Abstract
Background
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the lumbar spine is commonly used to identify the source of low back pain (LBP); however, its use has been questionable. Throughout the years, numerous lumbar phenotypes (e.g., endplate abnormalities, Modic changes, black disc) have been studied as possible pain generators. High-intensity zones (HIZs) are of particular interest as they may represent annular tears. However, for over three decades, there has been heated debate as to whether these imaging biomarkers are synonymous with LBP. Therefore, the following study addressed a systematic review of the reported literature addressing the relationship of HIZs and LBP.
Methods
A systematic review was conducted via MEDLINE, SCOPUS, Cochrane, PubMed, PubMed Central, EMBASE via Ovid, and Web of Science with the following search terms: “HIZ,” “high intensity zone,” or “high intensity zones” and “low back pain,” “pain,” “lumbago,” and/or “sciatica.” Specific exclusion criteria were also maintained. Two independent reviewers searched the literature, selected the studies, and extracted the data.
Results
We identified six studies from our search strategy that met the inclusion criteria from a total of 756 possible studies. One cross-sectional population-based study and five comparison studies were identified, which provided information regarding the prevalence of HIZs. The prevalence of HIZs was 3 to 61% in subjects with LBP and 2 to 3% in subjects without LBP. Only three studies suggested a significant association between the presence of HIZ and LBP with or without sciatica.
Conclusions
Our systematic review has found evidence that HIZs may be a possible risk factor for LBP; however, a mismatch of the clinical relevance of HIZs between studies still remains. The available evidence is limited by small sample size, heterogeneous study populations, and lack of standardized imaging methods for phenotyping. HIZs may be important lumbar biomarkers that demand further investigation and should be considered in the global imaging assessment of the spine, which may have immense clinical utility. Further large-scale studies with standardized imaging and classification techniques as well as the assessment of patterns of HIZs are necessary to better understand their role with LBP development.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Low back pain (LBP) is one of the most disabling conditions in the world and is associated with tremendous socioeconomic and health-care consequences [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the lumbar spine is a frequently used imaging tool to characterize spine pathology and possibly identify the source of LBP [3]. Throughout the years, numerous lumbar phenotypes, such as endplate abnormalities, Modic changes, or black discs, have been identified and studied as potential pain generators to assist clinical decision-making and predicting outcomes [8,9,10,11,12]. However, there is often a discrepancy between what is noted on MRI and the clinical profile, leading to criticism regarding its utility in LBP management [13, 14]. One postulation for this mismatch is inappropriate phenotyping and its understanding. This may explain the unacceptable high incidence of failed spinal surgery and poor outcomes in LBP patients [8,9,10, 14,15,16,17,18,19].
High-intensity zones (HIZs) are one such lumbar phenotype and are characterized as high-intensity regions of the annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc noted on T2-weighted MRI (Figs. 1 and 2). HIZs were initially reported in 1992 by Aprill and Bogduk [19] as potential imaging biomarkers related to a symptomatic disc. HIZs may be a specific marker of discogenic LBP because of its correlation with pain after provocation discography [19]. Due to the invasive nature of discography, non-invasive MRI became popularized for the identification of HIZs, which expressed annular tears. However, throughout the years, contradictory studies have surfaced to debate the clinical implications of HIZs [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31]. This may be attributed to studies having no comparative symptomatic or control groups and utilizing heterogeneous populations.
In lieu of the above discrepancy of HIZs and their association with pain as well as the potential limitation of previous studies, the following study addressed a systematic review of the literature to address the association of HIZs with LBP.
