Abstract
Background
Traditional knowledge on ethnomedicinal plant is slowly eroding. The exploration, identification and documentation on utilization of ethnobotanic resources are essential for restoration and preservation of ethnomedicinal knowledge about the plants and conservation of these species for greater interest of human society.
Methods
The study was conducted at fringe areas of Chilapatta Reserve Forest in the foothills of the eastern sub-Himalayan mountain belts of West Bengal, India, from December 2014 to May 2016. Purposive sampling method was used for selection of area. From this area which is inhabited by aboriginal community of Indo-Mongoloid origin, 400 respondents including traditional medicinal practitioners were selected randomly for personal interview schedule through open-ended questionnaire. The questionnaire covered aspects like plant species used as ethnomedicines, plant parts used, procedure for dosage and therapy.
Results
A total number of 140 ethnomedicinal species was documented, in which the tree species (55) dominated the lists followed by herbs (39) and shrubs (30). Among these total planted species used for ethnomedicinal purposes, 52 species were planted, 62 species growing wild or collected from the forest for use and 26 species were both wild and planted. The present study documented 61 more planted species as compared to 17 planted species documented in an ethnomedicinal study a decade ago. The documented species were used to treat 58 human diseases/ailments including nine species used to eight diseases/ailments of domestic animals. Stomach-related problems were treated by maximum number of plants (40 species) followed by cuts and wounds with 27 plant species and least with one species each for 17 diseases or ailments. Maximum number of 12 diseases/ailments was cured by Melia azedarach followed by Centella asiatica and Rauvolfia serpentina which were used to cure 11 diseases/ailments each.
Conclusions
The list of 140 plant species indicates that the Chilapatta Reserve Forest and its fringe areas are rich in biodiversity of ethnobotanical plant species. Rauvolfia serpentina were the most valuable species in terms of its maximal use with higher use value. The documentation of 78 species maintained in the home gardens indicates the community consciousness on the conservation values of these ethnobotanical species. The communities should be encouraged with improved cultivation techniques of commercially viable ethnobotanical species through capacity building, timely policy intervention along with strong market linkage. This will ensure income generation and livelihood improvement and ultimate conservation of these species.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Due to globalization and green revolution, natural resources are rapidly dwindling due to the unsustainable anthropogenic activity. Consequently, the primary challenge to human society is the steady change in climate, reduction in biodiversity and dependence on external resources without giving emphasis on the enriched localised natural resources. In this setting, there is a need to explore the indigenous knowledge base for ecological, economic and environmental sustainability. Especially, forest fringe communities are associated with the forest for maintaining their livelihoods. Use of medicinal plants to treat various diseases has been part of human culture since ancient times [1]. Botanically derived medicinal plants play a major role in human society [2]. Traditional medicine forms a valuable resource for the development of new pharmaceuticals [3]. The exploration, utilization and conservation of these ethnobotanic resources are essential for restoration and preservation of traditional and indigenous knowledge [4, 5]. This acquired knowledge about the plants is very essential to be used in the near future [6]. Moreover, in developing countries now, the trend is to incorporate traditional medicines in local healthcare system and interest has increased among the researchers to explore the huge potential of ethnomedicinal knowledge for treating various diseases [7, 8].
In India and particularly in West Bengal people living in remote and rural localities are still dependent on traditional medicines for treatments of various ailments [9,10,11,12]. Indigenous people of Indo-Mongoloid origin inhabiting Chilapatta Reserve Forest in northern part of West Bengal are still using forest-originated products for their healthcare needs due to lack of availability of modern medical facilities and poor socio-economic condition [10]. The tendency of disinterestedness in old traditions is feared by elders as a major cause of losing this wealth of knowledge in coming time soon. Since traditional knowledge on ethnomedicinal plant is being eroded through acculturation and the loss of plant biodiversity along with indigenous people and their cultural background, hence, promoting research on these plants is crucial in order to safeguard this information for future societies for sustainable use and their conservation [13, 14].
Ethnomedicinal surveys provide data and information basis for conservation and sustainable utilization of local wild plants and also contribute to preserve cultural and genetic diversity. No new plant product, particularly wild, will be accepted by the urban population without proper testimony from specialists. The present study was therefore undertaken in the forest fringe area of Chilapatta Forest of West Bengal having objectives (i) document the ethnomedicinal plant species used by the community, (ii) tradition medicinal use and pattern and (iii) comparison of reported uses with different publications.
