecticide treatment intensities [5, 13]). For instance, intermediate treatment intensities would favor heterogeneous duplications over single-copy resistance alleles, despite the fact that they confer a lower resistance level, because they are also associated with a much lower fitness cost. However, heterogeneous duplications are outcompeted by single-copy resistance alleles when selective pressure is high because of a too low resistance level [5, 7]. In a constant environment, and as time passes, new alleles, with a more favorable evolutionary trade-off, and/or compensatory mutations are expected to be selected for (e.g. [14] in Lucilia cuprina, [11, 15,16,17] in Culex pipiens species complex and [18] in Anopheles gambiae). These contemporary evolutions of insecticide resistance are thus iconic examples of adaptive trajectories (“adaptive walk” in Orr [19]). The resistance alleles selected along these adaptive walks can result from simple nucleotide substitutions (e.g. affecting the target of insecticides), but various genetic architectures can also be selected for, for instance homogeneous duplications (aka gene amplification) or heterogeneous duplications [3, 20]. Different genetic architectures of resistance can be selected for precisely because they are associated with different evolutionary trade-offs [5, 21, 22]. Finally, the variation of treatment intensities in time and/or space can also generate balancing selection patterns that could (i) allow for the maintenance of susceptible and resistance alleles polymorphism in natural populations, (ii) select for alleles with more generalist trade-offs (e.g. [9, 10, 16]), but also (iii) maintain resistance allele polymorphism [23].
Among the most commonly used families of insecticides worldwide, organophosphate (OPs) and carbamate (CXs) insecticides target acetylcholinesterase (AChE1), encoded by the ace-1 locus, which terminates cholinergic neurotransmission by hydrolysis of acetylcholine (ACh). These insecticides bind to AChE1, thereby impeding ACh degradation and inducing death by tetany. Point mutations modifying the conformation of the AChE1 active site and preventing the binding of the insecticide have been selected for in many vector and pest species. In particular, the same amino acid substitution (G119S) has been repetitively and independently selected in many mosquito species [24, 25]. While conferring resistance to OPs and CXs, the G119S mutation has also been shown to decrease the activity of the resistant acetylcholinesterase (AChE1R) by about 60% compared with the wild-type protein (AChE1S) in both the West Nile virus vector Culex pipiens sensu lato and the malaria vector An. gambiae [26, 27]. In both species, this drastic reduction in affinity with its natural subtract probably explains a large part of the selective disadvantage endured by resistant mosquitoes in absence of insecticides compared to susceptible ones [4, 7, 12, 28, 29].
In recent studies of An. gambiae, all alleles carrying the G119S mutation (R alleles) have been found to be part of homogeneous duplications (several resistance copies in tandem, Rx alleles) or of heterogeneous duplications (pairing a susceptible and a resistance copy, D alleles), i.e. they were never found in the natural population in a single-copy state [18, 22, 30].
In the C. pipiens species complex, two different R alleles have been found widely spread across natural populations [23]: R1 is found in C. pipiens sensu stricto all over Europe and the Mediterranean area, and R2 is found worldwide in Culex quinquefasciatus. They are also found in many D alleles associated with local susceptible variants [23]. However, the possibility that some R alleles could, as in An. gambiae, actually be part of homogeneous duplications, as well as what phenotypic effects these different genomic architectures could induce, has not yet been investigated in C. pipiens species complex.
In the present study, we isolated the R1 and R2 alleles in laboratory strains sharing the genetic background of the susceptible reference strain, SLAB. We first showed that, while R1 is found in a single-copy state, R2 is part of a homogeneous duplication carrying three R copies. We then investigated the phenotypes conferred by these different alleles (protein activity, resistance level and dynamics in absence of insecticides) and showed that different evolutionary trade-offs are associated with the different genomic architectures. We finally discuss the implication of the present study from both evolutionary biology and more applied perspectives.
Materials and methods
Mosquito strains
Three mosquito laboratory strains were used in this study: SLAB [31], SR [32] and SRQ (this study). SLAB is fixed for a single-copy susceptible allele (SSLAB, isolated in California, C. quinquefasciatus). SR is fixed for R1 [24], a resistance allele isolated from Southern France and found in C. pipiens s.s. all over Europe and around the Mediterranean Sea [23, 33]. SRQ is fixed for R2 [24], a resistance allele found worldwide in C. quinquefasciatus [23] and isolated from a population from Martinique Island. The two resistance alleles were introgressed into the genetic background of the SLAB strain through at least 15 rounds of back-crossing. All strains thus share the same genetic background (> 99%) and differ from each other almost only in their ace-1 locus (although recombination around the ace-1 gene is not complete, most of the background effects would be eliminated).