Methods
Study search
A systematic review of the literature was performed in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for systematic review [32]. Two reviewers (MT, RY) independently searched the literature to identify potential articles based on pre-established exclusion and inclusion criteria. The literature search was conducted via MEDLINE, SCOPUS, Cochrane, PubMed, PubMed Central, EMBASE via Ovid, and Web of Science with the following search algorithm: “HIZ” “HIZs,” “high intensity zone” or “high intensity zones” and “low back pain” or “pain” or “lumbago” or “sciatica.” The databases were searched from their start of archiving until September 1 of 2017. The two reviewers also selected the articles and extracted the data.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Only prospective cohort studies and comparative, cross-sectional studies were included in this systematic review due to their high level of evidence. Studies involving the following procedures and methodologies were excluded: retrospective study designs, case series/reports, review articles, non-English studies, only available abstract of studies, review article/ operational protocol, history for spinal surgery or invasive discography, cadaveric study, prevalence studies with insufficient information, and only symptomatic subject studies.
Study selection
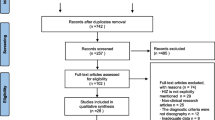
The initial search retrieved 756 retrieved articles. After removing 440 duplicates, the titles and abstracts of 316 publications were screened. We excluded 260 citations due to irrelevant studies, 2 citations due to non-English studies, 3 citations due to only abstract availability, 10 citations due to review articles, 2 citations due to case reports, 13 citations due to no control study, 12 citations due to history for spinal surgery or invasive discography, 2 citations due to cadaveric study, and 6 citations due to insufficient information on HIZ prevalence (Fig. 3). Finally, full-text assessment resulted in 6 eligible articles included in the final analysis. The definition and diagnostic criteria for HIZs varied among the studies (Table 1).
Statistical analyses
A meta-analysis was not performed due to the heterogeneity of the study design that would preclude pooling of studies. Qualitative assessment of the study parameters was performed. Lead author, study year, study design, characteristics, and outcome variables were extracted. HIZ prevalence rates of overall subjects with or without symptoms as well as per disc level, if available, were noted.
Results
Study characteristics
Of the six studies evaluated studies in this review, the year of publication ranged from 2000 to 2015. All six studies were prospective cohort or comparative studies. Table 1 shows the summary of definition of HIZs in the lumbar spine. Table 2 shows the study design, methodologies, and outcome of HIZs, such as prevalence of HIZs in symptomatic patients and controls, the highest prevalence at disc level, and association with LBP. All studies included both symptomatic patients and asymptomatic controls, with the reported mean age between 21 years to 50 years.
Prevalence and clinical implications of HIZ
Three comparative studies indicated the significant association between HIZs and LBP [12,13,14,15,16,17] (Table 3). Wang et al. [14] reported a clinical series, which included 623 patients (337 males and 286 females, age 50.1 ± 15.4 years), and 200 patients (32.1%) exhibited HIZs in at least one disc. Furthermore,33 LBP patients had multi-segmental HIZs (5.3%) with 24 LBP patients also having HIZs in adjacent discs (3.9%) and reported that 57.5% of HIZs patients were symptomatic, which was significantly higher than the percentage of patients who exhibited no HIZs (p = 0.023) by Pearson chi-square tests. Although the incidence of LBP was higher when the HIZ disc level was lower (i.e., L4/5 or L5/S1) and when multiple HIZs were identified, the association was statistically insignificant. Yang et al. [15] studied HIZs in 57 patients (28 male and 29 female) with disc protrusions undergoing lumbar discectomy. This study suggested that 61% (17/25 patients) of those with HIZs also had LBP as compared to only 32% (11/32 patients) of patients without HIZs. The median prevalence rate of HIZs is 39.1% in symptomatic patients and 21.3% in asymptomatic controls. Liu et al. [15] similarly studied LBP symptomatic patients (n = 72) and asymptomatic controls (n = 79). The prevalence of HIZs in patients with LBP and controls without LBP was 45.8% and 20.2%, respectively. After being adjusted with cerebrospinal fluid intensity, the mean signal of HIZs in patients with LBP was significantly brighter than in asymptomatic patients (57.6 ± 14.0% vs. 45.6 ± 7.2%, p < 0.001) in the quantitative measurements by Student t test.