Methods
Study area
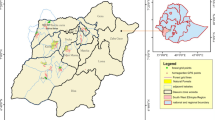
The present study was carried out at the forest fringe villages of Chilapatta Reserve Forest located in the sub-Himalayan mountain belts of West Bengal, India. The forest spreading over 41 km2 lies within the jurisdiction of Cooch Behar Wildlife Division in Alipurduar district (Fig. 1b). The forest is about 30 km away both from Cooch Behar and Alipurduar town, headquarters of Cooch Behar and Alipurduar district, and is transected by National Highway no. 31C. The fringe villages are Uttar Simlabari, Uttar Chaukakheti, Andu Basty, Bania Basty, Dakshin Mendabari, Uttar Mendabari, Kodal Basty, Kurmai Basty and Chilapatta Kumarpara. The elevation of the working site as measured by GPS (Garmin 72) was latitude 26° 32.85′ N and longitude 89° 22.99′ E. Mean altitude of the area was 47 m above MSL. The region is sub-tropical receiving average annual rainfall of 250–300 cm from south-west monsoon of which 80% is received from June to August. The summer and winter temperature are mild with 34 °C as the highest in the month of May while the lowest temperature is 7.5 °C during January. The forest villages with around 1000 households (average family size of 5–7 members) are inhabited by local communities of Indo-Mongoloid origin, including the Raj Bangshis, Mech, Ravas, Totos, Limbus, Lepchas, Nageshias, Uraons and Mundas. These fringe communities of the Chilapatta Reserve Forest are economically disadvantaged and thus depend on the forest and subsistence farming for their livelihoods.
Ethnobotanical data collection
The study was conducted from December 2014 to May 2016. The villages selected were purposive. An exhaustive list of households in each village was prepared with the active cooperation of State Forest Department and local village administration (‘Panchayat’). Prior informed consent and permission to interview the villagers was obtained from the village administration and each participant verbally. A pre-tested open-ended personal interview schedule was used to elucidate aspects like plant species used as ethnomedicines, plant parts used, procedure for dosage, diseases treated and therapy. Field surveys were conducted for collecting information through interviews. Only participants over 30 years of age were considered as respondents. The age of a person was reported significantly effecting traditional knowledge [15]. Thus, a total number of 400 respondents including traditional medicinal practitioners were selected randomly. Among the respondents, 91% were males. Females did not responded to our questionnaire without their male folk; and so only those female respondents were considered who responded independently. Forty-nine per cent of the respondents were in the age range of 33–52 years, 39% in range of 53–72 years and 12% in the range of 73–92 years. Majority of the respondents (71%) have attended school up to primary level or more. The schedule was administered to the respondent in local language, and the responses were recorded in English on the schedule.
The plant specimens were collected during the survey with the help of respondents. The specimens were mounted on herbarium sheets and were identified with the herbariums of Department of Forestry, Uttar Banga Krishi Viswavidyala, Pundibari, and Department of Botany, North Bengal University, Siliguri, West Bengal. The collected information on the ethnomedicinal plants was also cross checked with published available literature. For each species, the use value (UV), as adapted by [16] from the proposal of [17], was calculated. This quantitative method evaluates the relative importance of each medicinal species based on its relative use among informants. Use value is estimated as U/n, where U is the number of times a species is cited and n is the number of informants. The use value of each species is therefore based objectively on the importance attributed by the informants and does not depend on the opinion of the researcher [16]. The collected data were analysed by using Microsoft Excel.
Results and discussion
Ethnomedicinal richness
A total number of 140 ethnomedicinal species represented by 116 genera and 65 families used by the indigenous communities dwelling in the fringe areas of Chilapatta Reserve Forest were documented (Table 1). Out of these, 139 species were plants and one was fungus (Ganoderma lucidum). Among these total species documented, 52 species were planted by the indigenous communities of forest fringe area, 62 species were growing wild or collected from the forest for use and 26 species were both wild and planted. Of these ethnomedicinally used species, trees dominated the list with 55 species (21 planted, 19 wild while 15 both growing wild and planted/domesticated) followed by herbs with 39 species (15 planted and 18 wild while 6 both growing wild and planted/domesticated), shrubs with 30 species (10 planted and 17 wild while 3 both growing wild and planted/domesticated), climber with 12 species (4 planted and 8 wild), ferns are Christella dentata and Diplazium esculentum (both wild) and least used was a creeper (Ipomoea batatas—planted) and a fungus (wild).
The tree species were represented by 44 genera and 29 families, shrubs represented by 26 genera and 17 families, herbs represented by 36 genera and 25 families, climbers represented by 10 genera and seven families, ferns represented by two genera and two families and one genus and one family each represented creeper and fungus. Trees were dominated by genus Ficus with six species and family Moraceae with nine species; shrubs were dominated by genus Solanum with three species and families Apocynaceae, Fabaceae, Euphorbiaceae and Solanaceae with three species each; herbs were dominated by genera Ageratum, Centella and Curcuma with two species each and family Poaceae with five species; and climbers were dominated by genera Coccinia and Dioscorea with two species each and family Cucurbitaceae with four species (Table 1).