All strains were regularly checked for contamination: DNA was extracted from pools of first-instar larvae (~ 200 individuals per pool) and molecular tests, specific for each ace-1 allele (detailed below), were used to check the homogeneity of each strain.
Genotyping
The various strains can be easily distinguished using a single PCR and different restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs). After DNA extraction, following the protocol in [34], a ~ 600-bp fragment of the ace-1 gene, including intron 2 and most of exon 3 (with the resistance G119S mutation), was amplified using two generalist primers, Intron2dir1 and CpEx3rev, according to [35].
Susceptible vs. resistant
The G119S mutation creates an AluI restriction site [33] so that three genotypes can be distinguished (AluI RFLP test): susceptible homozygote (SS; one fragment, 597 bp), resistant homozygote (RR; two fragments, 496 and 101 bp) and heterozygote (RS; three fragments, 597, 496 and 101 bp); 5 µl of the PCR product was incubated for 2 h at 37 °C.
R1 vs. R2
The two different resistance alleles can be further distinguished by taking advantage of another single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) between R1 and R2 creating a Bfa1 restriction site in R2 (Additional File 1). This second RFLP test (Bfa1 RFLP test) distinguishes three genotypes, the homozygotes R1R1 (one fragment, 597 bp) and R2R2 (three fragments, 73, 132 and 392 bp) and the heterozygotes R1R2 (four fragments, 597, 73, 132 and 392 bp); 5 µl of the PCR product was incubated for 2 h at 37 °C.
Gene copy number quantification
ace-1 gene copy number was estimated for ten individuals of each resistant strain using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). Two individuals from the SLAB-susceptible strain were also used as controls. After DNA extraction, we dispensed 250 ng of genomic DNA and 1.5 μl of reaction mixture containing specific primers, each at a concentration of 0.8 μM and 0.75 μl of Master Mix (LightCycler 480 SYBR Green I Master, Roche), into the wells of a 384-well plate with a Labcyte Echo525 dispenser. We performed qPCR as follows: activation at 95 °C for 8 min followed by 45 cycles of 95 °C for 4 s, 67 °C for 13 s and 72 °C for 19 s. Melting curves were generated by a post-amplification melting step between 70 °C and 95 °C for Tm analysis. All quantifications were replicated three times for each DNA template. Two loci were amplified for each individual: ace-1 (primers: ‘Culexace1univdir3’ AGA AGG TGG ACG CAT GGA TG; ‘Culexace1univrev3’ ATC TGG ACG CAG GAG TTG G) and ace-2, a locus known to be in a single copy in these species (primers: ‘acequantidir’ GCA GCA CCA GTC CAA GG; ‘acequantirev’ CTT CAC GGC CGT TCA AGT AG) [36]. ace-1 over ace-2 copy-number ratios were determined by the advanced quantification method (LightCycler 480 software v.1.5.0). Standard reference curves were constructed with tenfold dilutions of a PCR product previously amplified with specific primers for each locus from SLAB DNA.
Phenotyping
Protein activity
We measured acetylcholinesterase (AChE1) activity for 48 individuals of each resistance strain, using spectrophotometry [37]. Adult mosquitoes were decapitated, and each head was individually homogenized in 400 μl of a phosphate buffer (0.25 M, pH7) supplemented with 1% Triton X-100. Homogenates were centrifuged (9.3 g for 3 min), and 100 μl of the supernatant was dispensed into each of two wells of a 96-well microtitration plate. We added 10 μl of propoxur, a carbamate insecticide, at 10−3 M and 10−1 M (diluted in ethanol) into the first and second well, respectively. The plate was incubated for 15 min at room temperature. We then added 100 μl of substrate solution (25 mM sodium phosphate, pH 7.0, 0.2 mM DTNB, 0.35 mM sodium bicarbonate, 2.5 mM acetylthiocholine) to each well. AChE1 activity was estimated by measuring the change in optical density following the cleavage of acetylthiocholine, as described by [38]. Optical density at 412 nm was recorded every minute for 15 min with an EL 800 microplate reader (Bio-Tek Instruments, Inc.). The mean slope of each reaction was calculated with KCjunior v1.41.4 analysis software (Bio-Tek Instruments, Inc.) and was used as a measurement of AChE1 activity in each well. Individual AChE1 activity was computed as the average activity between the two wells. To avoid any block or sex confounding effects, individuals from both sexes and the two strains were evenly distributed in the plates.
