Abstract
Cancer has become a major health issue worldwide, contributing to a high mortality rate. Tumor metastasis is attributed to the death of most patients. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) plays a vital role in inducing metastasis. During EMT, epithelial cells lose their characteristics, such as cell-to-cell adhesion and cell polarity, and cells gain motility, migratory potential, and invasive properties to become mesenchymal stem cells. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are closely associated with tumor metastasis and patient prognosis, as revealed by increasing lines of evidence. CircRNA is a type of single-stranded RNA that forms a covalently closed continuous loop. CircRNAs are insensitive to ribonucleases and are widespread in body fluids. This work is the first review on EMT-related circRNAs. In this review, we briefly discuss the characteristics and functions of circRNAs. The correlation of circRNAs with EMT has been reported, and we discuss the ways circRNAs can regulate EMT progression through EMT transcription factors, EMT-related signaling pathways, and other mechanisms. This work summarizes current studies on EMT-related circRNAs in various cancers and provides a theoretical basis for the use of EMT-related circRNAs in targeted management and therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
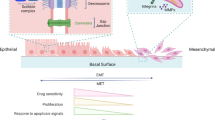
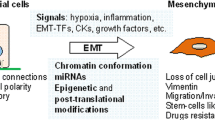
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is an important cellular event widely involved in physiologic and pathologic processes, including embryonic organ development [1, 2], wound healing, and tumor metastasis [3, 4]. During EMT, epithelial cells lose their characteristics, such as cell-to-cell adhesion and cell polarity. Instead, cells gain motility, migratory potential, and invasive properties, thereby becoming mesenchymal stem cells. The understanding of the mechanism of EMT progression has improved. The expression of epithelial markers, such as E-cadherin (E-cad), decreases and that of mesenchymal markers, such as N-cadherin (N-cad), vimentin, and claudin, increases during EMT progression. Multiple EMT transcription factors (EMT-TFs), including the Snail, Twist, and Zeb families, converge into EMT regulation. In addition to EMT-TFs, several signaling pathways have been identified, i.e., the transforming growth factor β (TGF-β)/Smad, Wnt/β-catenin, and Hedgehog signaling pathways. Noncoding RNAs can modulate EMT through EMT-TFs and EMT-related signaling pathways. Noncoding RNAs comprise a wide range of RNAs with different characteristics. This review mainly discusses the modulation of circRNAs in EMT progression.
CircRNA plays an important role in tumor metastasis. During EMT, circRNA absorbing miRNA attenuates the inhibition of the miRNA on EMT-related genes, such as EMT-TF/E-cad, N-cad, vimentin and cdc42. As a result, epithelial cells lose their characteristics, such as cell-to-cell adhesion and cell polarity. Instead, the cells gain motility, migratory potential, and invasive properties, becoming mesenchymal stem cells. In addition, EMT triggers primary tumor cells to enter the circulatory or lymphatic system. Then, circulating tumor cells are transported to distant tissues or organs to form secondary metastatic deposits through EMT. Of note, circRNAs secreted as exosomes are detected in serum/urine, which provides a novel strategy for the diagnosis and treatment of cancer
Circular RNA (circRNA) is a type of single-stranded RNA that forms a covalently closed continuous loop. In circular RNAs, unlike the known linear RNAs, the 3′ and 5′ ends normally present in an RNA molecule are linked. As a result, circRNAs are insensitive to ribonucleases. In 1976, the first circRNA was found in an RNA virus [5, 6]. In 1991, Nigor et al. [7] observed circRNAs in eukaryotes. CircRNAs were considered as an accidental byproduct until Jeck WR found two types of circRNA formations in 2013 [8]. With the rapid development of sequencing technology, the characteristics and functions of circRNAs have been revealed. Numerous circRNAs have been identified in humans. circRNAs exist widely in tissues, serum, and urine. CircRNAs have been identified as a determinant factor in many human diseases, including cardiovascular system diseases, neurological disorders, and cancer. Moreover, several studies have demonstrated that circRNAs can serve as prognostic biomarkers because of their characteristics [9,10,11,12,13].
This review summarizes current studies on EMT-related circRNAs in various cancers and provides a theoretical basis for the use of EMT-related circRNAs in targeted management and therapy.
Biogenesis of circRNAs
CircRNAs are classified into three categories: exon circRNA (ecRNA), circular intron RNA (ciRNA), and exon–intron circRNA (EIciRNA). In 2013, Jeck proposed that exon skipping and intron pairing are events that narrow the distance between splice sites and facilitate the back-splicing of pre-mRNA. This phenomenon results in circRNAs that lack 3′ and 5′ ends. In ecRNA and EIciRNA formation, circRNAs are linked by a 3′–5′ phosphodiester bond, whereas ciRNAs are linked by a 2′–5′ phosphodiester bond [14]. In general, the generation of linear RNA involves removing introns and linking exons in sequence. The competitive relationship between linear splicing and back-splicing determines the fate of hnRNA. As such, circRNA formation is precisely controlled. The two introns flanking the circularized exons, which have been found to be enriched in Alu repeats, can increase the efficiency of circularization [8, 15]. Some proteins regulate the biogenesis of circRNA, including RNA binding proteins (RBPs) and the spliceosome [16, 17]. The regulation of circRNA formation by proteins is complex and consists of positive and negative modulations. For example, quaking can promote circRNA biogenesis by binding to specific sites in the intron region [18]. In contrast, some proteins are negatively associated with the formation of circRNAs. Adenosine deaminase acting on RNA-1 (ADAR1), as an RNA-editing factor, reduces circRNA expression. Several studies have found that ADAR1 negatively modulates circRNA formation by interacting with DExH-box helicase 9 (DHX9) [19] and androgen receptor [20].
Function of circRNAs
After their discovery, circRNAs were misunderstood as the result of splicing errors. With the development of gene sequencing and other technologies, studies have found that circRNAs are involved in biological processes by being translated into peptides [21,22,23,24], binding to RBPs [25, 26], and sponging miRNAs [27, 28]. Among these processes, circRNAs most commonly act as miRNA sponges in tumor cells. CircRNAs have many miRNA binding sites. CircRNAs are often negatively correlated with miRNAs and repress miRNA activity. For example, circPRMT5 facilitates urothelial carcinoma of the bladder (UCB) cell metastasis by sponging tumor-suppressor miR-30c [9]. However, Piwecka M et al. illustrated that circRNAs can positively modulate miRNAs and decrease miRNA downstream genes [29]. CircRNAs can interact with RBPs, thus affecting nuclear translocation and modulating the targeted pathway. CircRNAs can also play a protein-coding role. Several studies on protein-coding circRNAs, which can be translated into peptides by binding to ribosomes, have been performed [21,22,23,24].
Databases of circRNAs
With the development of high-throughput sequencing technology, numerous circRNAs have been found and reported in databases [30] (Table 1). The circBase database mostly contains circRNAs of different species, such as human, mouse, and Latimeria organisms. Sequence information and evidence supporting the expression of circRNAs can be searched and downloaded [31]. The CircNet database includes transcriptome sequencing datasets and data on expression in specialized tissues [32]. The CircNet and starBase databases also provide data on networks between circRNAs, miRNAs, and targeted genes [32, 33]. Information on circRNAs and lncRNAs can also be found in the deepBase database. This database contains the sequencing datasets of a large amount of circRNAs [34]. The Circ2Traits database includes information on RNA-related diseases and RNA traits. It has classified thousands of circRNAs connected to hundreds of diseases [35]. Tissue-specific circRNAs are mostly found in the tissue-specific circRNA database (TSCD). TSCD contains data on the human and mouse genomes [36]. The cancer-specific circRNA database is the first database that fully comprises cancer-specific circRNAs. This database may provide a meaningful strategy for the control of tumor cells [37].
