Abstract
Background
Hypertension is the most common chronic disease, and most important risk factor for cardiovascular disease. This meta-analysis aimed to explore the association between hepatic lipase gene (LIPC) gene -250G/A (rs2070895) and -514C/T (rs1800588) polymorphisms and the susceptibility to hypertension.
Methods
Published studies were searched using the PubMed, Embase and Cochrane Library databases. Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) was used to assess the quality of the included studies. Sensitivity analysis was performed using “leave one out” method. Egger’s test was used to evaluate the publication bias. The random effect model was used to calculate the pooled effect size if P < 0.05 or I2 ≥ 50%; otherwise, the fixed effect model was selected.
Results
Four eligible studies, including 2599 participants, were enrolled in the included studies from 2007 to 2014. Quality evaluation revealed that each study had high NOS scores ranged from 5 to 7. The LIPC rs1800588 polymorphism was not found to be associated with the susceptibility to hypertension under all genetic models (T vs C, P = 0.38; CT vs CC, P = 0.46; TT vs CC, P = 0.38; TT vs CC + CT, P = 0.54; TT + CT vs CC, P = 0.34). Notably, the frequencies of the AA+GA genotypes of LIPC rs2070895 polymorphism were related to an increased risk of hypertension (AA+GA vs. GG, OR = 1.1954, 95% CI: 1.0001–1.4288, P = 0.05).
Conclusion
The LIPC rs2070895 polymorphism was found to be related to an increased risk of hypertension. However, LIPC rs1800588 polymorphism was not associated with the susceptibility to hypertension.
Similar content being viewed by others
Highlight
-
1.
The LIPC rs2070895 polymorphism was related to susceptibility with hypertension.
-
2.
The LIPC rs1800588 polymorphism was not strongly associated with the increased risk of hypertension.
Background
The main characteristic of hypertension [1,2,3] is increased arterial blood pressure including systolic and/or diastolic blood pressure [4, 5]; wherein the hypertension is diagnosed as systolic blood pressure higher than 140 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure higher than 90 mmHg, accompanied by the clinical syndrome of the function or organic damage to the heart, brain, kidney and other organs. Hypertension is the most common chronic disease [6] and an important risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
Hepatic lipase (LIPC), a member of the lipase family, is located on the long arm of chromosome 15 (15 q21) and has a total length of 35 kb, comprising nine exons and eight introns [7,8,9,10]. LIPC encodes hepatic triglyceride lipase, which is an extracellular protein synthesized by liver parenchyma cells and plays a critical role in lipoprotein metabolism. Hepatic lipase serves an important role inremodeling of low-density liporprotein, high-density lipoprotein, remnant, and the production of small, dense low density lipoprotein [11]. A previous study reported that the lipids and lipoprotein concentrations in blood serum are significantly correlated with primary hypertension and hyperhomocysteinemia [12]. Additionally, the triglycerides and the triglyceride to high-density liproprotein cholesterol ratio are strongly correlated with the incidence hypertension in Middle Eastern women [13]. These findings indicate that disruptions of hepatic lipase is a risk factor for hypertension. The -514C/T (rs1800588) and -250G/A (rs2070895) single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are two common variants in the promoter region of LIPC and both present obvious chain imbalance [7, 8]. LIPC mutation may be related to the occurrence of a variety of diseases. The -514 T allele of LIPC is associated with the occurrence of insulin resistance syndrome and type 2 diabetes [14]. The LIPC-250G/A loci polymorphism is related to insulin resistance and dyslipidemia [15]. Recent studies showed that mutations in the liver lipase gene are associated with coronary heart disease and cerebral infarction [16, 17]. The relationships between LIPC polymorphisms and metabolic diseases have been widely examined.
Hypertension is an important risk factor for cardiovascular disease including coronary heart disease and cerebral infarction, among others. An increasing number of studies has focused on LIPC gene and hypertension. However, many of these studies included small sample size, and showed controversial results. Thus, this meta-analysis was performed to pool the studies of the frequency distribution of LIPC rs2070895 and rs1800588 polymorphism in hypertension patients and normal individuals to determine the correlation between LIPC gene polymorphism and hypertension, as well as to provide information for guiding future clinical studies.
