Abstract
Endothelial dysfunction is a pathological status of the vascular system, which can be broadly defined as an imbalance between endothelium-dependent vasoconstriction and vasodilation. Endothelial dysfunction is a key event in the progression of many pathological processes including atherosclerosis, type II diabetes and hypertension. Previous reports have demonstrated that pro-inflammatory/immunoeffector cytokines significantly promote endothelial dysfunction while numerous novel anti-inflammatory/immunosuppressive cytokines have recently been identified such as interleukin (IL)-35. However, the effects of anti-inflammatory cytokines on endothelial dysfunction have received much less attention. In this analytical review, we focus on the recent progress attained in characterizing the direct and indirect effects of anti-inflammatory/immunosuppressive cytokines in the inhibition of endothelial dysfunction. Our analyses are not only limited to the importance of endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular disease progression, but also expand into the molecular mechanisms and pathways underlying the inhibition of endothelial dysfunction by anti-inflammatory/immunosuppressive cytokines. Our review suggests that anti-inflammatory/immunosuppressive cytokines serve as novel therapeutic targets for inhibiting endothelial dysfunction, vascular inflammation and cardio- and cerebro-vascular diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The endothelium has long been viewed not only as a monolayer of endothelial cells (EC) lining the lumen of all blood vessels to function as a protective biocompatible barrier between tissues and circulating blood, but also as a highly specialized, heterogeneous [1], dynamic, disseminated organ [2] with paracrine and autocrine functions which respond to alterations of hemodynamic forces and chemical stimuli. In its entirety, the endothelium is composed of 1 to 6 × 1013 EC covering a surface area of more than 1,000 square meters [3],[4]. Endothelial dysfunction is a systemic pathological condition, which can be defined as an imbalance between endothelium-dependent vasoconstriction and vasodilation. Endothelial dysfunction initiates a number of events that trigger EC activation, which predisposes the vessel wall to be stimulated by cardiovascular risk factors [5]. Specifically, endothelial dysfunction is associated with reduced nitric oxide (NO) production, increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, upregulation of cytokines and chemokines, decreased anticoagulant properties and enhanced platelet aggregation and leukocyte adherence. One related but more specific term known as endothelial activation is characterized by the upregulation of EC adhesion molecules such as intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and increased secretion of cytokines and chemokines, which facilitates trans-EC migrations of monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, leukocytes, B cells, natural killer cells, and T cells [6]. Perturbations in EC functions play important roles in the development of several major diseases including cardiovascular diseases, metabolic syndrome, systemic inflammatory diseases, and sepsis [7].
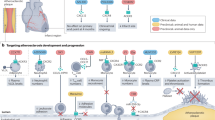
Cytokines, including lymphocyte-generated lymphokines, monocyte-produced monokines, chemokines [8], interferons, interleukins, adipocyte-secreted adipokines [9] and muscle-generated myokines [10] act by binding to their specific receptors in concert with specific cytokine inhibitors and soluble cytokine receptors, to regulate innate and adaptive immune responses. They are produced by many types of cells such as vascular EC, in response to the stimulations caused by metabolite-related danger signal-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) [11] and pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) [12] that include bacterial endotoxins, injury, or inflammatory mediators [13]. Cytokines can be divided into pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory (immunosuppressive) cytokines. Anti-inflammatory cytokines may either inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokine synthesis or control pro-inflammatory cytokine-mediated cellular activities [14],[15]. Numerous reviews have been published on the roles of pro-inflammatory cytokines on eliciting endothelial dysfunction [16]-[26] and many pro-inflammatory cytokine antagonists have been developed. These new cytokine anta-gonists include: a) etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab and certolizumab pegol as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) antagonists; b) Sant1, Sant5, and Sant7 as inter-leukin-6 (IL-6) receptor superantagonists; c) anakinra as IL-1 receptor antagonist; d) IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) as IL-1α and IL-1α antagonists; e) IL-18BP as IL-18 antagonist, and f) soluble Endoglin as transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) antagonist [27]. Potential the-rapeutic effects of these new inflammatory cytokine antagonists on endothelial dysfunction remain unclear. In addition, previous reports showed that anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10, members of the TGF-β family, and pro-resolving lipid mediators (such as lipoxins, resolvins, and protectins) may suppress pro-inflammatory signaling [28]. Moreover, recent studies have shown that the spectrum of anti-inflammatory cytokinesis expanding [29], which may hold promise for developing potential novel therapeutics and tools for the diagnosis and management of diseases [27]. However, the roles of anti-inflammatory cytokines in endothelial dysfunction have not been extensively analyzed. Therefore, the protective effects of anti-inflammatory cytokines against endothelial dysfunction are the focus of this review (Figure 1).
A new working model: Regulatory T cells and immunosuppressive/anti-inflammatory cytokines inhibit endothelial dysfunction. In physiological status, the interaction between endothelium-dependent vasoconstrictors (including Ang II, ET-1, ROS) and vasodilators (NO, EDHF and PGI2) maintain the endothelial function and equilibrium of vascular tone. The impairment of the balance between the vasoconstrictors and vasodilators is generally defined as the endothelial dysfunction. Under cardiovascular diseases risk factors stimuli, when vasodilation pathways being impaired or vasoconstriction being activated, endothelial dysfunction occurs. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) act on endothelial cells via cell-cell-interaction and/or immunosuppressive/antiinflammatory cytokines to inhibit endothelial dysfunction and restore normal vascular tone.
Endothelium-dependent regulation of vascular tone
Recent studies have demonstrated that endothelial dysfunction is a mechanistic link between atherosclerotic risk factors and an early development of vascular diseases, which is an independent predictor of future cardiovascular pathologies in patients with atherogenic risk factors or ischemic heart disease [30]. Although endothelial dysfunction may have a more generalized definition, current practical definition is related to the endothelial dysfunction of vascular tone. A healthy endothelium modulates vascular tone by producing numerous vascular dilators and constrictors. In clinical practices, flow-mediated dilation test is the standard tool used to assess endothelial function [31]. In addition, various reactivity tests, coupled with techniques measuring skin blood flux, are used to non-invasively explore both endothelial and neurovascular microvascular functioning in humans [32].
First described by Mulvany and Halpern, vascular tone is measured by using myography in mouse models [33]. This instrument is used for the examination of isolated arteries, with internal diameters between 100–400 μm that are independent of homeostatic mechanisms such as blood flow or autonomic nervous control [34]. The conditions near the physiological setting obtained in myograph allows in-depth characterization of intrinsic vascular tone reactions to physiological and pharmacological stimuli [35]. According to active tension-length relation, force production and the sensitivity of arteries to different agonists are dependent on the extent of stretch [36]. There are two types of myographs for measuring vascular function and studying vascular tones known as the pressure myograph and wire myograph (also see DMT website for an introduction http://www.dmt.dk/default.asp?Action=Details%26Item=543). Pressure myograph may have some advantages over wire myograph such like: 1) micro resistance arteries with internal diameters of less than 500 μm [37] can be studied whereas wire myograph is limited to large conduit arteries; 2) the risk to damage endothelium by wire is reduced; 3) the nature morphology of the arteries is maintained; and 4) the potential effects of a wide range of pressures and shear stress on artery dimension can be studied [35]. In addition, studying microarteries can be more informative than examining larger conduit arteries to understand the pathophysiological and molecular mechanisms underlying altered vascular tone in certain mouse models of cardiovascular diseases such as hypertension [35]. For example, endothelial dysfunction can be found in 2nd order mesenteric arteries but not in the aortic rings of mice fed with a high fat diet for 8 weeks [38]. In vessel rings pre-contracted with phenylephrine (PE; 1 μM) [39], vascular tone reactivity can be grouped into endothelium-dependent reactivity (to acetylcholine, ACh; 10 nM to 33 μM) and endothelium-independent reactivity (to sodium nitroprusside, SNP; 1 nM to 10 μM), therefore we focus our discussion mainly on endothelium-dependent pathways.
Since high myocardial oxygen extraction occurs at basal conditions, additional metabolic demands may be met by increasing the myocardial blood supply. The coronary artery is capable of increasing the basal flow by at least three folds. This maximum increase in coronary blood flow is defined as “coronary artery reserve”. This remarkable feature is regulated by various vasodilators and vasoconstrictors produced by coronary artery endothelial cells [40]. Not limited to coronary artery endothelium, endothelium generally are capable of producing vasodilators such as NO, prostacyclin (PGI2), and endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor (EDHF) as well as vasoconstrictors such as endothelin-1 (ET-1), angiotensin II (Ang II), and free radicals [2],[41] that maintain the physiologically balanced vascular tone.
Endothelium-derived vasodilators
Nitric oxide
Among several endothelium-dependent pathways that control vascular tone, the NO pathway is the most prominent in macrovasculature. NO is a key endothelium-derived relaxing factor, produced through the conversion of L-arginine to L-citrulline by the endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS). Once produced in EC, NO diffuses freely into the vascular smooth muscle cells (SMC) where it activates soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC), which in turn catalyzes the formation of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) and finally leads to the relaxation of the vascular smooth muscle [42]. NO is synthesized by a family of NO synthases (NOS) that include neuronal NOS (nNOS), eNOS and inducible NOS (iNOS). These three NOS share 50-60% homology at the amino acid sequence and all have an N-terminal oxygenase domain with heme-, L-arginine- and tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) binding domains, a central calmodulin (CaM)-binding domain, a C-terminal reductase domain with nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH), flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), and a flavin mononucleotide (FMN) binding site [43]. Biochemical and mechanical regulations of eNOS activity play an important role in physiological and pathophysiological responses. eNOS enzymatic activity can be regulated at multiple levels including gene transcription, mRNA stability, substrate, co-factor availability, post-translational modifications, and protein-protein interaction with heat shock protein 90(hsp90) and caveolins[44]. Phosphorylation of eNOS can take place at seven different phosphorylation sites at specific tyrosine (Y), serine (S) and threonine (T). The identified Y sites localize to Y81 and Y567, the S sites localize to S114, S615, S633, and S1177, and the T site localizes to T495 (based on the human eNOS sequence nomenclature) [43]. AKT-1-mediated phosphorylation of S615 and S1177 cooperate to enhance NO generation from eNOS at resting calcium levels, although there is a yin-yang relationship between T495 and S1177 with phosphorylation of one being correlated with dephosphorylation of the other. In addition, phosphorylation of eNOS at S114 decreases eNOS activity [43]. Mechanical shear stress activates eNOS by the phosphorylation of the serine residue 1177 and activation of protein kinase B (PKB, AKT), which itself is phosphorylated by phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) [45]. Different from the maintained phosphorylation of serine residue of eNOS in shear stress–stimulated cells, serine 1177 phosphorylation of eNOS in bradykinin-stimulated cells is transient. This eNOS activation requires an elevation in intracellular free calcium concentration, formation of a complex with calmodulin and the removal of the inhibitory caveolin from the activated eNOS complex, although NO production is not affected by the components of PI3K-AKT pathway [46].
