Abstract
Background
Crenosoma vulpis (Dujardin, 1845), the fox lungworm, is a metastrongyloid affecting the respiratory tract of red foxes (Vulpes vulpes), dogs (Canis familiaris) and badgers (Meles meles) living in Europe and North America. The scant data available on the intermediate hosts of C. vulpis, as well as the limited information about the morphology of the larvae may jeopardise epidemiological studies on this parasite.
Methods
Suitability and developmental time of C. vulpis in the common garden snail Cornu aspersum (= Helix aspersa) was assessed at selected days post-infection (i.e. 3, 6, 10, 15, 20 and 180). Nematodes were preserved in 70 % ethanol, cleared and examined as temporary mounts in glycerol for morphological descriptions of first- and third-stage larvae. In addition, nematodes collected from the dog and the experimentally infected snails were molecularly analysed by the amplification of the nuclear 18S rRNA gene.
Results
Specimens of C. aspersum digested before the infection (n = 10) were negative for helminth infections. Out of 115 larvae recovered from infected gastropods (mean of 9.58 larvae per snail), 36 (31.3 %) were localised in the foot and 79 (68.7 %) in the viscera. The 18S rDNA sequences obtained from larvae collected from the dog and the snail tissues displayed 100 % identity to the nucleotide sequence of C. vulpis.
Conclusions
Cornu aspersum is herein reported for the first time as a suitable intermediate host of C. vulpis. This snail species may play an important role for the infection of animals living in regions of the Mediterranean basin. In addition, this study provides more details on the morphological descriptions of L1 and L3 and supports future investigations on the epidemiology of this little known parasite.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The Superfamily Metastrongyloidea (Strongylida) includes nematode species that generally have gastropods and vertebrates as intermediate and definitive hosts, respectively [1, 2]. Crenosoma vulpis (Dujardin, 1845), commonly known as the fox lungworm, is a metastrongyloid affecting the respiratory tract of red foxes (Vulpes vulpes), dogs (Canis familiaris) and badgers (Meles meles) living in Europe and North America [3–6]. Larval stages dwell in snails and slugs, and third-stage larvae (L3) are infective to carnivore definitive hosts which feed on these gastropods [1]. Adult nematodes live in bronchioles, bronchi and trachea and produce first-stage larvae (L1) which are swallowed and passed in the faeces of infected animals in about 18–21 days post infection [1]. The infections are generally non-fatal with clinical presentations of various degrees, from subclinical to chronic respiratory syndrome, featured by lingering cough and retching [7, 8]. The better-known Angiostrongylus vasorum (Baillet, 1866) is another snail-borne nematode which shares some ecological and pathological features with C. vulpis [9]. Additionally, A. vasorum may also cause severe conditions due to coagulative, cardiovascular and neurological disorders in dogs [10], and its distribution seems to be increasing in previously reported and unreported geographical areas [11]. For example, A. vasorum has been frequently detected in Europe, Africa, North and South America [10], whereas C. vulpis has been diagnosed sporadically from dogs in the UK [12], Ireland [13], Switzerland [8], Germany [14], Belgium [15] and Italy [16]. For both parasites, wildlife animals are accounted as possible reservoir hosts of infection for domestic dogs [11, 17]. However, biological determinants shaping the epidemiology of C. vulpis have been poorly investigated. The diagnosis of lungworm infection relies on finding of L1 in the stool of infected animals by the Baermann technique [7], although a proper identification of the pathogens may be challenging due to the morphological similarities of closely related species [18]. The scant data available on the intermediate hosts of C. vulpis, as well as the limited information about the morphology of the larvae, may jeopardise epidemiological studies on this parasite [17]. In addition, snails and slugs experimentally demonstrated to act as intermediate hosts of C. vulpis (e.g. gastropods of the genera Deroceras, Helix, Succinea, and Cepaea) are mostly restricted to the northern and central regions of Europe [1]. Therefore, here we provide data on the development of C. vulpis in Cornu aspersum (= Helix aspersa), a common snail in regions of Mediterranean and north-western Europe, and report more details on the morphological descriptions of L1 and L3, instrumentally to support investigations on the epidemiology of this parasite.
