Abstract
Background
Takakura 3B ankle arthritis is featured as obliteration of ankle space with subchondral bone contact. Among these patients, some have medial distal tibial platform erosion. It is hard to treat this kind of patients. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the therapeutic outcomes of intra-articular opening osteotomy combined with lateral ligament reconstruction for Takakura 3B ankle arthritis with medial distal tibial platform erosion.
Methods
From September 2009 to May 2016, 17 patients with Takakura 3B ankle arthritis were reviewed, including 3 male and 14 female patients. All underwent the operation of intra-articular opening osteotomy combined with lateral ligament reconstruction. All patients were available for analysis. The main outcome measurements included TT angle, AOFAS score, VAS score, SF-36 scale, and AOS scale.
Results
All patients were followed for a mean follow-up of 87.2 months (range, 49 to 129 months). The VAS scale improved from 5.5 ± 1.6 to 2.3 ± 1.9. The mean AOFAS score improved from 47.7 ± 15.7 to 75.8 ± 12.0. The SF-36 scale improved from 41.6 ± 14.0 to 67.7 ± 14.6. The AOS improved from 60.9 ± 13.9 to 28.2 ± 17.7. The TT angle improved from 14.3 ± 5.0° to 5.3 ± 4.0°. The TAS and TLS changed from 83.4 ± 2.6° and 77.5 ± 2.3° to 90.7 ± 2.3° and 78.6 ± 2.2°. However, the LTAS was not corrected significantly.
Conclusion
Intra-articular opening osteotomy combined with lateral ligament reconstruction is an effective method to treat varus ankle arthritis with medial distal tibial platform erosion.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
According to Takakura and Tanaka, varus ankle arthritis was classified into four types: stage 1, early sclerosis and formation of osteophytes without changing of ankle joint space; stage 2, narrowing of medial joint space without subchondral bone contact; stage 3, obliteration of ankle space with subchondral bone contact; and stage 4, varus ankle joint with complete bone contact. Stage 3 was further classified into stages 3A and 3B. Stage 3B ankle arthritis was defined as obliteration of ankle space extended to the roof of the dome of the talus with subchondral bone contact [1, 2].
For young adults and those who do not want to sacrifice the native ankle joint, joint-sparing methods instead of total ankle replacement or ankle arthrodesis are very important. Supramalleolar osteotomy is an effective joint-sparing surgical treatment for varus-type ankle arthritis, especially those with small TAS angles [1,2,3,4,5,6,7].
In our practice, we do notice positive outcomes after supramalleolar osteotomy for stage 3B ankle arthritis [8]. However, in some cases, the varus talus repeatedly abrades the medial distal tibial platform after long walking. The medial tibial platform is eroded but the lateral tibial surface angle (LTAS) is normal. Previous studies reported a new kind of technique known as intra-articular opening medial tibial wedge osteotomy with good results [9, 10]. However, stage 3B ankle was considered not suitable for this osteotomy. In Myerson’s study, 4 patients had a type 3B deformity. Two of them underwent ankle arthrodesis and two underwent ankle replacement after the intra-articular opening osteotomy [9].
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the therapeutic outcomes of intra-articular opening osteotomy combined with lateral ligament reconstruction for Takakura 3B ankle arthritis with medial distal tibial platform erosion.
Materials and methods
The current study was approved by our institutional review board. From September 2009 to May 2016, 17 patients (17 ankles, 7 left and 10 right) with Takakura 3B ankle arthritis were reviewed, including 3 male and 14 female patients. All underwent the operation of intra-articular opening osteotomy combined with lateral ligament reconstruction. The mean age was 52.35 ± 8.05 years. The inclusion criteria were (1) Takakura stage 3B ankle arthritis, (2) medial distal tibial platform erosion, (3) normal lateral tibial surface, and (4) painful ankle arthritis undergoing at least 1-year conservative treatment.
The exclusion criteria were (1) end-stage ankle arthritis, (2) patients with neuropathic arthropathy or rheumatoid arthritis, (3) patients with regional infection around the ankle joint or had other ankle surgeries, and (4) patients with severe osteoporosis or large bone loss.
