Abstract
Background
Anthocyanins are metabolites of phenylpropanoid pathway, and involves in diverse processes of plant development and adaptation, which are regulated by the MYB-bHLH-WD40 (MBW) protein complexes. Many R2R3-MYB activators have been well characterized, but the MYB repressors in anthocyanin biosynthesis were recognized recently, which are also important in modulating phenylpropanoid metabolism in plants. The regulatory mechanism of anthocyanin biosynthesis in oil crop Brassica napus remains to be revealed.
Results
In this study, we identified an anthocyanin repressor BnCPC in B. napus. BnCPC encoded a typical R3-MYB protein containing a conserved [D/E]Lx2[R/K]x3Lx6Lx3R motif for interaction with bHLH proteins. Overexpression of BnCPC in B. napus inhibited anthocyanin accumulation, especially under anthocyanin inducible conditions. Protein–protein interaction and dual-luciferase assays confirmed that BnCPC could compete with BnPAP1 to interact with bHLHs (BnTT8 and BnEGL3), and repress the expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes (e.g., BnDFR) that activated by MBW complexes. Moreover, we found BnCPC inhibited the MBW complex-induced BnCPC activity.
Conclusions
Overall, this research demonstrated that BnCPC repressed anthocyanin biosynthesis by affecting the formation of MBW complex, and formed a feedback loop to regulate anthocyanin accumulation in B. napus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The colorful plant kingdom contains a wide variety of natural pigments that impart different colors to tissues and organs, such as leaf, stem, flower, fruit, and seed [1, 2]. Anthocyanins, betalains, and carotenoids are common natural pigments that play key roles in plant development and reproduction [3, 4]. Anthocyanins are a kind of water-soluble natural pigments in plants that are responsible for a wide range of colors ranging from orange/red to violet/blue [3, 5]. The anthocyanin accumulation contributes to plant pollination and seed dispersal, confers plant resistance to pest diseases, UV radiation, pathogen infection and herbivores, and can significantly improve plant tolerance to abiotic stresses [6,7,8,9,10]. Furthermore, anthocyanins are proved with potential health advantages [11, 12]. Due to its antioxidant properties, anthocyanins play essential roles in improving human immunity, body weight regulation, anti-aging, anti-cancer, and other health fields [13,14,15].
Anthocyanins are synthesized via the flavonoid branch of phenylpropanoid pathway, and the genes related to anthocyanin biosynthesis are categorized into early biosynthesis genes (EBGs) and late biosynthesis genes (LBGs) [16, 17]. The EBGs include chalcone synthase (CHS), chalcone isomerase (CHI), flavanone 3-hydroxylase (F3H), and flavanone 3′-hydroxylase (F3′H), which are involved in precursor biosynthesis for flavonoids. The LBGs such as dihydroflavonol 4-reductase (DFR), leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase (LDOX), and UDP-glucose: flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase (UF3GT) are involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis [18]. Since anthocyanins play important roles in absorbing photosynthetic light energy and in plant response to biotic and abiotic stresses, molecular regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis is valuable to achieve a balance between anthocyanin and proanthocyanidins (PAs), another main product of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway. Furthermore, strict regulation of anthocyanin content is necessary to balance photoprotection and light absorption in plants [10, 19]. In Arabidopsis, the EBGs are modulated by subgroup 7 R2R3-MYB transcription factors (MYB11, MYB12, and MYB111) [16, 20, 21], and the activation of LBGs requires MYB-bHLH-WD40 (MBW) protein complexes [20, 22, 23]. The R2R3-MYBs are key regulators in the spatial and temporal patterns of anthocyanin localization and deposition in plants [20]. Anthocyanin-related R2R3-MYB activators have been widely identified in various plants, such as AtMYB75 (PAP1), AtMYB90 (PAP2), AtMYB113, and AtMYB114 in Arabidopsis [22, 24,25,26], VvMYBA1, VvMYBA2, VvMYBA5, VvMYBA6, and VvMYBA7 in grape [27, 28], MdMYB1, MdMYB3, MdMYB10, and MdMYB110a in apple [29,30,31,32], PtrMYB57, PdMYB118, and PtrMYB119 in poplar [33,34,35]. These R2R3-MYBs mainly regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis through modulating the gene expression in flavonoid biosynthetic pathway. For instance, AtMYB75/90/113/114 formed complexes with bHLHs (GL3, EGL3, and TT8) and WD40 (TTG1) to regulate LDOX and DFR expression [36,37,38].
In addition to MYB activators, MYB repressors are also involved in regulating anthocyanin biosynthesis, including members of R2R3-MYB and R3-MYB [39]. Currently, anthocyanin-related MYB repressors have been identified in Arabidopsis, grape, and poplar [40]. The repressive activity of R2R3-MYBs was dependent on the repressive motif in the C-terminal [19]. For example, AtMYB4 in Arabidopsis, FaMYB1 in strawberry, PhMYB27 in petunia, and MaMYB4 in banana contained an ethylene-responsive element-associated amphiphilic repression (EAR) motif in the C-terminal domain, which was considered as a major domain repressing the transcription of anthocyanin structural genes [41,42,43]. TLLLFR motif, another conserved C-terminal domain was also existed in some R2R3-MYB (e.g., PtrMYB182 in Populus) and R3-MYB (e.g., AtMYBL2 in A. thaliana) repressors [44, 45]. AtMYBL2 negatively regulated anthocyanin biosynthesis through repressing DFR and TT8 expression [40, 44]. Other R3-MYB proteins, such as PhMYBx in petunia and AtCPC in Arabidopsis only contained a bHLH-binding motif in the R3 domain, and no repressive region has been identified with binding ability to the promoters of anthocyanin biosynthesis genes [10, 46]. In Arabidopsis and lily (Lilium spp.), the R3-MYB repressors affected the DFR promoter activity by binding bHLH protein as a competitive inhibitor, and affected the formation of MBW complex and inhibited anthocyanin accumulation [46, 47]. For instance, AtCPC repressed anthocyanin biosynthesis by competing with AtMYB75/90 to bind AtGL3/AtEGL3 and affecting MBW formation [46]. In grape hyacinth, MaMYBx regulated anthocyanin biosynthesis through binding to MabHLH1 and disrupting the MaMybA/MaAN2-MabHLH1 complex, and was able to repress flower pigmentation in tobacco [48]. Nevertheless, little is known about how MBW activators and MYB repressors cooperated in the anthocyanin regulatory network to precisely control flavonoid content in plants.
Rapeseed (Brassica napus L., 2n = 38) is a natural allotetraploid with great economic values and is widely cultivated as an oil crop in the world [49]. Due to the genome complexity compared with Arabidopsis, the regulation mechanism of anthocyanin biosynthesis in B. napus is more complicate and it has not been fully elucidated yet. Although many differentially expressed genes (DEGs) have been reported among rapeseed materials with different seed, leaf, or flower colors [50,51,52]. Hitherto, the functionally reported genes affecting anthocyanin biosynthesis in B. napus are structural genes (e.g., DFR, FLS, and LDOX) [52, 53] and transcription regulatory factors (PAP2.A7, BnGL3-1, and WRKY41-1) [54,55,56,57]. The MYB repressors involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis of B. napus have not been reported. Herein, we characterized BnCPC as an R3-MYB repressor that negatively regulated anthocyanin accumulation in B. napus. We found that BnCPC affected the formation of MBW complexes by interacting with bHLH proteins (BnTT8 or BnEGL3), thereby inhibiting the expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes. Furthermore, BnCPC was able to inhibit the MBW complex-induced BnCPC activity, to form a feedback regulation with MBW complexes in regulating anthocyanin biosynthesis.
