Abstract
Background
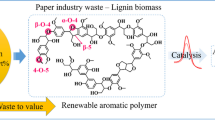
In the biorefinery utilizing lignocellulosic biomasses, lignin decomposition to value-added phenolic derivatives is a key issue, and recently biocatalytic delignification is emerging owing to its superior selectivity, low energy consumption, and unparalleled sustainability. However, besides heme-containing peroxidases and laccases, information about lignolytic biocatalysts is still limited till date.
Results
Herein, we report a promiscuous activity of tyrosinase which is closely associated with delignification requiring high redox potentials (>1.4 V vs. normal hydrogen electrode [NHE]). The promiscuous activity of tyrosinase not only oxidizes veratryl alcohol, a commonly used nonphenolic substrate for assaying ligninolytic activity, to veratraldehyde but also cleaves the 4-O-5 and Cα–Cβ bonds in 4-phenoxyphenol and guaiacyl glycerol-β-guaiacyl ether (GGE) that are dimeric lignin model compounds. Cyclic voltammograms additionally verified that the promiscuous activity oxidizes lignin-related high redox potential substrates.
Conclusion
These results might be applicable for extending the versatility of tyrosinase toward biocatalytic delignification as well as suggesting a new perspective for sustainable lignin utilization. Furthermore, the results provide insight for exploring the previously unknown promiscuous activities of biocatalysts much more diverse than ever thought before, thereby innovatively expanding the applicable area of biocatalysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Background
Biocatalysis is a useful and environmentally friendly approach in the fields of organic chemistry, pharmaceuticals, and biorefinery [1, 2]. To widen the enzymatic functionality of hoped-for reactions, some researchers have aimed to discover an overlooked inherent catalytic potential offered by nature known as catalytic promiscuity [3, 4]. Catalytic promiscuity is the ability of an enzyme to catalyze alternate reactions distinctly different from its primary catalysis [5] and a key factor in the evolution of new enzymatic functions from few ancestral generalist enzymes [3, 6]. Thus, the catalytic promiscuity of enzymes has been shown to be capable of catalyzing the hoped-for reactions through novel biocatalytic routes, thereby expanding the versatility of those enzymes [7].
Depletion of fossil fuels and climate change have accelerated research interest and effort on developing biorefinery using microbial fermentation which utilizes sugars obtained from lignocellulosic biomasses. Fermentable sugars are usually obtained from cellulosic and hemicellulosic components in biomasses by saccharification, whereas lignin is just pretreated for efficient saccharification. Thus, the strategy for utilizing lignin as sustainable feedstock for producing value-added phenolic derivatives is not still enough yet [8]. Even though various chemical pretreatments have been attempted in biorefinery, recently ligninolytic biocatalysts for pretreatment are emerging due to their superior selectivity, lower energy consumption, and unparalleled sustainability [9, 10]. In nature, heme-containing peroxidases such as lignin peroxidase (LiP, E.C. 1.11.1.14), manganese peroxidase (MnP, E.C. 1.11.1.13), versatile peroxidase (VP, E.C. 1.11.1.16), and dye-decolorizing peroxidase (DyP, E.C. 1.11.1.19) are known to be involved in delignification by catalyzing two-electron oxidation requiring a high redox potential of over +1.4 V (vs. normal hydrogen electrode [NHE]) with hydrogen peroxide as an electron acceptor [11, 12]. However, hydrogen peroxide, inevitably required for the catalysis of heme-containing peroxidases, often leads to critical inactivation by attacking and destroying the heme in the active site [13]. Laccase (E.C. 1.10.3.2) catalyzing low- or mid-redox potential compounds (usually < 1.0 V vs. NHE) is sometimes categorized as a ligninolytic biocatalyst; natural (e.g., vanillin) and artificial mediators (e.g., 2,2′-azinobis-(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonate) [ABTS] and 1-hydroxybenzotriazole [HBT]) often enhance the laccase activity for delignification [14]. Besides heme-containing peroxidases and laccase, information on other ligninolytic biocatalysts is very limited to date.
