Abstract
Cancer immunotherapy, especially immune checkpoint therapy, has revolutionized therapeutic options by reactivating the host immune system. However, the efficacy varies, and only a small portion of patients develop sustained antitumor responses. Hence, illustrating novel strategies that improve the clinical outcome of immune checkpoint therapy is urgently needed. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) has been proved to be an efficient and dynamic posttranscriptional modification process. It is involved in numerous RNA processing, such as splicing, trafficking, translation and degradation. Compelling evidence emphasizes the paramount role of m6A modification in the regulation of immune response. These findings may provide a foundation for the rational combination of targeting m6A modification and immune checkpoints in cancer treatment. In the present review, we summarize the current landscape of m6A modification in RNA biology, and highlight the latest findings on the complex mechanisms by which m6A modification governs immune checkpoint molecules. Furthermore, given the critical role of m6A modification in antitumor immunity, we discuss the clinical significance of targeting m6A modification to improve the efficacy of immune checkpoint therapy for cancer control.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The immune system functions as a guardian of the host by initiating immune responses against harmful pathogens and tumor cells. However, undue response is responsible for chronic or exaggerated inflammation and autoimmune diseases. Immune checkpoints play pivotal roles in regulating the magnitude of immune responses, thus maintaining immune homeostasis and self-tolerance. Whereas, tumor cells could also utilize immune checkpoints to evade immune surveillance, inhibit antitumor immune response, and eventually result in tumorigenesis and tumor progression [1]. Immune checkpoint therapy, a monoclonal antibody-based blockade, has driven a revolution in the field of cancer treatment [2]. To date, a variety of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for clinical application [3]. However, the low response rate, innate or acquired drug resistance and immunotherapy-related adverse events (irAEs) challenge the utility of clinical application. Therefore, the discovery of novel strategies that can be combined with ICIs is of utmost importance to maximize therapeutic benefit.
RNA modification has been reported for more than 70 years [4]. Due to the advancements in high-throughput sequencing technology, at least 160 types of RNA modifications have been identified [5]. N6-methyladenosine (m6A), the methylation of adenosine at the N6 site, is regarded as the foremost and most abundant posttranscriptional process in eukaryotic messenger RNAs (mRNAs) and noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) [6]. Approximately 1 – 4 m6A sites are detected in 1000 adenosine nucleotide residues [7]. As shown in a previous study, m6A modification mainly occurs in the “RRACH” sequence (where R = A or G; H = A, C, or U) [7], and is highly enriched in the 3' untranslated region (3' UTR), in the vicinity of stop codons in mRNAs or near the last exon in ncRNAs [7, 8]. Increasing evidence has revealed that m6A modification is involved in multiple aspects of biological activities, especially tumorigenesis and tumor progression [9].
The functions of m6A modification and immune checkpoints have been studied extensively in recent decades, and a range of immune checkpoints have been reported to be supervised in an m6A-dependent manner. In this review, we introduce the biological roles of m6A modification and immune checkpoints, and elaborate the recent progress in understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying m6A-modified immune checkpoints. To verify the potency of m6A in clinical application, we provide an overview of the up-to-date knowledge and future perspectives of m6A modification in cancer treatment. Furthermore, recent attempts to combine targeting m6A modification and immune checkpoints as a promising synergistic strategy for cancer therapy, as well as the potential limitations, are discussed.
RNA m6A modification and the regulators
RNA m6A modification, a dynamic, reversible and multilayered posttranscriptional process [10], is orchestrated by three types of enzymes: methyltransferases (writers), demethylases (erasers) and binding proteins (readers) [11]. On account of the great breakthrough in epitranscriptomics, an increasing number of writers, erasers and readers have been discovered. In the following section, we summarize the current landscapes of m6A regulators in RNA metabolism (Table 1, Fig. 1).
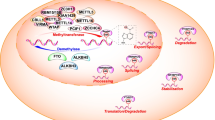
Mechanisms of RNA m6A modification. The adenosine (A) in mRNA is methylated to form N6-methyladenosine (m6A) via the core subunit of the methyltransferase complex (MTC) constitute by METTL3-METTL14-WTAP, and other writers, such as METTL5, METTL16, VIRMA, ZCCHC4, ZC3H13, CBLL1, RBM15 and RBM15B. m6A can be removed by erasers, including FTO, ALKBH3 and ALKBH5. The biological roles of m6A in RNA metabolism are exerted by readers, including YTHDF1/2/3, YTHDC1/2, IGF2BP1/2/3, and HNRNPC/HNRNPG/HNRNPA2B1
m 6 A methyltransferases/writers
The m6A modification is catalyzed via the formation of a methyltransferase complex (MTC) that contains several writers, including methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3), methyltransferase-like 5 (METTL5), methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14), methyltransferase-like 16 (METTL16), Wilms tumor 1-associated protein (WTAP), Vir-like m6A methyltransferase associated (VIRMA, also called KIAA1429), zinc finger CCHC-type containing 4 (ZCCHC4), zinc finger CCCH-type containing 13 (ZC3H13), Cbl proto-oncogene-like 1 (CBLL1, also known as HAKAI), and RNA-binding motif protein 15 (RBM15) and its paralogue RBM15B [12, 13].
METTL3, METTL14 and WTAP constitute the core subunits of the MTC. As the unique catalytic component of MTC, METTL3 alone carries limited catalytic activity, which is markedly intensified when it is integrated with METTL14 [14]. METTL14 shows no catalytic activity, but is essential for recognizing substrate RNAs, and functions as a scaffold for METTL3 [15]. In the writing process, WTAP stabilizes the core MTC, formed by METTL3 and METTL14, and promotes m6A installation by recruiting the complex to nuclear speckles [16]. The other subunits carry specific functions. VIRMA transports the MTC to the 3' UTR or stop codon regions of mRNAs [17]. RBM15 and its paralogue RBM15B facilitate the binding of METTL3 and WTAP, and then recruit the complex to specific RNA-binding sites [17, 18]. By interacting with WTAP, ZC3H13 maintains the MTC in nuclear speckles and increases its catalytic function [19]. ZCCHC4 is critical for adding m6A to the 28S ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), and mediating the distribution and translation of rRNAs [20].
In addition to the canonical writers, many novel writers with diverse functions have been identified in recent studies. METTL5 participates in the m6A modification of 18S rRNAs [21]. Similar to the METTL3-METTL14 complex, METTL5 shows metabolic stability by forming a heterodimeric complex with its coactivator TRMT112 [21]. METTL16 is a recently discovered, independent and active writer. It drives m6A at the 3' UTR of mRNAs and at the A43 site of U6 small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) [22]. Additionally, METTL16 plays a crucial role in RNA stability and splicing regulation [23, 24]. Phosphorylated CTD interacting factor 1 (PCIF1), a cap-specific adenosine methyltransferase (CAPAM), mediates m6A modification on 2'-O-methylated adenosine present at the 5' end of mRNAs (m6Am) [25].
m 6 A demethylases/erasers
The erasers, capable of removing m6A from RNAs, enable m6A modification to be a dynamic and reversible process. To date, two proteins, fat mass- and obesity- associated protein (FTO) and AlkB homolog 5 (ALKBH5), have been identified as canonical m6A erasers [26, 27]. As two members of the Fe2+/α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase family, FTO and ALKBH5 can successively convert m6A to N6-hydroxymethyladenosine (hm6A), N6-formyladenosine (f6A) and adenosine [28]. Recent studies have indicated that ALKBH5 may function in a more direct manner by removing the methyl group of m6A, converting m6A to adenine [29]. Additionally, FTO can catalyze the demethylase activity on other types of RNA methylation, including N6,2'-O-dimethyladenosine (m6Am) on mRNAs and snRNAs, as well as m1A on tRNAs [28, 30]. Overexpression of FTO has been found in a set of tumors, such as glioblastoma (GBM), melanoma, breast cancer (BC) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML), highlighting the m6A-dependent oncogenic role of FTO, as well as the tight relationship between impaired FTO expression and short survival time in the cancer context [31,32,33,34]. ALKBH5 seems to specifically demethylate m6A on single-stranded RNAs [29]. Dysregulated in numerous malignancies, ALKBH5 plays oncogenic or antitumor roles as an m6A demethylase, depending on the tumor type. Studies have revealed that ALKBH5 functions as a tumor promotor in GBM, gastric cancer, ovarian cancer and AML [35,36,37,38]. However, an antitumor role of ALKBH5 has been demonstrated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), pancreatic cancer and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) [39,40,41]. In addition, ALKBH3 is defined as a novel and multifunctional m6A eraser. In contrast to mRNA or rRNA, tRNA is the preferred substrate of ALKBH3 [42]. Furthermore, ALKBH3 has been reported to function as an m1A demethylase [43].
m 6 A binding proteins/readers
The biological function of m6A is performed by the recruitment of certain binding proteins, which selectively integrate with methylated RNAs to affect their metabolism. Readers of m6A are mainly comprised of YT521-B homology (YTH) domain family proteins (YTHDF1/2/3), YTH domain-containing proteins (YTHDC1/2), insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding proteins (IGF2BP1/2/3) and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (HNRNPC/HNRNPG/HNRNPA2B1). YTHDF1/2/3 and YTHDC1/2 have been extensively studied and can be classified into three types according to their cellular location: cytoplasmic YTHDF1, YTHDF2 and YTHDF3; nucleocytoplasmic YTHDC2; and nuclear YTHDC1 [44]. YTHDF1 has been reported to bind to m6A near the stop codons of mRNAs and recruit factors to initiate RNA translation [45]. YTHDF2 selectively binds to m6A-methylated mRNAs and mediates their decay by recruiting the CCR4–NOT deadenylase complex [46]. YTHDF3 functions as a fortifier to YTHDF1 and YTHDF2 [47]. As a nuclear reader, YTHDC1 recruits and modulates serine- and arginine-rich splicing factor 3 (SRSF3) to localize to the binding site of pre-mRNAs, and regulates their alternative splicing [48]. In addition, YTHDC1 recognizes the target mRNAs and ncRNAs to facilitate their exporting from nucleus [49]. Recent studies have revealed that YTHDC1 induces the decay of chromosome-associated regulatory RNAs (carRNAs), including promoter-associated RNAs, enhancer RNAs and repeat RNAs [50]. YTHDC2 increases the translation capacity of target mRNAs, while decreases their abundance [51]. IGF2BP1/2/3 are involved in promoting the translation and stability of mRNAs by recognizing the consensus GG(m6A)C sequence [52]. By recognizing primary miRNAs (pri-miRNAs), HNRNPA2B1 promotes the maturation of miRNAs [53]. Both HNRNPC and HNRNPG are known as indirect readers since they do not bind to the m6A modification sites directly, but selectively bind to the newly formed structure altered by m6A modification, which is called “m6A switch” [54].
Immune checkpoints
Immune checkpoints, which function as brakes, play essential roles in maintaining homeostasis of the immune system by limiting the magnitude of immune response. Owing to their durable efficacy and minimal side effects, ICIs have revolutionized cancer treatment and led to immunotherapy being adopted as a treatment strategy following surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy [55, 56]. A large number of immune checkpoints have been explored in recent decades, including but not limited to cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein-4 (CTLA-4), programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1), programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1), T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing-3 (TIM-3), lymphocyte activation gene-3 (LAG-3), T cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain (TIGIT), V-domain Ig suppressor of T cell activation (VISTA), B7 homolog 3 (B7-H3) and B and T cell lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) [57]. Our review focuses mainly on the most extensively studied immune checkpoints, namely, CTLA-4, PD-1 and PD-L1, whose expression has been reported to be manipulated in an m6A-dependent manner (Table 2, Fig. 2). The interplay between the m6A modification and other immune checkpoints is still being elucidated.