Besides being the main determinant of the basal vascular tone, NO serves as a natural counterpart to the actions of potent endothelium-derived contracting factors such as Ang II and ET-1. In turn, these factors can also regulate the expression of NOS and NO production [47]-[49]. Reduced NO bioavailability, resulting from either insufficient production or increased degradation of NO, is one of the dominant features of endothelial dysfunction. eNOS requires critical cofactors, such as FAD, NADPH and BH4, to facilitate NO production [50]. In the absence of adequate levels of L-arginine or an essential amount of the cofactors, eNOS may become uncoupled and generate ROS including superoxide anions (O2-), and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) instead of nitrogen species [51]. Therefore, the availabilities of L-arginine and eNOS cofactors FAD, NADPH, and BH4 are very important for NO availability and endothelial function.
Endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor
EDHF pathway also plays a significant role in vascular tone regulation, especially in small resistant vessels. It triggers potassium ions (K+) efflux, which prevents voltage-dependent calcium channel activation, leading to a decrease of the intracellular calcium concentration and relaxation of vascular SMC [52]. The chemical identity of EDHF has not yet been identified. In some cases, it has been found that members of the arachidonic acid (AA) derivatives known as eicosatrienoic acids (EETs) can mediate vasodilation. Agonists such as bradykinin stimulate endothelial G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) provoking an increase in intracellular calcium in the EC, which activates phospholipase A2 (PLA2) mediated AA production. AA metabolism by cytochrome P450 2C (CYP4502C) generates EET, which can stimulate calcium dependent potassium (KCa+) channels. Open KCa+ channels allows for an efflux and accumulation of K+ into the myoendothelial space that triggers the transmission of endothelial cell hyperpolarization to the vascular smooth muscle via gap junctions. In turn, smooth muscle cell hyperpolarization results in relaxation by the closing of voltage-gated channels leading to a fall in Ca2+ concentration and subsequent vasodilation [53]. Myoendothelial gap junctions play an important role in electrotonic spread hyperpolarization between EC and SMC. In a number of blood vessels in which myoendothelial coupling is strong, such as in the rat mesenteric artery, the EDHF pathway occurs. While in adult rat femoral artery, in which the smooth muscle and endothelial layers are not coupled electrically, EDHF pathway does not occur even though acetylcholine evokes hyperpolarization in the EC [54]. KCa+ channels have been divided into three types, small-conductance (SK-Ca+), intermediate-conductance (IKCa+) and large-conductance (BKCa+) channels. A combination of apamin (a specific inhibitor of SKCa+) and charybdotoxin (a non-selective inhibitor of BKCa+, IKCa+ and voltage-dependent K+-channels), which has been demonstrated to act selectively on endothelium [55], can completely block EHDF-mediated relaxation [56],[57]. SKCa+ and IKCa+ channels are abundant in EC and their activation clearly engages in EDHF-induced vasodilation [58]. Meanwhile, as a specific inhibitor of BKCa+ , iberiotoxin cannot substitute for charybdotoxin or exclude the role of BKCa+ in EDHF-mediated response [59]. BKCa+ has been identified in SMC along with three other types of K+ channels, voltage-dependent K+(Kv) channels, ATP-sensitive K+(KATP) channels, and inward rectifier K+(Kir) channels [60]. In addition, a study found that IKCa+ channels are expressed in proliferative SMC rather than normal SMC, which in turn can define the physiological properties of vascular smooth muscle [61].
Besides K+ and EETs, H2O2 also activates calcium-dependent potassium channels and has been demonstrated to function as a pivotal EDHF [62]. H2O2 plays an important role in coronary auto-regulation in cooperation with NO and adenosine [63]. In mouse mesenteric arteries, catalase can inhibit ACh-induced endothelium-dependent relaxation and cause hyperpolarization by catalyzing the decomposition of H2O2 to water and oxygen. This suggests H2O2 may also perform the role of EDHF in mouse mesenteric arteries [64]. However, catalase does not inhibit non-NO-, non-PGI2-mediated vasodilation in all arteries [63]-[65]. Upon ACh stimulation in eNOS knockout mice, the endothelium-produced H2O2 reduces dramatically, which indicates that eNOS is a major source of H2O2. In addition, a redox variant of NO, nitroxyl anion (NO-), has been proved to be an endogenously derived EDHF that can induce preserved vascular relaxation in the aorta from Ang II-treated hypertensive mice [66],[67]. Recently, H2S has also been suggested to be an EDHF. H2S causes vascular EC and SMC hyperpolarization and vasodilation by activating the KATP, SKCa+ and IKCa+ channels through cysteine S-sulfhydration [68].
It has long been accepted that, unlike NO, which induces vasodilation in large conductance arteries, EDHF regulates vascular tone and reactivity in small resistance vessels [69]. However, recent in vivo studies found that cytochrome P-450-related EDHF is involved in the regulation of the peripheral conduit artery diameter at rest but not in the control of the basal vascular resistance in the healthy human forearm [70]. After inhibition of NO and prostacyclin, the inhibition of EET synthesis further decreases radial arterial blood flow and diameter. This indicates that EETs plays a potential compensatory role in maintaining basal tone when NO availability is diminished. In addition, it has been demonstrated that in hypercholesterolemia KCa+ channel-mediated vasodilation compensates for the reduced NO bioavailability [71]. Furthermore, the activity of EDHF is much higher in individuals with multiple risk factors than that in healthy subjects when compared to NO.
Prostacyclin
Prostacyclin, also termed as PGI2 is also an endothelium-released effective vasodilator, which functions by binding to GPCRs(G-protein-coupled receptors) to stimulate the production of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) that subsequently activates protein kinase A (PKA) and leads to smooth muscle relaxation and vasodilation. PGI2 also inhibits vasoconstriction, platelet activation and further coagulation by counteracting the effects of the vasoconstrictor thromboxane A2 (TXA2). PGI2 and TXA2 are produced from AA metabolism mediated by cyclooxygenase (COX). There are two isoforms of COX, which mainly differ in their pattern of expression. COX-1 is expressed in most tissues, whereas COX-2 is usually absent but induced by various physiologic stimuli. COX-1 mostly produces TXA2 while the induction of COX-2 is associated with an increase in PGI2 production [72]. P38 and P44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways mediate the induction of COX-2. In recent years, the wildly accepted COX-2-dependent PGI2 production pathway has been challenged by the direct measurement of circulating PGI2 levels rather than by the use of urinary markers, which unveiled that it is COX-1, not COX-2, that is responsible for PGI2 production in healthy individuals [73]. The opposite conclusions engender controversy of PGI2 testing [74], although specific COX-2 inhibitors increase the risk of cardiovascular events, which supports that vascular COX-2 is an important protein for maintaining vascular hemostasis [72]-[74].
The three endothelium-dependent vasodilation pathways, NO, EDHF, and PGI2 do not appear to be mutually exclusive but act synergistically in a complex manner to maintain the vasculature health. In addition, the roles of these three components may vary among the vascular beds in different sizes and tissue locations [69]. Moreover, different pathways vary in time course. Many studies have shown that EDHF is more important during the earlier phase of endothelial dysfunction while NO and PGI2 are primarily responsible for later and more sustained parts of the vasodilator in response to acetylcholine or bradykinin in various arteries [75],[76].
Endothelium-derived vasoconstrictors
Reactive oxygen species
As analyzed in our recent review [77], ROS can be derived from the transfer of electrons to molecular oxygen in the mitochondrial respiratory systems [78],[79] or produced by the activity of NADPH oxidases, which is co-localized with eNOS in subcellular compartments within EC [80]. This observation provides a direct link between NADPH oxidase and the endothelial function in humans. Small and transient amounts of O2- can be beneficial for the endothelial function, through activation of eNOS via Src (a homolog gene highly similar to the v-src gene of Rous sarcoma virus)/PI3-kinase/Akt pathway [51]. High levels of ROS generated in pathological situations will reduce NO bioavailability by the binding of O2- to form peroxynitrite (ONOO-). This ONOO- coupling with NO results in an imbalance of vascular tension. In addition, NADPH-derived H2O2 impairs endothelial function by amplifying itself in vascular disease [81]. Elevated levels of ROS have been associated with endothelial dysfunction developed in diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, obesity, atherosclerosis [82]-[86] and sepsis [87]. In addition, several inflammatory cytokines are induced by oxidant stress [88],[89] while cytokines themselves in turn lead to increased levels of ROS and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) in acute or chronic inflammation [90].
Angiotensin II
Ang II is part of the renin-angiotensin system that causes vasoconstriction, which increases blood pressure. Ang II stimulates Gq protein in vascular SMC, which increases intracellular calcium levels by an IP3-dependent mechanism that consequently leads to contraction. In addition, Ang II enhances vascular arginase activity that impairs NO production by decreasing L- arginine availability [91],[92]. It has been demonstrated that the p38 MAPK pathway participates in this arginase upregulation [93]. Moreover, Ang II also increases superoxide production, which leads to eNOS uncoupling [48],[94] in EC. Meanwhile, other studies demonstrated that the activation of the COX-1 pathway is involved in Ang II-induced development of endothelial dysfunction in small resistance arteries [95],[96].