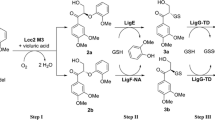
In order to broaden the enzymatic diversity of pretreating lignocellulosic biomasses and to increase the information about ligninolytic biocatalysts, we focused on tyrosinase (E.C. 1.14.18.1) which shows two catalytic activities for various phenolic compounds using O2 as the electron acceptor: o-hydroxylation of monophenol to diphenol by a cresolase activity and oxidation of diphenol to quinone by a catecholase activity [15]. In addition, we paid special attention to the fact that lignin is a highly branched phenolic-based natural polymer and thus evaluated whether tyrosinase possesses a promiscuous activity associated with delignification. In this study, it was verified that (i) tyrosinase has a promiscuous activity for oxidizing veratryl alcohol which is the most commonly used nonphenolic substrate for assaying ligninolytic activity; (ii) cyclic voltammogram additionally shows the promiscuous activity for oxidizing lignin-related high redox potential substrate; and (iii) the promiscuous activity cleaves the 4-O-5 and Cα–Cβ bonds in phenolic lignin model dimers independently of cation mediators (e.g., ABTS).
Results and discussion
Tyrosinase has a promiscuous activity for oxidizing a lignin-related nonphenolic substrate
Veratryl alcohol is the most widely used nonphenolic substrate for assaying ligninolytic activity [16,17,18,19,20], because the redox potential for oxidizing veratryl alcohol to veratraldehyde (>1.4 V vs. NHE) is similar to that for cleaving the β-O-4 linkage in lignin [21]. Hence, the promiscuous activity of tyrosinase for delignification was initially examined with veratryl alcohol that is a nonphenolic and thus not a primary substrate for the cresolase and catecholase activities of tyrosinase. The catalytic product was analyzed with GC–MS. As a result, tyrosinase catalyzed the conversion of veratryl alcohol to veratraldehyde, and then the latter was identified by GC–MS with a retention time of 10.95 min (red line in Fig. 1) and a mass spectrum of authentic veratraldehyde (Fig. 1; Additional file 1: Table S1). Because the detection of veratryl alcohol by GC–MS was more sensitive than that of veratraldehyde, the consumed veratryl alcohol was quantified for calculating the degree of conversion and the specific activity, resulting in about 6.2% and 52.5 mU mg−1, respectively. Given that tyrosinase oxidized veratryl alcohol to veratraldehyde, tyrosinase was found to have a promiscuous activity for oxidizing a nonphenolic substrate with a high redox potential which is associated with a ligninolytic activity. Table 1 summarizes the kinetic parameters of the promiscuous activity of tyrosinase and LiP a well-known ligninolytic biocatalyst. Tyrosinase oxidized veratryl alcohol with a k cat of 0.12 s−1 and a K m of 0.31 mM, whereas the negative control (no tyrosinase) did not show any absorbance change. LiP was found to have a k cat of 13.72 s−1 and a K m of 3.54 mM. Even though tyrosinase had a tenfold lower catalytic efficiency (k cat/K m) than that of LiP due to a lower turnover number (k cat) and a higher binding affinity (K m), the promiscuous activity seems to provide an opportunity for exploring a previously unknown versatility of tyrosinase as a ligninolytic biocatalyst [22].
The catalytic promiscuity in tyrosinase oxidizes veratryl alcohol to veratraldehyde. Gas chromatographic (GC) profile and mass spectra of the catalytic product using veratryl alcohol as the substrate in the absence (control, blue line) and presence of 100 unit tyrosinase (reactant, red line). The analyte was extracted with ethyl acetate. The chromatographic peaks were identified by the retention time and mass spectra library (NIST02). Authentic standard chemicals were used to double check the identified substrates and products (standards, black line). Inset: (i) mass spectrum and (ii) magnification of the peak at 10.95 min, and (iii) mass spectrum of the peak at 14.63 min
Cyclic voltammetry verifies that tyrosinase has a catalytic promiscuity for oxidizing a nonphenolic lignin-related substrate with a high redox potential
To further study the redox potential of tyrosinase during veratryl alcohol oxidation, cyclic voltammetry was performed. Figure 2a represents that tyrosinase itself did not show any oxidation peaks, but tyrosinase with veratryl alcohol as the substrate exhibited a definite oxidation peak at +1.22 V (vs. Ag/AgCl). As shown in Fig. 2b, no oxidation peaks were observed in the cyclic voltammograms of veratryl alcohol and veratraldehyde alone. Given that tyrosinase, veratryl alcohol, and veratraldehyde were not oxidized under the scan range (−1.5 to +1.5 V), the oxidation peak appearing at +1.22 V (vs. Ag/AgCl) in the mixture of tyrosinase and veratryl alcohol might be the result of tyrosinase-driven veratryl alcohol oxidation. When tyrosinase catalyzed veratryl alcohol oxidation, deprotonation of the veratryl alcohol was detected at the anode, and subsequently a definite oxidation peak was observed. Additionally, the oxidation potential (+1.22 V vs. Ag/AgCl corresponding to +1.43 V vs. NHE) was consistent to the oxidation potential of LiP for veratryl alcohol oxidation (>1.4 V vs. NHE) [21]. Consequently, the cyclic voltammogram shown in Fig. 2a provides evidence confirming that tyrosinase has the catalytic promiscuity for oxidizing nonphenolic lignin-related substrate with the high redox potential (i.e., veratryl alcohol).
