Abstract
Background
This study contributes to the current ethnomedicinal knowledge of the Swat Valley, Pakistan. District Swat possesses remarkable biodiversity owing to its varied topographical and climatic conditions, prompting a distinct human-plant association. Our hypothesis is that the presence of such a great biodiversity has shaped into a formal ethnobotanical culture in the area transmitted through generations. We suspect that the versatility of some plant species has greater influence on the culture. Therefore, the prime objective of the study is to understand this unique human-plant relationship in the valley and to create scientific roots for the selection and practice of herbs in the ethnobotanical domain of the district.
Methods
Primary data were collected using questionnaires and face-to-face interviews with the locals. The data collected were used for calculating some important indices, i.e. relative frequency of citation (RFC), participant agreement ratio (PAR), frequency of citation (FC), Smith’s Salience Index (SI), Relative Importance Index (RII), Cultural Value Index (CVI) and a newly proposed, Ali’s Conservation Priority Index (CPI). Index scores were used as key identifier of the ethnobotanically important plants of the area.
Results
Residents of the Swat Valley have listed plant uses in 15 use categories. Around 9% of the respondents have a common consensus on the selection and use of plants for the treatment of evil eye with similar results for body cuts (8.2%) followed by psychological/neural ailments (8.0%). Respondents agree that Berberis lyceum Royle. dominates in all five indices. Skimmia laureola Franch. also constitutes one of the central plants of the ethnobotanical domain, ranking second in the SI, fifth in the RII, seventh in CVI, and third in the Cultural Importance Index. It holds the thirty-fifth position in the CPI. Over 80% of the population treat different diseases with herbal remedies. In the common ethnobotanical domain of the area, plants like Mentha longifolia L., Berberis lyceum, and Skimmia laureola are very important and have high salience and importance values, thus suggesting these plants are versatile for their uses in the study area.
Conclusion
In conclusion, only some plant species are prioritised for their use in the ethnobotanical domain of the community. Medicinal and aromatic plant (MAP) usage is widespread in the Swat Valley. The ethnobotanical knowledge could be used as a tool to understand the adaptability of a specific taxon in the area and the possible conservation risk to their existence.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Plants and humans have a close and inseparable connection, not just ecologically, but socio-culturally since the existence of human beings. Plants in general and high-value medicinal and aromatic plants (MAPs), specifically, have a long history of use as a source of cheap and effective remedy for various ailments [1]. The use of MAPs can be traced back 7000 years [2]. Plants have always been an integral part of various cultures, i.e. the Sumerian clay tablet, a 4000-year-old medical script, documents the most primitive known plant therapies for various ailments.
Like other parts of the developing world, a significant portion of the population in Pakistan use medicinal plants traditionally for treating ailments and health disorders. There is an immense volume of literature available where a variety of studies have been carried out to document the intricate relationship between MAPs’ use in the aboriginals’ sociocultural and religious practices in various parts of Pakistan. Some of these findings suggest that the use of herbal therapies is directly or indirectly linked to the culture of the area [3,4,5], but no one has presented any sound proof of this relationship by applying modern statistical techniques. The current study was aimed to provide empirical bases for the presence of an ethnomedicinal culture in the Northern parts of Pakistan, where lies the great mountain system of Hindu Kush.
The beautiful Swat Valley which lies in the complex Hindu Kush mountain system possesses a surprising biodiversity due to its varied geographical and climatic conditions [6,7,8]. Swat Valley is known internationally for its green mountains and beautiful transparent fast-flowing rivers. The valley has varied topography with an altitudinal range of 700 to 6000 m above the average sea level (AASL), providing a complex biodiversity hotspot for researchers to be explored and protected. This complex topography gives rise to a complex biota and thus a surprisingly unique man-plant relationship (ethnobotany).
People of the area only living in the towns and cities have reasonable access to the modern health facilities, although a larger segment of the population living in the rugged mountains has little to no access to these facilities. Remote communities have established a connection to their immediate plant resources, which not only provide them with medicines but also act as an important resource of income generation, and are therefore of great significance to be understood, documented, and conserved [9,10,11].
Most of the inhabitants of the Swat Valley are the descendants of Akhozai subdivision of the Yusufzai Afghans (Pukhtuns/Pashtuns), living here for centuries [12]. The Kohistan area of the valley is primarily populated by Ghawris in the north while Torwalis resides in the southern rims. It is believed that the people of Indus Kohistan are Dardic, an old Indo-Aryan tribe [12]. Most of the residents of the valley are Muslims by religion with further subdivisions of Sayads (Saidan), Miaas (Miagaan), Sahibzadaas (Sahibzaadgan) and Mulaas (Mulayan) [13].
Swat Valley has mild to severe weather patterns influenced significantly by the altitudinal variation of the Valley. Phytogeographically, the area is considered part of the Sino-Japanese region with a monsoon season in the months of summer [6].