Contribution of circRNAs to epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition regulation
Cell–cell contact and cytoskeletal proteins undergo changes during EMT. A decrease in the expression of the epithelial marker E-cad is possibly a significant event, whereas the levels of mesenchymal markers, such as N-cad and vimentin, increase [38,39,40,41]. Several EMT-TFs, such as the Snail, Twist, slug, and ZEB families, are known regulators during EMT. They can bind to E-boxes to regulate EMT markers [42,43,44,45,46]. Some signaling pathways, particularly the Wnt/β-catenin, TGF-β/SMAD, and Notch pathways, may induce EMT [39, 47,48,49]. Here, we provide up to date information on circRNAs involved in EMT mechanisms.
CircRNA control of EMT-TFs
Regulation of snail by circRNAs
Several circRNAs are potentially involved in regulating EMT-TFs, which are considered fundamental players in EMT. Snail is an EMT-TF and is positively correlated with EMT progression [50, 51]. For example, circRNA_0084043 is significantly upregulated in melanoma tissues. Bioinformatics analysis and luciferase reporter assays have confirmed that circRNA_0084043 directly interacts with miR-153-3p and that Snail is directly targeted by miR-153-3p. Therefore, circRNA_0084043 overexpression upregulates Snail expression and promotes EMT progression. The circRNA_0084043/miR-153-3p/Snail axis is the first discovery in melanoma related to circRNA. CircRNAs provide a potential new use for targeted therapy for melanoma [52]. A human circRNA microarray has been used to explore the upregulated circRNA_000284 in cervical cancer cells. Similarly, miR-506 has been identified as a circRNA-000284-associated miRNA by performing a luciferase reporter assay and through anti-AGO2 RNA precipitation. In addition, Snail-2 has been confirmed as a direct target of miR-506. As a result, circRNA-000284 can indirectly increase Snail-2 expression and promote invasion, migration, and metastasis [53]. CircPRMT5 serves as a sponge for miR-30c in UCB, relieving the miR-30c-mediated repression of Snail-1. Increased circPRMT5 facilitates UCB cell metastasis by downregulating Snail-1-related E-cad and increasing vimentin and N-cad [9]. Studies on circRNAs and Snail are few, and additional studies on the mechanism of the regulation of Snail by circRNAs are still needed.
Regulation of twist on vimentin by circRNAs
Twist as an important EMT-TF that directly or indirectly governs the transcription of EMT-associated genes, thereby decreasing epithelial markers, such as E-cad, and increasing mesenchymal cell markers, including vimentin [54]. Cullin2 (Cul2) is a core component of multiple ElonginB/C-CUL2/5-SOCS-box protein (ECS) E3 ubiquitin–protein ligase complexes that mediate the ubiquitination of target proteins [55, 56]. A study has validated that Twist1 promotes Cul2 transcription by binding to the Cul2 promoter and increases the pre-mRNA levels of Cul2. As a result, Twist1 upregulates Cul2 circRNA (circRNA_10720) expression. CircRNA_10720 is positively associated with EMT and promotes metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. CircRNA_10720 regulates vimentin by sponging a series of miRNAs. This research hypothesizes that miR-490-5p is the main absorbed miRNA that regulates vimentin, as shown by a luciferase reporter assay. CircRNA_10720 knockdown counteracts the effect of Twist1 by promoting metastasis through the upregulation of vimentin [57]. This process provides a novel mechanism of how Twist regulates vimentin via a circRNA.
TGF-β/Smad pathway-related circRNAs
Previous studies have demonstrated that TGF-β can enhance the EMT process. The TGF-β/Smad pathway has been demonstrated to be a positive regulator in the growth and metastasis of various cancer types [58, 59]. Wang L et al. reported that circPTK2 inhibits non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) metastasis by disrupting oncogenic miR-429 and miR-200b-3p and promoting transcriptional intermediary factor 1γ (TIF1γ) expression [60]. TIF1γ, which is considered as a negative regulator of the TGF-β/Smad pathway [61, 62], represses the TGF-β-related EMT. Zeng K et al. demonstrated that the high expression level of circANKS1B can be indicative of a poor prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). The upregulated circANKS1B has been implicated in promoting breast cancer invasion and metastasis. The pro-metastatic effect of circANKS1B is mediated through the interaction with miR-148a-3p and miR-152-3p, thereby increasing upstream transcription factor 1 (USF1) expression [63]. USF1 binds to TGF-β1 in murine tissues [64]. Zeng K et al. confirmed that upregulated USF1 can interact with TGF-β1 in TNBC tissues to substantially upregulate the expression of vimentin, p-Smad2, and p-Smad3 but significantly decrease the expression of E-cad. Moreover, circANKS1B expression is regulated by USF1. USF1 overexpression upregulates circANKS1B expression via the splicing factor Epithelial splicing regulatory protein 1 (ESRP1), showing that a positive feedback regulatory loop is formed between circANKS1B, USF1, and ESRP1 [63]. Splicing factors (SFs) can also regulate circRNA formation and EMT progression by inserting SF-binding motifs into flanking introns, which has been demonstrated in several research reports [18, 63, 65, 66].
Wnt pathway-related circRNAs
In general, the Wnt pathway can be classified as a canonical pathway (Wnt/β-catenin pathway) and a noncanonical pathway (Wnt/PCP and Wnt/Ca pathways). Here, we mainly discuss the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway. In brief, in the absence of Wnt signaling, β-catenin, Axin, glycogen synthase kinase-3, adenomatous polyposis coli (APC), and casein kinase 1 form a destruction complex in the cytoplasm in which the initially phosphorylated and subsequently ubiquitinated β-catenin is degraded by the proteasome. The presence of Wnt ligands blocks the formation of this complex. As a result, β-catenin accumulates to a certain level in the cytoplasm and then translocated into the nucleus to activate the Wnt-targeted genes [67,68,69,70]. The interaction between circRNAs and the Wnt/β-catenin pathway to promote cancer progression has been demonstrated (Table 2).
Frizzled gene family proteins (FZDs) are important cell surface receptors in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and consists of FZD1/2/3/6/7, FZD5/8, FZD4, and FZD9/10 subfamilies. FZDs are positive membrane receptors in the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and are significantly associated with cancer progression [71,72,73]. Guan F et al. demonstrated the obvious overexpression of circRNA_100,290 and FZD4 in colorectal cancer (CRC) and found their target relationship with miR-516b. CircRNA_100,290 not only increases proliferation and metastasis by regulating FZD4 but also upregulates the expression of MYC, CCD1, CCD2, TCF7, and SOX4, which are target genes of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway [74]. In thyroid cancer, circNEK6 is a competing endogenous RNA of FZD8 that absorbs miR-370-3p, resulting in the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. The upregulation of circNEK6 enhances the expression of c-myc and CCD1, whereas silencing FZD8 abrogates their expression [75]. Chen et al. demonstrated that hsa_circ_0000177 is a miR-638 sponge that targets FZD7. Furthermore, hsa_circ_0000177 activates the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and promotes the growth of glioma cells by enhancing FZD7 expression [76]. Xia et al. showed that circ-CBFB ultimately leads to CLL progression via the FZD3-induced activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by sponging miR-607 [77].
