Abstract
Background
We have previously shown that efficiency of ischemic conditioning is diminished in hypercholesterolemia and that autophagy is necessary for cardioprotection. However, it is unknown whether isolated hypercholesterolemia disturbs autophagy or the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathways. Therefore, we investigated whether isolated hypercholesterolemia modulates cardiac autophagy-related pathways or programmed cell death mechanisms such as apoptosis and necroptosis in rat heart.
Methods
Male Wistar rats were fed either normal chow (NORM; n = 9) or with 2% cholesterol and 0.25% cholic acid-enriched diet (CHOL; n = 9) for 12 weeks. CHOL rats exhibited a 41% increase in plasma total cholesterol level over that of NORM rats (4.09 mmol/L vs. 2.89 mmol/L) at the end of diet period. Animals were sacrificed, hearts were excised and briefly washed out. Left ventricles were snap-frozen for determination of markers of autophagy, mTOR pathway, apoptosis, and necroptosis by Western blot.
Results
Isolated hypercholesterolemia was associated with a significant reduction in expression of cardiac autophagy markers such as LC3-II, Beclin-1, Rubicon and RAB7 as compared to controls. Phosphorylation of ribosomal S6, a surrogate marker for mTOR activity, was increased in CHOL samples. Cleaved caspase-3, a marker of apoptosis, increased in CHOL hearts, while no difference in the expression of necroptotic marker RIP1, RIP3 and MLKL was detected between treatments.
Conclusions
This is the first comprehensive analysis of autophagy and programmed cell death pathways of apoptosis and necroptosis in hearts of hypercholesterolemic rats. Our data show that isolated hypercholesterolemia suppresses basal cardiac autophagy and that the decrease in autophagy may be a result of an activated mTOR pathway. Reduced autophagy was accompanied by increased apoptosis, while cardiac necroptosis was not modulated by isolated hypercholesterolemia. Decreased basal autophagy and elevated apoptosis may be responsible for the loss of cardioprotection reported in hypercholesterolemic animals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Hyperlipidemias have significant cardiac consequences, since they are among the major risk factors of ischemic heart diseases [1]. The role of atherosclerosis is well studied in these pathologies; however, myocardial effects of hyperlipidemias that do not result in atherosclerosis, such as isolated hypercholesterolemia, is less well understood. Hypercholesterolemia was previously shown to worsen cardiac systolic and diastolic function in cholesterol-fed rabbits [2]. Furthermore, we have previously shown that cholesterol feeding leads to mild contractile dysfunction and cardiac oxidative stress [3]. These data suggest that cardiac metabolism may be affected by hypercholesterolemia well before or even without the development of atherosclerosis. However, it is not well studied which molecular pathways are responsible for the cardiac metabolic effects of hypercholesterolemia.
Autophagy is a ubiquitous cellular housekeeping process [4–6], which is involved in protein quality control and cardiac cytoprotection [7–9]. It is known that autophagy is elevated under nutrient and oxidative stress in ischemia-reperfusion injury [10]. We have previously shown that ischemic preconditioning induces autophagy under normal conditions in adult rat hearts and that autophagy is necessary for cardioprotection by ischemic preconditioning [11]. Similarly, Rohailla et al. showed that remote ischemic preconditioning increases autophagy and decreased the expression of proteins related to the major regulator of autophagy the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in mice [12]. It is well established that activity of mTOR pathway modulates autophagy [13]. Previous data suggests that mTOR signaling might be elevated while autophagy is diminished in the hearts of hyperlipidemic Yucatan pigs [14], and we have shown that in mice diet-induced obesity results in disturbed cardiac autophagy which is accompanied by increased myocardial injury after ischemia/reperfusion [15]. Cardioprotective effects of ischemic conditioning are attenuated in the presence of cardiovascular risk factors such as aging [16, 17], diabetes [18, 19] and hyperlipidemia [20, 21]. Similarly, our previous studies demonstrated that cardioprotection by various forms of ischemic conditioning is impaired in cholesterol-fed rats [22–25]. However, there is no information whether isolated hypercholesterolemia modulates cardiac autophagy and mTOR pathways in rats.