The cyclic voltammetry. a The cyclic voltammograms of phosphate buffer (50 mM, pH 6.5) and tyrosinase with and without veratryl alcohol in phosphate buffer (50 mM, pH 6.5). Only in tyrosinase in the coexistence of veratryl alcohol, the oxidation peak was shown at +1.22 V vs. Ag/AgCl, which might be corresponding to +1.42 V vs. NHE. b The cyclic voltammogram of veratryl alcohol (1.7 mM) and veratraldehyde (1.7 mM) in phosphate buffer (pH 6.5). NO oxidation and reduction peaks were observed in each of veratryl alcohol and veratraldehyde. In all the cyclic voltammetries, glassy carbon, coiled Pt wire, and Ag/AgCl electrode were used as the working, counter, and reference electrode, respectively. Cyclic voltammetry was carried out using potentiostat/galvanostat controlled by commercial WMPG software. The scan rate was 50 mVs−1
The promiscuous activity of tyrosinase cleaves the 4-O-5 and Cα–Cβ bond in dimeric lignin model compounds
In order to verify whether the promiscuous activity of tyrosinase is able to cleave linkages in lignin, dimeric lignin model compounds were tested as substrates. 4-Phenoxyphenol [23] and guaiacyl glycerol-β-guaiacyl ether (GGE) [24] were used as the dimeric lignin model compounds to represent the 4-O-5 and β-O-4 linkages in lignin, respectively. When using 4-phenoxyphenol as the substrate, phenol was produced as the catalytic product (Fig. 3a; Additional file 1: Table S1). In addition, the clear 4-phenoxyphenol solution turned brown, and then, a dark brown precipitate was observed in a time-dependent manner. This phenomenon can be explained by quinone polymerization. The promiscuous activity of tyrosinase appeared to oxidatively cleave the 4-O-5 bond in 4-phenoxyphenol, thereby producing phenol and possibly 1,4-benzoquinone as shown in Fig. 3b. Phenol is a well-known primary substrate of tyrosinase and thus was sequentially converted to catechol and 1,2-benzoquinone by the cresolase and catecholase activities, respectively. Then, the 1,2-benzoquinone appeared to be polymerized through spontaneous oxidation, resulting in a dark brown precipitate [25]. In addition, we aimed to validate the 1,4-benzoquinone in the reaction sample. However, the authentic 1,4-benzoquinone was found to be unstable in the reaction conditions (pH 6.5 at 30 °C) and a small amount of brown precipitate was observed, which made it difficult to validate 1,4-benzoquinone in the reaction sample. To determine the degree of conversion and the specific activity, the consumed 4-phenoxyphenol was quantified by GC–MS and 3.04 mg L−1 of 4-phenoxyphenol was detected after a 24-h reaction, thereby indicating that the conversion rate and the specific activity for 4-phenoxyphenol were about 96.7% and 0.77 U mg−1, respectively.