Results
BnCPC encodes a CPC-type R3-MYB protein
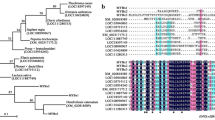
Six BnCPC homologues were identified in the rapeseed genome, which encoded proteins with 86 amino acids in length and contained a conserved R3-MYB domain. A phylogenetic analysis of known MYB repressors suggested that BnCPCs belonged to the CPC-type R3-MYB family, and were most conserved to AtCPC (Fig. 1A), which was a negative regulator of anthocyanin accumulation in Arabidopsis [46]. Multiple sequence alignment revealed that BnCPC contained an N-terminal R3-DNA binding domain with a conserved motif, [D/E]Lx2[R/K]x3Lx6Lx3R, for interaction with bHLH proteins (Fig. 1B). Other repressive domains such as EAR or TLLLFR motif were not found in BnCPCs, agreeing with the characteristics of other reported R3-MYB anthocyanin inhibitors (e.g., AtCPC and MaMYBx) [46, 48]. Based on the transcriptome data of B. napus from the BnTIR database, we found the BnCPC homologues were highly expressed in root and developing seeds, and BnaC04g50810D was highly expressed than other homologues at the transcriptional level (Additional file 1: Fig. S1A), which was used for functional analysis of BnCPC in this research. Transient expression assay of 35S::eGFP-BnCPC in tobacco leaves showed that BnCPC was a nuclei-localized transcription factor (Additional file 1: Fig. S1B). These findings indicated that BnCPC encoded a putative anthocyanin-related R3-MYB repressor in rapeseed.
Characterization of BnCPC proteins. A Phylogenetic relationship of BnCPC and other known MYB repressors in plants. BnCPC homologues were highlighted with the black rhombi. Alignment of full amino acid sequences of MYB repressors was done by MUSCLE software, and phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining method by MEGA software 7.0. Numbers at the nodes indicated the reliability percentage of bootstrap values based on 1000 replications. B Alignment and structural domains of BnCPC and MYB repressors. Protein sequences were aligned using ClustalX. The R2 and R3 domains were indicated with grayish white and gray boxes, respectively. Three α-helices of both R2 and R3 domains were indicated in boxes. The conserved MYB–bHLH interaction motif ([D/E]Lx2[R/K]x3Lx6Lx3R) of R3 domain was underlined with a black bar. The conserved motifs in the C-terminus were highlighted with boxes and numbers. C1 domain, LIsrGIDPxT/SHRxI/L; C2 domain (the EAR repression motif), pdLNLD/ELxiG/S; C3 domain (zinc-finger motif), Cx2Cx9CxC; C4 domain, GY/FDFLGL motif; C5 domain, TLLLFR repressor motif. The following GenBank or Arabidopsis TAIR accession numbers were used, PpMYB18 (KT159234.1), VvMYBC2-L1 (JX050227), VvMYBC2-L2 (ACX50288), VvMYBC2-L3 (KM046932), FaMYB1 (AF401220), MtMYB2 (XM_003616340), PtrMYB182 (KP723392), AtMYB4 (AF062860), PhMYB27 (AHX24372), MdMYB16 (HM122617), AtMYBL2 (AEE35154), IlMYBL1 (ASR83103.1), LhR3MYB1 (BBG71951.1), LhR3MYB2 (BBG71953.1), AtCPC (AT2G46410.1), PhMYBx (AHX24371.1), MlROI1 (AGC66791.1), SlMYBATV (NP_001352307), FhMYBx (MT210095), MaMYBx (QJH86892.1)
Analysis of BnCPC expression in anthocyanin inducible conditions
To understand the putative function of BnCPC in anthocyanin biosynthesis, we analyzed BnCPC expression pattern under anthocyanin inducible (cold and light) and non-inducible (dark) growth conditions, and found BnCPC was significantly induced after 3 h, 6 h and 24 h of cold treatment or light treatment, while no significant change was identified under dark treatment (Fig. 2A). Furthermore, we found the expression pattern of three anthocyanin biosynthetic genes, BnDFR, BnLDOX, and BnUF3GT, were similar to BnCPC, which were significantly up-regulated after 3 h, 6 h, and 24 h of light treatment, while these biosynthetic genes were continuously induced by cold treatment (Fig. 2B–D). These results indicated that BnCPC was up-regulated as the anthocyanin biosynthetic genes under the anthocyanin inducible conditions, suggesting that BnCPC might be correlated with anthocyanin biosynthesis in rapeseed.
The expression pattern of A BnCPC and B–D anthocyanin biosynthetic genes (BnDFR, BnLDOX, and BnUF3GT) under anthocyanin inducible (cold and light) and non-inducible (dark) growth conditions. Expression levels were standardized to B. napus Actin-7 (NC_027775.2), and the expression levels before treatment were set at 1. Values represented the mean ± SD (n = 3)
BnCPC overexpression reduces anthocyanin production in rapeseed
To investigate whether BnCPC is involved in regulating anthocyanin biosynthesis in B. napus, the cDNA of BnCPC (BnaC04g50810D) was overexpressed in rapeseed line J9712 under the control of CaMV 35S promoter, and three independent overexpressed lines (OE-CPC-6, OE-CPC-11, and OE-CPC-19) were used for phenotypic analysis (Additional file 1: Fig. S2). Under normal growth conditions (23 °C, 16 h light/8 h dark), we found the anthocyanin accumulation in hypocotyls of 7-day-old OE-CPC seedlings was less than that in J9712. And the cold-induced anthocyanin accumulation in J9712 was not observed in BnCPC overexpression lines (Fig. 3A, B). On the basis of RNA-seq analysis, we found all the LBGs (e.g., DFR, LDOX, UF3GT, and GSTF12) in flavonoid biosynthetic pathway were downregulated in BnCPC overexpression lines compared to J9712 under cold treatment (Additional file 1: Fig. S3, Additional file 2: Table S1). Besides, the F3′H and the regulatory genes BnTT8 and BnPAP1 (BnaCnn28030D) were also significantly downregulated in OE-CPC lines. In addition, qPCR analysis also confirmed that BnDFR, BnLDOX, and BnUF3GT expression were inhibited in OE-CPC lines compared with J9712 when grown under 23 °C and 10 °C (Fig. 3C). These DEGs might be responsible for the reduced anthocyanin accumulation in BnCPC overexpression lines.
BnCPC repressed anthocyanin accumulation in B. napus. A Phenotype of J9712 and BnCPC overexpression (OE-CPC) lines under low temperature (10 °C) and normal temperature (23 °C). Scale bar represented 1 cm. B Anthocyanin content in extracts from seedlings in A. (A530-0.25 × A657)/gram fresh weight was considered as the relative anthocyanin content. Three biological replicates were performed, and 10 plants were pooled as one replicate. FW, fresh weight. Values represented the mean ± SD (n = 3). Different letters represented statistically significant differences (two-way ANOVA, p < 0.05). C The expression level of BnDFR, BnLDOX, and BnUF3GT in rapeseed seedlings from A. Expression levels were normalized to B. napus Actin-7 (NC_027775.2), and the expression level of J9712 under normal temperature was set at 1. Values represented the mean ± SD (n = 3)
Furthermore, we analyzed the function of BnCPC in other growth conditions that induce anthocyanin biosynthesis, such as nitrogen deficiency (LN), sucrose, and jasmonic acid (JA) treatment. Under all tested stress and hormone treatments, the anthocyanin was more accumulated in the hypocotyls of J9712 than that grown in 1/2 MS or solid Hoagland medium with high nitrogen (HN), but it was barely accumulated in the OE-CPC lines grown under stress conditions (Additional file 1: Fig. S4A, B). The expression of anthocyanin biosynthesis related genes was repressed in BnCPC-overexpressed lines than J9712 when grown under nitrogen deficiency, sucrose and JA treatment. Meanwhile, we found BnDFR was much more repressed than other biosynthetic genes (Additional file 1: Fig. S4C). These results proved that BnCPC was a repressor of anthocyanin biosynthesis in rapeseed seedlings.
