Abstract
Background
Zoonotic Visceral Leishmaniasis (ZVL) is a vector-borne disease affecting humans and other mammals and caused by the protozoan parasite Leishmania (Leishmania) infantum (syn. L. chagasi), belonging to the L. donovani complex. The regions in Northern Argentina (above 32 °S) are its southern distribution limit in South America.
Results
We detected Leishmania sp. DNA (most likely belonging to the L. donovani complex) in 37.5 % of 32 grey foxes (Pseudalopex griseus) captured in Argentinean Patagonia (48°S and 50°S). Eleven monosexual pools of Amblyomma tigrinum ticks from eight different foxes (six grey foxes and two culpeo foxes P. culpaeus) were also positive. The southernmost known distribution limit for L. infantum, and the southernmost reported capture of a phlebotominae, had previously been 2000 and 750 km north of our study area, respectively.
Conclusions
This finding is significant because it markedly extends the distribution area of leishmaniasis; supports the existence of a sylvatic cycle in the absence of dogs; and has implications in transmission, indicating that either sand fly distribution is broader than currently thought or non-sand fly Leishmania maintenance is possible. Additional molecular, parasitological, epidemiological and entomological studies are still needed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Zoonotic Visceral Leishmaniasis (ZVL) is a vector-borne disease affecting humans and other mammals and caused by the protozoan parasite Leishmania (Leishmania) infantum (syn. L. chagasi), belonging to the L. donovani complex. It is believed that the parasite was brought to South America by European immigrants, perhaps many times, spreading rapidly due to migration, urbanization and trade [1, 2]. The current known distribution area in South America comprises most of Brazil, Venezuela, Paraguay, Northern Argentina, western Bolivia, eastern Peru and other minor foci north of these areas. The regions in Northern Argentina (above 32°S) are its southern distribution limit [3].
ZVL is a serious public health problem and its primary reservoir is the dog [4]. ZVL also causes dog morbidity and mortality in areas where it is endemic [5]. Disease incidence in endemic areas has increased, suggesting that existing control measures consisting of vector control and dog culling have not been effective. To explain this lack of effectiveness, the existence of alternative reservoir hosts has been proposed among other factors [4]. The possibility that peri-domestic and sylvatic transmission cycles operate concurrently, involving different primary reservoir species (e.g. a domestic and a wild host, respectively) with a link between the two cycles, has also been suggested [4]. Wild carnivores are among those species suspected of serving as sylvatic reservoirs. In endemic areas of South America, the crab-eating fox (Cerdocyon thous) has long been known to have a high prevalence of infection in some areas of Brazil [6], including in a non-endemic area [7], suggesting an independent enzootic fox cycle. In another endemic region, the Mediterranean Basin, a high prevalence of L. infantum has been confirmed in several species of wild carnivores [8].
Most of the studies enumerated above were carried out in human-dominated landscapes where dogs are abundant and act as primary reservoirs of Leishmania. Therefore, it is difficult to clearly demonstrate the capacity of a wild species to maintain the parasite in a purely sylvatic cycle. The aim of the present study was to determine the presence of Leishmania sp. in an abundant wild carnivore inhabiting a remote, non-endemic area of South America were dogs are scarce and sand flies are not known to be present.
Methods
Field methods
Foxes were captured from 2010 to 2013 in two study areas: Monumento Natural Bosques Petrificados National Park (MNBP; 47°58'S, 67°97'W), and Monte León National Park (ML; 50°14′S, 69°00′O), both in Santa Cruz province, Argentinean Patagonia (Fig. 1, Table 1). The dominant habitat is shrub-steppe with < 50 % cover. The climate is dry and cold, with frequent frosts. The mean annual temperature is 10 °C (ranging from -10 °C to 30 °C), and annual rainfall ranges from 100 to 300 mm. Dogs are very rare in the study areas, with few individuals in some ranches surrounding the parks. Unpublished preliminary data estimated South American grey fox (Pseudalopex griseus; syn. Lycalopex griseus) density at around 0.3 foxes/100 ha, and culpeo fox (P. culpaeus) density at around 0.1 foxes/100 ha (A. Travaini and A. Rodríguez, unpublished data). The grey fox is widespread in plains and mountains on both sides of the Andes in Chile and Argentina [9], whereas the culpeo fox is distributed throughout the Andes and hilly regions of South America from Colombia to Tierra del Fuego [10]. We captured 34 free-living foxes, including 32 grey and 2 culpeo foxes. Foxes were caught between November 2010 and October 2013 with Oneida Victor #1.5 soft-catch coil spring traps (Cleveland, OH, USA), anaesthetized with a combination of tiletamine and zolazepam (Zoletil, Virbac, Spain). Blood obtained from the cephalic vein was either applied (100 μl) to FTA™ Nucleic Acid Collection Cards (Whatman, Maidstone, Kent, UK), air-dried and stored in sealed plastic bags or kept in 95 % ethanol (Table 1) until further processing. Ticks were retrieved from nine of the captured foxes and stored in ethanol until analysis. Foxes were released at the capture site. For one culpeo fox, only ticks and no blood was obtained. All analyzed ticks were adults of the species Amblyomma tigrinum (Table 1). Identification was carried out using standard morphological criteria [11].