Endothelin-1
ET-1, a 21-aa peptide released by EC, is a natural counterpart of NO, which is normally kept in balance by many mechanisms. ET-1 and NO take part in a paracrine regulation of each other, and the release of ET-1 is blocked by endothelium-derived NO [97],[98]. In pathological situations, ET-1 upregulates the expression of caveolae-1, which appears to be a key negative regulator protein for eNOS activity which leads to eNOS inhibition [99]. In addition, ET-1 can also increase ROS production attributing to NO degradation [100]. Selective endothelin receptor type A (ETA) and dual (ETA + ETB) antagonists improve NO bioavailability and endothelial function in pathological situations. Transgenic mice that overexpress ET-1 specifically in EC (eET-1) have an increase of endothelial dysfunction, vascular remodeling, oxidative stress, and inflammation [100],[101]. Recently, a study demonstrated that ET-1-induced vascular hypertrophy and oxidative stress participate in innate immunity system activation [102],[103]. Overexpression of ET-1 in EC causes an increase in monocytes/macrophage infiltration into adventitia, which is similar to the findings in mice infused with Ang II [104]. Colony stimulation factor-1 (CSF1) deficiency, a gene mutation impairing monocyte and macrophage production and maturation, can prevent this vascular damage. This finding provides evidence of the roles of monocyte/macrophage as well as innate immunity in ET-1-induced vascular injury.
Role of anti-inflammatory cytokines in endothelial dysfunction
The delicate balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines determines the net effect of an inflammatory response. Perturbations in this equilibrium can drive the host defense immune response either towards chronic inflammation (pro-inflammatory) or towards healing (anti-inflammatory). Exposure of endothelial cells to pro-inflammatory cytokines leads to transient and reversible endothelial dysfunction [105],[106]. A number of anti-inflammatory treatment strategies improve endothelial function by preventing pro-inflammatory cytokine synthesis. Anti-inflammatory cytokines are a series of immune-regulatory molecules that control the pro-inflammatory cytokines response, which consequently reduces inflammation and promotes healing. In addition, an elevation in the level of anti-inflammatory cytokines can also be found in the development of vascular disease [107], which reflects an early compensatory mechanism and serves as an indicator of pro-inflammatory reactions. Major anti-inflammatory cytokines include IL-1Ra, IL-4, IL-10, IL-11, IL-13 and TGF-β. Several newly found cytokines, such as IL-33, IL-35, and IL-37 also participate in regulating the function of EC. The following will discuss two of these anti-inflammatory cytokines including IL-10 and TGF-β in detail.
Interleukin-10
IL-10 is an anti-inflammatory cytokine produced by many types of immune cells, such as monocytes, macrophages, type 2 T helper cells (Th2), mast cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs). Its primary biological function is to limit and terminate inflammatory responses and regulate the differentiation and proliferation of several immune cells. IL-10 receptor 1 (IL-10R1) and IL-10R2 are two subunits of the IL-10 receptor that are expressed by hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cells. The receptor expression has also been observed in endothelial cells [108],[109], which provides the structural evidence for IL-10 to not only counteract pro-inflammatory cytokines but also potentially inhibit endothelial dysfunction directly. Many studies have found that IL-10 is a key mediator of vascular protection in atherosclerosis, type II diabetes and hypertension [110]-[112]. IL-10 is shown to protect endothelial function by initiating the degradation of several cytokine mRNAs, inhibiting the production of monocyte/macrophage- and neutrophil-derived cytokines [113] and attenuating induction of superoxide generation within the vascular wall [114],[115]. Clinically, in patients with coronary artery disease, IL-10 serum level acts as an independent predictor of the endothelium-mediated vasodilator response of the forearm circulation [116]. Furthermore, IL-10 prevents the impairment of endothelial dysfunction induced by elevated levels of C-reactive proteins [116].
IL-10 also attenuates inflammatory responses by its antioxidant properties. It plays a protective role in blood vessels by inhibiting NADPH oxidase activity and ROS production [111],[117]. In addition, IL-10 can restore Ang II-induced endothelium-dependent relaxation impairment measured by wire myographs in healthy murine aorta rings [118]. Mechanistically, Ang II leads to endothelial dysfunction by increasing gp91phox (NOX2) expression, which is a subunit of NADPH oxidase, while IL-10 inhibits this response by normalizing NADPH oxidase protein expression. In IL-10 knockout (IL-10-/-) mice, carotid arteries and thoracic aortas show a marked augmentation of vascular dysfunction after systemic treatment with Ang II that can be prevented by the treatment with superoxide dismutase-mimetic compound TEMPOL [112]. In Ang II-infused hypertensive mice, IL-10 that is released by transferred CD4+CD25+ natural Treg cells from wild type mice significantly reduces NAPDH oxidase activity and systolic blood pressure; while the transfer of Tregs isolated from IL-10-/- mice has no effect on the hypertension mice. Collectively, these results suggest that IL-10 generated by the immunosuppressive Treg cells protects against Ang II-induced vascular dysfunction and hypertension development by suppressing oxidative stress [119].
In recent studies on aging, old IL-10-/- mice are shown to have stiffer vessels and more severe endothelium-dependent relaxation impairment than wild type mice, which can be reversed by a scavenger of superoxide [120]. In addition, gp91phox is significantly induced in IL-10-/- than that of wild type mice in aging vessels. Furthermore, it is demonstrated that IL-10 protects against age-related endothelial dysfunction by the inhibition of oxidative stress. Aside from oxidative stress, it was also found that there is an increase of COX-2 activity and consequently activation in thromboxane A2 receptor instead of PGI2 in older IL-10-/- mice [121].
In vitro, IL-10 suppresses the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interferon-γ (IFN-γ), IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6 by immune cells including T cells, monocytes, macrophages and dendritic cells to produce [113],[122]-[124]. Meanwhile, IL-10 blocks the activity of NF-κB [125], which is a key pro-inflammatory transcription factor [126]-[128]. In vivo, IL-10 dampens the pro-inflammatory effects of IL-1 and TNF by stimulating IL-1Ra and soluble TNF receptors (sTNFR) production [129]. In TNF-α-treated mouse models, impairment of vascular relaxation is accompanied with a reduction of eNOS, which can be counteracted by IL-10 which induces eNOS expression and attenuates superoxide production [130]. In addition, by using mouse aortic rings in a myograph, TNF-α triggers a significant decrease in ACh-induced relaxation, which can be restored by IL-10.
The Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription (JAK/STAT) signaling pathway plays an essential role in mediating the anti-inflammatory actions of IL-10 [131]. In human EC, IL-10 up-regulates eNOS expression and activity mediated by the activation of STAT3 [132]. IL-10 and IL-10 receptor interaction involves the JAK family tyrosine kinases Jak1 and Tyk3 that induce tyrosine phosphorylation and the activation of latent transcription factors STAT3, STAT1, and STAT5 [133],[134]. IL-10 inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokine production in the macrophages via a JAK/STAT3-dependent pathway [135]. In IL-10-/- mice, STAT3 phosphorylation induction does not occur.
Aside from the JAK/STAT pathway, recent studies suggest that IL-10 also confers endothelial protection through several other signaling pathways. IL-10 inhibits the IL-1-induced inhibitor of kappa B (IκB) expression, decreases IκB phosphorylation and causes an increase in the eNOS activity [136]. In addition, IL-10 is associated with the inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1/2) activity and the MAPK kinase (MEK)/ERK pathway [137]-[139]. In TNF-α-infused IL-10-/- mice there is an increase of total and phosphorylated ERK1/2 [140], and the aorta and mesenteric arteries isolated from those mice display increased contractile responses to ET-1 through the ETA receptor, which can be abrogated by the ERK1/2 inhibitor PD-98059. This result demonstrates that IL-10 attenuates ET-1 induced vascular injury through the inhibition of the ERK1/2 pathway.
Emerging evidence also suggests that IL-10 plays a major role in suppressing endothelial dysfunction in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced endotoxemia. In LPS-induced endotoxemia, activated ERK1/2 can induce higher expression of IL-10. IL-10 in turn restores eNOS-mediated relaxation by inhibiting production of ROS in monocytes and neutrophils. Meanwhile, it also decreases the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, leading to an attenuation of septic shock [141]. Mechanistically, IL-10 inhibits the transcription of several inflammatory genes that are induced by the Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling, such as COX-2, IL-8, and IL-1 [142],[143]. This response can be completely or partially abrogated by the PI3K or Akt1/2 inhibitor. The PI3K-Akt-glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) pathway regulates IL-10-induced gene expression and controls the ability of IL-10 to suppress a set of inflammatory genes [144].
In summary, as a cytokine synthesis inhibitor factor (CSIF), IL-10 inhibits a broad spectrum of the functions of activated monocytes/macrophages and T cells, including pro-inflammatory cytokine synthesis, and NO production. It also contributes to an essential part in the balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines.
Transforming growth factor-β
TGF-β is a multifunctional growth factor capable of inducing cell proliferation, differentiation, programmed cell death, and stimulating matrix deposition. TGF-β family members are also a set of pleiotropic secreted signaling molecules with unique and potent immunoregulatory properties that not only significantly contribute to establishing and maintaining the vascular wall integrity [145], but also participate in the process of wound healing and tissue fibrosis [146],[147]. Various types of cells, such as all the immune cell lines, secrete TGF-β. There are at least three isoforms including TGF-β1, TGF-β2 and TGF-β3, in which TGF-β1 is predominantly ex-pressed in the immune system and has long been known to mediate remarkable actions in the pathogenesis of many vascular diseases. TGF-β performs anti-inflammatory effects and plays an important role in inhibiting vascular disease. Three types of TGF-β receptors are highly expressed in endothelial cells, in which Type I and II receptors are expressed by all the endothelial cells while Type III receptors are mainly located in microvascular endothelial cells [148]. The expressions of TGF-β receptors in endothelial cells provide the structural evidence for TGF-β to not only counteract pro-inflammatory cytokines but also potentially inhibit endothelial dysfunction directly. Moreover, a significant increase in eNOS mRNA levels can be found in TGF-β treated EC [149]. In D-glucose stimulated human umbilical vein endothelium cells (HUVEC), TGF-β binds to type II TGF-β receptors and increases L-arginine transport and NO synthesis, which protects against hyperglycemia-induced endothelial dysfunction [150]. In addition, TGF-β1 knockout mice develop multifocal inflammatory disease associated with increased inflammatory cytokine production, which demonstrates that TGF-β is essential in immune suppression under physiological conditions [151].