Insufficient autophagy can promote programmed cell death, apoptosis [26], which results in cardiac damage [27]. Necroptosis (programmed necrosis) is another type of programmed cell death which occurs upon stimulation of death receptors in the absence of caspase-8 activation [28]. Disturbances in cellular energetics, excessive reactive oxygen species production or metabolic changes have been shown to elicit necroptosis and apoptosis [29–32]. It has been shown that apoptosis is upregulated in the hearts of hamsters on hypercholesterolemic diet [30]. Furthermore, Ye et al. showed that TNFα-induced oxidative stress increased necroptosis in parallel with autophagy [33]. Thus, we speculated that isolated hypercholesterolemia may also increase activation of pro-death pathways such as apoptosis and necroptosis in the rat heart.
Therefore, our hypothesis was that (1) cardiac autophagy is diminished in isolated hypercholesterolemia due to increased mTOR signaling, and that (2) pro-death pathways such as apoptosis or necroptosis are upregulated in hypercholesterolemia. Accordingly, the aims of the present study were to investigate the status of autophagy and mTOR pathways in isolated hypercholesterolemia and to examine apoptosis and necroptosis in a hypercholesterolemic rat model.
Methods
Animal model
Six-weeks-old male Wistar rats (Crl:WI Strain Code: 003; Charles River Laboratories, Wilmington, MA, USA) were fed with control chow (NORM; n = 9) or chow enriched with 2% cholesterol and 0.25% cholic acid (CHOL; n = 9) for 12 weeks (Table 1). Animals were allowed to food and water ad libitum and chow was changed daily. After the feeding period, body weight of animals were measured and they were anesthetized with diethyl ether and given 500 U/kg heparin i.v. Blood sample (500 μL) was taken from tail vein for further experiments. Hearts were excised and perfused with Krebs-Henseleit buffer according to Langendorff at 37 °C for 10 min as previously described [34]. Hearts were taken and snap-frozen for further biochemical assays.
Measurements of glucose and serum lipids
After the 12 week-weeks-long feeding period, glucose, cholesterol and triglyceride levels were measured from plasma of NORM and CHOL rats by colorimetric assays (Diagnosticum, Budapest, Hungary) as previously described [35].
Measurement of markers of autophagy, mTOR apoptosis and necroptosis by Western blot
Freeze-clamped left ventricles were ground in liquid nitrogen and homogenized with TissueLyser LT (Qiagen, Venlo, The Netherlands) in ice-cold RIPA homogenization buffer (Millipore, Darmstadt, Germany), containing phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride protease inhibitor (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (1 mM sodium orthovanadate, 100 mM sodium fluoride and 17.5 mM β-glycero-phosphate; Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA). Protein concentration was assessed with BCA kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Protein samples were resolved on 4–20% Criterion TGX gels (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) and transferred to Immun-Blot PVDF membranes (Bio-Rad). Equal protein loading was verified with Ponceau staining. Membranes were blocked with 5% nonfat milk (Bio-Rad) or bovine serum albumin (BSA; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA) or fish skin gelatin (FSG; Sigma) in Tris-buffered saline with 0.05% Tween 20 (TBS-T) for 2 h. Membranes were incubated with primary antibodies in 5% nonfat milk or BSA in TBS-T against late autophagy markers such as LC3 A/B, NBR1 and SQSTM1/p62; early autophagy markers such as Class-III PI3K, Beclin-1 and Rubicon; an autophago-lysosomal marker RAB7; mTOR pathway markers such as phospho-Akt [Thr308], phospho-Akt [Ser473], Akt, phospho-mTOR [Ser2448], mTOR, phospho- ribosomal S6 [Ser235/236], ribosomal S6 (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA), a modulator of autophagy and mTOR pathway; pro- and anti-apoptotic proteins such as BCL-2, BAX (Sigma) caspase-3 (Novus Biologicals, Littleton, Colorado, USA), necroptosis markers such as RIP1, RIP3 and MLKL (Sigma); and GAPDH (Cell Signaling) or Actin (Sigma) as loading controls. After three washes with TBS-T, secondary antibody conjugated to horseradish peroxidase was added for 1 h at room temperature (in 5% nonfat milk in TBS-T; Cell Signaling). Signals were detected with an enhanced chemiluminescence kit (Bio-Rad) by Chemidoc XRS+ (Bio-Rad) and quantitated in Image Lab 4.1 software (Bio-Rad). Antibodies bound to phospho-epitopes were removed with Pierce Stripping Buffer (Thermo) before incubation with antibodies detecting the total protein.
Statistical analysis
Values are expressed as mean ± standard error of mean (SEM). Statistical analysis was performed between groups by unpaired two-tailed t-test by using GraphPad Prism 5 software. A p < 0.05 value was considered significant.