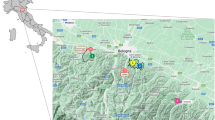
Map of South America, showing the accepted distribution area of Leishmania infantum (grey area) [3], the southernmost record of a Phlebotominae (black circle) [19], the southernmost record of a competent vector (black triangle) [31], the Bosques Petrificados National Monument (black star), and the Monte León National Park (white star)
Laboratory methods
Samples were processed in two independent laboratories: PCR protocol 1 was performed at the Facoltá di Medicina Veterinaria, Universitá degli Studi di Torino, Italy (Lab 1); and Protocol 2, at VetGenomics, a veterinary molecular diagnostic company in Barcelona, Spain (Lab 2). DNA was independently extracted in Labs 1 and 2. Total genomic DNA was extracted from a single 2 mm punch of the FTA™ Cards following manufacturer’s instructions (GenSolve DNA Recovery Kit, Whatman, Maidstone, Kent, UK). For blood samples preserved in ethanol, 25 mg of blood was washed with 1 ml of PBS to eliminate ethanol. DNA was isolated using a DNeasy® Blood & Tissue Kit (Qiagen, California, USA) in a QIAcube according to manufacturer’s instructions. DNA was also extracted in Lab 1 from 17 monosexual pools of ticks using GenElute Mammalian Genomic Miniprep Kit (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA).
Two PCR protocols were performed. Protocol 1 used the Leishmania donovani (sensu lato)-specific primers (RV1-RV2) amplifying a 145 bp segment of the highly reiterated minicircles of kinetoplast DNA [12]. Protocol 1 was used for diagnosis of both blood and tick-extracted DNA. Amplification with primers mRv1 and mRv2 and agar gel verification were carried out as described in Ferroglio et al. [13]. One positive (total genomic DNA extracted from a pure culture of L. infantum promastigotes) and two negative controls were included in each PCR assay. Positive PCR products were purified using NucleoSpin® Gel and PCR Clean-up kits (Macherey-Nagel GmbH & Co. KG, Düren, Germany) and sequenced to confirm PCR results (BMR Genomics, Padua, Italy).
Protocol 2 consisted of a real-time PCR using a set of primers targeting a 121 bp segment of a different region of the parasite kinetoplast minicircle, namely LEISH-1 and LEISH-2, following Francino et al. [14]. Positive PCR products were purified and sequenced using BigDye v3.1 Kit (Live Technologies, Karlsruhe, Germany) using the same primers as in the PCR.
Results
Twelve grey foxes (37.5 %) were positive for kinetoplast DNA by at least one of the protocols. Nine were positive by protocol 1 (Fig. 2), and six by protocol 2, with three foxes positive by both protocols 1 and 2. Readable sequences were obtained from four of the positive cases resulting from protocol 1, and two from protocol 2. BLAST analysis confirmed the PCR results (EMBL Nucleotide Sequence Database accession numbers: HF563611–HF563614 and LN794244). The obtained sequences showed the highest identity with L. infantum (four cases) and L. major (two cases) (Table 2). The single culpeo fox was negative. External lesions compatible with leishmaniasis were not observed.
Additionally, 11 monosexual pools of A. tigrinum (64.7 %) from eight different foxes were positive for Leishmania DNA by means of the PCR protocol 1, including ticks from one PCR-negative grey fox and the one culpeo fox for which blood was not available (Table 1). The presence of Leishmania DNA in one tick pool was confirmed with protocol 2 (Table 1) and sequenced, showing the maximum identity with L. donovani (Table 2).