Considering the climatic variability along with the biodiversity and the land-use patterns in the area, eight agricultural and ecological regions can be recognised [6]. These zones are as follows: (1) The sub-tropical humid zone: this zone is predominantly the lowlands of the valley with characteristic short winters and extended summers. The indicator species are Bauhinia variegata (L.) Benth., Phoenix spp., Reptonia buxifolia (Falc.) and Nannorrhops ritchiana (Griff.) Aitch.. (2) The sub-tropical dry zone: this zone covers most of the Swat Valley with the altitudinal range of 600 to 1000 m. The indicator species of this zone are Acacia modesta Wall. and Olea ferruginea Royle.. (3) The humid-temperate zone: the altitudinal range of this zone is from 1000 to 1500 m with hot and humid summer, especially, in June and July. The native tree species of this zone are Pinus roxburghii Sarg. and Quercus incana W. Bartram [6]. (4) The cool temperate zone: the altitudinal range of this zone is from 1500 to 2000 m with extended cold winter and petite summer. The common indicator species of the zone are Pinus wallichiana A. B. Jacks. and Quercus dilatata Royle. [6]. (5) The cold temperate zone: this is the most densely forested zone of the valley, ranging from 2000 to 2500 m altitudinally with Abies pindrow (Royle ex D. Don) and Picea smithiana (Wall.) Boiss. as the common indicator species [6]. (6) The subalpine zone: this zone is normally covered by snow for practically half of the year with an altitudinal range of 2500 to 3500 m. The indicator species of this zone are Betula utilis D. Don and Quercus semecarpifolia Sm. [6]. (7) The alpine zone and (8) the cold deserts are the highest points of the valley with an altitudinal range of 3500 to 6000 m above sea level. This zone lacks obvious macroflora.
It is obvious that these dissimilar ecological zones deliver micro-climates and habitats to an extensive variety of flora and fauna and are, therefore, endorsing to the establishment of complex man-plant ethnobotanical-cultures in the Swat Valley.
Ethnobotanical cultures can be protected if they are understood properly and the locals are given better stacks to hold on to. In many developed countries, especially North America and Western Europe, investors and the common public are equally, vigorously involved in the decision-making process at the managerial level and the opinions of the public are sought and considered before concluding on any future environmental policy [14, 15]. Common examples on the participation and consideration of public opinion can be seen in many cases in the UK, even on very minor issues, i.e. public consultation on hunting with dogs and other mammals [16, 17]. Scoring and quantifying the public opinion in environmental biology and ecology is sometimes an issue and requires large-scale ecological surveys and consultation of the public to make sure a reduced risk of human-wildlife conflict remains [10, 18, 19].
To extract and understand public opinion, questionnaires are considered as one of the cheapest and robust ways of obtaining large amount of quantitative data. Many examples include the usage of questionnaires in understanding the perception and attitudes of a community towards conservation strategies [7, 15]. Questionnaires are mostly aimed at the understanding of the actual behaviour of the subjects but also may focus on the hypothetical behaviour of the subjects [20]. The types and nature of the questionnaires can vary; for instance, closed-format questioning is a common practice in anthropology and ecology [15, 21]. Questionnaire surveys can be carried out in various means, i.e. post, telephone, and face to face interviews.
The review of literature of the ethnobotany of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KP) and Swat Valley shows that no one has ever attempted to quantify the use of plants or applied statistical indices to show their importance in the prevailing culture. In the oldest records, [22] studied the flora of the Upper Swat Valley while making key references to the ethnobotanical practices. Other regional study by [23], who conducted socio-phytological investigations on the Dabargai Hills of Swat District, identified some important plants of the area of therapeutic interest. Sulatanr Valley was investigated for its ethnobotany by [24] while [25] chose Malam Jaba mountains for the same. Cataloguing of important medicinal and economical plants was carried out by [26] of the Elum mountain. More recently, some scientists and armatures have expanded their work and studied large subvalleys of the Swat district [13, 27,28,29,30,31,32]. A few authors have attempted to specify their research on certain taxa and their ethno-ecological importance [33, 34], and some researchers [8] have attempted to explore the potential for in situ cultivation of MAPs and have obtained significantly positive results of the trials.
Most of the authors agree on the fact that the current practices regarding the use of MAPs and NTFPs are unsustainable and pose a serious threat to the biodiversity of the district. It is evident from the available literature on MAPs that none of the researchers have quantified the use of MAPs in Swat Valley. The current study is designed to understand the actual use of these plants through various quantitative measures like statistical indices, which could eventually help in understanding the versatility of some taxa and their links to the local ethnobotanical system. In the longer run, similar researches could help in developing fact-based strategies to conserve the flora and knowledge of the area.
Keeping in sight the prime objective of the study, questionnaires were designed to serve the precise purpose, i.e. to collect primary data from the inhabitants regarding the use of the plants, selection preference of the plants, and the conservation issues of the plants. The questionnaires included probe questions like as follows: how widespread is the ethnomedicinal knowledge in the study area? Precisely what plants constitute the cultural domain of the area? How aware are the people about the ecological relationship between trees and understory herbs? Is there any plant under serious stress from the anthropogenic stresses, i.e. exploitation by the traders? What stakes are there for the future biodiversity of the District Swat in terms of conservation?