Resistance level and bioassays
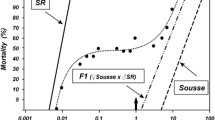
We used bioassays to assess the three strains’ resistance to an OP insecticide, temephos (PESTANAL®,96% purity). We incubated 20 late third-instar larvae for 24 h at 27 °C ± 2 °C in plastic cups containing 99 ml of distilled water to which we added 1 ml of insecticide solution at the required concentration (1 ml of ethanol in controls). Four replicates were performed for each concentration (from 0 to 0.07 g\(\upmu\).ml−1 see Additional File 2 for the complete dataset). Larval mortality was recorded after 24 h of exposure. We used the BioRssay R package (v.1.0.0 [39], https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=BioRssay) to analyze the dose-mortality responses of the different ace-1 alleles and calculate the LD50 of the different strains, i.e. the lethal dose for 50% of the sample.
Experimental evolution in population cages
Population cages were used to set up a competition experiment between the two resistance alleles in absence of insecticides. R1R1 and R2R2 individuals were crossed, and the resulting F1 (100% R1R2 individuals) was reared until adulthood under standard conditions (25 °C, > 60% humidity, 12:12 h light:dark). Adults were released into a new cage to mate freely and reproduce. Their offspring were raised and released in new cages to ensure discrete generations. The process was repeated 11 times (i.e. 11 generations) with three independent cages (i.e. replicates). Almost each generation, and for each cage, about a hundred second-instar larvae were genotyped using the Bfa1 RFLP test (see above) to measure the frequency of each genotype (R1R1, R1R2, R2R2). Allelic frequencies were then computed from genotypic frequencies.
We estimated the relative fitness of the various genotypes (R1R1, R1R2 and R2R2) using a deterministic genetic model (reproduction and selection, 11 cycles, no drift). The model was adjusted to the data and optimized using a maximum-likelihood approach as in Milesi et al. [5, 23]. For the reproduction step, the frequency of each genotype in the larvae of generation i was computed from the allelic frequencies (p) in the gametes of the previous generation, assuming panmixia (Eq. 1):
For each genotype g selection was then computed between larval and adult stages of generation i using the following genotype fitness: wR1R1 = 1, wR1R2 = 1 + h.s and wR2R2 = 1 + s, with h the dominance coefficient and s the selection coefficient, both varying between − 1 and 1 (Eq. 2):
The genotypic frequencies after selection were used to calculate the allelic frequencies in the gametes produced by the surviving adults (Eq. 3).
The first run of 100,000 simulations was used to explore the parameter space and provide the likelihood profile associated with different random pairs of h and s values (Eq. 4):
where n is the number of individuals of genotype g observed in the cages at generation i, and f is the frequency of the genotype g at generation i calculated for a given pair of h and s values using our deterministic genetic model. One million additional simulations were run with parameter ranges more limited around the maximal likelihood h and s pair to precisely estimate the coefficients and their support limits (rough equivalents to 95% confidence intervals), defined as h and s maximal and minimal values, resulting in a likelihood equal to the maximum likelihood minus 1.96, as in [5].
Statistical analyses
All the statistical analyses were conducted using the R software (R Core Team, https://www.r-project.org/):
We used the following linear model to compare ace-1 copy number between the various strains:
with \({\gamma }_{ij}\) the number of copies of the ace-1 gene in replicate i from strain j, \(\mu\) the population mean, \(\alpha\) is the fixed effect of strain j (SLAB, SR or SRQ) and \({\varepsilon }_{ij}\) the error term following a normal distribution \(\mathcal{N}(0, 1)\).
We used the following linear model to test the significance of the difference in AChE1 activity between the SR and SRQ strains:
with \({\gamma }_{ijkl}\) the AChE1 activity for individual i of strain j and sex k measured in plate l, \(\mu\) the population mean and \(\alpha\) the fixed effect of strain j (SR or SRQ). \(\beta\) and \(\delta\) are control for the fixed effects of sex k and plate l, respectively, and \({\varepsilon }_{ijkl}\) is the error term following a normal distribution \(\mathcal{N}(0, 1)\).
For both models, the significance of the various terms was tested using likelihood ratio tests (LRTs) comparing the full model with a model without the tested effect (‘anova’ function, R [40]). For both models, we also confirmed the absence of significant heteroskedasticity (‘bptest’ function, ‘lmtest’ R package [41]) and that the models’ residuals followed a normal distribution (‘shapiro.test’ function, ‘stats’ R package).
Finally, we used binomial proportion tests (‘prop.test’ function, ‘stats’ R package) to assess whether the allele frequencies at the end of the experimental evolution in cages (i.e. after 11 generations) differed from initial frequencies of 0.5 (100% R1R2 individuals).