In EC, TGF-β increases eNOS expression by activating Smad2, a transcription factor, which interacts with the eNOS promoter [149]. Meanwhile, NO inversely controls the transcription of TGF-β via the endothelial NO/cGMP/PKG pathway and interferes with TGF-β/Smad2 signaling in vitro and in vivo[149],[152]. With NO donor treatment, EC show a decreased response to TGF-β and suppressed TGF-β target gene expression. Reversely, in eNOS deficient mice, the impairment of NO signaling leads to the upregulation and activation of TGF-β, which accelerates vascular injuries. These results show that the TGF-β dependent effects are complex and can be modulated by NO bioavailability. In response to shear stress, TGF-β3 plays a protective role in maintaining EC homeostasis accompanied by eNOS phosphorylation that leads to the release of NO [153]. In a high salt intake mouse model, TGF-β induced by an excess salt diet restores endothelial NO production via AKT activation and NOS3 phosphorylation as well as alleviates arterial compliance impairment, which forms an inhibitory feedback loop during the vascular function alteration [154].
The inhibitory effects of TGF-β are also in association with Tregs, which perform important immunosuppressive effects [155]. TGF-β converts CD4+CD25+ effector T cells into CD4+CD25+ Treg cells by inducing Foxp3 expression. TGF-β signaling is not only required for the survival of peripheral Tregs, but also for the maintenance of Treg suppressive function. Further studies found that TGF-β1 secreted by effector T cells is dispensable for the development and maintenance of Treg cells, while local TGF-β1 production from infiltrating Treg cells appears to be required for Treg immunosuppressive functions [156]. It is well known that Treg cells play an active role in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases [157]. Treg adoptive transfer prevents Ang II–induced hypertension and alleviates aldosterone-induced impairment of the vasodilatory response of resistance mesenteric arteries to Ach [104]. The NOS inhibitor significantly decreases the protective effects of Treg cells, indicating that Treg cells confer protection against the Ang II induced vasodilatory responses through a NO-dependent pathway. In addition, Ang II–induced NADPH oxidase activity can be prevented by Treg adoptive transfer. Thus, the suppressive function in inhibiting both macrophages and T lymphocytes from Tregs is associated with Tregs' contribution to the inhibition of Ang II–induced oxidative stress.
All together, there is a considerable interest in TGF-β for its potential role to be used as a therapeutic target, which prevents endothelial dysfunction through either inducing NO production or counteracting oxidative stress.
Other anti-inflammatory cytokines
IL-37, previously known as IL-1 family member 7, has been identified as a new anti-inflammatory cytokine. It is expressed in several tissues and inflammatory cells. Mice with transgenic expressions of IL-37 are protected from LPS-induced endotoxemia and show markedly reduction of liver damage and improved lung and kidney function [158]. Meanwhile, through the interaction with intracellular smad3, IL-37 significantly decreases the expression of various pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6, IL-1β, IL-17 and IFN-γ both in plasma and organs when compared with vehicle-treat control mice. It has also been observed that IL-37 suppresses the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in macrophages and epithelial cells, but its role in regards to EC is yet to be explored.
IL-33, also a member of the IL-1 cytokine family, is another newly identified anti-inflammatory cytokine [159]. IL-33 shows various protective effects in the cardiovascular system when ligated with ST2 (IL-33 receptor), a member of the Toll-interleukin 1 receptor (TIR) superfamily. IL-33 markedly decreases the aortic sinus atherosclerotic lesion size in apolipoprotein E (ApoE)−/− mice fed on a high fat diet, which is accompanied by the induction of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 and reduction of IFN-γ in the serum [160]. In type II diabetes, IL-33 shows protective metabolic effects by improving insulin tolerance, as well as reducing fasting glucose and adiposity [161]. So far, the molecular mechanisms underlying IL-33's protective effects are not fully understood. Recently, it was found that IL-33 is widely expressed in normal human tissues such as branched blood vessels, lymphoid tissues, adipocytes, cardiac fibroblasts, and even in human tumors. As a novel nuclear marker, IL-33 has been identified as an endogenous alarm in the immune system when the endothelium gets injured during infection and stress [162].
IL-4 and IL-13 both decrease the sensitivity of vascular EC to complement-mediated killing and apoptosis through the activation of a PI3K/Akt Pathway [163]. In addition, IL-4 protects EC from complement injury by upregulating claudin-5 through JAK/STAT6 and FoxO1 activation [164].
As a member of the IL-12 family, IL-35 has been identified as a novel anti-inflammatory/immunosuppressive cytokine generated by Tregs [165] and B cells [166],[167]. We found that unlike IL-10 and TGF- β, IL-35 is not constitutively expressed in tissues and is mainly produced by inflammatory stimuli in EC, SMC and monocytes [168]. IL-35 also triggers CD4+CD25- T effector cell transformation into CD4+CD25+ independent of Foxp3 expression. However, the potential effect of IL-35 on endothelial dysfunction remains unknown.
MicroRNA and endothelial dysfunction
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a recently discovered class of posttranscriptional modulators of gene expression that have an essential role in vascular diseases [169],[170]. They are a group of highly conserved, small, non-coding RNAs that, after maturation and entry into the RNA interference pathway, inhibit specific gene expression. Specific microRNAs can be regulated by inflammatory stimuli and certain microRNAs can act as mediators of inflammatory stimuli. In a human acute monocytic leukemia cell line, LPS stimulates the expression of miR-146a, miR-132 and miR-155. Overexpression of miR-146a inhibits not only the expression of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase and TNF receptor-associated factor 6's [171], but also the expression of IL-6 and IL-8 [172],[173]. In turn, the induction of miR-155, which is mediated by NFκB and the activator protein-1 (Ap-1) pathway, inhibits the expression of IL-8 [174],[175], which ultimately demonstrates a negative feedback loop involving microRNAs in an inflammatory response. Some miRNAs were proven to be highly expressed in EC in vitro[176]. TNF induced miR-31, miR-17-3p and miR-126 significantly increase the expression of E-selectin, ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 in EC [177],[178]. Transfections with mimics of these miRNAs decrease neutrophil adhesion to EC [177]. miR-181b, which is decreased by TNF, can down-regulate the NF-kB-responsive genes such as VCAM-1 and E-selectin in EC in vitro and in vivo[179]. In miR-10a knockdown human aortic EC, MCP-1 (monocyte chemotactic protein 1), IL-6, IL-8, VCAM-1 and E-selectin are highly elevated, which contributes to athero-susceptible phenotypes in vivo[180], suggesting that miR-10a suppresses atherogenesis.
In the aspect of regulating vascular tone, a recent report found that miR-222/221 controls eNOS protein levels after a member of the RNase III family know as dicer is knockdown [181]. Induced by shear stress, miR-21 can stimulate the phosphorylation of NOS and thereby increase NO production [182]. In contrast, miR-155 causes a reduction of NO by decreasing NOS expression [183]. In addition to mediating NO-derived vasodilation, microRNAs also play a role in regulating vasoconstriction. A recent report [184] found that miR-125a/b-5p can suppress oxidized low density lipoprotein (oxLDL) induced ET-1 expression by directly repressing prepro-ET-1 mRNA expression.
In summary, working together with the classical anti-inflammatory cytokines, anti-inflammatory/anti-atherogenic microRNAs [169],[170], as a new concept we discussed, could be an important therapeutic target for protecting against endothelial dysfunction and controlling cardiovascular diseases.
Conclusions
Endothelial dysfunction has been known as a well-established response to cardiovascular risk factors and precedes the development of cardiovascular diseases. Anti-inflammatory cytokines protect against the impairment of endothelial function by counteracting the effects of pro-inflammatory cytokines and suppressing oxidative stress. Further studies performed on the inhibitory properties of anti-inflammatory cytokines on endothelial dysfunction may provide novel promising therapeutic strategies for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Authors' contribution
YS carried out the primary literature search and drafted the manuscript. ZC, XL, and VC provided material input and helped revising the manuscript. HW and XFY supervised the manuscript writing and provided field expertise. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Abbreviations
- AA:
-
Arachidonic acid
- Ach:
-
Acetylcholine
- Ang II:
-
Angiotensin II
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- BH4:
-
Tetrahydrobiopterin
- BKCa+:
-
Large-conductance channels
- cAMP:
-
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate
- cGMP:
-
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate
- COX:
-
Cyclooxygenase
- EC:
-
Endothelial cells
- EDHF:
-
Endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor
- EETs:
-
Eicosatrienoic acids
- eNOS:
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase
- ERK1/2:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases 1 and 2
- ET-1:
-
Endothelin-1
- ETA:
-
Endothelin receptor type A
- FAD:
-
Flavin adenine dinucleotide
- GTP:
-
Guanosine triphosphate
- GPCRs:
-
G-protein-coupled receptors
- H2O2:
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- ICAM-1:
-
Intercellular adhesion molecule-1
- IFN-γ:
-
Interferon-γ
- I-B:
-
Inhibitor of kappa B
- IKCa+:
-
Intermediate-conductance channels
- IL-1Ra:
-
IL-1 receptor antagonist
- IL-10-/-:
-
IL-10 knockout
- JAK:
-
JANUS kinase
- K+:
-
Potassium ions
- KATP:
-
ATP-sensitive K+(KATP) channels
- KCa+:
-
Calcium dependent potassium channels Kir, inward rectifier K+ channels
- Kv:
-
Voltage-dependent K+ channels
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MiRNAs:
-
MicroRNAs
- NADPH:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- O2−:
-
Superoxide anions
- ONOO−:
-
Peroxynitrite
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase
- PGI2:
-
Prostacyclin
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- STAT:
-
Signal transducers and activators of transcription
- SKCa+:
-
Small-conductance channels
- SMC:
-
Smooth muscle cells
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor-β
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- Treg:
-
Regulatory T cells
- TXA2:
-
Thromboxane A2
- VCAM-1:
-
Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1
References
Aird WC: Endothelial cell heterogeneity. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012, 2 (1): a006429-
Aird WC: Endothelium as an organ system. Crit Care Med. 2004, 32 (5 Suppl): S271-S279.
Jaffe EA: Cell biology of endothelial cells. Hum Pathol. 1987, 18 (3): 234-239.
Mai J, Virtue A, Shen J, Wang H, Yang XF: An evolving new paradigm: endothelial cells–conditional innate immune cells. J Hematol Oncol. 2013, 6: 61-
Deanfield J, Donald A, Ferri C, Giannattasio C, Halcox J, Halligan S, Lerman A, Mancia G, Oliver JJ, Pessina AC, Rizzoni D, Rossi GP, Salvetti A, Schiffrin EL, Taddei S, Webb DJ: Endothelial function and dysfunction. Part I: methodological issues for assessment in the different vascular beds: a statement by the Working Group on Endothelin and Endothelial Factors of the European Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2005, 23 (1): 7-17.
