Abstract
Successful expansion of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) would benefit the use of HSC transplants in the clinic. Angiopoietin-like 7 promotes the expansion of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPC) in vitro and ex vivo. However, the impact of loss of Angptl7 on HSPCs in vivo has not been characterized. Here, we generated Angptl7-deficient mice by TALEN-mediated gene targeting and found that HSC compartments in Angptl7-null mice were compromised. In addition, wild type (WT) HSPCs failed to repopulate in the BM of Angptl7-null mice after serial transplantations while the engraftment of Angptl7-deficient HSPCs in WT mice was not impaired. These results suggest that Angptl7 is required for HSPCs repopulation in a non-cell autonomous manner.
Similar content being viewed by others
Findings
The autologous-allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation has been developed for decades [1,2], and numerous attempts have been made to expand the HSCs population in vitro and in vivo [3-5]. Agiopoietin-like proteins belong to a 7-member family of secreted glycoproteins that share sequence homology with angiopoietins, which are important modulators of angiogenesis [6]. Several Angptl family proteins promote the expansion of murine and human HSPCs in vitro and ex vivo [7-9]. Angptl7 in the ECM of the trabecular meshwork plays an important role in the deposition and organization of the matrix of the outflow tissue [10]. Recently, we found that ANGPTL7 stimulated the proliferation of human HSPCs ex vivo (Yiren Xiao, unpublished data). In addition, we uncovered that Angptl7, which was secreted by murine bone marrow SSEA4+ mesenchymal cells (Additional file 1: Figure S1), stimulated expansion of murine HSCs ex vivo (Additional file 2: Figure S2). However, whether Angptl7 is redundant and dispensable or not for repopulation of HSPCs in vivo remains unknown. In this study, we generated Angptl7 knockout mice and revealed that Angptl7 is essential for HSPC repopulation in a non-cell autonomous way.
To investigate whether the loss of Angptl7 affected HSPCs in vivo, we generated Angptl7-null mice by TALEN-mediated gene targeting (Additional file 1: Figure S1a-1c). The procedures of gene targeting were described in (Additional file 3: Supplementary methods) and (Additional file 4: Table S1). Loss of Angptl7 in Angptl7-null mice was confirmed in the bone marrow (BM) by RT-PCR and Western blotting (Additional file 5: Figure S3d-3e). The Angptl7-null mice did not display an overt phenotype. There were no significant differences in either birth weights or adult weights among Angptl7 −/−, Angptl7 +/−, and Angptl7 +/+ mice (Additional file 6: Table S2). In addition, we found no significant differences in staining profiles T cells, B cells, myeloid cells, and erythroid cells among the Angptl7 −/−, Angptl7 +/− and Angptl7 +/+ mice (Figure 1a).
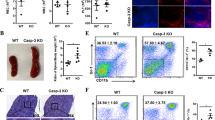
Reduced HSC in Angptl7 −/− mice. (a) Characterization of multiple hematopoietic lineages in BM. The major lineages of hematopoietic cells in BM in Angptl7 −/− Angptl7 +/− and Angptl7 +/+ mice were quantitated by flow cytometry analysis as erythroid cells (Ter119), myeloid cells (Ly6g and CD11b), T cells (CD3e) and B cells (CD19). Data represent the means +/− s.e.m (n = 5 for each group). (b, c) Comparison of the frequencies (b) and number (c) of Lin-Mac-1 + CD4- population in the fetal liver of Angptl7 −/− Angptl7 +/− and Angptl7 +/+ mice. Data represent the means +/− s.e.m (n = 10 for each group). *P < 0.05 versus Angptl7 −/− group for Angptl7 +/− and Angptl7 +/+. (d, e) Comparison of the frequencies (d) and number (e) of LSK population in the BM of Angptl7 −/− Angptl7 +/− and Angptl7 +/+ mice. Data represent the means +/− s.e.m (n = 6 for each group). *P < 0.05 versus Angptl7 −/− group for Angptl7 +/− and Angptl7 +/+ group. (f, g) Comparison of the frequencies (left) and number (right) of LT-HSCs in the BM of Angptl7 −/− Angptl7 +/− and Angptl7 +/+ mice. Data represent the means +/− s.e.m (n = 5 for each group). *P < 0.05 versus Angptl7 −/− group for Angptl7 +/− and Angptl7 +/+ group. (h) The colony numbers of CFU assays obtained from BM of Angptl7 −/− Angptl7 +/− and Angptl7 +/+ mice. Data represent the means +/− s.e.m (n = 3). *P < 0.05 versus bar 7 for bar 9.