Results and discussion
The goal of the present study was to investigate the potential existence of homogeneous duplications of the ace-1 locus in the C. pipiens species complex, similar to those found in An. gambiae, to assess the phenotypic effects of different genetic architectures and their role in adaptation to insecticides.
Higher ace-1 copy number partly restores protein activity levels
We first quantified the number of ace-1 copies in the three different strains, with the susceptible reference strain SLAB as a control. SLAB was found carrying a single-copy allele (mean = 1 ± 0.007 SD), and this was also the case for the resistant strain SR, carrying the R1 allele (mean = 1.03 ± 0.03 SD; mod. 1, t = 0.34, p = 0.74). However, we detected three copies of the ace-1 locus in the SRQ strain (mean = 3 ± 0.14 SD), indicating that the R2 allele is a homogeneous duplication (Rx), i.e. R23 allele (mod. 1, t = 25.8, p < 0.001, Fig. 1A). While several Rx alleles (aka homogeneous duplications) have recently been described in An. gambiae populations, with two to nine ace-1 copies [22, 30], this study is the first to report homogeneous duplications of the ace-1 resistance allele in mosquitoes from the C. pipiens species complex.
ace-1 copy number and resistant acetylcholinesterase activity. Left panel is the number of copies of ace-1 gene estimated using quantitative PCR for the susceptible strain, SLAB and the resistance strains SR and SRQ. Right panel shows the activity of the resistant acetylcholinesterase (AChE1R) estimated through spectrophotometry for the resistant strains SR (R1 allele, orange) and SRQ (R23 allele, blue), respectively
We then investigated whether having more ace-1 resistance copies would lead to higher activity of the resistant acetylcholinesterase (AChE1R, encoded by the R alleles). The activity AR of the resistant acetylcholinesterase was significantly higher in the SRQ strain (AR2 = 10.8 ± 1.4, three copies) than in the SR strain (AR1 = 6.3 ± 1.2; mod. 2, LRT: F = 269, df = 1, p < 0.001, Fig. 1B, Additional file 3: Table S1).
As in An. gambiae [22], it thus clearly appears that having a higher resistance copy number does increase the AChE1 protein activity. However, the protein activity did not increase in a strictly additive way with the number of copies of ace-1; R23 activity is 1.67 times higher than that of R1, not three times as was expected. In previous studies in An. gambiae and C. pipiens species complex conducted on heterogeneous duplications, D, AR was indeed found roughly proportional to the number of R copies [7, 21]. Here, the R1 and R23 alleles differ not only by their copy number but also in their ace-1 sequences (Additional file 1). As all R23 copies are identical (no variation over 3 kb of the ace-1 sequence in [23]), the departure from additivity observed could thus be explained by a lower per-copy activity for the proteins encoded by the C. quinquefasciatus R23 allele compared to the protein encoded by the C. pipiens s.s. R1 allele. Alternatively, the expression of the ace-1 gene in the SRQ strain could be somehow regulated. Finding more variation in copy number for the R2 allele, if any, would help settle this issue. For instance, in An. gambiae, for the homogeneous duplication Rx, the relation between the number of resistance copies and ACHE1R activity is not strictly additive, even though all copies are identical [22], strongly suggesting that ace-1 resistance copy expression is further regulated. Both hypotheses are not exclusive, and further studies are required to identify if and when regulation happens.
Alternative genetic architectures confer different evolutionary trade-offs
We then compared the phenotypic consequences of copy number variation at the ace-1 locus and first quantified the resistance levels associated with the different genotypes. As expected, both R1 and R23 alleles confer insecticide resistance compared with the susceptible strain (RR50 = 4.6 [3.7–5.7], 95% CI and 15 [12,13,14,15,16,17,18], respectively), but more importantly, the duplicated allele conferred a significantly higher resistance level than the single copy allele (R1/R23 resistance ratio RR50 = 3.2 [2.5–4.2], X2 = 61, df = 1, p < 0.001; Fig. 2 and Additional file 3: Table S2). We then addressed the selective disadvantages associated with the resistance alleles. Despite its obvious advantage in presence of insecticides, the SR strain was indeed repeatedly shown in previous studies to incur a strong selective disadvantage compared to SLAB in their absence (e.g. [28]). Rather than comparing both resistant strains to the susceptible one, we thus chose to directly assess whether R23 incurred a stronger or lesser disadvantage than R1 in absence of insecticide through a competition experiment in population cages: this set-up allows an integrative assessment of their relative fitness over the full life cycle and ensures that genetic background effects associated to each strain (e.g. resulting from their fixation process) are strongly reduced, as the alleles are mixed in the individuals of each generation [5].