Results
Elevated serum cholesterol level in hypercholesterolemic rats
We examined body weight at the 12th week of the diet and found no significant difference between groups (NORM: 551.5 ± 13.0 g vs. CHOL: 529.4 ± 12.2 g; p < 0.05). Serum cholesterol, triglyceride and glucose parameters were measured in control and cholesterol-fed rats to assess the state of lipid- and glucose homeostasis. After the feeding period, serum cholesterol level was elevated, although serum triglyceride and glucose levels were unchanged in CHOL group as compared to the NORM group, evidencing isolated hypercholesterolemia in CHOL animals (Table 2). In addition, in a previous study, CHOL animals displayed an altered lipoprotein pattern after 12 weeks of feeding [34].
Hypercholesterolemia downregulates autophagy
In order to establish whether hypercholesterolemia influences autophagy we measured cardiac expression of autophagy markers by Western blot. Hearts of cholesterol-fed animals exhibited a decrease in LC3-II, Beclin-1, Rubicon, and RAB7 (Fig. 1b-e), consistent with downregulation of autophagy initiation and vesicle traffic despite upregulation of the Class-III PI3K involved in autophagy initiation (Fig. 1f). No difference in the expression of markers of autophagic clearance NBR1 and SQSTM1/p62 proteins was detected between groups (Fig. 1g-h). These results suggest that both early and late phases of autophagy were attenuated in the heart of hypercholesterolemic rats.
Hypercholesterolemia downregulated cardiac autophagy. a Representative Western blots for autophagy-related proteins in the left ventricle of NORM and CHOL rats. b-h Quantification of LC3-I/II, Beclin-1, Class III PI3K, NBR1, SQSTM1/p62, RAB7 and Rubicon protein expressions as normalized to Actin. NORM (n = 4) vs. CHOL (n = 5); mean + SEM; *: p < 0.05)
Hypercholesterolemia activates mTOR in the heart
In order to investigate whether hypercholesterolemia affects mTOR pathway we measured the phosphorylation of mTOR and ribosomal S6 proteins. Our results showed that there was no significant difference in the expressions or phosphorylations of Akt and mTOR protein between groups; however, phosphorylation of ribosomal S6, a surrogate marker of mTOR complex activity, was elevated in CHOL group (Fig. 2b-e). These results indicate that mTOR activity was upregulated in hypercholesterolemia.
Hypercholesterolemia activated mTOR pathway. a Representative Western blots for mTOR pathway-related proteins in the left ventricle of NORM and CHOL rats. b-e Quantification of phospho-Akt [Ser473; Thr308], phospho-mTOR [Ser2448], and phospho-S6 [Ser235/236] protein expressions as normalized to the corresponding total proteins. NORM (n = 4) vs. CHOL (n = 5); mean + SEM; *: p < 0.05)
Apoptosis but not necroptosis is elevated in hypercholesterolemia
We also investigated whether decreased autophagy in hypercholesterolemia is associated with altered apoptotic and necroptotic pathways. Expression of apoptotic marker cleaved caspase-3 was significantly increased, while BCL-2/BAX protein expression ratio was unchanged (Fig. 3b-c). Furthermore, expression of RIP1, RIP3 and MLKL proteins, major markers of necroptosis, were unchanged (Fig. 3e-g). These results suggest that hypercholesterolemia upregulates apoptosis but not necroptosis in the heart.
Hypercholesterolemia activated apoptosis, but had no effect on cardiac necroptosis. a Representative Western blots for apoptosis-related protein expressions. b-c Quantification of cleaved caspase-3 expression normalized to Actin and ratio of BCL-2 to BAX. d Representative Western blots for necroptosis-related proteins. e-g Quantification of RIP1, RIP3, MLKL and cleaved caspase-3 as normalized to Actin protein expression. NORM (n = 5) vs. CHOL (n = 5); mean + SEM; *: p < 0.05)
Discussion
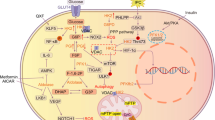
This is the first comprehensive analysis of cardiac autophagy and programmed cell death pathways of apoptosis and necroptosis in hypercholesterolemic rats. Here we have shown that hypercholesterolemia induces the attenuation of cardiac autophagy in parallel with the activation of mTOR pathway and an elevation of apoptosis. Moreover, this is the first demonstration that isolated hypercholesterolemia does not influence the expression of major markers of cardiac necroptosis (for schematic representation see Fig. 4).