Dickkopf-1 (DKK1) can specifically bind to LRP5/6, thereby interfering with the formation of the Wnt-LRP5/6-FZD complex and inhibiting the downstream pathway [78, 79]. Yao et al. illustrated that the significantly downregulated circ_0006427 is involved in the tumorigenesis of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) by releasing miR-6783-3p and by activating the Wnt signaling pathway through DKK1 knockdown. Circ_0006427 downregulation or DKK1 knockdown promotes cell migration and invasion [80]. Y. Jin et al. demonstrated a significant decrease in hsa_circ_0000523 and DKK1 in CRC and identified their target correlation with miR-31. A decreased DKK1 level not only enhances β-catenin in the nucleus but also promotes CRC proliferation [81].
APC is considered a negative regulator in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and is associated with the β-catenin destruction complex [82,83,84]. Hsa_circ_0002052 and APC2 are obviously decreased in osteosarcoma (OS) and are strongly correlated. As a result, the downregulation of hsa_circ_0002052 promotes proliferation and metastasis through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. MiR-1205 has been identified as a common target miRNA of hsa_circ_0002052 and APC2 and is upregulated in OS. Hsa_circ_0002052 also provides a novel therapeutic target for OS therapy [85].
ITCH is a E3 ubiquitin ligase enzyme and can inactivate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway by degrading phosphorylated dishevelled Dvl [86,87,88]. Dvl can bind to Axin, which is an important component of the β-catenin destruction complex, to positively modulate the β-catenin level. Several studies have demonstrated the positive relationship between circ-ITCH and ITCH. In TNBC, circ-ITCH exhibits breast tumor inhibition and can promote the expression of ITCH tumor suppressor by absorbing miR-214 and miR-17 [89]. Feng Li et al. illustrated the anti-oncogenic effect of circ-ITCH on glioma. Decreased circ-ITCH and ITCH can promote migration and invasion by sponging miR-214. In this mechanism, miR-214 and miR-17 can bind to the 3′UTR of ITCH to enhance ITCH expression [89, 90].
Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) exerts diverse effects on tumor cells as an oncoprotein or tumor suppressor [91,92,93]. Yao Y et al. demonstrated that circ_0001946 expression is increased in lung adenocarcinoma. Circ_0001946 upregulates SIRT1 and activates the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in LAC by targeting miR-135a-5p, thus promoting LAC progression [94]. However, the mechanism involving circRNA and SIRT1 remains largely unknown.
Previous studies have found that catenin beta-1 (CTNNBIP1) is a negative regulator in the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and can interact with β-catenin. Mechanistically, increasing evidence has shown that the CTNNBIP1/β-catenin interaction can prevent the formation of the β-catenin/TCF/LEF complex. As a result, it prevents the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway [95,96,97,98]. The upregulated circRNA_102171 facilitates the malignant behavior of papillary thyroid cancer by regulating the CTNNBIP1-mediated activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. CircRNA_102171 overexpression enhances the β-catenin/TCF/LEF interaction while blocking the association between CTNNBIP1 and β-catenin. Nevertheless, how circRNA_102171 modulates CTNNBIP1 still needs further studies [99].
Regulation of cell adhesion molecules and cytoskeletal proteins by circRNAs
In addition to the regulation exerted by circRNAs at the level of transcription factors and EMT-related signaling pathways, certain circRNAs function by directly or indirectly regulating the expression of cell adhesion molecules and cytoskeletal proteins. Such deregulated circRNAs can act either as tumor suppressors or oncogenes to control cell proliferation, migration and metastasis. For example, circ_0058063 promotes bladder cancer progression by sponging miR-145-5p and regulating CDK6 expression [100]. In HCC, the circRNA circMTO1 (mitochondrial translation optimization 1 homologue) significantly downregulated and circMTO1 overexpression suppressed HCC cell proliferation and invasion by sponging oncogenic miR-9. Moreover, circMTO1 is an important circRNA in bladder cancer tissue. A decreased circMTO1 level was positively correlated with bladder cancer cell metastasis. Further research found that circMTO1 was able to sponge miR-221, and ectopic expression of circMTO1 negatively regulated the E-cad/ N-cad pathway to inhibit bladder cancer cell EMT by competing for miR-221 [101].
Several circRNAs have been demonstrated to regulate vimentin transcription. For instance, Tao Wang et al. reported on the role of circP4HB in NSCLC. In NSCLC, circP4HB levels are significantly higher than in healthy lung. Of note, vimentin has a documented role in promoting EMT and metastasis in NSCLC as a regulator of cell to cell adhesion and cell motility. Interestingly, circP4HB can positively regulate vimentin and enhance EMT and metastatic disease through miR-133a-5p sequestration [102]. A recent circRNA profiling study showed that circRBM23 expression was upregulated, whereas miR-138 expression was decreased, in HCC tissues. Downregulation of circRBM23 decreased cell viability, proliferation, and migration and promoted the expression of miR-138 and its related target genes vimentin and CCND3 [103]. Thus, the circRNA-miRNA-vimentin regulatory axis in EMT is important for tumor invasion and metastasis.
Protocadherins (PCDHs) are classified as the largest subgroup within the cadherin superfamily of calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion molecules that are mainly expressed in the nervous system and have been implicated in neural cell-cell interactions. Little is known about the functions of PCDHs, but some members, such as PCDH8 and PCDH10, have been shown to suppress tumor activity [104,105,106,107], suggesting that PCDHs may act as tumor suppressors by influencing tumor growth and metastasis. In prostate cancer (PCa), Zhan Yang et al. have shown that an Amotl1-derived circRNA termed circAMOTL1L, is downregulated in PCa and that low expression of circAMOTL1L facilitates PCa cell migration and invasion by downregulating E-cad and upregulating vimentin, which leads to EMT and PCa progression. Mechanistically, the study demonstrated that circAMOTL1L serves as a sponge for binding miR-193a-5p in PCa cells, relieving the miR-193a-5p-mediated repression of the Pcdha gene cluster, which is a subset of PCDHs [108].