Cleavage of 4-O-5 bond in 4-phenoxyphenol by the catalytic promiscuity of tyrosinase. a GC profile and mass spectra (MS) of the catalytic product using 4-phenoxyphenol in the absence (control, blue line) and presence of 100 unit tyrosinase (reactant, red line). The analyte was extracted with ethyl acetate. The chromatographic peaks were identified by the retention time and mass spectra library (NIST02). The authentic standard chemicals were used to confirm the identified (standard, black line). Inset: (i) mass spectrum and (ii) magnification of the peak at 10.15 min, and (iii) mass spectrum of the peak at 39.7 min. b Reaction scheme illustrates the catalytic promiscuity cleaves the 4-O-5 bond in 4-phenoxyphenol. The catalytic product phenol is a primary substrate of tyrosinase (cresolase activity)
Furthermore, GGE, a dimeric lignin model compound that includes a β-O-4 bond, which is the most prevalent linkage in lignin (>50%) [26], might be decomposed by the promiscuous activity of tyrosinase. As shown in Fig. 4a, one of the catalytic products was detected at 10.497 min in high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) profile which was the same retention time as that of authentic vanillin. The estimated catalytic product vanillin was additionally verified by GC–MS (Fig. 4b; Additional file 1: Table S1). Furthermore, we quantified the produced vanillin; after a 24-h reaction, 12.28 mg L−1 of vanillin were detected, thereby representing a conversion, specific activity, and vanillin production rate of 16.1%, 1.3 mU mg−1, 0.078 μmol h−1 mg−1, respectively. Vanillin is a useful compound which can be obtained from lignocellulose, but the information about enzymatic conversion of lignocellulose to vanillin has been limited. Instead, there are several reports about microbial vanillin production from lignocellulose: Kumar et al. utilized a natural bacterial consortium for valorizing lignocellulosic biomass and produced vanillin with the conversion of 0.36% [27]. In addition, vanillin dehydrogenase-deleted Rhodococcus jostii RHA1 has been reported to convert 0.38% of wheat straw lignocellulose to vanillin [28].
Decomposition of guaiacyl glycerol-β-guaiacyl ether (GGE) by the catalytic promiscuity of tyrosinase. a HPLC profile of GGE and vanillin in the control without tyrosinase and in the reaction sample which includes tyrosinase. The chromatographic peaks were identified by the retention time and authentic standard chemicals. b GC–MS of the catalytic product when using GGE as the substrate in the presence of 500 unit tyrosinase (red line). Black line represents authentic vanillin standard. Inset: mass spectrum of the peak at 10.31 min c Reaction scheme illustrates that the catalytic promiscuity cleaves the Cα–Cβ bond in GGE
Because the substrate, GGE, was not detected under the GC–MS conditions used for the vanillin analysis (using a HP-Innowax column), derivatization with tetramethylsilane (TMS) was carried out to analyze GGE. As a result, GGE-TMS was detected at a retention time of 26.1 in a GC–MS equipped with a HP-Ultra2 column (Additional file 1: Fig. S1, Table S1). In the HPLC profile (Fig. 4a), one unidentified peak at 18.929 min was also observed in the reaction sample. GC–MS analysis indicated that the estimated m/z value of the unidentified product was of 272 (Additional file 1: Table S1). It is not clear how the unidentified product was formed. A possible mechanism would be a further conversion of catalytic product (other than vanillin) to an unidentified product by tyrosinase. In accordance with Ahmad et al., bacterial DyP, one of the ligninolytic heme-containing peroxidases, catalyzes GGE to vanillin and guaiacol [12]. In addition, Chen et al. validated that DyP from Thermomonospora curvata would have a potential for lignin degradation and proposed the catalytic mechanism for decomposing GGE to guaiacol oligomer [29]. Besides DyP, ligninolytic heme-containing peroxidases have been known to easily convert guaiacol to guaiacol-oligomer [12, 19, 24]. As with DyP from Rhodococcus jostii RHA1 [12], the catalytic promiscuity of tyrosinase seemed to cleave the Cα–Cβ bond in GGE, yielding vanillin (Fig. 4c) and possibly an unstable o-(2-hydroxyethyl)guaiacol radical. The unstable o-(2-hydroxyethyl)guaiacol radical might be further catalyzed to guaiacol and 2-hydroxyacetaldehyde by the tyrosinase, and then guaiacol might be polymerized to an unidentified product with a m/z of 272 as shown in Fig. 4c: given that (i) the reduction of compound II to resting state in DyP initiates the conversion of o-(2-hydroxyethyl)guaiacol to guaiacol [12] and (ii) the redox potential of compound II/resting state in peroxidases is estimated ranging from +0.93 to +1.26 V [30], the promiscuous activity of tyrosinase oxidizing a high redox potential substrate veratryl alcohol (+1.22 V) might convert o-(2-hydroxyethyl)guaiacol to guaiacol. Additionally, Garcia-Molina et al. demonstrated the catalytic activity of tyrosinase on guaiacol [31]. Therefore, the promiscuous activity of tyrosinase seemed to directly cleave the Cα–Cβ bond according to vanillin formation and possibly guide the cleavage of the β-O-4 bond in GGE. However, further identification on the degradation products of GGE by tyrosinase is required to elucidate the degradation mechanism.