As HSCs undergo dramatic expansion in fetal liver during embryo development [11-13], we examined the fetal liver HSC compartment and found that the percentages and numbers of Lin-Mac-1 + CD4- population, which was highly enriched of HSCs in fetal liver [14,15], were significantly lower in the fetal livers of Angptl7 −/− mice than that in Angptl7 +/− and Angptl7 +/+ mice (Figure 1b-c). In addition, we found the percentages and numbers of Lin-Sca-1 + c-Kit + (LSK) population in the BM of adult Angptl7 −/− mice were significantly lower than that in Angptl7 +/− and Angptl7 +/+ mice (Figure 1d-e). Further analysis showed that Angptl7 −/− mice had fewer long-term HSCs (Lin−Sca-1+Kit+Flk2−CD34−) than Angptl7+/− and Angptl7 +/+ mice (Figure 1f-g). Cloning forming assay results showed that BM cells from Angptl7 −/− mice had fewer granulocyte/monocyte progenitors (CFU-GM), but similar numbers of erythroid precursors (CFU-E/BFU-E) and hematopoietic progenitors (CFU-GEMM) than WT BM (Figure 1h). Therefore, Angptl7-deficient BM had normal levels of terminally differentiated hematopoietic cells, but decreased myeloid progenitors. To investigate whether other angiopoietin-like proteins compensate the loss of Angptl7 in BM, we compared the expression levels of other angiopoietin-like proteins in Angptl7-deficient BM stromal cells to that in WT BM stromal cells and found that their expression levels did not significantly change due to loss of Angptl7 (Additional file 7: Figure S4).
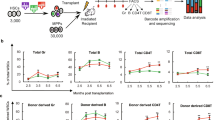
Since Angptl7 is secreted by stromal cells and binds to HSPCs [9], we speculated that Angptl7 may play a non-cell autonomous role in reconstitution of the hematopoietic system. To evaluate the hypothesis, we compared the extent of repopulation of HSCs in Angptl7 −/−, Angptl7 +/− and Angptl7 +/+ recipient mice. After WT donor BM cells were injected into lethally irradiated Angptl7 −/− Angptl7 +/− or Angptl7 +/+ recipients without competitors (Figure 2a), we found that the reconstitution efficiencies of HSCs were similar among Angptl7 −/−, Angptl7 +/− and WT recipient mice (Figure 2b), but the frequencies and numbers of LT-HSCs in Angptl7 −/− recipients were significantly lower than that in Angptl7 +/− and WT recipients, suggesting that Angptl7 supports the maintenance of the HSC pool in BM (Figure 2c-d). Continuously the BM cells from the primarily repopulated Angptl7 −/−, Angptl7 +/− and WT recipient mice were collected for secondary transplantation. We found that the repopulating activity of cells originating from the primary Angptl7 −/− recipients was significantly decreased compared with those from the primary Angptl7 +/− and WT recipients at different time points (Figure 2e). To test whether Angptl7 had a cell-intrinsic effect on HSCs, we transplanted Angptl7 −/−, Angptl7 +/− or WT BM cells into lethally irradiated WT recipients and measured the frequencies of donor cells in recipient mice (Figure 2f). We found the repopulation efficiencies, percentages, and numbers of donor Angptl7 −/−, Angptl7 +/− and WT LT-HSCs were similar in WT recipients (Figure 2g-i). We further transplanted the BM cells from the primary recipient mice to lethally irradiated WT mice. The repopulation efficiencies of secondary transplantation were similar among Angptl7 −/−, Angptl7 +/− and WT donors at indicated time points (Figure 2j). Overall, these results suggest that Angptl7 promoted HSC repopulation in a non-cell autonomous manner in vivo.