Regulation of cell motility and metastasis by circRNAs through rho GTPases
Carcinoma cells that undergo EMT reorganize the epithelial actin cytoskeleton into one with actin stress fibers and form migratory organelles, such as lamellipodia and filopodia. In this way, cells acquire directional motility and metastatic potential [109]. Rho GTPases belong to the group of small G proteins that cycle between an inactive GDP-bound state and active GTP-bound state. Among the members of the Rho GTPase family, RhoA, cdc42 and Rac have been studied in most detail. RhoA facilitates the formation of actin stress fibers, while cdc42 and Rac1 generally assist in filopodia and lamellipodia formation. Rho-kinase (ROCK), as the downstream effector of RhoA, induces myosin light chain (MLC) phosphorylation by inhibiting MLC phosphatase to enhance myosin contractility. ROCK also activates LIM kinase (LIMK) and then represses cofilin. The Rho/ROCK/MLC/myosin and Rho/ROCK/LIMK/cofilin pathways all facilitate stress fiber formation. Moreover, actin polymerization dependent on mDia is an essential factor for the assembly of stress fibers [110, 111]. CircHIAT1 expression was suppressed by androgen receptor (AR) in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). Interestingly, circHIAT1 could stabilize the expression of miR-195-5p/29a-3p/29c-3p as a reservoir. It has been demonstrated that the downregulating miR-195-5p/29a-3p/29c-3p targets the cdc42 3′-UTR to enhance the migration and invasion of ccRCC cells. Notably, upregulation of AR-targeting cdc42 significantly promoted filopodia formation, while the increase could be partially reversed by CircHIAT1 overexpression [112]. Jie Li et al. investigated the role of circ-IARS in pancreatic cancer tissues. Circ-IARS was secreted by pancreatic cancer cells and upregulated in plasma exosomes. Then, circ-IARS enters HUVECs through exosomes. In this study, upregulation of circ-IARS in HUVECs changed their biological functions. It has been demonstrated that circ-IARS sponges miR-122 to increase RhoA activity and F-actin expression and reduce ZO-1 expression. As a result, circ-IARS/RhoA modulates the permeability of the endothelial monolayer to promote metastasis [113].
Other pathways related to circRNAs
High-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) is considered a chromatin-binding factor that regulates HCC progression [114,115,116]. HMGB1 knockdown can significantly attenuate the migration and invasion behavior [117, 118]. Li S et al. demonstrated the correlation between a circRNA and the HMGB1/RAGE pathway. Upregulating circRNA_101,368 suppresses miR-200a expression, thus enhancing the metastasis of HCC cells by activating the miR-200a-mediated HMGB1/RAGE pathway [119].
MiR-7 is considered a tumor cell suppressor whose dysregulation facilitates malignant behavior [120, 121]. The experimental basis for the targeted treatment from the perspective of the circRNA CDR1as/miR-7 pathway has been validated in several cancer cells. Su C et al. demonstrated that the remarkably increase in ciRS-7 (circRNA CDR1as) induces the metastasis of NSCLC cells through the miR-7 downstream NF-κB pathway [122]. Furthermore, the circRNA CDR1as/miR-7 pathway regulates the EMT phenotype. Furthermore, a miR-7 inhibitor can enhance the metastatic ability of HCC and OS cells [123, 124].
Yu J et al. linked the circRNA cSMARCA5/miR-17-3p/miR-181b-5p/TIMP3 regulatory pathway to EMT in HCC [125]. TIMP3 has been reported to be a tumor cell suppressor in several studies and inactivates the EMT program [126, 127]. It has been found that the decrease in circRNA cSMARCA5 facilitates HCC cell migration and metastasis and downregulates TIMP3 transcription by absorbing miR-17-3p and miR-181b-5p [125].
Human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are multipotent cells that possess the ability to self-renew and differentiate into mesodermal lineage cells [128, 129]. Due to this differentiation potential and other properties to regenerate injured tissues indirectly via growth factor secretion and immunomodulation, MSCs hold promise for regenerative medicine. A full understanding of the molecular mechanisms that regulate the maintenance of human MSC identity and their uncommitted state is helpful for improving therapeutic efficacy. Stem cell plasticity and identity are controlled by master regulatory genes and complex circuits involving noncoding RNAs [130,131,132]. Alessandro Cherubini et al. showed that compared to that in differentiated mesodermal cells, circFOXP1 levels were enriched in MSCs. The authors demonstrated a direct interaction between circFOXP1 and miR-17-3p/miR-127-5p, which resulted in the modulation of the EGFR and noncanonical Wnt pathways. They found a regulatory role for circFOXP1 as a gatekeeper of pivotal stem cell molecular networks [133]. Yanjie Wang et al. demonstrated that circRNA_014511 could affect the expression of P53, regulate cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest, and influence the radiosensitivity of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMMCs) by adsorbing miR-29b-2-5p. Furthermore, Yan-Jing Zhu et al. found that circZKSCAN1 suppressed cell stemness in HCC by regulating the function of the RBP fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP), whose downstream target gene is cell cycle and apoptosis regulator 1 (CCAR1) and showed that CCAR1 acts as a coactivator of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and upregulates cell stemness [134].
Conclusions and future perspectives
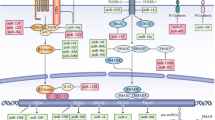
Metastasis is an important factor causing malignant tumor behavior. A number of circRNAs have been correlated with tumor cell EMT regulation (Fig. 1). CircRNAs are closely associated with tumor progression and patient prognosis. However, unlike studies on other noncoding RNAs, further efforts are needed to produce several EMT-related circRNAs. Furthermore, this work is the first review on the associations between circRNAs and EMT. The exact mechanisms of how circRNAs regulate EMT remain unclear. CircRNA-based diagnostics and treatments have many challenges. The former involves a low circRNA expression level and advanced detection measures. The latter includes the requirement of safety and effectiveness and the absence of off-target effects. CircRNAs are promising novel cancer markers because of their ribonuclease insensitivity and widespread expression in body fluids. Some studies have suggested that exosomal circRNAs are stable. Thus, future studies should further develop several EMT-related circRNAs associated with various types of cancers and characterize the function of circulating circRNAs, especially exosomal circRNAs, to make a potent therapy to directly target circRNAs. Overall, identifying the specific functions and mechanisms of circRNAs in EMT will provide novel and powerful perspectives on tumor management.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- ADAR1:
-
Adenosine deaminase acting on RNA-1
- APC:
-
Adenomatous polyposis coli
- AR:
-
Androgen receptor
- BMMCs:
-
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- CCAR1:
-
Cell cycle and apoptosis regulator 1
- ccRCC:
-
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- circRNA:
-
Circular RNA
- ciRNA:
-
Circular intron RNA
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- CTNNBIP1:
-
Catenin beta-1
- Cul2:
-
Cullin2
- DHX9:
-
DExH-box helicase 9
- DKK1:
-
Dickkopf-1
- E-cad:
-
E-cadherin
- ecRNA:
-
Exon circRNA
- ECS:
-
ElonginB/C-CUL2/5-SOCS-box protein
- EIciRNA:
-
Exon–intron circRNA
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
- EMT-TFs:
-
EMT transcription factors
- ESRP1:
-
Epithelial splicing regulatory protein 1
- FMRP:
-
Fragile X mental retardation protein
- FZDs:
-
Frizzled gene family proteins
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- HMGB1:
-
High-mobility group box 1
- LIMK:
-
LIM kinase
- LUAD:
-
Lung adenocarcinoma
- MLC:
-
Myosin light chain
- MSCs:
-
Human mesenchymal stem cells
- N-cad:
-
N-cadherin
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small-cell lung carcinoma
- OS:
-
Osteosarcoma
- Pca:
-
Prostate cance
- Pcdha:
-
Protocadherin-α
- RBP:
-
RNA binding protein
- ROCK:
-
Rho-kinase
- SFs:
-
Splicing factors
- SIRT1:
-
Sirtuin 1
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor β
- TIF1γ:
-
The transcriptional intermediary factor 1γ
- TNBC:
-
Triple-negative breast cancer
- TSCD:
-
Tissue-specific circRNA database
- UCB:
-
The urothelial carcinoma of the bladder
- USF1:
-
The upstream transcription factor 1
References
Matoba R, Morizane Y, Shiode Y, Hirano M, Doi S, Toshima S, Araki R, Hosogi M, Yonezawa T, Shiraga F. Suppressive effect of AMP-activated protein kinase on the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in retinal pigment epithelial cells. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0181481.
