Abstract
Background
Obtaining instantaneous gas exchanges data is fundamental to gain information on photosynthesis. Leaf level data are reliable, but their scaling up to canopy scale is difficult as they are acquired in standard and/or controlled conditions, while natural environments are extremely dynamic. Responses to dynamic environmental conditions need to be considered, as measurements at steady state and their related models may overestimate total carbon (C) plant uptake.
Results
In this paper, we describe an automatic, low-cost measuring system composed of 12 open chambers (60 × 60 × 150 cm; around 400 euros per chamber) able to measure instantaneous CO2 and H2O gas exchanges, as well as environmental parameters, at canopy level. We tested the system’s performance by simulating different CO2 uptake and respiration levels using a tube filled with soda lime or pure CO2, respectively, and quantified its response time and measurement accuracy. We have been also able to evaluate the delayed response due to the dimension of the chambers, proposing a method to correct the data by taking into account the response time (\({t}_{0}\)) and the residence time (τ). Finally, we tested the system by growing a commercial soybean variety in fluctuating and non-fluctuating light, showing the system to be fast enough to capture fast dynamic conditions. At the end of the experiment, we compared cumulative fluxes with total plant dry biomass.
Conclusions
The system slightly over-estimated (+ 7.6%) the total C uptake, even though not significantly, confirming its ability in measuring the overall CO2 fluxes at canopy scale. Furthermore, the system resulted to be accurate and stable, allowing to estimate the response time and to determine steady state fluxes from unsteady state measured values. Thanks to the flexibility in the software and to the dimensions of the chambers, even if only tested in dynamic light conditions, the system is thought to be used for several applications and with different plant canopies by mimicking different environmental conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Despite being the most important biological process on Earth, photosynthesis still presents mechanisms that are not deeply understood and it is considered a matter of priority interest for new pioneering research fields [5, 45]. By converting solar energy into chemical energy, plants accumulate biomass by which several human activities depend on, as food, fodder, litter and fuelwood [12, 49]. Due to the rise in food demands [2, 44] and, more general, in plant-derived products, the newest research is aiming to target those processes in photosynthesis that would improve the overall crop yield [22, 23, 33]. This can be achieved in laboratories and tested in green houses where, however, it is difficult to mimic real field conditions. In fact, in natural environments, plants are affected simultaneously by several abiotic conditions (i.e. changes in temperature, light intensity, humidity) and biological interactions, which could translate into uncertainties in the experimental results [4, 20].
To facilitate the translation of information from the laboratory to the field, it is also necessary to mimic natural environmental conditions within growth chambers [15]. For example, simulating dynamic light conditions is necessary to retrieve canopy scale data that would reflect environmental variability [4]. In fact, whereas most of the past experiments and models considered photosynthesis at the steady state [10, 11, 17, 43, 48, 53], the importance of considering some photosynthetic processes in their transient states has been recognized [9, 14, 31, 46, 47]. Plants are exposed to fluctuating irradiance due to the movements of clouds, the effect of wind and the gaps within the canopy [35, 39]. How plants respond to these dynamic conditions affects carbon dioxide (CO2) uptake and final biomass yield. Plants can adjust to the dynamic environmental conditions by regulating the stomata [8, 26, 37], by moving their chloroplasts within the leaves or by moving their leaves within the canopy [16], by regulating photochemical properties [14], by activating Calvin Cycle enzymes and by controlling photo-protective processes [41]. Therefore, continuous measurements of gas exchanges are necessary to unravel the effects of dynamic environmental conditions on plants.
Gas exchange methods at leaf level are usually based on a leaf cuvette connected to an Infrared Gas Analyser (IRGA) measuring the difference among external and internal CO2 concentration (closed systems) or between the inlet and the outlet air (open systems). These methods allow the estimation of several physiological parameters such as, for example, net photosynthesis and stomatal conductance [21, 28]. When gas exchange measurements are combined with chlorophyll fluorescence, several other parameters related to photochemistry and the primary reactions of photosynthesis (i.e. light-harvesting and energy dissipation) can be retrieved [6, 27]. Leaf level data are reliable and repeatable, but these data can be hardly scaled up at whole plant or whole canopy scale, in particular in dynamic conditions, unless using cross-scale modelling [52].
Growth chamber systems allow direct CO2 gas exchange measurements at plant or small canopy scales. In open chambers, net carbon (C) exchange is estimated by measuring the inlet flux and the difference between inlet and outlet CO2 concentrations; in closed chambers, the change with time in CO2 concentration within the chamber headspace is measured and the assimilation rate is then calculated [12, 51]. While open chambers can measure gas exchange for long time periods, closed chambers can be used only for short time periods in order to avoid increase in air temperature or water condensation [24]. Several growth chamber systems have been described in the literature [3, 12, 30], but some of them showed low ability to control environmental conditions [29, 42], are not adapted to long-term continuous measurements [3] or are rather expensive (see [54] for a comprehensive review of space growth chambers).