Mechanisms of inhibition of T cell activation induced by CTLA-4 and PD-1. Tumor cells or antigen-presenting cells transmit stimulatory and inhibitory signals to modulate T cell activation. The T cell receptor (TCR) interacts with the major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-peptide complex presented by antigen-presenting cells (APCs). CD28-CD80/CD86 interaction induced costimulatory signaling promotes T cell activation. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTL A-4) decreases CD28 signaling by competing for the shared ligands (CD80/CD86). The CTLA-4-CD80/CD86 interaction induces inhibitory signaling by protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) or Src homology 2 domain-containing phosphatase 2 (SHP2). Upon the binding of programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) with programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1)/programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L2), the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) and immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif (ITSM) motifs in PD-1 are phosphorylated, resulting in the recruitment of phosphatases SHP1 and SHP2. This activity leads to the dephosphorylation of key molecules in the TCR and CD28 signaling pathways, thereby inhibiting T cell activation
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 4 (CTLA-4)
CTLA-4 is predominantly expressed on T cells and to a lesser degree on activated B cells, dendritic cells (DCs), monocytes and granulocytes. CTLA-4 has been identified as a negative regulator of T cell activation after antigenic stimulation of the T-cell receptor (TCR) [58]. The full activation of T cells requires three signaling pathways: (1) TCR binding with the major histocompatibility complex (MHC)–peptide complex presented by antigen-presenting cells (APCs); (2) CD80 (B7-1)/CD86 (B7-2) on APCs integrating with the costimulatory molecule CD28 on T cells; and (3) cytokines produced by T cells regulating immune responses [59].
As a transmembrane protein, CTLA-4 mainly localizes in the intracellular compartments. Upon the activation of T cells, CTLA-4 is translocated to the cell surface. TCR signaling increases CTLA-4 glycosylation and surface level abundance by stimulating hexosamine metabolism and the N-glycan-branching pathway [60]. CTLA-4 in exosomes can be recycled back to the cell surface to increase its surface expression level [61]. CTLA-4 functions as a major coinhibitory receptor by competing with CD28 for the shared B7 ligands (CD80/CD86) during the priming phase of immune response [62]. It decreases CD28 signaling mainly in two ways. First, CTLA-4 on T cells reduces the expression of CD80/CD86 on APCs in a trans-endocytosis manner [63]. Second, CTLA-4 binds to CD80/CD86 with a higher affinity than CD28 and initiates an inhibitory signaling mediated through phosphatases, such as protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) or Src homology 2 domain-containing phosphatases (SHPs) [64]. PP2A is a vital serine-threonine phosphatase, assisting in maintaining cell homoeostasis by blocking kinase-mediated intracellular signaling pathways [65]. Upon the activation of TCR, CTLA-4 associates with PP2A to suppress the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT pathway [66]. In addition, SHP2 can be recruited by the YVKM motif in CTLA-4 cytoplasmic domain to inhibit T cell activation [67].
PD-1/PD-L1
PD-1 is a negative regulator of immune response. It is abundantly expressed on the surface of most activated immune cells, such as B cells, T cells, macrophages, DCs and Langerhans’ cells [68]. As a type I transmembrane protein receptor, PD-1 contains an immunoglobulin V (Ig-V)-like extracellular domain, a transmembrane domain and a cytoplasmic domain [69]. Two motifs in the cytoplasmic domain of PD-1, named immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) and immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif (ITSM), are essential for the inhibitory function of PD-1.
PD-L1 and PD-L2 are two ligands for PD-1, which belong to the B7 family of type I transmembrane proteins. PD-L1, the production of which is induced by IFN-γ, is primarily expressed on endothelial cells, tumor cells and activated leukocytes, including T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, B cells, DCs and macrophages. PD-L2, the expression of which is regulated by IL-4, is predominantly found on activated DCs and macrophages [70]. Both of the ligands consist of two extracellular domains (an Ig-V domain and Ig-C domain), a transmembrane domain and a short cytoplasmic domain that carries nonclassical signaling motifs with unclear functions [71]. PD-1 antagonists, which block binding of both PD-L1 and PD-L2 to PD-1, show clinical efficiency similar to that of PD-L1 antagonists. Therefore, PD-L1, but not PD-L2, is believed to be the dominant inhibitory ligand of PD-1 [72].
PD-1 exerts its inhibitory effect on T cells primarily through intracellular signaling pathway. Engagement of PD-1 with its ligands results in phosphorylation of ITIM and ITSM motifs [73]. Phosphorylated ITSM and ITIM are critical for the recruitment of phosphatases SHP1 and SHP2, which in turn dephosphorylate key molecule in TCR and CD28 signaling pathways [74, 75], thereby attenuating downstream pathways, such as the PI3K/AKT, ZAP70, RAS, ERK, VAV and phospholipase Cγ (PLCγ) pathways [74, 76,77,78,79,80]. All these pathways ultimately lead to dampened T cell activation, proliferation and cytokine production. Moreover, even with the SHP1/2 genes knocked down, PD-1 can inhibit proliferation and cytokine production in primary T cells, suggesting an alternative signaling mechanism that initiates PD-1 signaling pathway activation [81]. Additionally, PD-L1-containing exosomes secreted by tumor cells can activate the PD-1 pathway and suppress T cell activity in draining lymph nodes [82].
Role of m6A modification in regulating immune checkpoints
Compelling studies have revealed critical roles for m6A modification in innate and adaptive immunity, especially in modulating immune checkpoints. In this review, we elaborate on the roles of m6A modification in the regulation of immune checkpoints, and attempt to explore the underlying mechanisms (Table 3, Fig. 3).
m6A regulators alter immune checkpoint expression in tumors. Among writers, METTL3 enhances PD-L1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), and augments CD80 and CD86 in DCs and macrophage, respectively. For erasers, FTO increases PD-1 and PD-L1 expression in melanoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC), respectively; FTO also ascends the expression of PD-L1, PD-L2 and LILRB4 in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). For readers, YTHDC1 escalates the expression of PD-L1 in NSCLC; YTHDF1 boosts the expression of CD80 in DCs, and descends the expression of PD-L1 in NSCLC; YTHDF2 decreases the expression of PD-L1 in ICC and NSCLC, as well as the expression of LILRB4 in AML
m6A writers and immune checkpoints
In recent decades, m6A writers, especially METTL3, have been shown to be abnormally expressed and to play critical roles in the development of a wide range of neoplasms. Dysregulated METTL3 expression in tumors exerts a great impact on antitumor immunity. In testicular germ cell tumors (TGCTs), the expression of METTL3 is decreased, which is positively correlated with the tumor infiltration of CD8 + T cells, CD4 + T cells and NK cells [83]. In cervical cancer (CC), the expression of METTL3 is upregulated, and shows a positive relation to the CD33 + myeloid derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), which function as negative regulators in antitumor immunity [84]. In BC, the expression of METTL3 is positively associated with the tumor infiltration of CD8 + T cells, helper T cells and activated NK cells, and is negatively associated with the expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2 [85]. METTL3-induced m6A modification, with high abundance in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), augments PD-L1 expression and restrains CD8 + T cells activation, promoting cancer cell metastasis and proliferation. Meanwhile, METTL3 knockdown results in the opposite result, suggesting METTL3 as a promising therapeutic target for OSCC [86]. Plakophilin 3 (PKP3) is a member of the arm repeat family of catenin proteins [87] and its activity is highly correlated with the progression and metastasis of various tumors. However, its role in the regulation of immune checkpoints mediated by m6A modification remains unrevealed [88]. A recent study reported that METTL3-methylated m6A modification restrains CD8 + T cell infiltration by indirectly upregulating PKP3, thereby suppressing the immune response in NSCLC. Furthermore, PKP3 integrates with the RNA-binding protein FXR1 to stabilize OTUB1 mRNA [89], which in turn elevates PD-L1 expression, indicating a positive correlation between METTL3 and PD-L1 expression in vitro [90].
Costimulatory molecules, such as CD40, CD80 and CD86, play critical roles in the immune response. However, the effect of m6A modification in innate immunity which is exerted by manipulating the expression of costimulatory molecules requires further investigation. DCs exhibit critical antigen-presenting functions in both innate and adaptive immunity [91]. A recent study revealed that METTL3-mediated m6A modification promotes DC activation and function by increasing CD40, CD80 and cytokine IL-12 expression in a NF-κB signaling dependent manner. Depletion of METTL3 dampens the antigen presentation property of DCs both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, by promoting the translation of CD40, CD80 and Tirap transcripts in DCs, METTL3-mediated m6A modification augments T cell activation and enhances cytokine production [92]. Macrophages are critical immune cells in tissue homeostasis, inflammation, and pathologies [93]. The role and mechanism of m6A modification in macrophage polarization remain concealed. METTL3 expression is boosted following M1 macrophage polarization, and is proclaimed to markedly increase the stability and expression of signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) mRNA, which is a crucial transcription factor involved in the polarization of macrophages [94]. Disruption of METTL3 activity induces a marked inhibition of both IFN-γ-induced CD86 protein and reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby interfering with M1 macrophage polarization [95]. Additionally, a bioinformatics study showed that METTL3 is positively correlated with the expression of CD80, CD86, PD-L1, intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM) 1 and ICAM3 in HCC. These findings indicate that METTL3 plays a critical role in immune cell infiltration and tumor microenvironment (TME) reshaping [96].
METTL14 serves as a structural support for METTL3 to exert its unique catalytic activity. Abnormal expression of METTL14 has been observed in diverse malignancies, indicating its nonnegligible role in tumor progression [97]. However, studies on the effect of METTL14 on immunotherapy are still preliminary, and more experimental data are need. METTL3/METTL14 adjusts the TME and cytotoxic CD8 + T cell infiltration in mismatch-repair-proficient or microsatellite instability-low colorectal cancer (pMMR-MSI-L CRC). Silencing METTL3/METTL14 enhances the efficacy of immune checkpoint therapy by modulating the production of cytokines and chemokines in the TME. Mediated by YTDHF2, METTL3/METTL14 knockdown stabilizes STAT1 and Irf1 mRNAs, and promotes IFN‐γ‐STAT1‐Irf1 signaling, which in turn sensitizes tumor cells to PD‐1 inhibition. Additionally, depletion of METTL3/METTL14 sensitizes tumor cells to IFN‐γ treatment [98]. The role of METTL14 in immune cell infiltration has also recently attracted considerable attention. According to a bioinformatics study, the expression of METTL14 is downregulated in BC, and exhibits a positive association with the infiltration of CD4 + T cells, CD8 + T cells, neutrophils, macrophages and dendritic cells, as well as a negative correlation with regulatory T (Treg) cell infiltration [99]. Another bioinformatics study demonstrates that METTL14 is downregulated in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) and is negatively correlated with the infiltration of Treg cells [100].
m 6 A erasers and immune checkpoints
Various studies have elucidated that aberrantly expressed m6A erasers are associated with tumor progression by intrinsically regulating immune checkpoints [101, 102]. The oncogenic function of FTO in melanoma is manifested by increased tumor growth and inhibited host responses to anti-PD-1 therapy. The study concludes that PD-1 expression is induced via the autophagy/NF-κB/FTO axis, suggesting that the FTO/PD-1 axis is a vital component of adaptive immunity. Furthermore, FTO knockdown increases YTHDF2-mediated m6A modification of oncogenes, including PD-1, CXCR4 and SOX10, and sensitizes melanoma cells to IFN-γ and anti-PD-1 treatment [32].