Methods
Gastropod maintenance
One-year-old Cornu aspersum (n = 100) snails were purchased from a farming centre located in Barletta (Puglia, Italy). The snails were housed in a plastic box in a temperature-controlled room (21 ± 1 °C) and fed every second day with lettuce and water for two months until beginning of the study. At the arrival and one day prior to the infection, ten snails were sacrificed, digested and microscopically examined to assess the absence of any helminth infection.
L1 collection and experimental infection of gastropods
Nematode larvae were isolated from the faeces of a 6-year-old naturally infected male Dachshund dog referred to the Parasitology Laboratory of the University of Bari (Puglia, Italy) due to respiratory distress. Faeces were collected and examined by Baermann technique for three consecutive days in order to recover nematode larvae. After the centrifugation of the faecal solution at 600 g for 5 min, the sediment was observed under light microscopy. The larvae obtained were morphologically and molecularly identified as C. vulpis (see below). The dog was successfully treated with a single application of moxidectin/imidacloprid spot on solution (AdvocateⓇ, Bayer Animal Health, Leverkusen, Germany) soon after the diagnosis of canine crenosomosis.
Single infective doses of 100 L1 were collected under a light microscope (LeicaⓇ, DM LB2) and utilized for infecting snails as follows. Two days unfed snails were individually placed in the infection chamber consisting of six well cell culture plate (CorningⓇ; CellBINDⓇ; Sigma-AldrichⓇ, St. Louis, Missouri, USA) containing a potato slice (0.3 cm thick) and the infective dose. Specimens were left in the infection chambers for 48 h and subsequently returned to their box.
Suitability and developmental time of C. vulpis in C. aspersum was assessed by artificially digesting two portions (i.e. muscular foot and viscera) of two snails per time-point (i.e. 3, 6, 10, 15, 20 days post-infection, dpi). In addition, six infected snails were gradually placed at 4 °C in order to favour gastropods hibernation, replaced at laboratory condition, and analysed at 180 dpi.
Each snail was digested in 100 ml HCl solution (pH 2.2) and 3 mg/ml of pepsin (Sigma-AldrichⓇ, St. Louis, Missouri, USA). The suspension was heated on a magnetic stirrer at 37 °C for 75 min, sifted through a 250 μm sieve to remove undigested material, transferred to 50 ml plastic tubes and centrifuged at 600 g for 5 min, and morphologically and molecularly analysed.
Morphological and molecular identification of larvae
The suspension obtained from the gastropods digestion was microscopically examined and larvae were morphologically identified according to previous descriptions [19, 20]. The nematodes were preserved in 70 % ethanol and subsequently cleared and examined as temporary mounts in glycerol. Drawings were made with a compound microscope Leica DM LB2 (with differential interference contrast) equipped with a drawing tube. Digital images and measurements were taken using Leica LASⓇ AF 4.1 software. Metrical data are given in micrometres as the range, followed by the mean in parentheses.
For molecular identification, larval specimens of C. vulpis were isolated from the suspension using a 10 μl micropipette and stored in phosphate buffer saline (PBS) solution. Genomic DNA was extracted using a commercial kit (DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit, Qiagen, GmbH, Hilden, Germany), in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions, and a partial fragment of nuclear 18S rRNA (~1700 bp) gene was amplified as previously described [21]. The amplicons were purified and sequenced, in both directions using the same primers as for PCR, employing the Taq Dye Deoxy Terminator Cycle Sequencing Kit (v.2, Applied Biosystems, Foster City, California, USA) in an automated sequencer (ABI-PRISM 377). Sequences were compared with those available in the GenBank database, using Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST – http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi).
Ethics statement
An ethical approval was not necessary since the present study did not involve the experimental use of vertebrates neither human patients nor protected animal species. The procedures on the infected dog were carried out with the owner’s consent.
Results
Specimens of C. aspersum digested at the arrival (n = 5) and one day prior to the infection (n = 5) were negative for helminth infections. Larvae of C. vulpis were found in ten out of 12 (83.3 %) experimentally infected snails. The number and developmental stages of larvae detected from foot and viscera of each snail are shown in Table 1. Out of 115 larvae recovered from infected gastropods (mean of 9.58 larvae per snail), 36 (31.3 %) were localised in the foot and 79 (68.7 %) in the viscera. The 18S rDNA sequences obtained from larvae collected from the snail tissues displayed 100 % identity to the nucleotide sequence of C. vulpis available in GenBank (accession no. KR920038).
