Abstract
Background
Expansion of the myocardial extracellular volume (ECV) is a surrogate measure of focal/diffuse fibrosis and is an independent marker of prognosis in chronic heart disease. Changes in ECV may also occur after myocardial infarction, acutely because of oedema and in convalescence as part of ventricular remodelling. The objective of this study was to investigate changes in the pattern of distribution of regional (normal, infarcted and oedematous segments) and global left ventricular (LV) ECV using semi-automated methods early and late after reperfused ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI).
Methods
Fifty patients underwent cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging acutely (24 h–72 h) and at convalescence (3 months). The CMR protocol included: cines, T2-weighted (T2 W) imaging, pre−/post-contrast T1-maps and LGE-imaging. Using T2 W and LGE imaging on acute scans, 16-segments of the LV were categorised as normal, oedema and infarct. 800 segments (16 per-patient) were analysed for changes in ECV and wall thickening (WT).
Results
From the acute studies, 325 (40.6%) segments were classified as normal, 246 (30.8%) segments as oedema and 229 (28.6%) segments as infarct. Segmental change in ECV between acute and follow-up studies (Δ ECV) was significantly different for normal, oedema and infarct segments (0.8 ± 6.5%, −1.78 ± 9%, −2.9 ± 10.9%, respectively; P < 0.001). Normal segments which demonstrated deterioration in wall thickening at follow-up showed significantly increased Δ ECV compared with normal segments with preserved wall thickening at follow up (1.82 ± 6.05% versus −0.10 ± 6.88%, P < 0.05).
Conclusion
Following reperfused STEMI, normal myocardium demonstrates subtle expansion of the extracellular volume at 3-month follow up. Segmental ECV expansion of normal myocardium is associated with worsening of contractile function.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Find the latest articles, discoveries, and news in related topics.Background
Following ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), even with immediate mechanical reperfusion therapy, 24–30% patients develop adverse left ventricular (LV) remodelling [1, 2]. LV remodelling is a predictor of heart failure, and hence is associated with morbidity and mortality. Post infarct, the acute loss of myocardial function results in an abrupt increase in LV loading conditions that induces a unique pattern of remodelling involving the normal (non-infarcted non-oedematous myocardium), oedematous (injured with oedematous myocardium) and infarcted myocardium [3].
The chronic phase of LV remodelling involves compensatory myocyte hypertrophy and alterations in ventricular geometry to distribute the increased wall stresses more evenly [4]. Early pre-clinical studies have speculated that the ‘normal’ non-infarcted myocardium also undergoes changes due to increased wall stress [5, 6]. There is limited evidence to support these concepts in humans. Additionally, it remains unknown if these changes in tissue composition of normal myocardium have any impact on regional contractility.
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) offers comprehensive multi-parametric structural and functional assessment in patients with STEMI [7]. Using early gadolinium enhancement (EGE) and late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) imaging, accurate assessment of infarct characteristics (infarct size, transmurality of scar, presence of microvascular obstruction and LV thrombus) can be made. T2-weighted (T2 W) imaging allows to diagnose and quantify the extent of myocardial oedema following acute ischaemic injury [8, 9]. Native T1-mapping can also detect acute ischaemia and combined with post contrast T1 mapping allows quantification of the extra-cellular volume (ECV) [10,11,12,13].
This study aimed to investigate whether ECV expansion of normal myocardium occurs after STEMI and whether it is associated with a reduction in contractile function between baseline and follow up assessment. We also sought to determine the baseline CMR parameters that are most strongly associated with segmental functional change at follow up.
Methods
Study population
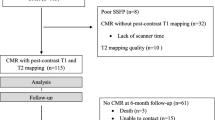
Patients with acute STEMI were prospectively enrolled from a single UK tertiary centre. The study design is detailed in Fig. 1.
The inclusion criteria were as follows: patients with first time acute STEMI treated by primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PPCI) within 12-h of onset of chest pain. Acute STEMI was defined as per current international guidelines [14]. Exclusion criteria included: previous myocardial infaction, coronary artery bypass grafting, known cardiomyopathy, estimated glomerular filtration rate < 30 ml/min/1.73 m2, haemodynamic instability (requiring on-going intravenous therapy or respiratory support) and contraindication to CMR imaging. After revascularization, all patients received standard post-myocardial infarction secondary prevention therapy at the discretion of the treating physician, and were enrolled in a cardiac rehabilitation programme if they were deemed suitable [15].