Comparison of reconstitution capacity of HSC in Angptl7 −/− Angptl7 +/− and Angptl7 +/+ mice. (a) Experimental design for assessing the repopulation efficiency in Angptl7-null BM environment. (b) Comparison of the repopulation efficiency in BM of Angptl7 −/− Angptl7 +/− and Angptl7 +/+ recipients. Data represent the means +/− s.e.m. (n = 8 for each group). (c, d) Comparison of the frequencies (c) and number (d) of LT-HSCs in BM of Angptl7 −/− Angptl7 +/− and Angptl7 +/+ recipients. Data represent the means +/− s.e.m. (n = 8 for each group). *P ≤ 0.05 for bar 9 versus bar 7 and bar 8. (e) Comparison of the second transplantation repopulation efficiency in BM of Angptl7 −/− Angptl7 +/− and Angptl7 +/+ recipients as referred in (a). Data represent the means +/− s.e.m (n = 7 for each group). *P ≤ 0.05 for bar 6 versus bar 4 and bar 5, for bar 9 versus bar 7 and bar 8, for bar 12 versus bar 10 and bar 11. (f) Experimental design effect of endogenous deletion of Angptl7 in HSCs. Angptl7 −/− Angptl7 +/− or Angptl7 +/+ donor BM CD45.2 cells (5x105 cells) were transplanted into lethally irradiated WT CD45.1 recipient mice. (g) Comparison of the repopulation efficiency of donor BM Angptl7 −/− Angptl7 +/− and Angptl7 +/+cells. Data represent the means +/− s.e.m. (n = 8 for each group). (h, i) Comparison of the frequencies (h) and number (i) of donor Angptl7 −/− Angptl7 +/− and Angptl7 +/+ LT-HSCs in BM of WT recipients. Data represent the means +/− s.e.m. (n = 8 for each group). (j) Comparison of the repopulation efficiency of Angptl7 −/− Angptl7 +/− and Angptl7 +/+ donor BM cells in second recipients mice as described in (f). Data represent the means +/− s.e.m (n = 8 for each group).
In this study, we demonstrated that deficiency of Angptl7 in the BM niche as a lack of exogenous Angptl7 stimulation impaired the reconstitution of HSCs in lethally irradiated mice, whereas endogenous deletion of Angptl7 in HSCs did not affect repopulation of HSCs in lethally irradiated mice. Thus, Angptl7 was indispensable for BM microenvironment to support HSC repopulation.
References
Attal M, Harousseau JL, Stoppa AM, Sotto JJ, Fuzibet JG, Rossi JF, et al. A prospective, randomized trial of autologous bone marrow transplantation and chemotherapy in multiple myeloma. Intergroupe Francais du Myelome. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:91–7.
Lin R, Liu Q. Diagnosis and treatment of viral diseases in recipients of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J Hematol Oncol. 2013;6:94.
Liao W, Aguila JR, Yao Y, Yang J, Zieve G, Jiang Y, et al. Enhancing bone marrow regeneration by SALL4 protein. J Hematol Oncol. 2013;6:84.
Gschweng E, De Oliveira S, Kohn DB. Hematopoietic stem cells for cancer immunotherapy. Immunol Rev. 2014;257:237–49.
Kharfan-Dabaja MA, Hamadani M, Reljic T, Nishihori T, Bensinger W, Djulbegovic B, et al. Comparative efficacy of tandem autologous versus autologous followed by allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Hematol Oncol. 2013;6:2.
Hato T, Tabata M, Oike Y. The role of angiopoietin-like proteins in angiogenesis and metabolism. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2008;18:6–14.
Ikushima YM, Arai F, Nakamura Y, Hosokawa K, Kubota Y, Hirashima M, et al. Enhanced Angpt1/Tie2 signaling affects the differentiation and long-term repopulation ability of hematopoietic stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;430:20–5.
Zhang CC, Kaba M, Ge G, Xie K, Tong W, Hug C, et al. Angiopoietin-like proteins stimulate ex vivo expansion of hematopoietic stem cells. Nat Med. 2006;12:240–5.
Zheng J, Umikawa M, Cui C, Li J, Chen X, Zhang C, et al. Inhibitory receptors bind ANGPTLs and support blood stem cells and leukaemia development. Nature. 2012;485:656–60.
Comes N, Buie LK, Borras T. Evidence for a role of angiopoietin-like 7 (ANGPTL7) in extracellular matrix formation of the human trabecular meshwork: implications for glaucoma. Genes Cells. 2011;16:243–59.
Huang XJ. Current status of haploidentical stem cell transplantation for leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. 2008;1:27.
Toyama H, Arai F, Hosokawa K, Ikushima YM, Suda T. N-cadherin + HSCs in fetal liver exhibit higher long-term bone marrow reconstitution activity than N-cadherin- HSCs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;428:354–9.
Sugiyama D, Kulkeaw K, Mizuochi C, Horio Y, Okayama S. Hepatoblasts comprise a niche for fetal liver erythropoiesis through cytokine production. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;410:301–6.