Morphological features of C. vulpis larvae
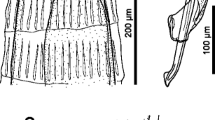
First-stage larvae (n = 10) filiform C-shaped, 253–280 (274) long, 12–14 wide (Fig. 1a). Body curved ventrally, lateral alae extending from head region to posterior third of tail (Fig. 2b, c). Anterior extremity triangular, with rounded apex (Figs. 1a and 2a). Tail 31–34 (33) long, straight or bent dorsally with pronounced narrowing anterior to pointed tip (Fig. 2c). Mouth opening situated dorsally to anterior apex; buccal cavity thin, c. 3 long. Oesophagus 99–113 (111) long, composed of cylindrical muscular procorpus 27–33 long and c.5 wide, followed by cylindrical metacorpus similar in length and c.4 wide, isthmus long and c.3 wide, gradually widening into pear-shaped bulb 7–8 wide (Fig. 2a). Nerve-ring at 55–62 (59) from anterior extremity. Excretory pore obscure, situated at level just posterior to nerve-ring. Genital primordium small, oval, at 156–173 (169) from anterior extremity. Ratio oesophagus length to body length 0.399–0.431 (0.407); ratio distance from anterior extremity to genital primordium to body length 0.598–0.637 (0.619).
First stage larvae of Crenosoma vulpis recovered from Baermann funnel. Anterior extremity, lateral view, note the junction between the muscular procorpus and metacorpus (black arrowhead), the nerve-ring (black arrow) and the oesophago-intestinal junction (white arrow) (a); Lateral alae along the body at the level of the oesophago-intestinal junction, dorsoventral view (b); Tail, dorsoventral (C1) and lateral (C2) view; note the lateral alae (arrowheads) and the narrowing anterior to the pointed tip (black arrow) (c)
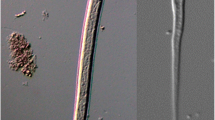
Third-stage larvae (see Table 2 for main morphological measurements). Body curved ventrally (Figs. 1b and 3a, g). Lateral alae extending from anterior body region to posterior half of tail. Mouth opening situated at blunt anterior extremity (Fig. 3b, e). Buccal cavity distinct, 10–12 long, c.2 wide. Oesophagus long, claviform, gradually widens posteriorly to the nerve-ring (Fig. 3a, c, f), anterior 25–30 long portion muscular followed by granular portion (Fig. 3e). Nerve-ring situated anterior to mid-length of oesophagus (Fig. 1b). Excretory pore situated just posterior to nerve-ring. Genital primordium small, oval. Tail conical, posterior half bent dorsally with distinct narrowing anterior to tail tip (Fig. 3d, h).
Third stage larvae of Crenosoma vulpis at different days post-infection (dpi), lateral view. Larva at 10 dpi, note the oesophago-intestinal junction (arrowhead) (a); Anterior extremity at 10 dpi (b); Posterior part of oesophagus at 10 dpi (c), note the oesophago-intestinal junction (arrowhead) and the loose cuticle of the second larval stage; Tail extremity at 10 dpi (d); Anterior extremity at 14 dpi (e), note the border between smooth and glandular parts of the oesophagus (arrowhead); Larva observed in vivo at 15 dpi (f), note the oesophago-intestinal junction (arrowhead); Larva at 150 dpi (g); Tail extremity at 180 dpi (h)
Discussion
The finding of C. aspersum snail as a suitable intermediate host of C. vulpis, together with the detailed morphological descriptions of L1 and L3, represent a step forward in the understanding of this lungworm. Although the measurements of L1 fall within the ranges previously reported for C. vulpis [19, 20], the pointed tail tip of this larval stage was not as elongate as reported in [20]. In addition, a complex morphology of the oesophagus has been herein described (i.e. muscular procorpus, followed by metacorpus, isthmus and basal bulb). The early L3 enclosed into the cuticle of the second larval stage (10 dpi) exhibited a similar morphology to that of L3 collected later on (i.e. 15, 20 and 180 dpi), but were distinct by the thinner body and oesophagus (see Table 2). The L3 had similar morphology of the anterior extremity, the oesophagus and the tail to those described by [19], except for their shorter body (383–509 vs 458–549 μm). In addition, L3 had oesophagus with a distinct anterior muscular portion followed by a longer granular portion, resembling those of other members of Metastrongyloidea, i.e. Angiostrongylus cantonensis (Chen, 1935), A. vasorum and Aelurostrongylus abstrusus (Railliet, 1898) [22]. Knowledge of the morphology of the larvae may be instrumental to explore the biology of C. vulpis, such as the L3 emergence from intermediate hosts, as already described for A. cantonensis, A. vasorum, Troglostrongylus brevior (Gerichter, 1949) and A. abstrusus [23–26]. In this study, L3 were found in the infected gastropods after six months at 4 °C, indicating that hibernated C. aspersum may potentially infect the definitive hosts soon after the overwintering. Therefore, in the Mediterranean regions featured by mild winter, infected snails readily available in the early spring season may cause the infection of susceptible animals by C. vulpis.