The cultivated ethnomedicinal plant species were grown/planted by the respondents in their home garden, and it was found during the survey that almost all the respondents were maintaining a home garden contributing to conservation of the species they were using. Similar documentation was also reported by [10]. In total, 78 ethnomedicinal plant species were documented to be maintained in the home gardens by the indigenous community residing in and around the Chilapatta Reserve Forest of West Bengal. Similar report on home gardens maintaining rich biodiversity of ethnomedicinal plants was also reported from Ethiopia [18]. There are ample of similar documentation from the plains and Himalayan region of West Bengal including Sikkim Himalayas [18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27].
A similar study from the same study area a decade ago [10] reported 79 ethnomedicinal plant species represented by 41 families and 68 genera. This means an increment of use of 61 ethnomedicinal plant species by the community. A decade ago, the community were growing only 17 species in their home garden [10] but now, it increased to 78 species (present study). This increased the entries of ethnomedicinal plant species in the list which was documented a decade ago. This may be because of plant accessibility and visibility in the cultural landscape [28] increasing accessibility to obtain useful plants. The farther the species grows from home, the less frequently it is used, but if the plants are more desirable than well-known, species growing near home, it is worthwhile to domesticate these plants instead of undertaking long trips now and then. Plant accessibility and visibility in the cultural landscape [28] seem to have important factors influencing strategies for obtaining useful plants. Researchers conducting studies in different parts of the world indicate that knowledge of ethnomedicinal plants increases in proportion to their proximity to human habitations [29,30,31]. People usually know less about plants growing far from their homes and more about species that grow nearby. The same principle applies to use: people usually choose plants that grow in the immediate vicinity of their place of residence for ethnomedicinal use [32,33,34]. This explains the reason in increment in the number of planted ethnomedicinal plant species over a decade period in the study area.
Ethnomedicinal uses
The documented species were used to treat 58 human diseases or ailments. Eight diseases of animals were also reported to be treated by some of the documented species (Table 2) of humans and domestic animals, respectively. The ethnomedicinal information documented for these species was also validated with earlier studies (Tables 2 and 3). Thirty plant species which were not reported in previous studies from the area. Stomach-related problems were documented to be treated by the maximum number of plants (40 species) followed by cuts and wounds with 27 plant species and least with one species each for 17 diseases or ailments (Table 3). It was noted that the common day-to-day problems (fever, stomach-related disorders cuts, wounds and burns) were treated with many species. It was documented that the communities were treating severe diseases like cancer, pox, ulcer, tuberculosis, typhoid, malaria, pneumonia and bronchitis. An earlier study on Rava community using 41 ethnomedicinal species was also documented [35]. Nine plant species were also used as ethnoveterinary medicines to cure diseases/ailments like tongue and mouth problem; cough, cold and worms; lactation problem; fatigue/weakness; diarrhoea; cuts and wounds; and appetiser (Tables 2 and 3). There are many ethnomedicinal studies that similarly documented the use of plant species used as ethnoveterinary medicines [1, 36,37,38,39].
Among the documented species, 92 species were used to cure multiple problems, while the rest were used to cure single disease each (Tables 2 and 3). Similar observation was also reported by [40]. The fungus Ganoderma lucidum is used for asthma and lung problem. It also lowers cholesterol. According to the respondents, Terminalia chebula is used to treat almost all diseases and mainly is used as an appetiser and to cure gastroenteritis, jaundice, liver, pneumonia, cough and cold. The maximum number of 12 diseases/ailments was cured by Melia azedarach followed by Centella asiatica and Rauvolfia serpentina which were used to cure 11 diseases/ailments each.
The majority of the plant species (108) had more than one part that was medicinally important (Table 2) as was also documented by [41]. The indigenous communities mainly used the leaf of the plant for their ethnomedicinal uses as this part was maximum used with 83 species followed by the fruit (55 species), and least was the seed with four species (Fig. 1a). The leaves of the ethnomedicinal plants were also documented to be used by the majority of remedies in traditional medicines in several reports [20, 41]. The fruit was also reported as dominant and widely used part for traditional medicines [11, 26]. The other parts used were branch (32 species), stem (28 species), bark (26 species), flower (23 species) and rhizome/tuber (eight species). The whole plant of 24 species was used for ethnomedicinal purposes. Destructive harvesting is done when the whole plant is used. Even the sap, latex, resin and pulp of the plant species were also used. Harvesting patterns of the leaves or foliage, root, rhizomes and tubers indicate their possibility of vulnerability for becoming endangered as was earlier observed [10].
Proper selection of species, parts, as well as preparation and administration methods were very important in traditional healthcare systems. Ethnomedicinal formulations were administered both externally (skin, nasal, eye and dental) and internally as oral doses (Table 2) as was also observed by [10]. Most of the preparations were a mixture of different plant species, and in few cases, only one plant species was used. Different parts of a single species were also used to cure different diseases. Almost all plant parts were used to prepare different medicinal formulations: roots, rhizomes, tubers, bark, leaves, flowers, fruit, seeds, young shoots, whole plants, and gum and latex. Doses of these preparations were not standardised but administered on the basis of age, physical appearance and intensity of the illness. Children were usually administered with smaller doses than adult. The course of frequency of treatment is decided by the type of disease and its severity.
