Abstract
Background
Although anterolateral decompression and instrumentation has several advantages in treating thoracolumbar burst fractures, the risk factors for supplementary posterior instrumentation are still unclear.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed 238 patients who underwent anterolateral decompression and instrumentation for single-level thoracolumbar burst fractures from January 2010 and March 2012. The influences of several potential risk factors that might affect supplementary posterior instrumentation were assessed using univariate and multivariate analyses.
Results
Twenty seven patients who developed worsening back pain without neurological deterioration after the anterolateral approach treatment need further posterior instrumentation fixation. The univariate analysis showed that age, disruption of the posterior longitudinal ligament complex (PLC), and fracture level were the risk factors for supplementary posterior instrumentation. However, age and integrity of the PLC were the independent risk factors for supplementary posterior instrumentation by multivariate analyses.
Conclusions
Supplemental posterior instrumentation was necessary in 11.3% of cases following anterolateral decompression and instrumentation in the present study. Older age and disruption of the PLC were the independent risk factors in prediction of supplementary posterior instrumentation in treating thoracolumbar burst fractures.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
About 20% of thoracic and lumbar fractures belong to thoracolumbar burst fractures [1,2]. This kind of fracture is frequently associated with neurologic deficits because of encroachment on the neural elements and at times owing to the dynamic nature of the injury.
To some extent, management of thoracolumbar burst fractures is according to clinical and radiographic criteria [3-17]. The purpose of orthopedic surgery includes decompression of the neural elements, restoration of vertebral body height, correction of spinal deformity, and stabilization. Furthermore, surgery can be performed through a posterior approach [18-21] or through an anterolateral retroperitoneal flank approach [22-27], based on the necessity and extent of decompression.
The anterolateral retroperitoneal flank approach allows the surgeon to conduct corpectomy and decompression of the canal. Bone fragments can be withdrawed from the canal under direct vision. After corpectomy, the vertebral column is reconstructed by inserting a prosthesis or graft, restoring height and correcting spinal angulation. When placing anterior instrumentation, the hardware generally incorporates one level above and one level below the fracture.
However, there are about 10% patients who meet failure after anterolateral decompression and stabilization. They need further posterior instrumentation [24,25,27]. Currently, supplementary posterior instrumentation was performed in cases of symptomatic settling and angulation of the spine or instability in spite of anterior instrumentation.
At present, the risk factors for predicting supplementary posterior instrumentation after anterolateral decompression and instrumentation in treating thoracolumbar burst fractures are still unclear. Thus, the purpose of the present study is to identify risk factors that contribute to the need for posterior instrumentation after anterolateral decompression and stabilization for single-level thoracolumbar burst fractures using a multivariate statistical model.
Materials and methods
Patients
Between January 2010 and March 2012, 238 patients (178 females, 60 males; mean age, 63.2 years; range, 42–87 years) who underwent anterolateral approach and/or posterior approach for single-level thoracolumbar burst fractures at our institution and were followed up for at least 1 year after the procedure were retrospectively enrolled in this study (Figures 1 and 2). The inclusion criterion was that the fractures existed in the anterior and middle columns as described by Denis [2] and fell into groups A3.1–A3.3 of Magerl et al. [28]. The Thoracolumbar Injury Classification and Severity Score (TLICS) [29,30] utilizes the presence or absence of neurological deficit, the integrity of the posterior longitudinal ligament complex (PLC), and the morphology of the fracture (compression, burst, or dislocation). The patients who underwent surgery had a TLICS score of 4 or greater. Exclusion criteria were patients with other types of thoracolumbar fractures, or vertebral fractures above T10, or those patients without follow-up at least 1 year. The study protocol was approved by the local institutional review board and ethics committee. All patients provided written informed consent.
A 58-year-old woman sustained a fall from ground level. (A) lateral x-ray shows burst fracture of T12. (B) MRI shows the burst fracture and canal compromise. (C) AP x-ray show good apposition of the rectangular footplates and the adjacent endplates. One week later the patient was experiencing disabling back pain upon mobilization in thoracolumbar orthosis. Posterior minimally invasive pedicle screws were placed. (D) AP x-ray shows stable and satisfactory spinal alignment.