Yang XF, Yin Y, Wang H: Vascular inflammation and atherogenesis are activated via receptors for pamps and suppressed by regulatory t cells. Drug Discov Today Ther Strateg. 2008, 5 (2): 125-142.
Boisrame-Helms J, Kremer H, Schini-Kerth V, Meziani F: Endothelial dysfunction in sepsis. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2013, 11 (2): 150-160.
Hansell C, Nibbs R: Professional and part-time chemokine decoys in the resolution of inflammation. Sci STKE. 2007, 2007 (384): e18-
Trayhurn P, Wood IS: Signalling role of adipose tissue: adipokines and inflammation in obesity. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005, 33 (Pt 5): 1078-1081.
Pedersen BK, Febbraio MA: Muscles, exercise and obesity: skeletal muscle as a secretory organ. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012, 8 (8): 457-465.
Miller YI, Choi SH, Wiesner P, Fang L, Harkewicz R, Hartvigsen K, Boullier A, Gonen A, Diehl CJ, Que X, Montano E, Shaw PX, Tsimikas S, Binder CJ, Witztum JL: Oxidation-specific epitopes are danger-associated molecular patterns recognized by pattern recognition receptors of innate immunity. Circ Res. 2011, 108 (2): 235-248.
Jialal I, Kaur H, Devaraj S: Toll-like receptor status in obesity and metabolic syndrome: a translational perspective. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014, 99 (1): 39-48.
Lackie JM: A Dictionary of Biomedicine. 2010, Oxford University Press, Oxford
Munoz C, Carlet J, Fitting C, Misset B, Bleriot JP, Cavaillon JM: Dysregulation of in vitro cytokine production by monocytes during sepsis. J Clin Invest. 1991, 88 (5): 1747-1754.
Kasai T, Inada K, Takakuwa T, Yamada Y, Inoue Y, Shimamura T, Taniguchi S, Sato S, Wakabayashi G, Endo S: Anti-inflammatory cytokine levels in patients with septic shock. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol. 1997, 98 (1): 34-42.
Murdaca G, Spano F, Cagnati P, Puppo F: Free radicals and endothelial dysfunction: potential positive effects of TNF-alpha inhibitors. Redox Rep. 2013, 18 (3): 95-99.
Kusuhara M, Isoda K, Ohsuzu F: Interleukin-1 and occlusive arterial diseases. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2006, 4 (3): 229-235.
Aroor AR, McKarns S, Demarco VG, Jia G, Sowers JR: Maladaptive immune and inflammatory pathways lead to cardiovascular insulin resistance. Metabolism. 2013, 62 (11): 1543-1552.
Deanfield JE, Halcox JP, Rabelink TJ: Endothelial function and dysfunction: testing and clinical relevance. Circulation. 2007, 115 (10): 1285-1295.
Pober JS, Sessa WC: Evolving functions of endothelial cells in inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007, 7 (10): 803-815.
Bautista LE: Inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, and the risk of high blood pressure: epidemiologic and biological evidence. J Hum Hypertens. 2003, 17 (4): 223-230.
Hadi HA, Carr CS, Al Suwaidi J: Endothelial dysfunction: cardiovascular risk factors, therapy, and outcome. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2005, 1 (3): 183-198.
van den Oever IA, Raterman HG, Nurmohamed MT, Simsek S: Endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, and apoptosis in diabetes mellitus. Mediators Inflamm. 2010, 2010: 792393-
Cai H, Harrison DG: Endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases: the role of oxidant stress. Circ Res. 2000, 87 (10): 840-844.
Cai H: Hydrogen peroxide regulation of endothelial function: origins, mechanisms, and consequences. Cardiovasc Res. 2005, 68 (1): 26-36.
Xu J, Zou MH: Molecular insights and therapeutic targets for diabetic endothelial dysfunction. Circulation. 2009, 120 (13): 1266-1286.
Sprague AH, Khalil RA: Inflammatory cytokines in vascular dysfunction and vascular disease. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009, 78 (6): 539-552.
Frangogiannis NG: Regulation of the inflammatory response in cardiac repair. Circ Res. 2012, 110 (1): 159-173.
Banchereau J, Pascual V, O'Garra A: From IL-2 to IL-37: the expanding spectrum of anti-inflammatory cytokines. Nat Immunol. 2012, 13 (10): 925-931.
Sitia S, Tomasoni L, Atzeni F, Ambrosio G, Cordiano C, Catapano A, Tramontana S, Perticone F, Naccarato P, Camici P, Picano E, Cortigiani L, Bevilacqua M, Milazzo L, Cusi D, Barlassina C, Sarzi-Puttini P, Turiel M: From endothelial dysfunction to atherosclerosis. Autoimmun Rev. 2010, 9 (12): 830-834.
Stoner L, Sabatier MJ: Use of ultrasound for non-invasive assessment of flow-mediated dilation. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2012, 19 (5): 407-421.
Roustit M, Cracowski JL: Assessment of endothelial and neurovascular function in human skin microcirculation. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013, 34 (7): 373-384.
Mulvany MJ, Halpern W: Mechanical properties of vascular smooth muscle cells in situ. Nature. 1976, 260 (5552): 617-619.
Spiers A, Padmanabhan N: A guide to wire myography. Methods Mol Med. 2005, 108: 91-104.
Shahid M, Buys ES: Assessing murine resistance artery function using pressure myography.J Vis Exp 2013, (76):e50328.,
Bridges LE, Williams CL, Pointer MA, Awumey EM: Mesenteric artery contraction and relaxation studies using automated wire myography.J Vis Exp 2011, (55):e3119.,
Mulvany MJ, Aalkjaer C: Structure and function of small arteries. Physiol Rev. 1990, 70 (4): 921-961.
Lei C, Yu B, Shahid M, Beloiartsev A, Bloch KD, Zapol WM: Inhaled nitric oxide attenuates the adverse effects of transfusing stored syngeneic erythrocytes in mice with endothelial dysfunction after hemorrhagic shock. Anesthesiology. 2012, 117 (6): 1190-1202.
Cheng Z, Jiang X, Kruger WD, Pratico D, Gupta S, Mallilankaraman K, Madesh M, Schafer AI, Durante W, Yang X, Wang H: Hyperhomocysteinemia impairs endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor-mediated vasorelaxation in transgenic cystathionine beta synthase-deficient mice. Blood. 2011, 118 (7): 1998-2006.
Gutierrez E, Flammer AJ, Lerman LO, Elizaga J, Lerman A, Fernandez-Aviles F: Endothelial dysfunction over the course of coronary artery disease. Eur Heart J. 2013, 34 (41): 3175-3181.
Cheng Z, Yang X, Wang H: Hyperhomocysteinemia and endothelial dysfunction. Curr Hypertens Rev. 2009, 5 (2): 158-165.
Pacher P, Beckman JS, Liaudet L: Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiol Rev. 2007, 87 (1): 315-424.
Rafikov R, Fonseca FV, Kumar S, Pardo D, Darragh C, Elms S, Fulton D, Black SM: eNOS activation and NO function: structural motifs responsible for the posttranslational control of endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity. J Endocrinol. 2011, 210 (3): 271-284.
Kashiwagi S, Atochin DN, Li Q, Schleicher M, Pong T, Sessa WC, Huang PL: eNOS phosphorylation on serine 1176 affects insulin sensitivity and adiposity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013, 431 (2): 284-290.
Dimmeler S, Fleming I, Fisslthaler B, Hermann C, Busse R, Zeiher AM: Activation of nitric oxide synthase in endothelial cells by Akt-dependent phosphorylation. Nature. 1999, 399 (6736): 601-605.
Fleming I, Fisslthaler B, Dimmeler S, Kemp BE, Busse R: Phosphorylation of Thr(495) regulates Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity. Circ Res. 2001, 88 (11): E68-E75.
Olson SC, Dowds TA, Pino PA, Barry MT, Burke-Wolin T: ANG II stimulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression in bovine pulmonary artery endothelium. Am J Physiol. 1997, 273 (2 Pt 1): L315-L321.
Marasciulo FL, Montagnani M, Potenza MA: Endothelin-1: the yin and yang on vascular function. Curr Med Chem. 2006, 13 (14): 1655-1665.
Salvemini D, Misko TP, Masferrer JL, Seibert K, Currie MG, Needleman P: Nitric oxide activates cyclooxygenase enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993, 90 (15): 7240-7244.
Andrew PJ, Mayer B: Enzymatic function of nitric oxide synthases. Cardiovasc Res. 1999, 43 (3): 521-531.
Anselm E, Chataigneau M, Ndiaye M, Chataigneau T, Schini-Kerth VB: Grape juice causes endothelium-dependent relaxation via a redox-sensitive Src- and Akt-dependent activation of eNOS. Cardiovasc Res. 2007, 73 (2): 404-413.
Feletou M, Vanhoutte PM: EDHF: an update. Clin Sci (Lond). 2009, 117 (4): 139-155.
Ozkor MA, Quyyumi AA: Endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor and vascular function. Cardiol Res Pract. 2011, 2011: 156146-
Sandow SL, Tare M, Coleman HA, Hill CE, Parkington HC: Involvement of myoendothelial gap junctions in the actions of endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor. Circ Res. 2002, 90 (10): 1108-1113.
Doughty JM, Plane F, Langton PD: Charybdotoxin and apamin block EDHF in rat mesenteric artery if selectively applied to the endothelium. Am J Physiol. 1999, 276 (3 Pt 2): H1107-H1112.
Corriu C, Feletou M, Canet E, Vanhoutte PM: Endothelium-derived factors and hyperpolarization of the carotid artery of the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1996, 119 (5): 959-964.
Murphy ME, Brayden JE: Apamin-sensitive K + channels mediate an endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization in rabbit mesenteric arteries. J Physiol. 1995, 489 (Pt 3): 723-734.
Hannah RM, Dunn KM, Bonev AD, Nelson MT: Endothelial SK(Ca) and IK(Ca) channels regulate brain parenchymal arteriolar diameter and cortical cerebral blood flow. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2011, 31 (5): 1175-1186.
Chataigneau T, Feletou M, Duhault J, Vanhoutte PM: Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids, potassium channel blockers and endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization in the guinea-pig carotid artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1998, 123 (3): 574-580.