Conclusion
Given that tyrosinase exhibits a broad substrate specificity for various phenolic compounds and that lignin is a highly branched phenolic-based natural polymer, we herein explored the novel promiscuous activity of tyrosinase closely associated with delignification. Tyrosinase not only oxidizes veratryl alcohol, the most widely used nonphenolic substrate for assaying ligninolytic activity, but also cleaves the 4-O-5 and Cα–Cβ bonds in dimeric lignin model compounds. Consequently, tyrosinase seems to be applicable for biocatalytic pretreatment in biorefinery utilizing lignocellulosic biomass as a sustainable feedstock. Furthermore, the results provide a new perspective for sustainable lignin utilization to produce value-added phenolic derivatives.
Even if higher substrate specificity is a unique feature of a biocatalyst distinguishable from a chemical catalyst, recently reported promiscuous activities have been considered as favorable properties in numerous applications [22]. In accordance with Nam et al., the higher substrate specificity in a biocatalyst is a result of the evolution from promiscuous activities in ancestral generalist biocatalysts [6]. In this study, we, for the first time, identified the valuable catalytic promiscuity of tyrosinase associated with delignification. The results discussed herein could extend the versatility of tyrosinase as a promising ligninolytic biocatalyst under mild operational conditions (neutral pH using O2 as the electron acceptor). Given that the higher substrate specificity in a biocatalyst is a result of the evolution from promiscuous activities [6], the results provide insight into further understanding of how the lignocellulose-degrading biocatalytic specificity has evolved from promiscuous ancestral biocatalysts which might be much more diverse than ever thought before.
Tyrosinase has been studied for a long time in various fields including in bioremediation for detoxifying phenolics [32], in pharmaceutics for L-DOPA production [15, 33, 34], and in bioelectronics for detecting phenolics [35]. Nevertheless, the structure-based catalytic mechanism of tyrosinase has not been actively discussed until Matoba et al. reported the X-ray crystal structure of tyrosinase from Streptomyces castaneoglobisporus [36]. Based on the recently verified structure of tyrosinase from Agaricus bisporus (PDB ID:2Y9W) [37, 38], we will aim to suggest a catalytic mechanism for the promiscuous activity in the near future.
Methods
Enzymes and chemicals
Tyrosinase from Agaricus bisporus, LiP from Phanerochaete chrysosporium, veratryl alcohol (96%), veratraldehyde (99%), 4-phenoxy phenol (99%), benzyl phenyl ether (98%), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, 99%), and benzyl benzoate (99%) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, USA). GGE (97%) and trimethylchlorosilane (TMCS, 1%) in N,O-bis(trimethylsilyl) trifluoroacetamide (BSTFA) [BSTFA + TMCS] were purchased from Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd (Tokyo, Japan) and Supelco analytical (Bellefonte, USA), respectively. To remove trace impurities such as metal salts, tyrosinase was solubilized in phosphate buffer (50 mM, pH 6.5) and then purified with an ultrafiltration device with a cutoff of 10 kDa (Merck Millipore, MA, USA). All other chemicals were used as the highest grade available without further purification.
Reaction
The catalytic promiscuity of tyrosinase was tested with the following substrates: 10 mM veratryl alcohol. Due to the low solubility in the aqueous phase, 0.5 mM of 4-phenoxyphenol and GGE were used in phosphate buffer (pH 6.5) and 0.625% DMSO, respectively. The reaction was initiated by adding 100 (for veratryl alcohol and 4-phenoxyphenol) or 500 U (for GGE) of tyrosinase into 1 mL of a substrate solution in 50 mM phosphate buffer (pH 6.5). One U of tyrosinase converts 1 μmol of l-tyrosine to L-DOPA per min at pH 6.5 and 25 °C. All reactions were conducted at 30 °C for 24 h.