Sakabe M, Ikeda K, Nakatani K, Kawada N, Imanaka-Yoshida K, Yoshida T, Yamagishi T, Nakajima Y. Rho kinases regulate endothelial invasion and migration during valvuloseptal endocardial cushion tissue formation. Dev Dyn. 2006;235:94–104.
Feldkoren B, Hutchinson R, Rapoport Y, Mahajan A, Margulis V. Integrin signaling potentiates transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta1) dependent down-regulation of E-cadherin expression - important implications for epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in renal cell carcinoma. Exp Cell Res. 2017;355:57–66.
Nishiyama M, Tsunedomi R, Yoshimura K, Hashimoto N, Matsukuma S, Ogihara H, Kanekiyo S, Iida M, Sakamoto K, Suzuki N, et al. Metastatic ability and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in induced cancer stem-like hepatoma cells. Cancer Sci. 2018;109:1101–9.
Kolakofsky D. Isolation and characterization of Sendai virus DI-RNAs. Cell. 1976;8:547–55.
Sanger HL, Klotz G, Riesner D, Gross HJ, Kleinschmidt AK. Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976;73:3852–6.
Nigro JM, Cho KR, Fearon ER, Kern SE, Ruppert JM, Oliner JD, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. Scrambled exons. Cell. 1991;64:607–13.
Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, Slevin MK, Burd CE, Liu J, Marzluff WF, Sharpless NE. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA. 2013;19:141–57.
Chen X, Chen RX, Wei WS, Li YH, Feng ZH, Tan L, Chen JW, Yuan GJ, Chen SL, Guo SJ, et al. PRMT5 circular RNA promotes metastasis of urothelial carcinoma of the bladder through sponging miR-30c to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:6319–30.
Suzuki H, Tsukahara T. A view of pre-mRNA splicing from RNase R resistant RNAs. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15:9331–42.
Memczak S, Papavasileiou P, Peters O, Rajewsky N. Identification and characterization of circular RNAs as a new class of putative biomarkers in human blood. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0141214.
Zhang C, Wang X, Chen Y, Wu Z, Zhang C, Shi W. The down-regulation of hsa_circ_0012919, the sponge for miR-125a-3p, contributes to DNA methylation of CD11a and CD70 in CD4(+) T cells of systemic lupus erythematous. Clin Sci (Lond). 2018;132:2285–98.
Bahn JH, Zhang Q, Li F, Chan TM, Lin X, Kim Y, Wong DT, Xiao X. The landscape of microRNA, Piwi-interacting RNA, and circular RNA in human saliva. Clin Chem. 2015;61:221–30.
Shen T, Han M, Wei G, Ni T. An intriguing RNA species--perspectives of circularized RNA. Protein Cell. 2015;6:871–80.
Zhang XO, Wang HB, Zhang Y, Lu X, Chen LL, Yang L. Complementary sequence-mediated exon circularization. Cell. 2014;159:134–47.
Khan MA, Reckman YJ, Aufiero S, van den Hoogenhof MM, van der Made I, Beqqali A, Koolbergen DR, Rasmussen TB, van der Velden J, Creemers EE, Pinto YM. RBM20 regulates circular RNA production from the titin gene. Circ Res. 2016;119:996–1003.
Liang D, Tatomer DC, Luo Z, Wu H, Yang L, Chen LL, Cherry S, Wilusz JE. The output of protein-coding genes shifts to circular RNAs when the pre-mRNA processing machinery is limiting. Mol Cell. 2017;68:940–954 e943.
Conn SJ, Pillman KA, Toubia J, Conn VM, Salmanidis M, Phillips CA, Roslan S, Schreiber AW, Gregory PA, Goodall GJ. The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of circRNAs. Cell. 2015;160:1125–34.
Aktas T, Avsar Ilik I, Maticzka D, Bhardwaj V, Pessoa Rodrigues C, Mittler G, Manke T, Backofen R, Akhtar A. DHX9 suppresses RNA processing defects originating from the Alu invasion of the human genome. Nature. 2017;544:115–9.
Shi L, Yan P, Liang Y, Sun Y, Shen J, Zhou S, Lin H, Liang X, Cai X. Circular RNA expression is suppressed by androgen receptor (AR)-regulated adenosine deaminase that acts on RNA (ADAR1) in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8:e3171.
Wang Y, Wang Z. Efficient backsplicing produces translatable circular mRNAs. RNA. 2015;21:172–9.
Yang Y, et al. Novel Role of FBXW7 Circular RNA in Repressing Glioma Tumorigenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2018;110(3):304–15.
Legnini I, Di Timoteo G, Rossi F, Morlando M, Briganti F, Sthandier O, Fatica A, Santini T, Andronache A, Wade M, et al. Circ-ZNF609 is a circular RNA that can be translated and functions in Myogenesis. Mol Cell. 2017;66:22–37 e29.
Granados-Riveron JT, Aquino-Jarquin G. The complexity of the translation ability of circRNAs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1859:1245–51.
Zeng Y, Du WW, Wu Y, Yang Z, Awan FM, Li X, Yang W, Zhang C, Yang Q, Yee A, et al. A circular RNA binds to and activates AKT phosphorylation and nuclear localization reducing apoptosis and enhancing cardiac repair. Theranostics. 2017;7:3842–55.
Yang ZG, Awan FM, Du WW, Zeng Y, Lyu J, Wu GS, Yang W, Yang BB. The circular RNA interacts with STAT3, increasing its nuclear translocation and wound repair by modulating Dnmt3a and miR-17 function. Mol Ther. 2017;25:2062–74.
Han D, Li J, Wang H, Su X, Hou J, Gu Y, Qian C, Lin Y, Liu X, Huang M, et al. Circular RNA circMTO1 acts as the sponge of microRNA-9 to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Hepatology. 2017;66:1151–64.
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK, Kjems J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 2013;495:384–8.
Piwecka M, et al. Loss of a mammalian circular RNA locus causes miRNA deregulation and affects brain function. Science. 2017;357(6357).
Szabo L, Salzman J. Detecting circular RNAs: bioinformatic and experimental challenges. Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17:679–92.
Glazar P, Papavasileiou P, Rajewsky N. circBase: a database for circular RNAs. RNA. 2014;20:1666–70.
Liu YC, Li JR, Sun CH, Andrews E, Chao RF, Lin FM, Weng SL, Hsu SD, Huang CC, Cheng C, et al. CircNet: a database of circular RNAs derived from transcriptome sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:D209–15.
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH, Yang JH. starBase v2.0: decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:D92–7.
Zheng LL, Li JH, Wu J, Sun WJ, Liu S, Wang ZL, Zhou H, Yang JH, Qu LH. deepBase v2.0: identification, expression, evolution and function of small RNAs, LncRNAs and circular RNAs from deep-sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:D196–202.
Ghosal S, Das S, Sen R, Basak P, Chakrabarti J. Circ2Traits: a comprehensive database for circular RNA potentially associated with disease and traits. Front Genet. 2013;4:283.