Discussion
This represents the detection of an infected mammalian host 2000 km south of the currently accepted southern boundary for the distribution of the parasite [15, 16]. The only member of the L. donovani complex known to be present in South America is L. infantum (syn. L. chagasi). This is in agreement with most of our BLAST results, including the sequence obtained from the positive tick, though L. major showed the highest identity in two cases. This is likely due to the fact that L. infantum and L. major share a high proportion of kinetoplast DNA because they both belong to the subgenus Leishmania (Leishmania). Moreover, L. major is not present in South America. Therefore, we hypothesize that the detected DNA most likely indicates infection with L. infantum or closely related Leishmania. In any case, the obtained sequence homologies are too low to incriminate a Leishmania species and the actual identity of the detected parasite should be further investigated.
Our finding is significant for three main reasons. First, it markedly extends the geographical distribution of the parasite. Thus, L. infantum may be present in other undetected foci in southern South America, as was recently revealed in North America, where dogs from several US states and Canada had leishmaniasis [17]. We recommend that medical and veterinary practitioners from non-endemic areas include leishmaniasis when performing differential diagnoses because leishmaniasis may pass unnoticed [18].
Secondly, a role for wildlife in the epidemiology of leishmaniasis is further supported. The range of wild mammals in which L. infantum is detected is increasing, mainly amongst carnivores, rodents, marsupials, lagomorphs and even bats, some of which have been proven to be competent hosts by means of xenodiagnosis [4]. Recently, the existence of a sylvatic cycle in Northern Argentina was proposed in which the dogs would play the role of accidental host [19]. Given the scarcity of dogs in the study areas, with only a few dogs living on surrounding ranches, L. infantum appears to maintain a sylvatic cycle in Patagonia.
Thirdly, our finding has implications for Leishmania transmission. It is commonly accepted that phlebotomine sand fly transmission plays a central role in maintaining L. infantum infection because the spatial and temporal overlap of ZVL cases and the proven vector species show that sustained transmission does not generally occur in the absence of sand fly vectors [4]. Our results indicate that either sand fly distribution is broader than currently accepted, or that non-sand fly Leishmania maintenance is possible. Regarding sand fly distribution, the southernmost reported capture of a phlebotominae (Lutzomyia oswaldoi, without known vector capacity) was reported at 41 °S, 750 km north of MNBP [20]. Regarding Leishmania maintenance in the absence of sandflies, cases of autochthonous transmission of L. infantum have been described in northern Europe, where sand fly vectors are absent [21], and the sustained transmission of ZVL in foxhounds in non-endemic regions of North America was reported [22]. Autochthonous foci have also been found in parts of continental Europe and in the Alps [23, 24]. Recently, direct dog-to-dog contact was believed to be the most likely route of infection of L. infantum in the first autochthonous cases of canine leishmaniasis in New Caledonia because the affected dog was in close contact with two bitches imported from Spain [25]. Transmission by transfer of infected body fluids (e.g. by biting or sexual contact) [26] or congenitally [22], has been suggested to explain non-sand fly transmission. Congenital transmission to puppies has been confirmed experimentally [25]. Finally, Leishmania DNA has been found in ticks and fleas, suggesting their potential role in transmission ([27, 28]; this study). The ingestion of infected ticks is also an effective transmission route for certain tick-borne pathogens, and hamsters were experimentally infected with macerates of ticks collected from L. infantum-infected dogs [29]. Of course, the finding of infected ticks does not prove their role as a Leishmania vector, but it supports the presence of the parasite in the study area. Adult A. tigrinum feed predominantly on wild and domestic canids and occasionally on humans and others hosts, whereas nymphs typically infect rodents of the family Caviidae [30]. This family is represented in the study areas by the abundant southern mountain cavy (Microcavia australis). Thus, this rodent might be the reservoir of leishmaniasis in Patagonia and the role of this rodent in its epidemiology deserves further investigation.
Conclusions
In summary, we have demonstrated the presence of Leishmania DNA in wild foxes and ticks in Patagonia. Potential false positives due to contamination are ruled out because DNA was independently extracted and amplified in two different laboratories. The fact that protocol 1 yielded more positive cases than Protocol 2 can be due to a more successful DNA extraction in Lab 1 or to differences in the sensibility of the PCR protocol. Nevertheless, Lab 2 was able to detect Leishmania DNA in blood samples preserved in ethanol that were not analyzed in Lab 1 (Table 1).