Recently, L3 of A. vasorum were detected in C. aspersum at 15 dpi [27], which is longer than in C. vulpis (i.e. 10 dpi). However, since no other time-point previous to the 15th day has been examined [27], the data are not comparable. The lack of C. vulpis larval development in two of the infected snails (16.6 %), as well as of A. vasorum (i.e. 25 % [27]) may suggest the failure in the infection procedure but also the presence of an innate immunity. For example, snail resistance to trematode infection can be promoted by innate immunity [28] or by immunological factors related to species, strain and/or age of snails [29].
The recording of a new gastropod species as intermediate host and of the morphological features of L1 and L3 of C. vulpis herein reported will assist and encourage future research on the biology of this little known parasite.
Conclusions
Further investigations on the species of gastropods acting as intermediate hosts and on the genetic features of C. vulpis will contribute to understand the geographical distributions and risk factors associated with this parasitosis. For example, a preliminary molecular investigation of C. vulpis collected from foxes, dogs and one badger from Italy, revealed the existence of four haplotypes, which supported the existence of the transmission between wild and domestic carnivores [21]. However, further studies are needed to understand the role of different species of snails, slugs and vertebrate hosts in the ecology of C. vulpis.
References
Anderson RC. The superfamily Metastrongyloidea. In: Anderson RC, editor. Nematode parasites of vertebrates. Their development and transmission. Wallingford: CABI Publishing; 2000.
Spratt DM. Species of Angiostrongylus (Nematoda: Metastrongyloidea) in wildlife: a review. Int J Parasitol Parasites Wildl. 2015;4:178–89.
Levine ND. Nematode parasites of domestic animals and of man. 2nd ed. Minneapolis: Burgess Publishing Company; 1980.
Bihr T, Conboy GA. Lungworm (Crenosoma vulpis) infection in dogs on Prince Edward Island. Can Vet J. 1999;40:555–9.
Popiołek M, Jarnecki H, Łuczyński TA. Record of Crenosoma vulpis (Rudolphi, 1819) (Nematoda, Crenosomatidae) from the Eurasian badger (Meles meles L.) from Poland. Wiad Parazytol. 2009;55:437–9.
Barutzki D, Schaper R. Results of parasitological examinations of faecal samples from cats and dogs in Germany between 2003 and 2010. Parasitol Res. 2011;109(1):45–60.
Conboy G. Natural infections of Crenosoma vulpis and Angiostrongylus vasorum in dogs in Atlantic Canada and their treatment with milbemycin oxime. Vet Rec. 2004;155:16–8.
Unterer S, Deplazes P, Arnold P, Fluckiger M, Reusch CE, Glaus TM. Spontaneous Crenosoma vulpis infection in 10 dogs: laboratory, radiographic and endoscopic findings. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 2002;144:174–9.
Morgan ER, Shaw SE, Brennan SF, De Waal TD, Jones BR, Mulcahy G. Angiostrongylus vasorum: a real heartbreaker. Trends Parasitol. 2005;21:49–51.
Koch J, Willesen JL. Canine pulmonary angiostrongylosis: an update. Vet J. 2009;179:348–59. doi:10.1016/j.tvjl.2007.11.014.
Taylor CS, Garcia Gato R, Learmount J, Aziz NA, Montgomery C, Rose H, et al. Increased prevalence and geographic spread of the cardiopulmonary nematode Angiostrongylus vasorum in fox populations in great Britain. Parasitology. 2015;142:1190–5. doi:10.1017/S0031182015000463.
Cobb MA, Fisher MA. Crenosoma vulpis infection in a dog. Vet Rec. 1992;130:452.