BnCPC represses the MBW complex-induced BnDFR activity
We used transient expression assay in tobacco to analyze the putative molecular mechanism of BnCPC in repressing anthocyanin biosynthesis, and found co-infiltration of 35S:BnPAP1 with 35S:BnTT8 or 35S:BnEGL3 induced purple pigmentation in tobacco leaves, but no pigmentation was observed when 35S:BnPAP1 + 35S:BnTT8 or 35S:BnPAP1 + 35S:BnEGL3 were co-infiltrated with 35S:BnCPC. Besides, co-transformation of 35S:BnTTG1 enhanced the pigmentation induced by 35S:BnPAP1 + 35S:BnTT8/35S:BnEGL3, which were also inhibited by 35S:BnCPC (Fig. 4A). Quantitative analysis also confirmed the function of BnPAP1-BnTT8/BnEGL3-BnTTG1 in inducing anthocyanin biosynthesis, and the role of BnCPC as an anthocyanin repressor (Fig. 4B). This agreed with the previous studies that CPC-type R3-MYBs play as repressors in anthocyanin biosynthesis by preventing the formation of MBW complexes [19, 40].
BnCPC repressed the BnDFR promoter activity by interfering with the formation of MBW complexes. A BnCPC inhibits anthocyanin accumulation mediated by MBW complexes in tobacco leaves. Tobacco leaves were infiltrated with BnPAP1 + BnTT8 ± BnCPC, BnPAP1 + BnEGL3 ± BnCPC, BnPAP1 + BnTT8 + BnTTG1 ± BnCPC, BnPAP1 + BnEGL3 + BnTTG1 ± BnCPC and cultured for 8 days. B Relative anthocyanin content in extracts from leaves in A. Independent-samples t-test was used for statistical analysis in comparison with the controls (**p ≤ 0.01). C BnCPC inhibited the MBW complex-induced BnDFR promoter activity. Values represent the mean ± SD (n = 6). Different letters represented statistically significant differences (one-way ANOVA, p < 0.05)
We used dual-luciferase reporter assay in tobacco to test the effect of BnCPC on anthocyanin biosynthetic genes, and found that co-transformation of BnPAP1 + BnTT8 or BnPAP1 + BnTT8 + BnTTG1 significantly enhanced the activity of BnDFR promoter. But the BnDFR promoter activity was significantly repressed when BnCPC was co-introduced with BnPAP1 + BnTT8 and BnPAP1 + BnTT8 + BnTTG1. Besides, BnCPC also repressed the BnDFR activity induced by BnPAP1 + BnEGL3 and BnPAP1 + BnEGL3 + BnTTG1 (Fig. 4C). Thus, we may speculate that BnCPC inhibits the activity of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes by influencing MBW complexes.
BnCPC interacts with bHLH proteins of MBW complexes
As mentioned above, BnCPC contained a conserved motif for bHLH interaction, and it also affected the BnDFR activity by influencing MBW complexes. Here we adopted yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) assay to analyze the interactions between BnCPC and BnTT8/BnEGL3, aiming to illustrate how BnCPC affects the function of anthocyanin-related MBW complexes. The results showed that BnCPC interacted with BnTT8 and BnEGL3 in yeast cells (Fig. 5A). Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assay confirmed the interaction between BnCPC and BnTT8/BnEGL3 (Fig. 5B). GST pull-down assay was also used to validate the interaction between BnCPC and BnTT8/BnEGL3 (Fig. 5C). These results revealed that BnCPC physically interacted with BnEGL3 and BnTT8 both in vitro and in vivo.
BnCPC competes with BnPAP1 to affect MBW formation
We conducted competitive binding assays to analyze whether BnCPC affects the MBW complex by competing with the MYB component (e.g., BnPAP1). Strong yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) signals were detected in nuclei when BnPAP1-nYFP and BnTT8-cYFP were transiently co-expressed in tobacco leaves. But it was impaired after 35S::BnCPC was co-transformed with BnPAP1-nYFP and BnTT8-cYFP. Similar results were observed when 35S::BnCPC was co-expressed with BnPAP1-nYFP and BnEGL3-cYFP (Fig. 6A). The expression level of BnPAP1, BnTT8, and BnEGL3 were not significantly changed in the infiltrated tobacco leaves, even when 35S::BnCPC was co-expressed (Fig. 6B, C). This confirmed that the binding ability between BnPAP1 and BnTT8 or BnEGL3 was affected by BnCPC, not by the expressional changes of BnPAP1/BnTT8/BnEGL3. We further tested whether BnCPC could interfere with the interaction between BnPAP1 and BnTT8/BnEGL3 with pull-down assay. Competitive binding experiments proved that the binding ability between BnPAP1 and BnTT8/BnEGL3 were impaired with the increase of BnCPC content (Fig. 6D). Taken together, these results demonstrated that BnCPC was capable to compete with BnPAP1 to bind BnTT8/BnEGL3, thus affected the formation of MBW complexes.
BnCPC competes with BnPAP1 to affect MBW formation. A BiFC analysis showed that BnCPC affected the interaction of BnPAP1 with BnTT8/BnEGL3. YFP fluorescence was observed 48 h after co-expression. Scale bar represented 100 μm. B and C qPCR analysis of BnCPC, BnTT8, BnEGL3, and BnPAP1 expression in A. Expression level was standardized to tobacco Actin (JQ256516.1). Values represented the mean ± SD (n = 3). D Competitive binding assays of BnCPC and BnPAP1 for BnTT8/BnEGL3
BnCPC was induced by MBW complex
To validate whether the components of MBW could regulate BnCPC expression to modulate appropriate anthocyanin biosynthesis, we analyzed the gene expression pattern under anthocyanin inducible (cold and light) and non-inducible (dark) conditions (Fig. 7A–C). qRT-PCR analysis revealed that both BnCPC and BnPAP1 were significantly induced by cold and light treatment at 3 h cold and 6 h light treatments; while BnCPC and BnPAP1 were not significantly induced under dark treatment. Unlike BnPAP1, BnTT8 and BnEGL3 expression were not induced by cold or light treatments. This suggested that the expression of BnCPC and BnPAP1 were coordinately regulated by anthocyanin inducible growth conditions. Furthermore, we used dual-luciferase reporter assay to confirm the regulatory relationship among BnCPC, BnPAP1, BnTT8, and BnEGL3. We found that a single BnPAP1, BnTT8, or BnEGL3 was unable to enhance BnCPC promoter activity. While both BnPAP1 + BnTT8 and BnPAP1 + BnEGL3 significantly induced the promoter activity of BnCPC, which were repressed when BnCPC was co-transformed (Fig. 7D). This indicated that BnCPC could be induced by BnPAP1 and BnTT8/BnEGL3, the major components of MBWs. This agreed with previous reports that anthocyanin activators could activate MYB repressors, resulting in negative feedback regulation in anthocyanin biosynthesis [48, 50, 58]. Thus, BnCPC regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis by competing with BnPAP1 to bind BnTT8/BnEGL3 and affects MBW formation, and BnCPC could form a feedback regulation in inhibiting the MBW complex-induced BnCPC activity.
Regulatory relationships between BnCPC and the anthocyanin activators. A–C The expression pattern of BnCPC, BnPAP1, BnTT8, and BnEGL3 under anthocyanin inducible (cold and light) and non-inducible (dark) growth conditions. Expression levels were standardized to B. napus Actin-7 (NC_027775.2), and the expression levels of BnCPC before treatment were set at 1. Values represented the mean ± SD (n = 3). D Dual-luciferase assays of BnPAP1, BnTT8, BnEGL3, BnPAP1 + BnTT8/BnEGL3, and BnCPC + BnPAP1 + BnTT8/BnEGL3 effects on the activity of BnCPC promoter. Values represent the mean ± SD (n = 6). Different letters represented statistically significant differences (one-way ANOVA, p < 0.05)
Discussion
Anthocyanins are important secondary metabolites that could be induced by various environmental stimuli, such as strong light, low temperature, high sucrose concentration, drought stress, and hormones [59, 60]. For better adaptation to the changing environment, plants have evolved a series of mechanisms to regulate the anthocyanin biosynthesis. In most plants, anthocyanin accumulation is regulated by the MBW protein complexes, and R2R3-MYBs are pivotal to determine the MBW functions and the spatio-temporal localization/deposition of anthocyanins [20, 61]. Due to the genome complexity and lack of anthocyanin mutants, the regulatory network of anthocyanin biosynthesis has not been fully elucidated in rapeseed. Many putative genes associated with anthocyanin biosynthesis have been screened through comparative analysis of rapeseeds with color variations in different tissues (e.g., seed coat, leaf, and petal), including BnDFR, BnLDOX, BnUF3GT, BnTT8, BnTT19 and BnPAP2 [54, 62, 63]. However, the repressors involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis have not been reported in B. napus. Here, we characterized a MYB repressor BnCPC, which negatively regulated anthocyanin accumulation by inhibiting the function of MBW protein complexes.