Xia S, Feng J, Lei L, Hu J, Xia L, Wang J, Xiang Y, Liu L, Zhong S, Han L, He C. Comprehensive characterization of tissue-specific circular RNAs in the human and mouse genomes. Brief Bioinform. 2017;18:984–92.
Xia S, Feng J, Chen K, Ma Y, Gong J, Cai F, Jin Y, Gao Y, Xia L, Chang H, et al. CSCD: a database for cancer-specific circular RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46:D925–9.
Kalluri R, Neilson EG. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2003;112:1776–84.
Kalluri R, Weinberg RA. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 2009;119:1420–8.
Lee JM, Dedhar S, Kalluri R, Thompson EW. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: new insights in signaling, development, and disease. J Cell Biol. 2006;172:973–81.
Nieto MA, Huang RY, Jackson RA, Thiery JP. Emt: 2016. Cell. 2016;166:21–45.
Eger A, Aigner K, Sonderegger S, Dampier B, Oehler S, Schreiber M, Berx G, Cano A, Beug H, Foisner R. DeltaEF1 is a transcriptional repressor of E-cadherin and regulates epithelial plasticity in breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 2005;24:2375–85.
Batlle E, Sancho E, Franci C, Dominguez D, Monfar M, Baulida J, Garcia De Herreros A. The transcription factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:84–9.
Hajra KM, Chen DY, Fearon ER. The SLUG zinc-finger protein represses E-cadherin in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2002;62:1613–8.
Comijn J, Berx G, Vermassen P, Verschueren K, van Grunsven L, Bruyneel E, Mareel M, Huylebroeck D, van Roy F. The two-handed E box binding zinc finger protein SIP1 downregulates E-cadherin and induces invasion. Mol Cell. 2001;7:1267–78.
Kang Y, Massague J. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions: twist in development and metastasis. Cell. 2004;118:277–9.
Zhou B, Liu Y, Kahn M, Ann DK, Han A, Wang H, Nguyen C, Flodby P, Zhong Q, Krishnaveni MS, et al. Interactions between beta-catenin and transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathways mediate epithelial-mesenchymal transition and are dependent on the transcriptional co-activator cAMP-response element-binding protein (CREB)-binding protein (CBP). J Biol Chem. 2012;287:7026–38.
Tse JC, Kalluri R. Mechanisms of metastasis: epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and contribution of tumor microenvironment. J Cell Biochem. 2007;101:816–29.
Yang J, Weinberg RA. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: at the crossroads of development and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 2008;14:818–29.
Stanisavljevic J, Loubat-Casanovas J, Herrera M, Luque T, Pena R, Lluch A, Albanell J, Bonilla F, Rovira A, Pena C, et al. Snail1-expressing fibroblasts in the tumor microenvironment display mechanical properties that support metastasis. Cancer Res. 2015;75:284–95.
Millanes-Romero A, Herranz N, Perrera V, Iturbide A, Loubat-Casanovas J, Gil J, Jenuwein T, Garcia de Herreros A, Peiro S. Regulation of heterochromatin transcription by Snail1/LOXL2 during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Mol Cell. 2013;52:746–57.
Luan W, Shi Y, Zhou Z, Xia Y, Wang J. circRNA_0084043 promote malignant melanoma progression via miR-153-3p/Snail axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;502:22–9.
Ma HB, Yao YN, Yu JJ, Chen XX, Li HF. Extensive profiling of circular RNAs and the potential regulatory role of circRNA-000284 in cell proliferation and invasion of cervical cancer via sponging miR-506. Am J Transl Res. 2018;10:592–604.
Shibue T, Weinberg RA. EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: the mechanistic link and clinical implications. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2017;14:611–29.
Cai W, Yang H. The structure and regulation of Cullin 2 based E3 ubiquitin ligases and their biological functions. Cell Div. 2016;11:7.
Petroski MD, Deshaies RJ. Function and regulation of cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:9–20.
Meng J, Chen S, Han JX, Qian B, Wang XR, Zhong WL, Qin Y, Zhang H, Gao WF, Lei YY, et al. Twist1 regulates vimentin through Cul2 circular RNA to promote EMT in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2018;78:4150–62.
Liu RY, Zeng Y, Lei Z, Wang L, Yang H, Liu Z, Zhao J, Zhang HT. JAK/STAT3 signaling is required for TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2014;44:1643–51.
Massague J. TGFbeta in Cancer. Cell. 2008;134:215–30.
Wang L, Tong X, Zhou Z, Wang S, Lei Z, Zhang T, Liu Z, Zeng Y, Li C, Zhao J, et al. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0008305 (circPTK2) inhibits TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis by controlling TIF1gamma in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer. 2018;17:140.
Dupont S, Zacchigna L, Cordenonsi M, Soligo S, Adorno M, Rugge M, Piccolo S. Germ-layer specification and control of cell growth by Ectodermin, a Smad4 ubiquitin ligase. Cell. 2005;121:87–99.
He W, Dorn DC, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Moore MA, Massague J. Hematopoiesis controlled by distinct TIF1gamma and Smad4 branches of the TGFbeta pathway. Cell. 2006;125:929–41.
Zeng K, He B, Yang BB, Xu T, Chen X, Xu M, Liu X, Sun H, Pan Y, Wang S. The pro-metastasis effect of circANKS1B in breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 2018;17:160.
Zhu Y, Casado M, Vaulont S, Sharma K. Role of upstream stimulatory factors in regulation of renal transforming growth factor-beta1. Diabetes. 2005;54:1976–84.
Ashwal-Fluss R, Meyer M, Pamudurti NR, Ivanov A, Bartok O, Hanan M, Evantal N, Memczak S, Rajewsky N, Kadener S. circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol Cell. 2014;56:55–66.
Yu CY, Li TC, Wu YY, Yeh CH, Chiang W, Chuang CY, Kuo HC. The circular RNA circBIRC6 participates in the molecular circuitry controlling human pluripotency. Nat Commun. 2017;8:1149.
MacDonald BT, Tamai K, He X. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell. 2009;17:9–26.
Stamos JL, Weis WI. The beta-catenin destruction complex. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013;5:a007898.
Aberle H, Bauer A, Stappert J, Kispert A, Kemler R. Beta-catenin is a target for the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. EMBO J. 1997;16:3797–804.
Rao TP, Kuhl M. An updated overview on Wnt signaling pathways: a prelude for more. Circ Res. 2010;106:1798–806.
Wu W, Dang S, Feng Q, Liang J, Wang Y, Fan N. MicroRNA-542-3p inhibits the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting FZD7/Wnt signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;482:100–5.
Liu X, Yan Y, Ma W, Wu S. Knockdown of frizzled-7 inhibits cell growth and metastasis and promotes chemosensitivity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells by inhibiting Wnt signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;490:1112–8.
Li G, Su Q, Liu H, Wang D, Zhang W, Lu Z, Chen Y, Huang X, Li W, Zhang C, et al. Frizzled7 promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and Stemness via activating canonical Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in gastric Cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 2018;14:280–93.
Fang G, Ye BL, Hu BR, Ruan XJ, Shi YX. CircRNA_100290 promotes colorectal cancer progression through miR-516b-induced downregulation of FZD4 expression and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;504:184–9.