Mode of preparation included juice, paste, decoction, powder, infusion and chewing raw plant parts. The administration of the therapy is raw, dried form in small pieces or powdered, solution or mixed with water/milk/honey and paste/lotion. Generally, fresh part of the plant is used for the preparation of medicine [42]. The majority of formulations were prepared as juice followed by paste and decoction. Usually, the underground parts were used in dried form as was also earlier reported [40, 43]. The preference for roots and rhizomes to prepare traditional remedies follows the scientific basis that roots generally contain high concentrations of bioactive compounds [44]. There are several reports on the administration of ethnomedicine by various authors [11, 12, 20, 22, 41]. It was also observed that herbal treatment is still preferred by the residents for bone fracture and dislocation over modern treatment. Senior citizens trust more upon traditional treatment system over the modern methods as they believe no side effect with the traditional ethnomedicine. Similar observations were also documented by [10]. The present study documented 140 ethnomedicinal plant species from North Bengal, of which 62 species were also reported in earlier studies [19, 20, 39, 45,46,47,48,49] from north India with similar ethnomedicinal uses. The medicinal uses of the species also reported from north India is compared with our study and is presented in Table 4.
Use value
The use value of a species indicates the ethnobotanical importance of a particular species in an area or by a community. The higher the value for a species, the higher is the importance of the species i.e. were most utilised or exploited. The use value range found was 0.01–0.13 (Table 1) The highest use value of 0.13 was estimated for Centella asiatica, followed by Terminalia arjuna and Oroxylum indicum each with 0.09; Musa sp., Ocimum sanctum and Leucas aspera each with 0.08; and Dillenia indica with use value of 0.07. Use values of 0.05 were found for Justicia adhatoda, Mangifera indica, Diplazium esculentum, Dioscorea belophylla and Azadirachta indica, while Terminalia bellirica, Morus alba, Moringa oleifera, Cynodon dactylon and Aegle marmelos had a use value of 0.06. Use value on medicinal ethnobotanical plants was also earlier reported and similar conclusions made [50,51,52]. These species were utilised because of their therapeutic uses in multiple diseases and were abundantly available in wild and were also all grown in the home gardens.
Conservation status
Various authors have feared that these ethnomedicinal species are disappearing from the wild due to unsustainable exploitation of these species and destruction of habitat of these species due to deforestation. Workers had reported the conservation status of medicinal plants of the Terai region [53] and Darjeeling Himalayas [54, 55] of West Bengal. In this study, the documented plant species were compared with these reports for the conservation status of these plant species. It was found that 38 ethnomedicinal plant species documented in this study were reported of their conservation status from Darjeeling Himalayas also (Table 1). According to the Darjeeling studies, plant species were classified as abundant, common, endangered, frequent, planted, rare and sparse and the number of documented species falling in these categories were four, five, three, five, five, three and 13, respectively (Table 1). Another study from the Terai region of West Bengal [53] also classified the plant species in terms of conservation status like rare, frequent and sparse, and 31 ethnomedicinal plant species documented in this study (Table 1) were categorised according to their conservation status in the Terai study.
Many plants growing wild and traditionally used are endemic and have become rare, threatened or endangered [56, 57], so they need to be conserved. Reserves of ethnomedicinal plants in developing countries are diminishing and in danger of extinction as a result of growing trade demands for cheaper products and new plant-based therapeutic markets in preference to more expensive target-specific drugs and biopharmaceuticals [11]. Genetic biodiversity of ethnobotanic plants is continuously under the threat of extinction as a result of commercial exploitation, grazing, environment-unfriendly harvesting techniques, loss of growth habitats and unmonitored trade of medicinal plants [58,59,60,61] This is because ethnomedicinal plants were freely harvested by users from their immediate environment either for their own use or traded domestically [62, 63]. The harvesting of these multiple use species can put them under threat [62] but can also lead to better chances for their conservation [63] especially through home gardens.
Conclusions
The Chilapatta Reserve Forest and its fringe areas are rich in biodiversity of ethnomedicinal plant species. A total of 140 plant species represented by 116 genera and 65 families were documented for medicinal purpose. Majority of the plant species (108) have more than one part that was medicinally important. The indigenous communities mainly used the leaf of the plant for their ethnomedicinal uses. The curing of 58 human diseases from these documented plant species itself explains the importance of this area in national and international interest. Gastric problem is common in this area and 40 plant species were used for the treatment of this disease. Centella asiatica and Rauvolfia serpentina were the most valuable species in terms of its maximal use with higher use value. Comparison with the previous regional ethnomedicinal studies, we observed that 30 plant species documented in the present study were not having earlier reports. This means that the use of 30 plant species have been reported for the first time from this area for ethnomedicinal use. It was found that 38 ethnomedicinal plant species documented in this study were earlier reported for their conservation status from adjoining areas including endangered, frequent, planted, rare and sparse. The communities should be encouraged with improved cultivation techniques of commercially viable ethnomedicinal species through capacity building, timely policy intervention along with strong market linkage. This will ensure income generation and livelihood improvement and ultimate conservation of these species. The present information may serve as a baseline data to initiate further research for newly reported species for new compounds and biological activities which can be of immense value for societies to survive.
