Abstract
Background
Investigation of insecticide resistance mechanisms is considered a vital first step towards the creation of effective strategies to control resistant mosquitoes and manage mosquito-borne diseases. Our previous study revealed that NYD-OP7 may be associated with deltamethrin resistance in Culex pipiens pallen. However, the precise function of NYD-OP7 in deltamethrin resistance is still unclear. In this study, we investigated the role of NYD-OP7 in the molecular mechanisms underlying pyrethroid resistance.
Results
Knockdown of NYD-OP7 not only increased the susceptibility of the mosquitoes to deltamethrin in vivo but also simultaneously repressed both expression and enzyme activity of its downstream effector molecule, phospholipase C (PLC) and expression of several insecticide resistance-related P450 genes. Knockdown of PLC also sensitized the mosquitoes to deltamethrin and reduced the expression of the P450 genes.
Conclusions
Our results revealed that NYD-OP7 and its downstream effector PLC contribute to deltamethrin resistance by regulating the expression of P450s in Cx. pipiens pallens.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Mosquitoes can transmit numerous serious infectious diseases, such as malaria, dengue fever, Zika, West Nile fever, chikungunya, yellow fever, Rift Valley fever, La Crosse encephalitis, Japanese encephalitis and filariasis [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. Chemical insecticides are one of the mainstay strategies for the control of mosquito vectors. Unfortunately, the heavy reliance on pesticide has led to the development of resistance in vectors, making insecticide use ineffective [11]. Resistance to insecticides has been reported in many mosquito species, implicating a major obstacle for the control of vector-borne diseases [12,13,14].
Many studies have indicated that insecticide resistance is actually a complex phenotype of polygenic inheritance phenomenon [15,16,17,18,19]. To date, three major mechanisms are responsible for insecticide resistance in mosquitoes: alterations in the target sites, increased metabolic detoxification, and reduced cuticular penetration [20,21,22]. In addition, many genes that are not associated with the above-mentioned mechanisms may be involved in insecticide resistance. For example, several Anopheles gambiae genes, such as sodium/calcium exchanger, peptidases, and genes responsible for lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, were highly expressed in an insecticide-resistant strain [16]. The upregulation of protease genes were also observed in pyrethroid resistant Cx. quinquefasciatus [23]. A previous study in our laboratory also identified several differentially expressed genes, such as arrestin, glycogen branching enzyme or prophenoloxidase gene, between the deltamethrin-susceptible (DS) strain and deltamethrin-resistant (DR) strain in Cx. pipiens pallens [24,25,26]. However, the potential roles of these genes in the development of the resistance phenotype are unclear. Further functional characterizations are needed to help in understanding the relationships between these genes and resistance processes.
Opsins, which belong to the G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily, are primarily involved in the visual signaling cascade [27]. In invertebrates, activation of the downstream effector molecule phospholipase C (PLC) is critical in the phototransduction cascades [28]. Previous studies have indicated that GPCR members have broader and more diverse functions than as light sensors in animals. For example, OPN3 is an asthma susceptibility gene that plays a role in immune modulation [29]. Rhodopsin may serve as the ATP-independent phospholipid flippase [30]. UV-sensitive and blue color-sensitive opsins were found to be overexpressed in DDT-resistant Drosophila, suggesting opsins may be associated with insecticide resistance [31]. The GPCR signaling pathway can regulate resistance-related P450 genes in Cx. quinquefasciatus [32].
In our previous study, suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH) analysis revealed that NYD-OP7 (GenBank: AY749413), which belongs to the invertebrate Gq-coupled opsin subfamily, was overexpressed at the transcriptional level in the laboratory-selected DR strain of Cx. pipiens pallens [33]. Furthermore, the overexpression of NYD-OP7 increased the resistance of Aedes albopictus C6/36 cells to deltamethrin in vitro [34]. Although these results suggest NYD-OP7 is associated with deltamethrin resistance, there are still many unanswered questions regarding the functions of NYD-OP7 in the development of the resistance. In particular, the mechanism underlying the regulation of insecticide resistance by NYD-OP7 needs to be elucidated.