Nelson MT, Quayle JM: Physiological roles and properties of potassium channels in arterial smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1995, 268 (4 Pt 1): C799-C822.
Neylon CB, Lang RJ, Fu Y, Bobik A, Reinhart PH: Molecular cloning and characterization of the intermediate-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channel in vascular smooth muscle: relationship between K(Ca) channel diversity and smooth muscle cell function. Circ Res. 1999, 85 (9): e33-e43.
Larsen BT, Gutterman DD, Sato A, Toyama K, Campbell WB, Zeldin DC, Manthati VL, Falck JR, Miura H: Hydrogen peroxide inhibits cytochrome p450 epoxygenases: interaction between two endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factors. Circ Res. 2008, 102 (1): 59-67.
Yada T, Shimokawa H, Hiramatsu O, Kajita T, Shigeto F, Goto M, Ogasawara Y, Kajiya F: Hydrogen peroxide, an endogenous endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor, plays an important role in coronary autoregulation in vivo. Circulation. 2003, 107 (7): 1040-1045.
Matoba T, Shimokawa H, Nakashima M, Hirakawa Y, Mukai Y, Hirano K, Kanaide H, Takeshita A: Hydrogen peroxide is an endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor in mice. J Clin Invest. 2000, 106 (12): 1521-1530.
Morikawa K, Shimokawa H, Matoba T, Kubota H, Akaike T, Talukder MA, Hatanaka M, Fujiki T, Maeda H, Takahashi S, Takeshita A: Pivotal role of Cu, Zn-superoxide dismutase in endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization. J Clin Invest. 2003, 112 (12): 1871-1879.
Wynne BM, Labazi H, Tostes RC, Webb RC: Aorta from angiotensin II hypertensive mice exhibit preserved nitroxyl anion mediated relaxation responses. Pharmacol Res. 2012, 65 (1): 41-47.
Andrews KL, Irvine JC, Tare M, Apostolopoulos J, Favaloro JL, Triggle CR, Kemp-Harper BK: A role for nitroxyl (HNO) as an endothelium-derived relaxing and hyperpolarizing factor in resistance arteries. Br J Pharmacol. 2009, 157 (4): 540-550.
Mustafa AK, Sikka G, Gazi SK, Steppan J, Jung SM, Bhunia AK, Barodka VM, Gazi FK, Barrow RK, Wang R, Amzel LM, Berkowitz DE, Snyder SH: Hydrogen sulfide as endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor sulfhydrates potassium channels. Circ Res. 2011, 109 (11): 1259-1268.
Shimokawa H, Yasutake H, Fujii K, Owada MK, Nakaike R, Fukumoto Y, Takayanagi T, Nagao T, Egashira K, Fujishima M, Takeshita A: The importance of the hyperpolarizing mechanism increases as the vessel size decreases in endothelium-dependent relaxations in rat mesenteric circulation. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1996, 28 (5): 703-711.
Bellien J, Joannides R, Iacob M, Arnaud P, Thuillez C: Evidence for a basal release of a cytochrome-related endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor in the radial artery in humans. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006, 290 (4): H1347-H1352.
Ozkor MA, Murrow JR, Rahman AM, Kavtaradze N, Lin J, Manatunga A, Quyyumi AA: Endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor determines resting and stimulated forearm vasodilator tone in health and in disease. Circulation. 2011, 123 (20): 2244-2253.
Caughey GE, Cleland LG, Penglis PS, Gamble JR, James MJ: Roles of cyclooxygenase (COX)-1 and COX-2 in prostanoid production by human endothelial cells: selective up-regulation of prostacyclin synthesis by COX-2. J Immunol. 2001, 167 (5): 2831-2838.
Kirkby NS, Lundberg MH, Harrington LS, Leadbeater PD, Milne GL, Potter CM, Al-Yamani M, Adeyemi O, Warner TD, Mitchell JA: Cyclooxygenase-1, not cyclooxygenase-2, is responsible for physiological production of prostacyclin in the cardiovascular system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012, 109 (43): 17597-17602.
Ricciotti E, Yu Y, Grosser T, Fitzgerald GA: COX-2, the dominant source of prostacyclin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013, 110 (3): E183-
Tare M, Parkington HC, Coleman HA: EDHF, NO and a prostanoid: hyperpolarization-dependent and -independent relaxation in guinea-pig arteries. Br J Pharmacol. 2000, 130 (3): 605-618.
Dautzenberg M, Just A: Temporal characteristics of nitric oxide-, prostaglandin-, and EDHF-mediated components of endothelium-dependent vasodilation in the kidney. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2013, 305 (9): R987-R998.
Li X, Fang P, Mai J, Choi ET, Wang H, Yang XF: Targeting mitochondrial reactive oxygen species as novel therapy for inflammatory diseases and cancers. J Hematol Oncol. 2013, 6: 19-
Addabbo F, Montagnani M, Goligorsky MS: Mitochondria and reactive oxygen species. Hypertension. 2009, 53 (6): 885-892.
Zhang JG, Nicholls-Grzemski FA, Tirmenstein MA, Fariss MW: Vitamin E succinate protects hepatocytes against the toxic effect of reactive oxygen species generated at mitochondrial complexes I and III by alkylating agents. Chem Biol Interact. 2001, 138 (3): 267-284.
Yang B, Rizzo V: TNF-alpha potentiates protein-tyrosine nitration through activation of NADPH oxidase and eNOS localized in membrane rafts and caveolae of bovine aortic endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007, 292 (2): H954-H962.
Cai H: NAD(P)H oxidase-dependent self-propagation of hydrogen peroxide and vascular disease. Circ Res. 2005, 96 (8): 818-822.
Houstis N, Rosen ED, Lander ES: Reactive oxygen species have a causal role in multiple forms of insulin resistance. Nature. 2006, 440 (7086): 944-948.
Mugge A, Elwell JH, Peterson TE, Hofmeyer TG, Heistad DD, Harrison DG: Chronic treatment with polyethylene-glycolated superoxide dismutase partially restores endothelium-dependent vascular relaxations in cholesterol-fed rabbits. Circ Res. 1991, 69 (5): 1293-1300.
Miller FJ, Gutterman DD, Rios CD, Heistad DD, Davidson BL: Superoxide production in vascular smooth muscle contributes to oxidative stress and impaired relaxation in atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 1998, 82 (12): 1298-1305.
Langenstroer P, Pieper GM: Regulation of spontaneous EDRF release in diabetic rat aorta by oxygen free radicals. Am J Physiol. 1992, 263 (1 Pt 2): H257-H265.
Oak JH, Cai H: Attenuation of angiotensin II signaling recouples eNOS and inhibits nonendothelial NOX activity in diabetic mice. Diabetes. 2007, 56 (1): 118-126.
Bulua AC, Simon A, Maddipati R, Pelletier M, Park H, Kim KY, Sack MN, Kastner DL, Siegel RM: Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species promote production of proinflammatory cytokines and are elevated in TNFR1-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS). J Exp Med. 2011, 208 (3): 519-533.
David F, Farley J, Huang H, Lavoie JP, Laverty S: Cytokine and chemokine gene expression of IL-1beta stimulated equine articular chondrocytes. Vet Surg. 2007, 36 (3): 221-227.
Vlahopoulos S, Boldogh I, Casola A, Brasier AR: Nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent induction of interleukin-8 gene expression by tumor necrosis factor alpha: evidence for an antioxidant sensitive activating pathway distinct from nuclear translocation. Blood. 1999, 94 (6): 1878-1889.
Zhang C: The role of inflammatory cytokines in endothelial dysfunction. Basic Res Cardiol. 2008, 103 (5): 398-406.
Bagnost T, Berthelot A, Bouhaddi M, Laurant P, Andre C, Guillaume Y, Demougeot C: Treatment with the arginase inhibitor N(omega)-hydroxy-nor-L-arginine improves vascular function and lowers blood pressure in adult spontaneously hypertensive rat. J Hypertens. 2008, 26 (6): 1110-1118.
Demougeot C, Prigent-Tessier A, Marie C, Berthelot A: Arginase inhibition reduces endothelial dysfunction and blood pressure rising in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Hypertens. 2005, 23 (5): 971-978.
Toque HA, Romero MJ, Tostes RC, Shatanawi A, Chandra S, Carneiro ZN, Inscho EW, Webb RC, Caldwell RB, Caldwell RW: p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) increases arginase activity and contributes to endothelial dysfunction in corpora cavernosa from angiotensin-II-treated mice. J Sex Med. 2010, 7 (12): 3857-3867.
Satoh M, Fujimoto S, Arakawa S, Yada T, Namikoshi T, Haruna Y, Horike H, Sasaki T, Kashihara N: Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker ameliorates uncoupled endothelial nitric oxide synthase in rats with experimental diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008, 23 (12): 3806-3813.
Virdis A, Colucci R, Neves MF, Rugani I, Aydinoglu F, Fornai M, Ippolito C, Antonioli L, Duranti E, Solini A, Bernardini N, Blandizzi C, Taddei S: Resistance artery mechanics and composition in angiotensin II-infused mice: effects of cyclooxygenase-1 inhibition. Eur Heart J. 2012, 33 (17): 2225-2234.
Cheng ZJ, Vapaatalo H, Mervaala E: Angiotensin II and vascular inflammation. Med Sci Monit. 2005, 11 (6): RA194-RA205.
Kourembanas S, McQuillan LP, Leung GK, Faller DV: Nitric oxide regulates the expression of vasoconstrictors and growth factors by vascular endothelium under both normoxia and hypoxia. J Clin Invest. 1993, 92 (1): 99-104.
Wiley KE, Davenport AP: Nitric oxide-mediated modulation of the endothelin-1 signalling pathway in the human cardiovascular system. Br J Pharmacol. 2001, 132 (1): 213-220.
Minshall RD, Sessa WC, Stan RV, Anderson RG, Malik AB: Caveolin regulation of endothelial function. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2003, 285 (6): L1179-L1183.
Amiri F, Virdis A, Neves MF, Iglarz M, Seidah NG, Touyz RM, Reudelhuber TL, Schiffrin EL: Endothelium-restricted overexpression of human endothelin-1 causes vascular remodeling and endothelial dysfunction. Circulation. 2004, 110 (15): 2233-2240.