Methods
In the study, two questionnaire surveys were conducted to record the plant uses in a particular cultural domain and to document metadata about the peoples’ perception of the biodiversity and conservation measures in the area. The data was also used to calculate some very important statistical indices. The questionnaire prompts were designed to elicit information about specific quantifiable variables after [35]. This method was chosen because it is robust and inexpensive and is commonly used in socio-ecological surveys [15], but to the ethnobotanical survey in the area, constituting its initial application.
Questionnaire 1 mainly concentrated on eliciting background information about the ethno-medicinal knowledge flow in the community and ecological understandings of the locals along with some secondary information. Questionnaire 2 aimed at the recording of ethnomedicinal uses of plants in a particular ethnobotanical domain and was used in order to find out the intricate links between the social and physical environment of the area. Before the commencement of the study, permission was sought from the University of Reading Ethics Committee on the use of the questionnaires. The committee suggested some changes; permission was granted after the requests were fulfilled. A team of three qualified residents assisted with the field trips, in the understanding of local cultural norms and to avoid unnecessary antagonism with the inhabitants of the area. Respondents were randomly selected [15, 32, 36] to get a representative sample of the population and to get a less probable selection from the population. The Snowball sampling method [37] was used with some minor modifications. The main modification to the Snowball method was to select the most learned person of the community who can recall more uses of the MAPs. Therefore, the respondents were minimised as we achieved the representative samples of the population.
We also used semi-structured and free-listing questionnaires coupled with face-to-face interviews of which most of the population sampled was cooperative and willing to respond to. Residents were found to have considerable knowledge of the plant uses and were aware of the plants’ habitats. The elders had better knowledge of the recipes and were given priority for interviews. Interviews were complemented with forest walks and, in some instances, if the locals were willing, asked to show the plant in the wild. Data concerning local plants, i.e. their names, their uses, part-use, recipes preparations, and administration were recorded. In total, 116 participants were interviewed and had their completed questionnaires collected. Questionnaires were made available in three different languages, English, Pashto, and Urdu. Plant specimens were identified by experts in the Department of Botany of the Government Postgraduate Jahanzeb College, Swat and some by experts at the University of Reading, UK, after proper preservation. Some of the plant specimens were stored in the University of Reading’s Herbarium. A checklist of all the ethnomedicinal plants and their uses was developed (Table 1). Free-listing was carried out after [38] by asking the respondents to list all the plants used in the local cultural domain. Free-lists for 16 different diseases and health problems were collected. The recorded data for Questionnaire 1 was analysed by using Microsoft Excel and statistical analyses were done by calculating various indices (Table 2) from the data. The formulae used for calculating these indices are mentioned in the results section for better clarity.
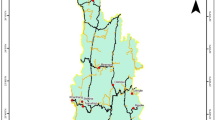
We have also used ArcGIS and WorldClim bioclimatic layers to develop thematic maps of the study area. The maps could provide visual interpretation of annual mean temperature layer in the study area correlating various areas of the valley with its high level of diversity (Fig. 1a, b).
Results
The results obtained from questionnaire 1 indicate that the population sampled constituted 77% male and 23% female. It was also evident that only 19% of the population sampled was unemployed and 81% were employed, some of which are directly linked with farming and livestock husbandry (Fig. 2). It is clear from the results that 85% of people use medicinal plants for treating different ailments; only 15% did not use any medicinal plants directly for treatment of ailments, although the use of such plants was part of their daily food, e.g. used as pot herbs, in making curries. Over half of the respondents (59%) acquired the ethnomedicinal knowledge from different parts of the society, not restricted to learn it from their family hierarchical lines (41%) while 69% of the respondents had more than one family member with the knowledge of use of the same medicinal plant (Fig. 1).
Respondent sex ratio and their employment status, use of medicinal plants (MAPs) and knowledge acquisition in Swat Valley are shown in percent. The percentage for different categories (♂ (male), ♀ (female), EM (employed), UE (unemployed), UMPAs (use of medicinal plants), NUOMAPs (no use of MAPs), FF (from family) and FOPOTS (from other parts of the society)) was calculated using excel and was superimposed into the graph configuration
Over 70% of the population were aware of the interactions between the presence of trees and the MAPs in association as a sub-flora (Fig. 3). Most of the respondents (88%) believed that the government were to blame for lack of response to the loss of the forest canopy and have claimed the current efforts towards the protection of the area’s forests as less-effective in comparison to the previous Swat State ruler. In the same manner, a great pessimism was found among the respondents as they consider that MAPs’ use is decreasing due to many reasons; the most noticeable being the gradual scarcity of the plants in the wild and high prices in the local market. Seventy-one percent of the respondents regarded a clear decline in the use of the ethnobotanical medicines. A majority (92%) of the respondents showed disappointment and pessimism towards the future of the forests in the area, while 66% of the respondents were either unwilling or unable to actively participate in the conservation measures (Fig. 2). This could be due to the limited available conservation projects which are predominantly run by non-governmental organizations (NGOs).