Methods
Search strategy
Relevant studies were searched using the PubMed, Embase and Cochrane Library databases. The following search keywords were used: (“Hypertension” OR “hypertensive” OR “High Blood Pressure”) AND (“LIPC” OR “hepatic lipase gene” OR “rs2070895” OR “-250G/A” OR “-514C/T” OR “C-480 T” OR “rs1800588”) AND (“polymorphic*” OR “genetic” OR “variant”). The search was performed by two reviewers. The retrieval deadline was May 1, 2018 with no language restrictions. This study followed the analysis criteria of Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses and the participants, interventions, comparison and outcome measures principle.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The included studies conformed to the following criteria: (1) the studies examined the frequency distribution of LIPC -250G/A and -514C/T polymorphisms in hypertension and non-hypertension patients; (2) the studies reported precise genotype or allele frequency data in both groups; (3) the study was a case-control analysis.
Additionally, the studies were excluded if: (1) the data were incomplete, and thus could not be statistically analyzed; (2) the studies were non-treatise literatures, such as reviews, letters, or comments; (3) the study was a repetitive publication or based on data used for multiple studies. In this case, only the most recent study or that with the most complete information was included.
Data extraction and quality evaluation
Two reviewers independently extracted relevant data from the included publications. The following information was extracted: name of first author, published year, study regions, detection method of genetic polymorphism, number of participants in hypertension and non-hypertension groups, number of each genotype with LIPC (rs2070895 and rs1800588) polymorphisms in both groups, and demographic characters including age and gender. The quality of each included study was evaluated based on the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) recommended by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality of the US [18]. Disputes were resolved by discussion with a third authorduring data extraction and quality evaluation.
Statistical analysis
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) test was performed based on the χ2 test to determine the genotype stability of LIPC polymorphisms in the control group [19]. R 3.12 was used to conduct the meta-analysis. The effect indicator was the odds ratio (OR) value and its corresponding 95% confidence interval (CI) [20]. Additonally, the pooled ORs of LIPC genotypes of rs2070895 and rs1800588 polymorphisms in all genetic inheritance models (allele, additive, recessive, and dominant models) were respectively calculated to analyze their relationships with the risk of hypertension. The heterogeneity test is based on the Q test and I2 statistics [21]. If the heterogeneity test showed significant results (P < 0.05 or I2 > 50%), the random effect model was used to calculate the combined effect value. Otherwise, the fixed effect model was selected to merge the data (P > 0.05 and I2 < 50%).
Publication bias and sensitivity analysis
Egger’s test was used to evaluate publication bias [22]. Sensitivity analysis was performed by “leaving one out” for all models.
Results
General characteristics of the selected publications
Using our search strategy, four related articles were identified [23,24,25,26]. The flow chart of the selection process of included publications is summarized in Fig. 1. A total of 83 studies were identified in PubMed (38), Embase (30) and Cochrane Library (15). After removing 14 repeated articles, 69 studies remainded. An additional 53 irrelevant articles were excluded, after which 16 studies remained. Subsequently, three studies were excluded after skimming the abstracts, including 1 letter and 2 case series or reports. Furthermore, 9 studies were excluded after reading the complete publication, which included 2 reviews, 5 unqualified data and 2 duplicated populations. As a result, four qualified studies were subjected to the meta-analysis (Fig. 1).
A total of 2599 participants were enrolled in the four included studies from 2007 to 2014. There were 1257 patients with hypertension in the case group, in which hypertensive disorder complicating pregnancy patients were included in studies by Bernard [23] and Lin [24], while 1342 healthy subjects were included as controls. The included studies were performed in Canada, Mexico, and China (Table 1). The main method used for SNP detection were PCR-ASO, PCR-RFLP and PCR-AIRS. There were no significant differences in demographic characteristics between the case and control groups of the included studies, with most patients being middle-aged and old, and of femlae gender. Analysis of the literature quality revelaed NOS scores is of 5–7 (Table 2), indicating a high quality. The results of HWE tests demonstrated that the genotypes distribution in controls was consistent with HWE in most included articles except for the control group of Yin’s study [26].