In this study, the expression levels of NYD-OP7 in the laboratory DS and DR strains of Cx. pipiens pallens were detected using western blotting, and our previous SSH and quantitative real-time (qPCR) analyses results were validated. The roles of NYD-OP7 and its downstream effector molecule PLC on insecticide resistance were also preliminarily investigated in vivo.
Methods
Mosquito strains
In this study, two laboratory strains of Cx. pipiens pallens were used. In 2010, the DS strain [50% lethal concentration (LC50) = 0.01 ppm] was obtained from the Jiangsu Institute of Parasitic Diseases in Wuxi (Jiangsu Province, China) and then maintained in our laboratory without exposure to any insecticides. The DR strain was selected from the early fourth-instar larvae of the DS strain with deltamethrin. Before selection, LC50 was determined using a larval bioassay and then used as the selection concentration. Finally, 58 generations of the DR strain were reared with an LC50 of 7.3 ppm. The mosquitoes were maintained at 28 °C, 70–80% relative humidity, and a constant light/dark photoperiod (16/8 h).
RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis
Total RNA was extracted from 5 female mosquitoes from each group by using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The integrity of the isolated total RNA was assessed using 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. The purity and concentration were checked with a spectrophotometer (NanoDrop, Wilmington, DE, USA). The RNA was used for cDNA synthesis only if the gel electrophoresis showed clear bands of 28S and 18S and the ratio of OD260/OD280 was within the range between 1.8 and 2.0 [35, 36]. cDNA was synthesized from 500 ng of total RNA by using the PrimeScriptRT Reagent Kit (TaKaRa, Tokyo, Japan), according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
qPCR analysis
qPCR was performed using the LightCycler® 96 Instrument (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) with Power SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (Applied Biosystems, Foster, USA), according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The reaction volume (20 μl) contained the Power SYBR Green PCR Master Mix, specific forward and reverse primers (Additional file 1: Table S1) and diluted cDNA. The PCR conditions were as follows: 50 °C for 2 min and 95 °C for 10 min, followed by 40 cycles at 95 °C for 15 s and 60 °C for 1 min. Both melting curve analysis and gel electrophoresis of the amplification products were performed to confirm that the primers amplified only a single product of the expected size. In addition, the qPCR products were sequenced for confirmation. The raw threshold cycle (Ct) values were used to quantify the target gene expression for each sample. The relative expression levels were normalized to the internal control β-actin by using the 2−ΔΔCt method [37]: target gene /β-actin = 2ΔCt, ΔCt = Ctβ-actin − Cttarget gene. Three technical and biological replicates were performed for qPCR analyses.
Preparation of NYD-OP7 antibody
The amino acid sequence of NYD-OP7 was submitted to the BepiPred 1.0 server (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/BepiPred/), and the epitope (CVASGATTASDEKA) was predicted. The peptide of 14 amino acids was chemically synthesized and used as an immunogen to immunize 2 female New Zealand white rabbits. Before inoculation, the 2 rabbits were bled to obtain 30 to 50 ml of preimmune serum as the negative control. The primary immunization consisted of 1000 μl of the immunogen [1 μg/μl, dissolved in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)] mixed with an equal volume of Freund’s complete adjuvant. For the subsequent immunizations, 500 μl of the immunogen (1 μg/μl, dissolved in PBS) was mixed with an equal volume of Freund’s incomplete adjuvant. After 4 immunizations, the antiserum was harvested and subjected to affinity purification (SAB Biotech, Nanjing, China). The sensitivity of the developed NYD-OP7 antibody was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA, ELISA > 1:128,000). We checked the specificity of the antibody by western blot, which showed only one band and the same molecular weight as the target protein.