Cardiac catheterization
Coronary angiography and revascularisation were performed in a standard fashion as per current best practice guidelines [15, 16]. TIMI flow grades were assessed visually as described previously following coronary angioplasty [17].
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance
All patients underwent CMR imaging at either 1.5 Tesla (Ingenia CV, Philips Healthcare, Best, The Netherlands) or 3.0 Tesla (Achieva TX, Philips Healthcare, Best, The Netherlands). The choice of field strength was arbitrary and was predominantly dictated by availability of the scanners. A dedicated cardiac phased array receiver coil was used (1.5 T: 24-channel equipped with d-stream; 3 T: 32-channel). Acute CMR imaging was scheduled within 72-h of the index presentation and patients were invited to attend for a further CMR study at 3-months follow-up. The same field strength scanners were used for respective patients as for the acute scans.
Image acquisition
Cine, T2 W-imaging, EGE and LGE imaging were performed in contiguous stacks of short-axis slices covering the entire LV for each acquisition. The same slice geometry, position and 10 mm slice thickness were used for all pulse sequences.
T1-maps acquisition
Native and post-contrast T1-maps were planned using the ‘3-of-5’ approach [18]. Post-contrast T1-maps were timed at 15 min after contrast administration and LGE-imaging was performed at 16–20 min.
Image analysis
For each pulse sequence, images with artefact were repeated until any artefact was removed or minimized. The highest quality images were used for analysis. Cine, T2 W-images, EGE-images and LGE-images were evaluated offline using MASS research software (Version 2016EXP, Leiden University Medical Centre, Leiden, The Netherlands).
Basic CMR image analysis, T1-maps quality assurance checks, pulse sequence parameters and imaging protocol are described in the online Additional file 1.
Categorising of left ventricular segments
Sixteen segments of the LV excluding the apex, adapted from the 17 segments of the American Heart Association (AHA) model [19], were visually assessed on acute CMR scans and labelled as 1) normal segment (no oedema on T2 W-imaging and no infarct on LGE-imaging), 2) oedema segment (predominantly oedema on T2 W-imaging with no infarct on LGE-imaging 3) infarct segment (presence of any infarction on LGE-imaging with/without oedema on T2 W-imaging).
Myocardial wall thickening analysis
Segmental myocardial systolic wall thickening (WT) analysis was performed for each slice based on endo- and epi-cardial contours. For each segment, end-diastolic and end-systolic wall thickness (EDWT and ESWT, respectively [mm]) were recorded as per previously published literature [20]. This method has demonstrated high intra-inter-observer agreement [21]. Myocardial systolic segmental WT ([mm]) was calculated as absolute change in EDWT and ESWT. For each LV segment, delta change of WT was derived. Functional improvement of segments was defined as positive delta change of WT from baseline to follow-up and vice versa. Additionally, radial strain was computed using endo−/epi- cardial contours through-out the complete cardiac cycle as per previously described methods [22].
Extracellular volume map analysis
ECV maps were generated for the 3 slices (base, mid and apex) from pre−/post-contrast T1-maps and haematocrit as per the standard techniques [10]. The endocardial and epicardial contours were outlined to define myocardium in the 3 slices. Microvascular obstruction (MVO) contours were imported from EGE imaging. Mean ECV values were generated for each segment of the 16 segments excluding the MVO in the infarct zone. Left ventricular global ECV was calculated by multiplication of the averaged per-patient ECV values (for all the 16 segments) and indexed LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV). Similarly, left ventricular myocyte cell volume was calculated by using the previously published formula: (1-global ECV)*(indexed LVEDV) [23]. For each patient, mean ECV values for different types of segments (normal, oedema and infarct) were generated on both acute and follow-up studies. For each patient, increase or decrease of ECV of all non-infarcted, healthy myocardium was defined as the change in the mean ECV of all segments and this was investigated for its association with patient characteristics (Table 1).
Adverse LV remodelling was defined as an absolute increase of LV end-systolic volumes >15% at 3 months follow-up [24, 25].