Shows the role of the main drug market, medicinal plant use in family, plant extraction, importance of the trees in the area, view about the government role, trend in the use of MAPs, future perception of forest conservation and self-role in conservation in Swat valley are depicted. The parameters, i.e. PBFTMT (plant bought from the main town), FAWE (from anywhere else), OFMU (other family member use), NOFUI (no other family use it), DFTF (direct from the forests), FTM (from the market), MAPsDOT (MAPs dependent on trees), MAPsNDOT (MAPs not dependent on trees), NER (no effective role), LE/E (less effective/effective), D (decreases), I/NC (increase/no change), NS/LS (not safe/less safe), S (safe), AI (active involvement) and NR/CPR (no role/cannot play role) are shown in percentage
Data analysis and results from questionnaire 2
The use reports (UR) for medicinal plants were calculated after [39, 40] on the bases of the ethnobotanical information: participant i states the usage of the plant species s in a use-category (disease/health issue) u. The terminology was adopted from [40] where NS represent species (s1, s2,……., sNS) in the entire number of use categories NC (u1, u2, ……uNC) while participants were denoted by N (i1, i2, …..iN). So, the highest value of URsui can be 1 when a combination is found or zero if no combination is observed; assuming the variables are constant the, URs can be expressed as:
As indicated by the Eq. 1, the UR of all the respondents (from i1 to iN) are summed up in individual use group for the species (e.g. the number of respondents who specified the use of the plant species in the disease) and secondly all the UR of each category (from u1 to uNC) is summed, i.e. the entirety of all the uses of the species in the 16 diseases or health issues. Various indices were calculated (Table 2) to understand the cultural importance of the medicinal plant use and the hidden risk factors to their conservation.
Relative frequency of citation (RFC)
This index is not dependent upon the variable of the use-category (see Eq. 2) and can be very simply extracted by dividing the frequency of citation (FC), by the numeral of participants (N) under the study [40]. FC denotes the number of participants recording the species, regardless of the use-category.
Relative Importance Index (RII)
This index was created by [40], based on the use categories of the species only and does not consider the sub-categories of the use [40]. The following equation (see Eq. 3) was used for calculating RII for 103 species used by the local community of the Swat District. In the equation, RFC (max) is the relative frequency of citation over the maximum while RNU (max) is a relative value of the use categories over the maximum (for more details see [40]). This index ranges from 0 to 1; 0 is where no one mentions the use of the species while 1 is where all the respondents indicate the use of the plants in all the use categories.
Smith’s Salience Index (SI)
The free-listing interviews and questionnaires were very useful to calculate Smith’s Salience Index, which includes the frequency of mention and the spot of items in free lists [41]. The value ranges from 0 to 1, with 1 being highly salient. The average saliency is calculated for all the species across the different use categories. Using the symbology after [42], the following formula (see Eq. 4) was used, where rj is the place of the item j in the free-list, and n is the number of all the objects in the lists.
Participant Agreement Ratio (PAR)
We used this to estimate the agreement of the community regarding the use of different plant species in each use category. Previously, this consensus analysis was called―informant consensus factor (ICF) by [5] but [43] named it as Respondents’ Agreement Ratio, while we are suggesting the term PAR. Using the formula (see Eq. 5) below, nur is the number of records in each class and nt is the quantity of plants used in that group. The range is from 0 to 1, where 1 shows the limited number of plant used in a use category, i.e. a high degree of consensus among the local population for the use of medicinal plants.
Cultural Value Index (CVI)
This index (CV in the original text of [44]) is one of the most useful indices used in ethno-biology, first introduced by [19] following the multiplication of the factors of [7]. The following formula (see Eq. 6) can be used for calculating the index, where three factors are multiplied together: NUs is the times of use categories, NC is the total figure of use groups, FCs is the number of participants mentioning the species to be useful in all categories and N is the total number of participants under study. The third factor is the sum of all the uses cited by the different participants in a category and is divided by the sum of the participants.
For example, in the current survey, Mentha longifolia was reported to be used only in two categories, i.e. gastric problems and throat infections, so its NUs = 2; the total number of use categories are 16, so NC = 16 (NUs/NC = 2/16). The FCs value for Mentha longifolia is 27, as many people suggested the plant being useful out of 39 which is the total number of the respondents (N), e.g. (FCs/N = 27/39). Twenty-six people considered the plant being useful in gastric problems and one person recorded it being useful in throat infection, so the third factor of the formula would be 26/39 + 1/39. Combining all the three factors CVs or CVI = (2/16) × (27/39) × (26/39 + 1/39) = 0.0599. The range of this index is from 0 to NC, where 0 is the condition where there is no mention of the plant being useful.
Cultural Importance Index (CII)
This is another useful index and is part of the cultural value index discussed above. As seen in the CVI, this particular index not only makes use of the quantity of use of the plant species but the spread of use in different use categories and was thus called by [40], the index of versatility of a species.
The Cultural Importance Index is considered a sub-factor of the Cultural Value Index, and both have the same function, i.e. understanding the spread of a medicinal plant in a cultural domain (see Eq. 7).