Besides of the growth chamber systems, other systems have been developed in the last decades such as phytotrones [19] and the ‘exotic’ Biosphere 2 Laboratory [38], with the idea of allowing complete control of environmental variables [19] and the scaling up of the measured values from the laboratory to model ecosystems [32]. Nevertheless, even if relevant tests have been performed, the conditions found within these systems are often dissimilar to natural conditions that it is, again, difficult to relate these results to field data [20].
On the other hand, canopy gas exchange measurements can be continuously measured in the field using micro-meteorological techniques, such as eddy covariance [7, 25, 50]. These systems have been demonstrated to be reliable even though can be used only in specific site conditions (i.e. flat terrain, large footprint areas, atmospheric stability,[1]). Moreover, as several abiotic factors can simultaneously change in the field (i.e. light, temperature, humidity, etc.), it is then difficult to isolate the effects of the fluctuations of each single factor on instantaneous C exchanges at such a scale. Therefore, it is relevant to design growth chamber for continuous gas exchange measurements able to control different environmental factors and to simulate natural dynamics at canopy scale.
In this study we describe a novel automatic, low-cost system based on 12 open chambers able to measure instantaneous CO2 and H2O gas exchange and environmental conditions at canopy level. The system is flexible and allows to mimic different light conditions, either static or dynamic, allowing a good characterization of canopy photosynthesis comparable to field data. To our knowledge, few other growth chamber systems have this ability to mimic natural environmental conditions and have been described systematically including prices of the components, allowing a user-friendly reproduction of the system [34].
A new low-cost and scalable whole plant gas exchange system
Description of the system
The system (DYNAMISM, acronym for DYNAMIc photoSynthesis Measurements) we describe here is composed of twelve 0.54 m3 commercial growth chambers (60 × 60 × 150 cm; Secret Jardin, model Dark Dryer). The inlet ambient air is sucked into each chamber by a Blauberg inline mixed flow fan (diameter: 10 cm; flowrate: 102 m3 h−1) from a 4.5 m3 buffer chamber (150 × 150 × 200 cm; Secret Jardin, model Dark Street DS150). The buffer is needed to keep inlet CO2 and H2O concentrations as stable as possible during measurements and to control air temperature and humidity inside the growth chambers using an air conditioner. The inlet flow rate is measured at each chamber using a miniature air flow transmitter (E + E Elektronik, model EE671) placed before the inline fan and can be easily regulated by opening/closing the holes at the top and at the side of the chamber. The overpressure created inside each chamber by the flow fan avoids possible CO2 leakage or contamination during the measurements. Each air flow transmitter was calibrated against a reference mass flow meter before setting up the system (E + E Elektronik, model EE776; Additional file 1: Figure S1).
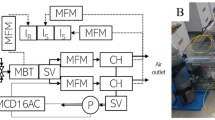
Air temperature inside each chamber is measured using a thermistor (Measurement Specialties, Inc., model 10K3A1 Series 1) placed above the LEDs, while inlet air pressure is measured at the inlet of the main pipeline using an integrated pressure sensor (Freescale Semiconductor, Inc., model MPX4115A). A schematic representation of the system is reported in Fig. 1: the main pipeline starting from the buffer is made up of pipes with a diameter of 20 cm; chamber connecting pipes are 10 cm in diameter; the pipes connecting the buffer to outside the lab (outdoor) are 30 cm in diameter.
A Schematic representation of DYNAMISM. The 12 chambers (not all represented here) are connected to the bigger chamber that acts as a buffer. The buffer is itself connected to outdoor and has an air conditioning inside to keep the temperature and humidity more stable, and a pressure sensor. The air flows from the buffer to the chambers. Air is sampled within each chamber and analysed by the Licor-7000 (IRGA). Each chamber is equipped with a LED system, a mass flow meter to measure the inlet flowrate, a solar bar, a thermistor and an aquarium pump placed at the top chamber. Chamber sampling and data acquisition is made through a CR1000X datalogger which itself controls a multiplexer and a relay controller (SDM CD16-AC). B Example of the control of the CR1000X output variables through the RTMC software. In this case, in the main screen are shown the CO2 and H2O changes in real-time in the sampled chamber, as well as other environmental parameters. Then in each chamber the desired parameters can be monitored, here we have set an alarm for chamber temperatures higher than 40° and a slider input to change incident PPFD
Instantaneous net canopy CO2 flux (A; µmol CO2 m−2 s−1) and instantaneous evapotranspiration (E; mol H2O m−2 s−1) are measured as differences in CO2 (μmol CO2 mol−1) and H2O (mmol H2O mol−1), respectively, in the air stream flowing through each chamber using a LI-7000 gas analyzer (Licor, USA) in differential mode. Inlet CO2 and H2O concentrations (i.e. concentration inside the buffer) are measured by pumping the air through a LI-840 gas analyzer and then to LI-7000 Cell A (reference). The outlet CO2 and H2O concentrations (i.e. concentration at the top of each chamber) are measured by pumping the air to the LI-7000 Cell B (sample) using an aquarium pump placed inside each chamber (Hailea, model ACO9602; flow rate: 7.2 l min−1). Reference and sample CO2 and H2O concentrations, air temperature and air pressure are recorded by a datalogger (CR1000X, Campbell Scientific, USA) by parsing the digital output of the LI-7000.