References
Van der Merwea D, Swana GE, Botha CJ. Use of ethnoveterinary medicinal plants in cattle by Setswana-speaking people in the Madikwe area of the North West Province of South Africa. J S Afr Vet Assoc. 2001;72:189–96.
Lewis WH, Elwin Lewis MP. Medical botany plants affecting human health. New York: Wiley; 2003. p. 812.
Iwu MM. African medicinal plants in the search for new drugs based on ethnomedicinal leads. In: Chadwick DJ, Marsh J, editors. Ethnobotany and the search for new drugs, Ciba foundation symposium 185. Chichester: Wiley; 1994. p. 116–29.
Reddy BM. Wild edible plants of Chandrapur district, Maharashtra, India. Indian J Nat Prod Resour. 2012;3:110–7.
Payyappallimana U, Fadeeva Z. Traditional knowledge and biodiversity. Yokohama: United Nations University-IAS; 2013.
Narzary H, Brahma S, Basumatary S. Wild edible vegetables consumed by BodoTribe of Kokrajhar District (Assam), North-East India. Arch Appl Sci Res. 2013;5:182–90.
Jain DL, Baheti AM, Jain SR, Khandelwal KR. Use of medicinal plants among tribes in Satpuda region of Dhule and Jalgaon districts of Maharashtra—an ethnomedicinal survey. Indian J Tradit Knowl. 2010;9:152–7.
Jeyaprakash K, Ayyanar M, Geetha KN, Sekar T. Traditional uses of medicinal plants among the tribal people in Theni districts (Western Ghats), Southern India. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2011;1:S20–5.
Kumar B, Vijayakumar M, Govindarajan R, Pushpangadan P. Ethnopharmacological approaches to wound healing—exploring medicinal plants of India. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007;114:103–13.
Shukla G, Chakravarty S. Ethnomedicinal plant use of Chilapatta reserved forest in West Bengal. Indian Forester. 2012;138:1116–24.
Biswakarma S, Sarkar BC, Shukla G, Pala NA, Chakravarty S. Traditional application of ethnomedicinal plants in Naxalbari area of West Bengal, India. Int J Usufruct Manag. 2015;16:36–42.
Sarkar BC, Biswakarma S, Shukla G, Pala NA, Chakravarty S. Documentation and utilization pattern of ethnomedicinal plants in Darjeeling Himalayas, India. Int J Usufruct Manag. 2015;16:3–11.
Kar A, Goswami NK, Saharia D. Wild edible plants sold in the local market of Garo hills, Meghalaya. J Frontline Res Arts Sci. 2012;2:69–78.
Suresh CP, Bhutia KD, Shukla G, Pradhan K, Chakravarty S. Free list of wild edible fruit species of Sikkim Himalayas and their uses. Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on Minor Fruits and Medicinal Plants for Better Lives 2013; pp.17-37.
Geng Y, Zhang Y, Ranjitkar S, Huai H, Wang Y. Traditional knowledge and its transmission of wild edibles used by the Naxi in Baidi Village, northwest Yunnan province. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2016;12:10–30.
Ferreira FS, Brito SV, Ribeiro SC, Almeido WO, Alves RRN. Zoo therapeutics utilized by residents of the community PocoDantas, Crato-CE, Brazil. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2009;5:21.
Phillips O, Gentry AH, Reynel C, Wilkin P, Galvez-Durand CB. Quantitative ethnobotany and Amazonian conservation. Conserv Biol. 2002;8:225–48.
Mekonen T, Giday M, Kelbessa E. Ethnomedicinal study of home garden plants in Sebeta-Awas District of the Oromia Region of Ethiopia to assess use, species diversity and management practices. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2015;11:64–76.
Ikram S, Bhatti KH, Parvaiz M. Ethnomedicinal studies of aquatic plants of district Sialkot, Punjab (Pakistan). J Med Plants Stud. 2014;2:58–63.
Amjad MS, Arshad M, Qureshi R. Ethnomedicinal inventory and folk uses of indigenous plants from PirNasoora National Park, Azad Jammu and Kashmir. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2015;5:234–41.
Hamidou A, Boube M, Mahamane L, Ali M, Mahamane S, Bellefontaine R. Uses and preferences of woody species in two protected forests of Dan Kada Dodo and Dan Gado in Niger. J Hortic For. 2015;7:149–59.