Depletion of FTO in human colon cancer cells markedly reduces the expression of both PD-L1 mRNA and protein in an IFN-γ signaling-independent manner, highlighting the positive role of FTO in PD-L1 regulation [103]. Additionally, Liu et al. reported that FTO-mediated m6A demethylation allowed tumor cells to escape immune surveillance by regulating glycolytic metabolism, and restrained T cell immune responses in melanoma and lung cancer. By interfering glycolytic activity in tumors, FTO knockdown elevated the antitumor efficacy of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and inhibited tumor growth in vivo. The synergistic application of FTO inhibitor and ICI restrained tumor growth, and prolonged overall survival, suggesting that targeting m6A modification regulators is a potential strategy to elevate immune checkpoint therapy efficacy [104]. Overexpressed FTO induced by decitabine in AML increased the expression of immune checkpoints in an m6A-dependent manner. Moreover, FTO depletion significantly dampened the expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2, as well as a newly characterized potent immune checkpoint, leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B4 (LILRB4). The study emphasizes the critical role of FTO in regulating immune checkpoints, and propounds the bright prospect of targeting FTO in antitumor therapy [101].
ALKBH5 is reported to regulate the infiltration of Treg cells and MDSCs in the TME, and to inhibit the sensitivity of immune checkpoint therapy by modulating the m6A abundance and RNA stability of Mct4/Slc16a3 [105]. In melanoma cells and CRC cells, ALKBH5 knockdown altered both the recruitment of the immune cell subpopulation and the transcriptome of tumor cells. An enhanced therapeutic response to PD-1 inhibitor has also been observed in genetically mutated or ALKBH5 downregulated tumor cells, highlighting the pivotal role of ALKBH5 in the regulation of immune checkpoint therapy [105]. A recent experiment revealed that ALKBH5-mediated m6A demethylation directly inhibited PD-L1 expression on tumor cells and macrophages and the infiltration and cytotoxicity of T cells in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC). Depletion of tumor-intrinsic ALKBH5 enhanced m6A modification on PD-L1 mRNA, and promoted its degradation in a YTHDF2-dependent manner. This ALKBH5-PD-L1 regulatory axis may provide novel insights into immune checkpoint therapy and response prediction [106].
m 6 A readers and immune checkpoints
Readers are the true executors of m6A modification and control the fates of target RNAs. m6A modification of specific oncogenic RNA promoted PD-L1 expression and inhibited CD8 + T cell infiltration in a YTHDC1-dependent manner [90]. YTHDF1-mediated m6A modification suppressed the function of DCs by augmenting the translation of lysosomal protease transcripts in ovalbumin (OVA)-expressing B16 melanoma. Silenced YTHDF1 in DCs restrained lysosomal proteolysis and promoted the cross-presentation of tumor antigens, leading to promoted cross-priming of CD8 + T cells and enhanced therapeutic efficacy of anti-PD-L1. Furthermore, the combination treatment of YTHDF1 knockdown and anti-PD-L1 led to a complete tumor regression that overwhelmed the monotherapy groups evaluated, indicating that YTHDF1 depletion in combination with an ICI is a novel strategy to enhance the therapeutic efficacy [107]. Additionally, a previous study focusing on the role of m6A modification in the activation of DCs found that YTHDF1 was positively correlated with the translation of CD80 and CD40 mRNAs. Furthermore, YTHDF1 knockdown downregulated the expressions levels of these transcripts [92]. Another study emphasized that YTHDF1 and YTHDF2 in lung cancer cells were independent favorable prognostic indicators for recurrence-free survival. YTHDF1 and YTHDF2 expression was positively correlated with TILs density and negatively associated with PD-L1 expression. YTHDF1 and YTHDF2 knockdown enhanced PD-L1 expression in tumor cells [108].
The correlation between YTHDF2 and tumor immunotherapy has attracted considerable attention. LILRB4 is a novel immune checkpoint [109]. YTHDF2 knockdown in AML stabilizes LILRB4 mRNA, suggesting an antitumor role for YTHDF2 [101]. A bioinformatics analysis of ccRCC indicated that YTHDF2 expression was positively associated with the infiltration of immune cells, including B cells, CD8 + T cells, CD4 + T cells, macrophages, neutrophils, and DCs [110]. Additionally, positive correlations between the expression of YTHDF2 and immune checkpoints, including PD-1, TIM-3 and CTLA-4, have been observed in lower-grade glioma (LGG), emphasizing a role for YTHDF2 as a novel prognostic biomarker [111]. Moreover, another bioinformatics study demonstrated a positive correlation between the expression of m6A regulators and immune checkpoints, including TIM-3, LAG-3, PD-1, PD-L1, CTLA-4 and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) [112]. Although the totality of the bioinformatics data indicates their correlation, the specific mechanisms by which m6A readers in orchestrating immune checkpoints are still largely unknown, and the research is still in its infancy. Therefore, a large amount of experimental and clinical data are needed.
The application of m6A modification and ICIs for cancer treatment
Given the prominent role played by m6A modification in antitumor immunity, especially the manipulation of immune checkpoints, a wide range of studies have explored advantages of targeting m6A modification to improve the efficiency of immune checkpoint therapy (Fig. 4).
Therapeutic strategies targeting m6A modification. A. Targeting m6A regulators by ncRNAs, including miRNAs, lncRNAs, circRNAs, siRNAs and shRNAs to orchestrate the expression of m6A regulators. B. Nanoparticles (NPs), such as OsSx-PEG, GNRa-CSP12 and GNPIPP12MA, manipulate m6A modification in distinct manners; nanoparticles have also been developed to encapsulate drugs, siRNAs and circRNAs to regulate m6A modification. C. CRISPR‒Cas-based gene editing technologies for site-specific m6A methylation. D. Small-molecules targeting m6A regulators
Targeting m 6 A regulators by ncRNAs
Extensive studies have elucidated the pivotal roles of m6A modification and its regulators in cancer development, as well as in antitumor immunity remodeling. Therefore, directly targeting m6A regulators may endow us with a promising strategy for cancer treatment. ncRNAs have clarified our perception of their pivotal roles in biological and pathological processes, especially their therapeutic potential in cancer treatment. In this review, we describe the currently available gene regulation strategies based on ncRNAs in preclinical studies to identify the roles of m6A modification in immune checkpoint therapy. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) refer to a series of noncoding RNAs that carry great gene regulation potential. They contribute to the inhibited translation or degradation of target mRNAs [113]. Notably, several miRNAs have been reported to directly target m6A regulators [114]. For example, a negative correlation between the expression of miR-33a and METTL3 has been reported. MiR-33a contributes to the suppression of METTL3 mRNA by directly binding to its 3' UTR, which in turn inhibits the progression of NSCLC [115]. Similarly, miR-145 has been reported to target the 3' UTR of YTHDF2, and thus dampen its expression, resulting in enhanced global m6A mRNA expression in HCC. Downregulated YTHDF2 is critical for inhibited tumor progression of HCC [116]. These findings of the effects of miRNAs on tumors provide valuable insights into the potential roles of miRNAs in tumor progression via fine-tuned m6A modification. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are also involved in the regulation of m6A modification in various neoplasms. LINC00470 integrates with METTL3 and reduces the stability of the tumor suppressor phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), which in turn promotes GC progression [117]. LncRNA GAS5-AS1 has been reported to associate with ALKBH5, and alter the m6A modification of GAS5, thus restraining cervical cancer progression [118]. CircRNAs have been reported to participate in the regulation of m6A modification. In a recent study of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), the circGARS/miR-19a signaling pathway was shown to regulate the expression of YTHDF2 to alter the activation of the immune response, which was mediated by tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3) [119]. In group 3 innate lymphoid cells (ILC3s), circZbtb20 has been reported to promote ALKBH5-mediated demethylation on target mRNA, thus enhancing its stability [120]. RNA interferences, such as that mediated by small interfering RNA (siRNA) and short hairpin RNA (shRNA), demonstrate great therapeutic potency by orchestrating m6A modification. A recent study indicated that METTL3-mediated m6A modification promoted PD-L1 expression, inhibited CD8 + T cell infiltration, and induced tumor cell immune evasion in NSCLC. SiRNA-induced METTL3 knockdown augmented the therapeutic efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy in an NSCLC mouse model [90]. The oncogenic role of METTL3 has also been observed in OSCC, while shRNA-mediated METTL3 knockdown dampened PD-L1 expression and intensified CD8 + T cell activation [86]. In conclusion, these findings from studies on ncRNAs have expanded our understanding of their roles in modulating epigenic regulation and provide us new therapeutic tools targeting m6A modification in cancer treatment.
Engineered nanoparticles targeting m 6 A modification
Nanoparticles (NPs) are promising biomaterials and drug delivery tools that effectively facilitate immunotherapy and enhance potency with reduced toxic side effects [121]. FTO inhibitor-loaded glutathione-bioimprinted nanocomposites (GNPIPP12MA) are engineered to target the FTO/m6A pathway with glutathione depletion for synergistically improving anti-leukemia treatment efficiency. GNPIPP12MA upregulates the global m6A modification level and enhances anti-PD-L1 therapy efficacy by increasing the infiltration of cytotoxic T cells [122]. Hypoxia is involved in many aspects of oncology, such as tumor proliferation, cancer stem cell maintenance, cell death, angiogenesis and drug resistance [123, 124]. Nanocatalyst named OsSx-PEG (PEG = poly(ethylene glycol)) NP as O2 regulator were engineered in a recent study to reverse tumor hypoxia. Mechanistically, by retaining METTL3 expression and attenuating ALKBH5 expression, OsSx-PEG NPs increase the m6A-dependent mRNA degradation of hypoxia-related genes, which in turn relieves the hypoxia in the TME to enhance drug efficacy and overcome resistance [125]. Another study illustrated that newly developed bovine serum albumin (BSA)-templated Au, CuS and Gd2O3 NPs alter the global m6A expression level, thus impairing cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis [126]. NPs, such as lipid-based NPs, polymer-based NPs, and inorganic NPs, can be endocytosed by tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and then deliver drugs or RNAs into TAMs of the TME [127,128,129,130]. For example, lipid NPs loaded with C–C motif chemokine receptor 2 (CCR2) siRNA hinder the accumulation of TAMs in the TME [127]. Polymeric NPs were developed to deliver vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) siRNA and placental growth factor signaling (PIGF) siRNA to both tumor cells and TAMs, leading to suppressed tumor growth and metastasis [128]. Additionally, exosomes are regarded as extracellular nanovesicles [131], and are capable of transmitting specific oncogenic RNAs to promote NSCLC progression and drug resistance by upregulating the expression of METTL3 [132]. Notably, gold nanorods loaded with chitosan and a 12-mer peptide (GNRa-CSP12) were synthesized to elevate the efficiency of targeting and internalization in AML. GNRa-CSP12 was found to impede endogenous Fe2+-dependent m6A demethylase activity, thus promoting m6A modification on critical targets, including PKM, CD276 and SLC2A3, which manipulated immune checkpoint pathways involved in hypoxia and glycolysis, respectively. Furthermore, GNRa-CSP12 improved the therapeutic efficacy of anti-PD-L1 by increasing CD8 + T cell and CD4 + T cell infiltration, as well as IFN-γ production [133]. The success of nanoparticles use has heralded marked progress in cancer therapy due to their great efficiency and minor side effects. However, the design of delivery technologies for m6A modification is still in its nascent stage. Future work needs to be devoted to the investigation of novel delivery technologies to expand and develop advanced strategies targeting the epitranscriptome.