The sequential sampling of air inside the chambers is electronically controlled by the CR1000X through a 16 channel AC/DC controller (SDM CD16-AC, Campbell Scientific, USA), which stimulates each of the twelve 24 V solenoid valves connected to the aquarium pumps placed inside each chamber. Sampling frequency among the chambers, as well as sampling duration for each chamber, can be set by the user. A thirteen valve was connected to the main inlet within the buffer chamber allowing a periodic matching between Cell A and Cell B of the LI-7000. Such a matching is recommended in order to compensate for any differences in the two optical paths besides concentration differences. Outlet CO2 and H2O concentrations are thus corrected in post-processing and fluxes recomputed.
Each chamber is equipped with a 60 × 60 cm light system made up of 17 separate LED strips (Samsung SMD5630 “H-POWER", 185 W, 140 LED m−1, CRI90, Natural White, 4000 K). The light spectrum of the LEDs was measured using a fluorescence box (FloX, JB Hyperspectral Devices, Germany), and it well simulates the solar spectrum between 400 and 700 nm (Fig. 2). LEDs can be moved up and down inside the chambers depending on canopy height, and light intensity within each chamber is independently controlled by the CR1000X through a Modbus to voltage output converter (4E + Embedded Solutions, model DAT3028). The dimmer regulates the voltage signal (0–10 V) which determines the photosynthetic photon flux density (maximum PPFD = 1876 μmol m−2 s−1 at 10 cm distance when the number of LED strips per chamber is maximized).
The CR1000X can simulate daily solar radiation profile after the user sets the latitude and the longitude by computing solar elevation angle and knowing maximum PPFD or can simulate a fixed daily profile after the user chooses a fixed day of the year. Moreover, the user can simulate periodic light fluctuations around the hourly value by deciding the fluctuating range and the fluctuation period.
Transmitted radiation is measured using solar bars placed horizontally at the bottom of the canopy. Each bar is made of eight photodiodes in parallel (model S1087-01, Hamamatsu Photonics, Japan) with a 100 Ω resistance and was calibrated against a reference quantum sensor (Li-190R, Licor, USA) before setting up the system.
Finally, in Table 1 we report the list of all the major parts of the system, their technical specification and prices. The overall system cost is 5,000 euro (only 417 euro per chamber), without considering the reference sensors for calibrations, and the analyzers (LI-840 and LI-7000). One of the strengths of DYNAMISM is that any number of chambers is possible in the multiplexer mode, thus allowing to have a high number of replicates with a limited cost; nevertheless, if only a multiplexer is used, it will go in a repeated cycle.
Gas exchange calculations
E (in mol H2O m−2 s−1) and A (in µmol CO2 m−2 s−1) are computed according to the following equations:
where \({H}_{2}{O}_{in}\) and \({{CO}_{2}}_{in}\) are the H2O (in mmol H2O mol−1) and CO2 (in μmol CO2 mol−1) concentrations within the buffer chamber (inlet) and \({H}_{2}{O}_{chamber}\) and \({{CO}_{2}}_{chamber}\) are the concentrations in each chamber; \({air}_{flow}\) is the air flux entering the chamber (mol s−1) and S is the chamber area (0.36 m2). We adopted the micro-meteorological convention to indicate CO2 uptake (net photosynthesis, negative value) and release (respiration, positive value). Air flow from the miniature air flow transmitter is converted from m s−1 (flow) to mol s−1 (airflow) according to the equation:
where Stube is the tube area (0.10 × 0.10 m2), P is the inlet air pressure (Pa) and Tchamber is the air temperature inside the chamber (°C) and R is the universal constant of gases (8.3144598 m3 Pa K−1 mol−1).
Performance and accuracy of DYNAMISM
Before testing the system with a real plant canopy, we simulated six different photosynthesis levels (Asim; μmol CO2 m−2 s−1) at five different air flux velocities (from 0.73 to 2.73 m s−1) in order to assess its performance and accuracy. We did this by using a tube filled with soda lime connected to a pump (Hailea ACO9602) and placed inside one of the chambers. By doing so we were directly scrubbing the air (i.e. removing CO2) within the chamber and we were able to calculate the exact flux of simulated photosynthesis according to the equation:
where scrubflux is the scrub’s pump speed (l s−1) measured using a flowmeter (Sensirion SFM4100), P is the air pressure (constant at 101,300 Pa), T is air temperature (°C) and R is the universal constant of gases (8.3144598 m3 Pa K−1 mol−1). The pump was turned on for 10 min at a first level of scrub’s pump speed (0.02 l s−1), then the scrub’s pump speed was increased at the second target velocity for another 10 min, and so on for all the six levels of simulated photosynthesis. When the maximum level of scrub flux (pump speed = 0.2 l s−1) was reached, the same procedure was applied from the highest value to the lowest. Final measured net CO2 fluxes were calculated from the system’s acquired data for the last 60 s of each step according to Eq. 2. When comparing all the five pump flux velocities, we expect that the steady state is reached faster at higher fluxes without affecting the steady state itself. In order to compare measured values at different speed of the scrub pump, we normalized the data by multiplying the ΔCO2 values for \(Sx/\left({S}_{0}-Sx\right)\) where \(Sx\) is the CO2 scrubbed flux and S0 is the CO2 flux at time 0; then we further rescaled the data through a min–max normalization. As expected, the results of these tests clearly show that higher the air flux, faster the steady state is reached (Additional file 1: Figure S2).