Chen F, Feng Z, Zhu J, Liu P, Yang C, Huang R, Deng Z. Emerging roles of circRNA_NEK6 targeting miR-370-3p in the proliferation and invasion of thyroid cancer via Wnt signaling pathway. Cancer Biol Ther. 2018;19:1139–52.
Chen Z, Duan X. hsa_circ_0000177-miR-638-FZD7-Wnt signaling Cascade contributes to the malignant behaviors in glioma. DNA Cell Biol. 2018;37:791–7.
Xia L, Wu L, Bao J, Li Q, Chen X, Xia H, Xia R. Circular RNA circ-CBFB promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia through regulating miR-607/FZD3/Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;503:385–90.
Semenov MV, Tamai K, Brott BK, Kuhl M, Sokol S, He X. Head inducer Dickkopf-1 is a ligand for Wnt coreceptor LRP6. Curr Biol. 2001;11:951–61.
Mao B, Wu W, Li Y, Hoppe D, Stannek P, Glinka A, Niehrs C. LDL-receptor-related protein 6 is a receptor for Dickkopf proteins. Nature. 2001;411:321–5.
Yao Y, Hua Q, Zhou Y. CircRNA has_circ_0006427 suppresses the progression of lung adenocarcinoma by regulating miR-6783-3p/DKK1 axis and inactivating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;508:37–45.
Jin Y, Yu LL, Zhang B, Liu CF, Chen Y. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0000523 regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells as miRNA sponge. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2018;51:e7811.
Dokanehiifard S, Soltani BM. Hsa-miR-11181 regulates Wnt signaling pathway through targeting of APC2 transcripts in SW480 cell line. Gene. 2018;641:297–302.
Dow LE, O'Rourke KP, Simon J, Tschaharganeh DF, van Es JH, Clevers H, Lowe SW. Apc restoration promotes cellular differentiation and reestablishes crypt homeostasis in colorectal Cancer. Cell. 2015;161:1539–52.
Colnot S, Decaens T, Niwa-Kawakita M, Godard C, Hamard G, Kahn A, Giovannini M, Perret C. Liver-targeted disruption of Apc in mice activates beta-catenin signaling and leads to hepatocellular carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:17216–21.
Wu Z, Shi W, Jiang C. Overexpressing circular RNA hsa_circ_0002052 impairs osteosarcoma progression via inhibiting Wnt/beta-catenin pathway by regulating miR-1205/APC2 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;502:465–71.
Huang G, Zhu H, Shi Y, Wu W, Cai H, Chen X. Cir-ITCH plays an inhibitory role in colorectal cancer by regulating the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0131225.
Wan L, Zhang L, Fan K, Cheng ZX, Sun QC, Wang JJ. Circular RNA-ITCH suppresses lung Cancer proliferation via inhibiting the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:1579490.
Wei W, Li M, Wang J, Nie F, Li L. The E3 ubiquitin ligase ITCH negatively regulates canonical Wnt signaling by targeting dishevelled protein. Mol Cell Biol. 2012;32:3903–12.
Wang ST, Liu LB, Li XM, Wang YF, Xie PJ, Li Q, Wang R, Wei Q, Kang YH, Meng R, Feng XH. Circ-ITCH regulates triple-negative breast cancer progression through the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Neoplasma. 2019;66:232–9.
Li F, Ma K, Sun M, Shi S. Identification of the tumor-suppressive function of circular RNA ITCH in glioma cells through sponging miR-214 and promoting linear ITCH expression. Am J Transl Res. 2018;10:1373–86.
Holloway KR, Calhoun TN, Saxena M, Metoyer CF, Kandler EF, Rivera CA, Pruitt K. SIRT1 regulates Dishevelled proteins and promotes transient and constitutive Wnt signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:9216–21.
Liu S, Yang H, Hu B, Zhang M. Sirt1 regulates apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation in resveratrol-treated osteoarthritis chondrocytes via the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14:5057–62.
Wu Q, Wang Y, Qian M, Qiao Y, Zou S, Chen C, Zhang X, Chen Y, Zhao Y, Zhu G, et al. Sirt1 suppresses Wnt/betaCatenin signaling in liver cancer cells by targeting betaCatenin in a PKAalpha-dependent manner. Cell Signal. 2017;37:62–73.
Yao Y, Hua Q, Zhou Y, Shen H. CircRNA has_circ_0001946 promotes cell growth in lung adenocarcinoma by regulating miR-135a-5p/SIRT1 axis and activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;111:1367–75.
Fu X, Zhu X, Qin F, Zhang Y, Lin J, Ding Y, Yang Z, Shang Y, Wang L, Zhang Q, Gao Q. Linc00210 drives Wnt/beta-catenin signaling activation and liver tumor progression through CTNNBIP1-dependent manner. Mol Cancer. 2018;17:73.
Kosari-Monfared M, Nikbakhsh N, Fattahi S, Ghadami E, Ranaei M, Taheri H, Amjadi-Moheb F, Godazandeh GA, Shafaei S, Pilehchian-Langroudi M, et al. CTNNBIP1 downregulation is associated with tumor grade and viral infections in gastric adenocarcinoma. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:2895–904.
Qi W, Chen J, Cheng X, Huang J, Xiang T, Li Q, Long H, Zhu B. Targeting the Wnt-regulatory protein CTNNBIP1 by microRNA-214 enhances the Stemness and self-renewal of Cancer stem-like cells in lung adenocarcinomas. Stem Cells. 2015;33:3423–36.
Guo M, Zhang X, Wang G, Sun J, Jiang Z, Khadarian K, Yu S, Zhao Y, Xie C, Zhang K, et al. miR-603 promotes glioma cell growth via Wnt/beta-catenin pathway by inhibiting WIF1 and CTNNBIP1. Cancer Lett. 2015;360:76–86.
Bi W, Huang J, Nie C, Liu B, He G, Han J, Pang R, Ding Z, Xu J, Zhang J. CircRNA circRNA_102171 promotes papillary thyroid cancer progression through modulating CTNNBIP1-dependent activation of beta-catenin pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37:275.
Sun M, Zhao W, Chen Z, Li M, Li S, Wu B, Bu R. Circ_0058063 regulates CDK6 to promote bladder cancer progression by sponging miR-145-5p. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:4812–24.
Li Y, Wan B, Liu L, Zhou L, Zeng Q. Circular RNA circMTO1 suppresses bladder cancer metastasis by sponging miR-221 and inhibiting epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;508:991–6.
Wang T, Wang X, Du Q, Wu N, Liu X, Chen Y, Wang X. The circRNA circP4HB promotes NSCLC aggressiveness and metastasis by sponging miR-133a-5p. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;513:904–11.
Wang B, Chen H, Zhang C, Yang T, Zhao Q, Yan Y, Zhang Y, Xu F. Effects of hsa_circRBM23 on hepatocellular carcinoma cell viability and migration as produced by regulating miR-138 expression. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2018;33:194–202.
Yu J, Cheng YY, Tao Q, Cheung KF, Lam CN, Geng H, Tian LW, Wong YP, Tong JH, Ying JM, et al. Methylation of protocadherin 10, a novel tumor suppressor, is associated with poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:640–651 e641.
Dallosso AR, Hancock AL, Szemes M, Moorwood K, Chilukamarri L, Tsai HH, Sarkar A, Barasch J, Vuononvirta R, Jones C, et al. Frequent long-range epigenetic silencing of protocadherin gene clusters on chromosome 5q31 in Wilms’ tumor. PLoS Genet. 2009;5:e1000745.