MYB protein plays important roles in plant growth, development, and stress responses [64, 65]. In the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway of plants, R2R3-MYB proteins are well known as activators by forming MBW complexes with bHLHs and WD40 [61]. A few MYB repressors involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis have been identified, including AtMYBL2 and AtCPC [44, 46], MtMYB2 in Medicago truncatula [66], MaMYBx in grape hyacinth [48], PhMYBx and PhMYB27 in petunia [42], and PpMYB18 in peach [50]. These MYB repressors could be divided into two types, R2R3-MYB and R3-MYB. In this study, sequence alignment showed that BnCPCs contained an R3-MYB and a bHLH-binding domain with high similarity to the anthocyanin repressors reported in A. thaliana (e.g., AtCPC) and grape hyacinth (e.g., MaMYBx) (Fig. 1B). In addition, the phylogenetic analysis grouped BnCPC to the CPC-type R3-MYB subgroup, which included multiple anthocyanin negative regulatory proteins (Fig. 1A). To elaborate the molecular function of BnCPC in B. napus, we created the BnCPC overexpression lines and analyzed the anthocyanin accumulation in response to various external stimuli, including low temperature, sucrose, nitrogen deficiency, and JA treatments (Fig. 2; Additional file 1: Fig. S4). The results showed that BnCPC negatively regulated anthocyanin accumulation, especially under stress and hormone treatments. And the expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes was also repressed, indicating that BnCPC repressed anthocyanin biosynthesis through inhibiting related genes in the biosynthetic pathway.
As reported, MYB repressors affect anthocyanin accumulation mainly through active and passive inhibitions [19, 40]. The active suppressors usually contain repressive motifs in the C-terminal, which is crucial for the repressive activities. For instance, PhMYB27 in petunia and MdMYB16 in apple were identified as repressors in anthocyanin biosynthesis, and deletion of the C-terminal EAR motif led to loss of function as anthocyanin repressors [42, 67]. Another inhibition domain TLLLFR motif, was identified in the C-terminus of AtMYBL2 [44], which also existed in other MYB repressors (e.g., FhMYB27, VvMYBC2, and PtrMYB182) [45, 68, 69]. However, both EAR and TLLLFR repressive motifs were not identified in the BnCPC proteins (Fig. 1B), which indicated that BnCPCs were not active repressors. Passive MYB repressors usually regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis through intermolecular interactions with bHLHs of the MBW complexes [19]. To date, all the reported MYB repressors in anthocyanin accumulation contain a conserved R3 domain with a [D/E]Lx2[R/K]x3Lx6Lx3R motif that interacts with bHLHs [19, 39, 40]. Furthermore, MYB repressors compete with MYB activators for binding to bHLH, suggesting that the bHLH-binding motif is critical for the inhibitory function of MYB repressors. Previously, mutations in the bHLH-binding motif disrupted the interactions of PpMYB18 in peach and PtrMYB182 in poplar with the bHLHs [45, 50]. Similarly, the motifs required for binding bHLHs were also identified in BnCPCs (Fig. 1B), and the interaction between BnCPC and bHLHs (e.g., BnTT8 and BnEGL3) were further confirmed by in vitro and in vivo protein–protein interaction assays (Fig. 5). The negative regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis via affecting the MBW formation is common in plants [19, 40]. Based on the competitive BiFC and pull-down assays, we verified that BnCPC suppressed the interaction of MYB activator (BnPAP1) and bHLHs (BnTT8 or BnEGL3) by binding to the bHLHs, and affected the formation of MBW complexes (Fig. 6). Transient expression in tobacco leaves showed that BnCPC inhibited anthocyanin accumulation that induced by MBW complexes (Fig. 4A), indicating that BnCPC repressed the expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes by disrupting the MBW complexes. This hypothesis was confirmed by the BnDFR promoter activity analysis, which showed that BnCPC inhibited the BnDFR activity induced by BnPAP1-BnTT8/BnEGL3-BnTTG1 (Fig. 4C). In chrysanthemum, CmMYB#7 inhibited the transcriptional activation of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes by impairing the binding ability between CmMYB6 and CmbHLH2, while mutation of the bHLH-binding site on CmMYB#7 affected its repressive function on anthocyanin biosynthetic genes that activated by CmMYB6–CmbHLH2 complex [70]. Interestingly, the passive repressive mechanism was also identified in other transcription factors, such as HD-ZIP protein HAT1, SBP family protein SPL9, and JAZ proteins that inhibited anthocyanin accumulation by interacting with MYB activators or bHLHs, thus affecting the formation of MBW complexes [36, 37, 71].
In Arabidopsis, the expression of MYB repressors were correlated with anthocyanin accumulation or anthocyanin biosynthetic genes [40]. In Citrus, the expression of anthocyanin repressor CsMYB3 was correlated with an R2R3-MYB activator CsRuby1, and anthocyanin accumulation in different tissues of Citrus and relative species [58]. Similarly, PpMYB18 was predominantly expressed in the ripening fruit of blood-fleshed peach, but not expressed in the yellow- and white-fleshed fruits. Besides, the expression of anthocyanin repressor PpMYB18 was correlated with the MYB activator PpMYB10.1, which was able to activate PpUFGT and PpDFR promotor activities [50]. In the present study, BnCPC was up-regulated in anthocyanin inducible conditions, with similar expression pattern correlated with anthocyanin biosynthetic genes (BnDFR, BnLDOX, and BnUF3GT) and regulatory gene BnPAP1 (Figs. 2, 7A–C), suggesting a putative feedback loop via BnCPC in the regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis. Thus, we speculated that BnCPC could be induced by the components of anthocyanin-related MBW complex. And it was further confirmed that BnPAP1 together with BnTT8/BnEGL3 could significantly activate the promoter of BnCPC, but it was inhibited in combination with BnCPC. This feedback regulation loop should be important in the appropriate regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in rapeseed. It is common that MYBs paly dual roles and could compete with each other to regulate flavonoid biosynthesis in plants. In Arabidopsis, MYB4 interacted with TT8, repressed the MYB75/90 and TT2 expression of MBW complexes, thus affected the MBW activity in regulating flavonoid biosynthesis [72].
In summary, we propose a working model of BnCPC inhibiting anthocyanin biosynthesis in B. napus (Fig. 8). Under non-inducible growth conditions (e.g., dark condition), the anthocyanin activator BnPAP1 was expressed at a low level while BnCPC was continuously expressed to repress the formation of MBW complexes, thereby inhibited anthocyanin accumulation. Under anthocyanin inducible conditions (e.g., low temperature stress), BnPAP1 was induced and formed MBW complexes to activate transcription of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes (e.g., BnDFR, BnLDOX, and BnUF3GT) and promote anthocyanin accumulation. Meanwhile, BnCPC was up-regulated under stress conditions, and competed with BnPAP1 to interact with bHLHs (BnTT8 and BnEGL3), thus affected the MBW complex formation. Furthermore, BnCPC inhibited the MBW complex-induced BnCPC activity, and formed a feedback loop with MBWs to regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis.