We also simulated five respiration levels (Rsim) by injecting pure CO2 inside the chambers at two different air flux velocities (0.71 and 1.71 m s−1), following the same procedure (steps) described above for photosynthesis, using a gas mass flow controller for low flow rates (Bronkhorst, model F-201CV-100_RAD-00-Z). Rsim was computed according to the following equation:
where CO2injected is the CO2 injected flux (ml CO2 s−1), P is air pressure (101,300 Pa), S is chamber area (0.36 m2), Tchamber is chamber temperature (°C) and R is the universal constant of gases (8.3144598 m3 Pa K−1 mol−1).
The accuracy of DYNAMISM was finally assessed using a simple linear regression relating the measured values of CO2 after scrubbing the air or injecting pure CO2 with the values simulated with Eqs. 4 and 5. The system slightly overestimated CO2 fluxes (+ 7%, not significant) over the range from − 10 to 10 μmol CO2 m−2 s−1 (slope: 1.06; intercept: -0.85; R2 = 0.98; p < 0.001; Fig. 3).
Performance evaluation through a mass balance model
To further assess DYNAMISM accuracy, we performed a comparison among the measured ΔCO2 values (\({{CO}_{2}}_{in}\) – \({{CO}_{2}}_{chamber}\)), obtained after scrubbing the air or injecting pure CO2, with a physical model based on a mass balance approach: the change in CO2 concentration with time inside the chamber depends on the CO2 entering the chamber from the buffer (\({{CO}_{2}}_{in}\) in ppm) at a certain flux (F in mol s−1) minus the CO2 consumed by photosynthesis or released by respiration (\(Sx\) in µmol CO2 s−1) and the internal concentration within the chamber (\({{CO}_{2}}_{chamber}\) in ppm). Therefore, the physical model can be described by the following differential equation:
By integrating this differential equation and by assuming perfect mixing within the chamber, the following equation is obtained:
where S0 is the CO2 flux at time 0, V is the chamber volume (19.3 mol) and \({t}_{0}\) is the delay due to chamber dimension (in seconds).
Solving Eq. 7 for \(Sx\) results in:
In order to understand the error associated to \(Sx\) measurements due to errors in the measured variables (\(F\),\({S}_{0}\), \({t}_{0}\) and \({\Delta CO}_{2}\)), we made a sensitivity analysis. The total error was then computed according to Jordan and Sewell [13] by considering the partial derivatives of \(Sx\) per each measured variable:
where \(\stackrel{-}{F}\), \(\overline{{S_{0} }} ,~\overline{{\Delta CO_{2} }}\) and \(\stackrel{-}{{t}_{0}}\) indicate the range in parameters for which the partial derivative is computed being \(\stackrel{-}{F}=\left[0.2-0.6\right]\) mol s−1,\(\stackrel{-}{{S}_{0}}=[0-5]\) µmol CO2 s−1, \(\stackrel{-}{{t}_{0}}=\left[0-100\right]\) s \(,~\overline{{\Delta CO_{2} }} = \left[ {0 - 10} \right]\) ppm.
In Fig. 4, we reported the total error (T) and the errors related to F and \(\Delta {CO}_{2}\) only, as those due to \({S}_{0}\) and \({t}_{0}\) were smaller than 1% and thus negligible. According to our sensitivity analysis, the major source of error in the measurements of CO2 fluxes with DYNAMISM is related to F, especially at the highest air flux velocity (0.6 mol s−1), underlying the need to use an accurate flowmeter to assess it.
Total percentage error (T) and percentage errors due to changes in air flux velocity (F) and in \(\Delta {\mathrm{C}\mathrm{O}}_{2}\) (\(\Delta\)) calculated from the partial derivation of Eq. 8. The parameter changes (x axis) are shown as normalized values (i.e. percentage change [0–100]) but the actual ranges of parameters are: F = [0.2: 0.6] mol s−1 and \(\Delta {\mathrm{C}\mathrm{O}}_{2}\)=[0: − 10] ppm. The boxplots show the aggregated values for all 12 chambers
Correct for delays
The model described in Eqs. 7 and 8 allows to mathematically compute the delay of the measuring system (\({t}_{0}\)) due to the lengths of the tubes and the volume of the chamber, and the residence time (τ, unitless), which applies in case of no perfect mixing. In fact, in such last case, Eqs. 7 and 8 need to be changed by adding τ to the exponent value, which reads as \(\tau (t-{t}_{0})\). By first fitting the \(\Delta {CO}_{2}\) calculated according to Eq. 7 with the τ correction to the measured data and then using the fitted parameters values to compute \(Sx\) based on Eq. 8 (i.e. perfect mixing, no τ correction), it is possible to estimate τ and t0. If this procedure is repeated at least once per day in a chamber by scrubbing/injecting CO2, it is possible to have an estimate of both \(\tau\) and \({t}_{0}\) and correct the measured data for the delays (Fig. 5). In fact, as the structure of the canopy itself changes over time affecting the mixing within the chamber, this procedure allows having a daily correction of the data taking into account the delays.