Bioassay analysis. Probit-transformed mortality rates as a function of the log-dose of insecticide [temephos (R), an OP insecticide]. Colors and point shapes indicate the different strains. The fit from the linear model is provided (solid line) along with the 95% confidence intervals (dotted lines). The linearity of the log-responses has been checked using test.validity = T in the “mort.plot” function from the “BioRssay” R package
After 11 generations of direct competition, the frequency of the R1 allele rose significantly, from 0.5 to ~ 0.63 in all three replicates, out-competing the R23 duplicated allele (binomial test, all p < 0.004, Fig. 3A). To quantitatively estimate the fitness of the different genotypes, we then adjusted a model of reproduction-selection to the temporal genotypic data: we found that the heterozygous genotype (R1/R23) conferred the highest fitness (wR1R2 = 1.23 [1.14–1.21] support limits) and that the R1/R1 genotype (wR1R1 = 1) had much higher fitness than R23/R23 (0.62 [0.56–0.68], Fig. 3 and Additional file 3: Fig. S1).
Dynamics of the resistance alleles and selection coefficients estimations. Left panel represents the dynamics of the R1 allele (SR strain) frequency (± SD) over generations, in competition with the R2 allele (SRQ strain) in absence of insecticide (the dots of the 3 replicates are slightly offset for easier reading). The R1 allele dynamics predicted by the maximum likelihood fit of the reproduction-selection model is in red. Right panel represents the relative fitnesses along with their corresponding support limits (≈ 95% confidence intervals) of the different genotypes (R1R1 was used as the reference, hence fixed to 1), estimated through a maximum likelihood approach for the parameters’ values in the reproduction-selection model (see methods)
The strong fitness reduction incurred by resistant mosquitoes is thought to be associated with multiple pleiotropic deleterious effects, affecting many different life history traits, because of the reduced activity of the AChE1R [4, 7, 12, 28, 29, 42]. Accordingly, D alleles are thought to be selected because they reduce these deleterious effects by pairing a resistance copy (R, low AChE1 activity) and a susceptible copy (S, high AChE1 activity) in a heterogeneous duplication, thereby partly restoring the AChE1 activity to levels closer to those of susceptible alleles [21, 22]. However, the case of the homogeneous duplication Rx is less clear: we show in the present study that despite a higher global activity for R23 compared to R1, the former allele induces higher selective disadvantages (Fig. 3), which is also what was observed for R5 vs R3 alleles in An. gambiae [22].
The less-than-strictly-additive AChE1R activity for the R23 allele suggests that some deleterious effects could be associated with specific resistance alleles, potentially resulting from background deleterious mutations in the gene or its vicinity in the haplotype where the resistance mutation occurred. The fact that R23/R1 heterozygotes appear to incur a higher fitness than both homozygotes supports this hypothesis (Fig. 3): if both alleles are weighted by linked deleterious mutations, they can complement each other, i.e. if they are different between the two alleles, the heterozygote would incur a higher fitness (a similar explanation has been proposed for the complementation of strongly deleterious D alleles in C. pipiens s.l. [17, 23].). However, the overall activity remains higher for this allele compared to R1 (Fig. 1), and in An. gambiae it is the same ace-1 sequence that is present in five or three copies [22]. It thus suggests that the architecture itself, i.e. the mere fact of carrying more copies, induces selective disadvantages. This structural “cost” could result from deleterious mutations trapped into the amplicons, from the breakpoints of the duplication being located in functional regions or from dosage imbalance for other genes embedded in the duplicated alleles that might disrupt biochemical equilibrium, as previously proposed [22, 23, 35]. Though none of these hypotheses are exclusive, the latter has been favored in the case of An. gambiae duplications: in this species, a ~ 200-kb amplicon encompassing 11 genes in addition to ace-1 has been described, and a variant with a deletion of these other genes appears to be favored by selection in natural populations, probably because the deletion restores the gene balances [18]. Note that deleterious mutations in these closely linked genes could also explain the higher fitness of R23/R1 heterozygotes (Fig. 3). There is thus a strong incentive to characterize the genomic structure of the ace-1 duplications (either heterogeneous or homogeneous) in C. pipiens species complex too.