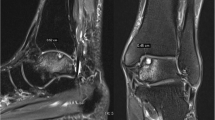
Weightbearing X-rays of ankle joint were performed for every patient preoperatively and postoperatively, including anteroposterior ankle views (AP) and lateral ankle views. In this study, we defined the lateral tibial articular surface angle (LTAS) as the angle between the axis of the tibia and the lateral tibial surface. The talar tilt angle (TT) was regarded as the angle between the distal articular surface of the tibia and the upper surface of the talus. The general tibial articular surface angle (TAS) was defined as the angle between the axis of the tibia and the whole tibial surface. The whole tibial surface was a line drawn from the medial apex of the mortise to the lateral apex of the mortise. The tibial lateral surface angle (TLS) is designated as the angle between the axis of the tibia and the surface of the distal tibia in the lateral view. The hindfoot alignment view, which was recommended by Saltzman and el-Khoury, was also performed to evaluate hindfoot alignment condition [11]. The tibial axis on anteroposterior and lateral radiographs was drawn by connecting the midpoint between the cortex at 13 cm and 8 cm proximal to the joint line. We routinely reviewed ankle MRI scans for every patient to evaluate the cartilage condition. We used the American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society Ankle-Hindfoot Score (AOFAS-AH), the visual analogue scale (VAS), the Short From-36 scale (SF-36), and the Ankle Osteoarthritis scale (AOS) to determine the functional outcome of patients at the final follow-up (Fig. 1).
Surgical technique
In this study, all ankle arthritis was varus type. The osteotomy approach was through a medial longitudinal incision. A K-wire was placed as a guide wire of osteotomy. Two or three K-wires were placed parallel to the ankle joint surface portion of the tibial platform within the subchondral bone just under the articular cartilage at the apex of the plafond angulation. They help the prevention of destruction of the talus cartilage from the saw blade during the osteotomy. It also acted as a hinge during deformity correction. Then the intra-articular osteotomy was performed. The intraoperation fluoroscopic assessment was performed to evaluate whether the tibial articular surface was normal. If the varus talus could not return to normal, then a release procedure of medial ankle ligament including the superficial and deep deltoid ligament was performed. Debridement of osteophytes was performed if there was impingement around the ankle joint such as the anterior distal tibial osteophyte to improve ankle motion through the medial incision and lateral incision. A wedged allograft was shaped and inserted into the osteotomy site and was fixed by a locking plate. The ankle joint was flexible, and we fixed it into a neutral position with 1–2 K-wires, which were removed 3–4 weeks postoperatively. In this position, the medial ligaments were sutured and lateral ligaments were reconstructed.
Lateral ligament reconstruction was performed via a minimally invasive method [12]. Fifteen patients used allograft, 2 patients autograft. Two guide wires were introduced at the distal end of the fibula, and then a tunnel was made. A hole was made at the lateral side of the talar neck. These were all through the lateral incision. A small incision was made at the lateral side of the middle portion of the calcaneus and a hole was made. The tendon graft was introduced through the tunnel, and the two ends of the tendon were then passed above the bone surface to the holes made at the talar neck and calcaneus fixed by two biodegradable inference screws. The ligament procedures were performed after fixation of osteotomy (Fig. 2).
A cast was used for 6 weeks. Part weight bearing was allowed 6 weeks postoperatively with the cast. Full weight bearing was allowed 2 to 3 months postoperatively. Patients came to the hospital 2 weeks, 6 weeks, 3 months, and 1 year postoperatively. All the patients were followed up annually.
Statistical methods
All analyses were performed with the SAS software version 8.1 (SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC). The results were given as means and standard deviation. The paired t test was used for assessing differences between preoperative and postoperative measurements. A p value less than 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.
Results
All patients were followed. Patients were followed for a mean follow-up of 87.2 months (range, 49 to 129 months). There was no loss of follow-up. The VAS scale improved from 5.5 ± 1.6 to 2.3 ± 1.9. The mean AOFAS score improved from 47.7 ± 15.7 to 75.8 ± 12.0. The SF-36 scale improved from 41.6 ± 14.0 to 67.7 ± 14.6. The AOS improved from 60.9 ± 13.9 to 28.2 ± 17.7. The TT angle improved from 14.3 ± 5.0° to 5.3 ± 4.0°. The TAS and TLS changed from 83.4 ± 2.6° and 77.5 ± 2.3° to 90.7 ± 2.3° and 78.6 ± 2.2°. However, the LTAS was not corrected significantly.
In this study, 2 patients rated their outcomes as “excellent” and 7 patients rated their outcomes as “good.” Four patients rated their results as “fair.” On the other hand, a “poor” outcome was observed in 4 patients because of the consistent discomfort. However, none of the patients underwent ankle joint arthroplasty or arthrodesis because of the cost involved or other reasons.