Estimating steady state \(\Delta \boldsymbol{C}{\boldsymbol{O}}_{2}\)
The described modelling framework also allows to determine steady state fluxes from unsteady state data by fitting Eq. 7 with the τ correction to \(\Delta {CO}_{2}\) measured values. To test this, we grew a soybean variety inside the chambers with fluctuating light conditions and measured the changing canopy photosynthetic rates. As the light was fluctuating (with a period of 2 min) it determined a continuous change in the \(\Delta {CO}_{2}\) due to canopy carbon assimilation (i.e. photosynthesis). Since fluctuations were very frequent, the measured values never reached steady state (Fig. 6A). The fitting procedure though allowed to have an estimate of the steady state values by fitting unsteady state \(\Delta {CO}_{2}\) values (Fig. 6B), showing that steady state is reached only after about 300 s (as also evident from Fig. 5).
Quantifying whole plant gas-exchange under fluctuating conditions
To test the accuracy of DYNAMISM in real conditions, we used a commercial soybean variety (Eiko, Asgrow, USA). Plants were sown in 96 pots (13 × 13 × 18 cm) with siliceous sand in order to have an inert substrate and to zeroing heterotrophic respiration (Rh). We used six chambers for the experiment, and we placed 16 pots chamber−1.
In three chambers, the LED system was set to simulate a fixed daily profile (June 21st) in Udine, Italy (latitude: 46.07 N; longitude: 13.23 E) with a maximum PPFD of 1000 µmol m−2 s−1 at noon (non-fluctuating light treatment, NF). In the other three chambers (fluctuating light treatment, F), light was fluctuated ± 50% with a period of 120 s around the hourly value measured in NF. By doing this, plants grown either in fluctuating or non-fluctuating light received the same total light intensity throughout the day. According to the light curve reported by Sakowska et al. [40], these fluctuations at midday (500–1500 µmol m−2 s−1) fall within the saturated range of the curve, therefore the highest values of light are saturating. It is than predictable that the cumulative average value (1000 µmol m−2 s−1) would entail a higher C assimilation than the cumulative fluctuating values. This though is not the case when the oscillations of light fall into the linear range of the light curve, as in the first (and last) hours of the day. In this case, we expect the average value of light to be translated into a similar accumulation of CO2.
LEDs were manually moved up inside the chambers as canopy grew thus to be at a constant distance of 13 cm above the plants throughout the experiment.
Each chamber was sampled for 290 s and A was calculated as average between 110 and 290 s thus to not consider the tube’s purging after chamber switch (t0 = 110 s). The matching procedure with the thirteenth valve was done every hour in order to compute the difference in CO2 and H2O concentration among the cell A and B of the LI-7000, thus correcting the data based on this value. Measurements were run for four weeks during which plants were regularly watered with the addition of a Hoagland solution twice per week (Table 2).
At the end of the experiment, we harvested four plants per chamber. Leaf area was measured using a LI-3000 (Licor, USA), stem and leaves were separated from roots and these lasts were gently washed to remove sand. Leaves, stems and roots were then dried at 70 °C for 48 h and then weighted. Because of the inert substrate used in the pots (no heterotrophic respiration, Rh), the measured CO2 flux corresponds to net primary production (NPP = A) instead of net ecosystem production (NEP = NPP – Rh), allowing a direct comparison between the cumulative A flux (gC m−2) at the end of the experiment and the total produced biomass (i.e. total dry weight; g m−2) by assuming a C content of 46.8% [40].
Considering the response time due to the dimension of the chambers (t0 = 110 s) the system was clearly able to detect instantaneous changes in A related to light fluctuations, while it measured stable A in non-fluctuating light conditions (Fig. 7).
Soybean CO2 fluxes in non-fluctuating (above) and fluctuating light conditions (below). Data are instantaneous measurements during one session (25th July at 10:00 am). Red lines represent photoflux density (PPFD), dots represent CO2 fluxes. CO2 fluxes data are corrected for the delayed response (t0 = 110 s). The lines represent 4 s averaged values. More negative values of A at higher PPFD values corresponds to higher photosynthesis (micro-meteorological convention)
On an hourly basis, the system responded as expected: from a positive CO2 flux during night (respiration) to a maximum net uptake (negative flux) at midday with a small variability among chambers (Fig. 8A). At the end of the experiment, cumulative fluxes were not significantly different from the total plant dry biomass measured at harvest (Fig. 8B), confirming the applicability of DYNAMISM to measure canopy CO2 fluxes.