On the other hand, three controversial results can be seen from larger scale population-based studies. One cross-sectional population-based study identified provided information regarding the prevalence of HIZs [21]. Based on this Northern Finland birth cohort of 554 subjects at 21 years of age, the prevalence of HIZs was reported as 3.2%. Takatalo et al. [21] found no association between HIZs and LBP in 554 Finnish young subjects. Similarly, Hancock et al. [24] reported that HIZs occurred in 30% of the patients with at least moderate pain of less than 6-week durations, and HIZs also occurred in 22% of the controls with no or one to two prior LBP episodes. Carragee et al. [20] suggested that the prevalence of HIZs in symptomatic subjects was 59% while the prevalence was 24% in the asymptomatic subjects. In addition, 33 (30.2%) of 109 discs were found to have a HIZ in the symptomatic group, as compared to only 13 (9.1%) of 143 discs in asymptomatic subjects. Further, this study noted that a high percentage of asymptomatic controls with degenerative disc changes were found to have HIZ, and these patients most often experienced pain with disc injection. The prevalence of HIZ was less than that of symptomatic participants, but the pain response on discography was equal in symptomatic and asymptomatic individuals.
Disc level involvement
Only two studies thoroughly assessed disc level involvement. Wang et al. [22] reported the highest prevalence of HIZs to be at L4/5 or L5/S1. Similarly, Liu et al. [23] also suggested that HIZs were more frequently seen in L4/5, followed by L5/S1.
Discussion
MRI is most commonly used in the diagnosis of patients with LBP [33]. However, there is often discrepancy and critique between the clinical profile and MRI findings [27, 33, 34]. HIZs are one of the MRI findings which may be a LBP generator. However, the association between HIZs and LBP has been under debate for the past two decades [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31]. To our knowledge, there is no systematic review of the literature which addressed the association of LBP with HIZs in both symptomatic patients and controls. The purpose of this systematic review was to assess the association between patients with HIZs and without HIZs in relation to pain. Six prospective cohort or comparative studies were included in our systematic review [20,21,22,23,24,25], whereby we analyzed the prevalence of HIZs and clinical significance of HIZs with regard to LBP. Results from this review suggest that HIZs was more prevalent in subjects with LBP than in subjects without LBP in three comparative studies. However, the other studies could not find the significant association of LBP with HIZs.
Then, the main ongoing debate regarding HIZs is whether they are symptomatic or not. Currently, there is no consensus as reports have contradictory evidence and are based on limited evidence from studies without control groups, underpowered, or heterogeneous population studies [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. Regarding some previous studies using discographic injection for HIZ, the relationship between the presence of lumbar HIZs with a concordant pain response on provocative discography was noted as a significant MRI biomarker of the diagnosis of discogenic LBP [11, 12]. On the other hand, Ricketson et al. [27] and Buirski et al. [34] were not able to demonstrate a statistically significant correlation between the presence of HIZs and pain concordant with the usual symptoms elicited during provocative discography [27, 34]. Furthermore, Carragee et al. [20] demonstrated that discographic injections provoked significant pain in approximately 70% of cases irrespective of whether patients had pain or not. This indicates that even though a discographic injection in a disc with an HIZ may produce significant pain, the disc may not be the cause of LBP [20]. Thus, provocative discographic studies are of limited use for determining symptomatology.
To better understand the clinical implications and pathogenesis of HIZs, the standard phenotype definition must be better characterized and classified. The prevalence of HIZs has been widely variable in previous studies due to difficulty of recognizing HIZs [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31]. With modern MRI technology, novel sequences allow better image acquisition and higher resolution so that HIZ can be easier identified as annular tears in any part of the annulus. Teraguchi et al. [12] suggested HIZ new phenotypes were classified based on six shape types based on the anterior and posterior intervertebral disc (anterior and posterior round type, posterior fissure type, posterior vertical type, anterior rim type, and anterior enlarged type) (Fig. 4). Therefore, a standard classification is more precise and comprehensive, and can be utilized for any future analysis regarding phenotype association and clinical relevance research.