Technical note
All the anterolateral approaches were performed by the primary spinal surgeon through the left flank according to standard practice [23-26]. After corpectomy, decompression of the thecal sac was ensured from pedicle to pedicle in the axial plane and from the rostral to the caudal intact endplates of the adjacent vertebrae. The anterior column was reconstructed, using iliac autografts or allografts. The carbon fiber-reinforced polymer cages or expandable titanium cages were used. The graft or cage with the largest footplate was consistently selected to reduce subsidence, or telescoping, of the graft or cage into the adjacent vertebral bodies. Cages were packed with artificial graft or autograft harvested from the patient during decompression, supplemented with corticocancellous allograft if necessary. To facilitate graft or cage insertion, distraction was applied on the rostral and caudal bodies through the bicortical screws. Screw length was calculated from axial CT scans before surgery. Overzealous distraction was avoided to prevent screw loosening or pullout. Gentle pressure on the gibbous in a ventral direction was also helpful. The position of the graft/cage was confirmed using both anteroposterior and lateral fluoroscopy. Lateral instrumentation with bicortical screws and dual rods was used in some cases. All patients wore a thoracolumbar clamshell orthosis postoperatively for 3 months.
The integrity of the PLC was evaluated by one of our authors who was blinded to the management or outcomes of the patients. The T1- and T2-weighted images and the short tau inversion recovery (STIR) sequence were used to assess the integrity of PLC consisting of the supra- and infraspinous ligaments, the ligamentum flavum, and the facet capsules [31-36]. Disruption was diagnosed when the black stripe representing the supraspinous ligament was discontinuous. Injury to the infraspinous ligaments was diagnosed with high signal intensity in the interspinous space produced by hemorrhage.
Potential risk factors
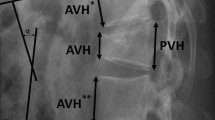
Data regarding age, gender, body mass index (BMI), America Spinal Injury Association (ASIA) impairment scale [37], segmental kyphosis as assessed on preoperative radiography, residual anteroposterior canal diameter as assessed on CT scans, fracture level, fracture age, and surgical approach were collected. ASIA impairment scale was used to assess the neurological deficit on initial examination and at follow-up. Segmental kyphosis was measured on lateral plane radiographs using the angle subtended between the adjacent intact endplates. Residual anteroposterior canal diameter at the injury site was measured from preoperative CT scans and expressed as a percentage of the intact diameter averaged between the rostral and caudal intact canal.
Statistical analysis
Factors associated with supplementary posterior instrumentation after anterolateral decompression and instrumentation were identified using univariate analysis. The data analysis was performed using SPSS version 19.0 (Chicago, IL, USA).Continuous data were compared between the two groups using the student t test, whereas discontinuous data were analyzed using the chi-squared test. All significance tests were two-tailed, with p < 0.05 representing statistical significance. In addition, a multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to identify which independent factors helped predict the supplementary posterior instrumentation after anterolateral decompression and instrumentation in treating thoracolumbar burst fractures.
Results
Characteristics of patients
A total of 238 patients with single-level vertebrae cases were finally included. The follow-up is 20.2 ± 8.1 months. Causes of injury were falls in 87, car accidents in 91, vehicle/motorcycle in 19, equestrian in 2, sports in 27, and other causes in 12. L1 was the affected level in 78, followed by T12 in 56, T11 in 51, L2 in 38, and T10 in 15. Surgery was undertaken 10.3 ± 4.4 days following injury, with a length of hospitalization of 17.5 ± 7.7 days. The residual canal on admission measured 45.7% ± 13.9%. Kyphotic angulations on admission, discharge, and last follow-up were 7.1 ± 9.1, 0.4 ± 6.5 (p < 0.05), and 1.2 ± 6.6 (p < 0.05), respectively (Table 1).
Characteristics of patients with supplementary posterior fixation
Twenty-seven patients developed worsening back pain without neurological deterioration after the anterolateral approach treatment. Nine patients had neurological deficit on admission, while others were intact. This clinical deterioration was caused by spinal settling and graft migration predominantly into the caudal endplate. Therefore, all of the 27 patients required supplementary posterior fixation, which was undertaken within 13.2 ± 4.5 days after the previous operation. The characteristics of patients with supplementary posterior fixation are presented in Table 2.
Risk factors by univariate analysis
Univariate analysis was performed to assess risk factors for supplementary posterior instrumentation after anterolateral decompression compared with other patients who were treated with anterolateral instrumentation alone. The results of univariate analysis showed that age, disruption of the PLC, and fracture level were the risk factors for supplementary posterior instrumentation (Table 2).
Risk factors by multivariate analysis
The associations observed after univariate analysis regarding the potential risk factors enabled the construction of a multivariate logistic regression model for a conjoint analysis to determine which characteristics are independently associated with the supplementary posterior instrumentation. The results of multiple logistic regression analysis are shown in Table 3. Age and integrity of the PLC were the independent risk factors for supplementary posterior instrumentation.