Quantitative data of meta-analysis
The present study was conducted to analyze the correlation of LIPC rs2070895 and rs1800588 polymorphisms with the susceptibility to hypertension in all genetic inheritance models. Initially, the heterogeneity test was performed. The appropriate effect model was used to calculate the combined effect value according to the P value and I2 statistics of Q test. The heterogeneity test revealed striking heterogeneity between studies associated with the LIPC rs1800588 polymorphism in additive and recessive models, as well as studies associated with the LIPC rs2070895 polymorphism in allele, additive and recessive models (P < 0.05, I2 > 50%). Therefore, the random effect model was used to calculate the OR value and 95% CI. A fixed effect model was used for data consolidation of other models of LIPC rs1800588 and rs2070895 polymorphisms because no obvious heterogeneity was found (P > 0.05, I2 < 50%). The merged results are presented in Table 2.
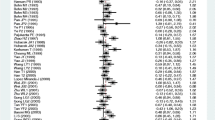
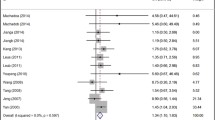
The meta-analysis results revealed no significant difference in the LIPC rs1800588 polymorphism between the hypertension group and non-hypertension group under all genetic models [allele model (T vs. C, OR = 0.9276, 95% CI: 0.7838–1.0979); additive model (TT vs. CC, OR = 0.7446, 95% CI: 0.3839–1.4441) and (CT vs. CC, OR = 0.9090, 95% CI: 0.7038–1.1741); recessive model (TT vs. CC + CT, OR = 0.8176, 95% CI: 0.4286–1.5597); dominant model (TT + CT vs. CC, OR = 0.8882, 95% CI: 0.6974; 1.1312)] (Fig. 2, Table 3). Notably, our results showed that LIPC rs2070895 polymorphism were significantly related to an increased hypertension risk under the dominant model (AA+GA vs. GG, OR = 1.1954, 95% CI: 1.0001–1.4288; Fig. 3, Table 3). However, there was no significant difference in three other genetic models [allele model (A vs. G, OR = 1.2428, 95% CI: 0.9664; 1.5982); additive model (AA vs. GG, OR = 1.7723, 95% CI: 0.8570; 3.6651) and (GA vs. GG, OR = 1.0693, 95% CI: 0.8128; 1.4067); recessive model (AA vs. GG + GA, OR = 1.7115, 95% CI: 0.8225; 3.5612)] (Fig. 3, Table 3). Because the OR values in all models were larger than 1, gene A under the dominant model in LIPC rs2070895 polymorphism may be a dominant risk factor for the susceptibility to hypertension.
Publication bias and sensitivity analysis
Analysis of publication bias demonstrated that the Egger’s test of LIPC rs1800588 and rs2070895 polymorphisms showed no publication bias, supporting the reliability of our results (Table 3). Sensitivity analysis was performed on all models by omitting each study. The results for the LIPC rs1800588 polymorphism were similar in all genetics models, indicating that the results were stable (Fig. 4). However, after eliminating the study by Lin [24], the results for the LIPC rs2070895 polymorphism under allele, additive (AA VS. GG) and dominant models were changed, and no changes was found in other models (Fig. 5).
Discussion
In this meta-analysis, we pooled related studies of the frequency distribution of LIPC -250G/A (rs2070895) and -514C/T (rs1800588) polymorphisms in hypertension patients and normal individuals to assess the relationship of LIPC gene polymorphisms and hypertension risk. The LIPC rs1800588 polymorphism did not appear to be associated with an increased risk of hypertension. Notably, the LIPC rs2070895 polymorphism frequencies were significantly increased in the hypertension group compared to in controls under the dominant model, and OR values of LIPC rs2070895 polymorphism under all models were larger than 1. Therefore, the LIPC rs2070895 polymorphism may be a risk factor for the susceptibility to hypertension.
The human HL protein encoded by the LIPC gene has phospholipase A1 and triglyceride hydrolytic enzyme activities, and plays an important role in plasma lipid transport [27]. It is well known that LIPC is independently involved in the reconstruction of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL) and metabolism of low density lipoprotein (LDL) [28]. Conthe et al. demonstrated that in patients with hypertension, the serum level of HDL-C was decreased [29]. Similarly, a lower serum HDL level may be a prognosis factor for patients with cardiovascular risk among essential hypertension patients [30]. In contrast, an increased LDL level is known to be associated with the new-onset and development of hypertension [31]. In general, dyslipidemia is significant risk factors for hypertension, which precedes the occurrence of clinical hypertension [32]. Thus, LIPC polymorphisms may be closely associated with increased risk of hypertension by regulating HDL, LDL, and other lipid metabolism levels.