Developing m 6 A editing system
CRISPR‒Cas9 was first described in bacterial and archaeal immunity, and is now being developed as a potent gene editing technology. Single guide RNA (sgRNA) recognizes specific DNA sequences adjacent to a specific protospacer-adjacent motif (PAM) and manipulates the DNA-cleavage activity of CRISPR‒Cas9. It is concluded that CRISPR‒Cas9 may serve as a promising approach to program m6A regulators in both tumor cells and immune cells. [134]. NK cells play central roles in innate immune system, and are pivotal for antitumor immunity as well [135]. It is reported that METTL3-mediated m6A modification promotes the antitumor immunity of NK cells in HCC. CRISPR‒Cas9 induced METTL3 knockdown impairs the homeostasis of NK cells by decreasing SHP-2 level, and inhibits their infiltration and function in the TME [136]. Depletion of METTL3/METTL14 using CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing technology sensitizes CRC cells and melanoma cells to anti-PD-1 therapy, and exhibits a synergetic effect by prolonging overall survival [98].
The application of the CRISPR‒Cas9 gene editing system has been further expanded by the construction of dCas9, which shows deficient in DNA-cleaving capacity [137]. To achieve site-specific m6A methylation or demethylation, a tool was engineered by tagging METTL3-METT14, FTO, or ALKBH5 to the N-terminus of RNA-targeting dCas9. These engineered m6A regulators can induce installation or removal of m6A without altering the primary sequence of target genes [138]. With the progress in gene editing technology, a new CRISPR‒Cas-based tool was developed by replacing dCas9 with dCas13 featured by smaller size, independence of PAMer oligonucleotide and minimal off-target activity [139]. Its applications and great potential have been demonstrated in previous studies in which METTL3/METTL3-METTL14 [140], FTO [50] or ALKBH5 [141] have been fused with catalytically inactive dCas13b. Ruminococcus flavefaciens Cas13d (previously named CasRx) carries the smallest dimension but most powerful targeted genome editing potency [142]. Recently, a bidirectional dCasRx-based m6A editing platform was engineered by conjugating dCasRx with METTL3 or ALKBH5, enabling m6A methylation or demethylation to occur at specific RNA sites [143]. These recently developed gene editing platforms provide optimal methods to manipulate the m6A modification on specific genes, offering novel strategies to elucidate the roles and underlying mechanisms of individual m6A regulators in fine-tuning immune checkpoints. However, experimental data are quite limited, and more research is warranted to develop novel m6A editors with superior precision and specificity for genome editing, especially for immune checkpoint therapy adjustment.
Candidate m 6 A-targeted compounds
A wide range of studies have confirmed that abnormally expressed m6A regulators contribute to carcinogenesis and progression. Therefore, compounds targeting m6A regulators may directly inhibit tumor cells or activate antitumor immunity in an immune checkpoint-dependent manner. To date, a series of small molecules targeting m6A regulators have been developed, among which FTO inhibitors are the most prolific (Table 4). Two newly discovered potent compounds, CS1 and CS2, directly bind to the enzymatic reaction center of FTO, and thus suppress the demethylase activity of FTO. In addition to dramatically inhibit the self-renewal of leukemia stem cells, CS1 and CS2 have been reported to reprogram the immune response by suppressing the expression of the recently characterized immune checkpoint LILRB4, sensitize leukemia cells to cytotoxic T cells, and abate immune escape in mice. Additionally, CS1 and CS2 display their antitumor roles in a broad range of solid tumors, including pancreatic cancer, BC and GBM [101]. Another FTO inhibitor, Dac51, restrains the glycolytic capacity of tumor cells by dampening FTO-mediated demethylation on Jun mRNA and Cebpb mRNA. It increases CD8 + T cell infiltration in the TME and acts synergistically with PD-L1 inhibitor in both melanoma cells and lung cancer cells [104]. FTO requires 2-oxoglutarate (2OG) and Fe (II) to catalyze its demethylation activity. R-2-hydroxyglutarate (R-2HG) is a 2OG analog and competitively binds to FTO, inhibiting its enzymatic activity [144]. In addition, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug called meclofenamic acid (MA) has been repurposed to inhibit the activity of FTO by specifically integrating with the active surface of FTO [31, 145]. Evidence has confirmed confirm that MA suppresses the proliferation of GBM stem cells and sphere formation in vitro and restrains the progression of GBM in vivo [146]. Moreover, two derivatives of MA, FB23 and FB23-2, exhibit significant inhibitory effects on FTO activity in AML, prostate cancer and uterine cervical cancer [147,148,149]. Similarly, entacapone, previously applied to Parkinson’s disease, has recently been identified as a potent FTO inhibitor [150, 151]. The combination of entacapone and imatinib (a tyrosine kinase inhibitor) is currently in an early phase I clinical study for the treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors [152]. Moreover, MO-I-50 has been reported to significantly suppress the survival and colony formation in triple-negative inflammatory breast cancer cells by inhibiting FTO activity [153]. Other compounds, such as Rhein, CHTB and N-CDPCB, play antitumor roles by disrupting the catalytic function of FTO [154,155,156].
Potent and selective molecules that target other m6A regulators are still in the stage of development, and more exploration is required. Great efforts have been directed to the identification of ALKBH5 inhibitors using high-throughput in silico screening technology. ALK-04, a small-molecule inhibitor of ALKBH5, functions synergistically with PD-1 inhibitor to suppress the growth of melanoma tumor in vivo [105]. Moreover, MV1035, another efficient ALKBH5 inhibitor, carries a favorable antitumor potency by suppressing the progression of GBM [157]. In addition, two other recently introduced ALKBH5 inhibitors, 2-[(1-hydroxy-2-oxo-2- phenylethyl)sulfanyl]acetic acid and 4-[(furan-2-yl)methyl]amino-1,2-diazinane-3,6-dione, suppressed the proliferation of leukemia with great potential [158]. Except for the small-molecular inhibitors of ALKBH5, novel agents are being investigated. As we noted above, ALKBH5 exerts its demethylase function in a 2OG and Fe2+ dependent manner [28]. Hence, targeting 2OG and Fe2+ seem to be promising strategies for targeting ALKBH5 in the future. Through in silico screening technology, four compounds, namely Asp295, Phe534, Arg536, and Asn539, are defined as derivatives of piperidine and piperazine, and act as activators of the METTL3-METTL14-WTAP complex by promoting m6A modification on target RNAs. However, their potential antitumor effect needs for further validation [159]. Two other METTL3 inhibitors (Compound 1 and Compound 2), which were verified in a structure-guided medicinal chemistry platform, can reduce the abundance of METTL3-methylated mRNAs and suppressing the proliferation of leukemia cells both in vivo and in vitro [146]. A recently discovered METTL3 inhibitor named STM2457 exerted a significant antitumor effect on leukemia both in vitro and in vivo, providing proof that METTL3 is a potential therapeutic target in antitumor therapy [160]. BTYNB, a potent and specific inhibitor of IGF2BP1, suppresses the proliferation of melanoma and ovarian cancer cells by downregulating the expression of target mRNAs, including c-Myc, β-TrCP1, eEF2 and E2F1 [161, 162]. Given the great antitumor effect of these agents by targeting m6A modification, increasing efforts have been made to explore novel m6A-targeted compounds, as well as their synergistic effect with immune checkpoint therapy. However, most of the current compounds are still in a preclinical stage of research, and only a few of them have been reported to be involved in the regulation of immune checkpoints. Hence, more detailed experimental data and randomized controlled clinical trials are warranted to further evaluate their roles in immune checkpoint regulation, as well as their safety and efficiency in patients.
Conclusion and perspective
Evidence is emerging to show that m6A modification plays a central role in numerous regulatory pathways, and ectopic m6A modification may result in catastrophic consequences, such as carcinogenesis and cancer progression. m6A-based therapies are of great therapeutic potential in cancer treatment, and may sensitize tumors to immune checkpoint therapy [163]. The synergistic combination of treatments targeting m6A modification and ICIs apparently presents a captivating and promising prospect in cancer treatment. In this review, we summarize recent progress in understanding the function and mechanism of m6A modification, and further discuss its roles in orchestrating the expression and function of immune checkpoints, such as CTLA-4, PD-1 and PD-L1. Furthermore, considering the prominent role played by m6A modification in cancers, we suggest interventions targeting m6A modification as potential therapeutic strategies. Finally, numerous proofs have indicated that strategies targeting m6A modification may synergistically strengthen the effect of immune checkpoint therapy. These combinations may spark novel ideas for better therapeutic efficacy in clinical application.