Discussion
About half of the thoracic and lumbar fractures occur at the thoracolumbar junction (T10–L2), and the majority of these fractures are burst in type involving the anterior and middle columns [3,6,22,25]. The therapeutic options include conservative treatment and surgery. For patients with burst fractures but neurologically intact, conservative treatment may be optimal [15,16]. Surgery is suitable for patients with neurological deficits or persistent pain and for patient whose fractures are deemed unstable with disruption of the posterior ligaments [35,36]. When anterior decompression is deemed unnecessary, posterior instrumentation may be sufficient [18,21]. However, when significant fragmentation of the vertebral body exists and there is poor apposition of the fragments and deformity, anterior grafts and instrumentation are advised [22,26]. Direct access for canal decompression, reconstruction of anterior column, and correction of kyphosis and instrumented fusion with single approach can be achieved by the anterior approach. Moreover, improvement in neurological function has been consistently demonstrated with relatively minimal complications [7,19,26].
In the present study, rods and bicortical screws were used to supple the strut graft and because of the limitations of plates in rigid compared with rods and bicortical screws. Other studies demonstrated the importance of the anterior strut graft by conducting a test that compares three anterior plates and three anterior rods and screws [38-40]. Although the strut graft was performed, settling continues to occur. In the present study, angulation was corrected significantly, from 7.1 ± 9.1 preoperatively to 0.4 ± 6.5 postoperatively, with a slight increase at follow-up to 1.2 ± 6.6 compared to preoperative. The above results are consistent to those of previous studies [22,26,27]. The loss of correction with the passage of time is commonly encountered, well tolerated, and attributed to settling. The more significant increase in angulation with time has been demonstrated in burst fractures when treated nonoperatively [12,13,15].
In the present study, 27 patients underwent supplemental posterior fixation for symptomatic settling of the cage into the superior endplate of the caudal vertebra. These patients did not experience an increase in deficit. Posterior instrumentation fixation was performed within the next few days of the index operation. Of the 27 patients requiring supplemental posterior instrumentation, 19 had PLC disruption compared with other patients who had successful anterior approach fusion. The multivariate analysis demonstrated that the PLC disruption correlated with the need for posterior fixation. The result was consistent with the previous studies that the PLC was of significance in spinal stability. Therefore, rigid posterior fixation is needed in treating thoracolumbar burst fractures.
Another independent risk factor for the need of supplemental posterior instrumentation was age. The mean age of patients needing further posterior fixation was higher than that of the anterolateral group. To some extent, the association of age with the need of supplementary posterior fixation might be attributed to the age-related decrease in bone mineral density [41,42]. However, the measurement of bone mineral density was not conducted in the present study as a routine.
The reoperation rate (11.3%) in the present study was comparable to that of other studies. McAfee et al. [25] conducted Kaneda instrumentation in treating thoracolumbar pathology. Two of 35 cases experienced failure who did need further posterior instrumentation. Kaneda et al. [24] conducted a study about treating thoracolumbar burst fractures by anterolateral Kaneda device. However, pseudoarthrosis was encountered in ten of 150 cases, and further posterior fixation was conducted in ten cases. Sasso et al. [27] performed anterior fusion in treating thoracolumbar burst fractures in 40 patients. Only three patients required additional posterior instrumentation because of disruption of PLC. In summary, different reoperation rates of the need for further posterior instrumentation may be affected by several factors, such as the recruited patients with differences in severity of injury and bone quality.
The limitations of the present study mainly include the following items: (1) Operator expertise and learning curve may be subjective risk factors. We are unable to cancel out the above effects. (2) We did not objectively measure the bone mineral density, which may place an influence on the reoperation rates. Moreover, patient’s comobilities, smoking status, and living condition which have not been evaluated may be all factors that may influence the risk of supplementary posterior instrumentation. (3) The study design, retrospective study, may place bias on the stability of the results.
Conclusion
In the present study, 27 of 238 patients in which the anterolateral decompression and instrumentation was undertaken in treating single-level thoracolumbar burst fractures did need additional posterior fixation. In univariate analysis, age, disruption of the PLC, and fracture level were the risk factors for further posterior fixation. However, older age and disruption of the PLC were the independent risk factors predicting supplementary posterior instrumentation in treating thoracolumbar burst fractures by multivariate analysis. Further prospective studies are still required to evaluate other potential factors about supplementary posterior instrumentation in treating thoracolumbar burst fractures.