Intra−/inter-observer segmental ECV assessment
For intra−/inter-observer assessments, 48 segments were selected from three randomly chosen scans. To test the inter-observer reliability of segmental ECV values, two blinded observers carried out independent segmentation of ECV-maps (PG and SC) in these segments. To test intra-observer reliability, one observer (PG) undertook a second blinded analysis after three months.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS® Statistics 21.0 (International Business Machines, Inc., Chicago, Illinois, USA). Normality of quantitative data was established using the Shapiro-Wilk test. Normally distributed continuous variables are expressed as mean ± SD and non-normally distributed are expressed as median (25th–75th quartile ranges). Demographic comparisons between patients with rise and fall of ECV at follow-up, in the normal myocardial segments, were performed with an independent samples t-test for normally distributed variables and by Mann-Whitney independent t-test for not normally distributed. For paired comparison in Table 2, Wilcoxon test was used. A repeated-measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed on demographic and global ECV (rise/fall) at follow-up. Linear regression was used to investigate which baseline study parameter was most strongly associated with number of segments with functional recovery at follow-up. Univariate analysis was performed for each variable separately. Step-wise multivariate linear regression was used for parameters with statistical significance from one-way analysis (p < 0.1). Intra−/inter-observer agreement was assessed by investigating the coefficient of variability (CV), concordance correlation coefficient (CCC), precision and accuracy. All statistical tests were 2-tailed; p values <0.05 were considered significant.
Sample size calculations
We used data of remote zone ECV from published literature using to inform the sample size calculations for this study. In a previous study, delta remote zone ECV in patients with/without adverse LV remodelling were: 0.9 ± 2.2% (with adverse LV remodelling, n = 8) versus 0.9 ± 0.9% (without adverse LV remodelling, n = 32) [26]. Using these data, as per the mean comparison method described by Machin et al., 295 normal segments were needed to investigate functional changes. [27]. Presuming 40% of myocardium is normal post STEMI, the study thus needed to recruit at least 46 patients to give a power of 80% at an alpha of 0.05.
Results
Patient characteristics
Seventy patients were considered for inclusion, of which 50 had baseline and follow-up CMR (Fig. 1). Acute scans were performed at a median of 48 h after the index presentation. 32 patients had CMR at 1.5 Tesla and 18 patients had CMR at 3 Tesla. All 50 patients were included in the statistical analysis. Clinical and patient demographics are detailed in Table 1.
Per-patient analysis
Patients were categorised into two groups depending on the rise/fall of normal myocardial ECV between baseline and follow-up studies (Table 1). Twenty-eight patients (56%) demonstrated an increase in average normal myocardial ECV at follow-up when compared to acute ECV. No significant differences were seen in baseline demographics between the two groups of patients with a rise or fall of delta-ECV. Patients with triple vessel disease were more prevalent in the group that showed a rise in ECV in normal segments (1 patient versus 7 patients, P = 0.05). There were no differences relating to the field strength of the scanner that was use and the 3 T patients, 10 patients (55.6%) demonstrated ECV expansion in normal myocardial versus 18 (56.2%) on the 1.5 T (P = 0.96 for comparison of 3 T and 1.5 T). LV mass reduced significantly from baseline to follow-up, but global ECV and myocyte cell volume showed no significant change (Table 2).
Per-segment analysis
800 segments were analysed acutely and at follow-up. From the acute studies, 325 (40.6%) segments were classified as normal, 246 (30.8%) segments were classified as oedema and 229 (28.6%) segments were classified as infarct segments. Myocardial oedema was only seen in the peri-infarct zone of the culprit vessel.
Intra−/inter-observer checks for segmental ECV
For the 48 segments which were analysed, intra-observer CV was 6%, with excellent CCC (0.94, 95% CI 0.90–97), high precision (0.95) and accuracy (0.99). For the inter-observer analysis, CV was 7%, with good CCC (0.92, 95% CI 0.87–95) and high precision (0.93) and accuracy (0.99).
Pattern of ECV change
Oedema and infarct segments demonstrated significant reductions in ECV at follow-up (Table 2). Conversely, there was a smaller but statistically significant rise in the ECV of normal myocardium at follow-up (P = 0.03).
Segmental change in ECV between acute and follow-up studies was significantly different for normal, oedema and infarct segments (0.8 ± 6.5% versus −1.78 ± 9% or −2.9 ± 10.9%; P < 0.001) (Fig. 2).