Jennings HM, Merrell J, Thompson JL, Heinrich M. Food or medicine? The food–medicine interface in households in Sylhet. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;167:97–104.
Li F, Zhuo J, Liu B, Jarvis D, Long C. Ethnomedicinal study on wild plants used by Lhoba people in Milin County, Tibet. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2015;11:23–33.
Łuczaj L, Stawarczyk K, Kosiek T, Pietras M, Kujawa A. Wild food plants and fungi used by Ukrainians in the western part of the Maramureş region in Romania. Acta Soc Bot Pol. 2015;84:339–46.
Singh U, Bharti AK. Ethnomedicinal study of plants of Raigarh area, Chhattisgarh, India. Int Res J Biol Sci. 2015;4:36–43.
Anand SP, Deborah S. Enumeration of wild edible fruits from Boda hills and Kolli hills. Int J Appl Biol Pharm Technol. 2016;7:96–102.
Shiracko N, Owuor BO, Gakuubi MM, Wanzala W. A survey of ethnobotany of the AbaWanga people in Kakamega county, western province of Kenya. Indian J Tradit Knowl. 2016;15:93–102.
Johnson LM, Hunn ES. Introduction. In: Johnson LM, Hunn ES, editors. Landscape ethnoecology: concepts of biotic and physical space. New York and Oxford: Berghahn Books 9; 2010. p. 1–11.
Frei B, Sticher O, Heinrich M. Zapotec and Mixe use of tropical habitats for securing medicinal plants in Mexico. Econ Bot. 2000;54:73–81.
Finerman R, Sackett R. Using home gardens to decipher health and healing in the Andes. Med Anthropol Q. 2003;17:459–82.
Sõukand R, Kalle R. Herbal landscape: the perception of the landscape as a source of medicinal plants. Trames. 2010;14(64/59):207–26.
Agelet A, Bonet MA, Vallès J. Home gardens and their role as a main source of medicinal plants in mountain regions of Catalonia (Iberian Peninsula). Econ Bot. 2000;54:295–309.
Stepp JR, Moerman DE. The importance of weeds in ethnopharmacology. J Ethnopharmacol. 2001;75:19–23.
Thomas E, Vandebroek I, Van Damme P, Goetghebeur P, Douterlungne D, Sanca S, Arrázola S. The relation between accessibility, diversity and indigenous valuation of vegetation in the Bolivian Andes. J Arid Environ. 2009;73:854–61.
Bose D. An ethno-medicobotanical investigation among Rava tribe of Jalpaiguri district .NBU. J Plant Sci. 2011;5:61–5.
Khan FM. Ethno-veterinary medicinal usage of flora of greater Cholistan desert (Pakistan). Pak Vet J. 2009;29:75–80.
Selvaraju A, Ayyanar M, Rathinakumar SS, Sekar T. Plants used in ethno-veterinary medicine by Malayali tribals in Salem district of Tamil Nadu, India. Med Plants. 2011;3:1–7.
Devendrakumar D, Anbazhagan M. Ethnoveterinary medicinal plants used in Perambalur District, Tamil Nadu. Res Plant Biol. 2012;2:24–30.
Verma RK. An ethnomedicinal study of plants used for the treatment of livestock diseases in Tikamgarh District of Bundelkhand, Central India. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2014;4:S460–7.
Uprety Y, Poudel RC, Gurung J, Chettri N, Chaudhary RP. Traditional use and management of NTFPs in Kanchenjunga Landscape: implications for conservation and livelihoods. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2016;12:19–77.
Bose D, Ghosh Roy J, Das Mahapatra (Sarkar) S, Datta T, Das Mahapatra S, Biswas H. Medicinal plants used by tribals in Jalpaiguri district, West Bengal, India. J Med Plants Stud. 2015;3:15–21.
Ignacimuthu S, Ayyanar M, SankaraSivaraman K. Ethnobotanical investigations among tribes in Madurai district of Tamil Nadu (India). J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2006;2:25–31. https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-4269-2-25.
Rokaya MB, Uprety Y, Poudel RC, Timsina B, Münzbergová Z, Asselin H, Tiwari A, Shrestha SS, Sigdel SR. Traditional uses of medicinal plants in gastrointestinal disorders in Nepal. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;158:221–9.
Moore PD. Trials in bad taste. Nature. 1994;370:410–1.
Singh A, Dubey NK. An ethnomedicinal study of medicinal plants in Sonebhadra district of Uttar, Pradesh, India with reference to their infection by foliar fungi. J Med Plants Res. 2012;6:2727–46.
Mathur A, Joshi H. Ethnobotanical studies of the Terai region of Kumaun, Uttarakhand, India. Ethnobot Res Appl. 2013;11:175–203.
Dar BA, Verma RK, Haq A. Ethnoveterinary value of some plant species utilized by rural people of Jhansi district, Bundelkhand region. Res J Agri Sci. 2011;2:321–4.