GC–MS analysis
After a 24-h reaction, the catalytic products from veratryl alcohol, 4-phenoxyphenol, and GGE were identified by GC–MS. The analytes were extracted with ethyl acetate (for veratryl alcohol, veratraldehyde, 4-phenoxyphenol, and phenol) or methyl chloride (for GGE and vanillin), and then, GC–MS analysis was performed with a 6890N GC interfaced with a 5975 MS (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, USA) under the following conditions: a fused polyethylene glycol HP-INNOWax capillary (30 m × 0.25 mm i.d., 0.25 μm, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, USA) and He (99.9999%) were used as the column and carrier gas at a constant flow rate (1.2 mL min−1), respectively. To analyze GGE, TMS derivatization was performed with BSTFA + TMCS, and a HP-Ultra2 column was used. Mass spectrometry was conducted in the electron impact mode (70 eV), and the ion source temperature was 230 °C. The temperature program of the oven is summarized in Additional file 1: Table S2. Chromatographic peaks were identified by the retention time and the mass spectra library (NIST02). Authentic standard chemicals were used to confirm the identification.
Cyclic voltammetry
A one-compartment electrochemical cell was constructed with a 3-electrode system for cyclic voltammetry. Glassy carbon, coiled Pt wire, and Ag/AgCl were used as the working, counter, and reference electrodes, respectively. Cyclic voltammetry was carried out using a potentiostat/galvanostat (WMPG1000K8, WonA Tech., Seoul, Korea) controlled by commercial WMPG software. In all cyclic voltammetries, the scan rate and the scan range were 50 mV s−1 and −1.5 to +1.5 V, respectively.
Kinetics
To determine the kinetic parameters, various concentrations of veratryl alcohol (0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, and 5.0 mM) were used, and the initial increase of absorbance was monitored at 310 nm (εveratraldehyde,310 nm = 9.3 mM−1 cm−1) with a UV-spectrophotometer (Shimazhu, UV-1240, Kyoto, Japan) at 30 °C [19]. To calculate the kinetic parameters shown in Table 1, the kinetic data were fitted into the Michaelis–Menten equation.
HPLC analysis
GGE and vanillin were analyzed by HPLC (Agilent 1200 HPLC system, CO, USA). The HPLC procedure was performed by injecting fractions using a reverse-phase Eclipse XDB-C18 column (4.6 × 150 mm, 5 μm, Agilent). Gradient separation was performed from distilled water (solvent A) to methanol (solvent B) using the following conditions: flow rate 1.0 mL min−1, column temperature 25 °C, time 0 min-5% B, time 5 min-25% B, time 10 min-40% B, time 30 min-50% B, time 35 min-100% B. Using a UV detector at 280 nm, authentic GGE and vanillin were detected at 13.522 and 10.497 min, respectively.
References
Bornscheuer UT, Huisman GW, Kazlauskas RJ, Lutz S, Moore JC, Robins K. Engineering the third wave of biocatalysis. Nature. 2012;485(7397):185–94.
Igarashi K. Cellulases: cooperative biomass breakdown. Nat Chem Biol. 2013;9(6):350–1.
Xue Y, Li L-P, He Y-H, Guan Z. Protease-catalysed direct asymmetric Mannich reaction in organic solvent. Sci Rep. 2012;2:761.
van Loo B, Jonas S, Babtie AC, Benjdia A, Berteau O, Hyvönen M, Hollfelder F. An efficient, multiply promiscuous hydrolase in the alkaline phosphatase superfamily. PNAS. 2010;107(7):2740–5.
Bornscheuer UT, Kazlauskas RJ. Catalytic promiscuity in biocatalysis: using old enzymes to form new bonds and follow new pathways. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2004;43(45):6032–40.
Nam H, Lewis NE, Lerman JA, Lee D-H, Chang RL, Kim D, Palsson BO. Network context and selection in the evolution to enzyme specificity. Science. 2012;337(6098):1101–4.
