Abstract
As a critical internal RNA modification in higher eukaryotes, N6-methyladenosine (m6A) has become the hotspot of epigenetics research in recent years. Extensive studies on messenger RNAs have revealed that m6A affects RNA fate and cell functions in various bioprocesses, such as RNA splicing, export, translation, and stability, some of which seem to be directly or indirectly regulated by noncoding RNAs. Intriguingly, abundant noncoding RNAs such as microRNAs, long noncoding RNAs, circular RNAs, small nuclear RNAs, and ribosomal RNAs are also highly modified with m6A and require m6A modification for their biogenesis and functions. Here, we discuss the interaction between m6A modification and noncoding RNAs by focusing on the functional relevance of m6A in cancer progression, metastasis, drug resistance, and immune response. Furthermore, the investigation of m6A regulatory proteins and its inhibitors provides new opportunities for early diagnosis and effective treatment of cancer, especially in combination with immunotherapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
N6-methyladenosine (m6A), first described in 1974 [1, 2], is a well-known internal modification of messenger RNAs (mRNAs) and noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs); it is widely conserved among eukaryotes ranging from yeast, plants, and flies to mammals and even occurs in viral RNAs with a nuclear phase [3, 4]. As the most abundant and important mRNA modification in mammals, m6A modification accounts for approximately 50% of the total methyl-labeled ribonucleosides [5] and 0.1–0.4% of all adenosines in total cellular RNAs with about 3–5 m6A sites per mRNA [6]. m6A is enriched in the consensus sequence RRACH (where R: A or G and H: A, C, or U) and highly occurs in 3′ untranslated regions (3′-UTRs), stop codons, and internal long exons [4, 7], thus showing an effect on mRNA metabolism, including splicing, export, translation, and decay [8]. Notably, approximately 67% of 3′ UTRs with m6A peaks also contain binding sites for ncRNAs such as microRNAs (miRNAs) [7], thus suggesting a possible mechanism by which m6A and ncRNAs co-regulate target mRNAs through cooperation or competition.
In addition to mRNAs, m6A has also been discovered in diverse ncRNAs such as miRNAs, long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), circular RNAs (circRNAs), ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs), and small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) [9, 10], and has been found to be essential for their metabolism and functions [11,12,13,14]. Furthermore, certain m6A regulatory proteins responsible for abnormal m6A modifications on ncRNAs are also involved in cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and drug resistance, suggesting a potential association between cancer and m6A ncRNA modification, and thus, offering a new opportunity for cancer diagnosis and treatment [15,16,17].
Although still in its infancy, efforts have been made to investigate the role of m6A in various types of ncRNAs. In this review, we generalize the recent progress in this field by our understanding of the interaction between m6A and ncRNAs with a focus on introducing the underlying regulatory mechanisms and biological consequences of m6A-modified ncRNAs, as well as the effects of ncRNAs on m6A mRNA modification. Finally, current knowledge and future perspectives of m6A in cancer diagnosis and treatment are also discussed, especially its relevant roles in immune response and immunotherapy.
m6A writers, erasers, and readers
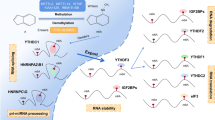
The effect of m6A modification is determined by m6A regulatory proteins comprising m6A methyltransferases (m6A writers), m6A demethylases (m6A erasers), and m6A-binding proteins (m6A readers) (Fig. 1). m6A writers usually refer to the m6A methylase complex consisting of methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3), methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14), Wilm’s tumor-associated protein (WTAP), RNA-binding motif protein 15 (RBM15) and its paralog RBM15B, and KIAA1429 (also known as vir-like m6A methyltransferase associated [VIRMA]). As the catalytic core, METTL3’s methyltransferase domain is catalytically active [18], while METTL14 functions as an RNA-binding platform to enhance the methyltransferase activity by forming a heterodimer with METTL3 [18]. WTAP is considered as a key adaptor protein that stabilizes the METTL3-METTL14 complex [19], and RBM15/15B helps to recruit the complex to methylate specific sites through interaction with METTL3 in a WTAP-dependent manner [20]. KIAA1429 is an important part of the m6A methylase complex, but its molecular function remains elusive [21]. Although a multitude of m6A modifications are installed by the METTL3-METTL14-WTAP-RBM15/15B-KIAA1429 complex, other m6A methyltransferases such as METTL16 [22,23,24], NSun2 [25], and ZCCHC4 [26], which seem to be introduced independently, are also indispensable for m6A formation, especially in some ncRNAs.
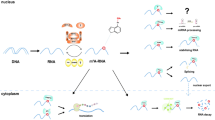
m6A modification on noncoding RNAs. m6A is deposited on ncRNAs by m6A writers consisting of the METTL3-METTL14-WTAP-RBM15/15B-KIAA1429 complex and many other methyltransferases such as METTL16, NSun2, and ZCCHC4. m6A can be removed by two m6A erasers: ALKBH5 and FTO. The function of m6A is mediated partly by m6A readers, which have been identified in members of the HNRNP family, the YTH domain-containing protein family, and NKAP. m6A is known to be involved in RNA biogenesis and functions, including miRNA processing, pre-mRNA splicing, RNA structure, RNA-RNA interaction, and RNA translation and degradation
As a dynamic and reversible RNA modification, m6A regulated by m6A writers and erasers exhibits the type of complexity seen with epigenetic modifications. Thus far, two demethylases have been identified as m6A erasers, namely alkB homolog 5 (ALKBH5) and fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO). However, in addition to m6A, FTO has also been shown to be responsible for the demethylation of N6, 2-O-dimethyladenosine (m6Am) in mRNAs and snRNAs [27, 28] and for the demethylation of N1-methyladenosine (m1A) in tRNAs [29] .
The m6A modifications that cause local changes in RNA structure can be recognized by selective RNA-binding proteins called m6A readers. The main m6A readers comprise the YT521-B homology (YTH) domain-containing protein family, including the nuclear YTHDC1 and the cytoplasmic YTHDC2, YTHDF1, YTHDF2, and YTHDF3. Other RNA-binding proteins, such as the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (HNRNP) family (HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPC, and HNRNPG) and NF-κB-associated protein (NKAP) can also affect RNA fate and cell functions through the specific recognition of m6A [30].
Roles of m6A methylation on ncRNAs in cancer
MicroRNAs
miRNAs are a class of noncoding single-stranded RNAs with a length of 21–25 nucleotides; they regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level by forming the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), which binds to the 3′-UTR of target mRNAs, resulting in either translational inhibition or mRNA degradation [31]. In recent years, m6A has been observed in miRNAs that target oncogenes or tumor suppressors and appears to participate in cancer progression by affecting miRNA biogenesis or stability.
m6A methylation promotes miRNA processing
As elucidated by Alarcón et al., altered METTL3 could affect the steady state levels of not only mRNAs but also several miRNAs such as let-7e, miR-25, miR-93, miR-126, miR-221/222, and miR-4485. Further, they revealed that m6A methylation is an important mechanism in miRNA biogenesis [12]. In the nucleus, miRNAs are first transcribed as long primary miRNAs (pri-miRNAs), which are subsequently processed into precursor miRNAs (pre-miRNAs) by the microprocessor complex comprising the double-stranded RNA-binding protein DGCR8 and the RNase III endonuclease DROSHA, and then cleaved by Dicer into mature single-stranded miRNAs in the cytoplasm [32]. As shown in previous studies, DGCR8 initiates miRNA maturation by recognizing the junction between the stem of a pri-miRNA hairpin and the flanking single-stranded RNA, and then recruits DROSHA. DROSHA cuts the two strands of the stem at a position close to the base of the main stem loop to produce a pre-miRNA product [33, 34]. Intriguingly, this engagement and processing of pri-miRNAs is m6A-dependent. METTL3 marks pri-miRNAs with m6A modification, allowing DGCR8 to recognize and bind its specific substrates rather than other secondary structures present in transcripts, thereby promoting the maturation of miRNAs and leading to an increase in miRNAs in cells [12].