Ten patients underwent calcaneal osteotomy. Thirteen patients recalled an old ankle sprain history. All of them had a long-term ankle sprain history (5–38 years). One patient had a lateral malleolar fracture history. Three patients had no incentive (Figs. 3 and 4) (Tables 1 and 2).
Discussion
The causes of varus-type ankle arthritis still remain unknown. In other studies, usually, ankle arthritis develops secondary to trauma [4, 7, 13]. However, in this study, more patients recalled an old ankle sprain history. We thought that maybe it was because of the weak lateral ligament resulted in varus-type ankle arthritis.
Takakura and Tanaka divided varus ankle arthritis into 4 stages, stages 1, 2, 3 (3A, 3B), and 4 [1, 2]. Did stage 3B ankle arthritis develop directly from stage 3A? This is controversial. We do not think all of the stage 3B ankle arthritis were evolved from stage 3A ankle arthritis. When the talus invert in ankle mortise, with long time of walking, the varus talus touches the tibia surface and abrades it gradually. So, maybe the stage 3B ankle arthritis developed directly from stage 2. In this kind of patients, the LTAS is usually normal, while the TAS angle is small. We thought that intra-articular opening osteotomy was helpful for 3B ankle arthritis with medial distal tibial platform erosion and the results bear this out.
One of the causes of varus-type ankle arthritis was chronic ankle instability [14, 15]. In this study, all patients underwent lateral ligament reconstruction. Most of the patients in our study recalled repeated ankle sprain histories. The weak lateral ligament resulted in a chronically unstable varus ankle. The medially driven talus causes chronic pressure to the medial malleolus, which makes medial malleolus no longer vertical [9]. Although some patients in this study had no ankle sprain histories, there were still ankle instabilities after the release of ligaments around the ankle joint and debridement of osteophytes. When the talus could return to normal during operation, we think lateral ligament reconstruction was very important to keep the talus in this position.
For varus ankle arthritis, especially Takakura stage 3 or 4 ankle arthritis, previous studies have reported good results of ankle arthrodesis or ankle replacement [16,17,18,19,20]. However, ankle arthrodesis is a joint sacrifice method to treat ankle arthritis, which restricts ankle movement. In this study, the mean age of patients was 52.35 ± 8.05 years. The patients are relatively young, so ankle arthroplasty may not be suitable for them. These patients were still very positive and want to keep their native ankle joint. Osteotomy provided the possibility to preserve their native ankle joint.
Previous studies reported that it was contraindication if the varus ankle was rigid and could not be corrected to normal under fluoroscopic examination before the surgery [9, 21]. However, in our study, we concern more about whether the varus ankle could return to normal intraoperatively or not. We performed a thorough release of ligaments and capsule around the ankle joint if the varus deformity could not be corrected after osteotomy. After the release and debridement procedure, the ankle joint was flexible and we fixed it into a neutral position with 1–2 K-wires, which were removed 3–4 weeks postoperatively. In this position, the medial ligaments were sutured and lateral ligaments were reconstructed. We think that whether the varus ankle could return to normal during operation matters more than preoperative condition. We care more about the joint cartilage than preoperative talar tilt angle.
We think the most important aspect of this kind of procedure is that there is enough residual articular cartilage. Ankle joints with more than 50% residual articular cartilage tend to get better prognosis than those that are not. So, we did an osteotomy procedure for this kind of ankle arthritis. We do not perform osteotomy surgery for stage 4 ankle arthritis. Joint cartilage of stage 4 ankle arthritis was always extensively destructed. For this kind of patients, even though realignment of the ankle joint may alleviate symptoms, joint damage will progress soon.
Conclusion
For Takakura 3B ankle arthritis with medial distal tibial erosion, intra-articular opening osteotomy combined with lateral ligament reconstruction is an effective method to treat this kind of varus ankle arthritis.
Availability of data and materials
All data and materials were in full compliance with the journal’s policy.
Abbreviations
- AOFAS:
-
The American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society Ankle-Hindfoot scores
- SF-36:
-
The Short Form (36) Health Survey
- VAS:
-
Visual analogue scale
- AOS:
-
Ankle Osteoarthritis scale
- TT:
-
Talar tilt angle
- TAS:
-
Tibial articular surface angle
- TLS:
-
Tibial lateral surface angle
- LTAS:
-
Lateral tibial articular surface angle
References
Takakura Y, Tanaka Y, Kumai T, Tamai S. Low tibial osteotomy for osteoarthritis of the ankle. Results of a new operation in 18 patients. J Bone Joint Surg (Br). 1995;77(1):50–4.