Lairson LL, Watts AG, Wakarchuk WW, Withers SG. Using substrate engineering to harness enzymatic promiscuity and expand biological catalysis. Nat Chem Biol. 2006;2(12):724–8.
Maity SK. Opportunities, recent trends and challenges of integrated biorefinery: part I. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2015;43:1427–45.
Larran A, Jozami E, Vicario L, Feldman SR, Podestá FE, Permingeat HR. Evaluation of biological pretreatments to increase the efficiency of the saccharification process using Spartina argentinensis as a biomass resource. Bioresour Technol. 2015;194:320–5.
Schroyen M, Vervaeren H, Vandepitte H, Van Hulle SWH, Raes K. Effect of enzymatic pretreatment of various lignocellulosic substrates on production of phenolic compounds and biomethane potential. Bioresour Technol. 2015;192:696–702.
Tuor U, Winterhalter K, Fiechter A. Enzymes of white-rot fungi involved in lignin degradation and ecological determinants for wood decay. J Biotechnol. 1995;41(1):1–17.
Ahmad M, Roberts JN, Hardiman EM, Singh R, Eltis LD, Bugg TDH. Identification of DypB from Rhodococcus jostii RHA1 as a lignin peroxidase. Biochemistry. 2011;50(23):5096–107.
Valderrama B, Ayala M, Vazquez-Duhalt R. Suicide inactivation of peroxidases and the challenge of engineering more robust enzymes. Chem Biol. 2002;9(5):555–65.
Bourbonnais R, Leech D, Paice MG. Electrochemical analysis of the interactions of laccase mediators with lignin model compounds. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 1998;1379(3):381–90.
Min K, Park D-H, Yoo YJ. Electroenzymatic synthesis of l-DOPA. J Biotechnol. 2010;146(1–2):40–4.
Blodig W, Smith AT, Doyle WA, Piontek K. Crystal structures of pristine and oxidatively processed lignin peroxidase expressed in Escherichia coli and of the W171F variant that eliminates the redox active tryptophan 171. Implications for the reaction mechanism. J Mol Biol. 2001;305(4):851–61.
Doyle WA, Blodig W, Veitch NC, Piontek K, Smith AT. Two substrate interaction sites in lignin peroxidase revealed by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochemistry. 1998;37(43):15097–105.
Goodwin DC, Aust SD, Grover TA. Evidence for veratryl alcohol as a redox mediator in lignin peroxidase-catalyzed oxidation. Biochemistry. 1995;34(15):5060–5.
Min K, Gong G, Woo HM, Kim Y, Um Y. A dye-decolorizing peroxidase from Bacillus subtilis exhibiting substrate-dependent optimum temperature for dyes and β-ether lignin dimer. Sci Rep. 2015;5:8245.
Pérez-Boada M, Ruiz-Dueñas FJ, Pogni R, Basosi R, Choinowski T, Martínez MJ, Piontek K, Martínez AT. Versatile peroxidase oxidation of high redox potential aromatic compounds: site-directed mutagenesis, spectroscopic and crystallographic investigation of three long-range electron transfer pathways. J Mol Biol. 2005;354(2):385–402.
Smith AT, Doyle WA, Dorlet P, Ivancich A. Spectroscopic evidence for an engineered, catalytically active Trp radical that creates the unique reactivity of lignin peroxidase. PNAS. 2009;106(38):16084–9.
Humble MS, Berglund P. Biocatalytic promiscuity. Eur J Org Chem. 2011;2011(19):3391–401.
Park HW, Hong UG, Lee YJ, Choi JH, Song IK. Catalytic decomposition of 4-phenoxyphenol to aromatics over Pd/XCs2.5H0.5PW12O40/ACA (x = 10, 20, 30, 40, and 50 wt%) catalysts. Appl Catal A. 2012;437–438:112–9.
Thanh Mai Pham L, Eom M-H, Kim YH. Inactivating effect of phenolic unit structures on the biodegradation of lignin by lignin peroxidase from Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2014;61–62:48–54.
Selinheimo E, Gasparetti C, Mattinen M-L, Steffensen CL, Buchert J, Kruus K. Comparison of substrate specificity of tyrosinases from Trichoderma reesei and Agaricus bisporus. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2009;44(1):1–10.