Proposed working model of BnCPC regulating anthocyanin biosynthesis in rapeseed. A Under non-inducible conditions (e.g., dark or non-stress conditions), BnPAP1 was lowly expressed and BnCPC was continuously induced to repress the expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes (e.g., BnDFR) by inhibiting MBW formation, thereby repressed anthocyanin accumulation. B Under inducible conditions (e.g., cold and other stress conditions), BnPAP1 was induced and formed MBW complexes to activate transcription of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes (e.g., BnDFR, BnLDOX, and BnUF3GT) and promote anthocyanin accumulation. BnCPC was up-regulated under stress conditions, and competed with BnPAP1 to interact with BnTT8/BnEGL3, thus affecting the MBW complex formation. BnCPC also inhibited the MBW complex-induced BnCPC activity, and formed a feedback loop with MBWs to regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis. Arrows and blunt arrows represent positive and negative regulation, respectively
Conclusions
In this study, an R3-MYB repressor BnCPC was identified with functions in regulating anthocyanin accumulation in rapeseed. BnCPC could repress anthocyanin biosynthesis by competing with BnPAP1 to interact with bHLHs (BnTT8 and BnEGL3) and affect the formation of MBW complexes, and repress the expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes (e.g., BnDFR) that activated by MBW complexes. Meanwhile, the MBW complexes could induce the expression of BnCPC. In general, this research revealed a negative feedback loop of BnCPC and MBW complexes that controlled anthocyanin biosynthesis in B. napus, which will be helpful to understand the regulatory mechanisms of R3-MYB repressors on anthocyanin accumulation.
Materials and methods
Plant materials and growth conditions
The B. napus line J9712 was used as transgenic acceptor and control. Both J9712 and transgenic lines were grown in the experimental field in Yangzhou University (Jiangsu, China) for reproduction. For gene expression pattern analysis under cold, light, and dark conditions, the 4-day-old seedlings of J9712 grown in 1/2 MS medium in dark condition, were transferred to anthocyanin inducible (continuous light and low temperature at 10 °C, or continuous light and normal temperature at 23 °C) and non-inducible (continuous dark and normal temperature at 23 °C) growth conditions, respectively [73, 74]. Then, three replicates of ten seedlings were collected at 0 h, 1 h, 3 h, 6 h, 9 h, 12 h, 24 h, and 48 h after treatment, and stored at − 80 °C for use. Furthermore, both J9712 and transgenic lines were grown under different stress conditions for seven days to analyze the BnCPC function in regulating anthocyanin biosynthesis. For cold stress, seeds were germinated in 1/2 MS medium and grown at 10 °C, 16 h light/8 h dark, using the seedlings grown at 23 °C as control. For other stresses, seedlings were grown in 1/2 MS containing 10% sucrose or 30 μM JA, or solid Hoagland medium with 3 mM or 0.3 mM NH4NO3 under 23 °C, 16 h light/8 h dark cycles. The seedlings were pooled as mentioned above, and stored at − 80 °C for gene expression analysis and anthocyanin content measurement. Nicotiana benthamiana were grown in a light incubator (22 °C, 16 h light/8 h dark), and the 4-week-old plants were used for transient expression assays.
Sequence and phylogenetic analysis
The protein sequences of BnCPC were downloaded from rapeseed genome database (http://www.genoscope.cns.fr/brassicanapus/), and the protein sequences of other known MYB repressors were downloaded from NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). Sequence conservation and phylogenetic analysis were conducted as reported before [75]. Multiple sequence alignment was performed with ClustalX (http://www.clustal.org/clustal2/). The phylogenetic tree was constructed with MEGA 7.0 (https://www.megasoftware.net/), using the neighbor-joining method.
Subcellular localization
To determine the subcellular localization of BnCPC, the full-length coding sequence (CDS) of BnCPC (BnaC04g50810D) was cloned from B. napus cv. ‘Darmor-bzh’ and ligated into pEGAD vector to construct 35S::eGFP-BnCPC. The 35S::eGFP-BnCPC and 35S::eGFP were transferred into Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain GV3101 by electroporation, and injected into the abaxial epidermis of N. benthamiana leaves for transient expression in dark for 48 h. The florescence images were captured using a confocal laser-scanning microscope (TCS SP8 STED, Leica, Germany). All primers are listed in Additional file 2: Table S2.
Stable transformation of BnCPC in B. napus
The CDS of BnCPC (BnaC04g50810D) was cloned into the pMDC83 vector to construct an overexpression vector of BnCPC. The 35S::BnCPC construct was used for hypocotyl transformation in B. napus line J9712 via A. tumefaciens strain GV3101 [76]. The transgenic lines were selected with 50 μg/mL hygromycin and confirmed with PCR amplification. All primers are listed in Additional file 2: Table S2.
Transient expression assay in tobacco leaves
For transient assay of transcription factors (e.g., BnPAP1, BnTT8, BnEGL3, BnTTG1, and BnCPC) in regulating anthocyanin biosynthesis, the CDSs were cloned into p35S vectors and introduced into A. tumefaciens GV3101 strain. The primers are listed in Additional file 2: Table S2. The different combinations of constructs were co-transformed into tobacco leaves. After overnight incubation in the dark and grown under normal photoperiod for eight days, the leaf samples around the injection site were sampled for anthocyanin content and qRT-PCR analysis [70].
Anthocyanin measurement
The anthocyanin content was measured according to the previous report with some modifications [77]. Briefly, 50 mg leaf sample was powdered and incubated in 200 μL extraction buffer (methanol containing 1% HCl) overnight at 4˚C in the dark. After centrifugation at 13,000 rpm for 10 min, the absorbance of the supernatant was measured at 530 and 657 nm. The relative anthocyanin content was calculated by (A530-0.25 × A657)/gram fresh weight. Three biological replicates were included for anthocyanin measurement.
Y2H assay
The CDSs of BnTT8, BnEGL3, and BnCPC were cloned into pGADT7 (AD) and pGBKT7 (BD). The primers are listed in Additional file 2: Table S2. The AD and BD vectors harboring target genes were co-transformed into yeast strain AH109 according to the manufacturer’s instructions of the Matchmaker Gold Yeast Two-Hybrid system (Clontech, Japan). The protein interactions were detected on SD-Trp/-Leu/-His/-Ade + X-α-Gal medium, using pGBKT7-53 and pGADT7-T as positive control, pGBKT7-Lam and pGADT7-T as negative control [78].
BiFC assay
The CDSs of BnCPC, BnTT8, and BnEGL3 were cloned into pVYNE and pVYCE to fuse with the N- or C-terminal fragments of YFP. The primers are listed in Additional file 2: Table S2. All constructs were transformed into A. tumefaciens strain GV3101, and different combinations of BiFC constructs were co-transformed into 4-week-old N. benthamiana. For competitive binding assay, 35S::BnCPC was co-transformed with different combinations of BiFC constructs. After culturing in dark for 48 h, the florescence images were observed using a confocal fluorescence microscope (TCS SP8 STED, Leica, Germany).
GST pull-down assay
The CDSs of BnCPC and BnPAP1 were cloned into the GST-tag-containing vector pGEX6p-1, while BnTT8 and BnEGL3 were cloned into His-tag-containing vector pET30a. Furthermore, BnCPC was also cloned into pET30a for competitive binding assay. All primers used are listed in Additional file 2: Table S2. The GST-BnCPC, GST-BnPAP1, His-BnCPC, His-BnTT8, and His-BnEGL3 constructs were transformed into Escherichia coli strain BL21 (DE3). The GST, GST-BnCPC, His-TT8 or His-EGL3 were immobilized using the ProteinIso® GST Resin or ProteinIso® Ni-NTA Resin (TransGen Biotech, Beijing, China). For pull-down assay, immobilized GST or GST-BnCPC were incubated with His-BnTT8 or His-BnEGL3 proteins at 4 °C for 2 h. For competitive binding assays, 5 μg of GST-PAP1 mixed with 5, 15, or 25 μg His-BnCPC were incubated with 5 μg of immobilized His-TT8 or His-EGL3 for 2 h. Beads were washed three times with the pull-down buffer. Proteins retained on beads were eluted by SDS-PAGE loading buffer and boiled for 5 min, then detected by anti-GST or anti-His.