This finding provides a new molecular mechanism for METTL3 in tumor growth and metastasis. As elucidated by Han et al., METTL3 promotes the maturation of miR-221/222 in bladder cancer cells by interacting with DGCR8. This m6A-dependent miR-221/222 maturation results in PTEN reduction and ultimately leads to bladder cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth. Moreover, the association between high METTL3 expression and poor prognosis in bladder cancer implies that METTL3 may become a new prognostic factor and therapeutic target for bladder cancer [35]. In colorectal cancer (CRC), METTL3 promotes cancer cell migration and invasion by facilitating the biogenesis of miR-1246, which reverses the inhibition of the MAPK pathway through the downregulation of the tumor suppressor SPRED2, thus enhancing the metastatic capacity of CRC [36].
In addition to interaction with DGCR8 to facilitate pri-miRNA processing, METTL3 has also been proven to promote miRNA biogenesis by increasing the Dicer splicing of pre-miRNA. In non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), the upregulated level of miR-143-3p in brain metastasis tissue plays an essential role in cancer progression. It has been found to trigger the invasion of blood-brain barrier model and increase the angiogenesis of lung cancer by silencing vasohibin-1 (VASH1), which modulates VEGFA degradation and tubulin depolymerization. Further studies have shown that the cleavage of pre-miR-143-3p is m6A-dependent and this miR-143-3p/VASH1 axis can be positively regulated by METTL3. This finding shows the role of m6A in pre-RNA processing for the first time and provides a new target for patients with NSCLC with brain metastasis [37].
By facilitating the recognition and binding of DGCR8 to pri-miRNAs, METTL14 can also mediate miRNA maturation in an m6A-dependent manner and inhibit carcinogenesis and metastasis. In hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), METTL14 has been proven to promote pri-miR-126 processing, while METTL14 depletion in HCC cells reduces m6A levels and miR-126 expression, leading to cancer cell migration and invasion [17]. In another study, METTL14 was found to suppress CRC progression by promoting the m6A-dependent maturation of miR-375, which could not only inhibit cancer cell proliferation by targeting Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1), but also suppress cancer cell migration and invasion through the miR-375/SP1 pathway [38]. Furthermore, the downregulation of METTL14 is closely related to malignant progression and poor recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS) of patients, suggesting the potential role of METTL14 in predicting tumor metastasis and recurrence [17, 38].
Additionally, m6A readers are also involved in miRNA biogenesis. Alarcón et al. reported that HNRNPA2B1 could bind to m6A marks on pri-miRNAs and promote miRNA processing by recruiting DGCR8 [39]. Consistent with this finding, a recent study on NSCLC showed that the overexpressed oncogenic lncRNA LINC01234 regulated miR-106b-5p maturation by interacting with HNRNPA2B1 to promote pri-miR-106b processing, leading to cryptochrome 2 (CRY2) silencing and c-Myc expression. Intriguingly, activated c-Myc in turn bound LINC01234 promoter to increase its transcription, thus creating a positive-feedback loop that led to NSCLC cell proliferation and tumor growth [40].
Another m6A reader NKAP can also act as an adaptor for this m6A-dependent pri-miRNA maturation. In pancreatic duct epithelial cells, DNA hypomethylation of METTL3 promoter induced by cigarette smoke promotes METTL3 expression and thereby facilitates oncogenic pri-miR-25 processing in an NKAP-dependent manner. Consequently, mature miR-25/miR-25-3p activates the oncogenic AKT-p70S6K signal by inhibiting PH domain leucine-rich repeat protein phosphatase 2 (PHLPP2), thereby triggering the malignant phenotype of pancreatic cancer cells [41].
In glioblastoma metastasis, the m6A reader HNRNPC directly bound to pri-miR-21 to promote miR-21 expression, whereas silencing of HNRNPC downregulated miR-21 and suppressed the AKT-p70S6K pathway, leading to the expression of PDCD4 and thus inhibiting cell migration and invasion [42].
m6A methylation inhibits miRNA processing
Intriguingly, with no changes observed in the primary transcripts, several mature miRNAs were downregulated after m6A demethylase FTO knockdown [43], suggesting the negative influence of m6A on miRNA biogenesis and/or stability.
Consistent with this finding, the methyltransferase NOP2/Sun domain family, member 2 (NSun2) abolishes the gene silencing function of miR-125b by inhibiting the processing of pri-miR-125b2 into pre-miR-125b2 and the cleavage of pre-miR-125b2 into miR-125b [25]. Furthermore, this Nsun2-dependent miR-125b downregulation, which could be promoted by proteinase-activated receptor 2 (PAR2), may ultimately contribute to cancer cell migration and lymphatic metastasis in CRC due to the enhanced expression of the miR-125b target gene GRB2-associated binding protein 2 (Gab2) [44].
In LCC9 breast cancer cells resistant to endocrine, the upregulated HNRNPA2B1 seems to play a more complex role in miRNA transcriptome regulation. In detail, HNRNPA2B1 overexpressed in endocrine-resistant breast cancer cells reduces the sensitivity to 4-hydroxytamoxifen and fulvestrant by upregulating miR-1266-5p, miR-1268a, and miR-671-3p and downregulating miR-29a-3p, miR-29b-3p, and miR-222 [45]. Although previous studies have shown that HNRNPA2B1 can bind to pri-miRNAs and interact with DGCR8 for miRNA processing [39], the mechanism by which HNRNPA2B1 downregulates miRNA remains unclear.
Collectively, these findings indicate an important and complicated role of m6A in miRNA biogenesis, and the underlying mechanism of m6A-mediated miRNA downregulation remains elusive. Because m6A regulates mRNA decay, the inhibition of miRNA processing may result from the decreased expression of miRNA processing factors including DGCR8, DROSHA, and Dicer, although Berulava et al. found no significant change in their mRNA levels after FTO knockdown [43]. Another possibility is that m6A modifications on certain miRNAs may be selectively recognized by other reader proteins responsible for miRNA degradation or instability, an m6A-mediated mechanism that has been demonstrated in mRNAs and several ncRNAs [46]. In conclusion, these studies reveal that m6A is a critical regulator of miRNA levels, and the diverse interactions between miRNA and m6A regulatory proteins require further investigation.
Long noncoding RNAs
Transcripts of more than 200 nucleotides in length, but lacking functional coding capacity are defined as long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs). In recent years, accumulating evidence demonstrates that lncRNAs control many aspects of gene expression and cellular biology at both transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels [47]. In an m6A mapping study, it was demonstrated that lncRNAs are also extensively m6A-modified [7].
m6A methylation acts as an RNA structural switch
RNA-binding proteins regulate the biological functions of their target RNAs by recognizing and binding to single-stranded RNA-binding motifs (RBMs), but these RBMs are often buried in local RNA structure, thus, avoiding interactions with RNA-binding proteins [48, 49]. Recently, m6A modification has been shown to act as a structural switch to affect RNA–protein interactions by modulating the structure of several RNAs, including metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript (MALAT1) [13], an lncRNA whose dysregulation has been consistently associated with the progression of various cancers, and has been recognized as a biomarker in many studies [50]. Methylation of residues A2577 and A2515 in MALAT1, either encompassing or proximal to the RRACH consensus motifs, makes it easier for the surrounding RNA sequence to bind HNRNPC and HNRNPG, respectively. However, METTL3/METTL14 knockdown decreases the accessibility of MALAT1 to these proteins and thereby inhibits cell proliferation [13, 51]. Although the specific effects of HNRNPC/HNRNPG binding to MALAT1 remain unclear, the binding of HNRNPC/HNRNPG genomewide to transcripts has been shown to influence RNA expression and alternative splicing pattern [52,53,54]. In another study, METTL16 was identified as a triple-stranded RNA-binding protein of MALAT1 and was shown to affect cell proliferation in Caenorhabditis elegans, thus, suggesting a potential relationship between the METTL16–MALAT1 complex and the oncogenic activity of MALAT1 [55].
m6A participates in the lncRNA-mediated ceRNA model
Several authors have proposed lncRNA-mediated regulatory models, where lncRNA acts as a competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) to regulate the activity and biological function of miRNA [56,57,58]. In nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), highly expressed m6A modifications increase the stability of the oncogenic lncRNA FAM225A, which promotes cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and migration by competitively absorbing miR-590-3p and miR-1275 like a sponge; thus, increasing their target integrin β3 (ITGB3) and activating the FAK/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway to promote NPC tumorigenesis and metastasis [59]. Similarly, the lncRNA LINC00958 promotes HCC lipogenesis and progression by sponging miR-3619-5p to increase hepatoma-derived growth factor (HDGF) expression, and this LINC00958/miR-3619-5p/HDGF axis could be positively regulated by METTL3, which increases the stability of LINC00958 in an m6A-dependent manner [60]. In NSCLC, METTL3-mediated m6A modification increases the levels and stability of MALAT1, which acts as a ceRNA to abolish the gene silencing function of miR-1914-3p, and thereby increases the downstream target YAP, leading to NSCLC metastasis and drug resistance to cisplatin [61]. These findings suggest the regulatory role of m6A in lncRNA-mediated ceRNA model related to cancer development and chemoresistance, and provides a new idea for cancer diagnosis and treatment.