Amiri F, Ko EA, Javeshghani D, Reudelhuber TL, Schiffrin EL: Deleterious combined effects of salt-loading and endothelial cell restricted endothelin-1 overexpression on blood pressure and vascular function in mice. J Hypertens. 2010, 28 (6): 1243-1251.
Javeshghani D, Barhoumi T, Idris-Khodja N, Paradis P, Schiffrin EL: Reduced macrophage-dependent inflammation improves endothelin-1-induced vascular injury. Hypertension. 2013, 62 (1): 112-117.
De Ciuceis C, Amiri F, Brassard P, Endemann DH, Touyz RM, Schiffrin EL: Reduced vascular remodeling, endothelial dysfunction, and oxidative stress in resistance arteries of angiotensin II-infused macrophage colony-stimulating factor-deficient mice: evidence for a role in inflammation in angiotensin-induced vascular injury. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005, 25 (10): 2106-2113.
Barhoumi T, Kasal DA, Li MW, Shbat L, Laurant P, Neves MF, Paradis P, Schiffrin EL: T regulatory lymphocytes prevent angiotensin II-induced hypertension and vascular injury. Hypertension. 2011, 57 (3): 469-476.
Bhagat K, Vallance P: Inflammatory cytokines impair endothelium-dependent dilatation in human veins in vivo. Circulation. 1997, 96 (9): 3042-3047.
Stenvinkel P: Endothelial dysfunction and inflammation-is there a link?. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2001, 16 (10): 1968-1971.
Herder C, Carstensen M, Ouwens DM: Anti-inflammatory cytokines and risk of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013, 15 (Suppl 3): 39-50.
Gleissner CA, Zastrow A, Klingenberg R, Kluger MS, Konstandin M, Celik S, Haemmerling S, Shankar V, Giese T, Katus HA, Dengler TJ: IL-10 inhibits endothelium-dependent T cell costimulation by up-regulation of ILT3/4 in human vascular endothelial cells. Eur J Immunol. 2007, 37 (1): 177-192.
Moore KW, de Waal MR, Coffman RL, O'Garra A: Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001, 19: 683-765.
Caligiuri G, Rudling M, Ollivier V, Jacob MP, Michel JB, Hansson GK, Nicoletti A: Interleukin-10 deficiency increases atherosclerosis, thrombosis, and low-density lipoproteins in apolipoprotein E knockout mice. Mol Med. 2003, 9 (1–2): 10-17.
Gunnett CA, Heistad DD, Faraci FM: Interleukin-10 protects nitric oxide-dependent relaxation during diabetes: role of superoxide. Diabetes. 2002, 51 (6): 1931-1937.
Didion SP, Kinzenbaw DA, Schrader LI, Chu Y, Faraci FM: Endogenous interleukin-10 inhibits angiotensin II-induced vascular dysfunction. Hypertension. 2009, 54 (3): 619-624.
Oberholzer A, Oberholzer C, Moldawer LL: Interleukin-10: a complex role in the pathogenesis of sepsis syndromes and its potential as an anti-inflammatory drug. Crit Care Med. 2002, 30 (1 Supp): S58-S63.
Gunnett CA, Heistad DD, Berg DJ, Faraci FM: IL-10 deficiency increases superoxide and endothelial dysfunction during inflammation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2000, 279 (4): H1555-H1562.
Haddad JJ, Fahlman CS: Redox- and oxidant-mediated regulation of interleukin-10: an anti-inflammatory, antioxidant cytokine?. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002, 297 (2): 163-176.
Fichtlscherer S, Breuer S, Heeschen C, Dimmeler S, Zeiher AM: Interleukin-10 serum levels and systemic endothelial vasoreactivity in patients with coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004, 44 (1): 44-49.
Dang PM, Elbim C, Marie JC, Chiandotto M, Gougerot-Pocidalo MA, El-Benna J: Anti-inflammatory effect of interleukin-10 on human neutrophil respiratory burst involves inhibition of GM-CSF-induced p47PHOX phosphorylation through a decrease in ERK1/2 activity. FASEB J. 2006, 20 (9): 1504-1506.
Zemse SM, Hilgers RH, Webb RC: Interleukin-10 counteracts impaired endothelium-dependent relaxation induced by ANG II in murine aortic rings. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007, 292 (6): H3103-H3108.
Kassan M, Galan M, Partyka M, Trebak M, Matrougui K: Interleukin-10 released by CD4(+)CD25(+) natural regulatory T cells improves microvascular endothelial function through inhibition of NADPH oxidase activity in hypertensive mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011, 31 (11): 2534-2542.
Kinzenbaw DA, Chu Y, Pena Silva RA, Didion SP, Faraci FM: Interleukin-10 protects against aging-induced endothelial dysfunction. Physiol Rep. 2013, 1 (6): e00149-
Sikka G, Miller KL, Steppan J, Pandey D, Jung SM, Fraser CD, Ellis C, Ross D, Vandegaer K, Bedja D, Gabrielson K, Walston JD, Berkowitz DE, Barouch LA: Interleukin 10 knockout frail mice develop cardiac and vascular dysfunction with increased age. Exp Gerontol. 2013, 48 (2): 128-135.
Fiorentino DF, Zlotnik A, Mosmann TR, Howard M, O'Garra A: IL-10 inhibits cytokine production by activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1991, 147 (11): 3815-3822.
Fiorentino DF, Zlotnik A, Vieira P, Mosmann TR, Howard M, Moore KW, O'Garra A: IL-10 acts on the antigen-presenting cell to inhibit cytokine production by Th1 cells. J Immunol. 1991, 146 (10): 3444-3451.
de Waal MR, Abrams J, Bennett B, Figdor CG, de Vries JE: Interleukin 10(IL-10) inhibits cytokine synthesis by human monocytes: an autoregulatory role of IL-10 produced by monocytes. J Exp Med. 1991, 174 (5): 1209-1220.
Asadullah K, Sterry W, Volk HD: Interleukin-10 therapy–review of a new approach. Pharmacol Rev. 2003, 55 (2): 241-269.
Csiszar A, Wang M, Lakatta EG, Ungvari Z: Inflammation and endothelial dysfunction during aging: role of NF-kappaB. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2008, 105 (4): 1333-1341.
Marchesi C, Paradis P, Schiffrin EL: Role of the renin-angiotensin system in vascular inflammation. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2008, 29 (7): 367-374.
Huang X, Gong R, Li X, Virtue A, Yang F, Yang IH, Tran AH, Yang XF, Wang H: Identification of novel pretranslational regulatory mechanisms for NF-kappaB activation. J Biol Chem. 2013, 288 (22): 15628-15640.
Seitz M, Loetscher P, Dewald B, Towbin H, Gallati H, Baggiolini M: Interleukin-10 differentially regulates cytokine inhibitor and chemokine release from blood mononuclear cells and fibroblasts. Eur J Immunol. 1995, 25 (4): 1129-1132.
Zemse SM, Chiao CW, Hilgers RH, Webb RC: Interleukin-10 inhibits the in vivo and in vitro adverse effects of TNF-alpha on the endothelium of murine aorta. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010, 299 (4): H1160-H1167.
Riley JK, Takeda K, Akira S, Schreiber RD: Interleukin-10 receptor signaling through the JAK-STAT pathway. Requirement for two distinct receptor-derived signals for anti-inflammatory action. J Biol Chem. 1999, 274 (23): 16513-16521.
Cattaruzza M, Slodowski W, Stojakovic M, Krzesz R, Hecker M: Interleukin-10 induction of nitric-oxide synthase expression attenuates CD40-mediated interleukin-12 synthesis in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2003, 278 (39): 37874-37880.
Wehinger J, Gouilleux F, Groner B, Finke J, Mertelsmann R, Weber-Nordt RM: IL-10 induces DNA binding activity of three STAT proteins (Stat1, Stat3, and Stat5) and their distinct combinatorial assembly in the promoters of selected genes. FEBS Lett. 1996, 394 (3): 365-370.
Finbloom DS, Winestock KD: IL-10 induces the tyrosine phosphorylation of tyk2 and Jak1 and the differential assembly of STAT1 alpha and STAT3 complexes in human T cells and monocytes. J Immunol. 1995, 155 (3): 1079-1090.
Pattison MJ, Mackenzie KF, Arthur JS: Inhibition of JAKs in macrophages increases lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine production by blocking IL-10-mediated feedback. J Immunol. 2012, 189 (6): 2784-2792.
Jojima T, Suzuki K, Hirama N, Uchida K, Hattori Y: Glimepiride upregulates eNOS activity and inhibits cytokine-induced NF-kappaB activation through a phosphoinoside 3-kinase-Akt-dependent pathway. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2009, 11 (2): 143-149.
D'Angelo G, Adam LP: Inhibition of ERK attenuates force development by lowering myosin light chain phosphorylation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2002, 282 (2): H602-H610.
Stumpf C, Lehner C, Yilmaz A, Daniel WG, Garlichs CD: Decrease of serum levels of the anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-10 in patients with advanced chronic heart failure. Clin Sci (Lond). 2003, 105 (1): 45-50.
Suttles J, Milhorn DM, Miller RW, Poe JC, Wahl LM, Stout RD: CD40 signaling of monocyte inflammatory cytokine synthesis through an ERK1/2-dependent pathway. A target of interleukin (il)-4 and il-10 anti-inflammatory action. J Biol Chem. 1999, 274 (9): 5835-5842.
Giachini FR, Zemse SM, Carneiro FS, Lima VV, Carneiro ZN, Callera GE, Ergul A, Webb RC, Tostes RC: Interleukin-10 attenuates vascular responses to endothelin-1 via effects on ERK1/2-dependent pathway. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009, 296 (2): H489-H496.
Noh KT, Son KH, Jung ID, Kang HK, Hwang SA, Lee WS, You JC, Park YM: Protein kinase C delta (PKCdelta)-extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) signaling cascade regulates glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) inhibition-mediated interleukin-10 (IL-10) expression in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced endotoxemia. J Biol Chem. 2012, 287 (17): 14226-14233.
Williams L, Bradley L, Smith A, Foxwell B: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 is the dominant mediator of the anti-inflammatory effects of IL-10 in human macrophages. J Immunol. 2004, 172 (1): 567-576.
Lang R, Patel D, Morris JJ, Rutschman RL, Murray PJ: Shaping gene expression in activated and resting primary macrophages by IL-10. J Immunol. 2002, 169 (5): 2253-2263.