Singh A, Singh GS, Singh PK. Medico-ethnomedicinal inventory of Renukoot forest division of district Sonbhadra, Uttar Pradesh, India. Indian J Nat Prod Resour. 2012;3:448–57.
Phondani PC, Maikhuri RK, Rawat LS, Farooquee NA, Kala CP, Vishvakarma SCR, Rao KS, Saxena KG. Ethnobotanical uses of plants among the Bhotiya tribal communities of Niti valley in Central Himalaya, India. Ethnobot Res Appl. 2010;8:233–44.
Sharma J, Gairola S, Gaur RD, Painuli RM. The treatment of jaundice with medicinal plants in indigenous communities of the sub-Himalayan region of Uttarakhand, India. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012;143:262–91.
Sharma J, Gairola S, Gaur RD, Painuli RM, Siddiqi TO. Ethnomedicinal plants used for treating epilepsy by indigenous communities of sub-Himalayan region of Uttarakhand, India. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013;150:353–70.
Sharma J, Gairola S, Gaur RD, Siddiqi TO, Painuli RM. Plants used for treatment of dysentery and diarrhoea by the Bhoxa community of district Dehradun, Uttarakhand, India. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013;150:969–1006.
Shukla G. Biomass production and vegetation analysis of Chilapatta reserve forest ecosystem of West Bengal. Pundibari West Bengal: Ph. D. Thesis. Uttar Banga Krishi Viswavidyalaya; 2010.
Chhetri DR, Basnet D, Chou PF, Kalikotay S, Chhetri G, Parajuli S. Current status of ethnomedicinal plants in the Darjeeling Himalaya. Curr Sci. 2005;89:264–8.
Yonzone R, Bhujel RB, Rai S. Genetic resources, current ecological status and altitude wise distribution of medicinal plants diversity of Darjeeling Himalaya of West Bengal, India. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2012;2:S439–45.
Pandey AR. Conservation of biodiversity: present status & future strategy. In: Pandey AK, editor. Taxonomy and biodiversity. Delhi: CBS Publishers; 1995. p. 44–51.
Bhujel RB. Studies on the dicotyledonous flora of Darjeeling district. Ph. D. Thesis. Siliguri: North Bengal University; 1996.
Farooquee NA, Saxena KG. Conservation and utilization of medicinal plants in high hills of Central Himalaya. Environ Conserv. 1996;23:75–80.
Kala CP. Indigenous knowledge of Bhotia tribal community on wool dying and its present status in the Garhwal Himalaya, India. Curr Sci. 2002;83:814–7.
Maikhuri RK, Nautiyal KS, Rao KS, Semwal RL. Indigenous knowledge of medicinal plant and wild edibles among the three tribal sub-communities of the Central Himalaya, India. Indigenous Knowl Dev Monit. 2000;8:7–13.
Ghosh A. Ethnomedicinal plants used in West Rahrr region of West Bengal. Nat Prod Radiance. 2008;75:461–5.
Dhillion SS, Shrestha PM. Conservation needs and regulations for locally managed forests in the highlands of Dolakha district, Nepal. In: Salleh H, Aziz S, editors. Environmental and development aspects of natural resource management in mountains. Singapore: Pelanduk Press; 2005.
Etkin NL. Local knowledge of biotic diversity and its conservation in rural Hausaland, Northern Nigeria. Econ Bot. 2002;56:73–88.
Rai MB. Medicinal plants of Tehrathum District, Eastern Nepal. Our Nature. 2003;1:42–8.
Bandyopadhyay S, Mukherjee SK. Wild edible plants of Koch Bihar district, West Bengal, India. Nat Prod Radiance. 2009;8:64–72.
Murad W, Azizullah A, Adnan M, Tariq A, Khan KU, Waheed S, Ahmad A. Ethnomedicinal assessment of plant resources of Banda Daud Shah, District Karak, Pakistan. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2013;9:77–86.
Sanghi SB. Study of some ethno-veterinary medicinal plants of Tendukheda, district Narsinghpur, Madhya Pradesh. Life Sciences Leaflets. 2014;55:1–5.
Takhar HK. Folk herbal veterinary medicines of southern Rajasthan. Indian J Tradit Knowl. 2004;3:407–18.
Verma P, Mathur AK, Jain SP, Mathur A. In vitro conservation of twenty-three over exploited medicinal plants belonging to the Indian sub continent. Sci World J. 2012;12 https://doi.org/10.1100/2012/929650.
Malla B, Chhetri RB. Ethnoveterinary practices of some plant species by ethnic people of Parbat district, Nepal. Kathmandu Univ J Sci Eng Technol. 2012;8:44–50.
Chettri D, Moktan S, Das AP. Ethnomedicinal studies on the tea garden workers of Darjeeling Hills. Pleione. 2014;8:124–32.