A Daily course of net primary production (NPP) measured five weeks after sowing. Closed and open symbols are fluctuating (F) and non-fluctuating (NF) light conditions, respectively. In the inner panel, the daily course of PPFD is reported. Negative NPP values denote C uptake following the micro-meteorological convention. B Total final biomass derived from fluxes and from plant dry weights at harvest for the two considered treatments. Any significant difference was found at harvest. Vertical bars are standard error (n = 3)
Discussion and conclusions
Several approaches have been used in the literature to obtain reliable measurements of CO2 assimilation. Leaf level data are mainly reliable but the scaling to plant or canopy scale is rather difficult. On the other hand, canopy scale methods exist and can capture CO2 exchange dynamics at bigger scales but suffer from several weaknesses [1, 36]. Therefore, to overcome these issues, many growth chamber systems have been developed in the last decades, but most of them lack the ability to measure dynamic environmental conditions, such as those generally occurring in the field, and/or are extremely expensive. We demonstrated that the main strength of DYNAMISM relies on its accuracy and stability (Figs. 3, 4 and 5), on the possibility to accurately estimate the response time and to correct for the intrinsic delays of the system (Fig. 6) and to determine steady state fluxes from unsteady state measured values (Fig. 7). Thus, it is able to efficiently capture the effect of fast fluctuating light on instantaneous CO2 gas exchanges (Fig. 8).
Finally, DYNAMISM can be used for several applications: different plant canopies can be monitored thanks to the flexibility in the software and to the dimension of the chambers, allowing to answer relevant biological questions.
Even though we focused our attention in this paper on light fluctuations, DYNAMISM could be used in the future also to simulate other dynamic environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity and CO2 concentration with some simple upgrades and at a limited cost. Thus, it can be potentially used to induce abiotic stresses, by simulating, for example, drought conditions, high light conditions (inducing photo-inhibition) and high environmental CO2 levels. Moreover, as a future development, we think to couple DYNAMISM with real-time fluorescence measurements to investigate photochemistry and the primary reactions of photosynthesis in dynamic environments as well as to use it for photosynthesis phenotyping [18].
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Acosta M, Juszczak R, Chojnicki B, Pavelka M, Havránková K, Lesny J, Krupková L, Urbaniak M, Machačová K, Olejnik J. CO2 fluxes from different vegetation communities on a Peatland ecosystem. Wetlands. 2017;37:423–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-017-0878-4.
Alexandratos N, Bruinsma J. World Agriculture Towards 2030/2050: The 2012 Revision Ch. 4, ESA/12-03. FAO; 2012.
Andriolo JL, Le Bot J, Gary C, Sappe G, Orlando P, Brunel B, Sarrouy C. An experimental set-up to study carbon, water, and nitrate uptake rates by hydroponically grown plants. J Plant Nutr. 1996;19:1441–62. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904169609365211.
Annunziata MG, Apelt F, Carillo P, Krause U, Feil R, Mengin V, Lauxmann MA, Köhl K, Nikoloski Z, Stitt M, Lunn JE. Getting back to nature: a reality check for experiments in controlled environments. J Exp Bot. 2017;68:4463–77. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erx220.
Bahadur B, Venkat M, Leela R, Diversity P. Plant biology and biotechnology. Plant Biol Biotechnol. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2286-6.
Baker NR. Chlorophyll fluorescence: a probe of photosynthesis in vivo. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2008;59:89–113. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092759.
Baldocchi DD. Assessing the eddy covariance technique for evaluating carbon dioxide exchange rates of ecosystems: Past, present and future. Glob Chang Biol. 2003;9:479–92. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2486.2003.00629.x.
Buckley TN. Modeling stomatal conductance. Plant Physiol. 2017;174:572–82. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.01772.
Chazdon RL, Pearcy RW. Photosynthetic responses to light variation in rainforest species. Oecologia. 1986;69:524–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00410358.
Farquhar GDS, von Caemmerer JAB. A biochemical model of photosynthetic CO2 assimilation in leaves of C 3 species. Planta. 1980;90:78–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386231.
Farquhar GD, Caemmerer SV, Berry JA. Models of Photosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 2001;125:42–5. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.125.1.42.
Hall DO. Photosynthesis and production in a changing environment—a field and laboratory manual. Berlin: Springer Science & Business Media; 2013.
Jordan KA, Sewell JI. Analysis of the problem. In: Henry ZA, editor. Instrumentation and measurement for environmental sciences. American Society of Agricultural Engineers; 1975.
Kaiser E, Matsubara S, Harbinson J, Heuvelink E, Marcelis LFM. Acclimation of photosynthesis to lightflecks in tomato leaves: interaction with progressive shading in a growing canopy. Physiol Plant. 2018;162:506–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12668.
Kaiser E, Morales A, Harbinson J. Fluctuating light takes crop photosynthesis on a rollercoaster ride. Plant Physiol. 2018;176:977–89. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.01250.
Kaiser E, Morales A, Harbinson J, Heuvelink E, Kromdijk J, Marcelis LFM. Dynamic photosynthesis in different environmental conditions. J Exp Bot. 2014;66:2415–26. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru406.