Ali’s Conservation Priority Index (CPI)
It is evident from the results above, that these indices can help explore the significance and versatility of plants in the field of anthropology and ethnobotany. However, they have no significance in estimating the conservation threat to this important flora. If we estimate the importance factor and calculate the plant part use in a particular culture by giving it a numerical value of a graduated scale in terms of their increasing risk, and then add it to the salience value and cultural importance index values of a plant, we can easily calculate a new index which we propose to be called as Ali’s Conservation Priority Index (CPI). The index can clearly demonstrate the extinction stress on a particular taxon. The index has proved to be very useful in identifying future vulnerable species in the study area and could be generalised to other places where no or little restriction persists from the authorities on the collection and exploitation of MAPs. Swat District is one of those regions where everyone has open access to the wild plant resources and can easily exploit the flora by over harvesting and over grazing, etc. The following formula (Eq. 8) for the index is recommended:
CPI = SI + RII + part-used value/3 (8)
In the formula, the SI is the Saliency Index of a plant species and the RII is the Relative Importance Index of the species under consideration. The Part-used value can be added from the Table 3 which signifies the importance in the distribution and extinction of a plant species. Those important MAPs which are used as a “whole organisms” in ethno-medicinal recipes or in any other economic or social practices of a culture are under highest risk of extinction and should be prioritised for conservation. The main condition of use of this index is that the plant under consideration must be the one collected from the wild. Plants of which only fruits or leaves are used in ethno-remedy or other socio-cultural practices are comparatively less prone to extinction. The value of the index ranges between 0 and 1, while 0 being no risk and 1 the highest risk and the one with the high value close to 1 should be prioritised for conservation in that region.
As trees can contribute many different parts which could be medicinally useful (i.e. wood, bark, twigs, leaves, fruits, seeds, resins), the value of the most important part is recommended for use. For example, if leaves and roots are both used as ethnomedicines, the value for roots shall be used from Table 3 for the calculation of CPI. The results suggest that over 60% of the recorded plants are herbs, 26% trees, 11% shrubs and less than 1% were climbers (Fig. 2). The angiosperm family of Lamiaceae was contributing nine species to the ethnomedicinal culture of the area, followed by the Apiaceae (7), Fabaceae (6), Rosaceae (5) and Solanaceae with (4) species. Asteraceae, Brassicaceae, Cucurbitaceae and Zingiberaceae contribute three while the rest of the families aid two species each.
The PAR values clearly indicate the highest degree of agreement. Over 8% of the residents agree on the choice of plants use for evil eye. This is followed by agreement on body cuts and psychological/neural disorders (about 8%). The highest PAR ranking for the use category of evil eye suggests that the people of the area still follow the old rituals and have a unanimous belief in the supernatural. Interestingly, the lowest PAR ranking was obtained for a very common health issue of headache (1.7%) (Table 4). Throat infections ranked fourth and gastric problems fifth in the ranking. Nutritional disorders ranked 15, suggesting that people have different approaches to maintain their dietary requirements and have low consensus on the plants consumed for solely nutritional purposes. This disagreement may also suggest that people are ill-informed about dietary requirements or a microculture exists in the different parts of the society.
From the free-listing results, it is obvious that the centre of the Ethnomedicine of the Swat Valley, based on the values of Salience Index, consists of: Berberis lycium, Thymus linearis, Mentha longifolia, Punica granatum, Curcuma longa, Ajuga bracteosa, Syzygium aromaticum and Skimmia laureola (Table 5). The key plant of the domain is Berberis lyceum ranking highest in all five indices. Skimmia laureola is also one of the central plants of the ethnobotanical domain, ranking second in the SI, fifth in the RII, seventh in CVI and third in the Cultural Importance Index. It was in the 35th position in the CPI. Mentha longifolia ranked third in the SI and RII suggests that the plant is quite well known in the study area and is normally prioritised for its use. This plant also ranked high in the CVI and CII rankings, fifth and second, respectively. The fourth ranking of the plant in the CPI puts it in the list of high conservation priority species (Table 5). Punica granatum is ranked fourth in the Saliency and Relative Importance Indices. Its third ranking in the CVI shows its higher versatility in the local cultural. The plant ranked 72nd in the CPI, shows a very low risk of extinction and thus does not require any immediate prioritisation for conservation in the regional conservation policies (Table 5).
Table 6 indicates that Berberis lycium Royle. has a high saliency value of (0.077) and shows the priority of use of the plant in the Swat District (Table 6). This plant also has the highest RII value (0.58) and the highest CVI (1.00). The highest value for CPI (0.6926) in Table 6 puts the plant in the highest threat level to extinction in the wild. Skimmia laureola was the second most salient (0.03) species of the area, and its familiarity and use makes it the second choice/option in the free lists, after Berberis lycium. The CVI value (0.02) puts the plant in seventh position in the ranking table (Tables 5 and 6). As the CVI values takes the use categories as well as the use reports into consideration, it is worth noting that Curcuma longa is not a plant locally grown or collected from the wild, but is imported from other parts of Pakistan or India. This pattern shows strong trade links of the local markets with national and international markets, and there is clear potential for growth in both imports and exports of the important MAPs. This may also mean that plants like Curcuma longa should be tried for cultivation in the valley, so that the import revenue is saved for other growth sectors. Cultivated plants have a great potential in the area, e.g. Allium sativum and Allium cepa, are not just widely cultivated and used in spices, i.e. curries, but are also well known for their therapeutic properties.