Western blot analysis
Proteins were extracted from the DS and DR strains of Cx. pipiens pallens with the RIPA lysis buffer (Beyotime, Shanghai, China) containing the protease inhibitor PMSF, according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The concentrations were determined using the BCA Protein Assay Kit (Pierce, Rockford, USA). Up to 40 μg of protein per lane was used for performing sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) with 12% gels. SDS-PAGE was performed at 80 V for 30 min and 120 V for 80 min. The proteins were then transferred to a polyvinylidene fluoride membrane for 40 min at 300 mA by using the Trans-Blot SD Cell and Systems (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). NYD-OP7 was detected using the prepared polyclonal antibody (1:1000) at 4 °C overnight and horseradish peroxidase–conjugated goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody (1:2000, Beyotime) for 2 h at 28 °C. The anti-tubulin monoclonal antibody (1:1000; CW Biotech, Beijing, China) was used as the internal control [24]. Chemiluminescence was detected using BeyoECL Plus (Pierce), according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Microinjection
The dsRNA of NYD-OP7 (dsNYD-OP7), siRNA of PLC (siPLC), and negative control (NC) were designed and synthesized by GenePharma (Shanghai, China; Additional file 2: Table S2). NC is a sequence generated from a nematode which showed no homology compared to mosquitoes. Two controls were used: an equivalent volume of DEPC water or NC. The microinjection experiment was performed using day 1 post-emergence female mosquitoes. About 360 ng of dsNYD-OP7, 364 ng of siPLC, or 350 ng of NC were injected into the side of the protocoel of the female mosquitoes with a microinjector (Drummond’s Nanoject II, # 3-000-205A, Pennsylvania, USA) attached to 3.5" needles (Drummond Scientific Company, # 3-000-203-G/X). Then, the mosquitoes were maintained in the insectary at 28 °C and a constant light/dark photoperiod (16/8 h) with 70–80% relative humidity. Three days post-injection, gene silencing efficiency on random selected mosquitoes was determined using qPCR, and the remaining mosquitoes were then selected for subsequent experiments.
CDC bottle bioassay
The resistance of the mosquitoes to insecticides was detected using the CDC bottle bioassay. The diagnostic dose used in the present study was determined using the calibration assay (http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/education_training/lab/bottlebioassay.html). In each bottle, 20 adult female mosquitoes were exposed to deltamethrin, and a bottle coated with acetone was used as the control. The final concentration of deltamethrin was 7.5 mg/ml. The numbers of dead and alive mosquitoes were recorded at 15 min intervals for 2 h (15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90, 105 and 120 min) or until all the mosquitoes died. The mosquitoes were considered dead if they could not fly or maintain an upright posture on the surface of the bottle. The total percentage mortality against time was calculated for all the replicates. The experiment was repeated 3 times.
PLC enzyme activity assay
PLC enzyme activity was analyzed in the dsNYD-OP7, siPLC, NC, and DEPC groups. Non-blood-fed female adult mosquitoes were rinsed 3 times with ddH2O to remove food particles and molted skin. PLC enzyme activity of the mosquitoes was detected using the tissue phospholipase C activity of continuous circulation colorimetric assay kit (Genmed Scientifics Inc., Wilmington, USA), according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The protein content in the supernatant was measured using the Enhanced BCA Protein Assay Kit (Beyotime). Each group was composed of 25 mosquitoes, and all the assays were performed in duplicate.
Statistical analysis
The data were analyzed using Student’s t-test and Chi-square test. A P-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All results were presented as mean and SEM values of 3 independent experiments.
Results
NYD-OP7 is differentially expressed in a DR strain of Cx. pipiens pallens
Expression of NYD-OP7 in the DS and DR strains of Cx. pipiens pallens were analyzed using western blotting. The level of NYD-OP7 expression in the DR strain was 2.2-fold higher than that in the DS strain (Fig. 1a, b). This finding further strengthened the evidence linking the overexpression of NYD-OP7 with deltamethrin resistance.