In addition to enhancing the stability of lncRNA to ensure its function, m6A also appears to be directly involved in RNA-RNA interactions. In mammalian embryonic stem cells (ESCs), linc1281 regulates ESC differentiation by binding and sequestering let-7 family miRNAs associated with cellular pluripotency. Intriguingly, according to the recent research conducted by Yang et al., this lincRNA-miRNA interaction is m6A-dependent as m6A-deficient A-G mutant or METTL3 downregulation abolishes the direct binding of let-7 to linc1281 without changing the levels of linc1281 [62]. However, it remains unclear whether there are m6A reader proteins that affect the m6A-dependent lincRNA-miRNA interactions.
m6A promotes XIST-mediated gene silencing
During the development of female mammals, silencing of gene transcription on the X chromosome is mediated by the lncRNA X-inactive specific transcript (XIST), but the underlying mechanisms remain unclear [63]. WTAP, a partner of METTL3 that affects m6A deposition on targets [19, 64], has been identified as a XIST-associated protein in a proteomic analysis [65]. Another study showed that RBM15 and its paralogue RBM15B are also involved in m6A formation on XIST, which seem to interact with METTL3 in a WTAP-dependent manner to form the m6A methylase complex, and bind to the target sites using their RNA-binding domains [20]. Further functional screening showed that efficient deposition of WTAP and RBM15/15B is necessary for XIST-mediated transcriptional repression, while METTL3 knockdown impairs the XIST function [20, 66]; thus, supporting the promoting role of m6A in XIST-mediated gene silencing. Moreover, the reader protein YTHDC1 has been identified and shown to enable this m6A-dependent transcriptional repression, but the detailed mechanism remains unclear [20].
Circular RNAs
CircRNAs are the back-splicing products of precursor mRNA [67] and exhibit widespread and cell type-specific m6A methylation features. Despite sharing m6A writers (METTL3/ METTL14) and readers (YTHDF1/YTHDF2) that interact with mRNAs, many m6A sites on circRNAs are different from those on mRNAs. In detail, m6A-circRNAs are usually derived from exons in mRNAs with no m6A methylation, whereas mRNAs with m6A methylation on the same exons that constitute m6A-circRNAs show less stability when recognized by YTHDF2; this suggests that m6A may occur during or after circRNA formation, but the underlying mechanism needs further study [68].
m6A promotes cytoplasmic export of circRNAs
In CRC cells, m6A methylation has been shown to mediate the cytoplasmic export of a crucial oncogenic circRNA, circNSun2. As elucidated by Chen et al., m6A-modified circNSun2 in the nucleus could be recognized by YTHDC1 and exported to the cytoplasm, and circNSun2 then stabilizes HMGA2 mRNA through the formation of the circNSun2/IGF2BP2/HMGA2 complex, eventually leading to the invasion of CRC cells and liver metastasis. Furthermore, because m6A-modified circNSun2 has been found to be frequently upregulated in tumor tissues and serum samples of patients with CRC with liver metastasis, circNSun2 may become a new diagnostic/prognostic biomarker and a potential therapeutic target for CRCs with liver metastasis [69].
m6A methylation drives circRNA translation
Yang et al. revealed that m6A modifications on circRNAs can function as internal ribosomal entry sites (IRESs) for the cap-independent protein translation. This m6A-driven translation of circRNAs could be enhanced by METTL3 and METTL14, while FTO-mediated demethylation of m6A may reduce this translation process. Both the m6A reader protein YTHDF3 and the translation initiation factor eIF4G2 are required. Further analysis revealed that hundreds of endogenous circRNAs containing m6A modifications are translatable, suggesting the general function of circRNA, which expands the human transcriptome and provides a fresh view on m6A modification in protein translation [14].
m6A methylation mediates circRNA degradation
Studies have shown that m6A regulates mRNA degradation triggered by YTHDF2 mainly through two different pathways: deadenylation via the CCR4/NOT complex and endoribonucleolytic cleavage by the HRSP12-RNase P/MRP complex [46]. However, Park et al. reported that a subset of m6A-modified circRNAs bound by YTHDF2 was also selectively downregulated via the HRSP12-RNase P/MRP endoribonuclease complex [70], which revealed the regulatory role of m6A in circRNA degradation and suggested a possible molecular mechanism.
Regarding the function of circRNA in immunity, Chen et al. reported that endogenous m6A-modified circRNAs bound by YTHDF2 were incapable of stimulating RIG-I, which was probably due to YTHDF2-mediated degradation of circRNAs [71], whereas exogenous circRNAs lacking m6A modification activated the RIG-I pathway, leading to interferon production and induction of innate immunity [72]. This finding revealed the function of m6A in distinguishing endogenous circRNAs from exogenous circRNAs and suggested the potential role of YTHDF2-mediated circRNA degradation in inhibiting innate immunity. Further, the administration of unmodified circRNAs led to antigen-specific T cell activation, antibody production, and tumor inhibition in vivo [72], thus providing a new view for the role of m6A-modified circRNAs in antitumor immunity.
Small nuclear RNAs
The splicing of the precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) is catalyzed by the multi-megadalton ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex known as spliceosome, which comprises five small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) and numerous non-snRNP proteins [73]. These snRNPs consisting of small nuclear RNAs (U1, U2, U4, U5, and U6 snRNA) and proteins constitute the core components of various spliceosomal complexes [74]. Several post-transcriptional modifications have been identified on snRNAs as well as m6A modifications on U2, U4, and U6 spliceosomal snRNAs [75].
m6A methylation on U6 snRNA regulates pre-mRNA splicing
Spliceosomal U6 snRNA carries an m6A modification on position 43 [76]. Recently, studies have revealed that this m6A43 modification on spliceosomal U6 snRNA is mediated by the m6A RNA methyltransferase METTL16 and is highly possible to be introduced during early stages in U6 snRNP biogenesis [23, 24]. Interestingly, A43 is located in the evolutionarily conserved U6 sequence, which is base-paired to the 5′ splice site of the pre-mRNA in the first catalytic step of splicing [77]. Mutations of this modified position have been found to impede such snRNA-mRNA interactions, which are fatal in yeast [78], and the failed attempts to knockout METTL16 in mammalian cells [23] further suggest that the METTL16-mediated m6A43 modification of spliceosomal U6 snRNA may have critical roles in mRNA splicing and biogenesis.
Ribosomal RNAs
Ribosomes are necessary for mRNA translation in eukaryotes. Ribosomes are composed of four ribosomal RNAs known as 5S, 5.8S, 18S, and 25S (yeast)/28S (human) rRNAs, and approximately 80 ribosomal proteins arranged into a small subunit (SSU) and a large subunit (LSU) [79, 80]. The structure, assembly, and function of ribosomes may be affected by the chemical modifications on rRNAs [80]. Thus far, two m6A modifications have been identified on rRNA: one is m6A4220 modification on 28S rRNA, and the other is m6A1832 modification on 18S rRNA [75, 81].
m6A methylation on rRNA affects mRNA translation
Recently, a new human m6A methyltransferase, ZCCHC4, has been found to promote liver tumor growth by regulating ribosome translation through modulating m6A4220 on 28S rRNA. In patients with HCC, the expression of ZCCHC4 and m6A on 28S rRNA in cancer tissues was significantly increased as compared to that in the surrounding healthy tissues, whereas ZCCHC4 knockout in a xenograft mouse model eliminates m6A modification on 28S rRNA and then decreases global translation activity, which contributes to the inhibition of HCC cell proliferation and reduction in liver tumor size; thus, highlighting the essential role of m6A rRNA modification in mRNA translation and tumor progression [26]. Consistent with this finding, van Tran et al. confirmed ZCCHC4 as a 28S rRNA m6A4220 methyltransferase that acts only on rRNAs [82], and further studies on the structure and regulation of ZCCHC4 in m6A methylation of 28S rRNA showed that the specific binding and methylation of ZCCHC4 to substrates depended on the stem loop structure of 28S rRNA [83]. In addition, the findings that ZCCHC4 is located in nucleoli, where the ribosomes are assembled, and ZCCHC4 interacts with proteins involved in RNA metabolism provide a possible mechanism by which ZCCHC4 influences RNA translation by regulating ribosomal assembly and biogenesis [84].