Dual-luciferase reporter assay
The dual-luciferase reporter assay was conducted in tobacco leaves as described in previous reports [79]. The BnCPC and BnDFR promoters were cloned into the pGreenII 0800-LUC vector to generate proBnCPC:LUC and proBnDFR:LUC as the reporters, respectively. The CDSs of BnCPC, BnTT8, BnEGL3, BnPAP1, and BnTTG1 were inserted into pGreenII 62-SK as the effectors. All constructs were transformed into A. tumefaciens strain GV3101 containing a helper plasmid pSoup. The tobacco plants were grown in a growth chamber with 16 h of daylight. The reporters and effecters were mixed in ratios of 2:8, 2:4:4, or 2:3:3:3, and the different combinations of A. tumefaciens were injected into tobacco leaves. Two days after cultured under 16 h light/8 h dark and 22 °C, the injected leaves were collected for firefly luciferase (LUC) and renilla luciferase (REN) activity analysis, using the Dual Luciferase Reporter Assay Kit (Vazyme, Nanjing, China) and a Tecan Infinite M200 Pro luminometer (TECAN, Männedorf, Switzerland). Six independent biological replicates were included for dual-luciferase reporter assay. All primers are listed in Additional file 2: Table S2.
Gene expression analysis
Three replicates of seedling samples of two BnCPC overexpression lines (OE-CPC-6, OE-CPC-11) and J9712 grown at 10 °C and 23 °C were collected for RNA-seq analysis [77]. Total RNA isolation and cDNA synthesis were performed with RNA isolator Total RNA Extraction Reagent (Vazyme, Nanjing, China) and the HiScript III RT SuperMix (Vazyme, Nanjing, China), respectively. PowerUp SYBR Green Master Mixes (Thermo, Waltham, MA, USA) and a StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR System (Thermo, Waltham, MA, USA) were used for qPCR analysis. The relative gene expression was calculated with the 2−△△Ct method [80], using B. napus Actin-7 (NC_027775.2) or N. benthamiana Actin (JQ256516.1) as internal controls. The qPCR primers are listed in Additional file 2: Table S2. The relative expression level of different BnCPC homologues in different tissues of rapeseed was obtained from transcriptome database BnTIR (http://yanglab.hzau.edu.cn/BnTIR) [81].
Statistical analysis
All the data were expressed as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 19.0. Independent-samples t-test was used to analyze significant difference between two samples. One-way ANOVA was carried out to compare statistical differences among groups with Duncan’s test. Significant differences were marked at p < 0.05 and p < 0.01 level.
Availability of data and materials
All the data pertaining to the present study have been included in the tables and figures of the manuscript, and the authors are pleased to share all the data and plant materials.
Abbreviations
- MBW:
-
MYB-bHLH-WD40
- EBGs:
-
Early biosynthesis genes
- LBGs:
-
Late biosynthesis genes
- CHS :
-
Chalcone synthase
- CHI :
-
Chalcone isomerase
- F3H :
-
Flavanone 3-hydroxylase
- F3′H :
-
Flavanone 3′-hydroxylase
- DFR :
-
Dihydroflavonol 4-reductase
- LDOX :
-
Leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase
- UF3GT :
-
UDP-glucose: flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase
- PAs:
-
Proanthocyanidins
- EAR:
-
Ethylene-responsive element-associated amphiphilic repression
- DEGs:
-
Differentially expressed genes
- JA:
-
Jasmonic acid
- HN:
-
High nitrogen
- Y2H:
-
Yeast two-hybrid
- BiFC:
-
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation
- YFP:
-
Yellow fluorescent protein
- LN:
-
Low nitrogen
- CDS:
-
Coding sequence
- AD:
-
pGADT7
- BD:
-
pGBKT7
- LUC:
-
Firefly luciferase
- REN:
-
Renilla luciferase
References
Sinopoli A, Calogero G, Bartolotta A. Computational aspects of anthocyanidins and anthocyanins: a review. Food Chem. 2019;297: 124898.
Yan HL, Pei XN, Zhang H, Li X, Zhang XX, Zhao MH, et al. MYB-mediated regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:3103.
Tanaka Y, Sasaki N, Ohmiya A. Biosynthesis of plant pigments: anthocyanins, betalains and carotenoids. Plant J. 2008;54:733–49.
Sigurdson GT, Tang PP, Giusti MM. Natural colorants: food colorants from natural sources. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol. 2017;8:261–80.
Wallace TC. Anthocyanins in cardiovascular disease. Adv Nutr. 2011;2:1–7.
Onkokesung N, Reichelt M, van Doorn A, Schuurink RC, van Loon JJ, Dicke M. Modulation of flavonoid metabolites in Arabidopsis thaliana through overexpression of the MYB75 transcription factor: role of kaempferol-3,7-dirhamnoside in resistance to the specialist insect herbivore Pieris brassicae. J Exp Bot. 2014;65:2203–17.
Kim S, Hwang G, Lee S, Zhu JY, Paik I, Nguyen TT, et al. High ambient temperature represses anthocyanin biosynthesis through degradation of HY5. Front Plant Sci. 2017;8:1787.
Liu Y, Tikunov Y, Schouten RE, Marcelis LFM, Visser RGF, Bovy A. Anthocyanin biosynthesis and degradation mechanisms in Solanaceous vegetables: a review. Front Chem. 2018;6:52.
Naing AH, Kim CK. Abiotic stress-induced anthocyanins in plants: their role in tolerance to abiotic stresses. Physiol Plant. 2021;172:1711–23.
Albert NW, Lewis DH, Zhang HB, Schwinn KE, Jameson PE, Davies KM. Members of an R2R3-MYB transcription factor family in Petunia are developmentally and environmentally regulated to control complex floral and vegetative pigmentation patterning. Plant J. 2011;65:771–84.
Yamuangmorn S, Prom UTC. The potential of high-anthocyanin purple rice as a functional ingredient in human health. Antioxidants. 2021;10:833.
Alam MA, Islam P, Subhan N, Rahman MM, Khan F, Burrows GE, et al. Potential health benefits of anthocyanins in oxidative stress related disorders. Phytochem Rev. 2021;20:705–49.
Zhu F. Anthocyanins in cereals: composition and health effects. Food Res Int. 2018;109:232–49.
Choi YJ, Fan MQ, Tang YJ, Yang HP, Hwang JY, Kim EK. In vivo effects of polymerized anthocyanin from grape skin on benign prostatic hyperplasia. Nutrients. 2019;11:2444.
Qi QQ, Chu MJ, Yu XT, Xie YN, Li YL, Du YM, et al. Anthocyanins and proanthocyanidins: chemical structures, food sources, bioactivities, and product development. Food Rev Int. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1080/87559129.2022.2029479.
Xu WJ, Grain D, Bobet S, Le Gourrierec J, Thevenin J, Kelemen Z, et al. Complexity and robustness of the flavonoid transcriptional regulatory network revealed by comprehensive analyses of MYB-bHLH-WDR complexes and their targets in Arabidopsis seed. New Phytol. 2014;202:132–44.
Chaves-Silva S, Santos ALD, Chalfun-Junior A, Zhao J, Peres LEP, Benedito VA. Understanding the genetic regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in plants–tools for breeding purple varieties of fruits and vegetables. Phytochemistry. 2018;153:11–27.
Lepiniec L, Debeaujon I, Routaboul JM, Baudry A, Pourcel L, Nesi N, et al. Genetics and biochemistry of seed flavonoids. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2006;57:405–30.
LaFountain AM, Yuan YW. Repressors of anthocyanin biosynthesis. New Phytol. 2021;231:933–49.
Liu JY, Osbourn A, Ma PD. MYB transcription factors as regulators of phenylpropanoid metabolism in plants. Mol Plant. 2015;8:689–708.