Our finding represents potential public and canine health implications that should be addressed by further research, including the complete identification of the Leishmania species, the infectiveness of foxes to sand flies, the presence of infection in domestic dogs and other potential reservoirs (i.e. cavies) in Patagonia, the occurrence of sand flies in the area, the potential role of other arthropods (fleas and ticks) as vectors, and other types of non-sand fly transmission, i.e. direct transmission between canids.
Ethics statement
The present research complied with the regulations on animal experimentation and welfare issued by the European Union (Directive 86/609/CE). Specifically, capture and handling of foxes was approved by the competent authorities on bioethics and biosecurity under permit CEBA-EBD-2011-05b (Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, Spain), and the competent authorities on nature protection under permit 479-2011 (National Parks Administration, Argentina).
References
Mauricio IL, Stothard JR, Miles MA. The strange case of Leishmania chagasi. Parasitol Today. 2000;16:188–9.
Kuhls K, Alam MZ, Cupolillo E, Ferreira GE, Mauricio IL, Oddone R, Feliciangeli MD, Wirth T, Miles MA, Schönian G. Comparative microsatellite typing of new world Leishmania infantum reveals low heterogeneity among populations and its recent old world origin. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2011;5:e1155.
World Health Organization. Control of the leishmaniases: report of a meeting of the WHO Expert Commitee on the Control of Leishmaniases. Geneva; 2010.
Quinnell RJ, Courtenay O. Transmission, reservoir hosts and control of zoonotic visceral leishmaniasis. Parasitology 2009;136:1915–34.
Baneth G, Solano-Gallego L. Global aspects of leishmaniases. In: Greene CE, editor. Infectious Diseases of the Dog and Cat, 4th edn. Philadelphia: Elsevier Science; 2012. p. 734–49.
Mello DA, Rego Junior FDA, Oshozo E, Nunes VL. Cerdocyon thous (L.) (Carnivora, Canidae) naturally infected with Leishmania donovani chagasi (Cunha & Chagas, 1973) in Corumba (Mato Grosso do Sul State, Brazil). Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 1988;83:259.
Millán J, Ferroglio E, Solano-Gallego L. Role of wildlife in the epidemiology of Leishmania infantum infection in Europe. Parasitol Res. 2014;113:2005–14.
Lainson R, Shaw JJ, Lins ZC. Leishmaniasis in Brazil: IV. The fox, Cerdocyon thous (L) as a reservoir of Leishmania donovani in Pará State, Brazil. Trans R Soc Trop. Med Hyg. 1969;63:741–5.
Jiménez JE, Lucherini M, Novaro AJ. Pseudalopex griseus. In: IUCN 2012. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2012.2. <www.iucnredlist.org>. 2008a. Downloaded on 28 March 2015.
Jiménez JE, Lucherini M, Novaro AJ. Pseudalopex culpaeus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2008: e.T6927A12815779. http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2008.RLTS.T6927A12815779.en. Downloaded on 20 April 2016.
Estrada-Peña A, Venzal JM, Mangold AJ, Cafrune MM, Guglielmone AA. The Amblyomma maculatum Koch, 1844 (Acari: Ixodidae: Amblyomminae) tick group: diagnostic characters, description of the larva of A. parvitarsum Neumann, 1901, 16S rDNA sequences, distribution and hosts. Syst Parasitol. 2005;60:99–112.
Lachaud L, Chabbert E, Dubessay P, Dereure J, Lamothe J, Dedet JP, Bastien, P. Value of two PCR methods for the diagnosis of canine visceral leishmaniasis and the detection of asymptomatic carriers. Parasitology 2002;125:197–207.
Ferroglio E, Romano A, Trisciuoglio A, Poggi M, Ghiggi E, Sacchi P, Biglino A. Characterization of Leishmania infantum strains in blood samples from infected dogs and humans by PCR-RFLP. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2006;100:636–41.
Francino O, Altet L, Sánchez-Robert E, Rodriguez A, Solano-Gallego L, Alberola J, Ferrer L, Sánchez A, Roura X. Advantages of real-time PCR assay for diagnosis and monitoring of canine leishmaniosis. Vet Parasitol. 2006;137:214–21.