In this study we showed first that isolated hypercholesterolemia downregulates cardiac autophagy and activates mTOR pathway. Autophagy-related pathways were previously studied in various swine models of mixed hyperlipidemia, which presented somewhat divergent results. Sellke et al. [14] studied swine models of mixed hyperlipidemia where they applied regional cardiac ischemia and assessed autophagy in non-ischemic myocardium. They demonstrated that cardiac mTOR activity was significantly elevated while autophagy marker LC3-II was diminished in hyperlipidemic Yucatan pigs. These findings are in good alignment with our results shown here, however, elsewhere hyperlipidemia decreased expression of Beclin-1, but not of LC3-II in Yorkshire swine [36], while in Ossabaw swine hyperlipidemia elevated cardiac LC3-II and Beclin-1 proteins [37]. Similarly to these findings, the status of cardiac autophagy in other metabolic disorders was also found to be unclear. Recently we showed that diet-induced obesity leads to decreased induction of autophagy in response to fasting in mice involving altered expression of numerous proteins related to metabolic pathways [15], which is in parallel to our current findings. However, in Long-Evans rats fed with high-fat diet we demonstrated only early signs of decreased mitophagy, but no major changes in overall cardiac autophagy or mTOR pathway [38]. In contrast, elsewhere metabolic syndrome induced by high-fat feeding increased cardiac LC3-II and SQSTM1/p62 in mice [39]. Overall, these reports and our current study demonstrate that complex metabolic disorders might modulate cardiac mTOR pathway and autophagy differentially depending on the animal model applied, and they also highlight that focused studies are necessary to decipher the role of specific metabolic pathways on autophagy.
Our results also demonstrated that apoptosis was upregulated by isolated hypercholesterolemia in the rat heart. We assessed an increased cleaved caspase-3 activation, however, the balance of pro- and anti-apoptotic BCL-2 proteins was unaffected by isolated hypercholesterolemia. Similarly, Cheng et al. reported that 8 weeks of cholesterol-enriched diet induced cardiac apoptosis in hamsters, associated with increased expression of BID and BAX [30]. These results correlate well with findings of Zhu et al. who showed that 12 weeks of hypercholesterolemic diet elevated cardiac expression of BAX, decreased BCL-xL but did not affect caspase-3 in swine [40]. Furthermore, Hsu et al. demonstrated that cardiac cleaved PARP was increased in obese C57BL/6 mice on a high fat diet [39]. On the contrary, Osipov et al. showed that hyperlipidemia did not exacerbate cardiac apoptosis after ischemia and reperfusion in a Yucatan swine model based on the findings of decreased cleaved PARP and no difference in activation of caspase-3 [29]. Hypercholesterolemia has also been shown to modulate apoptosis in other tissue types. For example, Perales et al. showed upregulated BAX expression in vascular smooth muscle cells exposed to 25-hydroxycholesterol [41]. Therefore, the majority of these results demonstrates that there is a strong relationship between increased cardiac apoptosis and hypercholesterolemia, although different models of hypercholesterolemia display varying constellations of altered apoptotic markers.
Although several publications report elevated cardiac apoptosis in hypercholesterolemia, data on cardiac necroptosis is scarce. Indeed, this is the first study which assessed the status of necroptosis in vivo in isolated hypercholesterolemia. Here we demonstrate that the expression of major markers of necroptosis are not modulated in the heart of cholesterol-fed rats. However, in a similar model of hypercholesterolemia, cardiac expression of RIP3 mRNA was increased [42], although no other measures of necroptosis were assessed. Nevertheless, these findings demonstrate that the effect of hypercholesterolemia on cardiac necroptosis needs further investigation.
Limitations of this study are that the investigation was performed only on male rats, therefore, we cannot exclude the possibility that sex influences the effect of hypercholesterolemia on cardiac death and survival mechanisms. Furthermore, we did not follow food consumption during the experiments. We did not investigate either the presence of autophagosomes with electron microscopy, or autophagic flux, or the phosphorylation of ribosomal S6 protein through the 90 kDa ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK), which might contribute to the phosphorylation of ribosomal S6 protein independently of the mTOR complex [43]. Another limitation is that the effect of hypercholesterolemia on autophagy, apoptosis, necroptosis and mTOR signaling pathways was assessed only in the left ventricular myocardium.