METTL5 has also been confirmed as a novel m6A writer responsible for the m6A1832 modification of 18S rRNA [82], and METTL16 has also been shown to interact with 5.8S, 18S, and 28S rRNAs [55], which require further investigation in the future.
As described above, m6A modifications modulated by several m6A regulatory proteins produce multiple biological functions in ncRNAs (Table 1).
ncRNAs regulate m6A methylation on mRNAs in cancer
miRNAs and m6A formation on mRNAs
Previous studies have shown that 67% of 3′-UTRs of mRNAs with m6A peaks contain more than one miRNA binding site, and the overall distribution of these two groups in 3′-UTRs is inversely related. In 3′-UTRs containing these two groups, m6A peaks usually precede miRNA binding sites, thus indicating a possible interaction between m6A and downstream-bound miRNA [7] (Fig. 2). On the one hand, m6A on lincRNA promotes the binding of miRNA [62], allowing us to wonder whether m6A proximity to miRNA binding sites is involved in miRNA-mRNA interaction and thereby regulates miRNA-mediated transcript inhibition mechanism. On the other hand, the observation that higher expression of miRNAs is usually accompanied by a higher proportion of m6A-modified target transcripts suggests that miRNAs may regulate m6A abundance on their target transcripts [7]. Consistently, Chen et al. reported that miRNAs could modulate m6A formation on mRNAs by promoting the binding of METTL3 through a sequence pairing mechanism, which increased m6A levels and allowed the reprogramming of mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) into pluripotent stem cells [85].
Association between m6A and miRNAs on 3′-UTRs of mRNAs. (A) m6A is more common on 3′-UTRs of mRNAs containing miRNA target sites. m6A is mostly deposited near the stop codon, whereas miRNA target sites are generally enriched in 3′ end of 3′-UTRs (B) m6A may regulate the binding and gene silencing function of the downstream-bound miRNAs. (C) miRNAs promote METTL3-mediated m6A formation on mRNAs through a sequence pairing mechanism
lncRNAs regulate m6A modification on RNAs
Recently, a class of antisense transcript-derived lncRNAs has been shown to play a role in cancer development by regulating the interaction between m6A regulatory proteins and their target mRNAs (Fig. 3). The writer protein KIAA1429 is highly expressed in HCC tissues and is closely correlated with poor prognosis in patients with HCC. KIAA1429 has been found to induce GATA3 mRNA degradation by modifying the 3′-UTR of GATA3 pre-mRNA with m6A, which abolishes the binding of HuR responsible for pre-mRNA processing and mRNA stability. Intriguingly, the lncRNA antisense to GATA3, GATA3-AS, could act as a guide to facilitate this KIAA1429-mediated m6A modification of GATA3 pre-mRNA, and thereby promotes the decrease in GATA3 expression, leading to the growth and metastasis of liver cancer [86].
In glioblastoma stem-like cells (GSCs), the m6A eraser ALKBH5 is highly expressed and predicts poor survival of patients with glioblastoma (GBM). As elucidated by Zhang et al., ALKBH5 promotes the tumorigenesis of GSCs by removing m6A from the FOXM1 nascent transcripts, which enhances mRNA stability and sustains FOXM1 expression. Additionally, the FOXM1-AS lncRNA, which is transcribed from the antisense strand of the FOXM1 gene, has been identified to promote this ALKBH5-FOXM1 interaction, and thereby, enhance FOXM1 expression and GSC proliferation [87]. Similarly, in cervical cancer (CC), lncRNA GAS5-AS1 is proven to interact with GAS5 and increase its stability by promoting the ALKBH5-dependent m6A demethylation, leading to the expression of the tumor suppressor GAS5, and thereby, inhibiting CC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion [88].
miRNAs regulate the expression of m6A regulatory proteins
miRNAs can also regulate m6A levels and biological functions by targeting the mRNAs of m6A regulatory proteins (Fig. 3). METTL3 is responsible for m6A modifications on mRNAs of several crucial oncoproteins related to cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in many cancers [89]. As elucidated by Du et al., miR-33a could prevent NSCLC progression by targeting the 3′-UTR of METTL3 mRNA and seems to be a promising target for treatment improvement for NSCLC [90]. Similarly, miR-4429, another potential therapeutic target in gastric cancer (GC), targets and downregulates METTL3 to inhibit m6A-induced stabilization of SEC62, which in turn inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in GC cells [91].
In breast cancer, miRNA let-7 g downregulates METTL3 expression by targeting its mRNA 3′-UTR, while hepatitis B X-interacting protein (HBXIP) improves METTL3 expression by inhibiting the function of let-7 g. Intriguingly, METTL3 could upregulate HBXIP in an m6A-dependent manner, which forms a positive feedback loop of HBXIP/let-7 g/METTL3/HBXIP, and thereby accelerates breast cancer cell proliferation [92].
In HCC, miR-145 inhibits tumorigenesis by targeting the mRNA of YTHDF2, resulting in suppressed YTHDF2 expression and decreased degradation of m6A-modified mRNAs and thus inhibiting HCC cell proliferation [93]. In addition, miR-744-5p leads to ovarian cancer cell death by targeting HNRNPC. The silencing of HNRNPC affects miR-21 expression and AKT phosphorylation, which ultimately contributes to apoptosis. It is worth mentioning that this effect is enhanced in combination with carboplatin treatment [94].
In summary, these findings revealed that ncRNAs can affect m6A modifications on mRNAs by targeting m6A writers, erasers, and readers in terms of both their expression and functions (Table 2), thus providing the foundation for further exploration of the roles of RNA epigenetic regulation patterns in cancers.
m6A as a diagnostic target of cancers
Given the critical roles of m6A in cancer cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and drug resistance, m6A modification and its regulatory proteins seem to be good diagnostic targets.
Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) derived from tumors can truly reflect the status and progression of the tumor. The finding that the levels of m6A are significantly elevated in CTCs from patients with lung cancer suggests that m6A in CTCs can be used as an early indicator to monitor and prevent cancer development and metastasis [16]. Furthermore, circRNAs showing a stable structure are promising biomarkers. In CRCs, the m6A-modified circNsun2, which has been proven to be positively associated with CRC cell aggressiveness, is frequently upregulated in serum and metastatic liver tissues, thus providing a novel diagnostic/prognostic predictor for colorectal liver metastasis [69]. Additionally, the early detection of m6A regulatory proteins may also be beneficial. In patients with bladder cancer, METTL3, which participates in cancer development by accelerating the m6A-dependent maturation of miR-221/222, is related to their poor prognosis [35]. In HCC, the methyltransferase METTL14 seems to be a good prognostic factor for cancer metastasis and recurrence because of its role in promoting the maturation of miR-126 that inhibits the metastasis of HCC [17]. Collectively, these findings provide new opportunities for the utilization of m6A in cancer diagnosis and prognosis.
m6A and immunology of cancers
The maladjustment of m6A machinery provides interesting targets for tumor therapy, including emerging checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. FTO-mediated m6A demethylation has been found to regulate the occurrence and development of many cancers such as glioblastoma and breast cancer [95]. Recently, several selective inhibitors of FTO have been investigated, among which meclofenamic acid (MA) [96, 97] and MO-I-500 [98] were found to effectively suppress glioblastoma progression and breast cancer cell survival by inhibiting the catalytic activity of FTO. Notably, Yang et al. reported that FTO in melanoma cells not only promoted tumorigenesis but also mediated anti-PD-1 resistance. Depletion of FTO suppressed the expression of PD-1 (PDCD1), CXCR4, and SOX10 genes through m6A/YTHDF2-mediated mRNA decay and thus sensitized melanoma cells to interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and anti-PD-1 blockade immunotherapy; this finding suggests that the combination of FTO inhibitors with anti-PD-1 treatment might be beneficial to reduce the resistance of melanoma to immunotherapy [99].