Identification of NYD-OP7 in the deltamethrin-susceptible (DS) and deltamethrin-resistant (DR) strains of Culex pipiens pallens. a Western blot analysis of NYD-OP7 in the DS and DR strains of Cx. pipiens pallens. The amounts of samples loaded were monitored by determining tubulin. b NYD-OP7 expression in the DR strain was about 2.2-fold higher than that in the DS strain at the protein level. The intensity of the protein band was normalized with tubulin band intensity in each corresponding lane
Role of NYD-OP7 in deltamethrin resistance
To identify the effects of NYD-OP7 on deltamethrin resistance, we injected dsNYD-OP7 into the DR strain. qPCR showed that the knockdown efficiency of NYD-OP7 was 45% when compared with the NC group (Fig. 2a). On the basis of the results of the CDC bottle bioassay, the group injected with dsNYD-OP7 showed a higher mortality rate compared to the NC group at 75, 90, 105 and 120 min, suggesting that knockdown of NYD-OP7 can sensitize mosquitoes to deltamethrin (Fig. 2b).
To clarify how NYD-OP7 plays a role in deltamethrin resistance, we tested changes in the expression and enzyme activity of its downstream effector PLC. The expression and enzyme activity of PLC decreased by 52% and 65%, respectively, in the dsNYD-OP7 group when compared to the NC group (Fig. 3a, b).
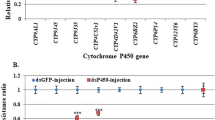
Since the GPCR signaling pathway can regulate P450 genes, which are strongly associated with the enhanced metabolic detoxification of insecticides, we also investigated the expression levels of a number of P450 genes. The qPCR results revealed a significant decrease in the expression levels of 5 P450 genes (CYP4G15, CYP9AL1, CYP9J39, CYP9J40, and CYP9J43) in the dsNYD-OP7 group when compared with the control (Fig. 4). Thus, our results indicate that the NYD-OP7/PLC regulatory signaling pathway, which governs P450 gene expression, may play a role in the regulation of resistance to deltamethrin in mosquitoes.
Expression levels of the P450 genes after injection of dsNYD-OP7. a Expression levels of CYP4G15 after dsNYD-OP7 injection. b Expression levels of CYP6BB4 after dsNYD-OP7 injection. c Expression levels of CYP6AA7 after dsNYD-OP7 injection. d Expression levels of CYP9AL1 after dsNYD-OP7 injection. e Expression levels of CYP9J39 after dsNYD-OP7 injection. f Expression levels of CYP9J40 after dsNYD-OP7 injection. g Expression levels of CYP9J43 after dsNYD-OP7 injection
Role of PLC in deltamethrin resistance
To confirm our hypothesis that the NYD-OP7/PLC regulatory signaling pathway is involved in deltamethrin resistance, we performed the knockdown of PLC. The qPCR results showed that the knockdown efficiency of PLC was 59% when compared with the control group (Fig. 5a). Moreover, the enzymatic activity of PLC in the siPLC group decreased by 62% (Fig. 5b). The CDC bottle bioassay showed the mortality rate of the siPLC group increased significantly at 90, 105 and 120 min (Fig. 5c), functionally confirming the involvement of PLC in deltamethrin resistance. Further examination of P450 expression in the siPLC group revealed reduced expression of CYP4G15, CYP9AL1, CYP9J39, and CYP9J43 (Fig. 6). However, inhibition of PLC had no effect on the expression of CYP9J40. Collectively, these results suggest that NYD-OP7 and its downstream effector PLC contribute to deltamethrin resistance by regulating the expression of P450s.