Although strategies simultaneously targeting m6A modification and immune checkpoints have demonstrated tremendous potential, numerous hurdles still impede their clinical application. First of all, m6A regulators play dual roles in cancers. For example, METTL3 promotes cancer progression in osteosarcoma, while it plays an antitumor role in renal cell carcinoma [164, 165]. Hence, the heterogenous expression and roles of m6A regulators in distinct tissues or cancer types need to be taken into consideration when they are combined with ICIs in the clinical settings. In addition, the quantity of m6A regulators and specific agents is still limited. Thus, more efforts are urgently needed to identify novel m6A regulators and effective m6A-targeted compounds. Moreover, numerous proof-of-concept studies depict the remarkable outcomes of interventions targeting m6A modification in combination with ICIs. However, the efficacy and cytotoxicity of these treatments remain undisclosed. Therefore, extra experimental and clinical data are warranted for developing future tumor treatment. As concluded, studies about m6A modification bring a new frontier to cancer research by illustrating a comprehensive understanding of epigenetic regulation in cancer, and providing additional insight into the molecular basis of tumorigenesis and immune response. Strategies that appropriately combine m6A-based therapy with ICIs hold great therapeutic potential. However, the mechanisms of which m6A affects immune checkpoints are complicated and remain not fully understood. Numerous findings indicate that m6A modification functions in a context-dependent manner and plays dual roles. Therefore, a better understanding of the phenomenon and an improved patient selection criterion will significantly enhance the outcomes of the combined therapy that warrant further studies.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- m6A:
-
N6-methyladenosine
- ICIs:
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors
- FDA:
-
Food and Drug Administration
- irAEs:
-
Immunotherapy-related adverse events
- mRNA:
-
Messenger RNA
- ncRNAs:
-
Noncoding RNAs
- 3'UTR:
-
3' Untranslated region
- MTC:
-
Methyltransferase complex
- METTL3:
-
Methyltransferase-like 3
- METTL5:
-
Methyltransferase-like 5
- METTL14:
-
Methyltransferase-like 14
- METTL16:
-
Methyltransferase-like 16
- WTAP:
-
Wilms tumor 1-associated protein
- VIRMA:
-
Vir-like m6A methyltransferase associated
- ZCCHC4:
-
Zinc finger CCHC-type containing 4
- ZC3H13:
-
Zinc finger CCCH-type containing 13
- CBLL1:
-
Cbl proto-oncogene-like 1
- RBM15:
-
RNA-binding motif protein 15
- rRNAs:
-
Ribosomal RNAs
- snRNA:
-
Small nuclear RNA
- PCIF1:
-
Phosphorylated CTD interacting factor 1
- CAPAM:
-
Cap-specific adenosine methyltransferase
- tRNA:
-
Transfer RNA
- FTO:
-
Fat mass and obesity associated protein
- ALKBH5:
-
AlkB homolog 5
- hm6A:
-
N6-hydroxymethyladenosine
- f6A:
-
N6-formyladenosine
- m6Am:
-
N6,2'-O-dimethyladenosine
- GBM:
-
Glioblastoma
- BC:
-
Breast cancer
- AML:
-
Acute myeloid leukemia
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small-cell lung cancer
- YTH:
-
YT521-B homology
- YTHDF:
-
YT521-B homology domain family
- YTHDC:
-
YTH domain-containing proteins
- IGF2BP:
-
Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding proteins
- HNRNPs:
-
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins
- SRSF3:
-
Serine- and arginine-rich splicing factor 3
- carRNA:
-
Chromosome-associated regulatory RNA
- pri-miRNA:
-
Primary miRNA
- CTLA-4:
-
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein-4
- PD-1:
-
Programmed cell death protein-1
- PD-L1:
-
Programmed cell death ligand 1
- TIM-3:
-
T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing-3
- LAG-3:
-
Lymphocyte activation gene-3
- TIGIT:
-
T cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain
- VISTA:
-
V-domain Ig suppressor of T cell activation
- B7-H3:
-
B7 homolog 3
- BTLA:
-
B and T cell lymphocyte attenuator
- DCs:
-
Dendritic cells
- TCR:
-
T-cell receptor
- MHC:
-
Major histocompatibility complex
- APCs:
-
Antigen-presenting cells
- PP2A:
-
Protein phosphatase 2A
- SHPs:
-
Src homology 2 domain-containing phosphatases
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- ITIM:
-
Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif
- ITSM:
-
Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif
- NK cell:
-
Natural killer cell
- PLCγ:
-
Phospholipase Cγ
- TGCT:
-
Testicular germ cell tumors
- CC:
-
Cervical cancer
- MDSCs:
-
Myeloid derived suppressor cells
- OSCC:
-
Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PKP3:
-
Plakophilin 3
- STAT1:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- ICAM:
-
Intercellular adhesion molecule
- TME:
-
Tumor microenvironment
- pMMR-MSI-L CRC:
-
Mismatch-repair-proficient or microsatellite instability-low colorectal cancer
- Treg cell:
-
Regulatory T cell
- ccRCC:
-
Clear cell Renal cell carcinoma
- TILs:
-
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes
- LILRB4:
-
Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B4
- ICC:
-
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- circRNA:
-
Circular RNA
- OVA:
-
Ovalbumin
- LGG:
-
Lower-grade glioma
- IDO1:
-
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
- shRNA:
-
Short hairpin RNA
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- lncRNA:
-
Long noncoding RNA
- PTEN:
-
Phosphatase and tensin homolog
- NPs:
-
Nanoparticles
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- TAMs:
-
Tumor-associated macrophages
- CCR2:
-
C–C motif chemokine receptor 2
- PIGF:
-
Placental growth factor signaling
- sgRNA:
-
Single guide RNA
- PAM:
-
Protospacer-adjacent motif
- 2OG:
-
2-Oxoglutarat
- R-2HG:
-
R-2-hydroxyglutarate
- MA:
-
Meclofenamic acid
References
Whiteside TL. Immune suppression in cancer: effects on immune cells, mechanisms and future therapeutic intervention. Semin Cancer Biol. 2006;16:3–15.
Schmid P, Adams S, Rugo HS, Schneeweiss A, Barrios CH, Iwata H, Diéras V, Hegg R, Im SA, Shaw Wright G, et al. Atezolizumab and Nab-Paclitaxel in Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:2108–21.
Grywalska E, Pasiarski M, Góźdź S, Roliński J. Immune-checkpoint inhibitors for combating T-cell dysfunction in cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2018;11:6505–24.
Rottman F, Shatkin AJ, Perry RP. Sequences containing methylated nucleotides at the 5’ termini of messenger RNAs: possible implications for processing. Cell. 1974;3:197–9.
Saletore Y, Meyer K, Korlach J, Vilfan ID, Jaffrey S, Mason CE. The birth of the Epitranscriptome: deciphering the function of RNA modifications. Genome Biol. 2012;13:175.
Li X, Ma S, Deng Y, Yi P, Yu J. Targeting the RNA m(6)A modification for cancer immunotherapy. Mol Cancer. 2022;21:76.
Dominissini D, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S, Schwartz S, Salmon-Divon M, Ungar L, Osenberg S, Cesarkas K, Jacob-Hirsch J, Amariglio N, Kupiec M, et al. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature. 2012;485:201–6.
Meyer KD, Saletore Y, Zumbo P, Elemento O, Mason CE, Jaffrey SR. Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation reveals enrichment in 3’ UTRs and near stop codons. Cell. 2012;149:1635–46.
Jaffrey SR, Kharas MG. Emerging links between m(6)A and misregulated mRNA methylation in cancer. Genome Med. 2017;9:2.
Jia G, Fu Y, He C. Reversible RNA adenosine methylation in biological regulation. Trends Genet. 2013;29:108–15.
Dai D, Wang H, Zhu L, Jin H, Wang X. N6-methyladenosine links RNA metabolism to cancer progression. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:124.
He L, Li H, Wu A, Peng Y, Shu G, Yin G. Functions of N6-methyladenosine and its role in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:176.
Shulman Z, Stern-Ginossar N. The RNA modification N(6)-methyladenosine as a novel regulator of the immune system. Nat Immunol. 2020;21:501–12.
Huang J, Yin P. Structural Insights into N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) Modification in the Transcriptome. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2018;16:85–98.
Wang X, Feng J, Xue Y, Guan Z, Zhang D, Liu Z, Gong Z, Wang Q, Huang J, Tang C, et al. Structural basis of N(6)-adenosine methylation by the METTL3-METTL14 complex. Nature. 2016;534:575–8.
Ping XL, Sun BF, Wang L, Xiao W, Yang X, Wang WJ, Adhikari S, Shi Y, Lv Y, Chen YS, et al. Mammalian WTAP is a regulatory subunit of the RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase. Cell Res. 2014;24:177–89.
Patil DP, Chen CK, Pickering BF, Chow A, Jackson C, Guttman M, Jaffrey SR. m(6)A RNA methylation promotes XIST-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature. 2016;537:369–73.
Knuckles P, Lence T, Haussmann IU, Jacob D, Kreim N, Carl SH, Masiello I, Hares T, Villaseñor R, Hess D, et al. Zc3h13/Flacc is required for adenosine methylation by bridging the mRNA-binding factor Rbm15/Spenito to the m(6)A machinery component Wtap/Fl(2)d. Genes Dev. 2018;32:415–29.
Wen J, Lv R, Ma H, Shen H, He C, Wang J, Jiao F, Liu H, Yang P, Tan L, et al. Zc3h13 Regulates Nuclear RNA m(6)A Methylation and Mouse Embryonic Stem Cell Self-Renewal. Mol Cell. 2018;69:1028-1038.e1026.
Ma H, Wang X, Cai J, Dai Q, Natchiar SK, Lv R, Chen K, Lu Z, Chen H, Shi YG, et al. N(6-)Methyladenosine methyltransferase ZCCHC4 mediates ribosomal RNA methylation. Nat Chem Biol. 2019;15:88–94.
van Tran N, Ernst FGM, Hawley BR, Zorbas C, Ulryck N, Hackert P, Bohnsack KE, Bohnsack MT, Jaffrey SR, Graille M, Lafontaine DLJ. The human 18S rRNA m6A methyltransferase METTL5 is stabilized by TRMT112. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:7719–33.
Pendleton KE, Chen B, Liu K, Hunter OV, Xie Y, Tu BP, Conrad NK. The U6 snRNA m(6)A Methyltransferase METTL16 Regulates SAM Synthetase Intron Retention. Cell. 2017;169:824-835.e814.
Warda AS, Kretschmer J, Hackert P, Lenz C, Urlaub H, Höbartner C, Sloan KE, Bohnsack MT. Human METTL16 is a N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) methyltransferase that targets pre-mRNAs and various non-coding RNAs. EMBO Rep. 2017;18:2004–14.
Shima H, Matsumoto M, Ishigami Y, Ebina M, Muto A, Sato Y, Kumagai S, Ochiai K, Suzuki T, Igarashi K. S-Adenosylmethionine Synthesis Is Regulated by Selective N(6)-Adenosine Methylation and mRNA Degradation Involving METTL16 and YTHDC1. Cell Rep. 2017;21:3354–63.
Sendinc E, Valle-Garcia D, Dhall A, Chen H, Henriques T, Navarrete-Perea J, Sheng W, Gygi SP, Adelman K, Shi Y. PCIF1 Catalyzes m6Am mRNA Methylation to Regulate Gene Expression. Mol Cell. 2019;75:620-630.e629.
Gerken T, Girard CA, Tung YC, Webby CJ, Saudek V, Hewitson KS, Yeo GS, McDonough MA, Cunliffe S, McNeill LA, et al. The obesity-associated FTO gene encodes a 2-oxoglutarate-dependent nucleic acid demethylase. Science. 2007;318:1469–72.
Jia G, Fu Y, Zhao X, Dai Q, Zheng G, Yang Y, Yi C, Lindahl T, Pan T, Yang YG, He C. N6-methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat Chem Biol. 2011;7:885–7.
Wei J, Liu F, Lu Z, Fei Q, Ai Y, He PC, Shi H, Cui X, Su R, Klungland A, et al. Differential m(6)A, m(6)A(m), and m(1)A Demethylation Mediated by FTO in the Cell Nucleus and Cytoplasm. Mol Cell. 2018;71:973-985.e975.
Zheng G, Dahl JA, Niu Y, Fedorcsak P, Huang CM, Li CJ, Vågbø CB, Shi Y, Wang WL, Song SH, et al. ALKBH5 is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and mouse fertility. Mol Cell. 2013;49:18–29.
Mauer J, Luo X, Blanjoie A, Jiao X, Grozhik AV, Patil DP, Linder B, Pickering BF, Vasseur JJ, Chen Q, et al. Reversible methylation of m(6)A(m) in the 5’ cap controls mRNA stability. Nature. 2017;541:371–5.
Cui Q, Shi H, Ye P, Li L, Qu Q, Sun G, Sun G, Lu Z, Huang Y, Yang CG, et al. m(6)A RNA Methylation Regulates the Self-Renewal and Tumorigenesis of Glioblastoma Stem Cells. Cell Rep. 2017;18:2622–34.