Stracke R, Jahns O, Keck M, Tohge T, Niehaus K, Fernie AR, et al. Analysis of PRODUCTION OF FLAVONOL GLYCOSIDES-dependent flavonol glycoside accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana plants reveals MYB11-, MYB12- and MYB111-independent flavonol glycoside accumulation. New Phytol. 2010;188:985–1000.
Gonzalez A, Zhao MZ, Leavitt JM, Lloyd AM. Regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway by the TTG1/bHLH/MYB transcriptional complex in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant J. 2008;53:814–27.
Wang XY, Wang XL, Hu QN, Dai XM, Tian HN, Zheng KJ, et al. Characterization of an activation-tagged mutant uncovers a role of GLABRA2 in anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2015;83:300–11.
Teng S, Keurentjes J, Bentsink L, Koornneef M, Smeekens S. Sucrose-specific induction of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis requires the MYB75/PAP1 gene. Plant Physiol. 2005;139:1840–52.
Bac-Molenaar JA, Fradin EF, Rienstra JA, Vreugdenhil D, Keurentjes JJ. GWA mapping of anthocyanin accumulation reveals balancing selection of MYB90 in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS ONE. 2015;10: e0143212.
Li T, Jia KP, Lian HL, Yang X, Li L, Yang HQ. Jasmonic acid enhancement of anthocyanin accumulation is dependent on phytochrome A signaling pathway under far-red light in Arabidopsis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;454:78–83.
Azuma A, Kobayashi S, Mitani N, Shiraishi M, Yamada M, Ueno T, et al. Genomic and genetic analysis of Myb-related genes that regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis in grape berry skin. Theor Appl Genet. 2008;117:1009–19.
Xie S, Lei YJ, Chen HW, Li JN, Chen HZ, Zhang ZW. R2R3-MYB transcription factors regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis in grapevine vegetative tissues. Front Plant Sci. 2020;11:527.
Takos AM, Jaffe FW, Jacob SR, Bogs J, Robinson SP, Walker AR. Light-induced expression of a MYB gene regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in red apples. Plant Physiol. 2006;142:1216–32.
Espley RV, Hellens RP, Putterill J, Stevenson DE, Kutty-Amma S, Allan AC. Red colouration in apple fruit is due to the activity of the MYB transcription factor, MdMYB10. Plant J. 2007;49:414–27.
Vimolmangkang S, Han YP, Wei GC, Korban SS. An apple MYB transcription factor, MdMYB3, is involved in regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis and flower development. BMC Plant Biol. 2013;13:176.
Umemura H, Otagaki S, Wada M, Kondo S, Matsumoto S. Expression and functional analysis of a novel MYB gene, MdMYB110a_JP, responsible for red flesh, not skin color in apple fruit. Planta. 2013;238:65–76.
Cho JS, Nguyen VP, Jeon HW, Kim MH, Eom SH, Lim YJ, et al. Overexpression of PtrMYB119, a R2R3-MYB transcription factor from Populus trichocarpa, promotes anthocyanin production in hybrid poplar. Tree Physiol. 2016;36:1162–76.
Wan SZ, Li CF, Ma XD, Luo KM. PtrMYB57 contributes to the negative regulation of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in poplar. Plant Cell Rep. 2017;36:1263–76.
Wang HH, Wang XQ, Yu CY, Wang CT, Jin YL, Zhang HX. MYB transcription factor PdMYB118 directly interacts with bHLH transcription factor PdTT8 to regulate wound-induced anthocyanin biosynthesis in poplar. BMC Plant Biol. 2020;20:173.
Zheng T, Tan WR, Yang H, Zhang LE, Li TT, Liu BH, et al. Regulation of anthocyanin accumulation via MYB75/HAT1/TPL-mediated transcriptional repression. PLoS Genet. 2019;15: e1007993.
Qi TC, Song SS, Ren QC, Wu DW, Huang H, Chen Y, et al. The jasmonate-ZIM-domain proteins interact with the WD-repeat/bHLH/MYB complexes to regulate Jasmonate-mediated anthocyanin accumulation and trichome initiation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell. 2011;23:1795–814.
Maier A, Schrader A, Kokkelink L, Falke C, Welter B, Iniesto E, et al. Light and the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1/SPA control the protein stability of the MYB transcription factors PAP1 and PAP2 involved in anthocyanin accumulation in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2013;74:638–51.
Chen LH, Hu B, Qin YH, Hu GB, Zhao JT. Advance of the negative regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis by MYB transcription factors. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2019;136:178–87.
Ma DW, Constabel CP. MYB repressors as regulators of phenylpropanoid metabolism in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2019;24:275–89.
Deng GM, Zhang S, Yang QS, Gao HJ, Sheng O, Bi FC, et al. MaMYB4, an R2R3-MYB repressor transcription factor, negatively regulates the biosynthesis of anthocyanin in banana. Front Plant Sci. 2020;11: 600704.
Albert NW, Davies KM, Lewis DH, Zhang H, Montefiori M, Brendolise C, et al. A conserved network of transcriptional activators and repressors regulates anthocyanin pigmentation in eudicots. Plant Cell. 2014;26:962–80.
Aharoni A, De Vos CH, Wein M, Sun Z, Greco R, Kroon A, et al. The strawberry FaMYB1 transcription factor suppresses anthocyanin and flavonol accumulation in transgenic tobacco. Plant J. 2001;28:319–32.
Matsui K, Umemura Y, Ohme-Takagi M. AtMYBL2, a protein with a single MYB domain, acts as a negative regulator of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2008;55:954–67.
Yoshida K, Ma D, Constabel CP. The MYB182 protein down-regulates proanthocyanidin and anthocyanin biosynthesis in poplar by repressing both structural and regulatory flavonoid genes. Plant Physiol. 2015;167:693–710.
Zhu HF, Fitzsimmons K, Khandelwal A, Kranz RG. CPC, a single-repeat R3 MYB, is a negative regulator of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant. 2009;2:790–802.
Sakai M, Yamagishi M, Matsuyama K. Repression of anthocyanin biosynthesis by R3-MYB transcription factors in lily (Lilium spp.). Plant Cell Rep. 2019;38:609–22.
Zhang H, Gong JX, Chen KL, Yao WK, Zhang BX, Wang JY, et al. A novel R3 MYB transcriptional repressor, MaMYBx, finely regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in grape hyacinth. Plant Sci. 2020;298: 110588.
Chalhoub B, Denoeud F, Liu SY, Parkin IA, Tang HB, Wang XY, et al. Plant genetics. Early allopolyploid evolution in the post-neolithic Brassica napus oilseed genome. Science. 2014;345:950–3.
Zhou H, Wang KL, Wang FR, Espley RV, Ren F, Zhao JB, et al. Activator-type R2R3-MYB genes induce a repressor-type R2R3-MYB gene to balance anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin accumulation. New Phytol. 2019;221:1919–34.
Li HB, Du Y, Zhang JK, Feng HM, Liu JG, Yang GL, et al. Unraveling the mechanism of purple leaf formation in Brassica napus by integrated metabolome and transcriptome analyses. Front Plant Sci. 2022;13: 945553.
Hao PF, Liu H, Lin BG, Ren Y, Huang L, Jiang LX, et al. BnaA03.ANS identified by metabolomics and RNA-seq partly played irreplaceable role in pigmentation of red rapeseed (Brassica napus) petal. Front Plant Sci. 2022;13: 940765.
Vu TT, Jeong CY, Nguyen HN, Lee D, Lee SA, Kim JH, et al. Characterization of Brassica napus flavonol synthase involved in flavonol biosynthesis in Brassica napus L. J Agric Food Chem. 2015;63:7819–29.
Chen DZ, Liu Y, Yin S, Qiu J, Jin QD, King GJ, et al. Alternatively spliced BnaPAP2.A7 isoforms play opposing roles in anthocyanin biosynthesis of Brassica napus L. Front Plant Sci. 2020;11:983.
Duan SW, Wang JJ, Gao CH, Jin CY, Li D, Peng DS, et al. Functional characterization of a heterologously expressed Brassica napus WRKY41-1 transcription factor in regulating anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Sci. 2018;268:47–53.