Conclusions
In conclusion, this is the first comprehensive analysis of autophagy and programmed cell death pathways in the hearts of hypercholesterolemic rats, demonstrating that autophagy is downregulated, while mTOR pathway and apoptosis are upregulated. This imbalance between pro-survival and death pathways might play a role in the abolition of cardioprotection in hypercholesterolemia. In addition, this is the first demonstration that expression of major markers of cardiac necroptosis is not modulated by isolated hypercholesterolemia.
Abbreviations
- BAX:
-
Apoptosis regulator BAX
- BCA:
-
Bicinchoninic acid
- BCL-2:
-
Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2
- BID:
-
BH3-interacting domain death agonist protein
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- CHOL:
-
Hypercholesterolemic
- Class-III PI3K:
-
Class-III phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- FSG:
-
Fish skin gelatin
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- LC3:
-
Microtubule-associated protein light chain 3
- MLKL:
-
Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- NBR1:
-
Neighbor of BRCA1 gene 1
- NORM:
-
Normocholesterolemic
- PARP:
-
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase
- PVDF:
-
Polyvinylidene fluoride
- RAB7:
-
Ras-related protein Rab-7a
- RIP1:
-
Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1
- RIP3:
-
Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 3
- RIPA:
-
Radioimmunoprecipitation assay
- RSK:
-
90 kDa ribosomal S6 kinase
- Rubicon:
-
Run domain Beclin-1-interacting and cysteine-rich domain-containing protein
- S6:
-
Ribosomal S6 protein
- SQSTM1/p62:
-
Sequestosome 1
- TBS-T:
-
Tris-buffered saline-Tween 20
References
D’Annunzio V, Donato M, Buchholz B, Perez V, Miksztowicz V, Berg G, Gelpi RJ. High cholesterol diet effects on ischemia-reperfusion injury of the heart. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012;90:1185–96.
Huang Y, Walker KE, Hanley F, Narula J, Houser SR, Tulenko TN. Cardiac systolic and diastolic dysfunction after a cholesterol-rich diet. Circulation. 2004;109:97–102.
Onody A, Csonka C, Giricz Z, Ferdinandy P. Hyperlipidemia induced by a cholesterol-rich diet leads to enhanced peroxynitrite formation in rat hearts. Cardiovasc Res. 2003;58:663–70.
Sciarretta S, Zhai P, Volpe M, Sadoshima J. Pharmacological modulation of autophagy during cardiac stress. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2012;60:235–41. 210.1097/FJC.1090b1013e3182575f3182561.
Giricz Z, Mentzer Jr RM, Gottlieb RA. Autophagy, myocardial protection, and the metabolic syndrome. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2012;60:125–32.
Gustafsson ÅB, Gottlieb RA. Recycle or die: The role of autophagy in cardioprotection. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008;44:654–61.
Yuan H, Perry CN, Huang C, Iwai-Kanai E, Carreira RS, Glembotski CC, Gottlieb RA. LPS-induced autophagy is mediated by oxidative signaling in cardiomyocytes and is associated with cytoprotection. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009;296:H470–479.
Hamacher-Brady A, Brady NR, Gottlieb RA. Enhancing macroautophagy protects against ischemia/reperfusion injury in cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:29776–87.
Gurusamy N, Lekli I, Mukherjee S, Ray D, Ahsan MK, Gherghiceanu M, Popescu LM, Das DK. Cardioprotection by resveratrol: a novel mechanism via autophagy involving the mTORC2 pathway. Cardiovasc Res. 2010;86:103–12.
Hariharan N, Zhai P, Sadoshima J. Oxidative stress stimulates autophagic flux during ischemia/reperfusion. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;14:2179–90.
Huang C, Yitzhaki S, Perry C, Liu W, Giricz Z, Mentzer Jr R, Gottlieb R. Autophagy induced by ischemic preconditioning is essential for cardioprotection. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2010;3:365–73.
Rohailla S, Clarizia N, Sourour M, Sourour W, Gelber N, Wei C, Li J, Redington AN. Acute, delayed and chronic remote ischemic conditioning is associated with downregulation of mTOR and enhanced autophagy signaling. PLoS One. 2014;9:e111291.
Sengupta S, Peterson TR, Sabatini DM. Regulation of the mTOR complex 1 pathway by nutrients, growth factors, and stress. Mol Cell. 2010;40:310–22.