Chen W, Supanwong K, Ohmiya K, Shimizu S, Kawakami H. Anaerobic degradation of veratrylglycerol-beta-guaiacyl ether and guaiacoxyacetic acid by mixed rumen bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985;50(6):1451–6.
Harshvardhan K, Suri M, Goswami A, Goswami T. Biological approach for the production of vanillin from lignocellulosic biomass (Bambusa tulda). J Cleaner Prod. 2017;149:485–90.
Sainsbury PD, Hardiman EM, Ahmad M, Otani H, Seghezzi N, Eltis LD, Bugg TDH. Breaking down lignin to high-value chemicals: the conversion of lignocellulose to vanillin in a gene deletion mutant of Rhodococcus jostii RHA1. ACS Chem Biol. 2013;8(10):2151–6.
Chen C, Shrestha R, Jia K, Gao PF, Geisbrecht BV, Bossmann SH, Shi J, Li P. Characterization of dye-decolorizing peroxidase (DyP) from Thermomonospora curvata reveals unique catalytic properties of A-type DyPs. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(38):23447–63.
Liers C, Aranda E, Strittmatter E, Piontek K, Plattner DA, Zorn H, Ullrich R, Hofrichter M. Phenol oxidation by DyP-type peroxidases in comparison to fungal and plant peroxidases. J Mol Catal B Enzym. 2014;103:41–6.
Garcia-Molina MD, Muñoz-Muñoz JL, Garcia-Molina F, García-Ruiz PA, Garcia-Canovas F. Action of tyrosinase on ortho-substituted phenols: possible influence on browning and melanogenesis. J Agric Food Chem. 2012;60(25):6447–53.
Faccio G, Kruus K, Saloheimo M, Thöny-Meyer L. Bacterial tyrosinases and their applications. Process Biochem. 2012;47(12):1749–60.
Min K, Kathavarayan T, Park K, Yoo YJ. Novel strategy for enhancing productivity in l-DOPA synthesis: the electroenzymatic approach using well-dispersed l-tyrosine. J Mol Catal B Enzym. 2013;90:87–90.
Min K, Park K, Park D-H, Yoo Y. Overview on the biotechnological production of l-DOPA. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015;99(2):575–84.
Min K, Yoo YJ. Amperometric detection of dopamine based on tyrosinase-SWNTs-Ppy composite electrode. Talanta. 2009;80(2):1007–11.
Matoba Y, Kumagai T, Yamamoto A, Yoshitsu H, Sugiyama M. Crystallographic evidence that the dinuclear copper center of tyrosinase is flexible during catalysis. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(13):8981–90.
Ismaya WT, Rozeboom HJ, Schurink M, Boeriu CG, Wichers H, Dijkstra BW. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of tyrosinase from the mushroom Agaricus bisporus. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2011;67(Pt 5):575–8.
Ismaya WT, Rozeboom HJ, Weijn A, Mes JJ, Fusetti F, Wichers HJ, Dijkstra BW. Crystal structure of Agaricus bisporus mushroom tyrosinase: identity of the tetramer subunits and interaction with tropolone. Biochemistry. 2011;50(24):5477–86.
Authors’ contributions
KM and YU conceived the study. KM performed experimental works and wrote the manuscript. TY and JK carried out MS analysis under supervision of YK. YHK reviewed and commented on the manuscript. HMW, BS, and YJY participated in coordination of the manuscript draft. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Sunghee Ahn at the Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS) for the kind discussion about the GC–MS analysis of GGE and vanillin.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during the study are included in this manuscript and Additional file.
Consent for publication
All authors approved the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology (NRF-2009-C1AAA001-0093286), and Korea Evaluation Institution of Industrial Technology funded by Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy (10049675). This work was also supported by the National Research Council of Science and Technology (NST) granted by the Korean government (MSIP) (No. CAP-11-04-KIST).
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional file
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Min, K., Yum, T., Kim, J. et al. Perspectives for biocatalytic lignin utilization: cleaving 4-O-5 and Cα–Cβ bonds in dimeric lignin model compounds catalyzed by a promiscuous activity of tyrosinase. Biotechnol Biofuels 10, 212 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-017-0900-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-017-0900-3