Ye SH, Hua SJ, Ma TT, Ma XW, Chen YP, Wu LM, et al. Genetic and multi-omics analysis reveal BnaA07.PAP2In-184-317 as the key gene conferring anthocyanin-based color in Brassica napus flowers. J Exp Bot. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erac312.
Gao CH, Guo Y, Wang JJ, Li D, Liu KG, Qi SH, et al. Brassica napus GLABRA3-1 promotes anthocyanin biosynthesis and trichome formation in true leaves when expressed in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2018;20:3–9.
Huang D, Tang ZZ, Fu JL, Yuan Y, Deng XX, Xu Q. CsMYB3 and CsRuby1 form an “activator-and-repressor” loop for the regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in citrus. Plant Cell Physiol. 2020;61:318–30.
Albert NW, Lewis DH, Zhang H, Irving LJ, Jameson PE, Davies KM. Light-induced vegetative anthocyanin pigmentation in Petunia. J Exp Bot. 2009;60:2191–202.
Gao HN, Jiang H, Cui JY, You CX, Li YY. Review: The effects of hormones and environmental factors on anthocyanin biosynthesis in apple. Plant Sci. 2021;312: 111024.
Xu WJ, Dubos C, Lepiniec L. Transcriptional control of flavonoid biosynthesis by MYB-bHLH-WDR complexes. Trends Plant Sci. 2015;20:176–85.
Mushtaq MA, Pan Q, Chen DZ, Zhang QH, Ge XH, Li ZY. Comparative leaves transcriptome analysis emphasizing on accumulation of anthocyanins in Brassica: molecular regulation and potential interaction with photosynthesis. Front Plant Sci. 2016;7:311.
He D, Zhang DW, Li T, Liu LL, Zhou DG, Kang L, et al. Whole-genome identification and comparative expression analysis of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes in Brassica napus. Front Genet. 2021;12: 764835.
Li JL, Han GL, Sun CF, Sui N. Research advances of MYB transcription factors in plant stress resistance and breeding. Plant Signal Behav. 2019;14:1613131.
Yang A, Dai XY, Zhang WH. A R2R3-type MYB gene, OsMYB2, is involved in salt, cold, and dehydration tolerance in rice. J Exp Bot. 2012;63:2541–56.
Jun JH, Liu CG, Xiao XR, Dixon RA. The transcriptional repressor MYB2 regulates both spatial and temporal patterns of proanthocyandin and anthocyanin pigmentation in Medicago truncatula. Plant Cell. 2015;27:2860–79.
Xu HF, Wang N, Liu JX, Qu CZ, Wang YC, Jiang SH, et al. The molecular mechanism underlying anthocyanin metabolism in apple using the MdMYB16 and MdbHLH33 genes. Plant Mol Biol. 2017;94:149–65.
Li YQ, Shan XT, Gao RF, Han TT, Zhang J, Wang YN, et al. MYB repressors and MBW activation complex collaborate to fine-tune flower coloration in Freesia hybrida. Commun Biol. 2020;3:396.
Cavallini E, Matus JT, Finezzo L, Zenoni S, Loyola R, Guzzo F, et al. The phenylpropanoid pathway is controlled at different branches by a set of R2R3-MYB C2 repressors in grapevine. Plant Physiol. 2015;167:1448–70.
Xiang LL, Liu XF, Li H, Yin XR, Grierson D, Li F, et al. CmMYB#7, an R3 MYB transcription factor, acts as a negative regulator of anthocyanin biosynthesis in chrysanthemum. J Exp Bot. 2019;70:3111–23.
Gou JY, Felippes FF, Liu CJ, Weigel D, Wang JW. Negative regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis by a miR156-targeted SPL transcription factor. Plant Cell. 2011;23:1512–22.
Wang XC, Wu J, Guan ML, Zhao CH, Geng P, Zhao Q. Arabidopsis MYB4 plays dual roles in flavonoid biosynthesis. Plant J. 2020;101:637–52.
Fan D, Wang XQ, Tang XF, Ye X, Ren S, Wang DH, et al. Histone H3K9 demethylase JMJ25 epigenetically modulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in poplar. Plant J. 2018;96:1121–36.
Zhou L, He YJ, Li J, Liu Y, Chen HY. CBFs function in anthocyanin biosynthesis by interacting with MYB113 in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Plant Cell Physiol. 2020;61:416–26.
Xie T, Yang WJ, Chen X, Rong H, Wang YP, Jiang JJ. Genome-wide identification and expressional profiling of the Metal Tolerance Protein gene family in Brassica napus. Genes. 2022;13:761.
Yang Y, Zhu KY, Li HL, Han SQ, Meng QW, Khan SU, et al. Precise editing of CLAVATA genes in Brassica napus L. regulates multilocular silique development. Plant Biotechnol J. 2018;16:1322–35.
Rabino I, Manicinelli M. Light, temperature, and anthocyanin production. Plant Physiol. 1986;81:922–4.
Xie T, Chen X, Guo TL, Rong H, Chen ZY, Sun QF, et al. Targeted knockout of BnTT2 homologues for yellow-seeded Brassica napus with reduced flavonoids and improved fatty acid composition. J Agric Food Chem. 2020;68:5676–90.
Hellens RP, Allan AC, Friel EN, Bolitho K, Grafton K, Templeton MD, et al. Transient expression vectors for functional genomics, quantification of promoter activity and RNA silencing in plants. Plant Methods. 2005;1:13.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−△△Ct method. Methods. 2001;25:402–8.
Liu DX, Yu LQ, Wei LL, Yu PG, Wang J, Zhao H, et al. BnTIR: an online transcriptome platform for exploring RNA-seq libraries for oil crop Brassica napus. Plant Biotechnol J. 2021;19:1895–7.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Prof. Yongmin Zhou (Huazhong Agriculture University) for offering the seeds of rapeseed line ‘J9712’.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundations (31972963, 32201744), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFE0108000), the Top Talent Support Program of Yangzhou University and the Jiangsu Qinglan Project, the Graduate Training Program for Innovation and Entrepreneurship (SJCX21_1602), the Project of Special Funding for Crop Science Discipline Development (yzuxk202006), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.X., X.Z., X.C., and H.Z. performed the experiments. T.X. and H.R. performed data analysis. T.X. drafted the manuscript. Y.W. and J.J. revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors consent to the publication of this manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Figure S1.
The temporospatial expression pattern (A) and subcellular localization (B) of BnCPC. GFP fluorescence was shown in green. Bars = 10 μm. DAF, days after flowering; GFP, green fluorescent protein. Figure S2. qPCR analysis of BnCPC expression in overexpression lines of rapeseed. Figure S3. DEGs related to flavonoid biosynthetic processes. Figure S4. BnCPC repressed anthocyanin accumulation under different anthocyanin-inducible conditions. (A) Phenotype of J9712 and BnCPC overexpression (OE-CPC) lines under sucrose, JA, low nitrogen (LN), and high nitrogen (HN) treatments. (B) Anthocyanin content in extracts from seedlings in (A). (A530-0.25 × A657)/gram fresh weight was considered as the relative anthocyanin content. Three biological replicates were performed, and 10 plants were pooled as one replicate. FW, fresh weight. Values represented the mean ± SD (n = 3). Different letters represented statistically significant differences (one-way ANOVA, p < 0.05). (C) The expression level of BnDFR, BnLDOX, and BnUF3GT in seedlings from (A). Expression levels were standardized to B. napus actin-7 (NC_027775.2), and the expression levels of J9712 under CK or HN were set at 1. Values represented the mean ± SD (n = 3).
Additional file 2: Table S1.
DEGs related to flavonoid biosynthetic processes. Table S2. Primers used in the present study.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, T., Zan, X., Chen, X. et al. An R3-MYB repressor, BnCPC forms a feedback regulation with MBW complex to modulate anthocyanin biosynthesis in Brassica napus. Biotechnol Biofuels 15, 133 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-022-02227-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-022-02227-6