Yang S, Wei J, Cui YH, Park G, Shah P, Deng Y, Aplin AE, Lu Z, Hwang S, He C, He YY. m(6)A mRNA demethylase FTO regulates melanoma tumorigenicity and response to anti-PD-1 blockade. Nat Commun. 2019;10:2782.
Niu Y, Lin Z, Wan A, Chen H, Liang H, Sun L, Wang Y, Li X, Xiong XF, Wei B, et al. RNA N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO promotes breast tumor progression through inhibiting BNIP3. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:46.
Li Z, Weng H, Su R, Weng X, Zuo Z, Li C, Huang H, Nachtergaele S, Dong L, Hu C, et al. FTO Plays an Oncogenic Role in Acute Myeloid Leukemia as a N(6)-Methyladenosine RNA Demethylase. Cancer Cell. 2017;31:127–41.
Zhang S, Zhao BS, Zhou A, Lin K, Zheng S, Lu Z, Chen Y, Sulman EP, Xie K, Bögler O, et al. m(6)A Demethylase ALKBH5 Maintains Tumorigenicity of Glioblastoma Stem-like Cells by Sustaining FOXM1 Expression and Cell Proliferation Program. Cancer Cell. 2017;31:591-606.e596.
Zhang J, Guo S, Piao HY, Wang Y, Wu Y, Meng XY, Yang D, Zheng ZC, Zhao Y. ALKBH5 promotes invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer by decreasing methylation of the lncRNA NEAT1. J Physiol Biochem. 2019;75:379–89.
Zhu H, Gan X, Jiang X, Diao S, Wu H, Hu J. ALKBH5 inhibited autophagy of epithelial ovarian cancer through miR-7 and BCL-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38:163.
Shen C, Sheng Y, Zhu AC, Robinson S, Jiang X, Dong L, Chen H, Su R, Yin Z, Li W, et al. RNA Demethylase ALKBH5 Selectively Promotes Tumorigenesis and Cancer Stem Cell Self-Renewal in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cell Stem Cell. 2020;27:64-80.e69.
Chen Y, Zhao Y, Chen J, Peng C, Zhang Y, Tong R, Cheng Q, Yang B, Feng X, Lu Y, et al. ALKBH5 suppresses malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma via m(6)A-guided epigenetic inhibition of LYPD1. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:123.
Tang B, Yang Y, Kang M, Wang Y, Wang Y, Bi Y, He S, Shimamoto F. m(6)A demethylase ALKBH5 inhibits pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis by decreasing WIF-1 RNA methylation and mediating Wnt signaling. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:3.
Jin D, Guo J, Wu Y, Yang L, Wang X, Du J, Dai J, Chen W, Gong K, Miao S, et al. m(6)A demethylase ALKBH5 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by reducing YTHDFs-mediated YAP expression and inhibiting miR-107/LATS2-mediated YAP activity in NSCLC. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:40.
Yue B, Song C, Yang L, Cui R, Cheng X, Zhang Z, Zhao G. METTL3-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification is critical for epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:142.
Esteve-Puig R, Climent F, Piñeyro D, Domingo-Domènech E, Davalos V, Encuentra M, Rea A, Espejo-Herrera N, Soler M, Lopez M, et al. Epigenetic loss of m1A RNA demethylase ALKBH3 in Hodgkin lymphoma targets collagen, conferring poor clinical outcome. Blood. 2021;137:994–9.
Meyer KD, Jaffrey SR. Rethinking m(6)A Readers, Writers, and Erasers. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2017;33:319–42.
Wang X, Zhao BS, Roundtree IA, Lu Z, Han D, Ma H, Weng X, Chen K, Shi H, He C. N(6)-methyladenosine Modulates Messenger RNA Translation Efficiency. Cell. 2015;161:1388–99.
Du H, Zhao Y, He J, Zhang Y, Xi H, Liu M, Ma J, Wu L. YTHDF2 destabilizes m(6)A-containing RNA through direct recruitment of the CCR4-NOT deadenylase complex. Nat Commun. 2016;7:12626.
Li A, Chen YS, Ping XL, Yang X, Xiao W, Yang Y, Sun HY, Zhu Q, Baidya P, Wang X, et al. Cytoplasmic m(6)A reader YTHDF3 promotes mRNA translation. Cell Res. 2017;27:444–7.
Xiao W, Adhikari S, Dahal U, Chen YS, Hao YJ, Sun BF, Sun HY, Li A, Ping XL, Lai WY, et al. Nuclear m(6)A Reader YTHDC1 Regulates mRNA Splicing. Mol Cell. 2016;61:507–19.
Roundtree IA, Luo GZ, Zhang Z, Wang X, Zhou T, Cui Y, Sha J, Huang X, Guerrero L, Xie P, et al: YTHDC1 mediates nuclear export of N(6)-methyladenosine methylated mRNAs. Elife. 2017;6.
Liu J, Dou X, Chen C, Chen C, Liu C, Xu MM, Zhao S, Shen B, Gao Y, Han D, He C. N (6)-methyladenosine of chromosome-associated regulatory RNA regulates chromatin state and transcription. Science. 2020;367:580–6.
Kretschmer J, Rao H, Hackert P, Sloan KE, Höbartner C, Bohnsack MT. The m(6)A reader protein YTHDC2 interacts with the small ribosomal subunit and the 5’-3’ exoribonuclease XRN1. RNA. 2018;24:1339–50.
Huang H, Weng H, Sun W, Qin X, Shi H, Wu H, Zhao BS, Mesquita A, Liu C, Yuan CL, et al. Recognition of RNA N(6)-methyladenosine by IGF2BP proteins enhances mRNA stability and translation. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20:285–95.
Alarcón CR, Goodarzi H, Lee H, Liu X, Tavazoie S, Tavazoie SF. HNRNPA2B1 Is a Mediator of m(6)A-Dependent Nuclear RNA Processing Events. Cell. 2015;162:1299–308.
Liu N, Dai Q, Zheng G, He C, Parisien M, Pan T. N(6)-methyladenosine-dependent RNA structural switches regulate RNA-protein interactions. Nature. 2015;518:560–4.
Kirkwood JM, Butterfield LH, Tarhini AA, Zarour H, Kalinski P, Ferrone S. Immunotherapy of cancer in 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:309–35.
Yang Y. Cancer immunotherapy: harnessing the immune system to battle cancer. J Clin Invest. 2015;125:3335–7.
Chen X, Song X, Li K, Zhang T. FcγR-Binding Is an Important Functional Attribute for Immune Checkpoint Antibodies in Cancer Immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 2019;10:292.
Walunas TL, Lenschow DJ, Bakker CY, Linsley PS, Freeman GJ, Green JM, Thompson CB, Bluestone JA. CTLA-4 can function as a negative regulator of T cell activation. Immunity. 1994;1:405–13.
Lim S, Phillips JB. Madeira da Silva L, Zhou M, Fodstad O, Owen LB, Tan M: Interplay between Immune Checkpoint Proteins and Cellular Metabolism. Cancer Res. 2017;77:1245–9.
Lau KS, Partridge EA, Grigorian A, Silvescu CI, Reinhold VN, Demetriou M, Dennis JW. Complex N-glycan number and degree of branching cooperate to regulate cell proliferation and differentiation. Cell. 2007;129:123–34.
Qureshi OS, Kaur S, Hou TZ, Jeffery LE, Poulter NS, Briggs Z, Kenefeck R, Willox AK, Royle SJ, Rappoport JZ, Sansom DM. Constitutive clathrin-mediated endocytosis of CTLA-4 persists during T cell activation. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:9429–40.
Scalapino KJ, Daikh DI. CTLA-4: a key regulatory point in the control of autoimmune disease. Immunol Rev. 2008;223:143–55.
Qureshi OS, Zheng Y, Nakamura K, Attridge K, Manzotti C, Schmidt EM, Baker J, Jeffery LE, Kaur S, Briggs Z, et al. Trans-endocytosis of CD80 and CD86: a molecular basis for the cell-extrinsic function of CTLA-4. Science. 2011;332:600–3.
van der Merwe PA, Bodian DL, Daenke S, Linsley P, Davis SJ. CD80 (B7–1) binds both CD28 and CTLA-4 with a low affinity and very fast kinetics. J Exp Med. 1997;185:393–403.
Perrotti D, Neviani P. Protein phosphatase 2A: a target for anticancer therapy. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:e229-238.
Chuang E, Fisher TS, Morgan RW, Robbins MD, Duerr JM, Vander Heiden MG, Gardner JP, Hambor JE, Neveu MJ, Thompson CB. The CD28 and CTLA-4 receptors associate with the serine/threonine phosphatase PP2A. Immunity. 2000;13:313–22.
He X, Xu C. Immune checkpoint signaling and cancer immunotherapy. Cell Res. 2020;30:660–9.
Ahmadzadeh M, Johnson LA, Heemskerk B, Wunderlich JR, Dudley ME, White DE, Rosenberg SA. Tumor antigen-specific CD8 T cells infiltrating the tumor express high levels of PD-1 and are functionally impaired. Blood. 2009;114:1537–44.
Zhang X, Schwartz JC, Guo X, Bhatia S, Cao E, Lorenz M, Cammer M, Chen L, Zhang ZY, Edidin MA, et al. Structural and functional analysis of the costimulatory receptor programmed death-1. Immunity. 2004;20:337–47.
Kamphorst AO, Wieland A, Nasti T, Yang S, Zhang R, Barber DL, Konieczny BT, Daugherty CZ, Koenig L, Yu K, et al. Rescue of exhausted CD8 T cells by PD-1-targeted therapies is CD28-dependent. Science. 2017;355:1423–7.
Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ, Sharpe AH. PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008;26:677–704.
Sun C, Mezzadra R, Schumacher TN. Regulation and Function of the PD-L1 Checkpoint. Immunity. 2018;48:434–52.
Freeman GJ, Long AJ, Iwai Y, Bourque K, Chernova T, Nishimura H, Fitz LJ, Malenkovich N, Okazaki T, Byrne MC, et al. Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte activation. J Exp Med. 2000;192:1027–34.
Hui E, Cheung J, Zhu J, Su X, Taylor MJ, Wallweber HA, Sasmal DK, Huang J, Kim JM, Mellman I, Vale RD. T cell costimulatory receptor CD28 is a primary target for PD-1-mediated inhibition. Science. 2017;355:1428–33.
Rota G, Niogret C, Dang AT, Barros CR, Fonta NP, Alfei F, Morgado L, Zehn D, Birchmeier W, Vivier E, Guarda G. Shp-2 Is Dispensable for Establishing T Cell Exhaustion and for PD-1 Signaling In Vivo. Cell Rep. 2018;23:39–49.
Parry RV, Chemnitz JM, Frauwirth KA, Lanfranco AR, Braunstein I, Kobayashi SV, Linsley PS, Thompson CB, Riley JL. CTLA-4 and PD-1 receptors inhibit T-cell activation by distinct mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:9543–53.
Riley JL. PD-1 signaling in primary T cells. Immunol Rev. 2009;229:114–25.
Yokosuka T, Takamatsu M, Kobayashi-Imanishi W, Hashimoto-Tane A, Azuma M, Saito T. Programmed cell death 1 forms negative costimulatory microclusters that directly inhibit T cell receptor signaling by recruiting phosphatase SHP2. J Exp Med. 2012;209:1201–17.