To summarize, the two ace-1 R alleles present different evolutionary trade-offs: while having a higher copy number of resistance allele confers a higher resistance level, and thus higher selective advantage in presence of OP and CX insecticides, it is also associated with higher selective disadvantages, revealed in absence of insecticide. Although the mutations occurred independently in the different species, the same relationships among R copy number, resistance level and selective disadvantages have been described in An. gambiae [22]. Similarly, the R23 duplicated allele would likely tend to be selected for in areas of intense selective pressure, its higher resistance surpassing its higher disadvantages, while the R1 single-copy allele would be favored in areas with more moderate intensity of treatment. This can reflect the ecology of the mosquito populations where these alleles were found: in the tropical areas where R23 was found, C. quinquefasciatus is the year-long vector of several viruses and thus probably subjected to more intense and regular treatments than in the Mediterranean area where R1 is found and where C. pipiens s.s. is less a vector than a summer nuisance (the female diapauses in winter). The genotyping of natural populations to look specifically for the presence of Rx homogeneous duplications of the ace-1 locus could confirm this hypothesis. It would also allow us to understand whether the number of copies is as variable as in An. gambiae (at least up to 6 copies [22]), whether the Rx alleles are only found in C. quinquefasciatus or are also found in C. pipiens s.s. and, if so, if they are found in populations experiencing higher treatment intensities. Finally, the recurrent selection of homogeneous duplications of the ace-1 resistance copies in phylogenetically distant species complexes (e.g. in Anopheles [18, 22, 30] and in Culex, this study), along with the high diversity of heterogeneous duplications already described in both species [7, 17, 23, 30, 35, 43,44,45], provides further support for a very high duplication rate of the ace-1 loci. It also highlights the versatility of adaptive responses that can result from such structural variants (i.e. as opposed to simple SNP): from a more quantitative resistance advantage resulting, at least in part, from the increased amount of protein produced for the homogeneous duplications (as also seen for metabolic resistances like esterases or P450 monooxygenases [46]) to a more qualitative advantage for the heterogeneous duplications that allow the fixation of a heterozygote advantage selected in more variable environments [5, 23]. Note however that the recurrent selection of architectures such as homogeneous duplications in distant lineages calls for more functional research to understand how producing more AChE1R proteins leads to higher resistance levels.
Conclusion
In C. pipiens species complex many different genetic architectures encompassing the ace-1 locus exist for resistance to OPs and CXs insecticides, which are each associated with a different evolutionary trade-off: the single-copy resistance allele provides resistance but is associated with a high selective disadvantage in absence of insecticides, while homogeneous duplications provide even higher resistance levels but are associated with higher selective disadvantages. Not only different genetic architectures could represent various steps along an adaptive walk, but there also are many ways to answer to the various intensities of selective pressure. While inspiring from an evolutionary perspective, the vector management view is clearly worrying, as this ‘toolbox’ allows mosquito populations to finely and quickly adjust to local treatment strategies in natural populations (particularly if one considers the various heterozygous combinations between the different alleles), which definitely represents a hindrance to vector control policies.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files: “Additional file 2.”
References
Georghiou GP. The evolution of resistance to pesticides. Annu Rev Ecol Syst. 1972. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.es.03.110172.001025.
Coleman M, Hemingway J, Gleave KA, Wiebe A, Gething PW, Moyes CL. Developing global maps of insecticide resistance risk to improve vector control. Malar J. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-017-1733-z.
Labbé P, David J-P, Alout H, Milesi P, Djogbénou L, Pasteur N, et al. 14 - Evolution of resistance to insecticide in disease vectors. In: tibayrenc MBT-G and E of ID Second E editor. London: Elsevier 2017 313–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-799942-5.00014-7.
Duron O, Labbé P, Berticat C, Rousset F, Guillot S, Raymond M, et al. High Wolbachia density correlates with cost of infection for insecticide resistant Culex pipiens mosquitoes. Evolution. 2006;60:303–14.
Milesi P, Weill M, Lenormand T, Labbé P. Heterogeneous gene duplications can be adaptive because they permanently associate overdominant alleles. Evol Lett. 2017;1:169–80.
Berticat C, Bonnet J, Duchon S, Agnew P, Weill M, Corbel V. Costs and benefits of multiple resistance to insecticides for Culex quinquefasciatus mosquitoes. BMC Evol Biol. 2008;8:104.
Assogba BS, Djogbénou LS, Milesi P, Berthomieu A, Perez J, Ayala D, et al. An ace-1 gene duplication resorbs the fitness cost associated with resistance in Anopheles gambiae, the main malaria mosquito. Sci Rep. 2015;5:1–12.