Glazer HP, Osipov RM, Clements RT, Sellke FW, Bianchi C. Hypercholesterolemia is associated with hyperactive cardiac mTORC1 and mTORC2 signaling. Cell Cycle. 2009;8:1738–46.
Andres AM, Kooren JA, Parker SJ, Tucker KC, Ravindran N, Ito BR, Huang C, Venkatraman V, Van Eyk JE, Gottlieb RA, Mentzer Jr RM. Discordant signaling and autophagy response to fasting in hearts of obese mice: Implications for ischemia tolerance. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016;311:H219–228.
Fenton RA, Dickson EW, Meyer TE, Dobson Jr JG. Aging reduces the cardioprotective effect of ischemic preconditioning in the rat heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2000;32:1371–5.
Schulman D, Latchman DS, Yellon DM. Effect of aging on the ability of preconditioning to protect rat hearts from ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2001;281:H1630–1636.
Galagudza MM, Nekrasova MK, Syrenskii AV, Nifontov EM. Resistance of the myocardium to ischemia and the efficacy of ischemic preconditioning in experimental diabetes mellitus. Neurosci Behav Physiol. 2007;37:489–93.
Kristiansen SB, Lofgren B, Stottrup NB, Khatir D, Nielsen-Kudsk JE, Nielsen TT, Botker HE, Flyvbjerg A. Ischaemic preconditioning does not protect the heart in obese and lean animal models of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2004;47:1716–21.
Yadav HN, Singh M, Sharma PL. Modulation of the cardioprotective effect of ischemic preconditioning in hyperlipidaemic rat heart. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010;643:78–83.
Gupta V, Goyal R, Sharma PL. Preconditioning offers cardioprotection in hyperlipidemic rat hearts: possible role of Dopamine (D2) signaling. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2015;15:77.
Giricz Z, Lalu MM, Csonka C, Bencsik P, Schulz R, Ferdinandy P. Hyperlipidemia attenuates the infarct size-limiting effect of ischemic preconditioning: role of matrix metalloproteinase-2 inhibition. J Pharmacol Experimental Ther. 2006;316:154–61.
Gorbe A, Varga ZV, Kupai K, Bencsik P, Kocsis GF, Csont T, Boengler K, Schulz R, Ferdinandy P. Cholesterol diet leads to attenuation of ischemic preconditioning-induced cardiac protection: the role of connexin 43. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;300:H1907–1913.
Ferdinandy P, Csonka C, Csont T, Szilvassy Z, Dux L. Rapid pacing-induced preconditioning is recaptured by farnesol treatment in hearts of cholesterol-fed rats: role of polyprenyl derivatives and nitric oxide. Mol Cell Biochem. 1998;186:27–34.
Kupai K, Csonka C, Fekete V, Odendaal L, van Rooyen J, Marais de W, Csont T, Ferdinandy P. Cholesterol diet-induced hyperlipidemia impairs the cardioprotective effect of postconditioning: role of peroxynitrite. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009;297:H1729–1735.
Nishida K, Yamaguchi O, Otsu K. Crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis in heart disease. Circ Res. 2008;103:343–51.
Gustafsson AB, Gottlieb RA. Bcl-2 family members and apoptosis, taken to heart. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007;292:C45–51.
Jouan-Lanhouet S, Riquet F, Duprez L, Vanden Berghe T, Takahashi N, Vandenabeele P. Necroptosis, in vivo detection in experimental disease models. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014;35:2–13.
Osipov RM, Bianchi C, Feng J, Clements RT, Liu Y, Robich MP, Glazer HP, Sodha NR, Sellke FW. Effect of hypercholesterolemia on myocardial necrosis and apoptosis in the setting of ischemia-reperfusion. Circulation. 2009;120:S22–30.
Cheng YC, Chang MH, Tsai CC, Chen TS, Fan CC, Lin CC, Lai CH, Tsai FJ, Lin JA, Huang CY. Garlic oil attenuates the cardiac apoptosis in hamster-fed with hypercholesterol diet. Food Chem. 2013;136:1296–302.
Zhang DW, Shao J, Lin J, Zhang N, Lu BJ, Lin SC, Dong MQ, Han J. RIP3, an energy metabolism regulator that switches TNF-induced cell death from apoptosis to necrosis. Science. 2009;325:332–6.
Vandenabeele P, Declercq W, Van Herreweghe F, Vanden Berghe T. The role of the kinases RIP1 and RIP3 in TNF-induced necrosis. Sci Signal. 2010;3:re4.