Patsoukis N, Brown J, Petkova V, Liu F, Li L, Boussiotis VA: Selective effects of PD-1 on Akt and Ras pathways regulate molecular components of the cell cycle and inhibit T cell proliferation. Sci Signal. 2012;5:ra46.
Sheppard KA, Fitz LJ, Lee JM, Benander C, George JA, Wooters J, Qiu Y, Jussif JM, Carter LL, Wood CR, Chaudhary D. PD-1 inhibits T-cell receptor induced phosphorylation of the ZAP70/CD3zeta signalosome and downstream signaling to PKCtheta. FEBS Lett. 2004;574:37–41.
Xu X, Hou B, Fulzele A, Masubuchi T, Zhao Y, Wu Z, Hu Y, Jiang Y, Ma Y, Wang H, et al: PD-1 and BTLA regulate T cell signaling differentially and only partially through SHP1 and SHP2. J Cell Biol. 2020;219.
Poggio M, Hu T, Pai CC, Chu B, Belair CD, Chang A, Montabana E, Lang UE, Fu Q, Fong L, Blelloch R. Suppression of Exosomal PD-L1 Induces Systemic Anti-tumor Immunity and Memory. Cell. 2019;177:414-427.e413.
Luo Y, Sun Y, Li L, Mao Y. METTL3 May Regulate Testicular Germ Cell Tumors Through EMT and Immune Pathways. Cell Transplant. 2020;29:963689720946653.
Ni HH, Zhang L, Huang H, Dai SQ, Li J. Connecting METTL3 and intratumoural CD33(+) MDSCs in predicting clinical outcome in cervical cancer. J Transl Med. 2020;18:393.
He X, Tan L, Ni J, Shen G. Expression pattern of m(6)A regulators is significantly correlated with malignancy and antitumor immune response of breast cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021;28:188–96.
Ai Y, Liu S, Luo H, Wu S, Wei H, Tang Z, Li X, Lv X, Zou C. METTL3 Intensifies the Progress of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma via Modulating the m6A Amount of PRMT5 and PD-L1. J Immunol Res. 2021;2021:6149558.
Lim V, Zhu H, Diao S, Hu L, Hu J. PKP3 interactions with MAPK-JNK-ERK1/2-mTOR pathway regulates autophagy and invasion in ovarian cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;508:646–53.
Li Y, Ju K, Wang W, Liu Z, Xie H, Jiang Y, Jiang G, Lu J, Dong Z, Tang F. Dinitrosopiperazine-decreased PKP3 through upregulating miR-149 participates in nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis. Mol Carcinog. 2018;57:1763–79.
Fischer-Kešo R, Breuninger S, Hofmann S, Henn M, Röhrig T, Ströbel P, Stoecklin G, Hofmann I. Plakophilins 1 and 3 bind to FXR1 and thereby influence the mRNA stability of desmosomal proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 2014;34:4244–56.
Liu Z, Wang T, She Y, Wu K, Gu S, Li L, Dong C, Chen C, Zhou Y. N(6)-methyladenosine-modified circIGF2BP3 inhibits CD8(+) T-cell responses to facilitate tumor immune evasion by promoting the deubiquitination of PD-L1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer. 2021;20:105.
Qian C, Cao X. Dendritic cells in the regulation of immunity and inflammation. Semin Immunol. 2018;35:3–11.
Wang H, Hu X, Huang M, Liu J, Gu Y, Ma L, Zhou Q, Cao X. Mettl3-mediated mRNA m(6)A methylation promotes dendritic cell activation. Nat Commun. 1898;2019:10.
DeNardo DG, Ruffell B. Macrophages as regulators of tumour immunity and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019;19:369–82.
Glass CK, Natoli G. Molecular control of activation and priming in macrophages. Nat Immunol. 2016;17:26–33.
Liu Y, Liu Z, Tang H, Shen Y, Gong Z, Xie N, Zhang X, Wang W, Kong W, Zhou Y, Fu Y. The N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A)-forming enzyme METTL3 facilitates M1 macrophage polarization through the methylation of STAT1 mRNA. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019;317:C762-c775.
Shen S, Yan J, Zhang Y, Dong Z, Xing J, He Y. N6-methyladenosine (m6A)-mediated messenger RNA signatures and the tumor immune microenvironment can predict the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9:59.
Zhou H, Yin K, Zhang Y, Tian J, Wang S. The RNA m6A writer METTL14 in cancers: Roles, structures, and applications. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021;1876:188609.
Wang L, Hui H, Agrawal K, Kang Y, Li N, Tang R, Yuan J, Rana TM. m(6) A RNA methyltransferases METTL3/14 regulate immune responses to anti-PD-1 therapy. Embo j. 2020;39:e104514.
Gong PJ, Shao YC, Yang Y, Song WJ, He X, Zeng YF, Huang SR, Wei L, Zhang JW. Analysis of N6-Methyladenosine Methyltransferase Reveals METTL14 and ZC3H13 as Tumor Suppressor Genes in Breast Cancer. Front Oncol. 2020;10:578963.
Xu T, Gao S, Ruan H, Liu J, Liu Y, Liu D, Tong J, Shi J, Yang H, Chen K, Zhang X. METTL14 Acts as a Potential Regulator of Tumor Immune and Progression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Front Genet. 2021;12:609174.
Su R, Dong L, Li Y, Gao M, Han L, Wunderlich M, Deng X, Li H, Huang Y, Gao L, et al. Targeting FTO Suppresses Cancer Stem Cell Maintenance and Immune Evasion. Cancer Cell. 2020;38:79-96.e11.
Wei C, Wang B, Peng D, Zhang X, Li Z, Luo L, He Y, Liang H, Du X, Li S, et al. Pan-Cancer Analysis Shows That ALKBH5 Is a Potential Prognostic and Immunotherapeutic Biomarker for Multiple Cancer Types Including Gliomas. Front Immunol. 2022;13:849592.
Tsuruta N, Tsuchihashi K, Ohmura H, Yamaguchi K, Ito M, Ariyama H, Kusaba H, Akashi K, Baba E. RNA N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO regulates PD-L1 expression in colon cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;530:235–9.
Liu Y, Liang G, Xu H, Dong W, Dong Z, Qiu Z, Zhang Z, Li F, Huang Y, Li Y, et al. Tumors exploit FTO-mediated regulation of glycolytic metabolism to evade immune surveillance. Cell Metab. 2021;33:1221-1233.e1211.
Li N, Kang Y, Wang L, Huff S, Tang R, Hui H, Agrawal K, Gonzalez GM, Wang Y, Patel SP, Rana TM. ALKBH5 regulates anti-PD-1 therapy response by modulating lactate and suppressive immune cell accumulation in tumor microenvironment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117:20159–70.
Qiu X, Yang S, Wang S, Wu J, Zheng B, Wang K, Shen S, Jeong S, Li Z, Zhu Y, et al. M(6)A Demethylase ALKBH5 Regulates PD-L1 Expression and Tumor Immunoenvironment in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2021;81:4778–93.
Han D, Liu J, Chen C, Dong L, Liu Y, Chang R, Huang X, Liu Y, Wang J, Dougherty U, et al. Anti-tumour immunity controlled through mRNA m(6)A methylation and YTHDF1 in dendritic cells. Nature. 2019;566:270–4.
Tsuchiya K, Yoshimura K, Inoue Y, Iwashita Y, Yamada H, Kawase A, Watanabe T, Tanahashi M, Ogawa H, Funai K, et al. YTHDF1 and YTHDF2 are associated with better patient survival and an inflamed tumor-immune microenvironment in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncoimmunology. 2021;10:1962656.
Stahl M, Goldberg AD. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Novel Combinations and Therapeutic Targets. Curr Oncol Rep. 2019;21:37.
Su G, Liu T, Han X, Sun H, Che W, Hu K, Xiao J, Li Y, Liu Y, Li W, Mei H. YTHDF2 is a Potential Biomarker and Associated with Immune Infiltration in Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:709548.
Lin X, Wang Z, Yang G, Wen G, Zhang H. YTHDF2 correlates with tumor immune infiltrates in lower-grade glioma. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12:18476–500.
Du Y, Ma Y, Zhu Q, Liu T, Jiao Y, Yuan P, Wang X. An m6A-Related Prognostic Biomarker Associated With the Hepatocellular Carcinoma Immune Microenvironment. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:707930.
Sun YM, Chen YQ. Principles and innovative technologies for decrypting noncoding RNAs: from discovery and functional prediction to clinical application. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13:109.
Huang W, Chen TQ, Fang K, Zeng ZC, Ye H, Chen YQ. N6-methyladenosine methyltransferases: functions, regulation, and clinical potential. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14:117.
Lin S, Choe J, Du P, Triboulet R, Gregory RI. The m(6)A Methyltransferase METTL3 Promotes Translation in Human Cancer Cells. Mol Cell. 2016;62:335–45.
Zhao Y, Chen Y, Jin M, Wang J. The crosstalk between m(6)A RNA methylation and other epigenetic regulators: a novel perspective in epigenetic remodeling. Theranostics. 2021;11:4549–66.
Yan J, Huang X, Zhang X, Chen Z, Ye C, Xiang W, Huang Z. LncRNA LINC00470 promotes the degradation of PTEN mRNA to facilitate malignant behavior in gastric cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;521:887–93.
Wang X, Zhang J, Wang Y. Long noncoding RNA GAS5-AS1 suppresses growth and metastasis of cervical cancer by increasing GAS5 stability. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11:4909–21.
Zhao X, Dong R, Zhang L, Guo J, Shi Y, Ge L, Wang J, Song Z, Ni B, You Y. N6-methyladenosine-dependent modification of circGARS acts as a new player that promotes SLE progression through the NF-κB/A20 axis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022;24:37.
Liu B, Liu N, Zhu X, Yang L, Ye B, Li H, Zhu P, Lu T, Tian Y, Fan Z. Circular RNA circZbtb20 maintains ILC3 homeostasis and function via Alkbh5-dependent m(6)A demethylation of Nr4a1 mRNA. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021;18:1412–24.
Riley RS, June CH, Langer R, Mitchell MJ. Delivery technologies for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2019;18:175–96.
Cao K, Du Y, Bao X, Han M, Su R, Pang J, Liu S, Shi Z, Yan F, Feng S. Glutathione-Bioimprinted Nanoparticles Targeting of N6-methyladenosine FTO Demethylase as a Strategy against Leukemic Stem Cells. Small. 2022;18:e2106558.
Jing X, Yang F, Shao C, Wei K, Xie M, Shen H, Shu Y. Role of hypoxia in cancer therapy by regulating the tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:157.
Keith B, Simon MC. Hypoxia-inducible factors, stem cells, and cancer. Cell. 2007;129:465–72.
Zheng Y, Ling Y, Zhang DY, Tan CP, Zhang H, Yang GG, Wang H, Ji LN, Mao ZW. Regulating Tumor N(6) -Methyladenosine Methylation Landscape using Hypoxia-Modulating OsS(x) Nanoparticles. Small. 2021;17:e2005086.
Pan J, Wang J, Fang K, Hou W, Li B, Zhao J, Ma X. RNA m(6)A Alterations Induced by Biomineralization Nanoparticles: A Proof-of-Concept Study of Epitranscriptomics for Nanotoxicity Evaluation. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2022;17:23.