Recently, accumulating evidence has demonstrated the critical role of m6A in both innate and adaptive immune response [71], suggesting the potential effect of m6A on tumor immunology. T cells regulate the entire adaptive immune response, and the research conducted by Li et al. showed the regulatory role of m6A modification in naïve T-cell homeostasis and differentiation, indicating that m6A could be a potential target in antitumor immunotherapy and autoimmune disease therapy [100]. Regarding regulatory T cells (Tregs), a specialized T-cell lineage that is closely related to self-tolerance and immunosuppression, Tong et al. reported that m6A could maintain Treg functions by targeting the IL-2/STAT5/SOCS signaling pathway [101]. Because tumor-infiltrating Tregs restrict the tumor-killing functions of CD8+ T cells in tumor microenvironment, combining selective downregulation of m6A levels in Tregs with tumor immunotherapy may be an effective new therapeutic strategy.
Dendritic cells (DCs) are essential antigen-presenting cells that induce antigen-specific T-cell responses. Han et al. showed that m6A modification controlled DC function by enhancing the translation of lysosomal protease transcripts in a YTHDF1-dependent manner. Knockdown of YTHDF1 limited lysosomal proteolysis in DCs and enhanced the cross-presentation of tumor antigens, leading to better cross-priming of CD8+ T cells and therapeutic efficacy of PD-L1 checkpoint blockade; this finding suggests that YTHDF1 depletion combined with emerging checkpoint blockade or DC vaccination can serve as potential therapeutic targets for immunotherapy [102]. On the other hand, Wang et al. reported that METTL3-mediated m6A modification could facilitate the translation of CD40, CD80, and TLR4 signaling adaptor Tirap mRNAs in DCs by binding to YTHDF1, which not only promoted antigen presentation and DC-based T-cell responses but also stimulated cytokine production through the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway [103]. Consistently, another study on LPS-induced inflammatory response showed that METTL3 was positively correlated with the expression of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, IL-8, GRO, Gro-α, and RANTES, whereas METTL3 inhibition suppressed NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways by affecting the alternative splicing of MyD88 [104] or the nuclear export of Traf6 mRNA [105]. Collectively, these findings revealed the flexible role of m6A in DC function and innate immunity, suggesting that the underlying mechanism of m6A in tumor immunology might be more complex and therefore needs further research.
Conclusions
The dynamic and reversible m6A methylation has been shown to regulate post-transcriptional gene expression through several mechanisms. In addition to mRNAs, multiple types of ncRNAs also require m6A methylation for proper biogenesis, and utilize base modifications to tune structure and functions.
The effects of m6A modification are determined by m6A readers, writers, and erasers. New approaches and techniques are needed to investigate the distribution and functions of m6A modification in ncRNAs, as well as the associated m6A regulatory proteins in more detail, which could not only help us to fully understand the significance of m6A modification and their contribution to the highly dynamic cellular processes, but also to expand our scope of knowledge in the multilayered gene expression control mechanisms.
Dysregulation of m6A and its regulatory proteins is related to the diagnosis and prognosis of various diseases, including cancers, and these associated m6A regulatory proteins might represent interesting therapeutic targets. It is worth noting that the development of clinically applicable selective and effective inhibitors of FTO and other m6A regulatory proteins may provide new and more effective treatment strategies to treat cancer, especially when used in combination with emerging immunotherapies.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
Abbreviations
- m6A:
-
N6-methyladenosine
- mRNAs:
-
Messenger RNAs
- ncRNAs:
-
Noncoding RNAs
- FTO:
-
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein
- 3′-UTRs:
-
3′ untranslated regions
- miRNAs:
-
MicroRNAs
- lncRNAs:
-
Long noncoding RNAs
- circRNAs:
-
Circular RNAs
- rRNAs:
-
Ribosomal RNAs
- snRNAs:
-
Small nuclear RNAs
- snoRNAs:
-
Small nucleolar RNAs
- METTL3:
-
Methyltransferase-like 3
- METTL14:
-
Methyltransferase-like 14
- WTAP:
-
Wilm’s tumor-associated protein
- RBM15:
-
RNA-binding motif protein 15
- ALKBH5:
-
AlkB homolog 5
- HNRNP:
-
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein
- NKAP:
-
NF-κB-associated protein
- RISC:
-
RNA-induced silencing complex
- pri-miRNAs:
-
Primary miRNAs
- pre-miRNAs:
-
Precursor miRNAs
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- MALAT1:
-
Metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript
- ceRNA:
-
Competitive endogenous RNA
References
Desrosiers R, Friderici K, Rottman F. Identification of methylated nucleosides in messenger RNA from Novikoff hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974;71(10):3971–5.
Perry RP, Kelley DE. Existence of methylated messenger RNA in mouse L cells. Cell. 1974;1(1):37–42.
Murik O, Chandran SA, Nevo-Dinur K, Sultan LD, Best C, Stein Y, Hazan C, Ostersetzer-Biran O. Topologies of N(6) -adenosine methylation (m (6) A) in land plant mitochondria and their putative effects on organellar gene expression. Plant J. 2019:10 1111/tpj.14589.
Fu Y, Dominissini D, Rechavi G, He C. Gene expression regulation mediated through reversible m (6) a RNA methylation. Nat Rev Genet. 2014;15(5):293–306.
Wei CM, Gershowitz A, Moss B. Methylated nucleotides block 5′ terminus of HeLa cell messenger RNA. Cell. 1975;4(4):379–86.
Rottman F, Shatkin AJ, Perry RP. Sequences containing methylated nucleotides at 5ʹ termini of messenger-RNAs — possible implications for processing. Cell. 1979;3:197–9.
Meyer KD, Saletore Y, Zumbo P, Elemento O, Mason CE, Jaffrey SR. Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation reveals enrichment in 3′ UTRs and near stop codons. Cell. 2012;149(7):1635–46.
Pan Y, Ma P, Liu Y, Li W, Shu Y. Multiple functions of m (6) a RNA methylation in cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2018;11(1):48.
Linder B, Grozhik AV, Olarerin-George AO, Meydan C, Mason CE, Jaffrey SR. Single-nucleotide-resolution mapping of m6A and m6Am throughout the transcriptome. Nat Methods. 2015;12(8):767–72.
Molinie B, Wang J, Lim KS, Hillebrand R, Lu ZX, Van Wittenberghe N, Howard BD, Daneshvar K, Mullen AC, Dedon P, Xing Y, Giallourakis CC. M (6) A-LAIC-seq reveals the census and complexity of the m (6) a epitranscriptome. Nat Methods. 2016;13(8):692–8.
Liu N, Zhou KI, Parisien M, Dai Q, Diatchenko L, Pan T. N6-methyladenosine alters RNA structure to regulate binding of a low-complexity protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(10):6051–63.
Alarcón CR, Lee H, Goodarzi H, Halberg N. SF. T. N6-methyladenosine marks primary microRNAs for processing. Nature. 2015;519(7544):482–5.
Liu N, Dai Q, Zheng G, He C, Parisien M, Pan T. N(6)-methyladenosine-dependent RNA structural switches regulate RNA-protein interactions. Nature. 2015;518(7540):560–4.
Yang Y, Fan X, Mao M, Song X, Wu P, Zhang Y, Jin Y, Yang Y, Chen LL, Wang Y, Wong CC, Xiao X, Wang Z. Extensive translation of circular RNAs driven by N(6)-methyladenosine. Cell Res. 2017;27(5):626–41.
Li Y, Xiao J, Bai J, Tian Y, Qu Y, Chen X, Wang Q, Li X, Zhang Y, Xu J. Molecular characterization and clinical relevance of m (6) A regulators across 33 cancer types. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):137.