Ying J, Li H, Seng TJ, Langford C, Srivastava G, Tsao SW, Putti T, Murray P, Chan AT, Tao Q. Functional epigenetics identifies a protocadherin PCDH10 as a candidate tumor suppressor for nasopharyngeal, esophageal and multiple other carcinomas with frequent methylation. Oncogene. 2006;25:1070–80.
Yu JS, Koujak S, Nagase S, Li CM, Su T, Wang X, Keniry M, Memeo L, Rojtman A, Mansukhani M, et al. PCDH8, the human homolog of PAPC, is a candidate tumor suppressor of breast cancer. Oncogene. 2008;27:4657–65.
Yang Z, Qu CB, Zhang Y, Zhang WF, Wang DD, Gao CC, Ma L, Chen JS, Liu KL, Zheng B, et al. Dysregulation of p53-RBM25-mediated circAMOTL1L biogenesis contributes to prostate cancer progression through the circAMOTL1L-miR-193a-5p-Pcdha pathway. Oncogene. 2019;38:2516–32.
Yilmaz M, Christofori G. Mechanisms of motility in metastasizing cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2010;8:629–42.
Lamouille S, Xu J, Derynck R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15:178–96.
Burridge K, Wennerberg K. Rho and Rac take center stage. Cell. 2004;116:167–79.
Wang K, Sun Y, Tao W, Fei X, Chang C. Androgen receptor (AR) promotes clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) migration and invasion via altering the circHIAT1/miR-195-5p/29a-3p/29c-3p/CDC42 signals. Cancer Lett. 2017;394:1–12.
Li J, Li Z, Jiang P, Peng M, Zhang X, Chen K, Liu H, Bi H, Liu X, Li X. Circular RNA IARS (circ-IARS) secreted by pancreatic cancer cells and located within exosomes regulates endothelial monolayer permeability to promote tumor metastasis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37:177.
Yan W, Chang Y, Liang X, Cardinal JS, Huang H, Thorne SH, Monga SP, Geller DA, Lotze MT, Tsung A. High-mobility group box 1 activates caspase-1 and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma invasiveness and metastases. Hepatology. 2012;55:1863–75.
Chen M, Liu Y, Varley P, Chang Y, He XX, Huang H, Tang D, Lotze MT, Lin J, Tsung A. High-mobility group box 1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through miR-21-mediated matrix metalloproteinase activity. Cancer Res. 2015;75:1645–56.
Li H, Huang W, Luo R. The microRNA-325 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression by targeting high mobility group box 1. Diagn Pathol. 2015;10:117.
Conti L, Lanzardo S, Arigoni M, Antonazzo R, Radaelli E, Cantarella D, Calogero RA, Cavallo F. The noninflammatory role of high mobility group box 1/toll-like receptor 2 axis in the self-renewal of mammary cancer stem cells. FASEB J. 2013;27:4731–44.
Chen RC, Yi PP, Zhou RR, Xiao MF, Huang ZB, Tang DL, Huang Y, Fan XG. The role of HMGB1-RAGE axis in migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;390:271–80.
Li S, Gu H, Huang Y, Peng Q, Zhou R, Yi P, Chen R, Huang Z, Hu X, Huang Y, Tang D. Circular RNA 101368/miR-200a axis modulates the migration of hepatocellular carcinoma through HMGB1/RAGE signaling. Cell Cycle. 2018;17:2349–59.
Shi Y, Luo X, Li P, Tan J, Wang X, Xiang T, Ren G. miR-7-5p suppresses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis of breast cancer cells mainly by targeting REGgamma. Cancer Lett. 2015;358:27–36.
Okuda H, Xing F, Pandey PR, Sharma S, Watabe M, Pai SK, Mo YY, Iiizumi-Gairani M, Hirota S, Liu Y, et al. miR-7 suppresses brain metastasis of breast cancer stem-like cells by modulating KLF4. Cancer Res. 2013;73:1434–44.
Su C, Han Y, Zhang H, Li Y, Yi L, Wang X, Zhou S, Yu D, Song X, Xiao N, et al. CiRS-7 targeting miR-7 modulates the progression of non-small cell lung cancer in a manner dependent on NF-kappaB signalling. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22:3097–107.
Yu L, Gong X, Sun L, Zhou Q, Lu B, Zhu L. The circular RNA Cdr1as act as an oncogene in hepatocellular carcinoma through targeting miR-7 expression. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0158347.
Xu B, Yang T, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Liu S, Shen M. CircRNA CDR1as/miR-7 signals promote tumor growth of osteosarcoma with a potential therapeutic and diagnostic value. Cancer Manag Res. 2018;10:4871–80.
Yu J, Xu QG, Wang ZG, Yang Y, Zhang L, Ma JZ, Sun SH, Yang F, Zhou WP. Circular RNA cSMARCA5 inhibits growth and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2018;68:1214–27.
Gu X, Fu M, Ding Y, Ni H, Zhang W, Zhu Y, Tang X, Xiong L, Li J, Qiu L, et al. TIMP-3 expression associates with malignant behaviors and predicts favorable survival in HCC. PLoS One. 2014;9:e106161.
Yu BF, Wu J, Zhang Y, Sung HW, Xie J, Li RK. Ultrasound-targeted HSVtk and Timp3 gene delivery for synergistically enhanced antitumor effects in hepatoma. Cancer Gene Ther. 2013;20:290–7.
Bianco P, Robey PG, Simmons PJ. Mesenchymal stem cells: revisiting history, concepts, and assays. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;2:313–9.
Kilian KA, Bugarija B, Lahn BT, Mrksich M. Geometric cues for directing the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:4872–7.
Flynn RA, Chang HY. Long noncoding RNAs in cell-fate programming and reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell. 2014;14:752–61.
Sacchetti B, Fatica A, Sorci M, Sorrentino A, Signore M, Cerio A, Felicetti F, Feo A, Pelosi E, Care A, et al. Effect of miR-204&211 and RUNX2 control on the fate of human mesenchymal stromal cells. Regen Med Res. 2017;5:2.
Ivey KN, Srivastava D. MicroRNAs as regulators of differentiation and cell fate decisions. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;7:36–41.
Cherubini A, Barilani M, Rossi RL, Jalal MMK, Rusconi F, Buono G, Ragni E, Cantarella G, Simpson H, Peault B, Lazzari L. FOXP1 circular RNA sustains mesenchymal stem cell identity via microRNA inhibition. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:5325–40.
Zhu YJ, Zheng B, Luo GJ, Ma XK, Lu XY, Lin XM, Yang S, Zhao Q, Wu T, Li ZX, et al. Circular RNAs negatively regulate cancer stem cells by physically binding FMRP against CCAR1 complex in hepatocellular carcinoma. Theranostics. 2019;9:3526–40.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81874183, 81872304 and 81672845), the Jiangsu Provincial Key Medical Discipline, and the Project of Invigorating Health Care through Science, Technology and Education (NO. ZDXKA2016014, ZDRCC2016009), and the Qing Lan Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BQ-S, ML-L and HY-Q were major contributor in writing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Shang, BQ., Li, ML., Quan, Hy. et al. Functional roles of circular RNAs during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Mol Cancer 18, 138 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1071-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1071-6