References
Bensch FV, Koivikko MP, Kiuru MJ, Koskinen SK. The incidence and distribution of burst fractures. Emerg Radiol. 2006;12(3):124–9.
Denis F. The three column spine and its significance in the classification of acute thoracolumbar spinal injuries. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1983;8(8):817–31.
Bailey CS, Dvorak MF, Thomas KC, Boyd MC, Paquett S, Kwon BK, et al. Comparison of thoracolumbosacral orthosis and no orthosis for the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures: interim analysis of a multicenter randomized clinical equivalence trial. J Neurosurg Spine. 2009;11(3):295–303.
Cantor JB, Lebwohl NH, Garvey T, Eismont FJ. Nonoperative management of stable thoracolumbar burst fractures with early ambulation and bracing. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18(8):971–6.
Dai LY. Remodeling of the spinal canal after thoracolumbar burst fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2001(382):119–123.
Dai LY, Jiang LS, Jiang SD. Conservative treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures: a long-term follow-up results with special reference to the load sharing classification. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(23):2536–44.
Hitchon PW, Torner J, Eichholz KM, Beeler SN. Comparison of anterolateral and posterior approaches in the management of thoracolumbar burst fractures. J Neurosurg Spine. 2006;5(2):117–25.
Hitchon PW, Torner JC, Haddad SF, Follett KA. Management options in thoracolumbar burst fractures. Surg Neurol. 1998;49(6):619–26. 6.
McCormack T, Karaikovic E, Gaines RW. The load sharing classification of spine fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994;19(15):1741–4.
Mumford J, Weinstein JN, Spratt KF, Goel VK. Thoracolumbar burst fractures. The clinical efficacy and outcome of nonoperative management. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18(8):955–70.
Reid DC, Hu R, Davis LA, Saboe LA. The nonoperative treatment of burst fractures of the thoracolumbar junction. J Trauma. 1988;28(8):1188–94.
Siebenga J, Leferink VJ, Segers MJ, Elzinga MJ, Bakker FC, Haarman HJ, et al. Treatment of traumatic thoracolumbar spine fractures: a multicenter prospective randomized study of operative versus nonsurgical treatment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(25):2881–90.
Tropiano P, Huang RC, Louis CA, Poitout DG, Louis RP. Functional and radiographic outcome of thoracolumbar and lumbar burst fractures managed by closed orthopaedic reduction and casting. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(21):2459–65.
Vaccaro AR, Lehman RJ, Hurlbert RJ, Anderson PA, Harris M, Hedlund R, et al. A new classification of thoracolumbar injuries: the importance of injury morphology, the integrity of the posterior ligamentous complex, and neurologic status. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(20):2325–33.
Willen J, Anderson J, Toomoka K, Singer K. The natural history of burst fractures at the thoracolumbar junction. J Spinal Disord. 1990;3(1):39–46.
Wood K, Buttermann G, Mehbod A, Garvey T, Jhanjee R, Sechriest V. Operative compared with nonoperative treatment of a thoracolumbar burst fracture without neurological deficit. A prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A(5):773–81.
Wood KB, Bohn D, Mehbod A. Anterior versus posterior treatment of stable thoracolumbar burst fractures without neurologic deficit: a prospective, randomized study. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;18 Suppl:S15–23.
Dai LY, Jiang LS, Jiang SD. Posterior short-segment fixation with or without fusion for thoracolumbar burst fractures. a five to seven-year prospective randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(5):1033–41.
Danisa OA, Shaffrey CI, Jane JA, Whitehill R, Wang GJ, Szabo TA, et al. Surgical approaches for the correction of unstable thoracolumbar burst fractures: a retrospective analysis of treatment outcomes. J Neurosurg. 1995;83(6):977–83.
McLain RF, Sparling E, Benson DR. Early failure of short-segment pedicle instrumentation for thoracolumbar fractures. A preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75(2):162–7.
McNamara MJ, Stephens GC, Spengler DM. Transpedicular short-segment fusions for treatment of lumbar burst fractures. J Spinal Disord. 1992;5(2):183–7.
Dai LY, Jiang LS, Jiang SD. Anterior-only stabilization using plating with bone structural autograft versus titanium mesh cages for two- or three-column thoracolumbar burst fractures: a prospective randomized study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(14):1429–35.
Heary RF, Kheterpal A, Mammis A, Kumar S. Stackable carbon fiber cages for thoracolumbar interbody fusion after corpectomy: long-term outcome analysis. Neurosurgery. 2011;68(3):810–8. 3.