Ye YC, Wang HJ, Yu L, Tashiro S, Onodera S, Ikejima T. RIP1-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and ROS production contributed to tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced L929 cell necroptosis and autophagy. Int Immunopharmacol. 2012;14:674–82.
Varga ZV, Kupai K, Szucs G, Gaspar R, Paloczi J, Farago N, Zvara A, Puskas LG, Razga Z, Tiszlavicz L, et al. MicroRNA-25-dependent up-regulation of NADPH oxidase 4 (NOX4) mediates hypercholesterolemia-induced oxidative/nitrative stress and subsequent dysfunction in the heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013;62:111–21.
Csont T, Bereczki E, Bencsik P, Fodor G, Gorbe A, Zvara A, Csonka C, Puskas LG, Santha M, Ferdinandy P. Hypercholesterolemia increases myocardial oxidative and nitrosative stress thereby leading to cardiac dysfunction in apoB-100 transgenic mice. Cardiovasc Res. 2007;76:100–9.
Sabe AA, Elmadhun NY, Dalal RS, Robich MP, Sellke FW. Resveratrol regulates autophagy signaling in chronically ischemic myocardium. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;147:792–8. Discussion 798-799.
Sabe AA, Elmadhun NY, Sadek AA, Chu LM, Bianchi C, Sellke FW. Differential effects of atorvastatin on autophagy in ischemic and nonischemic myocardium in Ossabaw swine with metabolic syndrome. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;148:3172–8.
Koncsos G, Varga ZV, Baranyai T, Boengler K, Rohrbach S, Li L, Schluter KD, Schreckenberg R, Radovits T, Olah A, et al. Diastolic dysfunction in prediabetic male rats: Role of mitochondrial oxidative stress. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016;311:H927–h943.
Hsu HC, Chen CY, Lee BC, Chen MF. High-fat diet induces cardiomyocyte apoptosis via the inhibition of autophagy. Eur J Nutr. 2016;55:2245–54.
Zhu XY, Daghini E, Rodriguez-Porcel M, Chade AR, Napoli C, Lerman A, Lerman LO. Redox-sensitive myocardial remodeling and dysfunction in swine diet-induced experimental hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis. 2007;193:62–9.
Perales S, Alejandre MJ, Palomino-Morales R, Torres C, Iglesias J, Linares A. Effect of oxysterol-induced apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells on experimental hypercholesterolemia. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2009;2009:456208.
Chtourou Y, Slima AB, Makni M, Gdoura R, Fetoui H. Naringenin protects cardiac hypercholesterolemia-induced oxidative stress and subsequent necroptosis in rats. Pharmacol Rep. 2015;67:1090–7.
Roux PP, Shahbazian D, Vu H, Holz MK, Cohen MS, Taunton J, Sonenberg N, Blenis J. RAS/ERK signaling promotes site-specific ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation via RSK and stimulates cap-dependent translation. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:14056–64.
Acknowledgements
We thank Melinda Károlyi-Szabó and Sebestyén Tuza for technical assistance.
Funding
The project is financed by Hungarian Scientific Research Fund (OTKA K109737), Scientific Grant Agency of the Ministry of Education, Science, Research and Sport of the Slovak Republic (VEGA 1/0638/12), Faculty of Pharmacy, Comenius University in Bratislava, Slovak Republic (FaF UK/19/2015). CC and ZG was supported by the János Bolyai Research Scholarship of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences. ZVV was supported by the National Program of Excellence (TÁMOP 4.2.4.A/1-11-1-2012-0001). NHLBI P01 HL112730 to RAG.
Availability of data and materials
The dataset supporting the conclusions of this article are available upon request to the corresponding author.
Authors’ contributions
ZG designed study, performed research, assisted with interpretation and writing. GK performed experiments, assisted with analyses of results and interpretation and writing. TR assisted with analyses of results and interpretation and writing. AS, AA contributed to acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data. ZV, TB and CC performed experiments with animals. PF and RAG designed the experiments, wrote and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This investigation conforms to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the US National Institutes of Health (NIH publication No. 85–23, revised 1996) and was approved by the animal ethics committee of the University of Szeged, Szeged, Hungary.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12944-017-0524-4.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Giricz, Z., Koncsos, G., Rajtík, T. et al. Hypercholesterolemia downregulates autophagy in the rat heart. Lipids Health Dis 16, 60 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-017-0455-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-017-0455-0