Reilly GA, McGarry JW, Martin M, Belford C. Crenosoma vulpis, the fox lungworm, in a dog in Ireland. Vet Rec. 2000;146:764–5.
Barutzki D, Schaper R. Endoparasites in dogs and cats in Germany 1999–2002. Parasitol Res. 2003;90:148–50.
Caron Y, Merveille A, Losson B, Billen F. Crenosoma vulpis infection in two young dogs in Belgium. Vet Rec Case Rep. 2014;2, e000098. doi:10.1136/vetreccr-2014-000098.
Rinaldi L, Calabria G, Carbone S, Carrella A, Cringoli G. Crenosoma vulpis in dog: first case report in Italy and use of the FLOTAC technique for copromicroscopic diagnosis. Parasitol Res. 2007;101:1681–4.
Tolnai Z, Széll Z, Sréter T. Environmental determinants of the spatial distribution of Angiostrongylus vasorum, Crenosoma vulpis and Eucoleus aerophilus in Hungary. Vet Parasitol. 2015;207:355–8.
Otranto D. Diagnostic challenges and the unwritten stories of dog and cat parasites. Vet Parasitol. 2015;212:54–61. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2015.06.002.
Wetzel R. Zur biologie des fuchslungenwurmes Crenosoma vulpis. Arch Wiss Prakt Tierheilk. 1940;75:445–50.
McGarry JW, Morgan ER. Identification of first-stage larvae of metastrongyles from dogs. Vet Rec. 2009;165:258–61.
Latrofa MS, Lia RP, Giannelli A, Colella V, Santoro M, D'Alessio N, et al. Crenosoma vulpis in wild and domestic carnivores from Italy: a morphological and molecular study. Parasitol Res. 2015;114:3611–7. doi:10.1007/s00436-015-4583-z.
Ash LR. Diagnostic morphology of the third-stage larvae of Angiostrongylus cantonensis, Angiostrongylus vasorum, Aelurostrongylus abstrusus, and Anafilaroides rostratus (Nematoda: Metastrongyloidea). J Parasitol. 1970;56:249–53.
Heyneman D, Lim BL. Angiostrongylus cantonensis: proof of direct transmission with its epidemiological implications. Science. 1967;158:1057–8.
Barçante TA, Barçante JM, Dias SR, Lima WS. Angiostrongylus vasorum (Baillet, 1866) Kamensky, 1905: emergence of third-stage larvae from infected Biomphalaria glabrata snails. Parasitol Res. 2003;91:471–5.
Giannelli A, Colella V, Abramo F, do Nascimento Ramos RA, Falsone L, Brianti E, et al. Release of lungworm larvae from snails in the environment: potential for alternative transmission pathways. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015;9, e0003722.
Colella V, Giannelli A, Brianti E, Ramos RA, Cantacessi C, Dantas-Torres F, et al. Feline lungworms unlock a novel mode of parasite transmission. Sci Rep. 2015;5:13105.
Di Cesare A, Crisi PE, Bartolini R, Iorio R, Talone T, Filippi L, et al. Larval development of Angiostrongylus vasorum in the land snail Helix aspersa. Parasitol Res. 2015;114:3649–55. doi:10.1007/s00436-015-4592-y.
Knight M, Ongele E, Lewis FA. Molecular studies of Biomphalaria glabrata, an intermediate host of Schistosoma mansoni. Int J Parasitol. 2000;30:535–41.
Ittiprasert W, Miller A, Myers J, Nene V, El-Sayed NM, Knight M. Identification of immediate response genes dominantly expressed in juvenile resistant and susceptible Biomphalaria glabrata snails upon exposure to Schistosoma mansoni. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2010;169:27–39.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
VC and DO conceived the study, contributed with data analysis and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. YM performed the drawings, the morphological descriptions of larval stages and contributed with data analysis. VC, MAC and RPL performed the experiments on snails. AG supported the laboratory activities and FDT critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Fabrizio Pampurini (Bayer Animal Health GmbH, Italy) for supporting the publication costs of this article.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Colella, V., Mutafchiev, Y., Cavalera, M.A. et al. Development of Crenosoma vulpis in the common garden snail Cornu aspersum: implications for epidemiological studies. Parasites Vectors 9, 208 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-016-1483-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-016-1483-8