Temporal changes in normal segmental ECV did not demonstrate any significant association with number of >50% transmural scar segments (Fig. 3).
Segmental ECV and WT
Acute segmental ECV demonstrated significant correlation to both acute segmental WT (P < 0.0001) and to follow-up segmental WT (P < 0.0001) (Table 3). There was a significant increase in ΔECV in normal segments which demonstrated deterioration in wall thickening (Table 3, Fig. 4). For the oedema and infarct segments, ΔECV was significantly different (less or no improvement) in segments with a decrease in wall thickening versus segments that demonstrated improvement in wall thickening (P < 0.05, Table 3, Fig. 5). All segments with functional improvement showed a reduction in follow-up ECV. The percentage of “normal” myocardial segments that demonstrated functional improvement and greater than normal acute baseline ECV (>28%) was not significantly different to “normal” segments with no functional recovery (54% versus 53%, P = 0.33).
Peak systolic radial strain results are detailed in the online ‘Supplementary material’. Acute ECV of the normal, oedema and infarct segments demonstrated an inverse relation to final follow-up radial strain (Fig. 6).
By univariable analysis of all demographic and CMR parameters, acute oedema and infarct segment ECVs demonstrated association to number of segments (per-patient) that had improvement in function (Table 4). On multivariable linear regression analysis, infarct ECV was most strongly associated with number of segments with functional improvement (beta = 0.4, P = 0.037).
Adverse LV remodelling
Acute myocardial ECV of normal segments was significantly higher in patients who demonstrated adverse LV remodelling (P = 0.04) (Table 5). Infarct and oedema acute ECV did not demonstrate a difference depending on the presence of adverse LV remodelling at follow-up.
Discussion
The present study demonstrates that 1) in reperfused STEMI, normal myocardial segments show a subtle expansion of the ECV between baseline and 3 month follow-up; 2) conversely, oedematous and infarcted segments show a significant reduction in ECV at follow up; 3) normal segments that demonstrate deterioration in segmental function at follow-up show a substantial increase in delta-ECV from baseline to follow up; 4) acute infarct ECV demonstrates the best association with the number of segments with functional recovery (Fig. 3) and 5) high acute normal myocardial segmental ECV is associated with adverse LV remodelling at follow-up.
Previous studies have already shown that ECV is raised in ‘remote’ myocardium in acute STEMI [26, 28]. Remote myocardium is defined as the AHA segment 180-degrees from the infarct territory with normal motion and no LGE [26, 28]. In the present study, we chose to assess all segments that did not have evidence of oedema or infarction and in order to avoid misinterpretation with the standard definition of ‘remote’ myocardium, defined these as ‘normal’ segments. Carberry et al. demonstrated that acute remote zone ECV post STEMI is associated with certain baseline patient characteristics (male gender, body mass index and history of diabetes) [28]. They also showed that the remote zone ECV was associated with the level of baseline N-terminal pro b-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP). In our study the number of patients with angiographic triple vessel disease was marginally higher in patients with increased normal myocardial ECV when compared to patients with 0−/1−/2-vessel disease (Table 1, P = 0.05). We speculate that in triple vessel disease, coronary steal may reduce flow in non-culprit vessels due to better flow down the revascularised culprit vessel, which may cause adverse tissue level remodelling [29,30,31]. Other possible mechanisms which influence non-infarcted myocardium include increased loading conditions secondary to infarct characteristics. For example, Litwin et al.’s pre-clinical work demonstrated that the extra-cellular matrix of the non-infarcted normal myocardium undergoes expansion mainly due to increased wall stresses [6].
Associations of segmental ECV and segmental and global function have been studied previously [26, 32, 33]. Collins et al. demonstrated that the segmental extent of fibrosis is associated with segmental function in non-ischaemic cardiomyopathy [33]. Additionally, they demonstrated that this linear association was still relevant in patients with preserved global function and in patients with no late gadolinium enhancement. Our study has now shown that mean ECV is also associated with segmental function in patients with acute STEMI. Bulluck et al. demonstrated that mean segmental ECV in the remote myocardium is raised acutely post STEMI (18). Their mean segmental remote myocardial ECV values are comparable to the present study’s ‘normal’ myocardial segment ECV (27.9 ± 2.1%).