Leuschner F, Dutta P, Gorbatov R, Novobrantseva TI, Donahoe JS, Courties G, Lee KM, Kim JI, Markmann JF, Marinelli B, et al. Therapeutic siRNA silencing in inflammatory monocytes in mice. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29:1005–10.
Song Y, Tang C, Yin C. Combination antitumor immunotherapy with VEGF and PIGF siRNA via systemic delivery of multi-functionalized nanoparticles to tumor-associated macrophages and breast cancer cells. Biomaterials. 2018;185:117–32.
Li K, Lu L, Xue C, Liu J, He Y, Zhou J, Xia Z, Dai L, Luo Z, Mao Y, Cai K. Polarization of tumor-associated macrophage phenotype via porous hollow iron nanoparticles for tumor immunotherapy in vivo. Nanoscale. 2020;12:130–44.
Ovais M, Guo M, Chen C. Tailoring Nanomaterials for Targeting Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Adv Mater. 2019;31:e1808303.
Théry C, Zitvogel L, Amigorena S. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:569–79.
Xie H, Yao J, Wang Y, Ni B. Exosome-transmitted circVMP1 facilitates the progression and cisplatin resistance of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting miR-524-5p-METTL3/SOX2 axis. Drug Deliv. 2022;29:1257–71.
Du Y, Han M, Cao K, Li Q, Pang J, Dou L, Liu S, Shi Z, Yan F, Feng S: Gold Nanorods Exhibit Intrinsic Therapeutic Activity via Controlling N6-Methyladenosine-Based Epitranscriptomics in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. ACS Nano 2021.
Shen B, Zhang W, Zhang J, Zhou J, Wang J, Chen L, Wang L, Hodgkins A, Iyer V, Huang X, Skarnes WC. Efficient genome modification by CRISPR-Cas9 nickase with minimal off-target effects. Nat Methods. 2014;11:399–402.
Chiossone L, Dumas PY, Vienne M, Vivier E. Natural killer cells and other innate lymphoid cells in cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018;18:671–88.
Song H, Song J, Cheng M, Zheng M, Wang T, Tian S, Flavell RA, Zhu S, Li HB, Ding C, et al. METTL3-mediated m(6)A RNA methylation promotes the anti-tumour immunity of natural killer cells. Nat Commun. 2021;12:5522.
Gilbert LA, Larson MH, Morsut L, Liu Z, Brar GA, Torres SE, Stern-Ginossar N, Brandman O, Whitehead EH, Doudna JA, et al. CRISPR-mediated modular RNA-guided regulation of transcription in eukaryotes. Cell. 2013;154:442–51.
Liu XM, Zhou J, Mao Y, Ji Q, Qian SB. Programmable RNA N(6)-methyladenosine editing by CRISPR-Cas9 conjugates. Nat Chem Biol. 2019;15:865–71.
Xie S, Jin H, Yang F, Zheng H, Chang Y, Liao Y, Zhang Y, Zhou T, Li Y. Programmable RNA N(1) -Methyladenosine Demethylation by a Cas13d-Directed Demethylase. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021;60:19592–7.
Wilson C, Chen PJ, Miao Z, Liu DR. Programmable m(6)A modification of cellular RNAs with a Cas13-directed methyltransferase. Nat Biotechnol. 2020;38:1431–40.
Li J, Chen Z, Chen F, Xie G, Ling Y, Peng Y, Lin Y, Luo N, Chiang CM, Wang H. Targeted mRNA demethylation using an engineered dCas13b-ALKBH5 fusion protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48:5684–94.
Wessels HH, Méndez-Mancilla A, Guo X, Legut M, Daniloski Z, Sanjana NE. Massively parallel Cas13 screens reveal principles for guide RNA design. Nat Biotechnol. 2020;38:722–7.
Xia Z, Tang M, Ma J, Zhang H, Gimple RC, Prager BC, Tang H, Sun C, Liu F, Lin P, et al. Epitranscriptomic editing of the RNA N6-methyladenosine modification by dCasRx conjugated methyltransferase and demethylase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49:7361–74.
Su R, Dong L, Li C, Nachtergaele S, Wunderlich M, Qing Y, Deng X, Wang Y, Weng X, Hu C, et al. R-2HG Exhibits Anti-tumor Activity by Targeting FTO/m(6)A/MYC/CEBPA Signaling. Cell. 2018;172:90-105.e123.
Huang Y, Yan J, Li Q, Li J, Gong S, Zhou H, Gan J, Jiang H, Jia GF, Luo C, Yang CG. Meclofenamic acid selectively inhibits FTO demethylation of m6A over ALKBH5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:373–84.
Lan Q, Liu PY, Bell JL, Wang JY, Hüttelmaier S, Zhang XD, Zhang L, Liu T. The Emerging Roles of RNA m(6)A Methylation and Demethylation as Critical Regulators of Tumorigenesis, Drug Sensitivity, and Resistance. Cancer Res. 2021;81:3431–40.
Soriano-Hernández AD, Galvan-Salazar HR, Montes-Galindo DA, Rodriguez-Hernandez A, Martinez-Martinez R, Guzman-Esquivel J, Valdez-Velazquez LL, Baltazar-Rodriguez LM, Espinoza-Gómez F, Rojas-Martinez A, et al. Antitumor effect of meclofenamic acid on human androgen-independent prostate cancer: a preclinical evaluation. Int Urol Nephrol. 2012;44:471–7.
Soriano-Hernandez AD, Madrigal-Pérez D, Galvan-Salazar HR, Martinez-Fierro ML, Valdez-Velazquez LL, Espinoza-Gómez F, Vazquez-Vuelvas OF, Olmedo-Buenrostro BA, Guzman-Esquivel J, Rodriguez-Sanchez IP, et al. Anti-inflammatory drugs and uterine cervical cancer cells: Antineoplastic effect of meclofenamic acid. Oncol Lett. 2015;10:2574–8.
Huang Y, Su R, Sheng Y, Dong L, Dong Z, Xu H, Ni T, Zhang ZS, Zhang T, Li C, et al. Small-Molecule Targeting of Oncogenic FTO Demethylase in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2019;35:677-691.e610.
Peng S, Xiao W, Ju D, Sun B, Hou N, Liu Q, Wang Y, Zhao H, Gao C, Zhang S, et al: Identification of entacapone as a chemical inhibitor of FTO mediating metabolic regulation through FOXO1. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11
Senek M, Nielsen EI, Nyholm D. Levodopa-entacapone-carbidopa intestinal gel in Parkinson’s disease: A randomized crossover study. Mov Disord. 2017;32:283–6.
Li B, Jiang J, Assaraf YG, Xiao H, Chen ZS, Huang C. Surmounting cancer drug resistance: New insights from the perspective of N(6)-methyladenosine RNA modification. Drug Resist Updat. 2020;53:100720.
Singh B, Kinne HE, Milligan RD, Washburn LJ, Olsen M, Lucci A. Important Role of FTO in the Survival of Rare Panresistant Triple-Negative Inflammatory Breast Cancer Cells Facing a Severe Metabolic Challenge. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0159072.
Chen B, Ye F, Yu L, Jia G, Huang X, Zhang X, Peng S, Chen K, Wang M, Gong S, et al. Development of cell-active N6-methyladenosine RNA demethylase FTO inhibitor. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:17963–71.
Qiao Y, Zhou B, Zhang M, Liu W, Han Z, Song C, Yu W, Yang Q, Wang R, Wang S, et al. A Novel Inhibitor of the Obesity-Related Protein FTO. Biochemistry. 2016;55:1516–22.
He W, Zhou B, Liu W, Zhang M, Shen Z, Han Z, Jiang Q, Yang Q, Song C, Wang R, et al. Identification of A Novel Small-Molecule Binding Site of the Fat Mass and Obesity Associated Protein (FTO). J Med Chem. 2015;58:7341–8.
Malacrida A, Rivara M, Di Domizio A, Cislaghi G, Miloso M, Zuliani V, Nicolini G. 3D proteome-wide scale screening and activity evaluation of a new ALKBH5 inhibitor in U87 glioblastoma cell line. Bioorg Med Chem. 2020;28:115300.
Selberg S, Seli N, Kankuri E, Karelson M. Rational Design of Novel Anticancer Small-Molecule RNA m6A Demethylase ALKBH5 Inhibitors. ACS Omega. 2021;6:13310–20.
Selberg S, Blokhina D, Aatonen M, Koivisto P, Siltanen A, Mervaala E, Kankuri E, Karelson M. Discovery of Small Molecules that Activate RNA Methylation through Cooperative Binding to the METTL3-14-WTAP Complex Active Site. Cell Rep. 2019;26:3762-3771.e3765.
Yankova E, Blackaby W, Albertella M, Rak J, De Braekeleer E, Tsagkogeorga G, Pilka ES, Aspris D, Leggate D, Hendrick AG, et al. Small-molecule inhibition of METTL3 as a strategy against myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 2021;593:597–601.
Mahapatra L, Andruska N, Mao C, Le J, Shapiro DJ. A Novel IMP1 Inhibitor, BTYNB, Targets c-Myc and Inhibits Melanoma and Ovarian Cancer Cell Proliferation. Transl Oncol. 2017;10:818–27.
Müller S, Bley N, Busch B, Glaß M, Lederer M, Misiak C, Fuchs T, Wedler A, Haase J, Bertoldo JB, et al. The oncofetal RNA-binding protein IGF2BP1 is a druggable, post-transcriptional super-enhancer of E2F-driven gene expression in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48:8576–90.
Zhang Z, Zhang C, Luo Y, Zhang G, Wu P, Sun N, He J. RNA N(6) -methyladenosine modification in the lethal teamwork of cancer stem cells and the tumor immune microenvironment: Current landscape and therapeutic potential. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11:e525.
Miao W, Chen J, Jia L, Ma J, Song D. The m6A methyltransferase METTL3 promotes osteosarcoma progression by regulating the m6A level of LEF1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;516:719–25.
Li X, Tang J, Huang W, Wang F, Li P, Qin C, Qin Z, Zou Q, Wei J, Hua L, et al. The M6A methyltransferase METTL3: acting as a tumor suppressor in renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2017;8:96103–16.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by National Key Research and Development Program (No. 2020YFA0712400), Special Foundation for Taishan Scholars (No. ts20190971), National Natural Science Foundation of China ( No. 81874119; No. 82072912; No. 82004122), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2020M682199), Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China (No. ZR2020QH335, No. ZR2019LZL003), Chen Xiao-ping Foundation for the Development of Science and Technology of Hubei Province (CXPJJH121001-2,021,003), 2021 Shandong Medical Association Clinical Research Fund – Qilu Special Project (YXH2022ZX02160), Foundation from Clinical Research Center of Shandong University (No.2020SDUCRCA015), Qilu Hospital Clinical New Technology Developing Foundation (No. 2019–3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors contributed as follows: writing – original draft preparation, X.Z.; writing – review & editing, C.L., T.C. and X.W.; figure preparation and editing, X.Z., W.L. and X.W.; supervision, Q.Y.; project administration, Q.Y.; funding acquisition, X.W. and Q.Y.. All authors reviewed the article and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Li, C., Chen, T. et al. Targeting RNA N6-methyladenosine to synergize with immune checkpoint therapy. Mol Cancer 22, 36 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-023-01746-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-023-01746-6