Tantely ML, Tortosa P, Alout H, Berticat C, Berthomieu A, Rutee A, et al. Insecticide resistance in Culex pipiens quinquefasciatus and aedes albopictus mosquitoes from La Réunion Island. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2010;40:317–24.
Ffrench-Constant RH, Steichen JC, Rocheleau TA, Aronstein K, Roush RT. A single-amino acid substitution in a gamma-aminobutyric acid subtype a receptor locus is associated with cyclodiene insecticide resistance in drosophila populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:1957–61.
Lenormand T, Harmand N, Gallet R. Cost of resistance: an unreasonably expensive concept. Rethink Ecol. 2018;3:51–70.
Labbé P, Sidos N, Raymond M, Lenormand T. Resistance gene replacement in the mosquito Culex pipiens: fitness estimation from long-term cline series. Genetics. 2009;182:303–12.
Lenormand T, Bourguet D, Guillemaud T, Raymond M. Tracking the evolution of insecticide resistance in the mosquito Culex pipiens. Nature. 1999;400:861–4.
Milesi P, Lenormand T, Lagneau C, Myl E. Relating fitness to long-term environmental variations in natura. Mol Ecol. 2016;21:5483–99.
Clarke GM. The genetic and molecular basis of developmental stability: The Lucilia story. Trends Ecol Evol. 1997;12:89–91.
Guillemaud T, Lenormand T, Bourguet D, Chevillon C, Pasteur N, Raymond M. Evolution of resistance in Culex pipiens : allele replacement and changing environment. Evolution. 1998;52:443–53.
Lenormand T, Guillemaud T, Bourguet D, Raymond M. Appearance and sweep of a gene duplication: adaptive response and potential for new functions in the mosquito Culex pipiens. Evolution. 1998;52:1705–12.
Labbé P, Berticat C, Berthomieu A, Unal S, Bernard C, Weill M, et al. Forty years of erratic insecticide resistance evolution in the mosquito Culex pipiens. PLoS Genet. 2007;3:e205.
Assogba BS, Alout H, Koffi A, Penetier C, Djogbénou LS, Makoundou P, et al. Adaptive deletion in resistance gene duplications in the malaria vector anopheles gambiae. Evol Appl. 2018;11:1245–56. https://doi.org/10.1111/eva.12619.
Orr HAA. The population genetics of adaptation: the distribution of factors fixed during adaptive evolution. Evolution. 1998;52:935–49.
Heckel DG. Perspectives on gene copy number variation and pesticide resistance. Pest Manag Sci. 2022;78:12–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.6631.
Labbé P, Milesi P, Yébakima A, Pasteur N, Weill M, Lenormand T. Gene-dosage effects on fitness in recent adaptive duplications: ace-1 in the mosquito Culex pipiens. Evolution. 2014;68:2092–101.
Assogba BS, Milesi P, Djogbénou LS, Berthomieu A, Makoundou P, Baba-Moussa LS, et al. The ace-1 locus is amplified in all resistant Anopheles gambiae mosquitoes: fitness consequences of homogeneous and heterogeneous duplications. PLOS Biol. 2016;14:e2000618.
Milesi P, Assogba BS, Atyame CM, Pocquet N, Berthomieu A, Unal S, et al. The evolutionary fate of heterogeneous gene duplications: a precarious overdominant equilibrium between environment, sublethality and complementation. Mol Ecol. 2018;27:493–507.
Weill M, Lutfalla G, Mogensen K, Chandre F, Berthomieu A, Berticat C, et al. Insecticide resistance in mosquito vectors. Nature. 2003;423:423–6.
Weill M, Berthomieu A, Berticat C, Lutfalla G, Nègre V, Pasteur N, et al. Insecticide resistance: a silent base prediction. Curr Biol. 2004;14:R552-3.
Bourguet D, Roig A, Toutant JP, Arpagaus M. Analysis of molecular forms and pharmacological properties of acetylcholinesterase in several mosquito species. Neurochem Int. 1997;31:65–72.
Alout H, Djogbénou L, Berticat C, Chandre F, Weill M. Comparison of Anopheles gambiae and Culex pipiens acetycholinesterase 1 biochemical properties. Comp Biochem Physiol B-Biochemistry Mol Biol. 2008;150:271–7.
Bourguet D, Guillemaud T, Chevillon C, Raymond M. Fitness costs of insecticide resistance in natural breeding sites of the mosquito Culex pipiens. Evolution. 2004;58:128–35.
Djogbénou L, Noel V, Agnew P. Costs of insensitive acetylcholinesterase insecticide resistance for the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae homozygous for the G119S mutation. Malar J. 2010;9:12.