Some studies showed a strong connection between the LIPC -250G/A (rs2070895) polymorphism and lipoprotein metabolism disease, such as hyperlipidemia [33, 34] and diabetes [8]. Additionally, differences in the HDL-C and LDL-C between Han and Bai Ku Yao populations may be related to the LIPC rs2070895 polymorphism under the dominant model (AA+GA vs. GG) [35]. Interestingly, our study revealed that the LIPC rs2070895 polymorphism was strongly related to an increased hypertension risk under the dominant model (AA+GA vs. GG).
The T allele in LIPC -514C/T polymorphism has been shown to be related to higher plasma HDL-C levels [36], and the T allele may decrease the susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [37]. Although one included study by Bernard et al. showed that TT homozygotes at LIPC -514 had a decreased risk of gestational hypertension compared to CC homozygotes [23], our results showed that the LIPC -514C/T (rs1800588) polymorphism was not associated with hypertension under all genetic models. Similarly, not all studies found an association between the LIPC -514C/T polymorphism and lipoprotein metabolism. A study of Iranian population revealed no difference in the frequency of the T allele between coronary heart disease and normal arteries [38]. Additionally, the C and T alleles frequencies of the -514C/T polymorphism showed no significant difference between coronary artery disease and normal groups [8, 39, 40]. These differences may be realted to differences in sample size, lifestyles, and gender of the study populations.
Heterogeneity test results revealed a significant difference between included studies. The potential heterogeneity sources included different regional living habits, living environments, and the economic development levels. Additionally, the effects of other confounding factors such as gender and age can lead to high heterogeneity.
There were some limitations in this research. First, because of incomplete data and the small sample sizes of the included studies, covariate correction and further subgroup analysis were not performed, although these factors may have confounded the results of the meta-analysis. Second, the population was not representative, as the population in Yin’s study (female) did not fit HWE. Third, the results of sensitivity analysis regarding the LIPC rs2070895 polymorphism in the allele, additive, and dominant models were unstable after elimination of Lin’s study, which requires further analysis. Fourth, hypertensive disorders complicating pregnancy may have affected our results.
In summary, the present study showed that the frequencies of the AA+GA genotypes of the LIPC rs2070895 polymorphism are related to an increased risk of hypertension. However, the LIPC rs1800588 polymorphism was not associated with the susceptibility to hypertension. Because the related studies and sample size were limited, the conclusions of this study should be verified by high-quality studies with larger sample size.
Abbreviations
- AHRQ:
-
Agency for healthcare research and quality
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- HDL:
-
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- HDPC:
-
Hypertensive disorder complicating pregnancy
- HWE:
-
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
- LDL:
-
Low density lipoprotein
- LIPC:
-
Hepatic lipase gene
- NOS:
-
Newcastle-Ottawa Scale
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- PICO:
-
Participants, interventions, comparison and outcome measures
- PRISMA:
-
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
- SNPs):
-
Single nucleotide polymorphisms
References
Liu C, Yang CX, Chen XR, Liu BX, Li Y, Wang XZ, Sun W, Li P, Kong XQ. Alamandine attenuates hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy in hypertensive rats. Amino Acids. 2018;50:1071–81.
Pappaccogli M, Covella M, Berra E, Fulcheri C, Di Monaco S, Perlo E, Burrello J, Monticone S, Rossato D, Rabbia F, Veglio F. Effectiveness of renal denervation in resistant hypertension: a meta-analysis of 11 controlled studies. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2018;25:1–10.
Tanaka R, Nolan RP. Psychobehavioral profiles to assist tailoring of interventions for patients with hypertension: latent profile. Analysis. 2018;20:e149.
Melville S, Teskey R. A comparison and calibration of a wrist-worn blood pressure monitor for patient management: assessing the reliability of innovative blood pressure devices. J Med Internet Res. 2018;20:e111.
Sakallioglu O, Polat C, Akyigit A, Cetiner H, Duzer S. Allergic rhinitis and arterial blood pressure: a population-based study. J Laryngol Otol. 2018;132:1–5.
Kanbay M, Onal EM, Afsar B, Dagel T, Yerlikaya A, Covic A, Vaziri ND. The crosstalk of gut microbiota and chronic kidney disease: role of inflammation, proteinuria, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus. Int Urol Nephrol. 2018;50:1–14.