Discussion
The herbal market of the major city (Mingora) of the valley plays a significant role in the continuous supply of MAPs to the major part of the community (62%). This may be due to the active role of the medicinal plant traders who normally hire local people as cheap labour for harvesting these plants from the wild and directly supply them to the market. However, this also shows the potential of further expansion of the MAPs trade, if an eco-friendly and sustainable approach is adopted.
Part of the study followed the basic pattern of cataloguing of plants and their uses like [22,23,24, 28, 30]. People perception has confirmed the findings [45] that the MAPs are under severe stress from overcultivation and deforestation. The need for conservation is ever high for these important plants [29].
People in most of the subvalleys of the Swat district have similar uses of these plants, as [29] confirms that from the subvalley of Shawar and Madayan. The results also confirm the findings of [32] which confirms the complex structure of the ethnobotanicals’ market. We can also confirm results that most of these plants share similar use categories in Swat districts. The results of [34] are in corroboration with our results which suggest that the overall population density of each plant is decreasing.
Domestication and ex situ conservation of the some therapeutically important medicinal plants have greater economic potentials [8]. Their tests on the domestication and cultivation of six medicinal plants in farm lands have positive results [8]. This confirms our observation that the plants imported from other regions could be tested for cultivation which could help boosting local economy.
Almost all the investigators agree on the fact that Swat is potentially a biological hot spot, not just for the country, but for the whole of South Asia, and can act as a trade hub of MAPs and Non-Timber Forest Products (NTFPs) [8, 13, 30, 32, 34]. Most of these authors agree that the current practices, regarding MAPs and NTFPs are unsustainable and pose a serious threat to the biodiversity of the district. Threats like deforestation and uprooting of medicinal plants [29] provide sound bases for the use of Ali’s Conservation Priority Index to quantitatively measure the threat level of individual plant species. Some researchers [30, 34] reported the habitat fragmentation and unwise use of these plants are the severe threats to their extinction. This means that when these plants lose their habitats they will lose their use in the traditional recipes and will eventually be excluded from the ethnobotanical domain of the area which could lead to more stress on the already ineffective government health facilities.
The current study is of great significance to the public health policies as it highlights the importance of the locally available natural phyto-products used by the residence. The greater majority of the ailments treated with the locally collected MAPs are reducing the stress on the scarcely available public health facilities of the area and at the same time saving financial resources of the destitute residents.
Conclusions
District Swat possesses remarkable biodiversity owing to its varied topographical and climatic conditions. The use of medicinal and aromatic plants in the valley is a common practice, as 85% residents used botanicals to treat various ailments. The common knowledge of use of the important flora in the area makes a unique and well-established ethnobotanical culture. The use of these plants shows a decreasing trend which can be clearly attributed to factors such as uncontrolled harvesting, insignificant role of the government towards conservation and presumably the lack of conservation knowledge and strategies; these factors will soon irreversibly damage the floristic biodiversity of the area, and consequently, the rich ethnomedicinal knowledge will vanish forever. It can be established, by interviewing the locals, that most of residents are well aware that the on-going degradation of the forest canopy is severely harming the sub-flora; however, most of them are unwilling or unable to effect change. There is also a blame game being played in the valley; locals are blaming the government and vice versa. The study has established that people and plants have a deep intricate relationship, and the people of the area have developed a certain cultural domain of the plant use. This also confirms that not all plants of the valley are equally utilised as herbal remedies but rather some plants are more versatile than others and have significantly more impact on the prevailing ethnobotanical culture.
The research has tried to establish a new concept of threat level to plants and highlighted index for conservation priority. This new index can be applied to areas where plants are openly collected from the wild. The index can calculate the extinction risk to a taxon, using the plant part used as an important factor. Plant parts used are given categorical values (Table 3). This index can also be defined as the extinction risk factor. The calculation of the index requires the Smith’s salience index value [41], as this value is the primary use of a certain item by persons or population. Adding the Smith’s Salience and Cultural Importance Indices which are the measures of versatility-diversity of use [18, 40], together with the part use value, and dividing them by three get the average value. The maximum theoretical value for CPI is 1, suggesting the plant needs to be put in the high priority list of conservation. If the plant is well known and highly versatile and, if its part use is putting it in danger of extinction, the stakes for its conservation would be very high.
The prime objective of the study was to understand the cultural domain of the ethnobotanicals use of the valley. The objective was achieved by concluding that only a few important plant species make the cultural domain of the local community. It was the first ever attempt to establish this fact systematically in the area. The usual trend of ethnomedicinal researches from the area focuses on the compilation of plant uses in general. This study is unique as it has quantitatively evaluated the ethnomedicinal knowledge in Swat Valley. We highly recommended that studies of similar nature in the area be conducted on a much wider scale, to document and understand the socio-cultural practices of the area and to envisage a policy for conservation of the flora and the invaluable knowledge related to it.
References
Salganik MJ, Heckathorn DD. Sampling and estimation in hidden populations using respondent-driven sampling. Sociolo Method. 2004;34:193–239.