Grau-Bové X, Lucas E, Pipini D, Rippon E, van Hof’t AE, Constant E, et al. Resistance to pirimiphos-methyl in West African Anopheles is spreading via duplication and introgression of the Ace1 locus. PLOS Genet. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1009253.
Georghiou GP, Metcalf RL, Gidden FE. Carbamate-resistance in mosquitos Selection of Culex pipiens fatigans Wiedemann (C quinquefasciatus say) for resistance to Baygon. Bull World Health Organ. 1966;35:691–708.
Berticat C, Boquien G, Raymond M, Chevillon C. Insecticide resistance genes induce a mating competition cost in Culex pipiens mosquitoes. Genet Res. 2002;79:41–7.
Alout H, Weill M. Amino-acid substitutions in acetylcholinesterase 1 involved in insecticide resistance in mosquitoes. Chem Biol Interact. 2008;175:138–41.
Roger SO, Bendich AJ. Extraction of DNA from plant tissues. In: Gelvin SB, Schilperoort RA, editors. Plant Molecular Biology Manual. Cambridge: Academic Publishers; 1988.
Labbé P, Berthomieu A, Berticat C, Alout H, Raymond M, Lenormand T, et al. Independent duplications of the acetylcholinesterase gene conferring insecticide resistance in the mosquito Culex pipiens. Mol Biol Evol. 2007;24:1056–67.
Weill M, Berticat C, Raymond M, Chevillon C. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction to estimate the number of amplified esterase genes in insecticide-resistant mosquitoes. Anal Biochem. 2000;285:267–70.
Bourguet D, Pasteur N, Bisset J, Raymond M. Determination of Ace 1 genotypes in single mosquitoes : toward an ecumenical biochemical test. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 1996;55:122–8.
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Featherstone RM. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1961;7:88–95.
Karunarathne P, Pocquet N, Labbé P, Milesi P. BioRssay: an R package for analyses of bioassays and probit graphs. Parasit Vectors. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-021-05146-x.
Crawley MJ. The R book. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.; 2007.
Zeileis A, Hothorn T. Diagnostic checking in regression relationships. R News. 2002;2:7–10.
Berticat C, Duron O, Heyse D, Raymond M. Insecticide resistance genes confer a predation cost on mosquitoes. Culex pipiens Genet Res. 2004;83:189–96.
Liebman KA, Pinto J, Valle J, Palomino M, Vizcaino L, Brogdon W, et al. Novel mutations on the ace-1 gene of the malaria vector Anopheles albimanus provide evidence for balancing selection in an area of high insecticide resistance in Peru. Malar J. 2015;14:1–10.
Alout H, Labbé P, Pasteur N, Weill M. High incidence of ace-1 duplicated haplotypes in resistant Culex pipiens mosquitoes from Algeria. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2011;41:29–35.
Osta MAMMA, Rizk ZZJ, Labbé P, Weill M, Knio K. Insecticide resistance to organophosphates in Culex pipiens complex from Lebanon. Parasit Vectors. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-5-132.
Dang K, Doggett SL, Veera Singham G, Lee C-Y. Insecticide resistance and resistance mechanisms in bed bugs, Cimex spp. (Hemiptera: Cimicidae). Parasit Vectors. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-017-2232-3.
Acknowledgements
We thank Patrick Makoundou for his technical help. The computations were enabled by resources in project SNIC 2022/22-23 provided by the Swedish National Infrastructure for Computing (SNIC) at UPPMAX, partially funded by the Swedish Research Council through grant agreement no. 2018-05973.
Funding
Open access funding provided by Uppsala University. This work was funded by the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR) ArchR project (ANR-20-CE34-0007) and PL’s grant from the Institut Universitaire de France (IUF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PL, PM and MW designed the study. JLC and SU performed the experiments. JC and PM analyzed the data. PM wrote the first draft of the manuscript and received input from all authors. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1:
Sequence alignment for R1 (SR) and R2 (SRQ). The primers used for the PCR amplification are indicated (light gray) as well as the restriction sites for the BfaI and AluI enzymes (darker gray, the triangles indicate restriction cuts). Mutations between the two sequences are in bold.
Additional file 2
. This file basically contains all the raw data supporting each analysis.
Additional file 3: Table S1
. Analysis of variance of model 1. Table S2. Bioassay analyses. Figure S1. Reproduction-selection model likelihood profiles.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Milesi, P., Claret, JL., Unal, S. et al. Evolutionary trade-offs associated with copy number variations in resistance alleles in Culex pipiens mosquitoes. Parasites Vectors 15, 484 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-022-05599-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-022-05599-8