Tanaka Y, Takakura Y, Hayashi K, Taniguchi A, Kumai T, Sugimoto K. Low tibial osteotomy for varus-type osteoarthritis of the ankle. J Bone Joint Surg (Br). 2006;88(7):909–13.
Krahenbuhl N, Zwicky L, Bolliger L, Schadelin S, Hintermann B, Knupp M. Mid- to long-term results of supramalleolar osteotomy. Foot Ankle Int. 2017;38(2):124–32.
Hintermann B, Knupp M, Barg A. Supramalleolar osteotomies for the treatment of ankle arthritis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016;24(7):424–32.
Ahn TK, Yi Y, Cho JH, Lee WC. A cohort study of patients undergoing distal tibial osteotomy without fibular osteotomy for medial ankle arthritis with mortise widening. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(5):381–8.
Lee WC, Moon JS, Lee K, Byun WJ, Lee SH. Indications for supramalleolar osteotomy in patients with ankle osteoarthritis and varus deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(13):1243–8.
Takakura Y, Takaoka T, Tanaka Y, Yajima H, Tamai S. Results of opening-wedge osteotomy for the treatment of a post-traumatic varus deformity of the ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998;80(2):213–8.
Xu Y, Xu XY. Medial open-wedge supramalleolar osteotomy for patients with Takakura 3B ankle osteoarthritis: a mid- to long-term study. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:7630868.
Mann HA, Filippi J, Myerson MS. Intra-articular opening medial tibial wedge osteotomy (plafond-plasty) for the treatment of intra-articular varus ankle arthritis and instability. Foot Ankle Int. 2012;33(4):255–61.
Becker AS, Myerson MS. The indications and technique of supramalleolar osteotomy. Foot Ankle Clin. 2009;14(3):549–61.
Saltzman CL. el-Khoury GY: the hindfoot alignment view. Foot Ankle Int. 1995;16(9):572–6.
Xu X, Hu M, Liu J, Zhu Y, Wang B. Minimally invasive reconstruction of the lateral ankle ligaments using semitendinosus autograft or tendon allograft. Foot Ankle Int. 2014;35(10):1015–21.
Knupp M, Bolliger L, Hintermann B. Treatment of posttraumatic varus ankle deformity with supramalleolar osteotomy. Foot Ankle Clin. 2012;17(1):95–102.
Harrington KD. Degenerative arthritis of the ankle secondary to long-standing lateral ligament instability. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979;61(3):354–61.
Noguchi K. Biomechanical analysis for osteoarthritis of the ankle. Nihon Seikeigeka Gakkai Zasshi. 1985;59(2):215–22.
Joo SD, Lee KB. Comparison of the outcome of total ankle arthroplasty for osteoarthritis with moderate and severe varus malalignment and that with neutral alignment. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B(10):1335–42.
Lee GW, Wang SH, Lee KB. Comparison of intermediate to long-term outcomes of total ankle arthroplasty in ankles with preoperative varus, valgus, and neutral alignment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100(10):835–42.
Trajkovski T, Pinsker E, Cadden A, Daniels T. Outcomes of ankle arthroplasty with preoperative coronal-plane varus deformity of 10 degrees or greater. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(15):1382–8.
Maenohara Y, Taniguchi A, Tomiwa K, Tsuboyama D, Kurokawa H, Kumai T, et al. Outcomes of bilateral vs unilateral ankle arthrodesis. Foot Ankle Int. 2018;39(5):530–4.
Grass R, Rammelt S, Biewener A, Zwipp H. Arthrodesis of the ankle joint. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2004;21(2):161–78.
Hintermann B, Ruiz R, Barg A. Novel double osteotomy technique of distal tibia for correction of asymmetric varus osteoarthritic ankle. Foot Ankle Int. 2017;38(9):970–81.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge all collaborating researchers in collecting information during this study. We would also like to thank the subjects whose participation made this investigation possible.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China grants (No. 81772372).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YX carried out the literature research, experimental studies, statistical analysis, and manuscript preparation. X-CL and G-CJ participated in the experimental studies and manuscript editing. X-YX made the concepts, study design, and experimental studies. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the ethics committee of Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine. A written consent to participate was provided by participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
All patients enrolled into the study agree to the use of patients’ data for research.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Li, Xc., Guo, Cj. et al. Intra-articular opening osteotomy combined with lateral ligament reconstruction for varus ankle arthritis. J Orthop Surg Res 16, 7 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-020-02143-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-020-02143-1