Goodman SM, Ghafoor A. The ethnobotany of Southern Baluchistan, Pakistan, with particular reference to medicinal plants. Fieldiana Botany. 1992;0,I-V:1–84.
Ahmad F. Geo-informatics application to investigate agricultural potential in Cholistan desert. J of Food Agric & Enviro. 2007;5:310–4.
Borgatti SP. Elicitation methods for cultural domain analysis. In: Schensul J, Le Compte M, editors. The Ethnographer's toolkit. Walnut Creek: Altamira Press; 1998.
Shinwari ZK, Gilani SS. Sustainable harvest of medicinal plants at Bulashbar Nullah, Astore (northern Pakistan). J Ethnopharmacol. 2003;84:289–98.
Ahmad H, Ahmed R. Agro ecology and biodiversity of the catchment area of Swat River. Nucleus. 2004;40(1–4):67–75.
Rahman IU, Khan N, Ali K. Classification and ordination of understory vegetation using multivariate techniques in the Pinus wallichiana forests of Swat Valley, northern Pakistan. Sci Nature. 2017;104:104–24.
Sher H, Mohammad A, Hazrat S. Forest resource utilization assessment for economic development of rural community in northern parts of Pakistan. J of Med Plan Res. 2010;17:1786–9.
Ali F, Khan N, Ali K, Imran K. Influence of environmental variables on the distribution of woody species in Muslim graveyards of Malakand Division, Hindukush Range Mountains of Pakistan. PAK J BOT. 2017;49(6):2357–66.
Herbert A, Gerry NP, McQueen MB, Heid IM, Pfeufer A, Illig T, Colditz G. A common genetic variant is associated with adult and childhood obesity. Science. 2006;312(5771):279–83.
Khan N, Ali F, Ali K, Shaukat S. Composition, structure and regeneration dynamics of Olea ferruginea Royle forests from Hindukush Ranges of Pakistan. J Mt Sci. 2015;12(3):647–58.
White PCL, Newton-Cross GA, Moberly RL, Smart JCR, Baker PJ, Harris S. The current and future management of wild mammals hunted with dogs in England and Wales. J Environ Manag. 2003;67:187–97.
Yousufzai SA, Khan N, Wahab M, Ajaib M. Ethnomedicinal study of Marghazar Valley, Pakistan. Int J Biol Biotechnol. 2010;7:409–16.
Ali K, Khan S, Khan N, Khan W, Rahman IU, Ullah F, Ali K, Nisar M. Ethnobotanical and ecological study of Punica granatum L. in Dir district, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Regulatory Mechanisms in Biosystems. 2018;8(4):656–61.
Turner MG. Landscape heterogeneity and disturbance. Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 1987.
Ali M, Begum R, Ali K, Nisar M, Khan W, Hassan N, Uddin N, Wadood SF, Zaman SU, Rahman IU, Khan N. Ethnobotanical survey of wild medicinal plants of Tirat Valley District, Swat, Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa. J Biodiversity Environmental Sci. 2017;11:91–101.
Bachmair S, Stahl K, Collins K, Hannaford J, Acreman M, Svoboda M, Knutson C, Smith KH, Wall N, Fuchs B, Crossman ND. Drought indicators revisited: the need for a wider consideration of environment and society. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Water. 2016;3(4):516–36.
Ali K, Farman U, Khan N, Rahman IU, Ullah S, Khan W, Ali M, Uddin N, Nisar M. Ethnobotanical and ecological study of Myrtus communis (L.) in Bajaur agency (FATA) Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. J Biodiversity Environ Sci. 2017;11(1):152–64.
Turner MG, Hargrove WW, Gardner RH, Romme WH. Effects of fire on landscape heterogeneity in Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming. J of Veg Sci. 1994;5:731–42.
Holsman RH, Peyton RB. Stakeholder attitudes toward ecosystem management in southern Michigan; 2003.
Ali K, Rahman IU, Khan N. Species response to the changing climate: a case study of Acacia modesta Wall, in the Swat District, Northern Pakistan. Paper proceedings of International conference on climate change and social issues, Dubai, UAE. 2014;1(3):9–15.
Rehman M. Medicinal plants of upper Swat. M.Sc. Thesis, Department of Botany. Peshawar: University of Peshawar; 1987.
Khaliq A. Phytosociological and ethnobotanical studies on plant resources of Dabargai hills, District Swat, Pakistan. M.Sc. Thesis, Department of Botany, University of Peshawar. 1995.
Ahmad R. Ethnobotanical studies of Sulatnar Valley Swat. M.Sc Thesis, Department of Botany, Islamia College, University of Peshawar. 1997.
Iqbal I. Ethnobotanical studies of Malam Jaba, District Swat. M.Phil thesis, Department. Biol. Sci., QUA, Islamabad. 2000.
Khan A. Ethnobotanical studies of the mount Elum, District Bunir, M. Phil. Thesis, Department. Biological Science, QUA, Islamabad. 2001.
Rehman M, Ghafoor S. The natural resource and human ecology of Mount Elum District Swat. Consultancy Report. Pakistan: World Wildlife Fund Peshawar (WWF-P); 2000.