Kannan K, Wang Y, Lang M, Challa GS, Long SP, Marshall-Colon A. Combining gene network, metabolic and leaf-level models shows means to future-proof soybean photosynthesis under rising CO2. In Silico Plants. 2019;1:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1093/insilicoplants/diz008.
Keller B, Vass I, Matsubara S, Paul K, Jedmowski C, Pieruschka R, Nedbal L, Rascher U, Muller O. Maximum fluorescence and electron transport kinetics determined by light-induced fluorescence transients (LIFT) for photosynthesis phenotyping. Photosynth Res. 2019;140:221–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-018-0594-9.
Kingsland SE. Frits went’s atomic age greenhouse: the changing labscape on the lab-field border. J Hist Biol. 2009. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10739-009-9179-y.
Köhl KI, Laitinen RAE. From the greenhouse to the real world—Arabidopsis field trials and applications. Mol Mech Plant Adapt. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118860526.ch9.
Kölling K, George GM, Künzli R, Flütsch P, Zeeman SC. A whole-plant chamber system for parallel gas exchange measurements of Arabidopsis and other herbaceous species. Plant Methods. 2015;11:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-015-0089-z.
Kromdijk J, Głowacka K, Leonelli L, Gabilly ST, Iwai M, Niyogi KK, Long SP. Improving photosynthesis and crop productivity by accelerating recovery from photoprotection. Science (80-). 2016;354:857–61. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aai8878.
Long SP, Zhu XG, Naidu SL, Ort DR. Can improvement in photosynthesis increase crop yields? Plant Cell Environ. 2006;29:315–30. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2005.01493.x.
Luo C, Wang Z, Sauer TJ, Helmers MJ, Horton R. Portable canopy chamber measurements of evapotranspiration in corn, soybean, and reconstructed prairie. Agric Water Manag. 2018;198:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2017.11.024.
Matese A, Alberti G, Gioli B, Toscano P, Vaccari FP, Zaldei A. Compact_Eddy: a compact, low consumption remotely controlled eddy covariance logging system. Comput Electron Agric. 2008;64:343–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2008.07.002.
Matthews JSA, Vialet-Chabrand S, Lawson T. Acclimation to fluctuating light impacts the rapidity of response and diurnal rhythm of stomatal conductance. Plant Physiol. 2018;176:1939–51. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.01809.
Maxwell K, Johnson GN. Chlorophyll fluorescence—a practical guide. J Exp Bot. 2000;51:659–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsci.2018.02.001.
Millan-Almaraz JR, Torres-Pacheco I, Duarte-Galvan C, Guevara-Gonzalez RG, Contreras-Medina LM, de Romero-Troncoso RJ, Rivera-Guillen JR. FPGA-based wireless smart sensor for real-time photosynthesis monitoring. Comput Electron Agric. 2013;95:58–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2013.04.009.
Miller DP, Howell GS, Flore JA. A whole-plant, open, gas-exchange system for measuring net photosynthesis of potted woody plants. HortScience. 1996;31:944–6. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.31.6.944.
Mitchell CA. Measurement of photosynthetic gas exchange in controlled environments. HortScience. 1992;27:764–7. https://doi.org/10.21273/hortsci.27.7.764.
Morales A, Kaiser E, Yin X, Harbinson J, Molenaar J, Driever SM, Struik PC. Dynamic modelling of limitations on improving leaf CO2 assimilation under fluctuating irradiance. Plant Cell Environ. 2018;41:589–604. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.13119.
Nichol CJ, Pieruschka R, Takayama K, Frster B, Kolber Z, Rascher U, Grace J, Robinson SA, Pogson B, Osmond B. Canopy conundrums: Building on the Biosphere 2 experience to scale measurements of inner and outer canopy photoprotection from the leaf to the landscape. Funct Plant Biol. 2012;39:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP11255.
Ort DR, Merchant SS, Alric J, Barkan A, Blankenship RE, Bock R, Croce R, Hanson MR, Hibberd JM, Long SP, Moore TA, Moroney J, Niyogi KK, Parry MAJ, Peralta-Yahya PP, Prince RC, Redding KE, Spalding MH, van Wijk KJ, Vermaas WFJ, Von Caemmerer S, Weber APM, Yeates TO, Yuan JS, Zhu XG. Redesigning photosynthesis to sustainably meet global food and bioenergy demand. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2015;112:8529–36. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1424031112.
Padmanabha M, Streif S. Design and validation of a low cost programmable controlled environment for study and production of plants, mushroom, and insect larvae. Appl Sci. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9235166.
Pearcy RW. Sunflecks and photosynthesis in plant canopies. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 1990;41(1):421–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-0032(53)91189-2.
Pinto F, Damm A, Schickling A, Panigada C, Cogliati S, Müller-Linow M, Balvora A, Rascher U. Sun-induced chlorophyll fluorescence from high-resolution imaging spectroscopy data to quantify spatio-temporal patterns of photosynthetic function in crop canopies. Plant Cell Environ. 2016;39:1500–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12710.