Padal SB, Chandrasekhar P, Satyavathi K. Ethnomedicinal investigation of medicinal plants used by the tribes of PedabayaluMandalam, Visakhapatnam District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Int J Comput Eng Res. 2013;3:8–13.
Yonzone R, Rai S, Bhujel RB. Ethnomedicinal and aromatic plant diversity and resources of Darjeeling district of eastern Himalaya in India. Int J Adv Pharm Res. 2012;3:859–71.
Yonzone R, Rai S, Bhujel RB. Genetic diversity of ethnobotanical and medicinal plants resources of Darjeeling district, West Bengal, India. Int J Adv Pharm Res. 2012;3:713–29.
Joshi K, Joshi R, Joshi AR. Indigenous knowledge and uses of medicinal plants in Macchegaun, Nepal. Indian J Tradit Knowl. 2011;10:281–6.
Singh A, Singh RK, Bhardwaj R, Singh AK. Adaptations of culturally and nutritionally important traditional foods in Eastern Himalaya: a case study with Adi women of Arunachal Pradesh. Indian J Tradit Knowl. 2012;11:623–33.
Samar R, Shrivastava PN, Jain M. Ethnomedicinal study of traditional medicinal plants used by tribe of Guna District, Madhya Pradesh, India. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci. 2015;4:466–71.
Singh AG, Kumar A, Tewari DD. An ethnomedicinal survey of medicinal plants used in Terai forest of western Nepal. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2012;8:19–32.
Simbo DJ. An ethnomedicinal survey of medicinal plants in Babungo, Northwest Region, Cameroon. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2010;6:8–14.
Shrivastava S, Kanungo VK. Ethnomedicinal survey of Surguja district with special reference to plants used by Uraon tribe in treatment of diabetes. Int J Herb Med. 2013;1:127–30.
Malla S, Shukla G, Chakravarty S. Utilization and conservation of wild plants by the tribal communities of Tripura. Indian Forester. 2012;138:1002–7.
Ghosh SK, Guria N, Sarkar A, Ghosh A. Traditional herbal remedies for various ailments within the rural communities in the district of Bankura and Purulia, West Bengal, India. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2013;5:195–8.
Jose T, Sebastian A, Antony VT. Ethnomedicinal study of traditional medicinal plants used by indigenous people in North Kerala. Indian J Appl Res. 2015;5:184–6.
Das HB, Majumdar K, Datta BK, Ray D. Ethnomedicinal uses of some plants by Tripuri and Reang tribes of Tripura. Nat Prod Radiance. 2009;8:172–80.
Choudhary K, Singh M, Pillai U. Ethnobotanical survey of Rajasthan—an update. Am-Eurasian J Bot. 2008;1:38–45.
Sinhababu A, Banerjee A. Ethno-botanical study of medicinal plants used by tribals of Bankura district, West Bengal, India. J Med Plants Stud. 2013;1:98–104.
Mondal T, Mondal D, Mondal S. Conservation strategies of medicinal plants with reference to North Bengal for a better tomorrow. J Todays Biol Sci Res Rev. 2013;2:83–8.
Mondal T, Samanta S. An ethnomedicinal survey on medicinal plants of Ghatal block, West Midnapur District, West Bengal, India. Int J Curr Res Biosci Plant Biol. 2014;1:35–7.
Achar KG, Somashekhara Boosanur V, Shivanna MB. Ethno-medico-botanical knowledge of Tipturtaluk in Tumkur district of Karnataka, India. Indian J Tradit Knowl. 2015;1:147–54.
Konsam S, Thongam B, Handique AK. Assessment of wild leafy vegetables traditionally consumed by the ethnic communities of Manipur, northeast India. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2016;12:9–23.
Kumar A, Avasthe RK, Shukla G, Pradhan Y. Ethnobotanical edible plant biodiversity of Lepcha tribes. Indian Forester. 2012;138:798–803.
Hong H, Zhuo J, Lei Q, Zhou J, Ahmed S, Wang C, Long Y, Li F, Long C. Ethnobotany of wild plants used for starting fermented beverages in Shui communities of southwest China. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2015;11:42–62.
Tiţă I, Mogoşanu GD, Tiţă MG. Ethnomedicinal inventory of medicinal plants from the south-west of Romania. Farmacia. 2009;57:141–56.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all the participants in the study for providing ethnomedicinal information.
Funding
This study is self-financed.
Availability of data and materials
The data and material is available from the corresponding author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SB, NP, GS, and V designed the study, collected the data and developed the manuscript. MK, SC, RWB and AJR improved the manuscript and restructured the data analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Prior oral informed consent was obtained from the local communities as well as from all individual participants.
Consent for publication
All participants gave consent for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Raj, A.J., Biswakarma, S., Pala, N.A. et al. Indigenous uses of ethnomedicinal plants among forest-dependent communities of Northern Bengal, India. J Ethnobiology Ethnomedicine 14, 8 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13002-018-0208-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13002-018-0208-9