Systematic literature reviews offer an excellent opportunity to gain an overview of challenging topics. However, they also have some limitations that need to be addressed. Most abstracts and studies were screened in this review, but a small number of relevant studies make interpretation of any data a challenge. Due to our strict inclusion criteria, there were only six studies included for review. Finally, there is always the danger of publication bias, particularly if the subject is new and perhaps controversial. Nonetheless, what our review stresses is that there is a paucity of high level of evidence studies addressing the clinical relevance of HIZs of the lumbar spine. Larger studies with in-depth statistical analyses of the HIZs in relation to disc levels and patterns therein are further needed to assess the true impact on pain development.
Conclusion
Since the original description of the HIZs in the 1990s, considerable interest has surrounded this spinal phenotype. Our systematic review has noted that HIZs of the lumbar spine may be related to pain; however, uniform consensus is not noted among studies. A more detailed investigation of the underlying pathology and topography/morphology of HIZs could be essential as well as its clustering with various spinal phenotypes can provide a unique complex phenotypic variant of this imaging finding. If found to be clinically relevant, this potential biomarker can be standardized for future clinical and research initiatives. These include correlating HIZs with symptoms, validating with cross-ethnic and cross-cohort studies, and potentially expanding its role as a pain biomarker in future initiatives. Therefore, utilizing a multimodal MRI approach to better characterize the HIZ phenotype is imperative to assist communication between study centers and aid large-scale analyses. Such information can be instrumental in predictive modeling as well as future omics studies.
Abbreviations
- HIZs:
-
High-intensity zones
- LBP:
-
Low back pain
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
References
Andersson GB. Epidemiological features of chronic low-back pain. Lancet. 1999;354:581–5.
Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2163–96.
Wong A, Karppinen J, Samartzis D. Low back pain in older adults: risk factors, management options and future directions. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2017;12:14.
Wong A, Samartzis D. Low back pain in older adults – the need for specific outcome and psychometric tools. J Pain Res. 2016;9:989–91.
Samartzis D, Ito K, Wang JC. Disc degeneration and pain. Global Spine J. 2013;3:125–6.
Karppinen J, Shen FH, Luk KDK, et al. Management of degenerative disc disease and chronic low back pain. Orthop Clin North Am. 2011;42:513–28.
Shen FH, Samartzis D, Andersson GBJ. Nonoperative management of acute and chronic low back pain. J Am Acad Ortho Surg. 2006;14:477–87.
Maatta JH, Karppinen JI, Luk KD, et al. Phenotype profiling of Modic changes of the lumbar spine and its association with other MRI phenotypes: a large-scale population-based study. Spine J. 2015;15:1933–42.
Maatta JH, Karppinen JI, Paananen M, Bow C, Keith DK, et al. Refined phenotyping of Modic changes: potential imaging biomarkers of prolonged severe low back pain and disability. Medicine. 2016;95:e3495.
Samartzis D, Borthakur A, Belfer I, et al. Novel diagnostic and therapeutic methods for intervertebral disc degeneration and low back pain. Spine J. 2015;15:1919–32.
Samartzis D, Mok F, Karppinen J, et al. Classification of Schmorl’s nodes of the lumbar spine and association with disc degeneration: a large-scale population-based MRI study. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2016;24:1753–60.
Teraguchi M, Samartzis D, Hashizume H, et al. Classification of high intensity zones of the lumbar spine and their association with other spinal MRI phenotypes: the Wakayama Spine Study. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0160111.
Boden SD, Davis DO, Dina TS, et al. Abnormal magnetic-resonance scans of the lumbar spine in asymptomatic subjects. A prospective investigation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1990;72:403–8.
Luk KD, Samartzis D. Intervertebral disc “dysgeneration”. Spine J. 2015;15:1915–8.
Mok FP, Samartzis D, Karppinen J, et al. Modic changes of the lumbar spine: prevalence, risk factors, and association with disc degeneration and low back pain in a large-scale population-based cohort. Spine J. 2016;16:32–41.
Samartzis D, Borthakur A, Belfer I, et al. Novel diagnostic and prognostic methods for disc degeneration and low back pain. Spine J. 2015;15:1919–32.