Antoniv TT, Ivashkiv LB: Interleukin-10-induced gene expression and suppressive function are selectively modulated by the PI3K-Akt-GSK3 pathway. Immunology. 2011, 132 (4): 567-577.
Pepper MS: Transforming growth factor-beta: vasculogenesis, angiogenesis, and vessel wall integrity. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1997, 8 (1): 21-43.
Massague J: The transforming growth factor-beta family. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990, 6: 597-641.
Roberts AB: Molecular and cell biology of TGF-beta. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1998, 24 (2–3): 111-119.
Morello JP, Plamondon J, Meyrick B, Hoover R, O'Connor-McCourt MD: Transforming growth factor-beta receptor expression on endothelial cells: heterogeneity of type III receptor expression. J Cell Physiol. 1995, 165 (1): 201-211.
Saura M, Zaragoza C, Cao W, Bao C, Rodriguez-Puyol M, Rodriguez-Puyol D, Lowenstein CJ: Smad2 mediates transforming growth factor-beta induction of endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression. Circ Res. 2002, 91 (9): 806-813.
Vasquez R, Farias M, Vega JL, Martin RS, Vecchiola A, Casanello P, Sobrevia L: D-glucose stimulation of L-arginine transport and nitric oxide synthesis results from activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases p42/44 and Smad2 requiring functional type II TGF-beta receptors in human umbilical vein endothelium. J Cell Physiol. 2007, 212 (3): 626-632.
Kehrl JH, Wakefield LM, Roberts AB, Jakowlew S, Alvarez-Mon M, Derynck R, Sporn MB, Fauci AS: Production of transforming growth factor beta by human T lymphocytes and its potential role in the regulation of T cell growth. J Exp Med. 1986, 163 (5): 1037-1050.
Saura M, Zaragoza C, Herranz B, Griera M, Diez-Marques L, Rodriguez-Puyol D, Rodriguez-Puyol M: Nitric oxide regulates transforming growth factor-beta signaling in endothelial cells. Circ Res. 2005, 97 (11): 1115-1123.
Walshe TE, dela Paz NG, D’Amore PA: The role of shear-induced transforming growth factor-beta signaling in the endothelium. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013, 33 (11): 2608-2617.
Ying WZ, Aaron KJ, Sanders PW: Transforming growth factor-beta regulates endothelial function during high salt intake in rats. Hypertension. 2013, 62 (5): 951-956.
Letterio JJ, Roberts AB: Regulation of immune responses by TGF-beta. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998, 16: 137-161.
Li MO, Wan YY, Flavell RA: T cell-produced transforming growth factor-beta1 controls T cell tolerance and regulates Th1- and Th17-cell differentiation. Immunity. 2007, 26 (5): 579-591.
Pastrana JL, Sha X, Virtue A, Mai J, Cueto R, Lee IA, Wang H, Yang XF: Regulatory T cells and Atherosclerosis. J Clin Exp Cardiolog. 2012, 2012 (Suppl 12): 2-
Nold MF, Nold-Petry CA, Zepp JA, Palmer BE, Bufler P, Dinarello CA: IL-37 is a fundamental inhibitor of innate immunity. Nat Immunol. 2010, 11 (11): 1014-1022.
Miller AM: Role of IL-33 in inflammation and disease. J Inflamm (Lond). 2011, 8 (1): 22-
Miller AM, Xu D, Asquith DL, Denby L, Li Y, Sattar N, Baker AH, McInnes IB, Liew FY: IL-33 reduces the development of atherosclerosis. J Exp Med. 2008, 205 (2): 339-346.
Miller AM, Asquith DL, Hueber AJ, Anderson LA, Holmes WM, McKenzie AN, Xu D, Sattar N, McInnes IB, Liew FY: Interleukin-33 induces protective effects in adipose tissue inflammation during obesity in mice. Circ Res. 2010, 107 (5): 650-658.
Moussion C, Ortega N, Girard JP: The IL-1-like cytokine IL-33 is constitutively expressed in the nucleus of endothelial cells and epithelial cells in vivo: a novel 'alarmin'?. PLoS One. 2008, 3 (10): e3331-
Grehan JF, Levay-Young BK, Fogelson JL, Francois-Bongarcon V, Benson BA, Dalmasso AP: IL-4 and IL-13 induce protection of porcine endothelial cells from killing by human complement and from apoptosis through activation of a phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway. J Immunol. 2005, 175 (3): 1903-1910.
Dalmasso AP, Goldish D, Benson BA, Tsai AK, Wasiluk KR, Vercellotti GM: Interleukin-4 induces up-regulation of endothelial cell claudin-5 through activation of FoxO1: role in protection from complement-mediated injury. J Biol Chem. 2014, 289 (2): 838-847.
Collison LW, Workman CJ, Kuo TT, Boyd K, Wang Y, Vignali KM, Cross R, Sehy D, Blumberg RS, Vignali DA: The inhibitory cytokine IL-35 contributes to regulatory T-cell function. Nature. 2007, 450 (7169): 566-569.
Wang RX, Yu CR, Dambuza IM, Mahdi RM, Dolinska MB, Sergeev YV, Wingfield PT, Kim SH, Egwuagu CE: Interleukin-35 induces regulatory B cells that suppress autoimmune disease. Nat Med. 2014, 20 (6): 633-641.
Shen P, Roch T, Lampropoulou V, O'Connor RA, Stervbo U, Hilgenberg E, Ries S, Dang VD, Jaimes Y, Daridon C, Li R, Jouneau L, Boudinot P, Wilantri S, Sakwa I, Miyazaki Y, Leech MD, McPherson RC, Wirtz S, Neurath M, Hoehlig K, Meinl E, Grützkau A, Grün JR, Horn K, Kühl AA, Dörner T, Bar-Or A, Kaufmann SH, Anderton SM: IL-35-producing B cells are critical regulators of immunity during autoimmune and infectious diseases. Nature. 2014, 507 (7492): 366-370.
Li X, Mai J, Virtue A, Yin Y, Gong R, Sha X, Gutchigian S, Frisch A, Hodge I, Jiang X, Wang H, Yang XF: IL-35 is a novel responsive anti-inflammatory cytokine–a new system of categorizing anti-inflammatory cytokines. PLoS One. 2012, 7 (3): e33628-
Virtue A, Wang H, Yang XF: MicroRNAs and toll-like receptor/interleukin-1 receptor signaling. J Hematol Oncol. 2012, 5: 66-
Virtue A, Mai J, Yin Y, Meng S, Tran T, Jiang X, Wang H, Yang XF: Structural evidence of anti-atherogenic microRNAs. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011, 16: 3133-3145.
Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ, Baltimore D: NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006, 103 (33): 12481-12486.
Bhaumik D, Patil CK, Campisi J: MicroRNAs: an important player in maintaining a balance between inflammation and tumor suppression. Cell Cycle. 2009, 8 (12): 1822-
Perry MM, Moschos SA, Williams AE, Shepherd NJ, Larner-Svensson HM, Lindsay MA: Rapid changes in microRNA-146a expression negatively regulate the IL-1beta-induced inflammatory response in human lung alveolar epithelial cells. J Immunol. 2008, 180 (8): 5689-5698.
Xiao B, Liu Z, Li BS, Tang B, Li W, Guo G, Shi Y, Wang F, Wu Y, Tong WD, Guo H, Mao XH, Zou QM: Induction of microRNA-155 during Helicobacter pylori infection and its negative regulatory role in the inflammatory response. J Infect Dis. 2009, 200 (6): 916-925.
Worm J, Stenvang J, Petri A, Frederiksen KS, Obad S, Elmen J, Hedtjarn M, Straarup EM, Hansen JB, Kauppinen S: Silencing of microRNA-155 in mice during acute inflammatory response leads to derepression of c/ebp Beta and down-regulation of G-CSF. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37 (17): 5784-5792.
Matsui J, Wakabayashi T, Asada M, Yoshimatsu K, Okada M: Stem cell factor/c-kit signaling promotes the survival, migration, and capillary tube formation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2004, 279 (18): 18600-18607.
Suarez Y, Wang C, Manes TD, Pober JS: Cutting edge: TNF-induced microRNAs regulate TNF-induced expression of E-selectin and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on human endothelial cells: feedback control of inflammation. J Immunol. 2010, 184 (1): 21-25.
Harris TA, Yamakuchi M, Ferlito M, Mendell JT, Lowenstein CJ: MicroRNA-126 regulates endothelial expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008, 105 (5): 1516-1521.
Sun X, Icli B, Wara AK, Belkin N, He S, Kobzik L, Hunninghake GM, Vera MP, Blackwell TS, Baron RM, Feinberg MW: MicroRNA-181b regulates NF-kappaB-mediated vascular inflammation. J Clin Invest. 2012, 122 (6): 1973-1990.
Fang Y, Shi C, Manduchi E, Civelek M, Davies PF: MicroRNA-10a regulation of proinflammatory phenotype in athero-susceptible endothelium in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010, 107 (30): 13450-13455.
Suarez Y, Fernandez-Hernando C, Pober JS, Sessa WC: Dicer dependent microRNAs regulate gene expression and functions in human endothelial cells. Circ Res. 2007, 100 (8): 1164-1173.
Hagiwara S, McClelland A, Kantharidis P: MicroRNA in Diabetic Nephropathy: Renin Angiotensin, AGE/RAGE, and Oxidative Stress Pathway. J Diabetes Res. 2013, 2013: 173783-
Sun HX, Zeng DY, Li RT, Pang RP, Yang H, Hu YL, Zhang Q, Jiang Y, Huang LY, Tang YB, Yan GJ, Zhou JG: Essential role of microRNA-155 in regulating endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation by targeting endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Hypertension. 2012, 60 (6): 1407-1414.
Li D, Yang P, Xiong Q, Song X, Yang X, Liu L, Yuan W, Rui YC: MicroRNA-125a/b-5p inhibits endothelin-1 expression in vascular endothelial cells. J Hypertens. 2010, 28 (8): 1646-1654.
Acknowledgements
This work is partially supported by NIH grants to Drs. XF. Yang and H. Wang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, Y., Cheng, Z., Li, X. et al. Immunosuppressive/anti-inflammatory cytokines directly and indirectly inhibit endothelial dysfunction- a novel mechanism for maintaining vascular function. J Hematol Oncol 7, 80 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-014-0080-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-014-0080-6