Huang W, Qi CB, Lv SW, Xie M, Feng YQ, Huang WH, Yuan BF. Determination of DNA and RNA methylation in circulating tumor cells by mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2016;88(2):1378–84.
Ma JZ, Yang F, Zhou CC, Liu F, Yuan JH, Wang F, Wang TT, Xu QG, Zhou WP, Sun SH. METTL14 suppresses the metastatic potential of hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating N(6) -methyladenosine-dependent primary MicroRNA processing. Hepatology. 2017;65(2):529–43.
Wang X, Feng J, Xue Y, Guan Z, Zhang D, Liu Z, Gong Z, Wang Q, Huang J, Tang C, Zou T. Structural basis of N6-adenosine methylation by the METTL3–METTL14 complex. Nature. 2016;534(7608):575–8.
Schöller E, Weichmann F, Treiber T, Ringle S, Treiber N, Flatley A, Feederle R, Bruckmann A, Meister G. Interactions, localization, and phosphorylation of the m (6) A generating METTL3-METTL14-WTAP complex. RNA (New York, NY). 2018;24(4):499–512.
Patil DP, Chen CK, Pickering BF, Chow A, Jackson C, Guttman M, Jaffrey SR. M (6) a RNA methylation promotes XIST-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature. 2016;537(7620):369–73.
Schwartz S, Mumbach MR, Jovanovic M, Wang T, Maciag K, Bushkin GG, Mertins P, Ter-Ovanesyan D, Habib N, Cacchiarelli D, Sanjana NE, Freinkman E, Pacold ME, Satija R, Mikkelsen TS, Hacohen N, Zhang F, Carr SA, Lander ES, Regev A. Perturbation of m6A writers reveals two distinct classes of mRNA methylation at internal and 5′ sites. Cell Rep. 2014;8(1):284–96.
Mendel M, Chen K-M, Homolka D, Gos P, Pandey RR, McCarthy AA, Pillai RS. Methylation of Structured RNA by the mA Writer METTL16 Is Essential for Mouse Embryonic Development. Molecular cell. 2018;71(6).
Pendleton KE, Chen B, Liu K, Hunter OV, Xie Y, Tu BP, Conrad NK. The U6 snRNA mA Methyltransferase METTL16 Regulates SAM Synthetase Intron Retention. Cell. 2017;169(5).
Warda AS, Kretschmer J, Hackert P, Lenz C, Urlaub H, Hobartner C, Sloan KE, Bohnsack MT. Human METTL16 is a N(6)-methyladenosine (m (6) a) methyltransferase that targets pre-mRNAs and various non-coding RNAs. EMBO Rep. 2017;18(11):2004–14.
Yuan S, Tang H, Xing J, Fan X, Cai X, Li Q, Han P, Luo Y, Zhang Z, Jiang B, Dou Y, Gorospe M, Wang W. Methylation by NSun2 represses the levels and function of microRNA 125b. Mol Cell Biol. 2014;34(19):3630–41.
Ma H, Wang X, Cai J, Dai Q, Natchiar SK, Lv R, Chen K, Lu Z, Chen H, Shi YG, Lan F, Fan J, Klaholz BP, Pan T, Shi Y, He C. N(6-)Methyladenosine methyltransferase ZCCHC4 mediates ribosomal RNA methylation. Nat Chem Biol. 2019;15(1):88–94.
Mauer J, Sindelar M, Despic V, Guez T, Hawley BR, Vasseur JJ, Rentmeister A, Gross SS, Pellizzoni L, Debart F, Goodarzi H, SR. J. FTO controls reversible m6Am RNA methylation during snRNA biogenesis. Nat Chem Biol 2019;15(4):340–347.
Mauer J, Luo X, Blanjoie A, Jiao X, Grozhik AV, Patil DP, Linder B, Pickering BF, Vasseur JJ, Chen Q, Gross SS, Elemento O, Debart F, Kiledjian M, Jaffrey SR. Reversible methylation of m (6) am in the 5′ cap controls mRNA stability. Nature. 2017;541(7637):371–5.
Wei J, Liu F, Lu Z, Fei Q, Ai Y, He PC, Shi H, Cui X, Su R, Klungland A, Jia G, Chen J, He C. Differential m (6) a, m (6) am, and m (1) a Demethylation mediated by FTO in the cell nucleus and cytoplasm. Mol Cell. 2018;71(6):973–85 e5.
Meyer KD, Jaffrey SR. Rethinking m (6) a readers, writers, and erasers. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2017;33:319–42.
Iwakawa H-O, Tomari Y. The functions of MicroRNAs: mRNA decay and translational repression. Trends Cell Biol. 2015;25(11):651–65.
Treiber T, Treiber N, Meister G. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis and its crosstalk with other cellular pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(1).
Nguyen TA, Jo MH, Choi Y-G, Park J, Kwon SC, Hohng S, Kim VN, Woo J-S. Functional anatomy of the human microprocessor. Cell. 2015;161(6):1374–87.
Kim B, Jeong K, Kim VN. Genome-wide Mapping of DROSHA Cleavage Sites on Primary MicroRNAs and Noncanonical Substrates. Mol Cell. 2017;66(2):258–69 e5.
Han J, Wang JZ, Yang X, Yu H, Zhou R, Lu HC, Yuan WB, Lu JC, Zhou ZJ, Lu Q, Wei JF. METTL3 promote tumor proliferation of bladder cancer by accelerating pri-miR221/ 222 maturation in m6A-dependent manner. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):110.
Peng W, Li J, Chen R, Gu Q, Yang P, Qian W, Ji D, Wang Q, Zhang Z, Tang J, Sun Y. Upregulated METTL3 promotes metastasis of colorectal Cancer via miR-1246/SPRED2/MAPK signaling pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1):393.
Wang H, Deng Q, Lv Z, Ling Y, Hou X, Chen Z, Dinglin X, Ma S, Li D, Wu Y, Peng Y, Huang H, Chen L. N6-methyladenosine induced miR-143-3p promotes the brain metastasis of lung cancer via regulation of VASH1. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):181.
Chen X, Xu M, Xu X, Zeng K, Liu X, Sun L, Pan B, He B, Pan Y, Sun H, Xia X, Wang S. METTL14 suppresses CRC progression via regulating N6-Methyladenosine-dependent primary miR-375 processing. Mol Ther. 2019.
Alarcón CR, Goodarzi H, Lee H, Liu X, Tavazoie S, SF T. HNRNPA2B1 is a mediator of m6A-dependent nuclear RNA processing events. Cell. 2015;162(6):1299–308.
Chen Z, Chen X, Lei T, Gu Y, Gu J, Huang J, Lu B, Yuan L, Sun M, Wang Z. Integrative analysis of NSCLC identifies LINC01234 as an oncogenic lncRNA that interacts with HNRNPA2B1 and regulates miR-106b biogenesis. Mol Ther. 2020.
Zhang J, Bai R, Li M, Ye H, Wu C, Wang C, Li S, Tan L, Mai D, Li G, Pan L, Zheng Y, Su J, Ye Y, Fu Z, Zheng S, Zuo Z, Liu Z, Zhao Q, Che X, Xie D, Jia W, Zeng MS, Tan W, Chen R, Xu RH, Zheng J, Lin D. Excessive miR-25-3p maturation via N(6)-methyladenosine stimulated by cigarette smoke promotes pancreatic cancer progression. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1858.
Park YM, Hwang SJ, Masuda K, Choi KM, Jeong MR, Nam DH, Gorospe M, Kim HH. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C1/C2 controls the metastatic potential of glioblastoma by regulating PDCD4. Mol Cell Biol. 2012;32(20):4237–44.
Berulava T, Rahmann S, Rademacher K, Klein-Hitpass L, Horsthemke B. N6-adenosine methylation in MiRNAs. PLoS One. 2015;10(2):e0118438.
Yang L, Ma Y, Han W, Li W, Cui L, Zhao X, Tian Y, Zhou Z, Wang W, Wang H. Proteinase-activated receptor 2 promotes cancer cell migration through RNA methylation-mediated repression of miR-125b. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(44):26627–37.