Remote (defined as normal myocardium in this study) myocardial dysfunction after STEMI is considered the main reason why some patients demonstrate function loss that is disproportionate to infarct size [30, 34]. Bogaert et al. demonstrated that remote myocardial dysfunction contributes significantly to the loss in global ventricular function. The present study confirms that normal myocardium with no obvious oedema or infarction can also be affected by functional loss measured by either LV wall thickening or radial strain. Additionally, this study further shows that normal myocardial segments after acute MI which demonstrate dysfunction also have significant extracellular matrix expansion. This could be explained by increased reactive fibrosis during the proliferative and maturation phase of remodelling, in the extracellular matrix of the normal myocardial segments, mainly due to higher wall shear stresses [35].
A recent study from our group demonstrated that acute ‘infarct zone’ ECV is predictive of regional and global LV functional recovery, and adds prognostic value over LGE [36]. Particularly for infarcts with higher transmural extent, acute infarct ECV was an additional predictor of functional recovery that can complement transmural infarct extent by LGE. In addition to these previously reported findings, we have now shown that acute infarct mean segmental ECV correlates with segmental functional recovery at follow-up and that a reduction in ECV in infarct segments is associated with improvement in regional function at follow-up.
This is the first in-vivo study that reports longitudinal changes in segmental ECV in non-infarcted normal, oedema and infarcted LV segments. Our data suggest that non-oedematous, non-infarcted normal LV myocardium undergoes remodelling with a subtle expansion of the extracellular matrix (Fig. 7). In particular, normal myocardial segments which demonstrate myocardial functional loss at follow-up have an increase in ECV.
Illustration to demonstrate changes in tissue composition post-acute reperfused myocardial infarction. The infarcted myocardial segments demonstrate reduction in overall ECV on follow-up as the damaged myocytes recover function even in the presence of scar. This leads to some function improvement in these infarcted segments. The oedema segments demonstrate significant reduction in ECV as the water content of extracellular matrix falls. Oedema segments also demonstrate significant improvement in function. The normal segments undergo physiological adaptation with involves increase in extracellular volume. This is likely to be the result of overall left ventricular remodelling
Limitations
Of 70 patients that underwent initial screening for recruitment only 50 patients underwent the entire protocol possibly introducing an element of selection bias. However, in a clinical study of acutely ill patients, exclusion or drop out of patients is common and our exclusion rate is within that reported in similar previous reports [9, 37]. There were other caveats to the present study: firstly, segments specifically classified as infarct also conceivably had oedema, which may have altered the results for respective segments. An important limitation of T1-mapping for clinical application is possible partial volume contamination from blood. Nevertheless, MOLLI sequences used in the present study, have been shown to be precise and reproducible [38]. The results of this study may be influenced by the tethering and local interaction of “adjacent” (to peri-infarct zone) normal myocardium. Changes in the adjacent normal myocardium may demonstrate a different pattern of temporal changes when compared to remote myocardium.
Conclusion
This study suggests that following reperfused STEMI, the ‘normal’ LV myocardium undergoes remodelling with a subtle expansion of the extracellular matrix. In particular, normal segments which have functional loss demonstrate significant expansion of the extracellular space. Additionally, acute myocardial ECV of normal segments was significantly higher in patients who experienced adverse LV remodelling. Myocardial segments with oedema and infarction demonstrate significant reduction in ECV.
Abbreviations
- AHA:
-
American Heart Association
- ANOVA:
-
a repeated-measures analysis of variance
- CCC:
-
concordance correlation coefficient
- CMR:
-
cardiovascular magnetic resonance
- CV:
-
coefficient of variability
- ECV:
-
extracellular volume
- EDWT:
-
end-diastolic wall thickness
- EGE:
-
early gadolinium enhancement
- ESWT:
-
end-systolic wall thickness
- LGE:
-
late gadolinum enhancement
- LV:
-
left ventricle/left ventricular
- LVEDV:
-
left ventricular end-distolic volume
- MVO:
-
microvascular obstruction
- NT-proBNP:
-
N-terminal pro b-type natriuretic peptide
- PPCI:
-
primary percutaneous coronary intervention
- STEMI:
-
ST-elevation myocardial infarction
- T2 W:
-
T2-weighted
- TIMI:
-
Thrombolysis In Myocardial Infarction
- WT:
-
wall thickening
References
Galli A, Lombardi F. Postinfarct Left Ventricular Remodelling: A Prevailing Cause of Heart Failure. Cardiol. Res. Pract. [Internet]. Hindawi Publishing Corporation; 2016 [cited 2016 Nov 20];2016:1–12 Available from: http://www.hindawi.com/journals/crp/2016/2579832/
Velagaleti RS, Pencina MJ, Murabito JM, Wang TJ, Parikh NI, D’Agostino RB, et al. Long-term trends in the incidence of heart failure after myocardial infarction. Circulation [Internet]. 2008 [cited 2016 Nov 20];118:2057–2062. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18955667.