Ali K, Hussain A. Comparative assessment of the conservation status in community protected forest of Sulatanr and the adjoining unprotected forests of Chitkarai. Swat, Report: WWF-P Pakistan. 2003.
Hamayun M, Khan SA, Kim HY, Na CI, Lee IJ. Traditional knowledge and ex situ conservation of some threatened medicinal plants of Swat Kohistan, Pakistan. Int J Bot. 2006;2:1811–9700.
Khan SM, Ahmad H, Ramzan M, Jan MM. Ethnomedicinal plant resources of Shawar Valley. Pak J Biol Sci. 2007b;10:1743–6.
Hamayun M. Traditional uses of some medicinal plants of Swat Valley Pakistan. Indian J Traditional Knowledge. 2007;6:636–41.
Sher H, Mukaram S, Hussain F. Traditional resource evaluation of some plants of Mastuj, District Chitral Pakistan. Pak J of Bot. 2007;39:339–54.
Sher H, Farrukh H. Ethnobotanical evaluation of some plant resources in Northern part of Pakistan. Afr J of Biotech. 2009;8(17):4066-76.
Alyemeni MN, Sher H. Impact of human pressure on the population structure of Persicaria amplexicaule, Valeriana jatamansi and Viola serpens, the naturally growing medicinal plants in Malam Jaba, Swat, Pakistan. J Medicinal Plants Res. 2010;4:2080–91.
Newing H. ‘Qualitative analysis’ in Newing H, Eagle C, Puri R, Watson C. Conducting research in conservation: social science methods and practice. London: Routledge; 2010.
Khan A, Khan N, Ali K, Rahman IU. An assessment of the floristic diversity, life-forms and biological spectrum of vegetation in Swat Ranizai, District Malakand, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Sci Technol Dev. 2017;36(2):61–78.
Obiri JAF, Lawes MJ. Attitudes of coastal-forest users in Eastern Cape Province to management options arising from new South African forest policies. Enviro Conserv. 2002;29:519–29.
Ali K, Ullah F, Khan N, Rahman IU, Ullah S, Khan W, Ali M, Uddin N, Nisar M. Ethnobotanical and ecological study of Myrtus communis (L.) in Bajaur agency (FATA) Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. J of Biod and Envir Sci (JBES). 2017;11(1):152–64.
Khan N, Ali K, Shawkat SS, Muhammad Z. Distribution of Pinus roxburghii Sargent associations with environmental correlates in the Swat Hindukush range of Pakistan under current and future climate scenarios. Turk J Bot. 2016;40:1603–7.
Sultan-I-Rome. Administrative system of the Princely State of Swat. J of the res Soc of Pakistan. 2006;
Smith JJ. Using Anthropac 3.5 and a spreadsheet to compute a free-list salience index. Cultu Anthropo Methods. 1993;9:8–12.
Collins WD, Ramaswamy V, Schwarzkopf MD, Sun Y, Portmann RW, Fu Q, Casanova SEB, Dufresne JL, Fillmore DW, Forster PMD, Galin VY, Gohar lK, Ingram WJ, Kratz DP, Lefebvre MP, Li J, Marquet P, Oinas V, Tsushima Y, Uchiyama T, Zhong WY. Radiative forcing by well-mixed greenhouse gases: estimates from climate models in the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Fourth Assessment Report (AR4). J of GeophyResear. 2006;111:D14317.
LEV B, Marsh J, Soulsby L, Winter M. Report of the committee of inquiry into hunting with dogs in England and Wales. Norwich: HMSO; 2000.
Ghorbani A, Langenberger G, Feng L, Sauerborn J. Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants utilised by Hani ethnicity in Naban River Watershed National Nature Reserve, Yunnan, China. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011;134:651–67.
Adnan SM, Khan AA, Latif A, Shinwari KZ. Threats to the sustainability of ethnomedicinal uses in Northern Pakistan (a case study of Miandam Valley, District Swat, NWFP, Pakistan). Lyonia. 2006;11(2):87–96.
Acknowledgements
We wholeheartedly thank all the participants for taking part and sharing their treasured knowledge with us. We are also thankful to the anonymous reviewers for all their useful recommendations and contributions, especially, Mr. Mark Schulze, Mr. Muhammad Dala, and Mr. Emanuel for their valuable input. We humbly acknowledge Mr. Shah Wazir Khan (Khaki) for his continuous support in the dissemination and collection of the questionnaires in various parts of the Swat Valley.
Funding
This research was self-funded by the authors and no external or internal funding body has supported any part of the project.
Availability of data and materials
No personal data was collected from the interviewees and therefore no such data is kept or shared in any form. The questionnaires raw data is available on demand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KA, NK, and IUR designed the study and performed the field work; WK, MA, NUD, and MN analysed the data and drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Before conducting interviews, prior informed consent was obtained from all participants. No further ethics approval was required.
Consent for publication
This manuscript does not contain any individual person’s data and further consent for publication is not required.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
The Publisher remains neutral about jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, K., Khan, N., Rahman, IU. et al. The ethnobotanical domain of the Swat Valley, Pakistan. J Ethnobiology Ethnomedicine 14, 39 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13002-018-0237-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13002-018-0237-4