Klinge CM, Piell KM, Tooley CS, Rouchka EC. HNRNPA2/B1 is upregulated in endocrine-resistant LCC9 breast cancer cells and alters the miRNA transcriptome when overexpressed in MCF-7 cells. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):9430.
Lee Y, Choe J, Park OH, Kim YK. Molecular mechanisms driving mRNA degradation by mA modification. Trends Genet. 2020;36(3):177–88.
Kopp F, Mendell JT. Functional classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2018;172(3):393–407.
Ray D, Kazan H, Cook KB, Weirauch MT, Najafabadi HS, Li X, Gueroussov S, Albu M, Zheng H, Yang A, Na H, Irimia M, Matzat LH, Dale RK, Smith SA, Yarosh CA, Kelly SM, Nabet B, Mecenas D, Li W, Laishram RS, Qiao M, Lipshitz HD, Piano F, Corbett AH, Carstens RP, Frey BJ, Anderson RA, Lynch KW, Penalva LO, Lei EP, Fraser AG, Blencowe BJ, Morris QD, Hughes TR. A compendium of RNA-binding motifs for decoding gene regulation. Nature. 2013;499(7457):172–7.
Hentze MW, Castello A, Schwarzl T, Preiss T. A brave new world of RNA-binding proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(5):327–41.
Zhang X, Hamblin MH, Yin KJ. The long noncoding RNA Malat1: its physiological and pathophysiological functions. RNA Biol. 2017;14(12):1705–14.
Liu N, Zhou KI, Parisien M, Dai Q, Diatchenko L. T P. N6-methyladenosine alters RNA structure to regulate binding of a low-complexity protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(10):6051–30.
Fischl H, Neve J, Wang Z, Patel R, Louey A, Tian B, Furger A. hnRNPC regulates cancer-specific alternative cleavage and polyadenylation profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(14):7580–91.
König J, Zarnack K, Rot G, Curk T, Kayikci M, Zupan B, Turner DJ, Luscombe NM. ICLIP reveals the function of hnRNP particles in splicing at individual nucleotide resolution. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010;17(7):909–15.
Zhou KI, Shi H, Lyu R, Wylder AC, Matuszek Ż, Pan JN, He C, Parisien M, Pan T. Regulation of Co-transcriptional Pre-mRNA Splicing by m (6) A through the Low-Complexity Protein hnRNPG. Mol Cell. 2019;76(1):70–81 e9.
Brown JA, Kinzig CG, DeGregorio SJ, Steitz JA. Methyltransferase-like protein 16 binds the 3′-terminal triple helix of MALAT1 long noncoding RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(49):14013–8.
Chen X, Chen Z, Yu S, Nie F, Yan S, Ma P, Chen Q, Wei C, Fu H, Xu T, Ren S, Sun M, Wang Z. Long noncoding RNA LINC01234 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate CBFB expression by sponging miR-204-5p in gastric Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24(8):2002–14.
Cao C, Zhang T, Zhang D, Xie L, Zou X, Lei L, Wu D, Liu L. The long non-coding RNA, SNHG6-003, functions as a competing endogenous RNA to promote the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2017;36(8):1112–22.
Bossi L, Figueroa-Bossi N. Competing endogenous RNAs: a target-centric view of small RNA regulation in bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016;14(12):775–84.
Zheng ZQ, Li ZX, Zhou GQ, Lin L, Zhang LL, Lv JW, Huang XD, Liu RQ, Chen F, He XJ, Kou J, Zhang J, Wen X, Li YQ, Ma J, Liu N, Sun Y. Long noncoding RNA FAM225A promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma tumorigenesis and metastasis by acting as ceRNA to sponge miR-590-3p/miR-1275 and Upregulate ITGB3. Cancer Res. 2019;79(18):4612–26.
Zuo X, Chen Z, Gao W, Zhang Y, Wang J, Wang J, Cao M, Cai J, Wu J, Wang X. M6A-mediated upregulation of LINC00958 increases lipogenesis and acts as a nanotherapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13(1):5.
Jin D, Guo J, Wu Y, Du J, Yang L, Wang X, Di W, Hu B, An J, Kong L, Pan L, Su G. m (6) A mRNA methylation initiated by METTL3 directly promotes YAP translation and increases YAP activity by regulating the MALAT1-miR-1914-3p-YAP axis to induce NSCLC drug resistance and metastasis. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12(1):135.
Yang D, Qiao J, Wang G, Lan Y, Li G, Guo X, Xi J, Ye D, Zhu S, Chen W, Jia W, Leng Y, Wan X, Kang J. N6-Methyladenosine modification of lincRNA 1281 is critically required for mESC differentiation potential. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(8):3906–20.
Chen C-K, Blanco M, Jackson C, Aznauryan E, Ollikainen N, Surka C, Chow A, Cerase A, McDonel P, Guttman M. Xist recruits the X chromosome to the nuclear lamina to enable chromosome-wide silencing. Science (New York, NY). 2016;354(6311):468–72.
Ping XL, Sun BF, Wang L, Xiao W, Yang X, Wang WJ, Adhikari S, Shi Y, Lv Y, Chen YS, Zhao X, Li A, Yang Y, Dahal U, Lou XM, Liu X, Huang J, Yuan WP, Zhu XF, Cheng T, Zhao YL, Wang X, Rendtlew Danielsen JM, Liu F, Yang YG. Mammalian WTAP is a regulatory subunit of the RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase. Cell Res. 2014;24(2):177–89.
Chu C, Zhang QC, da Rocha ST, Flynn RA, Bharadwaj M, Calabrese JM, Magnuson T, Heard E. HY. C. Systematic discovery of Xist RNA binding proteins. Cell. 2015;161(2):404–16.
Moindrot B, Cerase A, Coker H, Masui O, Grijzenhout A, Pintacuda G, Schermelleh L, Nesterova TB, Brockdorff N. A pooled shRNA screen identifies Rbm15, Spen, and Wtap as factors required for Xist RNA-mediated silencing. Cell Rep. 2015;12(4):562–72.
Xiao M-S, Ai Y, Wilusz JE. Biogenesis and functions of circular RNAs come into focus. Trends Cell Biol. 2020;30(3):226–40.
Zhou C, Molinie B, Daneshvar K, Pondick JV, Wang J, Van Wittenberghe N, Xing Y, Giallourakis CC, Mullen AC. Genome-wide maps of m6A circRNAs identify widespread and cell-type-specific methylation patterns that are distinct from mRNAs. Cell Rep. 2017;20(9):2262–76.
Chen R-X, Chen X, Xia L-P, Zhang J-X, Pan Z-Z, Ma X-D, Han K, Chen J-W, Judde J-G, Deas O, Wang F, Ma N-F, Guan X, Yun J-P, Wang F-W, Xu R-H, Dan X. N6-methyladenosine modification of circNSUN2 facilitates cytoplasmic export and stabilizes HMGA2 to promote colorectal liver metastasis. Nature Communications. 2019;10(1).
Park OH, Ha H, Lee Y, Boo SH, Kwon DH, Song HK, Kim YK. Endoribonucleolytic Cleavage of mA-Containing RNAs by RNase P/MRP Complex. Molecular cell. 2019;74(3).
Paramasivam A, Vijayashree Priyadharsini J. Novel insights into m6A modification in circular RNA and implications for immunity. Cell Mol Immunol 2020.
Chen YG, Chen R, Ahmad S, Verma R, Kasturi SP, Amaya L, Broughton JP, Kim J, Cadena C, Pulendran B, Hur S, Chang HY. N6-Methyladenosine modification controls circular RNA immunity. Mol Cell. 2019;76(1):96–109 e9.
Wilkinson ME, Charenton C, Nagai K. RNA splicing by the Spliceosome. Annu Rev Biochem. 2019.
Shi Y. Mechanistic insights into precursor messenger RNA splicing by the spliceosome. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017;18(11):655–70.
Roundtree IA, Evans ME, Pan T. C H. dynamic RNAModifications in gene expression regulation. Cell. 2017;169(7):1187–200.
Shimba S, Bokar JA, Rottman F. Accurate and efficient a/−6-adenosine methylation in spliceosomal U6 small nuclear RNA by HeLa cell extract in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995;23(13):2421–6.