Sutton MGSJ, Sharpe N. Left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2000;101
Konstam MA, Kramer DG, Patel AR, Maron MS, Udelson JE. Left ventricular remodeling in heart failure: current concepts in clinical significance and assessment. JACC. Cardiovasc Imaging. [Internet]. 2011 [cited 2016 Nov 20];4:98–108. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21232712.
Pfeffer MA, Braunwald E. Ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. Experimental observations and clinical implications. Circulation [Internet]. 1990 [cited 2016 Sep 23];81:1161–1172. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2138525.
Litwin SE, Litwin CM, Raya TE, Warner AL, Goldman S. Contractility and stiffness of noninfarcted myocardium after coronary ligation in rats. Effects of chronic angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition. Circulation. 1991 [cited 2016 Nov 20];83:1028–1037. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1999008.
Garg P, Underwood SR, Senior R, Greenwood JP, Plein S. Noninvasive cardiac imaging in suspected acute coronary syndrome. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2017 Feb 11];13:266–275. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26911331.
Garg P, Kidambi A, Swoboda PP, Foley JRJ, Musa TA, Ripley DP, et al. The role of left ventricular deformation in the assessment of microvascular obstruction and intramyocardial haemorrhage. Int. J. Cardiovasc Imaging. Springer Netherlands; 2016 [cited 2016 Nov 6];1–10 Available from: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10554-016-1006-x
Garg P, Kidambi A, Foley JRJ, Musa T Al, Ripley DP, Swoboda PP, et al. Ventricular longitudinal function is associated with microvascular obstruction and intramyocardial haemorrhage. Open Hear. British Cardiovascular Society; 2016 [cited 2016 may 18];3:e000337. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27175286.
Moon JC, Messroghli DR, Kellman P, Piechnik SK, Robson MD, Ugander M, et al. Myocardial T1 mapping and extracellular volume quantification: a Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (SCMR) and CMR Working Group of the European Society of Cardiology consensus statement. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. [Internet]. BioMed Central; 2013 [cited 2016 Feb 27];15:92 Available from: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=3854458&tool=pmcentrez&rendertype=abstract
Kellman P, Wilson JR, Xue H, Ugander M, Arai AE. Extracellular volume fraction mapping in the myocardium, part 1: evaluation of an automated method. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. [Internet]. 2012 [cited 2016 Nov 20];14:63 Available from: http://jcmr-online.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1532-429X-14-63
Kellman P, Wilson JR, Xue H, Bandettini WP, Shanbhag SM, Druey KM, et al. Extracellular volume fraction mapping in the myocardium, part 2: initial clinical experience. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. [Internet]. 2012 [cited 2014 Sep 27];14:64 Available from: http://www.jcmr-online.com/content/14/1/63
Garg P, Broadbent DA, Swoboda PP, Foley JRJ, Fent GJ, Musa TA, et al. Acute Infarct Extracellular Volume Mapping to Quantify Myocardial Area at Risk and Chronic Infarct Size on Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance ImagingCLINICAL PERSPECTIVE. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2017 Jul 22];10:e006182. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28674085.
Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, Simoons ML, Chaitman BR, White HD, et al. Third universal definition of myocardial infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. [Internet]. 2012 [cited 2014 Nov 10];60:1581–1598. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22958960.
Steg PG, James SK, Atar D, Badano LP, Blömstrom-Lundqvist C, Borger MA, et al. ESC Guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation. Eur. Heart J. [Internet]. 2012 [cited 2014 Jul 9];33:2569–2619. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22922416.