Salomón OD, Rossi G, Sosa-Estani S, Spinelli G. Presencia de Lutzomyia longipalpis y situación de la leishmaniosis visceral en Argentina. Medicina (Buenos Aires). 2001;61:174–8.
Desjeux P. Leishmaniasis. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2004;2:692.
Duprey ZH, Steurer FJ, Rooney JA, Kirchhoff LV, Jackson JE, Rowton ED, Schantz PM. Canine visceral leishmaniasis, United States and Canada, 2000–2003. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:440–6.
Martín-Sanchez J, Navarro-Mari JM, Pasquau-Liano J, Salomón OD, Morillas-Márquez F. Visceral Leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania infantum in a Spanish patient in Argentina: What is the origin of the infection? Case Report BMC Infect Dis. 2004;4:20.
Barroso PA, Marco JD, Locatelli FM, Cardozo RM, Hoyos CL, Mora MC, García Bustos MF, López-Quiroga I, Mimori T, Gentile AG, Barrio AB, Korenaga M, Hashiguchi Y, Basombrío MA. Visceral leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania infantum in Salta, Argentina: Possible reservoirs and vectors. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2015;93:334–9.
Muzon J, Spinelli GR, Salomon OD, Rossi GC. A first record of Phlebotominae from Argentinean Patagonia (Diptera: Psychodidae: Phlebotominae). Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2002;97:797–8.
Harris MP. Suspected transmission of leishmaniasis. Vet Rec. 1994;135:339.
Boggiatto PM, Gibson-Corley KN, Metz K, Gallup JM, Hostetter JM, Mullin K, Petersen CA. Transplacental transmission of Leishmania infantum as a means for continued disease incidence in North America. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2011;5(4):e1019.
Ferroglio E, Maroli M, Gastaldo S, Mignone M, Rossi L. Canine leishmaniosis in Italy. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:1618–20.
Biglino A, Bolla C, Concialdi E, Trisciuoglio A, Romano A, Ferroglio E. Asymptomatic Leishmania infantum infection in an area of northwestern Italy (Piedmont region) where such infections are traditionally nonendemic. J Clin Microbiol. 2010;48:131–6.
Daval N, Marchal C, Guillaumot L, Hüe T, Ravel C, Keck N, Kasbari M. First report of autochthonous non-vectorial canine leishmaniasis in New Caledonia, south-western Pacific: implications for new control measures and recommendations on importation of dogs. Parasit Vectors. 2016;9:108.
Silva FL, Oliveira RG, Silva TM, Xavier MN, Nascimento EF, Santos RL. Venereal transmission of canine visceral leishmaniasis. Vet Parasitol. 2009;160:55–9.
Ferreira MG, Fattori KR, Souza F, Lima VM. Potential role for dog fleas in the cycle of Leishmania spp. Vet Parasitol. 2009;165:150–4.
Dantas-Torres F. Ticks as vectors of Leishmania parasites. Trends Parasitol. 2011;27:155–9.
Coutinho MT, Bueno LL, Sterzik A, Fujiwara RT, Botelho JR, De Maria M, Genaro O, Linardi PM. Participation of Rhipicephalus sanguineus (Acari: Ixodidae) in the epidemiology of canine visceral leishmaniasis. Vet Parasitol. 2005;128:149–55.
Nava S, Mangold AJ, Guglielmone AA. The natural hosts of larvae and nymphs of Amblyomma tigrinum Koch, 1844 (Acari: Ixodidae). Vet Parasitol. 2006;140:124–32.
Salomón OD, Basmajdian Y, Fernández MS, Santini MS. Lutzomyia longipalpis in Uruguay: the first report and the potential of visceral leishmaniasis transmission. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2011;106:381–2.
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank D.E. Procopio, M. Martínez, L. Martínez and the staff of the MNBP National Park for assistance during the fieldwork, and L. Altet and L. Serrano from VetGenomics for performing the real-time PCR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
JM conceived the study, contributed with funds, and drafted the manuscript. AT carried out the fieldwork. SZ, AT and EF identified the ticks and carried out the molecular genetic studies. JVLB carried out the fieldwork. EF helped to draft the manuscript. AR contributed with funds, carried out the field work, and helped to draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Millán, J., Travaini, A., Zanet, S. et al. Detection of Leishmania DNA in wild foxes and associated ticks in Patagonia, Argentina, 2000 km south of its known distribution area. Parasites Vectors 9, 241 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-016-1515-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-016-1515-4