Goodarzynejad H, Boroumand M, Behmanesh M, Ziaee S, Jalali A, Pourgholi L. Association between the hepatic lipase promoter region polymorphism (−514 C/T) and the presence and severity of premature coronary artery disease. J Tehran Heart Cent. 2017;12:119–27.
Mohammadzadeh G, Ghaffari MA, Bazyar M, Kheirollah A. Association between two common polymorphisms (single nucleotide polymorphism -250G/a and -514C/T) of the hepatic lipase gene and coronary artery disease in type 2 diabetic patients. Adv Biomed Res. 2016;5:27.
Smith CE, Van Rompay MI, Mattei J, Garcia JF, Garcia-Bailo B, Lichtenstein AH, Tucker KL, Ordovas JM. Dietary fat modulation of hepatic lipase variant −514 C/T for lipids: a crossover randomized dietary intervention trial in Caribbean Hispanics. Physiol Genomics. 2017;49:592–600.
Wang Y, Wang M, Zhang X, Nie J, Zhang M, Liu X, Ma L. The association between LIPC rs493258 polymorphism and the susceptibility to age-related macular degeneration. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016;13:1022.
Kobayashi J, Miyashita K, Nakajima K, Mabuchi H. Hepatic lipase: a comprehensive view of its role on plasma lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2015;22:1001.
Baszczuk A, Musialik K, Kopczyński J, Thielemann A, Kopczyński Z, Kęsy L, Dopierała G. Hyperhomocysteinemia, lipid and lipoprotein disturbances in patients with primary hypertension. Adv Med Sci. 2014;59:68–73.
Tohidi M, Hatami M, Hadaegh F, Azizi F. Triglycerides and triglycerides to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio are strong predictors of incident hypertension in middle eastern women. J Hum Hypertens. 2011;26:525.
Gómez P, Pérezjiménez F, Pérezjiménez F, Marín C, Moreno JA, Gómez MJ, Bellido C, Pérezmartínez P, Fuentes F, Paniagua JA. The −514 C/T polymorphism in the hepatic lipase gene promoter is associated with insulin sensitivity in a healthy young population. J Mol Endocrinol. 2005;34:331–8.
Pihlajamäki J, Karjalainen L, Karhapää P, Vauhkonen I, Taskinen MR, Deeb SS, Laakso M. G-250A substitution in promoter of hepatic lipase gene is associated with dyslipidemia and insulin resistance in healthy control subjects and in members of families with familial combined hyperlipidemia. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000;20:1789–95.
Fu Y, Ni PH, Ying YY, Liu JR, Song YJ, Xin XY, Guo ZL, Chen SD. The linkage disequilibrium of four loci in hepatic lipase promoter gene of cerebral infarction patients in Shanghai. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2007;87:2203–8.
Ji J, Herbison CE, Mamotte CD, Burke V, Taylor RR, van Bockxmeer FM. Hepatic lipase gene −514 C/T polymorphism and premature coronary heart disease. J Cardiovasc Risk. 2002;9:105–13.
Wells G, Shea B, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, Tugwell P: The Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. 2000.
Schaid DJ, Jacobsen SJ. Blased tests of association: comparisons of allele frequencies when departing from hardy-Weinberg proportions. Am J Epidemiol. 1999;149:706–11.
Liu T, Xu QE, Zhang CH, Zhang P. Occupational exposure to methylene chloride and risk of cancer: a meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control. 2013;24:2037–49.
Lau J, Ioannidis JP, Schmid CH. Quantitative synthesis in systematic reviews. Ann Intern Med. 1997;127:820–6.
Minder C, Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315:629–34.
Bernard N, Girouard J, Forest JC, Giguere Y. The combination of ApoCIII, hepatic lipase and hormono sensitive lipase gene polymorphisms suggests an association with susceptibility to gestational hypertension. J Hum Genet. 2007;52:244–54.
Lin H, Yin Z, Yu XY, Lin N, Lin Y, Chen J, Chen YZ, Lu KP, Liu HK. Variants -250G/a and -514C/T in the LIPC gene are associated with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy in Chinese women. Genet Mol Res. 2014;13:6126–34.
Rios-Gonzalez BE, Ibarra-Cortes B, Ramirez-Lopez G, Sanchez-Corona J, Magana-Torres MT. Association of polymorphisms of genes involved in lipid metabolism with blood pressure and lipid values in mexican hypertensive individuals. Dis Markers. 2014;2014:150358.