Morrison SJ, Hemmati HD, Wandycz AM, Weissman IL. The Purification and Characterization of Fetal Liver Hematopoietic Stem-Cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92:10302–6.
Wang L, Xiao H, Zhang X, Wang C, Huang H. The role of telomeres and telomerase in hematologic malignancies and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J Hematol Oncol. 2014;7:61.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDA01020310) to P. L., the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81272329 and 81200255 to P. L., and 81327801 to D. W.), the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (2011CB504004 and 2010CB945500) to D. W.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
Contribution: YX, XW, DP, and PL conceived the study and designed the experiments; YX, and XW, and XW designed the constructs used in this study; WY, YX, and WY performed the in vivo studies; YY and YX helped to perform FACS analysis and western blots; XW, LL, and DP generated genetic modified mouse strains in this study; YL, BX, PL, XL, LL, and DW contributed the discussion part of the manuscript; XL and BX provided vital new reagents and revised the manuscript; and PL, YY, and DP discussed and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Yiren Xiao and Xinru Wei contributed equally.
Additional files
Additional file 1: Figure S1.
Generation of Angptl7 knockout mice. (A) Angptl7 is highly expressed in BM CD45-SSEA4+ cells. BM cells were collected by flow cytometry and Angptl7 expression was measured by real-time RT-PCR. All the cells sorted for analysis were gated from the CD45- fraction. The results were normalized to β-actin mRNA levels and represent the means +/- s.e.m. *P < 0.05 versus bar 13 for bar 14. (B) Fluorescent microscopy imaging analyzes Angptl7 (green) and SEEA4 (red) cells in mouse BM cells. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue).
Additional file 2: Figure S2.
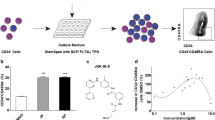
Treatment with Angptl7 induces the expansion of mouse HSPC. Left, Representative flow cytometric analysis of peripheral blood (PB) donor-derived CD45.1+ engraftment at 12 weeks after transplantation in mice transplanted with the progeny of 1× 105 bone marrow lin- cells after 7 days culture with TSF or TSF plus 500 ng ml−1 Angptl7. Right, The mean levels of donor CD45.1+ cells in the PB of CD45.2+ recipient mice at 12 weeks after transplantation of CD45.1+ bone marrow Lin − cells (1 × 105) or their progeny after 7 d of culture with TSF or TSF plus 500 ng ml−1 Angptl7. Data represent the means +/- s.e.m (n = 6 mice per group ). *P < 0.05 versus bar 2 and bar 3 for bar 1, bar 2 for bar 3.
Additional file 3:
Supplemental methods.
Additional file 4: Table S1.
Primer list used in generation of Angptl7-deficient mice.
Additional file 5: Figure S3.
(a) Top, the DNA sequences of Angptl7 locus targeted by Angptl7-TALENs are shown. The DNA-binding sites are in red, and the sequence between the DNA-binding sites is spacer region blue. There is a restriction site for the endonuclease DraIII between the two binding sites (blue). Bottom, schematic view of the design of TALENs targeting the Angptl7 locus. The Angptl7 donor vector contains two homologous arms on both sides of exon 1 of Angptl7, a splice acceptor, encoding cDNA of Venus, and puromycin (Puro) that was driven by PGK promoter. Angptl7-TALEN recognition sites (purple box), SD: splice donor, SA: splice acceptor. (b) Electropherograms around the TALEN spacer in the Angptl7 locus. The red boxes highlight the mice identified with Angptl7 mutations. (c) DNA sequences of the Angptl7 locus from live F0 mice identified in (b). ‘-’ represent deleted nucleotides. (d) The lack of Angptl7 in the BMs of Angptl7 knockout mice was confirmed by RT-PCR. (e) The lack of Angptl7 in the BMs of Angptl7 knockout mice was confirmed by western blots.
Additional file 6: Table S2.
The organ weight of Angptl7-deficient mice.
Additional file 7: Figure S4.
Relative expression levels of angiopoietin-like proteins in WT (+/+) and Angptl7-/-bone marrow stromal cells. The results were normalized to β-actin mRNA levels and represent the means +/- s.e.m. *P < 0.05 versus bar 11 for bar 12.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Y., Wei, X., Jiang, Z. et al. Loss of Angiopoietin-like 7 diminishes the regeneration capacity of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. J Hematol Oncol 8, 7 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-014-0102-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-014-0102-4