Levine GN, Bates ER, Bittl JA, Brindis RG, Fihn SD, Fleisher LA, et al. 2016 ACC/AHA Guideline Focused Update on Duration of Dual Antiplatelet Therapy in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines: An Update of the. Circulation [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2016 Apr 8];134:e123–e155 Available from: http://circ.ahajournals.org/lookup/doi/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000404
The Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) trial. Phase I findings. TIMI Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. [Internet]. 1985 [cited 2015 Dec 25];312:932–936. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4038784.
Messroghli DR, Bainbridge GJ, Alfakih K, Jones TR, Plein S, Ridgway JP, et al. Assessment of regional left ventricular function: accuracy and reproducibility of positioning standard short-axis sections in cardiac MR imaging. Radiology. 2005 [cited 2015 Aug 12];235:229–236. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15731374.
Cerqueira MD, Weissman NJ, Dilsizian V, Jacobs AK, Kaul S, Laskey WK, et al. Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for tomographic imaging of the heart. A statement for healthcare professionals from the Cardiac Imaging Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology of the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2002 [cited 2014 Nov 15];105:539–542. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11815441.
Nowosielski M, Schocke M, Mayr A, Pedarnig K, Klug G, Köhler A, et al. Comparison of wall thickening and ejection fraction by cardiovascular magnetic resonance and echocardiography in acute myocardial infarction. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. [Internet]. 2009 [cited 2016 Apr 10];11:22 Available from: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=2717065&tool=pmcentrez&rendertype=abstract
Rodrigues JCL, Rohan S, Dastidar AG, Trickey A, Szantho G, Ratcliffe LEK, et al. The Relationship Between Left Ventricular Wall Thickness, Myocardial Shortening, and Ejection Fraction in Hypertensive Heart Disease: Insights From Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Clin. Hypertens. [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2017 mar 4];18:1119–1127. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27316563.
Russo C, Jin Z, Homma S, Rundek T, Elkind MS V, Sacco RL, et al. Relationship of multidirectional myocardial strain with radial thickening and ejection fraction and impact of left ventricular hypertrophy: a study in a community-based cohort. Echocardiography [Internet]. NIH Public Access; 2013 [cited 2017 Jul 7];30:794–802. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23360509.
Fontana M, Banypersad SM, Treibel TA, Abdel-Gadir A, Maestrini V, Lane T, et al. Differential Myocyte Responses in Patients with Cardiac Transthyretin Amyloidosis and Light-Chain Amyloidosis: A Cardiac MR Imaging Study. Radiology Radiological Society of North America. 2015 [cited 2016 Dec 20];277:388–397 Available from: http://pubs.rsna.org/doi/10.1148/radiol.2015141744
Gerbaud E, Montaudon M, Chasseriaud W, Gilbert S, Cochet H, Pucheu Y, et al. Effect of ivabradine on left ventricular remodelling after reperfused myocardial infarction: A pilot study. Arch. Cardiovasc Dis.2014 [cited 2017 Jul 7];107:33–41. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24440004.
Huttin O, Coiro S, Selton-Suty C, Juillière Y, Donal E, Magne J, et al. Prediction of Left Ventricular Remodeling after a Myocardial Infarction: Role of Myocardial Deformation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One [Internet]. Public Library of Science; 2016 [cited 2017 Jul 7];11:e0168349. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28036335.
Bulluck H, Rosmini S, Abdel-Gadir A, White SK, Bhuva AN, Treibel TA, et al. Automated Extracellular Volume Fraction Mapping Provides Insights Into the Pathophysiology of Left Ventricular Remodeling Post-Reperfused ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction. J. Am. Heart Assoc. [Internet]. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2016 [cited 2016 Oct 13];5:e003555. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27402229.
Machin D, Campbell M, Fayers P PA. Sample Size Tables for Clinical Studies. Second Ed. Blackwell Sci. IBSN. 1997;18–20.
Carberry J, Carrick D, Haig C, Rauhalammi SM, Ahmed N, Mordi I, et al. Remote Zone Extracellular Volume and Left Ventricular Remodeling in Survivors of ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Hypertens. (Dallas, Tex. 1979) [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2016 Oct 13];68:385–391. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27354423.
Epstein FH, Wijns W, Vatner SF, Camici PG. Hibernating Myocardium. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998 [cited 2017 Jul 7];339:173–181. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9664095.