Expression levels of the P450 genes after injection of siPLC. a Expression levels of CYP4G15 after siPLC injection. b Expression levels of CYP9AL1 after siPLC injection. c Expression levels of CYP9J39 after siPLC injection. d Expression levels of CYP9J40 after siPLC injection. e Expression levels of CYP9J43 after siPLC injection
Discussion
Many diverse proteins with multiple functions are being identified. Opsin, which belong to a class of multifunctional proteins, has the roles of photoreceptor and the phospholipid flippase in human beings [30]. Our previous studies showed that NYD-OP7, which belongs to the GPCR family, may be involved in the development of insecticide resistance in Cx. pipiens pallens [34]. However, the exact mechanism is still unclear. Given the critical functions of the GPCR family in many essential biological and physiological processes, GPCRs have already been used as important targets for therapeutic interventions and provide a novel means of medical treatment for humans [38]. In insects, the GPCR signal transduction system has been shown to affect behavior, reproduction, osmoregulation, development and metabolism [39,40,41]. Moreover, recent studies have indicated that GPCRs could mediate insecticide resistance and provide opportunities for identifying new targets or vector control [32, 42]. Thus, a better understanding of the detailed role of NYD-OP7 and its signaling pathway in insecticide resistance would be helpful for the management and the control of mosquito-borne diseases.
In invertebrates, NYD-OP7 is a member of the Gq-coupled opsin subfamily, and an important step of the Gq-GPCR-mediated phototransduction pathway is activation of PLC [43]. In this study, knockdown of NYD-OP7 resulted in a simultaneous reduction in the mRNA transcriptional levels and enzyme activity of PLC in Cx. pipiens pallens. Furthermore, knockdown of NYD-OP7 or PLC resulted in decreased levels of resistance to deltamethrin in the mosquitoes. These findings suggest the potential role of the NYD-OP7/PLC signaling pathway in insecticide resistance in Cx. pipiens pallens.
P450s, which are phase I detoxification enzymes, are involved in the catabolism and anabolism of a diverse array of endogenous and xenobiotic compounds, such as insecticides [44]. The GPCR-mediated signaling pathway has been considered as a general regulatory factor for the expression of P450s in mosquitoes [32]. Thus, we hypothesized that the NYD-OP7/PLC signaling pathway may play a role in insecticide resistance through the regulation of the expression of P450 genes. To test our hypothesis, we examined the expression of P450 genes in dsNYD-OP7-injected mosquitoes and found that 5 P450 genes were downregulated after the knockdown of NYD-OP7. Knockdown of PLC decreased the expression of four P450 genes (one gene belongs to the CYP4 family and the other three genes belong to the CYP9 family). In insects, members of the CYP4 and CYP9 families have been associated with xenobiotic metabolism and play important roles in insecticide resistance [45,46,47]. Thus, our findings provide evidence that the NYD-OP7/PLC signaling pathway is involved in the development of resistance to deltamethrin in Cx. pipiens pallens by regulating the expression of the resistance-related P450 genes.
To date, the regulatory mechanisms of P450s are unclear. The expression of the resistance-related P450s is regulated by a variety of genetic and epigenetic factors. Our results revealed the role of the NYD-OP7/PLC signaling pathway in the regulation of P450 gene expression in mosquitoes. It is worth noting that CYP9J40 was regulated only by NYD-OP7, and its expression was not influenced by PLC. One explanation could be that the GPCR-mediated signaling pathway and its regulation of P450 expression is a complex network. PLC is not the only downstream effector regulated by NYD-OP7. Other downstream components may interact with NYD-OP7 to regulate other P450s.
In conclusion, our study demonstrates that the NYD-OP7 and its downstream effector PLC signaling pathway contribute to deltamethrin resistance by regulating the expression of P450 genes in Cx. pipiens pallens, which provides novel insights into the role of the GPCR signaling pathway in insecticide resistance. Our results also offer a reference for further studies on the regulation of the P450 genes in mosquitoes and other insect species.