Raines CA, Vialet-Chabrand S, Matthews JSA, Simkin AJ, Lawson T. Importance of fluctuations in light on plant photosynthetic acclimation. Plant Physiol. 2017;173:2163–79. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.01767.
Rascher U, Bobich EG, Lin GH, Walter A, Morris T, Naumann M, Nichol CJ, Pierce D, Bil K, Kudeyarov V, Berry JA. Functional diversity of photosynthesis during drought in a model tropical rainforest—the contributions of leaf area, photosynthetic electron transport and stomatal conductance to reduction in net ecosystem carbon exchange. Plant, Cell Environ. 2004;27:1239–56. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2004.01231.x.
Retkute R, Preston SP, Murchie EH, Johnson GN, Burgess AJ, Smith-Unna SE, Jensen OE. Exploiting heterogeneous environments: does photosynthetic acclimation optimize carbon gain in fluctuating light? J Exp Bot. 2015;66(9):2437–47. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv055.
Sakowska K, Alberti G, Genesio L, Peressotti A, Delle Vedove G, Gianelle D, Miglietta F. Leaf and canopy photosynthesis of a chlorophyll deficient soybean mutant. Plant Cell Environ. 2018;41(6):1427–37. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.13180.
Slattery RA, Vanloocke A, Bernacchi CJ, Zhu XG, Ort DR. Photosynthesis, light use efficiency, and yield of reduced-chlorophyll soybean mutants in field conditions. Front Plant Sci. 2017;8:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00549.
Smith JP, Edwards EJ, Walker AR, Gouot JC, Barril C, Holzapfel BP. A whole canopy gas exchange system for the targeted manipulation of grapevine source-sink relations using sub-ambient CO2. BMC Plant Biol. 2019;19:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-2152-9.
Song Q, Zhu X-G (2012) A model of canopy photosynthesis in rice that combines sub-models of 3D plant architecture, radiation transfer, leaf energy balance and C3 photosynthesis. In: Plant growth modeling, simulation, visualization and applications, vol. 4. IEEE. p. 360–6.
South PF, Cavanagh AP, Liu HW, Ort DR. Synthetic glycolate metabolism pathways stimulate crop growth and productivity in the field. Science. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aat9077.
Tanaka A, Makino A. Photosynthetic research in plant science. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009;50:681–3. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcp040.
Taylor SH, Long SP. Slow induction of photosynthesis on shade to sun transitions in wheat may cost at least 21% of productivity. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2016.0543.
Tomimatsu H, Tang Y. Effects of high CO2 levels on dynamic photosynthesis: carbon gain, mechanisms, and environmental interactions. J Plant Res. 2016;129:365–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-016-0817-0.
Van Der Tol C, Verhoef W, Timmermans J, Verhoef A, Su Z. An integrated model of soil-canopy spectral radiances, photosynthesis, fluorescence, temperature and energy balance. Biogeosciences. 2009;6:3109–29. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-6-3109-2009.
Vitousek PM, Ehrlich PR, Ehrlich AH, Matson PA. Appropriation of the products of photosynthesis. Bioscience. 1986;36:368–73.
Wang Z, Luo C, Sauer TJ, Helmers MJ, Xu L, Horton R. Canopy chamber measurements of carbon dioxide fluxes in corn and soybean fields. Vadose Zo J. 2018. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2018.07.0130.
Wheeler RM. Gas-exchange measurements using a large, closed plant growth chamber. HortScience. 1992;27:777–80.
Wu A, Song Y, van Oosterom EJ, Hammer GL. Connecting Biochemical photosynthesis models with crop models to support crop improvement. Front Plant Sci. 2016;7:1518. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01518.
Ye ZP, Suggett DJ, Robakowski P, Kang HJ. A mechanistic model for the photosynthesis-light response based on the photosynthetic electron transport of photosystem II in C3 and C4 species. New Phytol. 2013;199:110–20. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12242.
Zabel P, Bamsey M, Schubert D, Tajmar M. Review and analysis of over 40 years of space plant growth systems. Life Sci Sp Res. 2016;10:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lssr.2016.06.004.
Acknowledgements
Thanks to the technician Diego Chiabà for the fundamental help in constructing DYNAMISM.
Funding
GA was supported by funds of the University of Udine for his mission to Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH for the system development (PDM_VQR3_DI4A_MISSIONI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NS and GA constructed the growth chamber system and performed the experiments; NS wrote the article; AP and GA planned the experiments; OM and UR provided the facilities and gave suggestions on the experiments. All the authors agreed on the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1
: Figure S1. Calibration curve of the miniature air flow transmitters. The straight line represents the overall regression (all sensors). Figure S2. Changes in ΔCO2 at different air flux levels when scrubbing the air with soda lime. The data show all ramps (i.e. different pump speeds) normalized from 0 to 1 and averaged every 20 seconds.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Salvatori, N., Giorgio, A., Muller, O. et al. A low-cost automated growth chamber system for continuous measurements of gas exchange at canopy scale in dynamic conditions. Plant Methods 17, 69 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-021-00772-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-021-00772-z