Hassell MECJ, Vlastra W, Robbers L, Hirsch A, Nijveldt R, Tijssen JGP, et al. Long-term left ventricular remodelling after revascularisation for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction as assessed by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. Open Hear. [Internet]. 2017;4. Available from: http://openheart.bmj.com/content/4/1/e000569.abstract
Carluccio E, Biagioli P, Alunni G, Murrone A, Giombolini C, Ragni T, et al. Patients With Hibernating Myocardium Show Altered Left Ventricular Volumes and Shape, Which Revert After Revascularization. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. [Internet]. 2006 [cited 2017 Jul 7];47 Available from: http://www.onlinejacc.org/content/47/5/969?ijkey=13b01788051362944e2c90202bc381cfe1c3504e&keytype2=tf_ipsecsha
Levine JM, Collins JD, Murtagh G, Markl M, Carr JC, Choudhury L. Segmental late gadolinium enhancement and gadolinium extracellular volume in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. [Internet]. BioMed Central; 2016 [cited 2016 Oct 12];18:P155 Available from: http://jcmr-online.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1532-429X-18-S1-P155
Collins J, Sommerville C, Magrath P, Spottiswoode B, Freed BH, Benzuly KH, et al. Extracellular volume fraction is more closely associated with altered regional left ventricular velocities than left ventricular ejection fraction in nonischemic cardiomyopathy. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2016 Oct 12];8. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25552491.
Bogaert J, Bosmans H, Maes A, Suetens P, Marchal G, Rademakers FE. Remote myocardial dysfunction after acute anterior myocardial infarction: impact of left ventricular shape on regional function: a magnetic resonance myocardial tagging study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. [Internet]. 2000 [cited 2017 Jul 7];35:1525–1534. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10807456.
Talman V, Ruskoaho H. Cardiac fibrosis in myocardial infarction-from repair and remodeling to regeneration. Cell Tissue Res. [Internet]. Springer; 2016 [cited 2017 Jul 7];365:563–581. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27324127.
Kidambi A, Motwani M, Uddin A, Ripley DP, McDiarmid AK, Swoboda PP, et al. Myocardial extracellular volume estimation by CMR predicts functional recovery following acute MI. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016;2071
Garg P, Kidambi A, Swoboda PP, Foley JRJ, Musa TA, Ripley DP, et al. The role of left ventricular deformation in the assessment of microvascular obstruction and intramyocardial haemorrhage. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging. 2017 [cited 2016 Nov 22];33:361–370 Available from: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10554-016-1006-x
Kellman P, Hansen MS, Moon J, Messroghli D, Kellman P, Piechnik S, et al. T1-mapping in the heart: accuracy and precision. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. [Internet]. BioMed Central; 2014 [cited 2016 Dec 8];16:2 Available from: http://jcmr-online.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1532-429X-16-2
Acknowledgements
S.P. was funded by a British Heart Foundation fellowship (FS/10/62/28409) and by a British Heart Foundation chair (CH/16/2/32089). We thank Gavin Bainbridge, Caroline Richmond, Margaret Saysell and Petra Bijsterveld for their assistance in recruiting and collecting data for this study.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
The study protocol was approved by the National Research Ethics Service (12/YH/0169) and complied with the Declaration of Helsinki. All patients recruited in the study gave written informed consent.
Funding
This work was supported by the British Heart Foundation [FS/10/62/28409 and CH/16/2/32089to S.P.].
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PG was involved in recruitment, CMR analysis, statistics and drafted the study manuscript. DAB developed CMR protocol for the study. PPS, JRJF, GJF, TAM, DPR, BE, LED, AKM, PH, PGC and AK were major contributors in writing the manuscript. SC did CMR and basic statistical analysis. RJvG contributed substantially in smooth running of the core lab at Leiden (LUMC) and automated analysis. JPG and SP provided senior review of the final drafted manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for publication
All patients gave written informed consent before randomization.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Additional information
Dr. Stefan Neubaurer served as a Guest Editor for this manuscript.
Additional file
Additional file 1:
Detailed methods. Comprehensive additional information on the basic CMR image analysis, T1-maps quality assurance checks, pulse sequence parameters and imaging protocol. (PDF 76 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Garg, P., Broadbent, D.A., Swoboda, P.P. et al. Extra-cellular expansion in the normal, non-infarcted myocardium is associated with worsening of regional myocardial function after acute myocardial infarction. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 19, 73 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12968-017-0384-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12968-017-0384-0