Conclusions
In this study, we investigated the roles of NYD-OP7, which showed higher expression in the laboratory-selected DR strain of Cx. pipiens pallens. Depletion of NYD-OP7 by RNAi not only increased the susceptibility of the mosquitoes to deltamethrin but also simultaneously repressed both activity and expression of the downstream effector molecule, PLC, and expression of several insecticide resistance-related P450 genes. Knockdown of PLC also sensitized the mosquitoes to deltamethrin and reduced the expression of the P450 genes. These results show that NYD-OP7 and its downstream effector PLC play significant roles in pyrethroid resistance.
Abbreviations
- P450:
-
Cytochrome P450
- DR:
-
Deltamethrin-resistant
- DS:
-
Deltamethrin-susceptible
- PLC:
-
Phospholipase C
- GPCR:
-
G-protein-coupled receptor
- DDT:
-
Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane
- SSH:
-
Suppression subtractive hybridization
- qPCR:
-
Quantitative real-time PCR
- LC50:
-
50% lethal concentration
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- NC:
-
Negative control
- DEPC:
-
Diethyl pyrocarbonate
- OPN3 :
-
Opsin3
- PMSF:
-
Phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride
- SEM:
-
Standard error of the mean
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
References
White MT, Griffin JT, Churcher TS, Ferguson NM, Basanez MG, Ghani AC. Modelling the impact of vector control interventions on Anopheles gambiae population dynamics. Parasit Vectors. 2011;4:153.
Aziz AT, Al-Shami SA, Mahyoub JA, Hatabbi M, Ahmad AH, Rawi CS. An update on the incidence of dengue gaining strength in Saudi Arabia and current control approaches for its vector mosquito. Parasit Vectors. 2014;7:258.
López-Ruiz N, Montaño-Remacha MDC, Durán-Pla E, Pérez-Ruiz M, Navarro-Marí JM, Salamanca-Rivera C, et al. West Nile virus outbreak in humans and epidemiological surveillance, west Andalusia, Spain, 2016. Euro Surveill. 2018;23:17-00261.
McFee RB. Selected mosquito-borne illnesses - Chikungunya. Dis Mon. 2018;64:222–34.
Jambulingam P, Subramanian S, de Vlas SJ, Vinubala C, Stolk WA. Mathematical modelling of lymphatic filariasis elimination programmes in India: required duration of mass drug administration and post-treatment level of infection indicators. Parasit Vectors. 2016;9:501.
Nepomichene TNJJ, Raharimalala FN, Andriamandimby SF, Ravalohery JP, Failloux AB, et al. Vector competence of Culex antennatus and Anopheles coustani mosquitoes for Rift Valley fever virus in Madagascar. Med Vet Entomol. 2018;32:259–62.
Wilder-Smith A, Massad E. Estimating the number of unvaccinated Chinese workers against yellow fever in Angola. BMC Infect Dis. 2018;18:185.
Byrd BD. La Crosse encephalitis. A persistent arboviral threat in North Carolina. N C Med J. 2016;77:330–3.
Pearce JC, Learoyd TP, Langendorf BJ, Logan JG. Japanese encephalitis: the vectors, ecology and potential for expansion. J Travel Med. 2018;25:S16–26.
Yakob L, Walker T. Zika virus outbreak in the Americas: the need for novel mosquito control methods. Lancet Glob Health. 2016;4:e148-9.
Nauen R. Insecticide resistance in disease vectors of public health importance. Pest Manag Sci. 2007;63:628–33.
Awono-Ambene PH, Etang J, Antonio-Nkondjio C, Ndo C, Eyisap WE, Piameu MC, et al. The bionomics of the malaria vector Anopheles rufipes Gough, 1910 and its susceptibility to deltamethrin insecticide in North Cameroon. Parasit Vectors. 2018;11:253.
Okia M, Hoel DF, Kirunda J, Rwakimari JB, Mpeka B, Ambayo D, et al. Insecticide resistance status of the malaria mosquitoes: Anopheles gambiae and Anopheles funestus in eastern and northern Uganda. Malar J. 2018;17:157.