Samartzis D, Mok FP, Karppinen J, et al. Classification of Schmorl’s nodes of the lumbar spine and association with disc degeneration: a large-scale population-based MRI study. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2016;24:1753–60.
Wang HQ, Samartzis D. Clarifying the nomenclature of intervertebral disc degeneration and displacement: from bench to bedside. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7:1293–8.
Aprill C, Bogduk N. High-intensity zone: a diagnostic sign of painful lumbar disc on magnetic resonance imaging. Br J Radiol. 1992;65:361–9.
Carragee EJ, Paragioudakis SJ, Khurana S. 2000 Volvo Award winner in clinical studies: lumbar high-intensity zone and discography in subjects without low back problems. Spine. 2000;25:2987–92.
Takatalo J, Karppinen J, Niinimäki J, et al. Association of Modic changes, Schmorl’s nodes, spondylolytic defects, high-intensity zone lesions, disc herniations, and radial tears with low back symptom severity among young Finnish adults. Spine. 2012;37:1231–9.
Wang ZX, Hu YG. High-intensity zone (HIZ) of lumbar intervertebral disc on T2-weighted magnetic resonance images: spatial distribution, and correlation of distribution with low back pain (LBP). Eur Spine J. 2012;21:1311–5.
Liu C, Cai HX, Zhang JF, et al. Quantitative estimation of the high-intensity zone in the lumbar spine: comparison between the symptomatic and asymptomatic population. Spine J. 2014;14:391–6.
Hancock M, Maher C, Macaskill P, et al. MRI findings are more common in selected patients with acute low back pain than controls? Eur Spine J. 2012;21:240–6.
Yang H, Liu H, Li Z, et al. Low back pain associated with lumbar disc herniation: role of moderately degenerative disc and annulus fibrous tears. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8:1634–44.
Park KW, Song KS, Chung JY, et al. High-intensity zone on L-spine MRI: clinical relevance and association with trauma history. Asian Spine J. 2007;1:38–42.
Ricketson R, Simmons JW, Hauser BO. The prolapsed intervertebral disc. The high-intensity zone with discography correlation. Spine. 1996;21:2758–62.
Schellhas KP, Pollei SR, Gundry CR, et al. Lumbar disc high-intensity zone: correlation of magnetic resonance imaging and discography. Spine. 1996;2:79–86.
Lam KS, Carlin D, Mulholland RC. Lumbar disc high-intensity zone: the value and significance of provocative discography in the determination of the discogenic pain source. Eur Spine J. 2000;9:36–41.
Rankine JJ, Gill KP, Hutchinson CE, et al. The clinical significance of the high-intensity zone on lumbar spine magnetic resonance imaging. Spine. 1999;24:1913–9.
Peng B, Hou S, Wu W, et al. The pathogenesis and clinical significance of a high-intensity zone (HIZ) of lumbar intervertebral disc on MR imaging in the patient with discogenic low back pain. Eur Spine J. 2006;15:583–7.
Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation. BMJ. 2015;350:g7647.
Jensen MC, Brant-Zawadzki MN, Obuchowski N, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the lumbar spine in people without back pain. NEJM. 1994;331:69–73.
Buirski G, Silberstein M. The symptomatic lumbar disc in patients with low back pain: magnetic resonance imaging appearances in both a symptomatic and control population. Spine. 1993;18:1808–11.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MT performed the literature search, collected the data, interpreted the findings, and drafted the initial manuscript. RY performed the literature search, collected the data, interpreted the findings, and edited the final manuscript. JP-YC interpreted the findings and edited the final manuscript. DS conceived and designed this study, performed the literature review, interpreted the findings, assisted in drafting and editing the manuscript, supervised the study, and provided an administrative support. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This was a systematic review of the literature. Ethical approval and consent to participate is not applicable for such a study design.
Consent for publication
All authors have read and agree with the contents of this work, and have provided consent to publish.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Teraguchi, M., Yim, R., Cheung, J.PY. et al. The association of high-intensity zones on MRI and low back pain: a systematic review. Scoliosis 13, 22 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13013-018-0168-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13013-018-0168-9