Charenton C, Wilkinson ME, Nagai K. Mechanism of 5′ splice site transfer for human spliceosome activation. Science (New York, NY). 2019;364(6438):362–7.
Madhani HD, Bordonné R, Guthrie C. Multiple roles for U6 snRNA in the splicing pathway. Genes Dev. 1990;4:2264–77.
Khatter H, Myasnikov AG, Natchiar SK, Klaholz BP. Structure of the human 80S ribosome. Nature. 2015;520(7549):640–5.
Sloan KE, Warda AS, Sharma S, Entian KD, Lafontaine DLJ, Bohnsack MT. Tuning the ribosome: the influence of rRNA modification on eukaryotic ribosome biogenesis and function. RNA Biol. 2017;14(9):1138–52.
Sergiev PV, Aleksashin NA, Chugunova AA, Polikanov YS, Dontsova OA. Structural and evolutionary insights into ribosomal RNA methylation. Nat Chem Biol. 2018;14(3):226–35.
van Tran N, Ernst FGM, Hawley BR, Zorbas C, Ulryck N, Hackert P, Bohnsack KE, Bohnsack MT, Jaffrey SR, Graille M, Lafontaine DLJ. The human 18S rRNA m6A methyltransferase METTL5 is stabilized by TRMT112. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(15):7719–33.
Ren W, Lu J, Huang M, Gao L, Li D, Wang GG, Song J. Structure and regulation of ZCCHC4 in m (6) A-methylation of 28S rRNA. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):5042.
Pinto R, Vågbø CB, Jakobsson ME, Kim Y, Baltissen MP, O'Donohue M-F, Guzmán UH, Małecki JM, Wu J, Kirpekar F, Olsen JV, Gleizes P-E, Vermeulen M, Leidel SA, Slupphaug G, Falnes PØ. The human methyltransferase ZCCHC4 catalyses N6-methyladenosine modification of 28S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48(2):830–46.
Chen T, Hao YJ, Zhang Y, Li MM, Wang M, Han W, Wu Y, Lv Y, Hao J, Wang L, Li A, Yang Y, Jin KX, Zhao X, Li Y, Ping XL, Lai WY, Wu LG, Jiang G, Wang HL, Sang L, Wang XJ, Yang YG, Zhou Q. M (6) a RNA methylation is regulated by microRNAs and promotes reprogramming to pluripotency. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;16(3):289–301.
Lan T, Li H, Zhang D, Xu L, Liu H, Hao X, Yan X, Liao H, Chen X, Xie K, Li J, Liao M, Huang J, Yuan K, Zeng Y, Wu H. KIAA1429 contributes to liver cancer progression through N6-methyladenosine-dependent post-transcriptional modification of GATA3. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):186.
Zhang S, Zhao BS, Zhou A, Lin K, Zheng S, Lu Z, Chen Y, Sulman EP, Xie K, Bogler O, Majumder S, He C, Huang S. M (6) a Demethylase ALKBH5 maintains Tumorigenicity of Glioblastoma stem-like cells by sustaining FOXM1 expression and cell proliferation program. Cancer Cell. 2017;31(4):591–606 e6.
Wang X, Zhang J, Wang Y. Long noncoding RNA GAS5-AS1 suppresses growth and metastasis of cervical cancer by increasing GAS5 stability. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(8):4909–21.
Lin S, Choe J, Du P, Triboulet R, Gregory RI. The m (6) a methyltransferase METTL3 promotes translation in human Cancer cells. Mol Cell. 2016;62(3):335–45.
Du M, Zhang Y, Mao Y, Mou J, Zhao J, Xue Q, Wang D, Huang J, Gao S. MiR-33a suppresses proliferation of NSCLC cells via targeting METTL3 mRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;482(4):582–9.
He H, Wu W, Sun Z, Chai L. MiR-4429 prevented gastric cancer progression through targeting METTL3 to inhibit m (6) A-caused stabilization of SEC62. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;517(4):581–7.
Cai X, Wang X, Cao C, Gao Y, Zhang S, Yang Z, Liu Y, Zhang X, Zhang W, Ye L. HBXIP-elevated methyltransferase METTL3 promotes the progression of breast cancer via inhibiting tumor suppressor let-7g. Cancer Lett. 2018;415:11–9.
Yang Z, Li J, Feng G, Gao S, Wang Y, Zhang S, Liu Y, Ye L, Li Y, Zhang X. MicroRNA-145 modulates N(6)-Methyladenosine levels by targeting the 3′-Untranslated mRNA region of the N(6)-Methyladenosine binding YTH domain family 2 protein. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(9):3614–23.
Kleemann M, Schneider H, Unger K, Sander P, Schneider EM, Fischer-Posovszky P, Handrick R, Otte K. MiR-744-5p inducing cell death by directly targeting HNRNPC and NFIX in ovarian cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):9020.
Chen J, Du B. Novel positioning from obesity to cancer: FTO, an mA RNA demethylase, regulates tumour progression. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019;145(1):19–29.
Cui Q, Shi H, Ye P, Li L, Qu Q, Sun G, Sun G, Lu Z, Huang Y, Yang CG, Riggs AD, He C, Shi Y. M (6) a RNA methylation regulates the self-renewal and tumorigenesis of Glioblastoma stem cells. Cell Rep. 2017;18(11):2622–34.
Huang Y, Yan J, Li Q, Li J, Gong S, Zhou H, Gan J, Jiang H, Jia GF, Luo C, Yang CG. Meclofenamic acid selectively inhibits FTO demethylation of m6A over ALKBH5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(1):373–84.
Singh B, Kinne HE, Milligan RD, Washburn LJ, Olsen M. Important Role of FTO in the Survival of Rare Panresistant Triple-Negative Inflammatory Breast Cancer Cells Facing a Severe Metabolic Challenge. Plos One. 2016;11(7).
Yang S, Wei J, Cui YH, Park G, Shah P, Deng Y, Aplin AE, Lu Z, Hwang S, He C, He YY. m(6) A mRNA demethylase FTO regulates melanoma tumorigenicity and response to anti-PD-1 blockade. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):2782.
Li HB, Tong J, Zhu S, Batista PJ, Duffy EE, Zhao J, Bailis W, Cao G, Kroehling L, Chen Y, Wang G, Broughton JP, Chen YG, Kluger Y, Simon MD, Chang HY, Yin Z, Flavell RA. M(6) a mRNA methylation controls T cell homeostasis by targeting the IL-7/STAT5/SOCS pathways. Nature. 2017;548(7667):338–42.
Tong J, Cao G, Zhang T, Sefik E, Amezcua Vesely MC, Broughton JP, Zhu S, Li H, Li B, Chen L, Chang HY, Su B, Flavell RA, Li HB. M (6) a mRNA methylation sustains Treg suppressive functions. Cell Res. 2018;28(2):253–6.
Han D, Liu J, Chen C, Dong L, Liu Y, Chang R, Huang X, Liu Y, Wang J, Dougherty U, Bissonnette MB, Shen B, Weichselbaum RR, Xu MM, He C. Anti-tumour immunity controlled through mRNA m (6) a methylation and YTHDF1 in dendritic cells. Nature. 2019;566(7743):270–4.
Wang H, Hu X, Huang M, Liu J, Gu Y, Ma L, Zhou Q, Cao X. Mettl3-mediated mRNA m (6) a methylation promotes dendritic cell activation. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1898.
Feng Z, Li Q, Meng R, Yi B, Xu Q. METTL3 regulates alternative splicing of MyD88 upon the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in human dental pulp cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(5):2558–68.
Zong X, Zhao J, Wang H, Lu Z, Wang F, Du H, Wang Y. Mettl3 deficiency sustains long-chain fatty acid absorption through suppressing Traf6-dependent inflammation response. J Immunol. 2019;202(2):567–78.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81572262); Jiangsu Province’s Key Provincial Talents Program (ZDRCA2016028); 333 High Class Talented Man Project (BRA2016516); the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institution of China (18KJB320006); and the National Science and Technology Major Project (2017YFC1309201).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YS and WG designed the study. YC drafted the manuscript. YL and JH revised the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Lin, Y., Shu, Y. et al. Interaction between N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification and noncoding RNAs in cancer. Mol Cancer 19, 94 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01207-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01207-4