Ranson H, Lissenden N. Insecticide resistance in African Anopheles mosquitoes: a worsening situation that needs urgent action to maintain malaria control. Trends Parasitol. 2016;32:187–96.
Liu N, Liu H, Zhu F, Zhang L. Differential expression of genes in pyrethroid resistant and susceptible mosquitoes, Culex quinquefasciatus (S.). Gene. 2007;394:61–8.
Vontas J, Blass C, Koutsos AC, David JP, Kafatos FC, Louis C, et al. Gene expression in insecticide resistant and susceptible Anopheles gambiae strains constitutively or after insecticide exposure. Insect Mol Biol. 2005;14:509–21.
Xu Q, Wang H, Zhang L, Liu N. Kdr allelic variation in pyrethroid resistant mosquitoes, Culex quinquefasciatus (S.). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;345:774–80.
Liu N. Insecticide resistance in mosquitoes: impact, mechanisms, and research directions. Annu Rev Entomol. 2015;60:537–59.
Seixas G, Grigoraki L, Weetman D, Vicente JL, Silva AC, Pint J, et al. Insecticide resistance is mediated by multiple mechanisms in recently introduced Aedes aegypti from Madeira Island (Portugal). PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017;11:e0005799.
Burton MJ, Mellor IR, Duce IR, Davies TG, Field LM, Williamson MS. Differential resistance of insect sodium channels with kdr mutations to deltamethrin, permethrin and DDT. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2011;41:723–32.
Hemingway J, Karunaratne SH. Mosquito carboxylesterases: a review of the molecular biology and biochemistry of a major insecticide resistance mechanism. Med Vet Entomol. 1998;12:12.
Fang F, Wang W, Zhang D, Lv Y, Zhou D, Ma L, et al. The cuticle proteins: a putative role for deltamethrin resistance in Culex pipiens pallens. Parasitol Res. 2015;114:4421–9.
Reid WR, Zhang L, Liu F, Liu N. The transcriptome profile of the mosquito Culex quinquefasciatus following permethrin selection. PLoS One. 2012;7:e47163.
Sun Y, Zou P, Yu XY, Chen C, Yu J, Shi LN, et al. Functional characterization of an arrestin gene on insecticide resistance of Culex pipiens pallens. Parasit Vectors. 2012;5:134.
Xu Y, Yang M, Sun J, Qian J, Zhang D, Sun Y, et al. Glycogen branching enzyme: a novel deltamethrin resistance-associated gene from Culex pipiens pallens. Parasitol Res. 2008;103:449–58.
Zhou D, Hao S, Sun Y, Chen L, Xiong C, Ma L, et al. Cloning and characterization of prophenoloxidase A3 (proPOA3) from Culex pipiens pallens. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2012;162:57–65.
Ovchinnikov Yu A. Rhodopsin and bacteriorhodopsin. structure-function relationships. FEBS Lett. 1982;148:179–91.
Running Deer JL, Hurley JB, Yarfitz SL. G protein control of Drosophila photoreceptor phospholipase C. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:12623–8.
White JH, Chiano M, Wigglesworth M, Geske R, Riley J, White N, et al. Identification of a novel asthma susceptibility gene on chromosome 1qter and its functional evaluation. Hum Mol Genet. 2008;17:1890–903.
Menon I, Huber T, Sanyal S, B anerjee S, Barre P, Canis S, et al. Opsin is a phospholipid flippase. Curr Biol. 2011;1:149–53.
Pedra JH, McIntyre LM, Scharf ME, Pittendrigh BR. Genome-wide transcription profile of field- and laboratory-selected dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT)-resistant Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:7034–9.
Li T, Cao C, Yang T, Zhang L, He L, Xi Z, et al. A G-protein-coupled receptor regulation pathway in cytochrome P450-mediated permethrin-resistance in mosquitoes, Culex quinquefasciatus. Sci Rep. 2015;5:17772.