Kaneda K, Taneichi H, Abumi K, Hashimoto T, Satoh S, Fujiya M. Anterior decompression and stabilization with the Kaneda device for thoracolumbar burst fractures associated with neurological deficits. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997;79(1):69–83.
McAfee PC. Complications of anterior approaches to the thoracolumbar spine. Emphasis on Kaneda instrumentation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1994;(306):110–119
McDonough PW, Davis R, Tribus C, Zdeblick TA. The management of acute thoracolumbar burst fractures with anterior corpectomy and Z-plate fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(17):1901–8. 1909.
Sasso RC, Renkens K, Hanson D, Reilly T, McGuire RJ, Best NM. Unstable thoracolumbar burst fractures: anterior-only versus short-segment posterior fixation. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2006;19(4):242–8.
Magerl F, Aebi M, Gertzbein SD, Harms J, Nazarian S. A comprehensive classification of thoracic and lumbar injuries. Eur Spine J. 1994;3(4):184–201.
Patel AA, Vaccaro AR. Thoracolumbar spine trauma classification. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010;18(2):63–71.
Rihn JA, Anderson DT, Harris E, Lawrence J, Jonsson H, Wilsey J, et al. A review of the TLICS system: a novel, user-friendly thoracolumbar trauma classification system. Acta Orthop. 2008;79(4):461–6.
Emery SE, Pathria MN, Wilber RG, Masaryk T, Bohlman HH. Magnetic resonance imaging of posttraumatic spinal ligament injury. J Spinal Disord. 1989;2(4):229–33.
Haba H, Taneichi H, Kotani Y, Terae S, Abe S, Yoshikawa H, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging for detecting posterior ligamentous complex injury associated with thoracic and lumbar fractures. J Neurosurg. 2003;99(1 Suppl):20–6.
Lee HM, Kim HS, Kim DJ, Suk KS, Park JO, Kim NH. Reliability of magnetic resonance imaging in detecting posterior ligament complex injury in thoracolumbar spinal fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(16):2079–84.
Oner FC, van Gils AP, Faber JA, Dhert WJ, Verbout AJ. Some complications of common treatment schemes of thoracolumbar spine fractures can be predicted with magnetic resonance imaging: prospective study of 53 patients with 71 fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(6):629–36.
Radcliff K, Kepler CK, Rubin TA, Maaieh M, Hilibrand AS, Harrop J, et al. Does the load-sharing classification predict ligamentous injury, neurological injury, and the need for surgery in patients with thoracolumbar burst fractures?: Clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;16(6):534–8.
Radcliff K, Su BW, Kepler CK, Rubin T, Shimer AL, Rihn JA, et al. Correlation of posterior ligamentous complex injury and neurological injury to loss of vertebral body height, kyphosis, and canal compromise. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(13):1142–50.
Burns S, Biering-Sorensen F, Donovan W, Graves DE, Jha A, Johansen M, et al. International standards for neurological classification of spinal cord injury, revised 2011. Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil. 2012;18(1):85–99.
Brodke DS, Gollogly S, Bachus KN, Alexander MR, Nguyen BK. Anterior thoracolumbar instrumentation: stiffness and load sharing characteristics of plate and rod systems. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(16):1794–801.
Kallemeier PM, Beaubien BP, Buttermann GR, Polga DJ, Wood KB. In vitro analysis of anterior and posterior fixation in an experimental unstable burst fracture model. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2008;21(3):216–24.
Maiman DJ, Pintar F, Yoganandan N, Reinartz J. Effects of anterior vertebral grafting on the traumatized lumbar spine after pedicle screw-plate fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18(16):2423–30.
Khosla S, Riggs BL. Pathophysiology of age-related bone loss and osteoporosis. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2005;34(4):1015–30.
Riggs BL, Melton ILR, Robb RA, Camp JJ, Atkinson EJ, Peterson JM, et al. Population-based study of age and sex differences in bone volumetric density, size, geometry, and structure at different skeletal sites. J Bone Miner Res. 2004;19(12):1945–54.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Haixu Chen for his support in obtaining the approval of the ethics committee in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
The design of the study was done by Y-SJ. JC and QS prepared the manuscript and assisted in the study processes. J-YL, C-XB, JD and C-YZ assisted in the data collection. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Jia, YS., Sun, Q. et al. Multivariate analysis of risk factors for predicting supplementary posterior instrumentation after anterolateral decompression and instrumentation in treating thoracolumbar burst fractures. J Orthop Surg Res 10, 17 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-015-0155-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-015-0155-2