Yin RX, Wu JZ, Liu WY, Wu DF, Cao XL, Miao L, Htet Aung LH, Zhang L, Long XJ, Li M, Pan SL. Association of several lipid-related gene polymorphisms and blood pressure variation in the Bai Ku Yao population. Am J Hypertens. 2012;25:927–36.
Deursen vD. Transcriptional regulation of the human hepatic lipase gene: relation to glucose and lipid metabolism, vol. 1791. Rotterdam: Erasmus University Rotterdam; 2012. p. 229–37.
Carr MC, Ayyobi AF, Murdoch SJ, Deeb SS, Brunzell JD. Contribution of hepatic lipase, lipoprotein lipase, and cholesteryl ester transfer protein to LDL and HDL heterogeneity in healthy women. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002;22:667–73.
Conthe P, Gómezfernández P, Fd Á, Fernándezpérez C, Gonzálezesteban J, Ceacalvo L. HDL cholesterol and cardiovascular disease in a population with hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. RICARHD study. Rev Clin Esp. 2009;209:227–33.
Zhulepiya.simayi, Chen YL, Buhailiqiemu.maimaiti: Study on relationship between serum HDL level with prognosis of essential hypertension. Chongqing Med. 2013;42:869-71.
Cicero AF, Rosticci M, Baronio C, Morbini M, Parini A, Grandi E, D'Addato S, Borghi C. Serum LDL cholesterol levels and new onset of arterial hypertension: an 8-year follow-up. Eur J Clin Investig. 2015;44:926–32.
Pavithran P, Nandeesha H, Madanmohan BZ, Sathiyapriya V, Shenoy P, Sunil S, Shyma P. Dyslipidemia antedates occurrence of clinical hypertension in non-diabetic, non-obese male subjetcs. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. 2007;51:96.
Bertolini S, Pisciotta L, Di Scala L, Langheim S, Bellocchio A, Masturzo P, Cantafora A, Martini S, Averna M, Pes G, et al. Genetic polymorphisms affecting the phenotypic expression of familial hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis. 2004;174:57–65.
Jimenez-Gomez Y, Perez-Jimenez F, Marin C, Gomez P, Moreno R, Delgado J, Perez-Martinez P, Gomez MJ, Lopez-Miranda J. The -250G/a polymorphism in the hepatic lipase gene promoter influences the postprandial lipemic response in healthy men. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2008;18:173–81.
Meng L, Ruixing Y, Yiyang L, Xingjiang L, Kela L, Wanying L, Lin Z, Weixiong L, Dezhai Y, Shangling P. Association of LIPC -250G>a polymorphism and several environmental factors with serum lipid levels in the Guangxi Bai Ku Yao and Han populations. Berlin: Springer; 2010.
Farid MAK, Azizi F, Hedayati M, Daneshpour MS, Shamshiri AR, Siassi F. Association between CETP Taq1B and LIPC -514C/T polymorphisms with the serum lipid levels in a group of Tehran's population: a cross sectional study. Lipids Health Dis. 2010;9:1–7.
Zhan Q, Li YY, Nie YQ, Zhou YJ, Yl DU, Sha WH, Wang H. Association of hepatic lipase gene promoter polymorphism -514C/T with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2008;16:375–8.
Samani KG, Noori M, Nobar MR, Chaleshtory MH, Farrokhi E, Amin MD. The −514C/T polymorphism of hepatic lipase gene among Iranian patients with coronary heart disease. Iran J Public Health. 2012;41:59–65.
Ghatrehsamani K, Darabi M, Rahbani M, Hashemzadeh CM, Farrokhi E, Noori M. Combined hepatic lipase -514C/T and cholesteryl ester transfer protein I405V polymorphisms are associated with the risk of coronary artery disease. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2009;13:809.
Zambon A, Deeb SS, Pauletto P, Crepaldi G, Brunzell JD. Hepatic lipase: a marker for cardiovascular disease risk and response to therapy. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2003;14:179–89.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XZ contributed to the conception and design of the research. YR contributed to the statistical analysis and writing of the manuscript. HL contributed to the data collection and data analysis. YW contributed to the data collection and conducting the study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Ren, Y., Li, H. et al. Association of LIPC -250G/A and -514C/T polymorphisms and hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lipids Health Dis 17, 238 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-018-0884-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-018-0884-4