Wu HW, Tian HS, Wu GL, Langdon G, Kurtis J, Shen B, et al. Culex pipiens pallens: identification of genes differentially expressed in deltamethrin-resistant and -susceptible strains. Pestic Biochem Phys. 2004;79:75–83.
Hu XB, Sun Y, Wang WJ, Yang MX, Sun LX, Tan WB, et al. Cloning and characterization of NYD-OP7, a novel deltamethrin resistance associated gene from Culex pipiens pallens. Pestic Biochem Phys. 2007;88:82–91.
Muyal JP, Muyal V, Kaistha BP, Seifart C, Fehrenbach H. Systematic comparison of RNA extraction techniques from frozen and fresh lung tissues: checkpoint towards gene expression studies. Diagn Pathol. 2009;4:9.
Glasel JA. Validity of nucleic acid purities monitored by 260nm/280nm absorbance ratios. Biotechniques. 1995;18:62–3.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TJ. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 2001;25:402–8.
Wise A, Gearing K, Rees S. Target validation of G-protein coupled receptors. Drug Discov Today. 2002;7:235–46.
Mitri C, Soustelle L, Framery B, Bockaert J, Parmentier ML, Grau Y. Plant insecticide L-canavanine repels Drosophila via the insect orphan GPCR DmX. PLoS Biol. 2009;7:e1000147.
Bai H, Zhu F, Shah K, Palli SR. Large-scale RNAi screen of G protein-coupled receptors involved in larval growth, molting and metamorphosis in the red flour beetle. BMC Genomics. 2011;12:388.
Baile CA, Della-Fera MA. Peptidergic control of food intake in food-producing animals. Fed Proc. 1984;43:2898–902.
Audsley N, Down RE. G protein coupled receptors as targets for next generation pesticides. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2015;67:27–37.
Terakita A, Takahama H, Hariyama T, Suzuki T, Tsukahara Y. Light-regulated localization of the beta-subunit of Gq-type G-protein in the crayfish photoreceptors. J Comp Physiol A. 1998;183:411–7.
Chen W, Lee MK, Jefcoate C, Kim SC, Chen F, Yu JH. Fungal cytochrome p450 monooxygenases: their distribution, structure, functions, family expansion, and evolutionary origin. Genome Biol Evol. 2014;6:1620–34.
Ishak IH, Kamgang B, Ibrahim SS, Riveron JM, Irving H, Wondji CS. Pyrethroid resistance in Malaysian populations of dengue vector Aedes aegypti is mediated by CYP9 family of cytochrome P450 genes. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017;11:e0005302.
Yang Y, Chen S, Wu S, Yue L, Wu Y. Constitutive overexpression of multiple cytochrome P450 genes associated with pyrethroid resistance in Helicoverpa armigera. J Econ Entomol. 2006;99:1784–9.
David JP, Strode C, Vontas J, Nikou D, Vaughan A, Pignatelli PM, et al. The Anopheles gambiae detoxification chip: a highly specific microarray to study metabolic-based insecticide resistance in malaria vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:4080–4.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 81672056, 81672058 and 81772227) and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Availability of data and materials
All data analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its additional files.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DZ, BYD, BS, LM and YS performed the experiments. DZ, BYD and YX wrote the manuscript and prepared the figures. YS and CLZ conceived the idea and coordinated the project. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All animal procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Nanjing Medical University for the use of laboratory animals (Protocol No. 582/2017).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Additional files
Additional file 1:
Table S1. Primers for NYD-OP7, PLC, and several P450 genes. (DOC 22 kb)
Additional file 2:
Table S2. List of dsNYD-OP7, siPLC, and NC sequences. (DOCX 12 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, D., Duan, B., Xu, Y. et al. NYD-OP7/PLC regulatory signaling pathway regulates deltamethrin resistance in Culex pipiens pallens (Diptera: Culicidae). Parasites Vectors 11, 419 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-018-3011-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-018-3011-5